The Effects of Inclisiran on the Subclinical Prothrombotic and Platelet Activation Markers in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
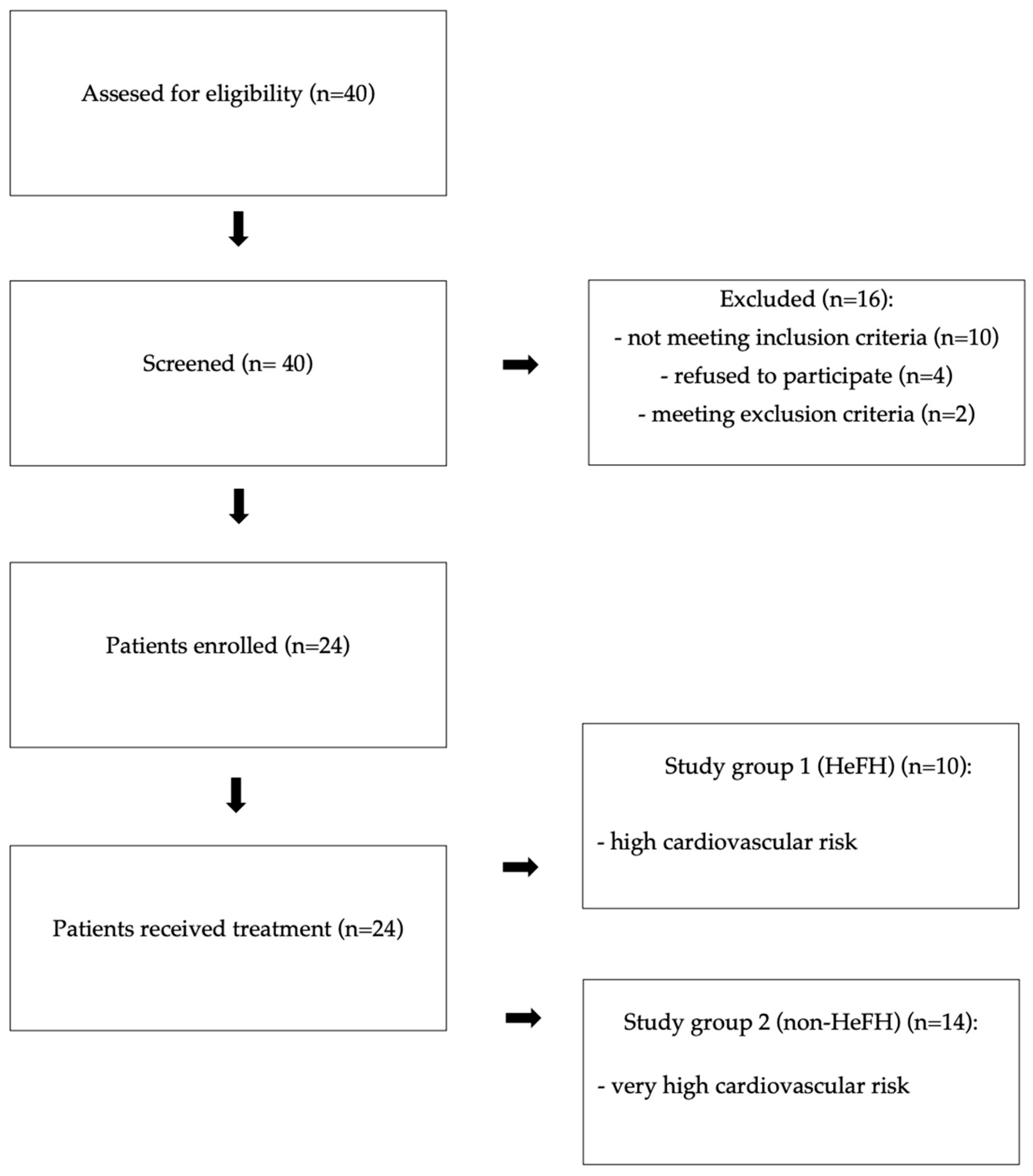
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Assessment of Laboratory Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analyses
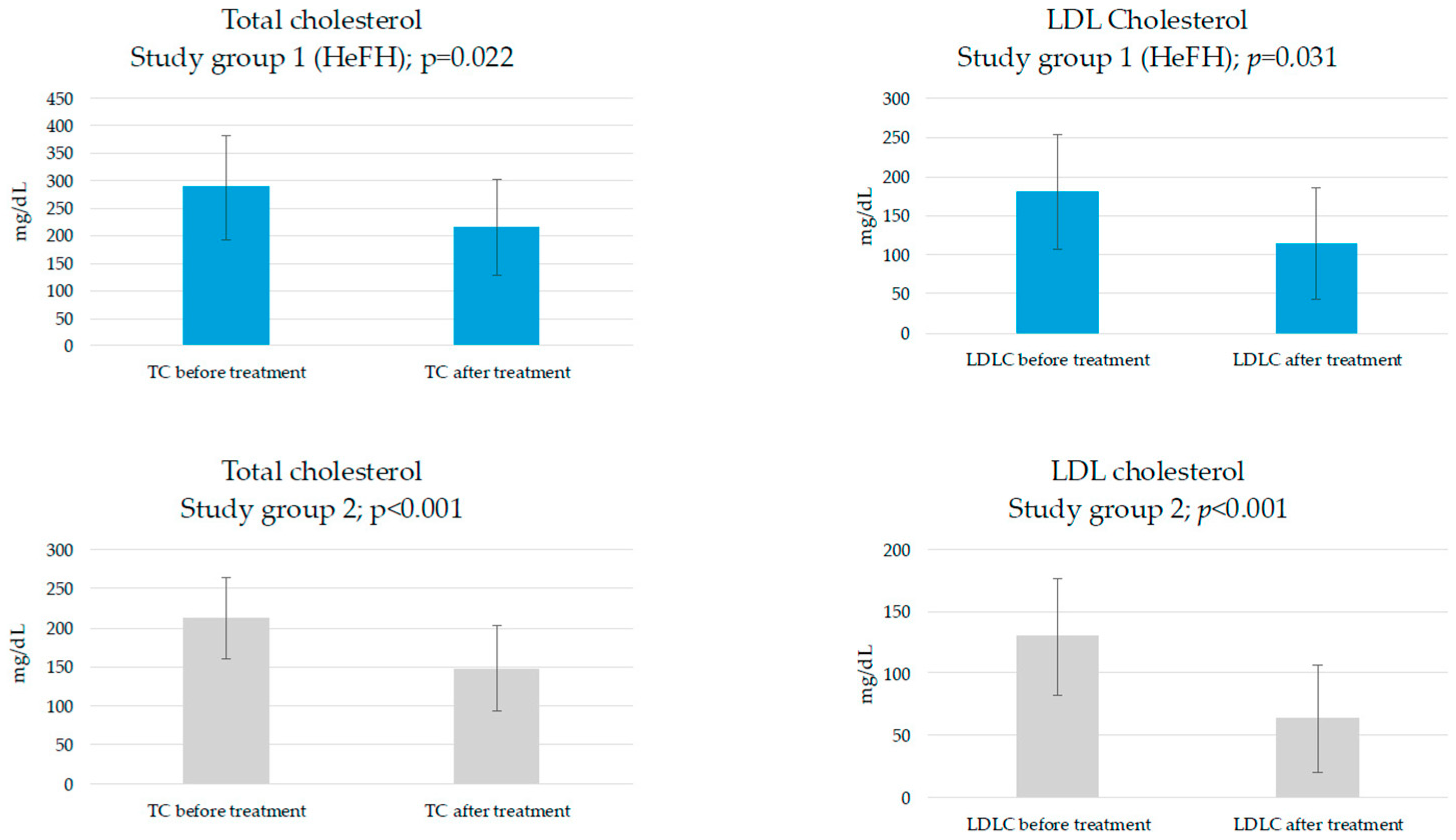
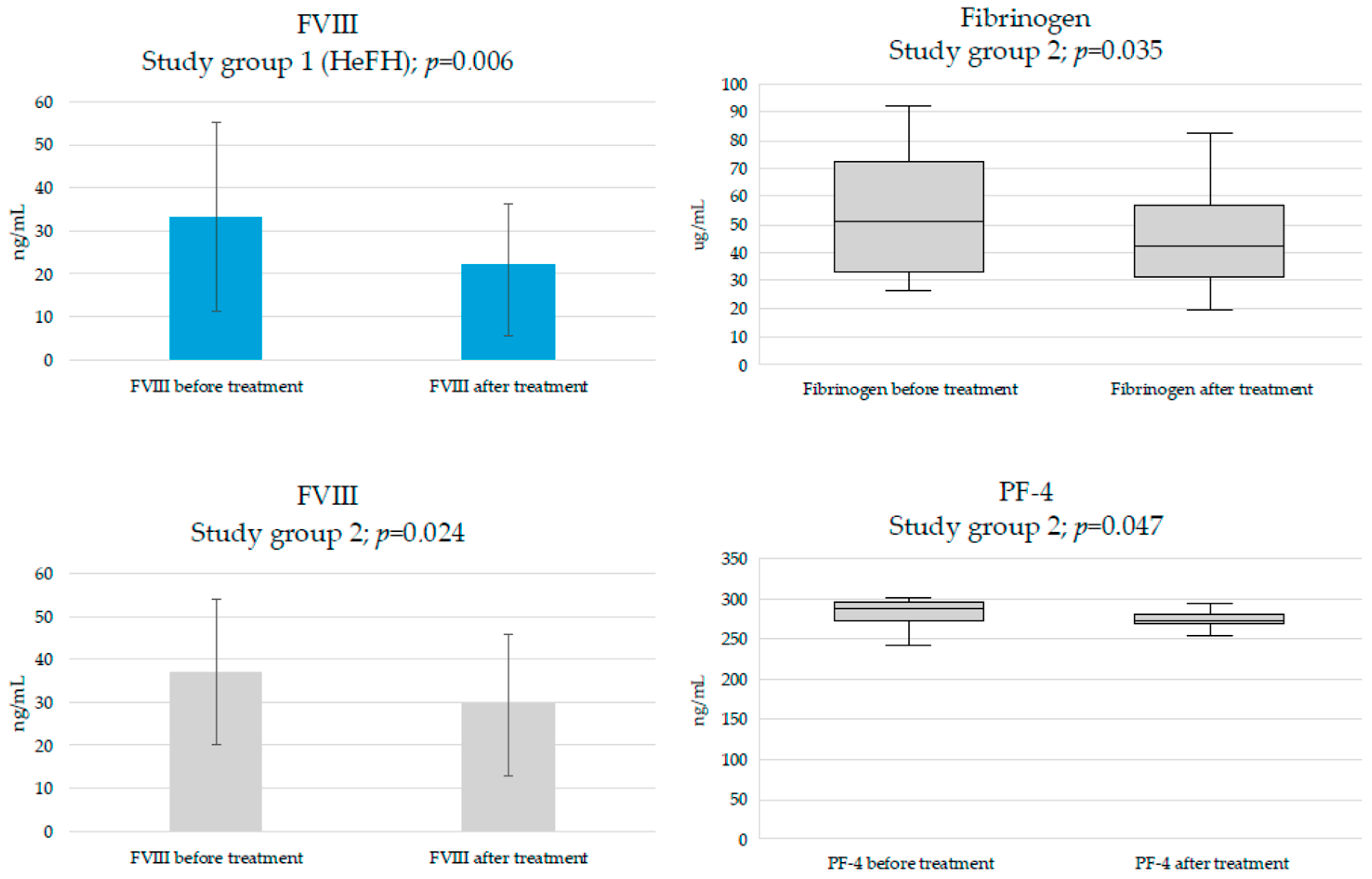
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| apoB | Apolipoprotein B |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| APTT | Activated partial thromboplatin time |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| CD36 | Cluster of differentiation 36 |
| CD40L | Cluster of differentiation 40 ligand |
| CD62P | P-selectin |
| CK | Creatine kinase |
| DLCN | Dutch Lipid Clinic Network |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| EGF-A | Epidermal growth factor homology domain A of LDLDR |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| GalNAc | Triantennary N-acetylgalactosamine |
| GGT | Gamma-glutamyl transferase |
| GPIIb/IIIa | Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa |
| FVIII | Coagulation factor VIII |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HDL-c | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration |
| HeFH | Heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia |
| HGB | Hemoglobin |
| IL-18 | Interleukin-18 |
| INR | International normalized ratio |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDL-c | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration |
| LDLR | Receptor for LDLC |
| LRP-1 | LDL-related protein-1 |
| MPV | Mean platelet volume |
| M-W | Mann–Whitney test |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide |
| NYHA | New York Heart Association |
| oxLDL | Oxidized LDL |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| PCSK9 | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 |
| PCSK9i | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor |
| PCSK9 mabs | Monoclonal antibodies against PCSK9 |
| PF-4 | Platelet factor-4 |
| PLT | Platelet count |
| RBC | Red blood cell count |
| RCTs | Randomized controlled trials |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| sCD62P | Soluble P-selectin |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| SMC | Smooth muscle cells |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TF | Tissue factor |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| TSH | Thyroid-stimulating hormone |
| WBC | White blood cell count |
References
