The Importance of Mehran Score to Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with TAVI: A Large Multicenter Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
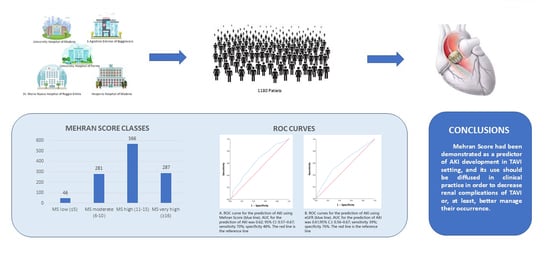
3. Results
4. Discussion
Study Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TAVI | Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| AS | Aortic stenosis |
| AR | Aortic regurgitation |
| MR | Mitral regurgitation |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| BAV | Balloon aortic valvuloplasty |
| STS | Society of thoracic surgery |
| EF | Ejection fraction |
| MS | Mehran Score |
| CKD-EPI | Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| SAVR | Surgery aortic valve replacement |
| OAC | Oral anticoagulation |
| PM | Pacemaker |
| SR | Sinus rhythm |
| MACE | Major adverse cardiovascular events |
References
- Iung, B.; Delgado, V.; Rosenhek, R.; Price, S.; Prendergast, B.; Wendler, O.; De Bonis, M.; Tribouilloy, C.; Evangelista, A.; Bogachev-Prokophiev, A.; et al. Contemporary Presentation and Management of Valvular Heart Disease. Circulation 2019, 140, 1156–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, S.; Cairns, B.J.; Iung, B. The modern epidemiology of heart valve disease. Heart 2016, 102, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahanian, A.; Beyersdorf, F.; Praz, F.; Milojevic, M.; Baldus, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Capodanno, D.; Conradi, L.; De Bonis, M.; De Paulis, R.; et al. 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 561–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, M.; Hasan, W.; Andreas, M.; Winkler, B.; Weiss, G.; Adlbrecht, C.; Delle-Karth, G.; Grabenwöger, M. Evaluating the Association between Contrast Medium Dosage and Acute Kidney Injury in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Using Different Predictive Models. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, G.; Sannino, A.; Capodanno, D.; Perrino, C.; Capranzano, P.; Barbanti, M.; Stabile, E.; Trimarco, B.; Tamburino, C.; Esposito, G. Impact of postoperative acute kidney injury on clinical outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: A meta-analysis of 5,971 patients. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 86, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhmidi, Y.; Bleiziffer, S.; Piazza, N.; Hutter, A.; Opitz, A.; Hettich, I.; Kornek, M.; Ruge, H.; Brockmann, G.; Mazzitelli, D.; et al. Incidence and predictors of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Am. Heart J. 2011, 161, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, R.; Aymong, E.D.; Nikolsky, E.; Lasic, Z.; Iakovou, I.; Fahy, M.; Mintz, G.S.; Lansky, A.J.; Moses, J.W.; Stone, G.W.; et al. A simple risk score for prediction of contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention: Development and initial validation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Généreux, P.; Piazza, N.; Alu, M.C.; Nazif, T.; Hahn, R.T.; Pibarot, P.; Bax, J.J.; Leipsic, J.A.; Blanke, P.; Blackstone, E.H.; et al. Valve Academic Research Consortium 3: Updated Endpoint Definitions for Aortic Valve Clinical Research. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 2717–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.M.; Kumbhani, D.J.; Alexander, K.P.; Calhoon, J.H.; Desai, M.Y.; Kaul, S.; Lee, J.C.; Ruiz, C.E.; Vassileva, C.M. 2017 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in the Management of Adults With Aortic Stenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1313–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, J.; Nijenhuis, V.J.; Delewi, R.; Hermanides, R.S.; Holvoet, W.; Dubois, C.L.; Frambach, P.; De Bruyne, B.; van Houwelingen, G.K.; Van Der Heyden, J.A.; et al. Aspirin with or without Clopidogrel after Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Implantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijenhuis, V.J.; Brouwer, J.; Delewi, R.; Hermanides, R.S.; Holvoet, W.; Dubois, C.L.; Frambach, P.; De Bruyne, B.; Van Houwelingen, G.K.; Van Der Heyden, J.A.; et al. Anticoagulation with or without Clopidogrel after Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Implantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1696–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Hoshi, T.; Kakefuda, Y.; Harunari, T.; Watabe, H.; Hiraya, D.; Akiyama, D.; Abe, D.; Takeyasu, N.; Aonuma, K. Effect of the Mehran risk score for the prediction of clinical outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention. J. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, M.B.; Smith, C.R.; Mack, M.; Miller, D.C.; Moses, J.W.; Svensson, L.G.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Webb, J.G.; Fontana, G.P.; Makkar, R.R.; et al. Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Implantation for Aortic Stenosis in Patients Who Cannot Undergo Surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, M.B.; Smith, C.R.; Mack, M.J.; Makkar, R.R.; Svensson, L.G.; Kodali, S.K.; Thourani, V.H.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Miller, D.C.; Herrmann, H.C.; et al. Transcatheter or Surgical Aortic-Valve Replacement in Intermediate-Risk Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.H.; Popma, J.J.; Reardon, M.J.; Yakubov, S.J.; Coselli, J.S.; Deeb, G.M.; Gleason, T.G.; Buchbinder, M.; Hermiller, J., Jr.; Kleiman, N.S.; et al. Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Replacement with a Self-Expanding Prosthesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1790–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyregod, H.G.; Søndergaard, L.; Ihlemann, N.; Franzen, O.; Andersen, L.W.; Hansen, P.B.; Olsen, P.S.; Nissen, H.; Winkel, P.; Gluud, C.; et al. The Nordic Aortic Valve Intervention (NOTION) trial comparing transcatheter versus surgical valve implantation: Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2013, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherner, M.; Wahlers, T. Acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangas, G.; Iakovou, I.; Nikolsky, E.; Aymong, E.D.; Mintz, G.S.; Kipshidze, N.N.; Lansky, A.J.; Moussa, I.; Stone, G.W.; Moses, J.W.; et al. Contrast-Induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary interventions in relation to chronic kidney disease and hemodynamic variables. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizzi, F.; Burattini, O.; Cafaro, A.; Spione, F.; Salemme, L.; Cioppa, A.; Fimiani, L.; Rimmaudo, F.; Pignatelli, A.; Palmitessa, C.; et al. Early acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Predictive value of currently available risk scores. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2022, 70, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, V.E.; Campos, C.M.; Bacelar, A.; Abizaid, A.A.; Mangione, J.A.; Lemos, P.A.; Esteves, V.; Caramori, P.; Sampaio, R.O.; Tarasoutchi, F.; et al. Performance of Prediction Models for Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury after Transcutaneous Aortic Valve Replacement. Cardiorenal Med. 2021, 11, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zungur, M.; Gul, I.; Tastan, A.; Damar, E.; Tavli, T. Predictive Value of the Mehran Score for Contrast-Induced Nephropathy after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation in Patients with Aortic Stenosis. Cardiorenal Med. 2016, 6, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, E.; Akçay, F.A.; Esen, S.; Emren, S.V.; Karaca, M.; Nazlı, C.; Kırış, T. Predictive Value of the Modified Mehran Score for Contrast-Induced Nephropathy After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Angiology 2023, 000331972311512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, D.P.; Anderson, M.D.; Sutton, T.A. Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney Injury. In Comprehensive Physiology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1303–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfritz, M.; Shahin, M.; Nietlispach, F.; Taramasso, M.; Denegri, A.; Moccetti, M.; Pedrazzini, G.; Moccetti, T.; Keller, L.S.; Ruschitzka, F.; et al. Baseline Predictors of Renal Failure in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 31, E289–E297. [Google Scholar]
