Retrospective Analysis of the Effectiveness of Oral Semaglutide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Effect on Cardiometabolic Parameters in Japanese Clinical Settings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
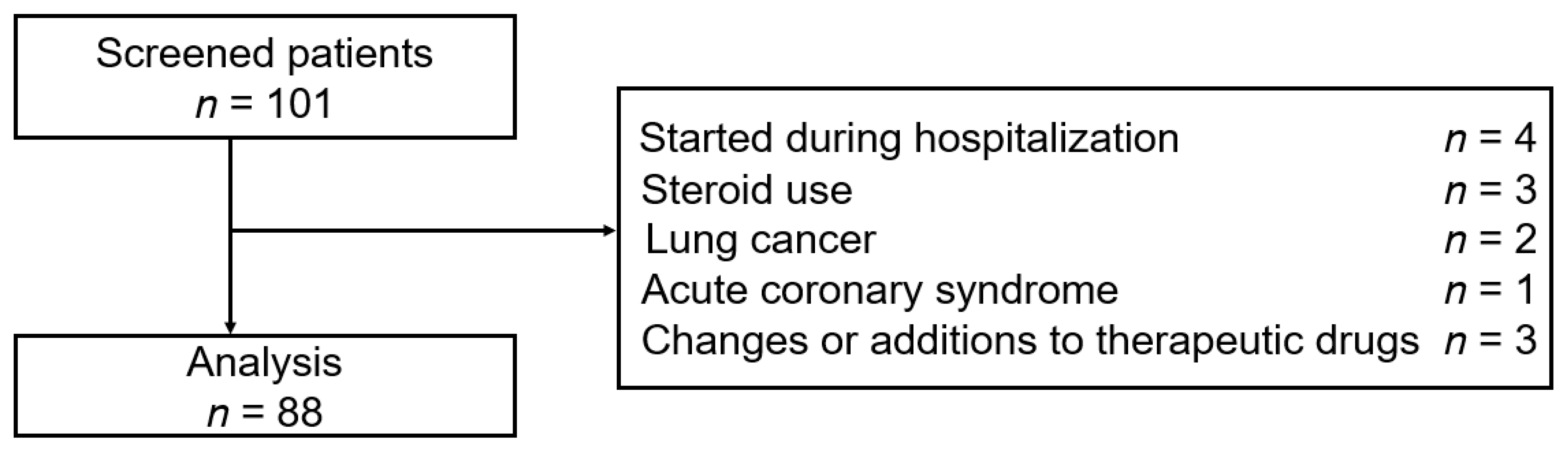
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Changes in HbA1c and BW
3.3. Evaluating Cardiometabolic Parameters
3.4. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andersen, A.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. A pharmacological and clinical overview of oral semaglutide for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. Drugs 2021, 81, 1003–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1925–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.; Morgan, A.R.; Bain, S.C.; Davies, S.; Hicks, D.; Brown, P.; Yousef, Z.; Dashora, U.; Viljoen, A.; Beba, H.; et al. Meeting the challenge of virtual diabetes care: A consensus viewpoint on the positioning and value of oral semaglutide in routine clinical practice. Diabetes Ther. 2022, 13, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S.; Kapoor, N. Oral semaglutide: Dosage in special situations. Diabetes Ther. 2022, 13, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, S.T.; Bækdal, T.A.; Vegge, A.; Maarbjerg, S.J.; Pyke, C.; Ahnfelt-Rønne, J.; Madsen, K.G.; Schéele, S.G.; Alanentalo, T.; Kirk, R.K.; et al. Transcellular stomach absorption of a derivatized glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaar7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Donsmark, M.; Dungan, K.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Franco, D.R.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; et al. Oral semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with Type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.F. The development of oral semaglutide, an oral GLP-1 analog, for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetol. Int. 2020, 11, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thethi, T.K.; Pratley, R.; Meier, J.J. Efficacy, safety and cardiovascular outcomes of once-daily oral semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: The Pioneer programme. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1263–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.J. Efficacy of semaglutide in a subcutaneous and an oral formulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 645617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Rørth, R.; Jhund, P.S.; Docherty, K.F.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Køber, L.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J.V. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussher, J.R.; Greenwell, A.A.; Nguyen, M.A.; Mulvihill, E.E. Cardiovascular effects of incretin-based therapies: Integrating mechanisms with cardiovascular outcome trials. Diabetes 2022, 71, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muskiet, M.H.A.; Tonneijck, L.; Smits, M.M.; van Baar, M.J.B.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Hoorn, E.J.; Joles, J.A.; van Raalte, D.H. GLP-1 and the kidney: From physiology to pharmacology and outcomes in diabetes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.M.Y.; Ghouri, N.; McGuire, D.K.; Rutter, M.K.; Sattar, N. Meta-analyses of results from randomized outcome trials comparing cardiovascular effects of SGLT2is and GLP-1RAs in Asian versus White patients with and without Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, D.; Deenadayalan, S.; Horio, H.; Kaneto, H.; Jensen, T.B.; Terauchi, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Inagaki, N. Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: A subgroup analysis by baseline variables in the Pioneer 9 and Pioneer 10 trials. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seino, Y.; Kuwata, H.; Yabe, D. Incretin-based drugs for type 2 diabetes: Focus on East Asian perspectives. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7 (Suppl. 1), 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabe, D.; Seino, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Seino, S. β cell dysfunction versus insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in East Asians. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2015, 15, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakei, M.; Yoshida, M.; Dezaki, K.; Ito, K.; Yamada, H.; Funazaki, S.; Kawakami, M.; Sugawara, H.; Yada, T. Glucose and GTP-binding protein-coupled receptor cooperatively regulate transient receptor potential-channels to stimulate insulin secretion. Endocr. J. 2016, 63, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosida, M.; Dezaki, K.; Uchida, K.; Kodera, S.; Lam, N.V.; Ito, K.; Rita, R.S.; Yamada, H.; Shimomura, K.; Ishikawa, S.E.; et al. Involvement of cAMP/EPAC/TRPM2 activation in glucose- and incretin-induced insulin secretion. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3394–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, D.; Yamada, Y.; Kaku, K.; Nishida, T.; Sato, T.; Seino, Y. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide in Japanese individuals with type 2 diabetes by baseline age and body mass index. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Hahn, S.; Oh, T.J.; Park, K.S.; Cho, Y.M. Differences in the HbA1c-lowering efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues between Asians and non-Asians: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.M.; Cho, Y.K.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, W.J.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, C.H.; Nauck, M.A. Asian subpopulations may exhibit greater cardiovascular benefit from long-acting glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: A meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Diabetes Metab. J. 2019, 43, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Yoshida, M.; Suzuki, D.; Funazaki, S.; Nagashima, S.; Masahiko, K.; Kiyoshi, O.; Hara, K. Effectiveness and safety of once-weekly semaglutide in Japanese patients with Type 2 diabetes in treatment intensification: A retrospective observational single-center study. Diabetes Ther. 2022, 13, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratley, R.E.; Crowley, M.J.; Gislum, M.; Hertz, C.L.; Jensen, T.B.; Khunti, K.; Mosenzon, O.; Buse, J.B. Oral Semaglutide Reduces HbA1c and Body Weight in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Regardless of Background Glucose-Lowering Medication: PIONEER Subgroup Analyses. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 1099–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, D.; Nakamura, J.; Kaneto, H.; Deenadayalan, S.; Navarria, A.; Gislum, M.; Inagaki, N. PIONEER 10 Investigators Safety and efficacy of oral semaglutide versus dulaglutide in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (Pioneer 10): An open-label, randomised, active-controlled, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Katagiri, H.; Hamamoto, Y.; Deenadayalan, S.; Navarria, A.; Nishijima, K.; Seino, Y. PIONEER 9 investigators Dose-response, efficacy, and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (Pioneer 9): A 52-week, phase 2/3a, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroda, V.R.; Bauer, R.; Christiansen, E.; Haluzík, M.; Kallenbach, K.; Montanya, E.; Rosenstock, J.; Meier, J.J. Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide by subgroups of patient characteristics in the Pioneer phase 3 programme. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1338–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Aroda, V.R.; Buse, J.B.; Cariou, B.; Harris, S.B.; Hoff, S.T.; Pedersen, K.B.; Tarp-Johansen, M.J.; Araki, E. PIONEER 8 Investigators Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of oral semaglutide versus placebo added to insulin with or without metformin in patients with Type 2 diabetes: The Pioneer 8 trial. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 2262–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, R.; Sakuramachi, Y.; Seino, Y.; Murotani, K.; Kuwata, H.; Tatsuoka, H.; Hamamoto, Y.; Kurose, T.; Seino, Y.; Yabe, D. Retrospective analysis of liraglutide and basal insulin combination therapy in Japanese type 2 diabetes patients: The association between remaining β-cell function and the achievement of the glycated hemoglobin target 1 year after initiation. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, R.; Yabe, D.; Kuwata, H.; Murotani, K.; Kurose, T.; Seino, Y. Retrospective analysis of safety and efficacy of liraglutide monotherapy and sulfonylurea-combination therapy in Japanese type 2 diabetes: Association of remaining β-cell function and achievement of HbA1c target one year after initiation. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, K.; Brooks, A.; Almazedi, F.; Hoff, S.T.; Boschini, C.; Baekdal, T.A. Oral semaglutide improves postprandial glucose and lipid metabolism, and delays gastric emptying, in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 1594–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, K.; Tojjar, D.; Yamada, S.; Toda, K.; Patel, C.J.; Butte, A.J. Ethnic differences in the relationship between insulin sensitivity and insulin response: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, J.B.; Dalla Man, C.; Overgaard, R.V.; Ingwersen, S.H.; Tornøe, C.W.; Pedersen, M.; Tanaka, H.; Ohsugi, M.; Ueki, K.; Lynge, J.; et al. Ethnic differences in insulin sensitivity, β-cell function, and hepatic extraction between Japanese and Caucasians: A minimal model analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 4273–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, J.B.; Pedersen, M.; Tanaka, H.; Ohsugi, M.; Overgaard, R.V.; Lynge, J.; Almind, K.; Vasconcelos, N.M.; Poulsen, P.; Keller, C.; et al. Body composition is the main determinant for the difference in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology between Japanese and Caucasians. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramoto, A.; Matsushita, M.; Kato, A.; Yamamoto, N.; Koike, G.; Nakamura, M.; Numata, T.; Tamakoshi, A.; Tsushita, K. Three percent weight reduction is the minimum requirement to improve health hazards in obese and overweight people in Japan. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 8, e466–e475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, M.; Okada, Y.; Kanai, M.; Takahashi, A.; Momozawa, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Iwata, N.; Ikegawa, S.; Hirata, M.; Matsuda, K.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 112 new loci for body mass index in the Japanese population. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, S.M.; Burgess, D.J.; Yeazel, M.W.; Hellerstedt, W.L.; Griffin, J.M.; van Ryn, M. Impact of weight bias and stigma on quality of care and outcomes for patients with obesity. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Fan, J.G.; Wei, L.; Shi, J.P.; Zheng, M.H. Chinese MAFLD Clinical Research Network Promoting the term MAFLD: China in action. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.D.; Cai, J.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Shapiro, M.D.; Sung, K.C.; Somers, V.K.; Chahal, C.A.A.; George, J.; Chen, L.L.; et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and implications for cardiovascular risk and disease prevention. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Dyslipidemia. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Baseline Characteristics (n = 88) | |
|---|---|
| Men/women (n) | 55/33 |
| Age (years) | 62 (53.8–68) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.3 (0.61) |
