The Prenatal Diagnosis and Perinatal Management of Congenital Long QT Syndrome: A Comprehensive Literature Review and Recent Updates
Abstract
1. Introduction
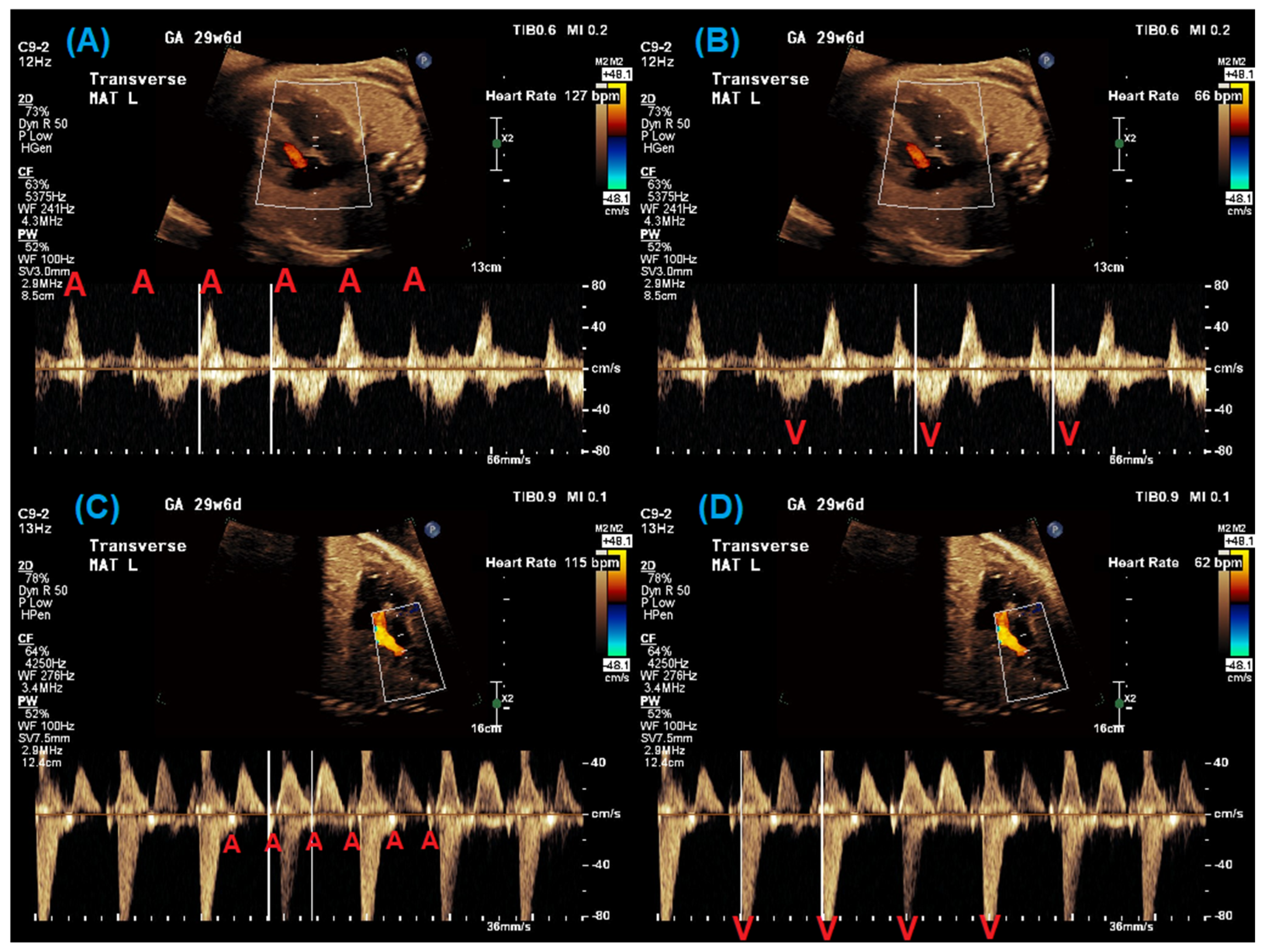
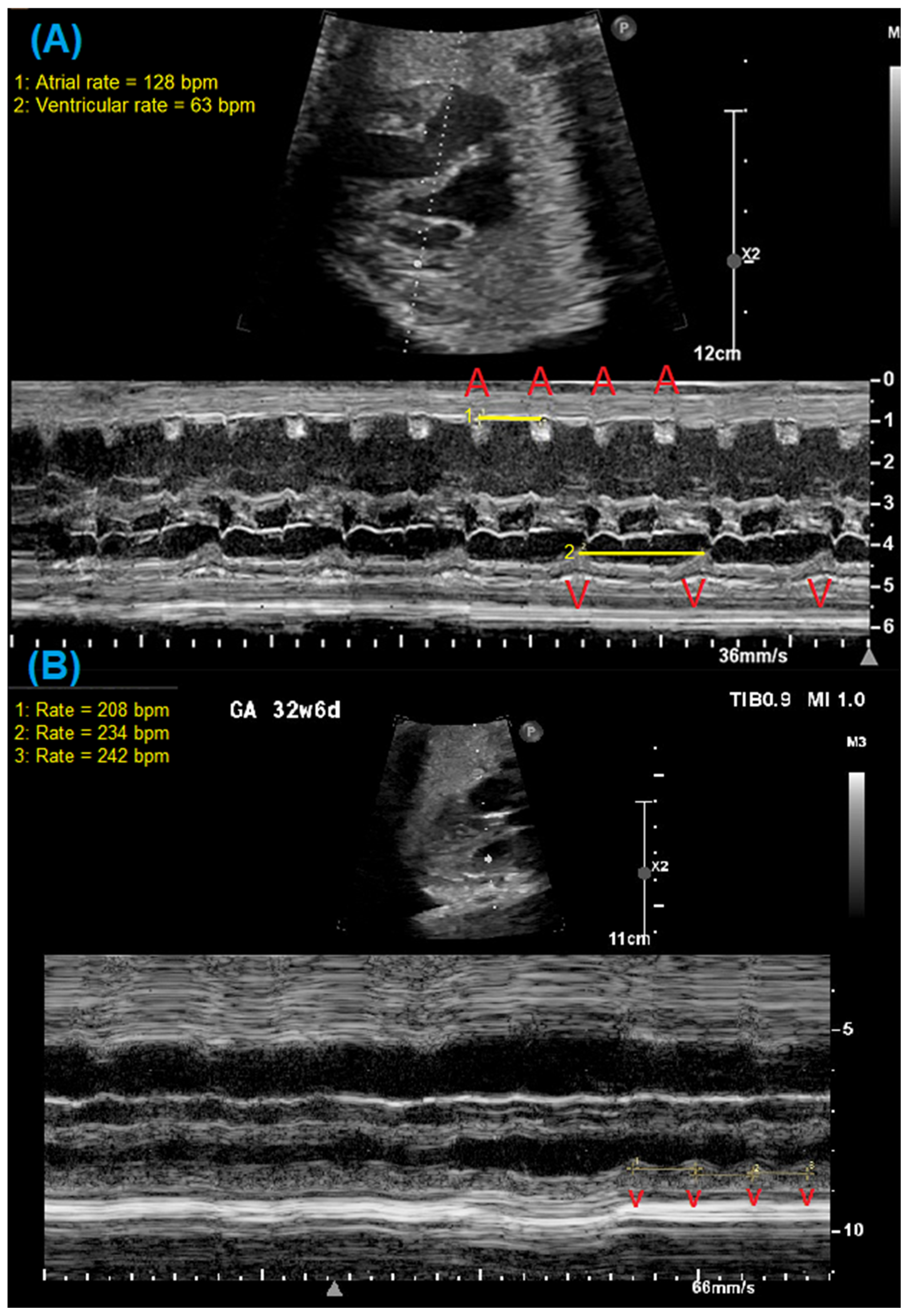
2. Fetal Diagnosis of Long QT Syndrome
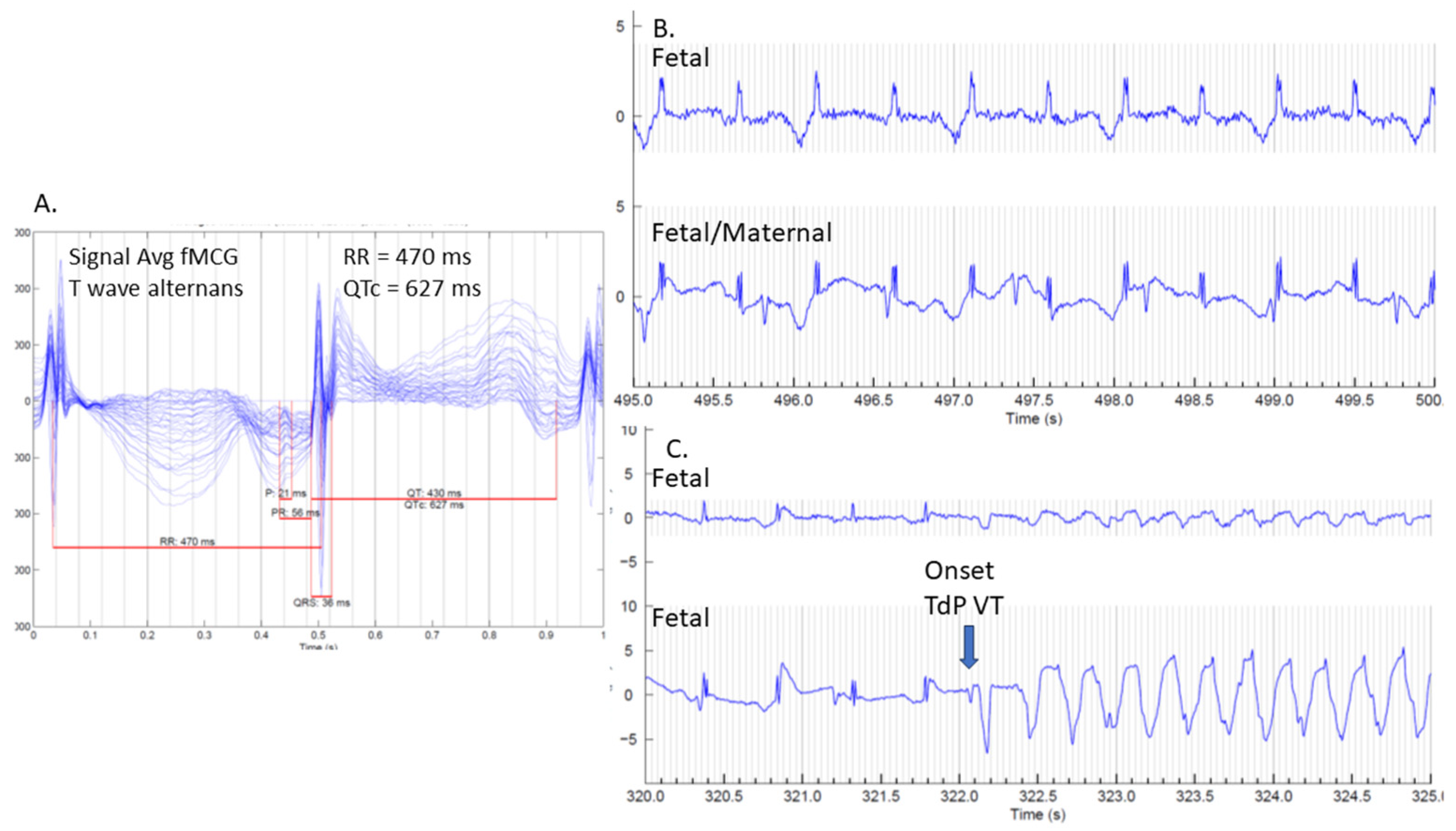
3. Utility of Fetal Magnetocardiography
4. Genetics
4.1. Genetics of LQTS
4.2. Genetic Testing Approaches
4.3. Genetic Test Results
4.4. Postnatal Genetics Considerations
5. Fetal Management
6. Postnatal Management
6.1. Delivery Location and Delivery-Room Resource Preparation
6.2. Management of Torsades de Pointes
6.3. Management of Bradycardia
6.4. Antiarrhythmic Therapy for Long-Term Management
6.5. Pacemaker of Intracardiac Defibrillator Insertion for Long-Term Management
7. Multi-Disciplinary Team Approach
8. Future Directions
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LQTS | Long QT syndrome |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| AV | Atrioventricular |
| BPM | Beats per minute |
| FHR | Fetal heart rate |
| fMCG | Fetal magnetocardiography |
| SQUID | Superconducting quantum interference device |
| TdP | Torsades de Pointes |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| NIFECG | Noninvasive fetal electrocardiography |
| fECG | Fetal electrocardiogram |
| LVIRT | Left ventricular isovolumetric relaxation time |
| CVS | Chorionic villus sampling |
| VUS | Variants of uncertain significance |
| MFM | Maternal–fetal medicine |
| HFHRM | Home fetal heart rate monitoring |
| ICD | Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator |
References
- Chivers, S.; Ovadia, C.; Regan, W.; Zidere, V.; Vigneswaran, T.; Sharland, G.; Rosenthal, E.; Seed, P.T.; Simpson, J.M.; Williamson, C. Systematic Review of Long Qt Syndrome Identified During Fetal Life. Heart Rhythm 2023, 20, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zidere, V.; Vigneswaran, T.V.; Dumitrascu-Biris, I.; Regan, W.; Simpson, J.M.; Homfray, T. Presentation and Genetic Confirmation of Long Qt Syndrome in the Fetus. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2022, 8, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz Peter, J.; Stramba-Badiale, M.; Crotti, L.; Pedrazzini, M.; Besana, A.; Bosi, G.; Gabbarini, F.; Goulene, K.; Insolia, R.; Insolia, R.; et al. Prevalence of the Congenital Long-Qt Syndrome. Circulation 2009, 120, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, M.; Ushinohama, H.; Sato, S.; Ohno, S.; Hata, T.; Horigome, H.; Tauchi, N.; Sumitomo, N.; Nishihara, E.; Hirono, K.; et al. Screening of 1-Month-Old Infants with Prolonged Qt Interval and Its Cutoff Value. Circ. J. 2025, 148, CJ-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofbeck, M.; Ulmer, H.; Heidi, U.; Ernst, B.; Beinder, E.; Sieber, E.; Helmut, S. Prenatal Findings in Patients with Prolonged Qt Interval in the Neonatal Period. Heart 1997, 77, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killen, S.A.S.; Strasburger, J.F. Diagnosis and Management of Fetal Arrhythmias in the Current Era. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2024, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotti, L.; Tester, D.J.; White, W.M.; Bartos, D.C.; Insolia, R.; Besana, A.; Kunic, J.D.; Will, M.L.; Velasco, E.J.; Bair, J.J.; et al. Long Qt Syndrome-Associated Mutations in Intrauterine Fetal Death. JAMA 2013, 309, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.; Strasburger, J.F.; Cuneo, B.F.; Wakai, R.T. Complex and Novel Arrhythmias Precede Stillbirth in Fetuses with De Novo Long Qt Syndrome. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e008082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polic, A.; Killen, S.A.S.; Strasburger, J.F.; Kannankeril, P.J.; Wakai, R.T.; Patel, S.S. Low Baseline Fetal Heart Rate Leads to Diagnosis of Long Qt Syndrome Type 1. JACC Case Rep. 2024, 29, 102183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell Jason, L.; Cuneo, B.F.; Etheridge, S.P.; Horigome, H.; Weng, H.