Digital Technology 4.0 on Halal Supply Chain: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods


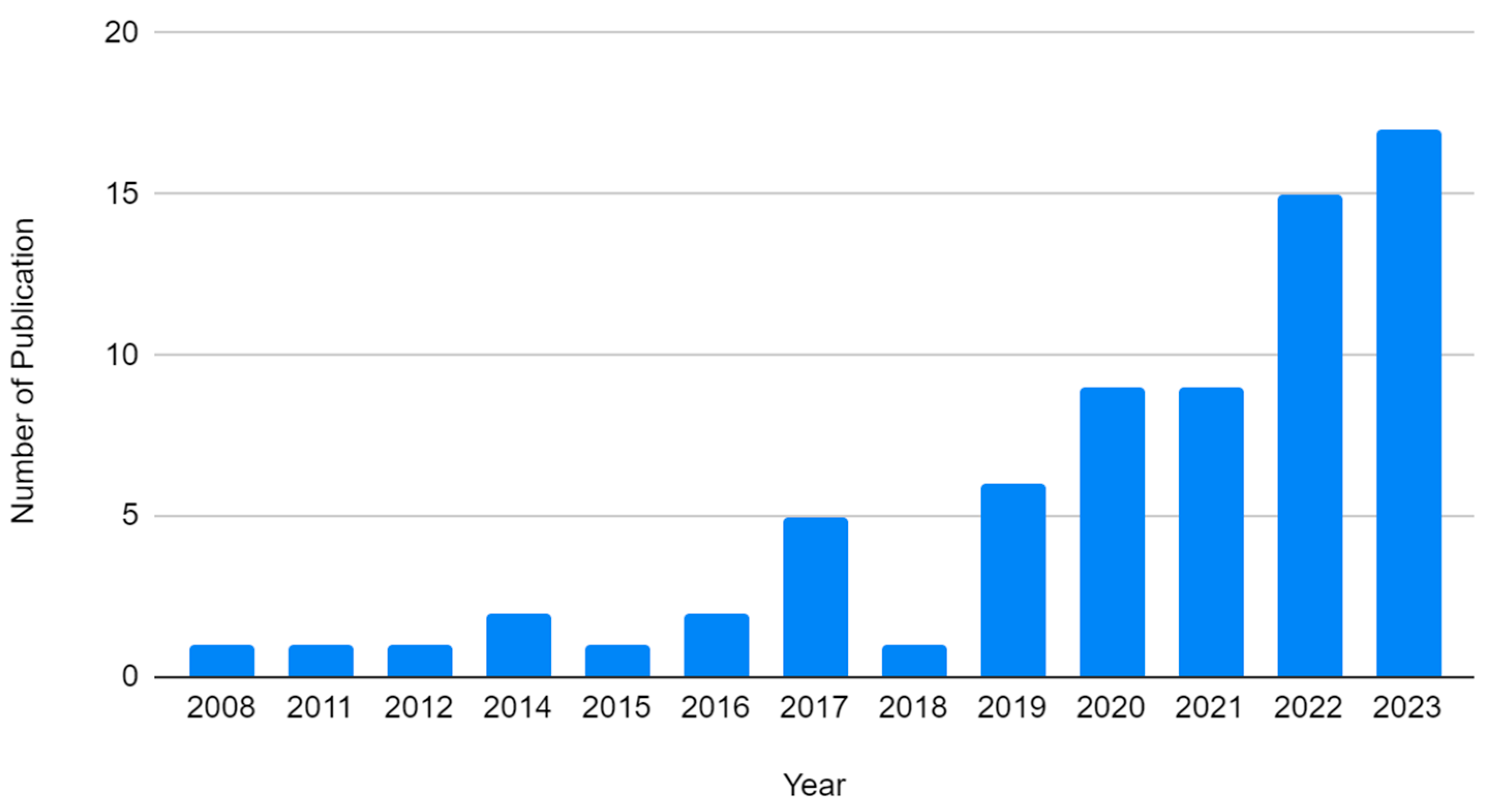
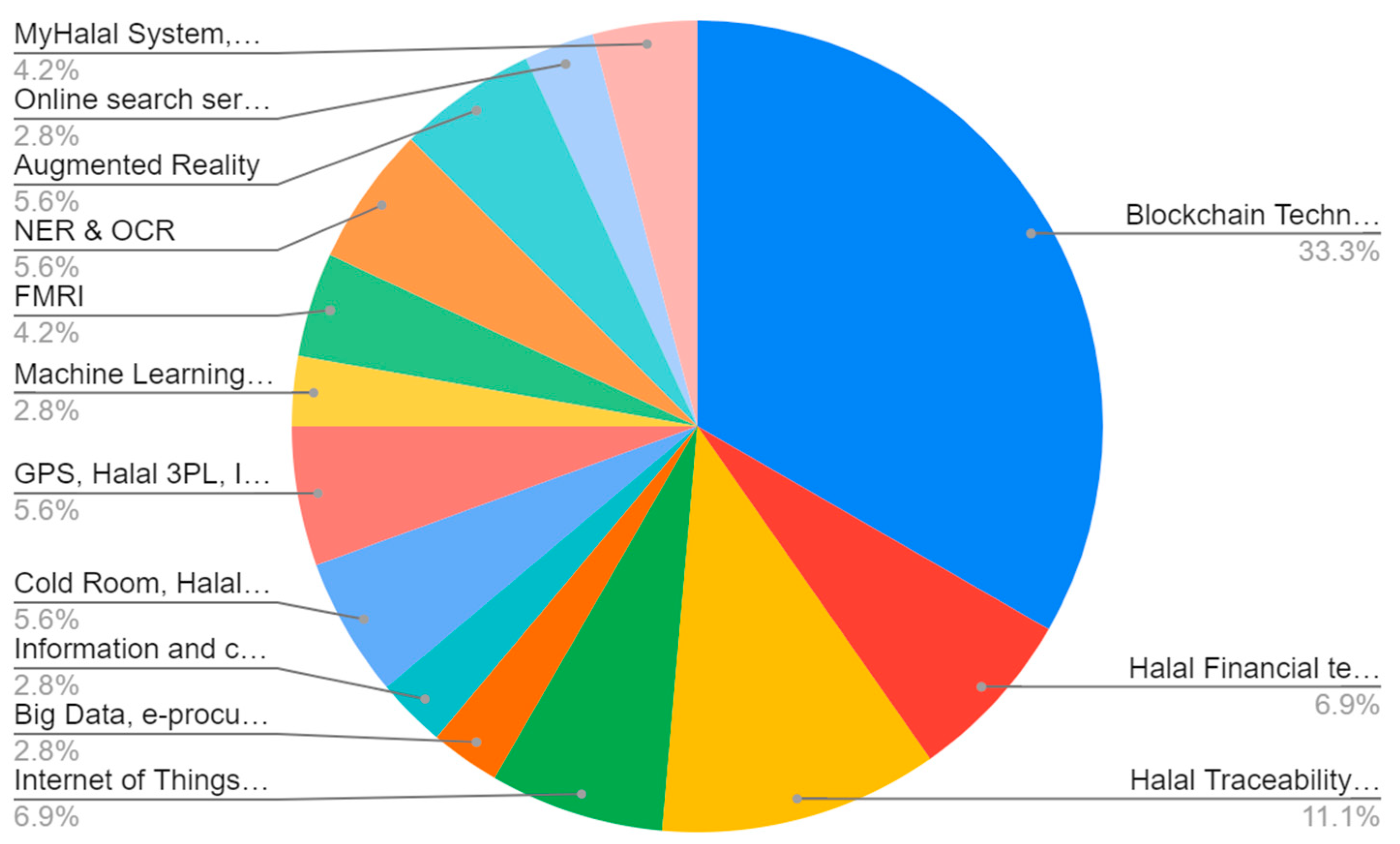
3. Results
4. Discussion
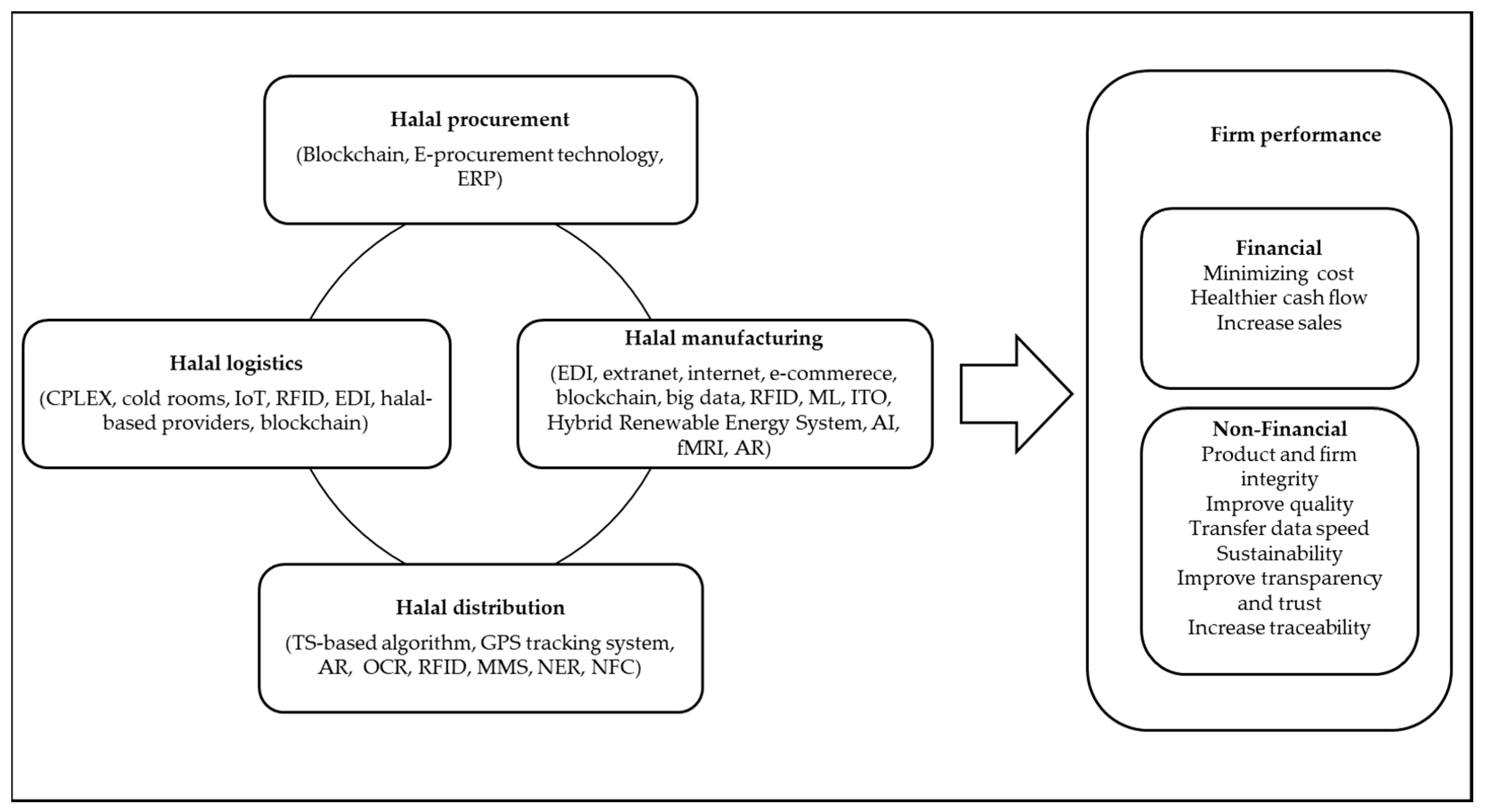
4.1. Halal Procurement
4.2. Halal Manufacturing
4.3. Halal Distribution
4.4. Halal Logistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Authors | Year | Findings | Technology in Halal Distribution | Firm Performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial | Non-Financial | ||||
| [40] | 2023 | The experiments conducted on numerical data and life-sized instances validate the proposed model and algorithm for optimizing halal product distribution while minimizing transportation costs and ensuring the integrity of halal products | TS-based algorithm | Minimizing transportation costs | Ensure the integrity of Halal products |
| [56] | 2016 | This article describes the Halal tracer technology, which enables tracking and tracing of cargo and vehicles carrying Halal commodities throughout the shipping process. | GPS tracking system (Halaltracer Technology) | x | Assist the firm in tracking and tracing products and vehicles carrying halal goods during the shipping process so that it is more effective and verification can be done automatically. |
| [71] | 2022 | focuses on the application of named-entity recognition (NER) and optical character recognition (OCR) for identifying halal food ingredients in Indonesia | NER and OCR | x | Ensuring products received by consumers are in accordance with halal standards |
| [85] | 2019 | Efficient segregation relies on effective communication, where the term ‘halal supply chain’ is encoded in shipping documents, on cargo labels, and within the ICT system. | Blockchain Technology | x | Improve traceability of halal documents |
| [92] | 2023 | Special tags are used to trace food products from the farm to the consumer and back, enabling the tracing of halal food items from consumer to producer, thereby reducing the risk of contamination | Blockchain, RFID, QR Code | x | Increase consumer trust to buy halal products |
| [94] | 2017 | The augmented reality technology scans the product’s brand to showcase its halal status. The results indicate user satisfaction with the application, deeming it useful and user-friendly. | OCR and Augmented Reality | x | Improve efficiency in checking the halal status of products |
| [95] | 2016 | Enable consumers to efficiently verify the Halal status of products wirelessly. | RFID | x | The verification of the product’s Halal status becomes straightforward, as each tag embedded in food packages is assigned a unique identification number. |
| [96] | 2008 | Camera phone-based MMS applications offer a cost-effective and efficient means to expedite the Halal verification process compared to entering text via SMS. | MMS camera phone-based | Production cost savings | Effective way method to accelerate the Halal verification procedure. |
| [97] | 2012 | The system can promptly verify and recognize product information, confirming their Halal status in real time. | MyHalal system | x | Improve verification of halal product status in real-time |
| [98] | 2017 | The augmented reality technology scans the brand of the product to display its halal status. | OCR and Augmented Reality | x | Enhance the efficiency of verifying the halal status of products. |
| [99] | 2017 | The test results indicate that the developed application can identify Halal products based on the labeled information. | OCR and Web Service | x | Improve the effectiveness of confirming the halal status of products. |
| [101] | 2017 | The use of augmented reality can detect halal product status | Augmented Reality | x | Enhance the efficiency of verifying the halal status of products. |
| Authors | Year | Findings | Technology in Halal Manufacturing | Firm Performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial | Non-Financial | ||||
| [24] | 2020 | The use of technology in the family halal food business can improve the effectiveness of their supply chain, leading to improved product quality and meeting customers’ requirements | EDI, Extranet, Internet, and electronic commerce | Applying technology in the company’s supply chain requires an investment, which requires huge amounts of funds for the family business owners, especially in the halal food industry. | Technology can improve the effectiveness of supply chain processes in family halal food businesses. However, it does not necessarily lead to increased efficiency. |
| [42] | 2023 | The Halal Supply Chain Management Transactions (HSCMT) prototype includes a payment gateway that can be embedded into a Halal SME owners’ e-commerce site, creating a holistic Halal Financial technology (FinTech) transaction permissibility dashboard. | Halal Financial Technology (FinTech) | Enhance business strategy by minimizing costs | The developed HSCMT prototype increases the effectiveness of Halal Supply Chain Management for Malaysia Halal SME Owners (MHSO) with an average usability score of 83.67. |
| [45] | 2022 | The model Blockchain-Based Traceability system can be enhanced to be a national standard tool to develop the economy towards a sustainable supply chain. | Blockchain Technology | The use of Blockchain with the Avalanche platform is more cost-effective than the Ethereum network | Blockchain-Based Traceability System to Support the Indonesian Halal Supply Chain Ecosystem |
| [46] | 2021 | Blockchain technology has the potential to improve the Halal Supply Chain by enhancing trust, transparency, and information disclosure between supply chain participants. Permissioned Blockchain, such as Hyperledger Fabric, is suitable for the Halal Supply Chain as it ensures transaction security, speed, and effective data transfer. | Permissioned Blockchain (Hyperledger Fabric) | x | Permissioned Blockchain is useful for the Halal Supply Chain not just because it can secure transactions from some of the halal issues (trust, transparency, and information disclosure) but also because the transaction speed and rate to transfer data are very effective |
| [48] | 2022 | The results show that the most significant factors for the non-Halal sustainable food supply chain in dictators are food consumption, food safety, food security, resilience, and food waste management. The most crucial indicators of a Halal sustainable food supply chain consist of Halal certification, Halal supply chain trust, Islamic values, and Halal food safety. | Big Data (Data-driven) | x | Improve the firm’s ability to be more sustainable in the halal food chain process |
| [49] | 2022 | The technology with the smart contract is proposed with inputs from three Blockchain software providers with the aim to create a conceptual framework that integrates both Halal processes and technologies to improve traceability of Halal food supply chain from farm to fork | Blockchain Technology | x | Improve the halal food supply chain’s traceability from farm to fork. |
| [51] | 2020 | This study provides an integrated model that explains 73.19% of the variance in intention to participate in blockchain-based Halal traceability systems. | Blockchain Technology | Investing in blockchain technology requires a lot of resources, especially in terms of costs. | Can improve halal traceability |
| [52] | 2021 | The article outlines the elements of the halal supply chain, including human resources, processes, environment, accreditations, logistics, and traceability. The objective is to enhance productivity and quality for food manufacturers involved in the production of halal products. | Radio Frequency Identification Device (RFID) with Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point | Reduce the cost of product removal from the market | Preventing the occurrence of product recalls, especially in terms of halal assurance, will lead to the level of customer trust and confidence in the integrity of the halal industry |
| [42] | 2023 | The study proposes a Halal transaction compliance process using a weighted compliance scorecard (WCS) to determine the permissibility of individual transactions in fintech-embedded e-commerce. | Fintech (Halal Transaction Compliance Protocol) | This fintech can bridge international transactions. | It can assist firms in tracking financial activities. |
| [54] | 2022 | The research found that with contributions from all supply chain players, blockchain-enabled halal fashion traceability enables end customers to get comprehensive data from the initial supply chain stage (sourcing) to their wardrobe. | Blockchain Technology | x | Ensuring transparency and security related to Halal Fashion Traceability |
| [55] | 2023 | The findings reveal that adopting blockchain technology positively and significantly affects Halal supply chain performance and firm competitiveness | Blockchain Technology | Benefits from the tracking system made possible by blockchain technology include evidence of the transparent flow of finances, information, and goods from producer to customer. | Supporting blockchain technology’s accessibility can improve traceability and transparency, connecting upstream and downstream flows that influence improvements in the efficiency of the Halal supply chain’s performance. |
