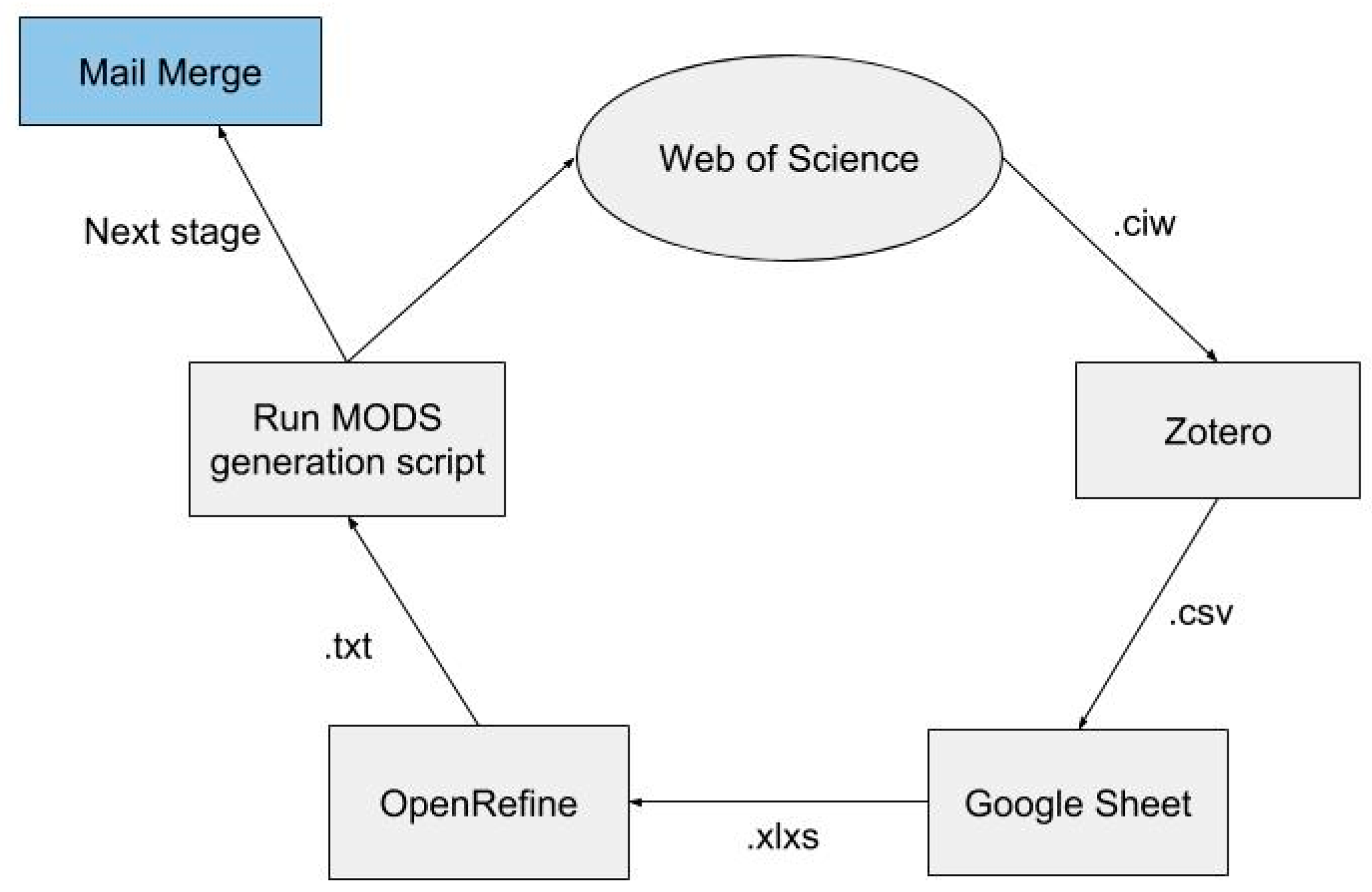
This content recruitment workflow is a component of a larger Open Access (OA) implementation plan proposed to the Florida State University (FSU) Faculty Senate by University Libraries staff following the adoption of an institutional OA policy in 2016. The challenge and goal of this plan is scaling repository operations by gathering author content and encouraging faculty to submit their manuscripts without the robust technical services of a commercial solution, such as Symplectic Elements. Commercial solutions were initially explored, however, it was soon determined that the annual cost to the library was too high to support. FSU Libraries operates their institutional repository (IR) on the open source platform Islandora, migrating from bepress in 2015. This migration occurred well before the Elsevier acquisition of bepress, fueling many institutions to look at open source platforms as an IR to support their community’s open scholarship. FSU’s migration from bepress to Islandora was made possible by having more resources, a new developer was hired, there was a pre-existing familiarity with Drupal, consortial hosting through Florida Virtual Campus (FLVC), and an active development community [
1].
In the last four years, the repository has expanded to include content other than theses and dissertations, such as capstone projects, technical/research reports, video ethnographies, journal articles, undergraduate research posters and honors theses, 3D models, and data sets. Following the adoption of the OA policy, a small team of librarians in the Office of Digital Research and Scholarship developed a plan to address the low faculty self-submission rates of journal publications to the repository. This plan pairs a metadata harvesting workflow and semi-automated metadata record creation with outreach emails to researchers about recent publications, providing them with information regarding the OA policy and the opportunity to upload their manuscript to the IR. Knowledge shared by the open community was invaluable in constructing this workflow and the goal of this work is to highlight those key resources, as well as to report on our progress recruiting content.