- Barbanti, M.; Gargiulo, G.; Tamburino, C. Renal dysfunction and transcatheter aortic valve implantation outcomes. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2016, 14, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilard, M.; Eltchaninoff, H.; Iung, B.; Donzeau-Gouge, P.; Chevreul, K.; Fajadet, J.; Leprince, P.; Leguerrier, A.; Lievre, M.; Prat, A.; et al. Registry of Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Implantation in High-Risk Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgura, F.A.; Arrotti, S.; Magnavacchi, P.; Monopoli, D.; Gabbieri, D.; Banchelli, F.; Tondi, S.; Denegri, A.; D’Amico, R.; Guiducci, V.; et al. Kidney dysfunction and short term all-cause mortality after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 81, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Low MS n = 46 | Moderate MS n = 281 | High MS n = 566 | Very High MS n = 287 | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age and anthropometric factors | ||||||
| Age | Years ± SD | 76.8 ± 8.2 | 79.9 ± 9.9 | 82.8 ± 5.1 | 83.6 ± 4.1 | <0.001 |
| Gender | F% (n) | 60.9 (28) | 47.3 (133) | 52.7 (298) | 54.4 (156) | 0.20 |
| BMI | Kg/m2 ± SD | 27.1 ± 4.6 | 26.7 ± 4.3 | 27.0 ± 6.5 | 26.5 ± 4.8 | 0.60 |
| CV Risk factors and Comorbidity | ||||||
| Diabetes | % | 4.3 (n = 2) | 8.5 (n = 24) | 21.6 (n = 122) | 53.0 (n = 152) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | % | 63.0 (n = 29) | 67.4 (n = 188) | 69.9 (n = 395) | 70.4 (n = 202) | 0.66 |
| Hypertension | % | 80.4 (n = 37) | 89.3 (n = 251) | 87.3 (n = 494) | 90.2 (n = 259) | 0.20 |
| Smoker | % | 36.4 (n = 12) | 36.2 (n = 84) | 31.2 (n = 123) | 32.6 (n = 63) | 0.61 |
| NYHA class | <0.001 | |||||
| NYHA I | % | 9.1 (n = 4) | 1.9 (n = 5) | 0.5 (n = 3) | 0 (n = 0) | |
| NYHA II | % | 79.5 (n = 35) | 41.5 (n = 110) | 7.5 (n = 42) | 1.4 (n = 4) | |
| NYHA III | % | 9.1 (n = 4) | 54.7 (n = 145) | 85.9 (n = 480) | 87.1 (n = 250) | |
| NYHA IV | % | 2.3 (n = 1) | 1.5 (n = 4) | 6.1 (n = 34) | 11.5 (n = 33) | |
| STS score | 0.45 | |||||
| Intermediate risk (4–8%) | % | 7.7 (n = 3) | 19.0 (n = 40) | 19.9 (n = 87) | 30.4 (n = 75) | |
| High risk (>8%) | % | 33.3 (n = 13) | 25.6 (n = 54) | 44.6 (n = 195) | 47.0 (n = 117) | |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | % | 8.9 (n = 4) | 14.6 (n = 41) | 15.4 (n = 87) | 16.0 (n = 46) | 0.65 |
| Cancer History | % | 8.7 (n = 4) | 9.3 (n = 26) | 10.6 (n = 60) | 10.9 (n = 31) | 0.89 |
| Prior Stroke | % | 9.1 (n = 3) | 12.1 (n = 28) | 9.9 (n = 39) | 12.9 (n = 25) | 0.66 |
| Prior myocardial infarction | % | 15.2 (n = 5) | 14.2 (n = 33) | 13.7 (n = 54) | 18.0 (n = 35) | 0.56 |
| Coronary artery disease | % | 21.7 (n = 10) | 33.6 (n = 94) | 30.7 (n = 173) | 28.7 (n = 82) | 0.34 |
| Prior CABG | % | 15.2 (n = 7) | 14.6 (n = 41) | 10.2 (n = 58) | 11.1 (n = 32) | 0.25 |
| Prior PCI | % | 10.9 (n = 5) | 21.0 (n = 59) | 24.4 (n = 138) | 22.0 (n = 63) | 0.16 |
| Prior BAV | % | 0 (n = 0) | 6.5 (n = 15) | 9.6 (n = 38) | 11.9 (n = 23) | 0.06 |
| Prior SAVR | % | 15.2 (n = 5) | 5.2 (n = 12) | 4.8 (n = 19) | 4.1 (n = 8) | 0.06 |
| Prior MVR | % | 6.1 (n = 2) | 2.6 (n = 6) | 2.3 (n = 9) | 2.6 (n = 5) | 0.63 |
| Laboratory findings | ||||||