| [57] | 2023 | The empirical analysis data suggest that knowledge and attitude show a significant impact on the intentions of SME owners to participate in waqf, while religiosity does not have a significant impact on the intentions of Malaysian and Indonesian SME owners to participate in waqf. | Digitalization and advanced technology through waqf funds (Financial Technology) | x | Increase sustainability of MSMEs in Malaysia and Indonesia by 90% through waqf participation |
| [58] | 2023 | Findings: A blockchain is identified as having the opportunity to promote value innovation in the halal industry through its features. This study defines a typology model of value innovation-based blockchain for the halal industry that takes place on a particular spectrum. | Blockchain Technology | x | More transparent transaction processes through decentralized protocols can increase the value of innovation in management decision-making in each operation process. |
| [59] | 2023 | The study results revealed that synergy and development patterns between Islamic banks and Muslim-friendly tourism should be carried out simultaneously. Six aspects to consider in building and developing the synergy include establishing partnership cooperation, optimizing the role of Islamic bank stakeholders and Muslim-friendly tourism, improving ACES (access, communication, environmental, and service infrastructure), intensifying education and literacy of the halal industry, innovating and transforming technology, and conducting clusters for the halal industry development. | Machine Learning and Digital Innovation Services | x | Adapting this technology will create a new offer to existing customers to be more loyal, and data collection will then be recorded, which ends in deep learning customer engagement always to provide an appropriate and satisfying service |
| [61] | 2022 | The study emphasizes the growing importance of a traceability system that is perceived to be easy and useful in the food industry, particularly for ensuring halal compliance. | Halal traceability system | “The use of a halal traceability system would assist our firm in reducing the operating cost”. | The adoption of a halal traceability system can enhance SME business and improve the integrity of the halal industry. |
| [62] | 2020 | Building an integrated Islamic financial ecosystem is crucial for improving the performance of the halal industry in Indonesia | Financial Technology | x | Increase synergy in the halal industry ecosystem by emphasizing the role of each institution in minimizing the problems related to the halal industry |
| [64] | 2015 | Information Technology Outsourcing (ITO) can be a solution to help SMEs in Malaysia accelerate their adoption of e-business, as they often lack the resources and skills to develop in-house IT applications. | Information Technology Outsourcing (ITO) | Lower labor specialization costs while simultaneously raising cash flow and the financial performance index. | Provides detailed factors in the relationship between IT Outsourcing and the company. |
| [65] | 2021 | The application of technology can have a positive and encouraging impact on improving the quality of life. The use of technology can improve the economy, education, and the healthcare industry. | Blockchain Technology | x | It can help companies identify the authenticity of halal certification processes to increase trust and ensure the authenticity of halal logos. |
| [66] | 2022 | The study provides valuable insights for government bodies and Halal logistics providers to enhance the adoption rate of Halal transportation and improve the Halal supply chain. | Halal Transportation System | Can save transportation costs incurred | The benefits of using the Halal transportation system among Halal food manufacturers are easing the doubts about Halal quality, increasing the image of the products, and another shape. |
| [20] | 2022 | Halal warehousing is a frequently emerging area around the world. Technology plays an essential role in halal warehousing. Both the variables of the technology have been found to be significant. | Halal Warehousing System | x | A firm can measure products/goods that are aligned with Halal specifications, value systems, and job responsibilities |
| [1] | 2021 | Technology plays a crucial role in managing risks in the HSCM, especially in terms of information management and communication. | Blockchain Technology, IoT, and RFID | x | Implementing technology-driven solutions can help in reducing risks associated with product adulteration, counterfeiting, and non-compliance with Halal requirements |
| [67] | 2020 | The research indicated that the D-loop region has potential utility for investigative purposes in the field of halal forensics, serving as the primary mitochondrial DNA segment for comparisons. | Displacement Loop mtDNA | x | Facilitate halal forensic investigations in determining the halalness of critical raw materials (animal) |
| [68] | 2020 | No notable differences in brain activity were observed when subjects observed Halal and non-Halal logos. However, significant alterations in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex were detected when meat images were associated with Halal and non-Halal labels. This implies that the impact of the Halal logo on perception is contingent upon its conjunction with a product. | functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). | x | Knowing consumer interest in buying halal products that have a halal logo |
| [70] | 2019 | The ventromedial prefrontal cortex activation increased significantly in all participants when exposed to Halal images, whether of raw or cooked meat, possibly due to the heightened emotional sensitivity of Muslim consumers. | functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). | x | Knowing consumer desires in choosing halal products |
| [72] | 2022 | This augmented reality application aims to enhance consumer awareness of halal cosmetic products and aid them in making informed decisions when purchasing cosmetic products. | Augmented Reality | The cost incurred to adopt this technology is quite expensive | Increase consumers’ awareness of buying halal cosmetics because it gives them experience before buying the product. |
| [73] | 2022 | To enhance their success prospects in Muslim markets, marketing managers of multinational companies should employ advertising messages emphasizing the ethical aspects of their products and utilizing cognitive appeals rather than emotional ones. | functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). | x | Facilitate marketing managers in making halal product advertisements by paying attention to the ethical and emotional aspects of customers |
| [74] | 2020 | FinTech firms ought to prioritize refining their products to align with Islamic Sharia principles rather than relying on the social environment to attract Muslim consumers for product purchases. | Sharia Fintech | x | Facilitate the tracking of transactions that comply with sharia principles. |
| [75] | 2021 | The study results showed that ensuring halal traceability in food products is essential for impacting consumers’ buying choices. | Blockchain Technology | x | Ensuring the halal traceability of a product, thus increasing consumer interest in buying the product |
| [76] | 2023 | The incorporation of blockchain technology into the management of the halal food supply chain is emphasized as a promising strategy to improve transparency, trust, and integrity. | Blockchain Technology | Can reduce the expenses associated with manual halal traceability processes. | Improve transparency and trust in the supply chain |
| [77] | 2021 | This study investigates the application of Blockchain technology to enhance the integration and accountability of data activities among stakeholders in the Halal Assurance System. The utilization of Blockchain aims to improve the traceability of halal products, ultimately fostering consumer trust and increasing awareness of the value of halal products. | Blockchain Technology | Minimize lost costs | Improve integration and accountability of Halal Assurance System stakeholder data activities. Can further increase consumer confidence and awareness of the value of halal products |
| [78] | 2022 | Challenges in implementing blockchain technology innovation | Blockchain Technology | x | Improved transparency, traceability, and timely decision-making |
| [79] | 2022 | Consumers of halal chicken products will be confident that the chicken slaughterhouse adhered to the halal assurance system in its critical halal-related processes | Blockchain Technology | Increase product sales | Increase the certainty that products have been processed in accordance with applicable halal standards |