Literature Review
A historical overview of institutional repositories, their purpose and development are outside the scope of this review. There is a vast amount of literature that surveys IR deposit rates, many concluding that average self-archiving rates are low across institutions. This literature review intends to cover literature that examines factors influencing faculty IR participation and content recruitment, as well as the strategies developed by libraries to address low self-archiving rates.
According to Clifford Lynch’s 2003 definition of a “mature” institutional repository, FSU’s research repository, DigiNole, is well on its way to becoming one [
2]. Starting with theses and dissertations, the IR expanded by curating faculty and student research publications, as well as teaching materials and gray literature. Institutional records and heritage materials are under the purview of the University Archivist and are not part of DigiNole. Recently, we have started uploading data sets to the IR and linking them to research publications to fulfil public access mandates. Despite this growth, DigiNole experiences what generally seems true for repositories: A low faculty participation rate.
There is quite a lot of ground covered by many publications over the years, examining IR growth rates and investigations into faculty deposit rates. In his 2008 American Library Association (ALA) presentation, Royster thought faculty members would see the value in the IR themselves after he met with them at department meetings, but the self–submission rate was less than 10% [
3]. After moving to a more mediated deposit method, rates improved to 15–20%, with most of the material being contributed by the Physics department [
3]. There is already an established culture of open access in Physics through the posting of pre-prints on arXiv, so this likely contributes to such a high compliance rate from the Physics department. Royster found that locating articles and checking their publishing permissions first before going to the author resulted in a response rate of 90% [
3]. What exactly is motivating authors to contribute and what is preventing them from doing so?
According to a 2014 publication, Dubinsky examined the growth rate of IRs operating on the Digital Commons platform. Dubinsky found that the lack of faculty participation can be attributed to copyright concerns, preference to deposit in a disciplinary repository, difficult submission process, fears of plagiarism, and a general lack of awareness of the IR [
4]. A survey of Texas A&M University (TAMU) faculty by Yang and Li in 2015, also found that faculty members had a significant lack of awareness about the IR and concerns regarding copyright [
5]. The authors did not specify the kinds of copyright concerns that the faculty had. They determined that the IR benefited from much more focused promotion, although there seemed to be an overall lack of knowledge regarding the existence of library resources on campus [
5]. As we saw with Royster, promoting the IR is not the solution IR managers want it to be, but there was a greater response to reviewing copyright permissions before reaching out to faculty members.
There is also evidence that faculty members perceive pre-print and post-print versions of articles to be of lower quality than that of the final PDF files posted by publishers [
5]. The posting of an article in a .docx file format may appear incomplete; however, the only differences between a post-print and a publisher PDF files should lie in the typesetting, nothing more. So, if the content is peer-reviewed and the content is no different from what the publisher is distributing, then is the objection merely in the appearance of the document? Yang and Li do not go into detail about why faculty members think that these versions are of lower quality, merely that OA journals are seen by many faculty members as less prestigious and of lower quality, as are the post-prints deposited in the IR [
5]. They also collected responses from faculty members regarding their opinions about TAMU possibly adopting an OA mandate. Despite how widely adopted OA policies are, TAMU faculty are skeptical of the value of an OA policy for obtaining grant funding or making their research more visible and some are intensely opposed, believing it is in violation of their academic freedom [
5]. FSU’s OA policy passed unanimously, but it did include a waiver for faculty members wanting the choice to opt out of the non-exclusive license. Only two submitted a waiver and waiver submissions are still available for submission on FSU’s OA policy website.
It seems that the value of a repository and OA ideals are not quite enough to significantly increase faculty participation, so what workflows are librarians creating to address faculty reluctance to submit their work, their concerns regarding copyright, but also educating faculty on the benefits and the existence of the IR? In 2011, Hanlon and Ramirez published the results of a survey targeting IR managers to identify copyright clearance trends in staffing and workflows. Most respondents used a mediated submissions model and the librarians checked copyright permissions instead of faculty [
6]. Kansas State University (KSU) reported checking publisher permissions with SHERPA/RoMEO, an online resource of publisher OA policies, or the publisher website if no entry for the journal existed in SHERPA [
7]. Interestingly, despite how many respondents relied on SHERPA or existing copyright directories, most did not share the copyright information they found with other institutions by submitting updates or entries to community-driven services like SHERPA [
6]. It seems that many institutions depend heavily on SHERPA/RoMEO for copyright clearance [
3,
6,
7]. Our own workflow would not be possible without SHERPA’s API.
In 2013, Madsen and Oleen share their original outreach workflow for which the IR manager is responsible. In summary, the IR managers contact faculty members about the benefits of the IR, check publisher permissions with SHERPA/RoMEO, obtain the manuscript from faculty, create a metadata record and coverpage for the manuscript, and reply to faculty with the repository URL [
7]. KSU eventually evolve their workflow with the development of a workflow management system with a local web client used to track submissions and create metadata from citations downloaded from external databases [
7]. Their workflow is very similar to the content requirement workflow I will be describing. Due to lack of funding and minimal staffing, libraries are essentially forced to creatively find solutions and, in some cases, build their own systems.