-Y.; Benson, D.W. Fetal Heart Rate Predictors of Long Qt Syndrome. Circulation 2012, 126, 2688–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry-Waterman, N.; Dara, B.; Bucholz, E.; Obregon, C.L.; Grenier, M.; Snyder, K.; Cuneo, B.F. Fetal Heart Rate < 3rd Percentile for Gestational Age Can Be a Marker of Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clur, S.B.; Vink, A.S.; Etheridge, S.P.; de Medina, P.G.R.; Rydberg, A.; Ackerman, M.J.; Wilde, A.A.; Blom, N.A.; Benson, D.W.; Herberg, U.; et al. Left Ventricular Isovolumetric Relaxation Time Is Prolonged in Fetal Long-Qt Syndrome. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2018, 11, e005797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.; Strasburger, J.F.; Wakai, R.T. Isovolumic Relaxation Time and Repolarization in Fetuses at Risk of Long Qt Syndrome. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 10, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabaneix, J.; Andelfinger, G.; Fournier, A.; Fouron, J.C.; Raboisson, M.J. Prenatal Diagnosis of Long Qt Syndrome with the Superior Vena Cava-Aorta Doppler Approach. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 207, e3–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker-Gussmann, A.; Eckstein, G.K.; Strasburger, J.F. Preventing and Treating Torsades De Pointes in the Mother, Fetus and Newborn in the Highest Risk Pregnancies with Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegorie, C.; Liu, B.; Thilaganathan, B.; Bhide, A.; Pan, Y. Antenatal Noninvasive Fetal Electrocardiography: A Literature Review. Matern.-Fetal Med. 2024, 06, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vullings, R.; van Laar, J. Non-Invasive Fetal Electrocardiography for Intrapartum Cardiotocography. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 599049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, N.; Funamoto, K.; Ingbar, C.; Mass, P.; Moak, J.; Wakai, R.; Strasburger, J.; Donofrio, M.; Khandoker, A.; Kimura, Y.; et al. Noninvasive Fetal Electrocardiography in the Diagnosis of Long Qt Syndrome: A Case Series. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2020, 47, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivers, S.C.; Vasavan, T.; Nandi, M.; Hayes-Gill, B.R.; Jayawardane, I.A.; Simpson, J.M.; Williamson, C.; Fifer, W.P.; Lucchini, M. Measurement of the Cardiac Time Intervals of the Fetal Ecg Utilising a Computerised Algorithm: A Retrospective Observational Study. JRSM Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 11, 20480040221096209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker-Gussmann, A.; Strasburger, J.F.; Wakai, R.T. Contribution of Fetal Magnetocardiography to Diagnosis, Risk Assessment, and Treatment of Fetal Arrhythmia. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e025224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker-Gussmann, A.; Strasburger, J.F.; Cuneo, B.F.; Wakai, R.T. Diagnosis and Treatment of Fetal Arrhythmia. Am. J. Perinatol. 2014, 31, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.; Lutter, W.; Strasburger, J.F.; Shah, V.; Baffa, O.; Wakai, R.T. Low-Cost Fetal Magnetocardiography: A Comparison of Superconducting Quantum Interference Device and Optically Pumped Magnetometers. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e013436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuneo, B.F.; Ovadia, M.; Strasburger, J.F.; Zhao, H.; Petropulos, T.; Schneider, J.; Wakai, R.T. Prenatal Diagnosis and in Utero Treatment of Torsades De Pointes Associated with Congenital Long Qt Syndrome. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joglar, J.A.; Kapa, S.; Saarel, E.V.; Dubin, A.M.; Gorenek, B.; Hameed, A.B.; de Melo, S.L.; Leal, M.A.; Mondesert, B.; Pacheco, L.D.; et al. 2023 Hrs Expert Consensus Statement on the Management of Arrhythmias During Pregnancy. Heart Rhythm 2023, 20, e175–e264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, L.; Wakai, R.; Tsao, S.; Strasburger, J.; Gotteiner, N.; Patel, A. Fetal Diagnosis of Kcnq1-Variant Long Qt Syndrome Using Fetal Echocardiography and Magnetocardiography. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 43, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Novelli, V.; Amin, A.S.; Abiusi, E.; Care, M.; Nannenberg, E.A.; Feilotter, H.; Amenta, S.; Mazza, D.; Bikker, H.; et al. An International, Multicentered, Evidence-Based Reappraisal of Genes Reported to Cause Congenital Long Qt Syndrome. Circulation 2020, 141, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, S.I.; Park, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.M.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.S.; Ahn, K.J.; Song, M.K.; et al. Application of Multigene Panel Sequencing in Patients with Prolonged Rate-Corrected Qt Interval and No Pathogenic Variants Detected in Kcnq1, Kcnh2, and Scn5a. Ann. Lab. Med. 2018, 38, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gakenheimer-Smith, L.; Meyers, L.; Lundahl, D.; Menon, S.C.; Bunch, T.J.; Sawyer, B.L.; Tristani-Firouzi, M.; Etheridge, S.P. Expanding the Phenotype of Cacna1c Mutation Disorders. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2021, 9, e1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerapandiyan, A.; Statland, J.M.; Tawil, R. Andersen-Tawil Syndrome. In Genereviews((R)); Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; NCBI: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kotta, M.C.; Sala, L.; Ghidoni, A.; Badone, B.; Ronchi, C.; Parati, G.; Zaza, A.; Crotti, L. Calmodulinopathy: A Novel, Life-Threatening Clinical Entity Affecting the Young. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotti, L.; Spazzolini, C.; Tester, D.J.; Ghidoni, A.; Baruteau, A.E.; Beckmann, B.M.; Behr, E.R.; Bennett, J.S.; Bezzina, C.R.; Bhuiyan, Z.A.; et al. Calmodulin Mutations and Life-Threatening Cardiac Arrhythmias: Insights from the International Calmodulinopathy Registry. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 2964–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, C.M.; Giudicessi, J.R.; Ye, D.; Tester, D.J.; Rohatgi, R.K.; Bos, J.M.; Ackerman, M.J. Long Qt Syndrome Type 5-Lite: Defining the Clinical Phenotype Associated with the Potentially Proarrhythmic P. Asp85asn-Kcne1 Common Genetic Variant. Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musunuru, K.; Hershberger, R.E.; Day, S.M.; Klinedinst, N.J.; Landstrom, A.P.; Parikh, V.N.; Prakash, S.; Semsarian, C.; Sturm, A.C.; American Heart Association Council on Genomic and Precision Medicine; et al. Genetic Testing for Inherited Cardiovascular Diseases: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2020, 13, e000067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieve, K.V.; Williams, L.; Daly, A.; Richard, G.; Bale, S.; Macaya, D.; Chung, W.K. Results of Genetic Testing in 855 Consecutive Unrelated Patients Referred for Long Qt Syndrome in a Clinical Laboratory. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomarkers 2013, 17, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westenskow, P.; Splawski, I.; Timothy, K.W.; Keating, M.T.; Sanguinetti, M.C. Compound Mutations: A Common Cause of Severe Long-Qt Syndrome. Circulation 2004, 109, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, D.J.; Will, M.L.; Haglund, C.M.; Ackerman, M.J. Compendium of Cardiac Channel Mutations in 541 Consecutive Unrelated Patients Referred for Long Qt Syndrome Genetic Testing. Heart Rhythm 2005, 2, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullally, J.; Goldenberg, I.; Moss, A.J.; Lopes, C.M.; Ackerman, M.J.; Zareba, W.; McNitt, S.; Robinson, J.L.; Benhorin, J.; Kaufman, E.S.; et al. Risk of Life-Threatening Cardiac Events among Patients with Long Qt Syndrome and Multiple Mutations. Heart Rhythm 2013, 10, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Shimizu, W.; Hayashi, K.; Yamagata, K.; Sakaguchi, T.; Ohno, S.; Makiyama, T.; Akao, M.; Ai, T.; Noda, T.; et al. Long Qt Syndrome with Compound Mutations Is Associated with a More Severe Phenotype: A Japanese Multicenter Study. Heart Rhythm 2010, 7, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, P.J.; Spazzolini, C.; Crotti, L.; Bathen, J.; Amlie, J.P.; Timothy, K.; Shkolnikova, M.; Berul, C.I.; Bitner-Glindzicz, M.; Toivonen, L.; et al. The Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome: Natural History, Molecular Basis, and Clinical Outcome. Circulation 2006, 113, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, M.J.; Priori, S.G.; Willems, S.; Berul, C.; Brugada, R.; Calkins, H.; Camm, A.J.; Ellinor, P.T.; Gollob, M.; Hamilton, R.; et al. Hrs/Ehra Expert Consensus Statement on the State of Genetic Testing for the Channelopathies and Cardiomyopathies This Document Was Developed as a Partnership between the Heart Rhythm Society (Hrs) and the European Heart Rhythm Association (Ehra). Heart Rhythm 2011, 8, 1308–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, A.A.M.; Semsarian, C.; Marquez, M.F.; Shamloo, A.S.; Ackerman, M.J.; Ashley, E.A.; Sternick, E.B.; Barajas-Martinez, H.; Behr, E.R.; Bezzina, C.R.; et al. European Heart Rhythm Association (Ehra)/Heart Rhythm Society (Hrs)/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (Aphrs)/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (Lahrs) Expert Consensus Statement on the State of Genetic Testing for Cardiac Diseases. Heart Rhythm 2022, 19, e1–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arscott, P.; Caleshu, C.; Kotzer, K.; Kreykes, S.; Kruisselbrink, T.; Orland, K.; Rigelsky, C.; Smith, E.; Spoonamore, K.; Haidle, J.L.; et al. A Case for Inclusion of Genetic Counselors in Cardiac Care. Cardiol. Rev. 2016, 24, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helm, B.M.; Freeze, S.L.; Spoonamore, K.G.; Ware, S.M.; Ayers, M.D.; Kean, A.C. The Genetic Counselor in the Pediatric Arrhythmia Clinic: Review and Assessment of Services. J. Genet. Couns. 2018, 27, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merc, M.D.; Kotnik, U.; Peterlin, B.; Lovrecic, L. Further Exploration of Cardiac Channelopathy and Cardiomyopathy Genes in Stillbirth. Prenat. Diagn. 2024, 44, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landstrom, A.P.; Kim, J.J.; Gelb, B.D.; Helm, B.M.; Kannankeril, P.J.; Semsarian, C.; Sturm, A.C.; Tristani-Firouzi, M.; Ware, S.M.; American Heart Association Council on Genomic and Precision Medicine; et al. Genetic Testing for Heritable Cardiovascular Diseases in Pediatric Patients: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2021, 14, e000086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, D.S.; Hauser, M.; Beckmann, B.M.; Wolf, C.M.; Hessling, G.; Oberhoffer-Fritz, R.; Wacker-Gussmann, A. Fetal Bradycardia Caused by Monogenic Disorders-a Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Practice Bulletin No. 162 Summary: Prenatal Diagnostic Testing for Genetic Disorders. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 127, 976–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, D.S.; Burkard, T.; Moscu-Gregor, A.; Gebauer, R.; Hessling, G.; Wolf, C.M. Reclassification of Genetic Variants in Children with Long Qt Syndrome. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2020, 8, e1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellefave-Castillo, L.M.; Cirino, A.L.; Callis, T.E.; Esplin, E.D.; Garcia, J.; Hatchell, K.E.; Johnson, B.; Morales, A.; Regalado, E.; Rojahn, S.; et al. Assessment of the Diagnostic Yield of Combined Cardiomyopathy and Arrhythmia Genetic Testing. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherny, S.; Olson, R.; Chiodo, K.; Balmert, L.C.; Webster, G. Changes in Genetic Variant Results over Time in Pediatric Cardiomyopathy and Electrophysiology. J. Genet. Couns. 