| [80] | 2023 | The supply chain in a large city presents numerous opportunities to capture and leverage relevant smart data, which can be utilized to enhance efficiency, transparency, and sustainability. | blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI) | x | Enhanced monitoring and assurance of adherence to diverse standards and sustainability across the supply chain. |
| [81] | 2022 | Utilizing appropriate technology can enhance documentation and transparency, proving effective in addressing these issues. | Blockchain Technology | The cost of implementing blockchain technology is quite high | Ensuring transparency in documentation involves effectively recording information and transactions. The system has demonstrated its security and transparency, as all involved parties have public access to transaction details. |
| [82] | 2019 | The findings of this research underscore the significance of having a “user-friendly” online search service accessible to Muslim consumers. | Online search service | x | Improving the effectiveness of halal product status search |
| [83] | 2023 | various technology platforms devised for the dengue vaccine, the recombinant subunit vaccine, and the DNA vaccine show potential for creating halal vaccine products. | Halal dengue vaccine technology | Affordable price | Improving prevention of dengue fever outbreaks |
| [84] | 2020 | The findings indicated a low level of adoption of IoT among halal agro-food SMEs for managing their business operations. | Internet of things | High costs | The implementation of IoT has undoubtedly established a reliable platform for the supply chain of halal agro-food SMEs. |
| [86] | 2019 | The primary concept of incorporating DOA with IoT technology gateways is to offer standardized access to diverse information and services related to products, including identification, description, search and retrieval, security, integrity, trust, and data typing. | digital object architecture (DOA) & RFID | x | The system provides effective technical guidelines for companies to monitor the entire product lifecycle using the Internet of Things. |
| [87] | 2022 | Smart contracts, encompassing traceability, decentralization, and anonymity, are introduced into the model as moderators to investigate their impact on the integrity of the halal supply chain. | Blockchain technology | x | Improve the integrity of the halal supply chain |
| [88] | 2023 | We discovered that achieving high accuracy in link prediction is feasible through the utilization of conventional machine learning methods. | Machine Learning | x | Improve the efficiency of checking the difference between halal products and non-halal products. |
| [89] | 2023 | Academics and industry practitioners are invited to improve traceability in the Halal supply chain and assurance pathway. | Blockchain technology | x | Improving transparency in halal supply chain and assurance pathways |
| [90] | 2019 | As the Halal Food sector experiences growth, organizations need to enhance their supply chain efficiency, and Blockchain emerges as a solution offering increased transparency and assurance of Halal compliance. | Blockchain technology | x | Improving transparency and assurance of halal compliance |
| [91] | 2021 | Blockchain technology can ensure the quality and halal attributes of food products. | Blockchain technology | Minimize tracking costs | Tracking speed is up to 10 times faster than conventional methods, leading to minimized losses through more targeted issue resolution. |
| [102] | 2017 | Employing NFC and RFID tags, as opposed to barcodes, reduces the risk of fraud in the halal food industry. | RFID and NFC | x | NFC and RFID mobile shopping technologies streamline the validation of halal status, allowing customers to do so effortlessly through their personal smartphones. |
| [103] | 2018 | The Muslim consumer’s view of online traceability as beneficial is shaped by three key factors: their inclination to trust, commitment to a healthy lifestyle, and the reputation of both the company and certification bodies. | Online Traceability | x | Improve company reputation |
| [104] | 2014 | Hybrid Renewable Energy System can minimize the excess energy that occurs during the production process. | Hybrid Renewable Energy System | x | Improving the sustainability of environmentally friendly businesses |
| [105] | 2011 | The combination of ICT (RFID) in the halal supply chain can be the answer to tracing and tracing issues in Malaysia. | RFID | x | Improving the integrity of halal products |
| Authors | Title | Year | Findings | Technology in Halal Procurement | Firm Performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial | Non-Financial | |||||
| [43] | 2023 | Based on the results of the hybrid method approach (ISM-MICMAC-System Dynamics), the flexibility criterion can influence other criteria. The following criteria are cost and traceability criteria | Blockchain Technology | Increase operational costs | x | Improved product quality due to well-managed traceability management |
| [50] | 2020 | The findings indicate that the quality of halal service providers and the retail sector’s readiness for technological adoption have a major impact on the effectiveness of halal logistics. | E-procurement technology | x | x | The use of technology can improve performance in order to speed up halal traceability. However, the use of technology needs to be balanced with the ability of employees to use this technology. |
| [93] | 2023 | A usability evaluation of an interactive application for halal products using optical character recognition and augmented reality technologies | The integration of blockchain and ERP can enhance corporate governance, leading to improved company performance in the long run. | Blockchain Technology and ERP | Reduce operational cost | Through effective management of halal product procurement, companies can guarantee the delivery of products with halal assurance to consumers. |
| Authors | Year | Findings | Technology in Halal Logistics | Firm Performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial | Non-Financial | ||||
| [41] | 2019 | The research highlights the importance of separating Halal and Haram (forbidden) products and considers the chain effect of Haram facilities on the entire Halal food logistics network. Furthermore, the paper investigates the optimal location and allocation of the Halal food logistics network, which includes farms, butcheries, and food plants that follow strict Islamic food regulations. | CPLEX and hybrid genetic algorithm | There are indications of an increase in costs in developing a halal logistics network. This is influenced by the amount of distance traveled. However, the increase in total network development costs does not mean that each cost element continues to increase | Improve the efficiency of locating farms, butcheries, and food plants |
| [44] | 2023 | The research results revealed the PLS warehouse process flow, their halal implementation in warehouse management, and their perception of the importance of halal warehouse practice for halal pharmaceutical products. This could offer significant insight to the manufacturers, patients, users, researchers, or academicians. | Pharmaniaga Lifescience (Cold rooms) | x | Increase efficient halal document checking and verification process |
| [47] | 2021 | The study highlights the importance of technology readiness in improving customer satisfaction and organizational operations in the halal meat industry. | Internet of Things (IoT), RFID, and EDI | x | The use of technology in halal logistics can improve the quality of information, the quality of personnel contact, order accuracy, order conditions, order discrepancies, and order expenditure amount. |
| [53] | 2022 | The development of a digitally enabled community in ASEAN, represented by internet and mobile phone users, may have a significant impact on the region’s potential to become a global leader in halal logistics. | Information and communication technologies (ICT)-Digitally-enable community | x | Improve the efficiency with which halal logistics are conducted, offer improved logistical organization, and boost halal performance. |
| [60] | 2023 | Building a Halal logistics brand through traceability technology and Halal training is crucial for logistics service providers to stand out in the competitive market and attract Sharia compliance-oriented consumers. | Halal Traceability Technology (Product ID and RFID) | x | The usage of Halal traceability technology in Halal logistics can significantly improve the performance of logistics service providers and enhance the market recognition of their Halal logistics brand. |
| [63] | 2020 | The emergent resource-capability of halal logistics services significantly impacts customer service innovation and cost advantages. Halal-based third-party logistics providers should focus on developing their resource capability to enhance competitiveness in the dynamic halal market. | Halal-based third-party logistics (3PL) providers | x | Halal-based 3PL providers with high and medium resource capabilities achieve greater customer service innovation and cost advantages significantly |
