CGA-VLP: High Accuracy Visible Light Positioning Algorithm Using Single Square LED with Geomagnetic Angle Correction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a VLP scheme based on the corrected geomagnetic angle (CGA-VLP) in which we relax the assumption on the minimum number of observable LEDs efficiently to one and improve the robustness in the harsh environment.
- The proposed methodology can correct the geomagnetic angles obtained from GS, which could be further applied to other algorithms.
- The scheme is evaluated in static and real-time environments through a tailor-made Android application and modulation drive, with pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR) functioning when LED is out of the camera’s FOV. The accuracy and real-time performance are both excellent for real applications.
2. Methodology
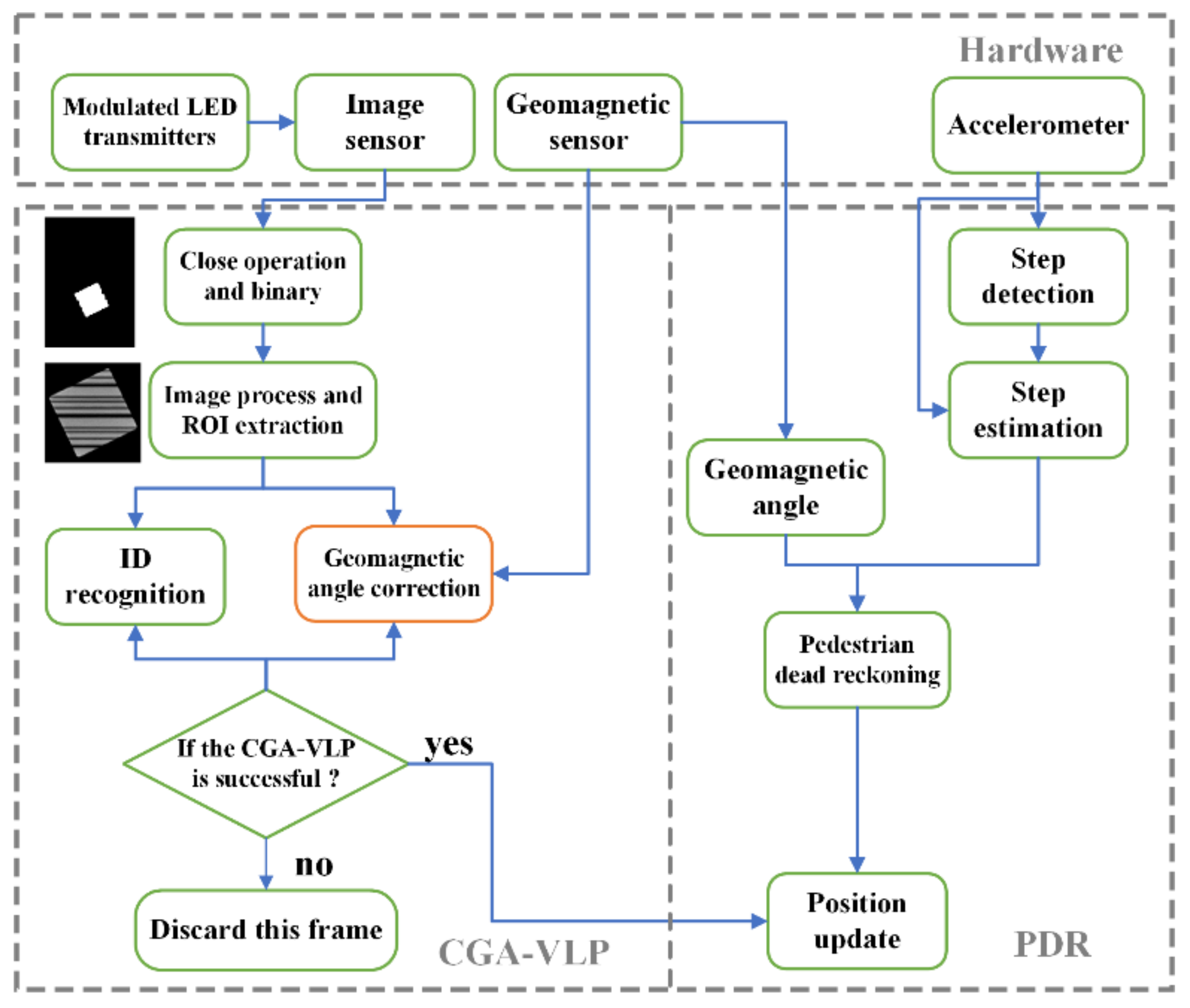
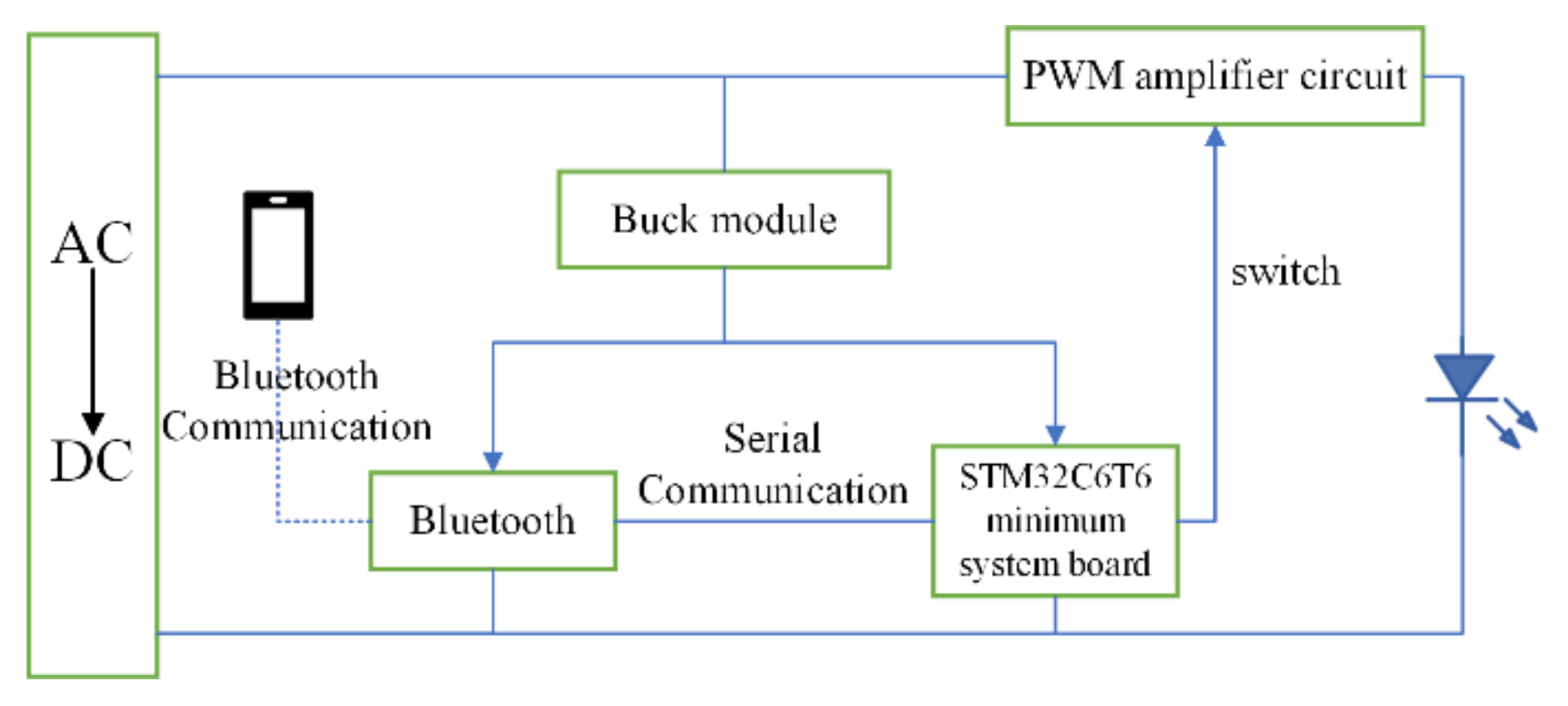
2.1. Overall Structure
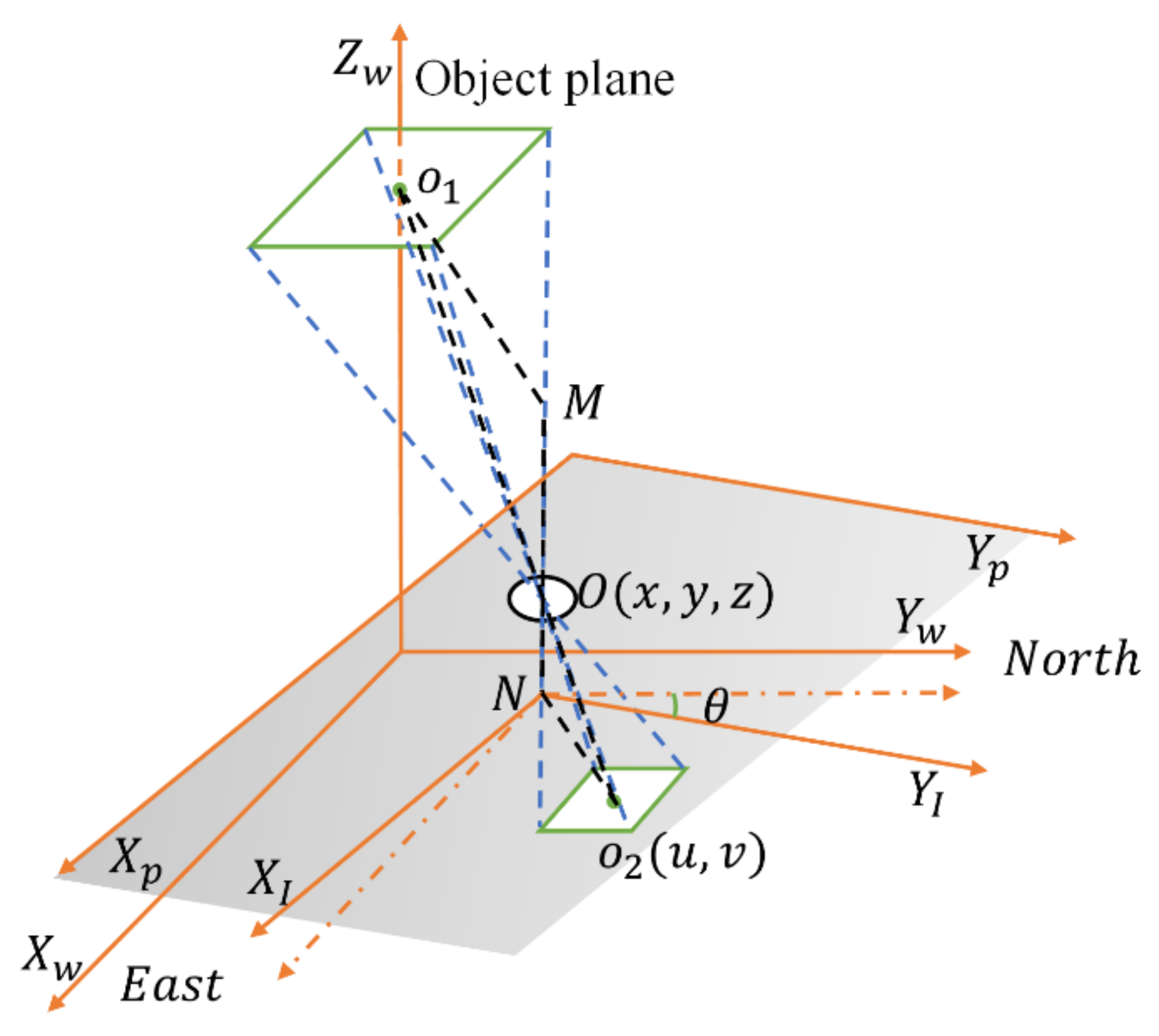
2.2. The Principle of Imaging Positioning
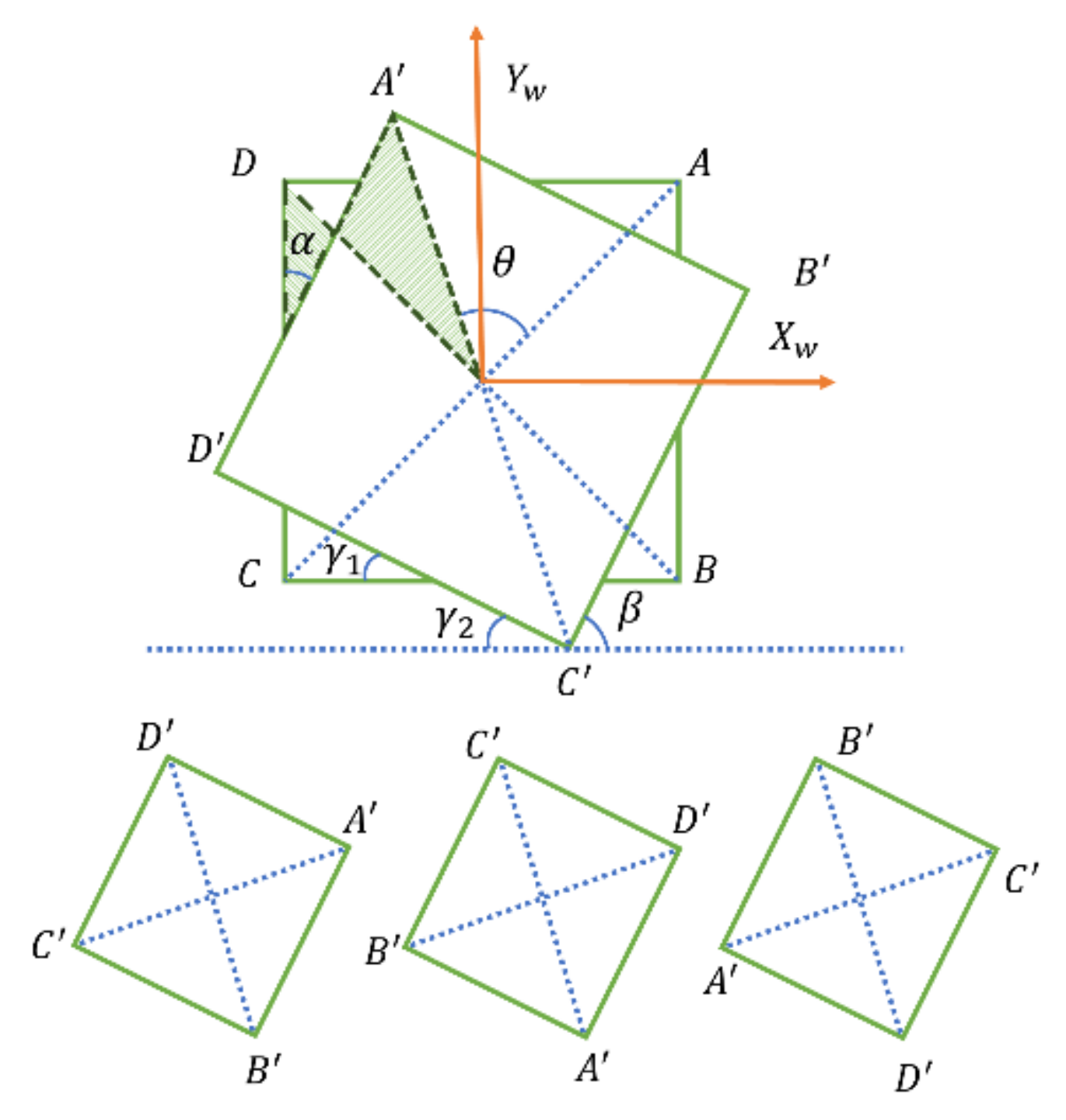
2.3. Geomagnetic Angle Correction
3. Experiments and Analysis
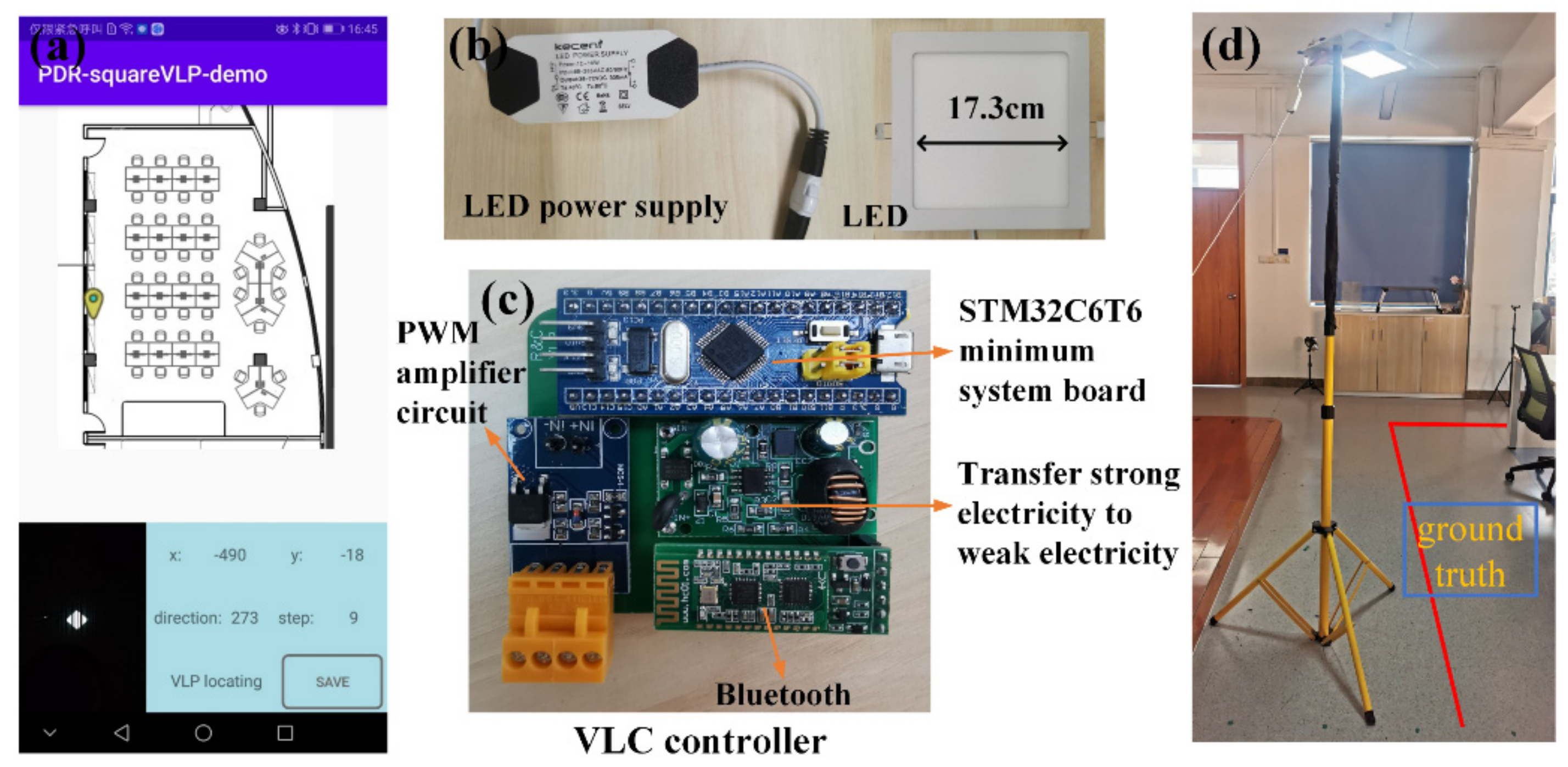
3.1. Receiver
3.2. Transmitters
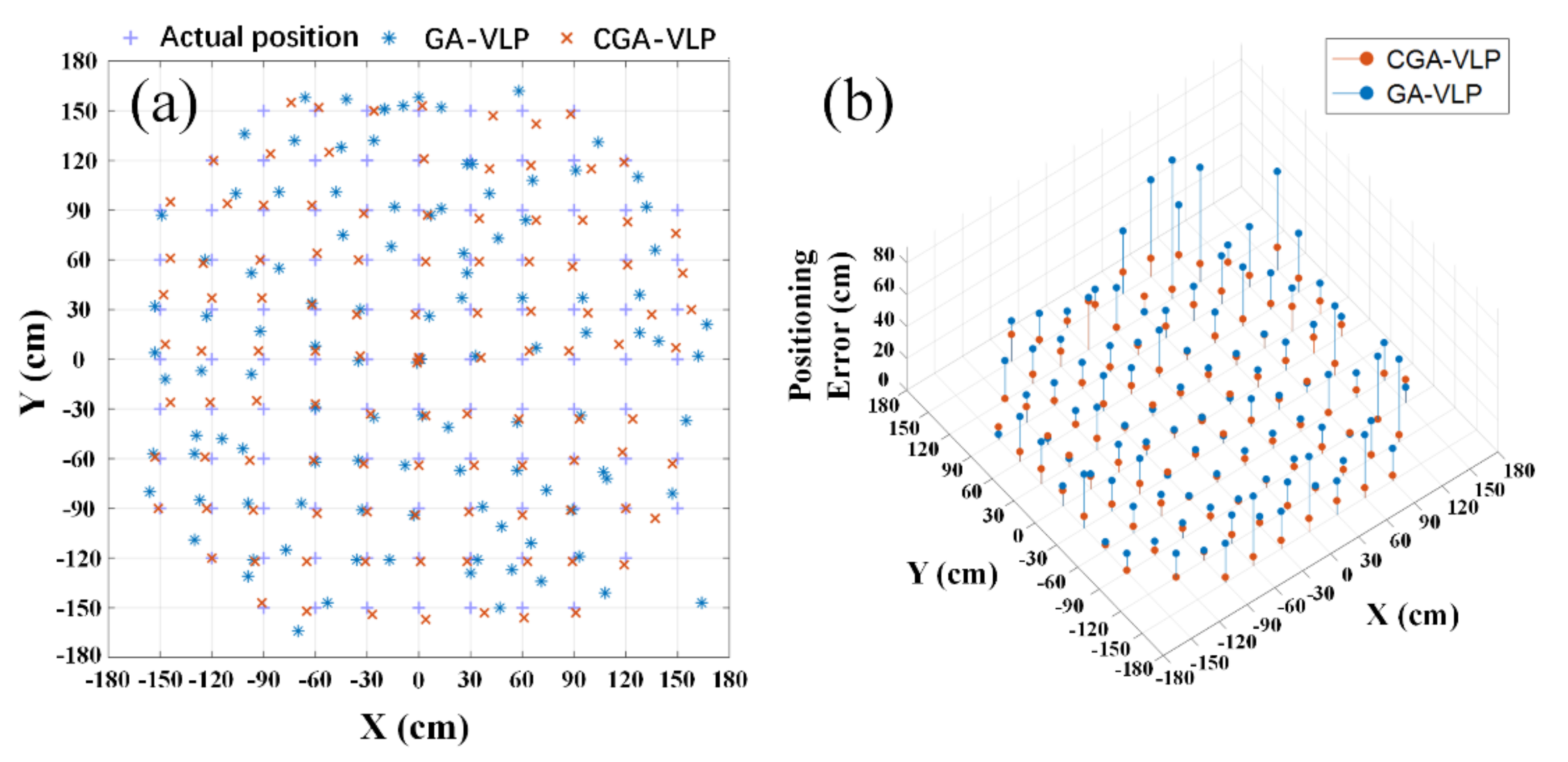
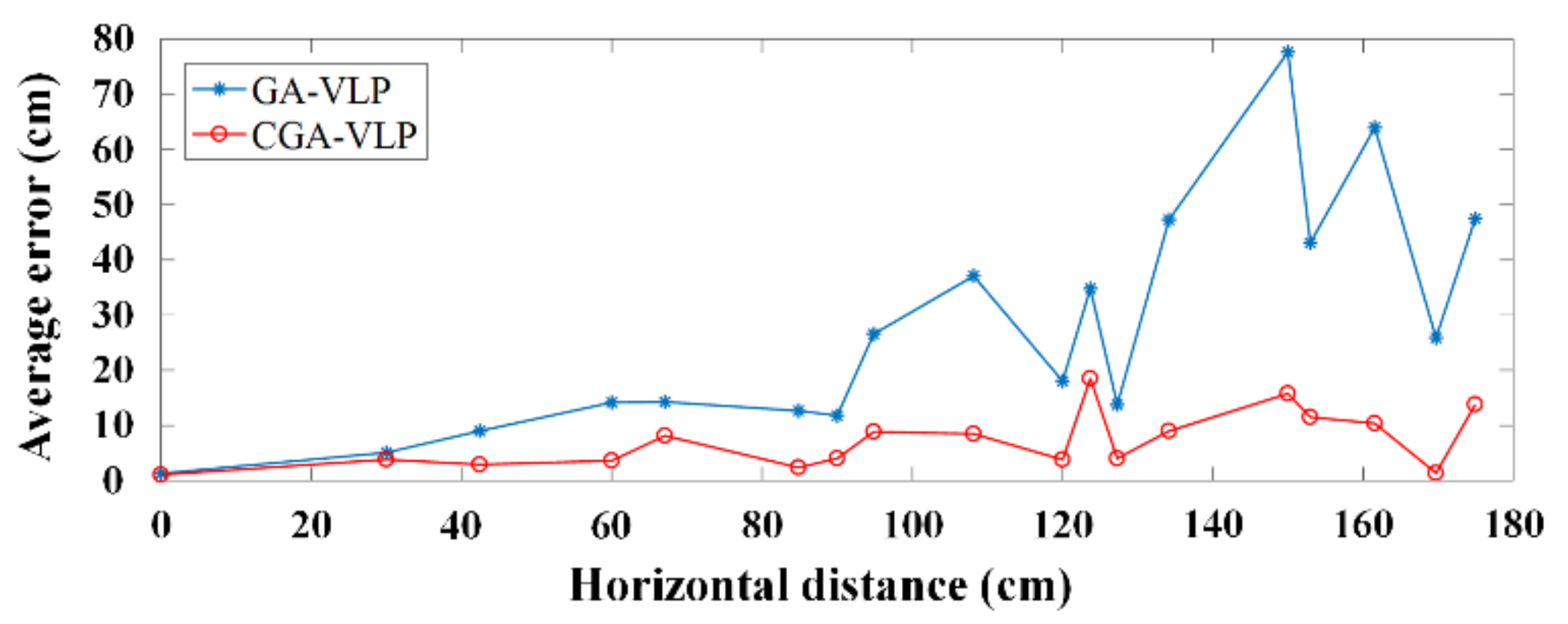