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Aparicio, H.J.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2021 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e254–e743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, W.; Lacey, B.; Sherliker, P.; Armitage, J.; Lewington, S. Epidemiology of Atherosclerosis and the Potential to Reduce the Global Burden of Atherothrombotic Disease. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Buring, J.E.; Badimon, L.; Hansson, G.K.; Deanfield, J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Tokgözoğlu, L.; Lewis, E.F. Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badimon, L.; Vilahur, G. Thrombosis formation on atherosclerotic lesions and plaque rupture. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freynhofer, M.K.; Bruno, V.; Wojta, J.; Huber, K. The Role of Platelets in Athero-Thrombotic Events. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 5197–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, A.; Libby, P.; Mitomo, S.; Yuki, H.; Araki, M.; Seegers, L.M.; McNulty, I.; Lee, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. Biomarkers associated with coronary high-risk plaques. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2022, 54, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzo, G.; Gentile, M.; Bresciani, A.; Mallardo, V.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Merone, P.; Cuomo, G.; Pacileo, M.; Sarullo, F.M.; Venturini, E.; et al. Inhibitors of Protein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9 (PCSK9) and Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS): The State-of-the-Art. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbel, P.A.; Navarese, E.P.; Tantry, U.S. Exploration of PCSK9 as a Cardiovascular Risk Factor: Is There a Link to the Platelet? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, M.P.; Dehkordi, S.H.H.; Moriarty, P.M.; Duell, P.B. Diagnosis and Treatment of Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2019, 8, e013225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokgozoglu, L.; Kayikcioglu, M. Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Global Burden and Approaches. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijgen, R.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Meijers, J.C.M. Increased coagulation factor VIII activity in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Blood 2011, 118, 6990–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadraersada, J.; Alva-Gallegos, R.; Skořepa, P.; Musil, F.; Mrštná, K.; Javorská, L.; Matoušová, K.; Krčmová, L.K.; Paclíková, M.; Carazo, A.; et al. Coagulation in familial hypercholesterolemic patients: Effect of current hypolipidemic treatment and anticoagulants. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 7343–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icli, A.; Aksoy, F.; Nar, G.; Kaymaz, H.; Alpay, M.F.; Nar, R.; Guclu, A.; Arslan, A.; Dogan, A. Increased Mean Platelet Volume in Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Angiology 2015, 67, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, A.; Narverud, I.; Øyri, L.K.L.; Bogsrud, M.P.; Aagnes, I.; Ueland, T.; Mulder, M.; Leijten, F.; Langslet, G.; Wium, C.; et al. Subjects with familial hypercholesterolemia have lower aortic valve area and higher levels of inflammatory biomarkers. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2021, 15, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhindsa, D.S.; Sandesara, P.B.; Shapiro, M.D.; Wong, N.D. The Evolving Understanding and Approach to Residual Cardiovascular Risk Management. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummelgaard, S.; Vilstrup, J.P.; Gustafsen, C.; Glerup, S.; Weyer, K. Targeting PCSK9 to tackle cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 249, 108480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebitus, C.; Steiner, B.; Veeman, M. The roles of human values and generalized trust on stated preferences when food is labeled with environmental footprints: Insights from Germany. Food Policy 2015, 52, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, C.P.; Blazing, M.A.; Giugliano, R.P.; McCagg, A.; White, J.A.; Théroux, P.; Darius, H.; Lewis, B.S.; Ophuis, T.O.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Ezetimibe Added to Statin Therapy after Acute Coronary Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2387–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.; Reith, C.; Emberson, J.; Armitage, J.; Baigent, C.; Blackwell, L.; Blumenthal, R.; Danesh, J.; Smith, G.D.; DeMets, D.; et al. Interpretation of the evidence for the efficacy and safety of statin therapy. Lancet 2016, 388, 2532–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.A.; Liao, J.K. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of statin pleiotropic effects. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 1529–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kounatidis, D.; Tentolouris, N.; Vallianou, N.G.; Mourouzis, I.; Karampela, I.; Stratigou, T.; Rebelos, E.; Kouveletsou, M.; Stamatopoulos, V.; Tsaroucha, E.; et al. The Pleiotropic Effects of Lipid-Modifying Interventions: Exploring Traditional and Emerging Hypolipidemic Therapies. Metabolites 2024, 14, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raschi, E.; Casula, M.; Cicero, A.F.; Corsini, A.; Borghi, C.; Catapano, A. Beyond statins: New pharmacological targets to decrease LDL-cholesterol and cardiovascular events. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 250, 108507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.G.; Farnier, M.; Krempf, M.; Bergeron, J.; Luc, G.; Averna, M.; Stroes, E.S.; Langslet, G.; Raal, F.J.; El Shahawy, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Alirocumab in Reducing Lipids and Cardiovascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Keech, A.C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S.D.