| [69] | 2021 | The paper suggests a conceptual framework named Traceability-Technology-Training (3T) as a directive for regulatory bodies to endorse company-level halal logistics initiatives through a bottom-up approach. | Blockchain technology | x | Improve efficiency in traceability during the logistics process so as to minimize product contaminations |
| [100] | 2014 | The use of ICT (RFID) can help companies in monitoring their transportation. | Information Communication Technology (ICT)-RFID | x | Improve the effectiveness of monitoring halal transportation |
References
- Khan, S.; Khan, M.I.; Haleem, A. Risk Assessment model for Halal Supply Chain using an integrated approach of IFN and D number. Arab. Gulf J. Sci. Res. 2019, 41, 338–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieman, M.; van der Vorst, J.G.A.J.; Ghazali, M.C. Principles in Halal Supply Chain Management. J. Islam. Mark. 2012, 3, 217–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Khan, M.I. Towards successful adoption of Halal logistics and its implications for the stakeholders. Br. Food J. 2017, 119, 1592–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qurtubi; Kusrini, E. Research in halal logistics and halal supply chain: Issue and area development. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 154, 01096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Talib, M.S.; Abdul Hamid, A.B. Halal logistics in Malaysia: A SWOT analysis. J. Islam. Mark. 2014, 5, 322–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieman, M. The application of Halal in supply chain management: In-depth interviews. J. Islam. Mark. 2011, 2, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri-Mirza, A. Global Halal Market—Statistics & Facts; Statista: Hamburg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbandeh, M. Halal Industry: Market Share by Sector Worldwide 2018–2024; Statista: Hamburg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.A.J.; Liu, J. The challenges of Islamic branding: Navigating emotions and halal. J. Islam. Mark. 2011, 2, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailani, S.; Iranmanesh, M.; Aziz, A.A.; Kanapathy, K. Halal logistics opportunities and challenges. J. Islam. Mark. 2017, 8, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, A.H.; Zainuddin, Y.; Ramayah, T. Applying the TOE Framework in the Halal Warehouse Adoption Study. J. Islam. Account. Bus. Res. 2017, 8, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Research on the Impact of Manufacturing Digital Technology Transfer on Knowledge Flow Based on Multilayer Regression; Atlantis Press: Dodrecht, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, E.W.T.; Peng, S.; Alexander, P.; Moon, K.K.L. Decision support and intelligent systems in the textile and apparel supply chain: An academic review of research articles. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogler, C.; Rauch, P. Discrete event simulation of multimodal and unimodal transportation in the wood supply chain: A literature review. Silva Fenn. 2018, 52, 9984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogler, C.; Rauch, P. Lead time and quality driven transport strategies for the wood supply chain. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2023, 47, 100946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, I.O.; Shevtshenko, E.; Rossi, T.; Strozzi, F. Industry 4.0 technologies as enablers of lean and agile supply chain strategies: An exploratory investigation. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2021, 32, 1150–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yue, X.; Jin, A.; Yen, D.C. Smart supply chain management: A review and implications for future research. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2016, 27, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekhnini, K.; Cherrafi, A.; Bouhaddou, I.; Benghabrit, Y.; Garza-Reyes, J.A. Supply chain management 4.0: A literature review and research framework. Benchmarking Int. J. 2020, 28, 465–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catur Wahyuni, H.; Waskito. Halal Risk Priority in Food Supply Chain Manajemen Based on A Technology Perspective. JBMP J. Bisnis Manaj. Dan Perbank. 2021, 6, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameenullah, A.; Hasnain, A.; Waqar, A. The Role of Technological, Organizational and Environmental Factors in the Adoption of Halal Warehousing. Hamdard Islam. 2022, 45, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsanto, B.; Firmansyah, E.A. A twenty years bibliometric analysis (2002–2021) of business economics research in ASEAN. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2023, 10, 2194467, Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.; Chung, L.; Kumar, A.; Zailani, S.; Tan, K.H. A sustainable Blockchain framework for the halal food supply chain: Lessons from Malaysia. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 170, 120870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, J.M.; Chandia, M.; Regenstein, J.M. Halal integrity in the food supply chain. Br. Food J. 2017, 119, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendayani, R.; Febrianta, M.Y. Technology as a driver to achieve the performance of family businesses supply chain. J. Fam. Bus. Manag. 2020, 10, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizki, D.; Hamzah, M.; Fakhiroh, Z.; Hendri, D. Best Practice Halal Integrity Management in The Logistic Chain Scheme: Analysis of Opportunities and Challenges. J. Islam. Econ. Laws 2023, 6, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusydiana, A.S.; Irfany, M.I.; As-Salafiyah, A.; Tieman, M. Halal supply chain: A bibliometric analysis. J. Islam. Mark. 2023, 14, 3009–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indarti, N.; Lukito-Budi, A.S.; Islam, A.M. A systematic review of halal supply chain research: To where shall we go? J. Islam. Mark. 2020, 12, 1930–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, M.S.; Abdul Hamid, A.B.; Zulfakar, M.H. Halal supply chain critical success factors: A literature review. J. Islam. Mark. 2015, 6, 44–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, D.I.; Vanany, I.; Ciptomulyono, U. Blockchain Application in Food Supply Chains: Bibliometric Analysis and Future Research. Int. J. Food Syst. Dyn. 2023, 14, 146–165. [Google Scholar]
- Masudin, I.; Rahmatullah, B.B.; Agung, M.A.; Dewanti, I.A.; Restuputri, D.P. Traceability System in Halal Procurement: A Bibliometric Review. Logistics 2022, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, N.I.I.B.; Zailani, S.; Aziz, A.A.; Rahman, M.K. Halal logistic services, trust and satisfaction amongst Malaysian 3PL service providers. J. Islam. Mark. 2022, 13, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, M.S.A. Identifying halal logistics constraints in Brunei Darussalam. J. Islam. Mark. 2020, 12, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsanto, B.; Mulyana, A.; Faisal, Y.A.; Shandy, V.M.; Alam, M. A Systematic Review on Sustainability-Oriented Innovation in the Social Enterprises. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsanto, B.; Permana, C. Understanding Sustainability-oriented Innovation (SOI) Using Network Perspective in Asia Pacific and ASEAN: A Systematic Review. JAS J. ASEAN Stud. 2019, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durach, C.F.; Kembro, J.; Wieland, A. A New Paradigm for Systematic Literature Reviews in Supply Chain Management. J. Supply Chain. Manag. 2017, 53, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioseliani, A.D.; Orekhovskaya, N.A.; Svintsova, M.N.; Panov, E.G.; Skvortsova, E.M.; Bayanova, A.R. Bibliometric Analysis of Articles on Digital Educational Environments. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 2023, 15, ep426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The prisma 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Med. Flum. 2021, 57, 444–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denyer, D.; Tranfield, D. Producing a Systematic Review. In The SAGE Handbook of Organizational Research Methods; Sage Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 671–689. [Google Scholar]
- Rusydiana, A.S.; Sari, M.; Yudhistira Adi Seputra, R.; Wachyudi, A.F. How Far has Halal Transportation been Researched? Libr. Philos. Pract. 2021. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85109929487&partnerID=40&md5=09825f7f934b5b0a794632c247c5a53d (accessed on 25 December 2023).