3.3. CGA-VLP System Positioning Accuracy
3.4. Dynamic Positioning
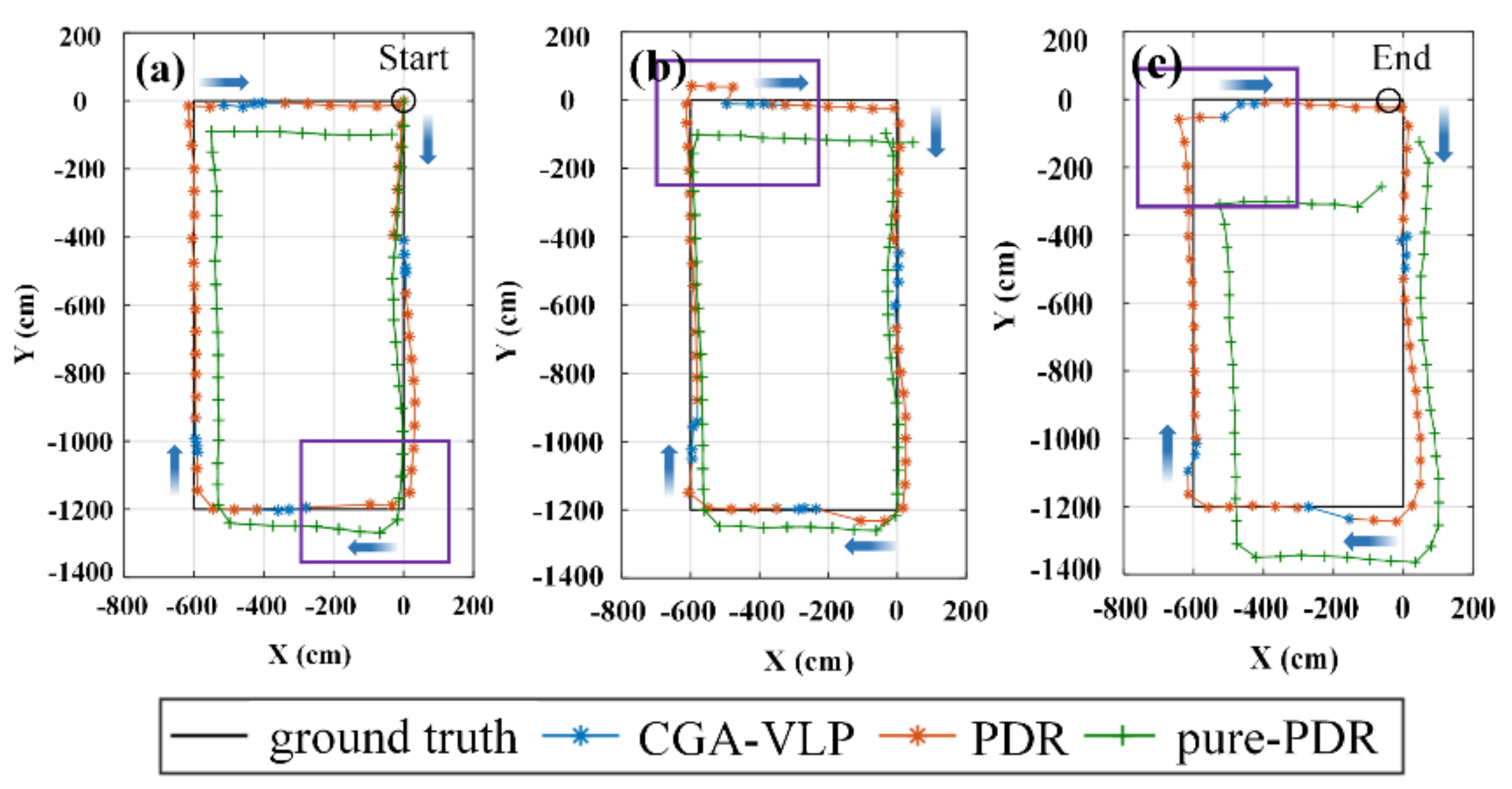
3.4.1. Accuracy of the Dynamic Positioning
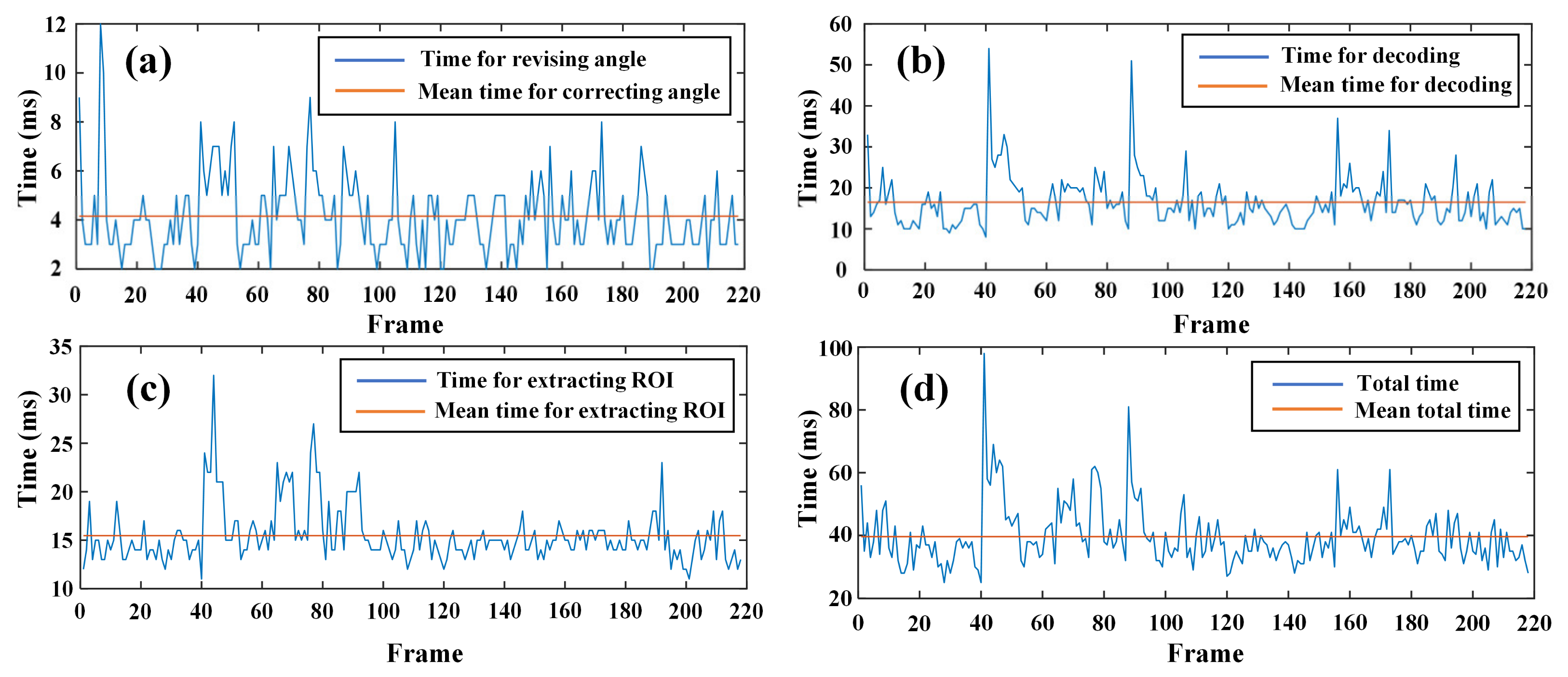
3.4.2. Real-Time Performance of the Dynamic Positioning
3.4.3. Accuracy of the CGA
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alletto, S.; Cucchiara, R.; Del Fiore, G.; Mainetti, L.; Mighali, V.; Patrono, L.; Serra, G. An indoor location-aware system for an IoT-based smart museum. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Hua, L.C.; Qi, L.N.; Yang, J.; Cao, P.; Cao, Y.; Wu, Y.P.; Thompson, J.; Haas, H. A survey of positioning systems using visible LED lights. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 1963–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Z.; Wen, S.S.; Yang, C.; Yuan, D.L.; Guan, W.P. Universal and effective decoding scheme for visible light positioning based on optical camera communication. Electronics 2021, 10, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, S.H. Enhancement of signal performance in LED visible light communications using mobile phone camera. IEEE Photonics J. 2015, 7, 7903607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, Z.M.; Han, Z.Z.; Liu, H.L.; Shen, Q.X.; Wu, Z.Q. LED based high accuracy indoor visible light