| eGFR CKD EPI | mL/min ± SD | 77.8 ± 15.1 | 68.3 ± 20.2 | 57.2 ± 19.2 | 43.0 ± 20.3 | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit | % | 40.5 ± 7.7 | 39.2 ± 4.1 | 37.0 ± 5.3 | 33.6 ± 4.4 | <0.001 |
| ECG characteristics | ||||||
| Right bundle brunch block | % | 4.3 (n = 2) | 10.7 (n = 30) | 6.9 (n = 39) | 7.7 (n = 22) | 0.19 |
| Left bundle branch block | % | 8.7 (n = 4) | 7.1 (n = 20) | 8.8 (n = 50) | 6.3 (n = 18) | 0.57 |
| Prior PM implantation | % | 8.9 (n = 4) | 6.8 (n = 19) | 9.0 (n = 51) | 10.8 (n = 31) | 0.40 |
| Atrial fibrillation | % | 30.4 (n = 14) | 27.8 (n = 78) | 24.2 (n = 137) | 30.0 (n = 86) | 0.28 |
| Echocardiographic parameters | ||||||
| Ejection Fraction | % | 56.8 ± 6.9 | 53.6 ± 9.5 | 53.1 ± 9.2 | 51.1 ± 10.1 | 0.001 |
| Severe AR | % | 17.2 (n = 5) | 12.9 (n = 28) | 12.7 (n = 48) | 15.0 (n = 27) | 0.80 |
| Severe MR | % | 20.0 (n = 6) | 16.1 (n = 35) | 17.5 (n = 65) | 30.9 (n = 55) | 0.001 |
| Procedural characteristics | ||||||
| Access type | 0.19 | |||||
| Trans-femoral | % | 89.1 (n = 41) | 86.1 (n = 241) | 82.8 (n = 467) | 82.6 (n = 237) | |
| Trans-apical | % | 8.7 (n = 4) | 9.3 (n = 26) | 11.3 (n = 64) | 8.4 (n = 24) | |
| Other | % | 2.2 (n = 1) | 4.6 (n = 13) | 5.9 (n = 33) | 9.1 (n = 26) | |
| Valve type | 0.23 | |||||
| Self expandable | % | 37.2 (n = 16) | 34.2 (n = 95) | 29.1 (n = 164) | 34.8 (n = 100) | |
| Balloon expandable | % | 62.8 (n =27) | 65.8 (n = 183) | 70.9 (n = 399) | 65.2 (n = 187) | |
| Amount of Contrast | mL ± SD | 142.2 ± 82.4 | 168.4 ± 82.8 | 174.1 ± 84.2 | 209.4 ± 86.7 | <0.001 |
| Hospitalization Lenght | Days ± SD | 8.1 ± 4.4 | 8.7 ± 7.2 | 9.4 ± 8.5 | 12.1 ± 5.5 | 0.005 |
| AKI (Univariate Analysis) | AKI (Multivariate Analysis) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p Value | HR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| MEHRAN Classes | 1.64 | 1.31–2.06 | <0.01 | 1.36 | 1.23–1.63 | <0.01 |
| Age | 1.02 | 0.99–1.05 | 0.15 | |||
| Diabetes | 1.26 | 0.88–1.81 | 0.20 | |||
| NYHA | 1.59 | 1.12–2.25 | <0.01 | 1.27 | 0.86–1.88 | 0.23 |
| eGFR CKD-EPI | 1.48 | 1.27–1.74 | <0.01 | 1.21 | 0.91–1.62 | 0.17 |
| Hematocrit | 0.96 | 0.94–1.01 | 0.06 | |||
| Contrast | 1.00 | 0.99–1.01 | 0.37 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arrotti, S.; Sgura, F.A.; Monopoli, D.E.; Siena, V.; Leo, G.; Morgante, V.; Cataldo, P.; Magnavacchi, P.; Gabbieri, D.; Guiducci, V.; et al. The Importance of Mehran Score to Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with TAVI: A Large Multicenter Cohort Study. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10060228
Arrotti S, Sgura FA, Monopoli DE, Siena V, Leo G, Morgante V, Cataldo P, Magnavacchi P, Gabbieri D, Guiducci V, et al. The Importance of Mehran Score to Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with TAVI: A Large Multicenter Cohort Study. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2023; 10(6):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10060228
Chicago/Turabian StyleArrotti, Salvatore, Fabio Alfredo Sgura, Daniel Enrique Monopoli, Valerio Siena, Giulio Leo, Vernizia Morgante, Paolo Cataldo, Paolo Magnavacchi, Davide Gabbieri, Vincenzo Guiducci, and et al. 2023. "The Importance of Mehran Score to Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with TAVI: A Large Multicenter Cohort Study" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 10, no. 6: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10060228
APA StyleArrotti, S., Sgura, F. A., Monopoli, D. E., Siena, V., Leo, G., Morgante, V., Cataldo, P., Magnavacchi, P., Gabbieri, D., Guiducci, V., Benatti, G., Vignali, L., Boriani, G., & Rossi, R. (2023). The Importance of Mehran Score to Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with TAVI: A Large Multicenter Cohort Study. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 10(6), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10060228