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Evolocumab and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lei, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, X. Effectiveness and safety of Inclisiran in hyperlipidemia treatment: An overview of systematic reviews. Medicine 2023, 102, e32728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk: The Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dec, A.; Niemiec, A.; Wojciechowska, E.; Maligłówka, M.; Bułdak, Ł.; Bołdys, A.; Okopień, B. Inclisiran—A Revolutionary Addition to a Cholesterol-Lowering Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, J.S.; A Kruip, M.J.H.; van der Meer, F.J.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Leebeek, F.W.G.; Cannegieter, S.C.; Lijfering, W.M. Rosuvastatin use improves measures of coagulation in patients with venous thrombosis. Eur. Hear. J. 2018, 39, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maligłówka, M.; Dec, A.; Bułdak, Ł.; Okopień, B. The Effects of Inclisiran on the Subclinical Inflammatory Markers of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Ji, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y. Risk factors for progression to type 2 diabetes in prediabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrints, C.; Andreotti, F.; Koskinas, K.C.; Rossello, X.; Adamo, M.; Ainslie, J.; Banning, A.P.; Budaj, A.; Buechel, R.R.; Chiariello, G.A.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Hear. J. 2024, 45, 3415–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raal, F.J.; Kallend, D.; Ray, K.K.; Turner, T.; Koenig, W.; Wright, R.S.; Wijngaard, P.L.; Curcio, D.; Jaros, M.J.; Leiter, L.A.; et al. Inclisiran for the Treatment of Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.K.; Wright, R.S.; Kallend, D.; Koenig, W.; Leiter, L.A.; Raal, F.J.; Bisch, J.A.; Richardson, T.; Jaros, M.; Wijngaard, P.L.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Inclisiran in Patients with Elevated LDL Cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidah, N.G.; Benjannet, S.; Wickham, L.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Jasmin, S.B.; Stifani, S.; Basak, A.; Prat, A.; Chrétien, M. The secretory proprotein convertase neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1 (NARC-1): Liver regeneration and neuronal differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, P.; van de Sluis, B.; Dullaart, R.P.; Born, J.v.D. Novel aspects of PCSK9 and lipoprotein receptors in renal disease-related dyslipidemia. Cell. Signal. 2019, 55, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maligłówka, M.; Kosowski, M.; Hachuła, M.; Cyrnek, M.; Bułdak, Ł.; Basiak, M.; Bołdys, A.; Machnik, G.; Bułdak, R.J.; Okopień, B. Insight into the Evolving Role of PCSK9. Metabolites 2022, 12, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccini, M.; Landmesser, U.; Rauch, U. Pleiotropic Effects of PCSK9: Focus on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, C.; Ruscica, M.; Camera, M.; Rossetti, L.; Macchi, C.; Colciago, A.; Zanotti, I.; Lupo, M.G.; Adorni, M.P.; Cicero, A.F.G.; et al. PCSK9 induces a pro-inflammatory response in macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Fan, Y.; Shahanawaz, J.; Reis, R.J.S.; Varughese, K.I.; Sawamura, T.; Mehta, J.L. Cross-talk between LOX-1 and PCSK9 in vascular tissues. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 107, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delluc, A.; Malécot, J.-M.; Kerspern, H.; Nowak, E.; Carre, J.-L.; Mottier, D.; Le Gal, G.; Lacut, K. Lipid parameters, lipid lowering drugs and the risk of venous thromboembolism. Atherosclerosis 2012, 220, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, C.; Kleiman, K.; Meng, H.; Knight, J.S.; Eitzman, D.T. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) Deficiency is Protective Against Venous Thrombosis in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.-G.; Xu, R.-X.; Li, S.; Guo, Y.-L.; Sun, J.; Li, J.-J. Relation of circulating PCSK9 concentration to fibrinogen in patients with stable coronary artery disease. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2014, 8, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, M.-M.; Liu, H.-H.; Guo, Y.-L.; Wu, N.-Q.; Dong, Q.; Qian, J.; Dou, K.-F.; Zhu, C.-G.; Li, J.-J. Association of circulating proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 concentration, prothrombin time and cardiovascular outcomes: A prospective cohort study. Thromb. J. 2021, 19, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.A.; Oleaga, C.; Eren, M.; Amaral, A.P.; Shang, M.; Lux, E.; Khan, S.S.; Shah, S.J.; Omura, Y.; Pamir, N.; et al. Role of PAI-1 in hepatic steatosis and dyslipidemia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarese, E.P.; Kolodziejczak, M.; Winter, M.-P.; Alimohammadi, A.; Lang, I.M.; Buffon, A.; Lip, G.Y.; Siller-Matula, J.M. Association of PCSK9 with platelet reactivity in patients with acute coronary syndrome treated with prasugrel or ticagrelor: The PCSK9-REACT study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 227, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camera, M.; Rossetti, L.; Barbieri, S.S.; Zanotti, I.; Canciani, B.; Trabattoni, D.; Ruscica, M.; Tremoli, E.; Ferri, N. PCSK9 as a Positive Modulator of Platelet Activation. JACC 2018, 71, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, X.; Jia, D.; Yao, Z.; Chang, L.; Pan, G.; Zhong, H.; et al. PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9) Enhances Platelet Activation, Thrombosis, and Myocardial Infarct Expansion by Binding to Platelet CD36. Circulation 2021, 143, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puteri, M.U.; Azmi, N.U.; Ridwan, S.; Iqbal, M.; Fatimah, T.; Rini, T.D.P.; Kato, M.; Saputri, F.C. Recent Update on PCSK9 and Platelet Activation Experimental Research Methods: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puteri, M.U.; Azmi, N.U.; Kato, M.; Saputri, F.C. PCSK9 Promotes Cardiovascular Diseases: Recent Evidence about Its Association with Platelet Activation-Induced Myocardial Infarction. Life 