positioning algorithm. Optik 2021, 243, 166853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Huai, J.; Hua, L.; Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, R. RSS-based visible light positioning using non-linear optimization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 14134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liu, H.; Han, Z.Z.; Ren, Z.M. Indoor High Precision Three-Dimensional Positioning System Based on Visible Light Communication Using Improved Hybrid Bat Algorithm. IEEE Photonics J. 2020, 12, 6802513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Q.; Sekercioglu, Y.A.; Neild, A.; Armstrong, J. Position accuracy of Time-of-Arrival based ranging using visible light with application in indoor localization systems. J. Lightwave Technol. 2013, 31, 3302–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-Y.; Hann, S.; Park, C.-S. TDOA-based optical wireless indoor localization using LED ceiling lamps. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2011, 57, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Niu, X.; Li, T.; Li, S.; Huang, C.; Niu, Q. Exploring Fast Fingerprint Construction Algorithm for Unmodulated Visible Light Indoor Localization. Sensors 2020, 20, 7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Q.; Lin, B.; Feng, L.H.; Lv, H.C. Hybrid indoor localization scheme with image sensor-based visible light positioning and pedestrian dead reckoning. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 3214–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hussain, B.; Yue, C.P. Arbitrarily tilted receiver camera correction and partially blocked LED image compensation for indoor visible light positioning. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 4800–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.B.; Yang, Z.; Long, S.; Wu, Z.Q.; Zhao, X.M.; Liang, F.N.; Jiang, Z.L.; Chen, Z. High-speed indoor navigation system based on visible light and mobile phone. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 8200711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Huang, L.; Wen, S.; Yan, Z.; Liang, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z. Robot localization and navigation using visible light positioning and SLAM fusion. J. Lightwave Technol. 2021, 39, 7040–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Gong, C.; Xu, Z.Y. Experimental indoor visible light positioning systems with centimeter accuracy based on a Commercial smartphone camera. IEEE Photonics J. 2018, 10, 7908717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, J.; Zheng, J. High precision indoor visible light positioning algorithm based on double LEDs using CMOS image sensor. Applied Sciences. 