- Kurniawati, D.A.; Handoko, A.; Piplani, R.; Rosdiahti, R. Optimized distribution of halal products using tabu search. J. Islam. Mark. 2023, 14, 1058–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Kwag Sil Ko, Y.D. Optimal design for the Halal food logistics network. Transp. Res. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2019, 128, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjudi, S.; Setik, R.; Raja Lope Ahmad, R.M.T.; Wan Hassan, W.A.; Md Kassim, A.A. Utilization of Business Analytics by SMEs In Halal Supply Chain Management Transactions. JOIV Int. J. Inform. Vis. 2023, 7, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, D.I.; Masudin, I.; Susanty, A.; Anna, I.D. Modeling of halal supplier flexibility criteria in the food supply chain using hybrid ISM-MICMAC: A dynamic perspective. Cogent Eng. 2023, 10, 2219106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.M.A.W.; Zatul-Illia, H.; Shofiyyah, M. Implementation of Halal Logistics in Halal Pharmaceutical Industry: A Study on Halal Warehouse System in Pharmaniaga Lifescience. Glob. J. Al Thaqafah 2023, SI, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamsyah, A.; Hakim, N.; Hendayani, R. Blockchain-Based Traceability System to Support the Indonesian Halal Supply Chain Ecosystem. Economies 2022, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surjandari, I.; Yusuf, H.; Laoh, E.; Maulida, R. Designing a Permissioned Blockchain Network for the Halal Industry using Hyperledger Fabric with multiple channels and the raft consensus mechanism. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masudin, I.; Jie, F.; Djajadikerta, H.G.; Widayat, W. The Effect of Halal Retail and Manufacturing Technology Readiness on Halal Meat Logistics Performance. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 2021, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.L.; Ha, H.M.; Tran, T.P.T.; Bui, T.D.; Lim, M.K.; Lin, C.W.; Helmi Ali, M. Data-driven on sustainable food supply chain: A comparison on Halal and non-Halal food system. J. Ind. Prod. Eng. 2022, 39, 430–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.; Gligor, D.; Ngah, A. Applying blockchain for halal food traceability. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2022, 25, 947–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masudin, I.; Jie, F.; Widayat, N.A. Impact of halal supplier service quality and staff readiness to adopt halal technology on halal logistics performance: A study of Indonesian halal meat supply chain. Int. J. Agil. Syst. Manag. 2020, 13, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hew, J.-J.; Wong, L.; Tan, G.W.; Ooi, K.; Lin, B. The Blockchain-Based Halal Traceability Systems: A Hype or Reality? Supply Chain. Manag. Int. J. 2020, 25, 863–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.; Aldeehani, A.; Alhajji, M.; Aziz, F.A. Development of integrated supply chain system in manufacturing industry. J. Comput. Methods Sci. Eng. 2021, 21, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, S.E.; Musari, K. ASEAN towards a global halal logistics through the digitally enabled community. Int. J. Asian Bus. Inf. Manag. 2022, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumarliah, E.; Li, T.; Wang, B.; Indriya, I. An examination of halal fashion supply chain management risks based on the fuzzy best-worst approach. Inf. Resour. Manag. J. 2021, 34, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendayani, R.; Fernando, Y. Adoption of Blockchain Technology to Improve Halal Supply Chain Performance and Competitiveness. J. Islam. Mark. 2022, 14, 2343–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, M.A.; Mansor, S.; Ahmad, N.; Adnan, W.A.W.; Muhammad Wali, I. The reliability of halal product transportation using gps tracking system. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2016, 90, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- Laila, N.; Ratnasari, R.T.; Ismail, S.; Mohd Hidzir, P.A.; Mahphoth, M.H. The intention of small and medium enterprises’ owners to participate in waqf: The case of Malaysia and Indonesia. Int. J. Islam. Middle East. Financ. Manag. 2023, 16, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purusottama, A.; Sunitiyoso, Y.; Simatupang, T.M. Exploring the potential of blockchain adoption for promoting value innovation: A case of the halal industry. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2023, 29, 2034–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhim, M.; Sonjaya, A.; Salim, Z.; Rahman, A.; Basmar, E.; Abdullah, R.; Ali, M. The Synergy of Islamic Banks and Muslim-Friendly Tourism: Patterns of Halal Industry Development in Indonesia. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2023, 18, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, Y.; Ika Sari, W.T.; Abideen, A.Z.; Mergeresa, F. Traceability Technology, Halal Logistics Brand and Logistics Performance: Religious Beliefs and Beyond. J. Islam. Mark. 2022, 14, 1007–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarulzaman, N.H.; Muhamad, N.A.; Mohd Nawi, N. An investigation of adoption intention of halal traceability system among food SMEs. J. Islam. Mark. 2022, 13, 1872–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, S.B.; Sekaryuni, R.; Widarjono, A.; Tohirin, A.; Sudarsono, H. Promoting Islamic financial ecosystem to improve halal industry performance in Indonesia: A demand and supply analysis. J. Islam. Mark. 2021, 12, 992–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorliza, K. Resource-capability of halal logistics services, its extent and impact on performance. J. Islam. Mark. 2021, 12, 813–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, R.; Ahmad, A.; Tang, A.Y.C. A Comparative Study on It Outsourcing Models for Malaysian SMEs e-Business Transformation. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290518613 (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Ariffin, M.F.M.; Hamid, M.F.A. Negotiating Halal Crimes: The Use of Block-Chain Technology. Glob. J. Al Thaqafah 2021, 11, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, A.H.; Thurasamy, R.; Mohd Salleh, N.H.; Jeevan, J.; Md Hanafiah, R.; Eneizan, B. Halal transportation adoption among food manufacturers in Malaysia: The moderated model of technology, organization and environment (TOE) framework. J. Islam. Mark. 2022, 13, 2563–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosiawan, A.; Rohman, A.; Zain, N.M. The use of Displacement Loop mtDNA in Halal Forensic Investigation in Indonesia. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2020, 13, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kwifi, O.S.; Gelaidan, H.M.H.; Fetais, A.H.M.A. Identifying the influence of the Halal logo on Muslim consumers’ attitudes using fMRI technology. J. Islam. Mark. 2020, 12, 1159–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.; Nazarudin, N.; Francis, F.J.; Muhamad, M.Z. Traceability-Technology-Training (3T) Framework for Halal Logistics at Small Medium Enterprises. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th International Conference on Research and Innovation in Information Systems (ICRIIS), IEEE, Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 25–26 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kwifi, O.S.; Abu Farha, A.; Ahmed, Z.U. Dynamics of Muslim consumers’ behavior toward Halal products: Exploration study using fMRI technology. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2019, 14, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairani, D.; Bangkit, D.A.; Rozi, N.F.; Masruroh, S.U.; Oktaviana, S.; Rosyadi, T. Named-Entity Recognition and Optical Character Recognition for Detecting Halal Food Ingredients: Indonesian Case Study. In Proceedings of the 2022 10th International Conference on Cyber and IT Service Management, CITSM 2022, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 20–21 September 2022; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidi, N.S.B.; Mohamad Kamil, M.H.F.; Norizan, A.R.; Aron, N.W.M. Halal Cosmetics Awareness Through Augmented Reality Application: To Assist Consumer in Cosmetic Product Purchase Decision Making. In Proceedings of the IVIT 2022—Proceedings of 1st International Visualization, Informatics and Technology Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1–2 November 2022; Husin, H.S., Wahab, M.H.A., Eds.; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kwifi, O.S.; Koku, P.S.; Abu Farha, A.K.; Al Halbadi, S.M. Do Islamic Ethics Influence Consumers’ Reaction to Advertising Messages of Certain Foods? Tracking Consumers’ Reaction Using fMRI Technology. J. Glob. Mark. 2022, 35, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, M.; Nurdin, N. The influence of halal product expectation, social environment, and fiqih knowledge on intention to use shariah financial technology products. Int. J. Innov. Creat. Change 2020, 13, 171–193. [Google Scholar]
- Azizah, S.N. Online Traceability of Halal Food Information to Protect Muslim Consumers in the Cyber Era. Int. J. Cyber Criminol. 2021, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Susanty, A.; Puspitasari, N.B.; Jati, S.; Selvina, O. Impact of internal and external factors on halal logistics implementation. J. Islam. Mark. 2022, 13, 1143–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardiyah, R.; Ismail, A.U.; Khairani, D.; Durachman, Y.; Rosyadi, T.; Masruroh, S.U. Conceptual Framework on Halal Meat Traceability to Support Indonesian Halal Assurance System (HAS 23000) using Blockchain Technology. In Proceedings of the 2021 9th International Conference on Cyber and IT Service Management, CITSM 2021, Bengkulu, Indonesia, 22–23 September 2021; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidin, S.S.; Yahya, N.; Othman, M.; Suliman, A.; Nghiem, T.-L.; Thu, T.N.T. Governing the Halal Supply Chain using Blockchain Technology in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Digital Transformation and Intelligence, ICDI 2022—Proceedings, Kuching, Malaysia, 1–2 December 2022; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 314–317. [Google Scholar]