2021, 30, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lint, F.H.M.; Mook, O.R.F.; Alders, M.; Bikker, H.; Deprez, R.H.L.D.; Christiaans, I. Large Next-Generation Sequencing Gene Panels in Genetic Heart Disease: Yield of Pathogenic Variants and Variants of Unknown Significance. Neth. Heart J. 2019, 27, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell-Smith, K.E.; Skinner, J.R.; Bos, J.M. Pre-Test Probability and Genes and Variants of Uncertain Significance in Familial Long Qt Syndrome. Heart Lung Circ. 2020, 29, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.S.; Bernhardt, M.; McBride, K.L.; Reshmi, S.C.; Zmuda, E.; Kertesz, N.J.; Garg, V.; Fitzgerald-Butt, S.; Kamp, A.N. Reclassification of Variants of Uncertain Significance in Children with Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes Is Predicted by Clinical Factors. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2019, 40, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, H.L.; Berg, J.S.; Brooks, L.D.; Bustamante, C.D.; Evans, J.P.; Landrum, M.J.; Ledbetter, D.H.; Maglott, D.R.; Martin, C.L.; Nussbaum, R.L.; et al. ClinGen—The Clinical Genome Resource. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.M.; Muenzen, K.; Biesecker, L.G.; Bowling, K.M.; Cooper, G.M.; Dorschner, M.O.; Driscoll, C.; Foreman, A.K.M.; Golden-Grant, K.; Greally, J.M.; et al. Variant Classification Concordance Using the Acmg-Amp Variant Interpretation Guidelines across Nine Genomic Implementation Research Studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 107, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, A.; Harrington, E.A.; Dunn, K.; Pariani, M.; Platt, J.C.K.; Grove, M.E.; Caleshu, C. Clinically Impactful Differences in Variant Interpretation between Clinicians and Testing Laboratories: A Single-Center Experience. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrai, A.K.; Funke, B.H.; Rehm, H.L.; Olesen, M.S.; Maron, B.A.; Szolovits, P.; Margulies, D.M.; Loscalzo, J.; Kohane, I.S. Genetic Misdiagnoses and the Potential for Health Disparities. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wain, K.E.; Azzariti, D.R.; Goldstein, J.L.; Johnson, A.K.; Krautscheid, P.; Lepore, B.; O’Daniel, J.M.; Ritter, D.; Savatt, J.M.; Riggs, E.R.; et al. Variant Interpretation Is a Component of Clinical Practice among Genetic Counselors in Multiple Specialties. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, B.M.; Ayers, M.D.; Kean, A.C. All Along the Watchtower: A Case of Long Qt Syndrome Misdiagnosis Secondary to Genetic Testing Misinterpretation. J. Genet. Couns. 2018, 27, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, C.; Grove, M.E.; Orland, K.; Spoonamore, K.; Caleshu, C. Clinical Cardiovascular Genetic Counselors Take a Leading Role in Team-Based Variant Classification. J. Genet. Couns. 2018, 27, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; McNally, E.M.; Ackerman, M.J.; Baty, L.C.; Day, S.M.; Kullo, I.J.; Madueme, P.C.; Maron, M.S.; Martinez, M.W.; Salberg, L.; et al. Establishment of Specialized Clinical Cardiovascular Genetics Programs: Recognizing the Need and Meeting Standards: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2019, 12, e000054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuneo, B.F.; Sonesson, S.E.; Levasseur, S.; Moon-Grady, A.J.; Krishnan, A.; Donofrio, M.T.; Raboisson, M.J.; Hornberger, L.K.; Van Eerden, P.; Sinkovskaya, E.; et al. Home Monitoring for Fetal Heart Rhythm During Anti-Ro Pregnancies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.; Strasburger, J.F.; Lutter, W.J.; Wakai, R.T. Repolarization Predictors of Fetal Long Qt Syndrome. Heart Rhythm O2 2020, 1, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasburger, J.F.; Eckstein, G.; Butler, M.; Noffke, P.; Wacker-Gussmann, A. Fetal Arrhythmia Diagnosis and Pharmacologic Management. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 62 (Suppl. S1), S53–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, A.S.; Silka, M.J.; Borquez, A.; Cuneo, B.; Dechert, B.; Jaeggi, E.; Kannankeril, P.J.; Tabulov, C.; Tisdale, J.E.; Wolfe, D.; et al. Pharmacological Management of Cardiac Arrhythmias in the Fetal and Neonatal Periods: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association: Endorsed by the Pediatric & Congenital Electrophysiology Society (Paces). Circulation 2024, 149, e937–e952. [Google Scholar]