2019, 9, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Lin, J.H.; Liu, M. Towards robust visible light positioning under LED shortage by visual-inertial fusion. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Pisa, Italy, 30 September–3 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhao, C.S.; Ding, G.Z.; Gong, J.; Liu, C.X.; Zhao, F.; Assoc Comp, M. A reliable and accurate indoor localization method using phone inertial sensors. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp), Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–8 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Y.; Mourikis, A.I. Online temporal calibration for camera-IMU systems: Theory and algorithms. Int. J. Rob. Res. 2014, 33, 947–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Liu, M. A tightly coupled VLC-inertial localization system by EKF. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3129–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Chen, K.; Tan, G.; Lu, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; He, T. Lips: A light intensity-based positioning system for indoor environments. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2016, 12, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhong, W.D.; Qian, K.M.; Zhang, S. A single LED positioning system based on circle projection. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 7905209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.P.; Huang, H.B.; Xu, Y.Z.; Wei, Z.H.; Yuan, S.C.; Lin, P.X.; Wu, H.; Lei, W.; Fang, J.B.; Chen, Z. A fast and high-accuracy real-time visible light positioning system based on single LED lamp with a beacon. IEEE Photonics J. 2020, 12, 7906512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Xiao, C.; Gao, J.; Ni, J.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, P.; Sun, G. A single LED lamp positioning system based on CMOS camera and visible light communication. Opt. Commun. 2019, 443, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.H.; Wan, H.; Li, X.X. A High-precision magnetic-assisted heading angle calculation method based on a 1D convolution neural network (CNN) in a complicated magnetic environment. Micromachines. Micromachines 2020, 11, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harle, R. A survey of indoor inertial positioning systems for pedestrians. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.H.; Wang, C.H.; Huang, T.