- Akbar, A.; Rakhmawati, N.A.; Vanany, I. Halal Blockchain Application for a Chicken Slaughtering Factory. Int. J. Food Syst. Dyn. 2022, 13, 321–334. [Google Scholar]
- Nizar, N.N.A.; Abidin, S.A.S.Z.; Taib, M.N. Smart Data for Sustainable Halal Supply Chain in Kuala Lumpur: A Proposal. In Proceedings of the 2023 19th IEEE International Colloquium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, CSPA 2023—Conference Proceedings, Kedah, Malaysia, 3–4 March 2023; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Novianti, D.; Haditjaroko, L.; Almunawar, M.N. Assurance information systems design for blockchain—Based micro, small and medium enterprises in Indonesia. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; Institute of Physics: London, UK, 2022; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giyanti, I.; Suparti, E.; Sutopo, W. Predicting online search intention for validating product halalness status. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Bangkok, Thailand, 5–7 March 2019; IEOM Society: Southfield, MI, USA, 2019; pp. 3571–3581. [Google Scholar]
- Lestari, C.S.W.; Handayani, S.; Novientri, G. Prospect of Dengue Vaccine Development with Halal Process-Based Technology. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2606, 030002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Tarmizi, H.; Kamarulzaman, N.H.; Abd Rahman, A.; Atan, R. Adoption of internet of things among Malaysian halal agro-food smes and its challenges. Food Res. 2020, 4, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieman, M.; Darun, M.R.; Fernando, Y.; Ngah, A.B. Utilizing Blockchain Technology to Enhance Halal Integrity: The Perspectives of Halal Certification Bodies; Xia, Y., Zhang, L.-J., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Bahri, M.; Yankovsky, A.; Kirichek, R.; Borodin, A. Smart system based on DOA IoT for products monitoring anti-counterfeiting. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th MEC International Conference on Big Data and Smart City, ICBDSC 2019, Muscat, Oman, 15–16 January 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulihuma, K.; Shibghatullah, A.S.B. Blockchain Technology for Halal Supply Chain Management. In Proceedings of International Conference on Artificial Life and Robotics; Jia, Y., Ito, T.J.-J.L., Eds.; ALife Robotics Corporation Ltd.: Oita, Japan, 2022; pp. 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Rakhmawati, N.A.; Wibowo, N.I.; Rinjeni, T.P.; Indasari, S.S.; Indriawan, A.; Indraswari, R. Halal Food Products Recommendation Based on Knowledge Graphs and Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the ICCTEIE 2023: 2023 International Conference on Converging Technology in Electrical and Information Engineering, Bandar Lampung, Indonesia, 25–26 October 2023; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Rahim, N.F. Rapid scoping review of blockchain adoption in halal industry supply chain. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2827, 030043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, G.R.; Liaqat, I.A.; Sharma, B. Blockchain Redefining: The Halal Food Sector. In Proceedings of the 2019 Amity International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AICAI 2019, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 4–6 February 2019; pp. 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Imanto, T.; Yazid, S. Blockchain Based Halal Food Production Tracking. In Proceedings of the IWBIS 2021: 6th International Workshop on Big Data and Information Security, Depok, Indonesia, 23–25 October 2021; pp. 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamed, N.N.; Vignesh, R.; Alam, T. Tracking and tracing the halal food supply chain management using blockchain, RFID, and QR code. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusnadi, A.; Arkeman, Y.; Syamsu, K.; Wijaya, S.H. Designing Halal Product Traceability System using UML and Integration of Blockchain with ERP. Regist. J. Ilm. Teknol. Sist. Inf. 2023, 9, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.C.; Nizam, S.S.M.; Arshad, H.; A’Isyah Ahmad Shukri, S.; Hashim, N.C.; Putra, H.M.; Abidin, R.Z. A usability evaluation of an interactive application for halal products using optical character recognition and augmented reality technologies. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1891, 020084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, N.H.A.A.; Mansor, H.; Hasbullah, N.F. Halal Kit Identifier Using Radio Frequency Identification Technology. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer and Communication Engineering: Innovative Technologies to Serve Humanity, ICCCE 2016, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 26–27 July 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Junaini, S.N.; Abdullah, J. MyMobiHalal 2.0: Malaysian mobile halal product verification using camera phone barcode scanning and MMS. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer and Communication Engineering 2008, ICCCE08: Global Links for Human Development, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–15 May 2008; pp. 528–532. [Google Scholar]
- Kassim, N.; Hashim, P.; Hashim, D.M.; Jol, H. New Approach of Samak Clay Usage for Halal Industry Requirement. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 121, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.C.; Nizam, S.S.M.; Arshad, H.; Shukri, S.A.A.; Abidin, R.Z.; Hashim, N.C.; Putra, H.M. A framework for halal products checking interactive application with OCR and AR technologies. J. Telecommun. Electron. Comput. Eng. 2017, 9, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Yuniarti, A.; Kuswardayan, I.; Hariadi, R.R.; Arifiani, S.; Mursidah, E. Design of integrated latext: Halal detection text using OCR (Optical character recognition) and web service. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Seminar on Application for Technology of Information and Communication: Empowering Technology for a Better Human Life, Semarang, Indonesia, 7–8 October 2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.I.I.; Razali, R.N.; Desa, M.I.; Husny, Z.J.M. Information Communication Technology Adoption Process for Malaysia Halal Transportation; Douglas, C., Ao, S.I., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Engineering and Computer Science; Newswood Limited: Hong Kong, China, 2014; pp. 1082–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, H.; Shukri, S.A.A.; Obeidy, W.K.; Abidin, R.Z. An interactive application for halal products identification based on augmented reality. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2017, 7, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, M.; Karbasi, M.; Shah, A.; Brohi, I.A.; Ali, N.I. An adoption of halal food recognition system using mobile Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and Near Field Communication (NFC). In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for the Muslim World, ICT4M 2016, Jakarta, Indonesia, 22–24 November 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sayogo, D.S. Online traceability for halal product information: Perceptions of Muslim consumers in Indonesia. J. Islam. Mark. 2018, 9, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad, M.I.; Radzi, M.A.M.; Wahab, N.I.A.; Hizam, H.; Mahmood, M.F. Optimal design of hybrid renewable energy system based on solar and biomass for halal products research institute, UPM. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies—Asia, ISGT ASIA 2014, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 20–23 May 2014; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 692–696. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrudin, S.S.M.; Illyas, M.I.; Desa, M.I. Tracking and tracing technology for halal product integrity over the supply chain. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics, ICEEI 2011, Bandung, Indonesia, 17–19 July 2011. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, H.S.; Abd Aziz, M.L.; Ahmad, M.R.; Faisol, N. Creating Innovation in Achieving Sustainability: Halal-Friendly Sustainable Port. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayati, J.; Vamelia, R.; Hammami, J.; Endri, E. Transparent distribution system design of halal beef supply chain. Uncertain Supply Chain. Manag. 2023, 11, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieman, M.; Ghazali, M.C. Principles in halal purchasing. J. Islam. Mark. 2013, 4, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, B.; Shaarani, S.M.; Bahron, A. Evaluation of knowledge, halal quality assurance practices and commitment among food industries in Malaysia. Br. Food J. 2016, 118, 2033–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, M.S.A.; Chin, T.A.; Fischer, J. Linking Halal Food Certification and Business Performance. Br. Food J. 2017, 119, 1606–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, F.R.; Abdullah, A.; Bakri, M.H.; Musa, H. Perception of small medium and enterprises towards Halal food supply chain in Malaysia. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 821–828. [Google Scholar]