- Donofrio, M.T. Predicting the Future: Delivery Room Planning of Congenital Heart Disease Diagnosed by Fetal Echocardiography. Am. J. Perinatol. 2018, 35, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, E.A.; Berul, C.I.; Donofrio, M.T. Prenatal Diagnosis of Long Qt Syndrome: Implications for Delivery Room and Neonatal Management. Cardiol. Young 2013, 23, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donofrio, M.T.; Levy, R.J.; Schuette, J.J.; Skurow-Todd, K.; Sten, M.B.; Stallings, C.; Pike, J.I.; Krishnan, A.; Ratnayaka, K.; Sinha, P.; et al. Specialized Delivery Room Planning for Fetuses with Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 111, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppenfeld, K.; Tfelt-Hansen, J.; de Riva, M.; Winkel, B.G.; Behr, E.R.; Blom, N.A.; Charron, P.; Corrado, D.; Dagres, N.; de Chillou, C.; et al. 2022 Esc Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3997–4126. [Google Scholar]
- Tzivoni, D.; Banai, S.; Schuger, C.; Benhorin, J.; Keren, A.; Gottlieb, S.; Stern, S. Treatment of Torsade De Pointes with Magnesium Sulfate. Circulation 1988, 77, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, S.M.; Stevenson, W.G.; Ackerman, M.J.; Bryant, W.J.; Callans, D.J.; Curtis, A.B.; Deal, B.J.; Dickfeld, T.; Field, M.E.; Fonarow, G.C.; et al. 2017 Aha/Acc/Hrs Guideline for Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation 2018, 138, e272–e391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koponen, M.; Marjamaa, A.; Hiippala, A.; Happonen, J.M.; Havulinna, A.S.; Salomaa, V.; Lahtinen, A.M.; Hintsa, T.; Viitasalo, M.; Toivonen, L.; et al. Follow-up of 316 Molecularly Defined Pediatric Long-Qt Syndrome Patients: Clinical Course, Treatments, and Side Effects. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, I.; Moss, A.J.; Peterson, D.R.; McNitt, S.; Zareba, W.; Andrews, M.L.; Robinson, J.L.; Locati, E.H.; Ackerman, M.J.; Benhorin, J.; et al. Risk Factors for Aborted Cardiac Arrest and Sudden Cardiac Death in Children with the Congenital Long-Qt Syndrome. Circulation 2008, 117, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, I.; Bradley, J.; Moss, A.; McNitt, S.; Polonsky, S.; Robinson, J.L.; Andrews, M.; Zareba, W.; Lqts Registry Investigators International. Beta-Blocker Efficacy in High-Risk Patients with the Congenital Long-Qt Syndrome Types 1 and 2: Implications for Patient Management. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2010, 21, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.J.; Zareba, W.; Hall, W.J.; Schwartz, P.J.; Crampton, R.S.; Benhorin, J.; Vincent, G.M.; Locati, E.H.; Priori, S.G.; Napolitano, C.; et al. Effectiveness and Limitations of Beta-Blocker Therapy in Congenital Long-Qt Syndrome. Circulation 2000, 101, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chockalingam, P.; Crotti, L.; Girardengo, G.; Johnson, J.N.; Harris, K.M.; van der Heijden, J.F.; Hauer, R.N.; Beckmann, B.M.; Spazzolini, C.; Rordorf, R.; et al. Not All Beta-Blockers Are Equal in the Management of Long Qt Syndrome Types 1 and 2: Higher Recurrence of Events under Metoprolol. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 2092–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zeitone, A.; Peterson, D.R.; Polonsky, B.; McNitt, S.; Moss, A.J. Efficacy of Different Beta-Blockers in the Treatment of Long Qt Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatrath, R.; Bell, C.M.; Ackerman, M.J. Beta-Blocker Therapy Failures in Symptomatic Probands with Genotyped Long-Qt Syndrome. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2004, 25, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, S.; Makiyama, T.; Melgari, D.; Yamamoto, Y.; Wuriyanghai, Y.; Yokoi, F.; Nishiuchi, S.; Harita, T.; Hayano, M.; Kohjitani, H.; et al. Propranolol Attenuates Late Sodium Current in a Long Qt Syndrome Type 3-Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Model. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankston, J.R.; Kass, R.S. Molecular Determinants of Local Anesthetic Action of Beta-Blocking Drugs: Implications for Therapeutic Management of Long Qt Syndrome Variant 3. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2010, 48, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, A.; Maragna, R.; Faragli, A.; Monteforte, N.; Bloise, R.; Memmi, M.; Novelli, V.; Baiardi, P.; Bagnardi, V.; Etheridge, S.P.; et al. Gene-Specific Therapy with Mexiletine Reduces Arrhythmic Events in Patients with Long Qt Syndrome Type 3. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagkaki, A.; Tsoutsinos, A.; Hatzidaki, E.; Tzatzarakis, M.; Parthenakis, F.; Germanakis, I. Mexiletine Treatment for Neonatal Lqt3 Syndrome: Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 674041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, P.J.; Priori, S.G.; Locati, E.H.; Napolitano, C.; Cantu, F.; Towbin, J.A.; Keating, M.T.; Hammoude, H.; Brown, A.M.; Chen, L.S.; et al. Long Qt Syndrome Patients with Mutations of the Scn5a and Herg Genes Have Differential Responses to Na+ Channel Blockade and to Increases in Heart Rate. Implications for Gene-Specific Therapy. Circulation 1995, 92, 3381–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorin, E.; Taub, R.; Medina, A.; Flint, N.; Viskin, S.; Benhorin, J. Long-Term Flecainide Therapy in Type 3 Long Qt Syndrome. Europace 2018, 20, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.I.; Izquierdo, I.; Medina, P.; Arnau, M.A.; Salvador, A.; Zorio, E. Flecainide, a Therapeutic Option in a Patient with Long Qt Syndrome Type 3 Caused by the Heterozygous V411m Mutation in the Scn5a Gene. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2012, 65, 1058–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.M.; Crotti, L.; Rohatgi, R.K.; Castelletti, S.; Dagradi, F.; Schwartz, P.J.; Ackerman, M.J. Mexiletine Shortens the Qt Interval in Patients with Potassium Channel-Mediated Type 2 Long Qt Syndrome. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e007280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Bahr, E.; Fenge, H.; Etzrodt, D.; Haverkamp, W.; Monnig, G.; Wedekind, H.; Breithardt, G.; Kehl, H.G. Long Qt Syndrome and Life Threatening Arrhythmia in a Newborn: Molecular Diagnosis and Treatment Response. Heart 2004, 90, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horigome, H.; Nagashima, M.; Sumitomo, N.; Yoshinaga, M.; Ushinohama, H.; Iwamoto, M.; Shiono, J.; Ichihashi, K.; Hasegawa, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Genetic Background of Congenital Long-Qt Syndrome Diagnosed in Fetal, Neonatal, and Infantile Life: A Nationwide Questionnaire Survey in Japan. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2010, 3, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berul, C.I.; Van Hare, G.F.; Kertesz, N.J.; Dubin, A.M.; Cecchin, F.; Collins, K.K.; Cannon, B.C.; Alexander, M.E.; Triedman, J.K.; Walsh, E.P.; et al. Results of a Multicenter Retrospective Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Registry of Pediatric and Congenital Heart Disease Patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, M.S.; Hill, S.L.; Cliff, D.L.; Swygman, C.A.; Foote, C.B.; Homoud, M.K.; Wang, P.J.; Estes, N.A., 3rd; Berul, C.I. Comparison of Frequency of Complications of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators in Children Versus Adults. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 83, 263–266, A5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedivash, A.; Hanisch, D.; Dubin, A.M.; Trela, A.; Chubb, H.; Motonaga, K.S.; Goodyer, W.R.; Maeda, K.; Reinhartz, O.; Ma, M.; et al. Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators in Infants and Toddlers: Indications, Placement, Programming, and Outcomes. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2022, 15, e010557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.P.; Gallotti, R.G.; Shannon, K.M.; Bos, J.M.; Sadeghi, E.; Strasburger, J.F.; Wakai, R.T.; Horigome, H.; Clur, S.A.; Hill, A.C.; et al. Genotype Predicts Outcomes in Fetuses and Neonates with Severe Congenital Long Qt Syndrome. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berul, C.I. Defibrillator Indications and Implantation in Young Children. Heart Rhythm 2008, 5, 1755–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimmins, S.; Vashit, S.; Doyle, L.; Harman, C.; Turan, O.; Turan, S. A Multidisciplinary Approach to Prenatal Treatment of Congenital Long Qt Syndrome. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2017, 43, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalona-Vargas, D.; Eswaran, H. Adaptable Sensor Arrays for Fetal Magnetocardiographic Measurements Using Optically-Pumped Magnetometers: A Pilot Study. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2020, 2020, 1803–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Haugaa, K.H.; Amlie, J.P.; Berge, K.E.; Leren, T.P.; Smiseth, O.A.; Edvardsen, T. Transmural Differences in Myocardial Contraction in Long-Qt Syndrome: Mechanical Consequences of Ion Channel Dysfunction. Circulation 2010, 122, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiec, K.; Kowalski, M.; Kumor, M.; Duliban, J.; Smigielski, W.; Hoffman, P.; Biernacka, E.K. Prolonged Left Ventricular Contraction Duration in Apical Segments as a Marker of Arrhythmic Risk in Patients with Long Qt Syndrome. Europace 2020, 22, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonaglioni, A.; Bruno, A.; Nicolosi, G.L.; Bianchi, S.; Lombardo, M.; Muti, P. Echocardiographic Assessment of Biventricular Mechanics of Fetuses and Infants of Gestational Diabetic Mothers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Children 2024, 11, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Wildenberg, S.; van Beynum, I.M.; Havermans, M.E.C.; Boersma, E.; DeVore, G.R.; Simpson, J.M.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Go, A.; Cornette, J.M.J. Fetal Speckle Tracking Echocardiography Measured Global Longitudinal Strain and Strain Rate in Congenital Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prenat. Diagn. 2024, 44, 1479–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, C.; Pruitt, C.; Donofrio, M.T.; Freud, L.R.; Lopez, L.; Minich, L.L.; Moon-Grady, A.J.; Ou, Z.; Punn, R.; Tacy, T.A.; et al. Normal Fetal Ventricular Strain Pilot Study. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2024, 38, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, M.; Lee, Y.M.; Bucholz, E.; Ross, E.L.; Galan, H.; Behrendt, N.; Micke, K.; Chow, F.S.; Zaretsky, M.V.; Cuneo, B.F. Successful Management of Fetal Torsades De Pointes and Long Qt Syndrome by a Cardio-Obstetrical Team. JACC Case Rep. 2023, 27, 102110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samples, S.; Cherny, S.; Madan, N.; Hong, J.; Mansukhani, S.A.; Strasburger, J.F.; Carr, M.R.; Patel, S.R. The Prenatal Diagnosis and Perinatal Management of Congenital Long QT Syndrome: A Comprehensive Literature Review and Recent Updates. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12040156
Samples S, Cherny S, Madan N, Hong J, Mansukhani SA, Strasburger JF, Carr MR, Patel SR. The Prenatal Diagnosis and Perinatal Management of Congenital Long QT Syndrome: A Comprehensive Literature Review and Recent Updates. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(4):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12040156
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamples, Stefani, Sara Cherny, Nitin Madan, Jeff Hong, Sheena A. Mansukhani, Janette F. Strasburger, Michael R. Carr, and Sheetal R. Patel. 2025. "The Prenatal Diagnosis and Perinatal Management of Congenital Long QT Syndrome: A Comprehensive Literature Review and Recent Updates" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 4: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12040156
APA StyleSamples, S., Cherny, S., Madan, N., Hong, J., Mansukhani, S. A., Strasburger, J. F., Carr, M. R., & Patel, S. R. (2025). The Prenatal Diagnosis and Perinatal Management of Congenital Long QT Syndrome: A Comprehensive Literature Review and Recent Updates. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(4), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12040156