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Chen, Y.S. An enhanced ZigBee indoor positioning system with an ensemble approach. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2012, 16, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, H. An-602 Using the adxl202 in Pedometer and Personal Navigation Applications; Analog Devices Inc.: Norwood, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.D. Improved Smartphone-Based Indoor Pedestrian Dead reckoning Assisted by Visible Light Positioning. IEEE Sen. J. 2019, 19, 2902–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.J.; Xia, L.Y.; Wu, D.J. Attitude and heading estimation for indoor positioning based on the adaptive cubature Kalman filter. Micromachines 2021, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.H.; Guan, W.P.; Wen, S.S.; Huang, L.Y.; Song, H.Z. Multirobot cooperative localization based on visible light positioning and odometer. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 7004808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LED Specifications | |
| Coordinates of LED1 (cm) | (−490,−28) |
| Coordinates of LED2 (cm) | (−1225,−300) |
| Coordinates of LED3 (cm) | (−1002,−620) |
| Coordinates of LED4 (cm) | (22,−148) |
| Rated voltage of the LED | 72 V |
| Power of the LED | 18 W |
| Mobile Phone Specifications | |
| Frame rate | 5 fps |
| Sampling rate of the accelerometer | 250 Hz |
| Resolution | 1920 × 1080 |
| Camera exposure time | 0.05 ms |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Wen, S.; Yuan, D.; Chen, J.; Huang, J.; Guan, W. CGA-VLP: High Accuracy Visible Light Positioning Algorithm Using Single Square LED with Geomagnetic Angle Correction. Photonics 2022, 9, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9090653
Yang C, Wen S, Yuan D, Chen J, Huang J, Guan W. CGA-VLP: High Accuracy Visible Light Positioning Algorithm Using Single Square LED with Geomagnetic Angle Correction. Photonics. 2022; 9(9):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9090653
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chen, Shangsheng Wen, Danlan Yuan, Junye Chen, Junlin Huang, and Weipeng Guan. 2022. "CGA-VLP: High Accuracy Visible Light Positioning Algorithm Using Single Square LED with Geomagnetic Angle Correction" Photonics 9, no. 9: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9090653
APA StyleYang, C., Wen, S., Yuan, D., Chen, J., Huang, J., & Guan, W. (2022). CGA-VLP: High Accuracy Visible Light Positioning Algorithm Using Single Square LED with Geomagnetic Angle Correction. Photonics, 9(9), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9090653