- Ahyar, M.; Wibowo, M.Y.P. Halal Industry and Islamic Banking: A Study of Halal Ecosystem Regulation in Indonesia. J. Financ. Islam. Bank. 2020, 2, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siska, S.; Rahmi, H.; Situmorang, A. The Effectiveness of Technical Guidance for Entrepreneurs in Small and Medium Enterprises in Facing Halal Certification. Indones. J. Halal Res. 2020, 2, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, M.S.A.; Hamid, A.B.A.; Chin, T.A. Can halal Certification Influence Logistics Performance? J. Islam. Mark. 2016, 7, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okdinawati, L.; Simatupang, T.M.; Arif, I.; Lestari, Y.D. Value Co-Creation Model of Halal Logistics Services. J. Ilm. Tek. Ind. 2021, 20, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Haleem, A.; Khan, S. Examining the Link between Halal Supply Chain Management and Sustainability. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2021, 71, 2793–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Bhutto, M.H.; Azhar, S.M. Integrative Review of Islamic Marketing. J. Islam. Mark. 2021, 13, 1264–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, N.M.; Supian, K.; Bojei, J. Relationship Between Halal Traceability System Adoptions on Halal Food Supply Chain Integrity and Performance. Int. J. Asian Soc. Sci. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, M.S.; Seyedghorban, Z.; Tahernejad, H.; Samson, D. Why emerging supply chain technologies initially disappoint: Blockchain, IoT, and AI. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2022, 31, 2517–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.; De Meyer, A.; Marques, A.S.; Pinho, T.M.; Boaventura-Cunha, J.; Van Orshoven, J.; Rosset, C.; Künzi, J.; Kaarle, J.; Nummila, K. Digital Technologies for Forest Supply Chain Optimization: Existing Solutions and Future Trends. Environ. Manag. 2018, 62, 1108–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogler, C.; Rauch, P. Game-Based Workshops for the Wood Supply Chain to Facilitate Knowledge Transfer. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2020, 19, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogler, C.; Rauch, P. Contingency Plans for the Wood Supply Chain Based on Bottleneck and Queuing Time Analyses of a Discrete Event Simulation. Forests 2020, 11, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogler, C. Discrete Event Simulation-Based Risk Analysis for Efficient, Sustainable and Resilient Transportation. Soud. Inženýrství. 2023, 34, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-García, S.; Gallego-García, D.; García-García, M. Sustainability in the agri-food supply chain: A combined digital twin and simulation approach for farmers. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 217, 1280–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Items | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Search Limitations | Scopus | Database other than Scopus |
| Keywords Search | Search string I: “Halal Supply Chain OR Halal Logistics” Search string II: (“Halal Supply Chain” OR “Halal Logistics” OR “Halal transport” OR “Halal procurement” OR “Halal product*” OR “Halal Delivery”) AND (“optimization” OR “simulation” OR “AI” OR “machine learning” OR “blockchain” OR “Technology”) | |
| Literature type | Peer review article, conference paper | Magazine articles, reports, non-indexed journals, Book Chapters, discontinued publications. |
| Abstract | Technology, digital, and innovation | Not included Technology, digital, and innovation |
| Language | English | Non-English |
| Timeline | 2008–2023 | Before 2000 |
| Authors | Halal Supply Chain | Firm Performance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halal Procurement | Halal Manufacturing | Halal Distribution | Halal Logistics | Financial | Non-Financial | ||
| [24] | 2020 | x | EDI, Extranet, Internet, and electronic commerce | x | x | x | Technology can improve the effectiveness of supply chain processes in family halal food businesses. |
| [40] | 2023 | x | x | TS-based algorithm | x | Minimizing transportation costs | Ensure the integrity of Halal products |
| [41] | 2019 | x | x | x | CPLEX and hybrid genetic algorithm | Minimizing cost | Improve the efficiency of locating farms, butcheries, and food plants |
| [42] | 2023 | x | Shariah Financial Technology (FinTech) | x | x | Enhance business strategy by minimizing costs | The developed HSCMT prototype increases the effectiveness of Halal Supply Chain Management for Malaysia Halal SME Owners (MHSO) with an average usability score of 83.67. |
| [43] | 2023 | Blockchain Technology | x | x | x | Increase operational costs | Improved product quality due to well-managed traceability management |
| [44] | 2023 | x | x | x | Pharmaniaga Lifescience (Cold rooms) | x | Increase efficient halal document checking and verification process |
| [45] | 2022 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | The use of Blockchain with the Avalanche platform is more cost-effective than the Ethereum network | Blockchain-Based Traceability System to Support the Indonesian Halal Supply Chain Ecosystem |
| [46] | 2021 | x | Permissioned Blockchain (Hyperledger Fabric) | x | x | x | Permissioned Blockchain is useful for the Halal Supply Chain not just because it can secure transactions from some of the halal issues (trust, transparency, and information disclosure) but also because the transaction speed and rate to transfer data are very effective. |
| [47] | 2021 | x | x | x | Internet of Things (IoT), RFID, and EDI | x | The use of technology in halal logistics can improve the quality of information, the quality of personnel contact, order accuracy, order conditions, order discrepancies, and order expenditure amount. |
| [48]. | 2022 | x | Big Data (Data-driven) | x | x | x | Improve the firm’s ability to be more sustainable in the halal food chain process |
| [49] | 2022 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | x | Improve the halal food supply chain’s traceability from farm to fork. |
| [50] | 2020 | e-procurement technology | x | x | x | x | The use of technology can improve performance in order to speed halal traceability. However, the use of technology needs to be balanced with the ability of employees to use this technology. |
| [51] | 2020 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | Investing in blockchain technology requires a lot of resources, especially in terms of costs. | Can improve halal traceability |
| [52] | 2021 | x | (RFID) with Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point | x | x | Reduce the cost of product removal from the market | Preventing the occurrence of product recalls, especially in terms of halal assurance, will lead to the level of customer trust and confidence in the integrity of the halal industry |
| [42] | 2023 | x | Shariah Fintech | x | x | This fintech can bridge international transactions. | It can assist firms in tracking financial activities. |
| [53] | 2022 | x | x | x | (ICT)-Digitally-enable community | x | Improve the efficiency with which halal logistics are conducted, offer improved logistical organization, and boost halal performance. |
| [54] | 2022 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | x | Ensuring transparency and security related to Halal Fashion Traceability |
| [55] | 2023 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | Benefits from the tracking system made possible by blockchain technology include evidence of the transparent flow of finances, information, and goods from producer to customer. | Supporting blockchain technology’s accessibility can improve traceability and transparency, connecting upstream and downstream flows that influence improvements in the efficiency of the Halal supply chain’s performance. |
| [56] | 2016 | x | x | GPS tracking system | x | x | Assist the firm in tracking and tracing products and vehicles carrying halal goods during the shipping process so that it is more effective and verification can be done automatically. |
| [57] | 2023 | x | Sharia Financial Technology | x | x | x | Increase sustainability of MSMEs in Malaysia and Indonesia by 90% through waqf participation |
| [58] | 2023 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | x | More transparent transaction processes through decentralized protocols can increase the value of innovation in management decision-making in each operation process. |
| [59] | 2023 | x | Machine Learning | x | x | x | Adapting this technology will create a new offer to existing customers to be more loyal, and data collection will then be recorded, which ends in deep learning customer engagement always to provide an appropriate and satisfying service. |
| [60] | 2023 | x | x | x | Product ID and RFID | x | The usage of Halal traceability technology in Halal logistics can significantly improve the performance of logistics service providers and enhance the market recognition of their Halal logistics brand. |