2022, 12, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barale, C.; Melchionda, E.; Morotti, A.; Russo, I. PCSK9 Biology and Its Role in Atherothrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphuisen, P.W.; Eikenboom, J.C.J.; Bertina, R.M. Elevated Factor VIII Levels and the Risk of Thrombosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovenschen, N.; Mertens, K.; Hu, L.; Havekes, L.M.; van Vlijmen, B.J.M. LDL receptor cooperates with LDL receptor–related protein in regulating plasma levels of coagulation factor VIII in vivo. Blood 2005, 106, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysiak, R.; Okopień, B.; Herman, Z.S. Effects of HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors on Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Processes. Drugs 2003, 63, 1821–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciullo, F.; Petito, E.; Falcinelli, E.; Gresele, P.; Momi, S. Pleiotropic effects of PCSK9-inhibition on hemostasis: Anti-PCSK9 reduce FVIII levels by enhancing LRP1 expression. Thromb. Res. 2022, 213, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marston, N.A.; Gurmu, Y.; Melloni, G.E.M.; Bonaca, M.; Gencer, B.; Sever, P.S.; Pedersen, T.R.; Keech, A.C.; Roselli, C.; Lubitz, S.A.; et al. The Effect of PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9) Inhibition on the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism. Circulation 2020, 141, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.-G.; Guo, Y.-L.; Li, S.; Xu, R.-X.; Dong, Q.; Li, J.-J. Fibrinogen and the Severity of Coronary Atherosclerosis among Adults with and without Statin Treatment: Lipid as a mediator. Heart Lung Circ. 2016, 25, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schol-Gelok, S.; Galema-Boers, J.M.; van Gelder, T.; Kruip, M.J.; van Lennep, J.E.R.; Versmissen, J. No effect of PCSK9 inhibitors on D-dimer and fibrinogen levels in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1412–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiak, M.; Hachula, M.; Kosowski, M.; Okopien, B. Effect of PCSK9 Inhibitors on Hemostasis in Patients with Isolated Hypercholesterolemia. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.E. PAI-1 and atherothrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1879–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, G.M.; Annarapu, G.; Carmona, E.; Nawarskas, J.; Clark, R.; Novelli, E.; Alvidrez, R.I.M. Platelets in Thrombosis and Atherosclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2024, 194, 1608–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.D.; Atkinson, T.M.; Lindner, J.R. Platelets and von Willebrand factor in atherogenesis. Blood 2017, 129, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korporaal, S.J.; Akkerman, J.-W.N. Platelet Activation by Low Density Lipoprotein and High Density Lipoprotein. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2006, 35, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijper, P.H.M.; Torres, H.I.G.; Houben, L.A.M.J.; Lammers, J.-W.J.; Zwaginga, J.J.; Koenderman, L. P-selectin and MAC-1 mediate monocyte rolling and adhesion to ECM-bound platelets under flow conditions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 64, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gils, J.M.; Zwaginga, J.J.; Hordijk, P.L. Molecular and functional interactions among monocytes, platelets, and endothelial cells and their relevance for cardiovascular diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 85, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondina, M.T.; Weyrich, A.S.; Zimmerman, G.A. Platelets as Cellular Effectors of Inflammation in Vascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1506–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nording, H.M.; Seizer, P.; Langer, H.F. Platelets in Inflammation and Atherogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleissner, C.A.; von Hundelshausen, P.; Ley, K. Platelet Chemokines in Vascular Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, A.; Manka, D.; von Hundelshausen, P.; Huo, Y.; Hanrath, P.; Sarembock, I.J.; Ley, K.; Weber, C. Deposition of Platelet RANTES Triggering Monocyte Recruitment Requires P-Selectin and Is Involved in Neointima Formation After Arterial Injury. Circulation 2002, 106, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbich, C.; Dernbach, E.; Aicher, A.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. CD40 Ligand Inhibits Endothelial Cell Migration by Increasing Production of Endothelial Reactive Oxygen Species. Circulation 2002, 106, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodadi, E. Platelet Function in Cardiovascular Disease: Activation of Molecules and Activation by Molecules. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barale, C.; Bonomo, K.; Frascaroli, C.; Morotti, A.; Guerrasio, A.; Cavalot, F.; Russo, I. Platelet function and activation markers in primary hypercholesterolemia treated with anti-PCSK9 monoclonal antibody: A 12-month follow-up. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebari-Benslaiman, S.; Galicia-García, U.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Olaetxea, J.R.; Alloza, I.; Vandenbroeck, K.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K.K.; Troquay, R.P.T.; Visseren, F.L.J.; A Leiter, L.; Wright, R.S.; Vikarunnessa, S.; Talloczy, Z.; Zang, X.; Maheux, P.; Lesogor, A.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of inclisiran in patients with high cardiovascular risk and elevated LDL cholesterol (ORION-3): Results from the 4-year open-label extension of the ORION-1 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Group 1 (HeFH); n = 10 | Study Group 2; n = 14 | Statistical Test | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 54 ± 10 | 63 ± 10 | Welch’s t-test | 0.032 |
