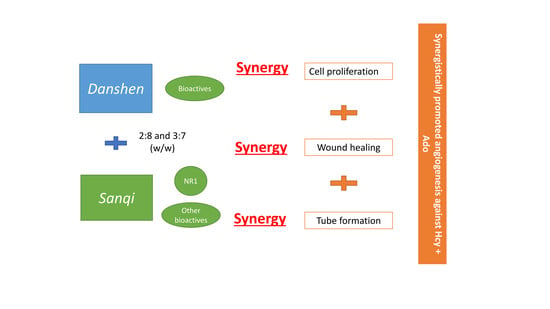
Synergistic Effects of Danshen (Salvia Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma) and Sanqi (Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma) Combination in Angiogenesis Behavior in EAhy 926 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line and Culture Conditions
2.2. Preparation of Herbal Samples and Their Chemical Compounds
2.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.4. Cell Migration (Scratch Wound Healing) Assay
2.5. Tube Formation Assay
2.6. Determination of Synergistic, Additive, or Antagonistic Interactions
2.7. Mechanistic Pathways
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of DS, SQ and DS-SQ on Hcy-Mediated Angiogenesis in EAhy 926 Cells
3.1.1. Effects of DS, SQ and DS-SQ on Cell Growth
3.1.2. Effects of DS, SQ and DS-SQ on Wound Healing
3.1.3. Effects of DS-SQ on Tube Formation
3.1.4. Synergy Analysis of Combination Effects of DS-SQ on Cell Proliferation, Wound Healing and Tube Formation
3.1.5. Mechanistic Pathways for DS-SQ on Hcy-Mediated Angiogenesis in EAhy 926 Cells
3.1.6. Angiogenic Effects of Chemical Compounds from DS and SQ on Hcy-Mediated Angiogenesis on EAhy 926 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, X.; Seto, S.W.; Chang, D.; Kiat, H.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Chan, K.; Bensoussan, A. Synergistic effects of Chinese herbal medicine: A comprehensive review of methodology and current research. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.H. An Encyclopaedia of Chinese Paired-Herbs; China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Potente, M.; Gerhardt, H.; Carmeliet, P. Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell 2011, 146, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Jin, K.; Xie, L.; Childs, J.; Mao, X.O.; Logvinova, A.; Greenberg, D.A. VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P.; Ng, Y.S.; Nuyens, D.; Theilmeier, G.; Brusselmans, K.; Cornelissen, I.; Ehler, E.; Kakkar, V.V.; Stalmans, I.; Mattot, V.; et al. Impaired myocardial angiogenesis and ischemic cardiomyopathy in mice lacking the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms VEGF164 and VEGF188. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.C.; Pan, W.Y.; Tseng, M.T.; Lin, K.J.; Yang, Y.P.; Tsai, H.W.; Hwang, S.M.; Chang, Y.; Wei, H.J.; Sung, H.W. Enhancement of cell adhesion, retention, and survival of HUVEC/cbMSC aggregates that are transplanted in ischemic tissues by concurrent delivery of an antioxidant for therapeutic angiogenesis. Biomaterials 2016, 74, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Angiogenesis Foundation about Angiogenesis. Available online: https://angio.org/about-angiogenesis/ (accessed on 7 July 2017).
- Fan, T.P.; Yeh, J.C.; Leung, K.W.; Yue, P.Y.; Wong, R.N. Angiogenesis: From plants to blood vessels. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.J.; Wan, J.B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, G.; Lin, H.C.; Seto, S.W.; Kwan, Y.W.; Lin, Z.X.; Wang, Y.T.; Lee, S.M.Y. Angiogenic effect of saponin extract from Panax notoginseng on HUVECs in vitro and zebrafish in vivo. Phytother. Res. PTR 2009, 23, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Chinese Pharmacopoeia; Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; Volume I, pp. 70–71. ISBN 978-5067-7343-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.X.; Lin, J.; Lou, J.; Shang, H.C. Status and thoughts of Chinese patent medicines seeking approval in the US market. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 20, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, F.; Wu, L.; Tian, J.; Jin, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, M.; Wei, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. The effectiveness and safety of a danshen-containing Chinese herbal medicine for diabetic retinopathy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter clinical trial. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Chang, L.; Guo, B.Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Wang, Y.L.; Jin, X.; Liu, S.Y.; Li, Y.J. Compound danshen dripping pill pretreatment to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 256268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Yao, Z.; Li, S.; Sun, H. Synergism of Chinese herbal medicine: Illustrated by danshen compound. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 7279361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, N.H.; Nakajima, K.; Uto, T.; Hai, N.T.; Long, D.D.; Ohta, T.; Oiso, S.; Kariyazono, H.; Shoyama, Y. Bioactive Triterpenes from the Root of salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Shin, S.H.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, M.J.; Roh, S.S.; Yokozawa, T.; Chung, H.Y. Magnesium Lithospermate B from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge Ameliorates Aging-Induced Renal Inflammation and Senescence via NADPH Oxidase-Mediated Reactive Oxygen Generation. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lay, I.S.; Chiu, J.H.; Shiao, M.S.; Lui, W.Y.; Wu, C.W. Crude extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza and salvianolic acid B enhance in vitro angiogenesis in murine SVR endothelial cell line. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Zhu, M.Z.; Guo, J.; Sun, J.Y.; Pei, J.M.; Huang, C. The study on angiogenesis activity of danggui, chuanxiong and danshen. Zhong yao cai Zhongyaocai J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2006, 29, 574–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.D.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, B.S.; Tong, Y.H. The effect of danshen on the angiogenesis of the frozen-thawed human fetal ovarian tissue after transplantation. Chin. J. Physiol. 2009, 25, 330–333. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, L.S.; Yue, P.Y.K.; Mak, N.K.; Wong, R.N.S. Role of microRNA-214 in ginsenoside-Rg1-induced angiogenesis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 38, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.W.; Pon, Y.L.; Wong, R.N.; Wong, A.S. Ginsenoside-Rg1 induces vascular endothelial growth factor expression through the glucocorticoid receptor-related phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and β-catenin/T-cell factor-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 36280–36288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebäck, T.; Schulz, M.; Koumoutsakos, P.; Detmar, M. Short technical reports. Biotechniques 2009, 46, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Homocysteine Studies Collaboration. Homocysteine and risk of ischemic heart disease and stroke: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2002, 288, 2015–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonna, P.; de Stefano, V.; Coppola, A.; Cirillo, F.; Cerbone, A.M.; Orefice, G.; Di Minno, G. Hyperhomocysteinemia and other inherited prothrombotic conditions in young adults with a history of ischemic stroke. Stroke 2002, 33, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kam, A.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Zhou, X.; Troung, J.; Chan, K. Nucleoside Transport Inhibition by Dipyridamole Prevents Angiogenesis Impairment by Homocysteine and Adenosine. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 18, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.W.; Yang, C.; Sit, A.S.; Lin, S.Y.; Ho, E.Y.; Leung, G.P. Physiological and pharmacological roles of vascular nucleoside transporters. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 59, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riksen, N.P.; Rongen, G.A.; Blom, H.J.; Russel, F.G.; Boers, G.H.; Smits, P. Potential role for adenosine in the pathogenesis of the vascular complications of hyperhomocysteinemia. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 59, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, M.; Rocha, M.; Esse, R.; Gonçalves, I., Jr.; Gomes, A.Q.; Teerlink, T.; Jakobs, C.; Blom, H.; Loscalzo, J.; Rivera, I. Cellular hypomethylation is associated with impaired nitric oxide production by cultured human endothelial cells. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, F.; Tan, H.; Liao, D.; Bryan, R.M.; Randhawa, J.K.; Rumbaut, R.E.; Durante, W.; Schafer, A.I.; Yang, X.; et al. Hyperhomocystinemia impairs endothelial function and eNOS activity via PKC activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 2515–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.Y.; Lu, S.C.; Lee, C.M.; Chen, Y.J.; Dugan, T.A.; Huang, W.H.; Chang, S.F.; Liao, W.S.; Chen, C.H.; Lee, Y.T. Homocysteine inhibits arterial endothelial cell growth through transcriptional downregulation of fibroblast growth factor-2 involving G protein and DNA methylation. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karar, J.; Maity, A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in angiogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, I.H.; Cao, L.; Wu, W.K.; Tan, H.M. Homocysteine-impaired angiogenesis is associated with VEGF/VEGFR inhibition. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2012, 4, 2525–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, H. Synergy research: Approaching a new generation of phytopharmaceuticals. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.J.; Xu, K.L.; Xu, Y.; Huang, B.G.; Wu, J.G. The study on the interactions between Danshen and Sanqi in Fufang Danshen prescription. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2003, 13, 186–189. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, G.F.; Xu, Q.; Xiao, H.B.; Liang, X.M. Influence of compatability ratio of Fufang Danshen on the dissolution of Danshen compositions. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2004, 22, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Chang, D.; Li, C.; Kam, A.; Low, M.; Bensoussan, A.; Chan, K. Synergistic effects of Danshen (Salvia Miltiorrhiza Radix et Rhizoma) and Sanqi (Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma) combination in inhibiting inflammation mediators in RAW264. 7 cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5758195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, D.W.S.; Koon, C.M.; Ng, C.F.; Leung, P.C.; Fung, K.P.; Poon, S.K.S.; Bik-San Lau, C. The roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) and Pueraria lobata (Gegen) inhibit atherogenic events: A study of the combination effects of the 2-herb formula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Chan, K. A multivariate analysis on the comparison of raw notoginseng (Sanqi) and its granule products by thin-layer chromatography and ultra-performance liquid chromatography. Chin. Med. 2015, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Kam, A.; Chang, D.; Li, C.; Bensoussan, A.; Chan, K. Synergistic Effects of Danshen (Salvia Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma) and Sanqi (Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma) Combination in Angiogenesis Behavior in EAhy 926 Cells. Medicines 2017, 4, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines4040085
Zhou X, Razmovski-Naumovski V, Kam A, Chang D, Li C, Bensoussan A, Chan K. Synergistic Effects of Danshen (Salvia Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma) and Sanqi (Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma) Combination in Angiogenesis Behavior in EAhy 926 Cells. Medicines. 2017; 4(4):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines4040085
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xian, Valentina Razmovski-Naumovski, Antony Kam, Dennis Chang, Chunguang Li, Alan Bensoussan, and Kelvin Chan. 2017. "Synergistic Effects of Danshen (Salvia Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma) and Sanqi (Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma) Combination in Angiogenesis Behavior in EAhy 926 Cells" Medicines 4, no. 4: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines4040085
APA StyleZhou, X., Razmovski-Naumovski, V., Kam, A., Chang, D., Li, C., Bensoussan, A., & Chan, K. (2017). Synergistic Effects of Danshen (Salvia Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma) and Sanqi (Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma) Combination in Angiogenesis Behavior in EAhy 926 Cells. Medicines, 4(4), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines4040085