| [61] | 2022 | x | Halal traceability system | x | x | “The use of a halal traceability system would assist our firm in reducing the operating cost”. | The adoption of a halal traceability system can enhance SME business and improve the integrity of the halal industry. |
| [62] | 2020 | x | Financial Technology | x | x | x | Increase synergy in the halal industry ecosystem by emphasizing the role of each institution in minimizing the problems related to the halal industry |
| [63] | 2020 | x | x | x | Halal-based third-party logistics (3PL) providers | x | Halal-based 3PL providers with high and medium resource capabilities achieve greater customer service innovation and cost advantages significantly |
| [64] | 2015 | x | Information Technology Outsourcing (ITO) | x | x | Lower labor specialization costs while simultaneously raising cash flow and the financial performance index. | Provides detailed factors in the relationship between IT Outsourcing and the company. |
| [65] | 2021 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | x | It can help companies identify the authenticity of halal certification processes to increase trust and ensure the authenticity of halal logos. |
| [66] | 2022 | x | Halal Transportation System | x | x | Can save transportation costs incurred | The benefits of using the Halal transportation system among Halal food manufacturers are easing the doubts about Halal quality and increasing the image of the products. |
| [20] | 2022 | x | Halal Warehousing System | x | x | x | The firm can measure products/goods that are aligned with Halal specifications, value systems, and job responsibilities. |
| [1] | 2021 | x | Blockchain Technology, IoT, and RFID | x | x | x | Implementing technology-driven solutions can help in reducing risks associated with product adulteration, counterfeiting, and non-compliance with halal requirements. |
| [67] | 2020 | x | Displacement Loop mtDNA | x | x | x | Facilitate halal forensic investigations in determining the halalness of critical raw materials (animal) |
| [68] | 2020 | x | functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). | x | x | x | Knowing consumer interest in buying halal products that have a halal logo |
| [69] | 2021 | x | x | x | Blockchain technology | x | Improve efficiency in traceability during the logistics process so as to minimize product contaminations |
| [70] | 2019 | x | functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). | x | x | x | Knowing consumer desires in choosing halal products |
| [71] | 2022 | x | x | NER and OCR | x | x | Ensuring products received by consumers are in accordance with halal standards |
| [72] | 2022 | x | Augmented Reality | x | x | The cost incurred to adopt this technology is quite expensive | Increase consumers’ awareness of buying halal cosmetics because it gives them experience before buying the product. |
| [73] | 2022 | x | functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). | x | x | x | Facilitate marketing managers in making halal product advertisements by paying attention to the ethical and emotional aspects of customers. |
| [74] | 2020 | x | Sharia Fintech | x | x | x | Facilitate the tracking of transactions that comply with Sharia principles. |
| [75] | 2021 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | x | Ensuring the halal traceability of a product, thus increasing consumer interest in buying the product |
| [76] | 2023 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | Can reduce the expenses associated with manual halal traceability processes. | Improve transparency and trust in the supply chain |
| [77] | 2021 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | Minimize lost costs | Improve integration and accountability of Halal Assurance System stakeholder data activities. Can further increase consumer confidence and awareness of the value of halal products |
| [78] | 2022 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | x | Improved transparency, traceability, and timely decision-making |
| [79] | 2022 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | Increase product sales | Increase the certainty that products have been processed in accordance with applicable halal standards. |
| [80] | 2023 | x | blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI) | x | x | x | Enhanced monitoring and assurance of adherence to diverse standards and sustainability across the supply chain. |
| [81] | 2022 | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | The cost of implementing blockchain technology is quite high | Ensuring transparency in documentation involves effectively recording information and transactions. The system has demonstrated its security and transparency, as all involved parties have public access to transaction details. |
| [82] | 2019 | x | Online search service | x | x | x | Improving the effectiveness of halal product status search |
| [83] | 2023 | x | Halal dengue vaccine technology | x | x | Affordable price | Improving prevention of dengue fever outbreaks |
| [84] | 2020 | x | Internet of things | x | x | High costs | The implementation of IoT has undoubtedly established a reliable platform for the supply chain of halal agro-food SMEs. |
| [85] | 2019 | x | x | Blockchain Technology | x | x | Improve traceability of halal documents |
| [86] | 2019 | x | digital object architecture (DOA) & RFID | x | x | x | The system provides effective technical guidelines for companies to monitor the entire product lifecycle using the Internet of Things. |
| [87] | 2022 | x | Blockchain technology | x | x | x | Improve the integrity of the halal supply chain |
| [88] | 2023 | x | Machine Learning | x | x | x | Improve the efficiency of checking the difference between halal products and non-halal products. |
| [89] | 2023 | x | Blockchain technology | x | x | x | Improving transparency in halal supply chain and assurance pathways |
| [90] | 2019 | x | Blockchain technology | x | x | x | Improving transparency and assurance of halal compliance |
| [91] | 2021 | x | Blockchain technology | x | x | Minimize tracking costs | Tracking speed is up to 10 times faster than conventional methods, leading to minimized losses through more targeted issue resolution. |
| [92] | 2023 | x | x | Blockchain, RFID, QR Code | x | x | Increase consumer trust to buy halal products |
| [93] | 2023 | Blockchain Technology and ERP | x | x | x | Reduce operational cost | Through effective management of halal product procurement, companies can guarantee the delivery of products with halal assurance to consumers. |
| [94] | 2017 | x | x | OCR and Augmented Reality | x | x | Improve efficiency in checking the halal status of products |
| [95] | 2016 | x | x | RFID | x | x | The verification of the product’s Halal status becomes straightforward, as each tag embedded in food packages is assigned a unique identification number. |
| [96] | 2008 | x | x | MMS camera phone-based | x | Production cost savings | Effective way method to accelerate the Halal verification procedure. |
| [97] | 2012 | x | x | MyHalal system | x | x | Improve verification of halal product status in real-time |
| [98] | 2017 | x | x | OCR and Augmented Reality | x | x | Enhance the efficiency of verifying the halal status of products. |
| [99] | 2017 | x | x | OCR and Web Service | x | x | Improve the effectiveness of confirming the halal status of products. |
| [100] | 2014 | x | x | x | Information Communication Technology (ICT)-RFID | x | Improve the effectiveness of monitoring halal transportation |
| [101] | 2017 | x | x | Augmented Reality | x | x | Enhance the efficiency of verifying the halal status of products. |
| [102] | 2017 | x | RFID and NFC | x | x | x | NFC and RFID mobile shopping technologies streamline the validation of halal status, allowing customers to do so effortlessly through their personal smartphones. |
| [103] | 2018 | x | Online Traceability | x | x | x | Improve company reputation |
| [104] | 2014 | x | Hybrid Renewable Energy System | x | x | x | Improving the sustainability of environmentally friendly businesses |
| [105] | 2011 | x | RFID | x | x | x | Improving the integrity of halal products |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harsanto, B.; Farras, J.I.; Firmansyah, E.A.; Pradana, M.; Apriliadi, A. Digital Technology 4.0 on Halal Supply Chain: A Systematic Review. Logistics 2024, 8, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010021
Harsanto B, Farras JI, Firmansyah EA, Pradana M, Apriliadi A. Digital Technology 4.0 on Halal Supply Chain: A Systematic Review. Logistics. 2024; 8(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarsanto, Budi, Joval Ifghaniyafi Farras, Egi Arvian Firmansyah, Mahir Pradana, and Ardi Apriliadi. 2024. "Digital Technology 4.0 on Halal Supply Chain: A Systematic Review" Logistics 8, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010021
APA StyleHarsanto, B., Farras, J. I., Firmansyah, E. A., Pradana, M., & Apriliadi, A. (2024). Digital Technology 4.0 on Halal Supply Chain: A Systematic Review. Logistics, 8(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010021