| Women, % | 80 | 35.7 | Chi-square with Yates’s correction test | 0.083 |
| Current antiplatelet therapy, % | 30 | 93 | 0.005 |
| Study Group 1 (HeFH); n = 10 | Study Group 2; n = 14 | Statistical Test | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC, K/μL | 5.9 ± 1.4 | 6.4 ± 1.1 | Welch’s t-test | 0.333 |
| RBC, M/μL | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 4.8 ± 0.6 | 0.333 | |
| HGB, g/dL | 13.7 ± 1.5 | 14.7 ± 1.4 | 0.126 | |
| PLT, K/μL | 247.6 ± 68.9 | 247.9 ± 42.4 | 0.99 | |
| MPV, fL | 10.7 ± 1 | 10.4 ± 1.2 | 0.534 | |
| TC, mg/dL | 287.6 ± 94.1 | 211.7 ± 52.7 | 0.038 | |
| LDLC, mg/dL | 180.8 ± 73.3 | 129.6 ± 46.8 | 0.072 | |
| HDLC, mg/dL | 57.5 (51.2–121.8) | 47.6 (41–59.6) | M-W | 0.064 |
| TG, mg/dL | 117.3 ± 50.8 | 144.9 ± 50.8 | Welch’s t-test | 0.206 |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 0.043 | |
| ALT, U/L | 26 ± 13.8 | 33 ± 16.9 | 0.28 | |
| AST, U/L | 24.7 (23.1–26.7) | 26 (19–31.1) | M-W | 0.886 |
| APTT, s | 30.6 (27.2–31.3) | 28 (26.3–34.5) | 0.815 | |
| INR | 0.92 (0.9–1) | 0.9 (0.9–1) | 0.76 | |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.7 (0.6–0.8) | 0.9 (0.8–1) | 0.053 | |
| CK, U/L | 152.5 (128.5–183.3) | 122.5 (66.5–166.3) | 0.187 | |
| Glucose, mg/dL | 93.9 (89–95.3) | 102 (98.5–106) | 0.009 | |
| HbA1c, % | 5.6 (5.2–5.7) | 6 (5.6–6.1) | 0.053 | |
| TSH, μIU/mL | 1.8 (1.4–2.9) | 1.5 (0.8–2.9) | 0.656 | |
| NT-proBNP, pg/mL | 95.4 (35.2–154.8) | 81 (39.48–183) | 0.721 | |
| Fibrinogen, µg/mL | 48.5 (29.1–59) | 51.4 (33.2–72.7) | 0.909 | |
| FVIII, ng/mL | 33.3 ± 22 | 37 ± 16.9 | Welch’s t-test | 0.666 |
| PAI-I, pg/mL | 848.8 (793.6–887.8) | 882.3 (829.2–924.5) | M-W | 0.689 |
| PF-4, ng/mL | 269 (258–285.5) | 286 (272–295.5) | 0.272 | |
| sP-selectin, ng/mL | 39.8 ± 13 | 47.1 ± 8.7 | Welch’s t-test | 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maligłówka, M.; Dec, A.; Bułdak, Ł.; Okopień, B. The Effects of Inclisiran on the Subclinical Prothrombotic and Platelet Activation Markers in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12090355
Maligłówka M, Dec A, Bułdak Ł, Okopień B. The Effects of Inclisiran on the Subclinical Prothrombotic and Platelet Activation Markers in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(9):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12090355
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaligłówka, Mateusz, Adrianna Dec, Łukasz Bułdak, and Bogusław Okopień. 2025. "The Effects of Inclisiran on the Subclinical Prothrombotic and Platelet Activation Markers in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 9: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12090355
APA StyleMaligłówka, M., Dec, A., Bułdak, Ł., & Okopień, B. (2025). The Effects of Inclisiran on the Subclinical Prothrombotic and Platelet Activation Markers in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(9), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12090355