| Baseline BW (kg) | 73.6 (1.58) |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 10.5 (5–18) |
| Baseline HbA1c (%) | 8.53 (0.17) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 72.5 (50.6–95.3) |
| Complications | n (%) |
| Ischemic heart disease, yes, n (%) | 17 (19.3) |
| Diabetic retinopathy, yes, n (%) | 9 (10.2) |
| Diabetic nephropathy, yes, n (%) | 30 (34.1) |
| Diabetic neuropathy, yes, n (%) | 9 (10.2) |
| Anti-diabetic drugs | n (%) |
| Sulfonylurea, n (%) | 10 (11.4) |
| Biguanides, n (%) | 39 (44.3) |
| Glinides, n (%) | 11 (12.5) |
| α-Glucosidase inhibitor, n (%) | 13 (14.8) |
| Thiazolidinedione, n (%) | 5 (5.7) |
| SGLT2 inhibitor, n (%) | 60 (68.2) |
| Imeglimin, n (%) | 2 (2.3) |
| DPP-4 inhibitor, n (%) | 41 (46.6) |
| OAD only, n (%) | 48 (54.5) |
| Insulin therapy, n (%) | 23 (26.1) |
| Basal insulin only, n (%) | 11 (12.5) |
| Bolus insulin only, n (%) | 1 (1.1) |
| IDegAsp, n (%) | 3 (3.4) |
| Basal-Bolus therapy, n (%) | 8 (9.1) |
| GLP-1RA, n (%) | 31 (35.2) |
| Liraglutide, n (%) | 3 (3.4) |
| Lixisenatide, n (%) | 3 (3.4) |
| Dulaglutide, n (%) | 17 (19.3) |
| Once-weekly semaglutide, n (%) | 8 (9.1) |
| Other drugs | |
| Statin use, yes, n (%) | 52 (59.1) |
| Fibrate use, yes, n (%) | 4 (4.5) |
| Ezetimibe use, yes, n (%) | 10 (11.4) |
| Anti-hypertensive drug, yes, n (%) | 48 (54.5) |
| Clinical Parameters | n | Baseline | After 6 Months | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AST (IU/L) | 88 | 22 (18–30.5) | 23 (19.5–28) | 0.065 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 88 | 24 (17.8–38.3) | 23 (20–32) | 0.008 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 88 | 74.5 (3.2) | 72.6 (3.3) | 0.055 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 72 | 177 (4.5) | 172 (4.2) | 0.009 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 86 | 49.5 (40.3–56) | 49 (41–57.8) | 0.462 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 87 | 146 (110–202) | 144 (114–181) | 0.028 |
| Non-HDL-C (mg/dL) | 71 | 120 (98–158) | 115 (98–149) | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamada, H.; Yoshida, M.; Funazaki, S.; Morimoto, J.; Tonezawa, S.; Takahashi, A.; Nagashima, S.; Masahiko, K.; Kiyoshi, O.; Hara, K. Retrospective Analysis of the Effectiveness of Oral Semaglutide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Effect on Cardiometabolic Parameters in Japanese Clinical Settings. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10040176
Yamada H, Yoshida M, Funazaki S, Morimoto J, Tonezawa S, Takahashi A, Nagashima S, Masahiko K, Kiyoshi O, Hara K. Retrospective Analysis of the Effectiveness of Oral Semaglutide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Effect on Cardiometabolic Parameters in Japanese Clinical Settings. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2023; 10(4):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10040176
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamada, Hodaka, Masashi Yoshida, Shunsuke Funazaki, Jun Morimoto, Shiori Tonezawa, Asuka Takahashi, Shuichi Nagashima, Kimura Masahiko, Otsuka Kiyoshi, and Kazuo Hara. 2023. "Retrospective Analysis of the Effectiveness of Oral Semaglutide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Effect on Cardiometabolic Parameters in Japanese Clinical Settings" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 10, no. 4: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10040176
APA StyleYamada, H., Yoshida, M., Funazaki, S., Morimoto, J., Tonezawa, S., Takahashi, A., Nagashima, S., Masahiko, K., Kiyoshi, O., & Hara, K. (2023). Retrospective Analysis of the Effectiveness of Oral Semaglutide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Effect on Cardiometabolic Parameters in Japanese Clinical Settings. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 10(4), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10040176





