Access Site Related Vascular Complications following Percutaneous Cardiovascular Procedures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Clinical Assessment
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Procedural Characteristics of Patients with ASC
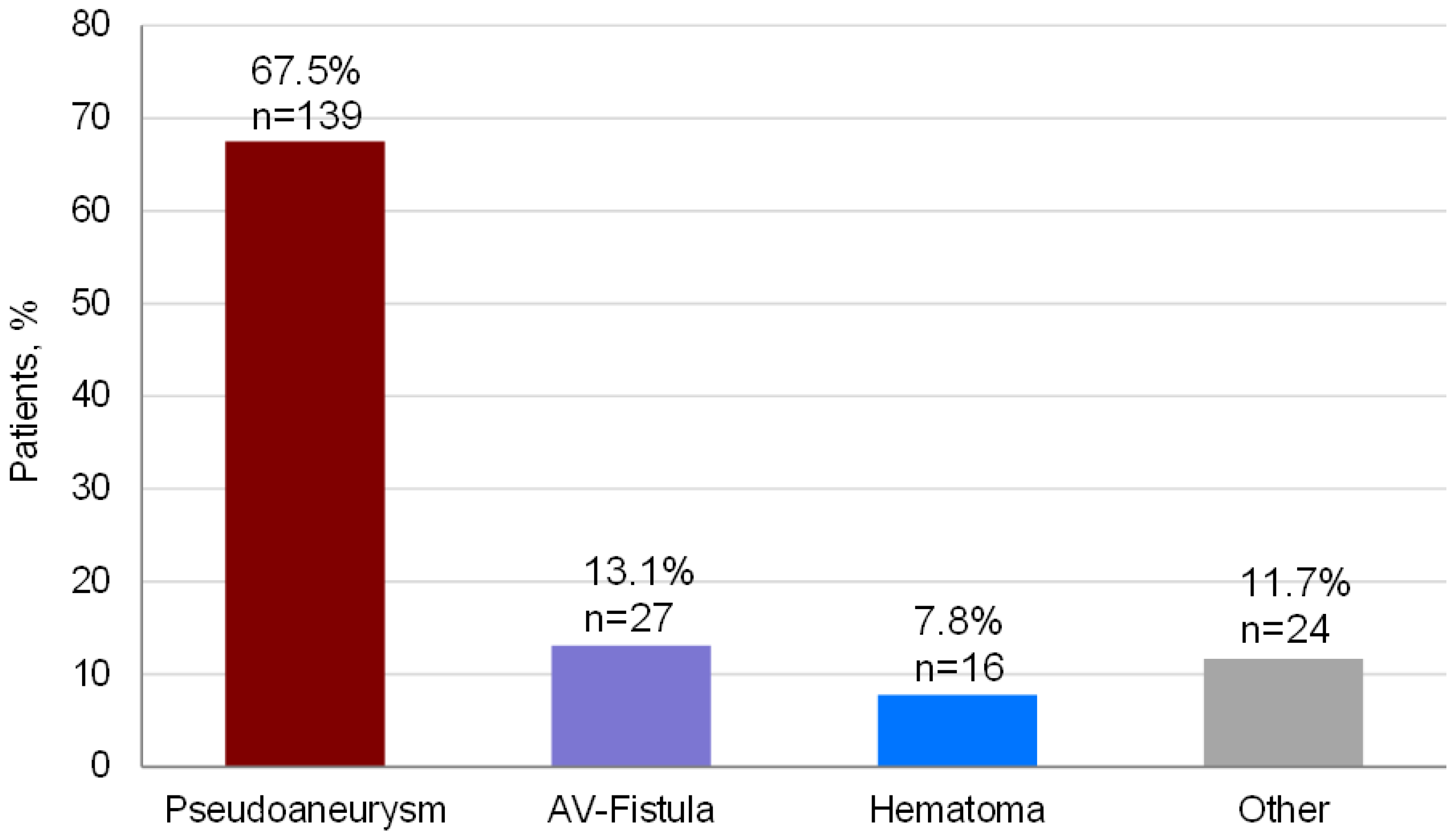
3.2. Type of Complication
3.3. Postprocedural Management of Complications
3.4. Outcome
4. Discussion
4.1. Procedure Types and Complication Rate
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goel, S.; Pasam, R.T.; Raheja, H.; Gotesman, J.; Gidwani, U.; Ahuja, K.R.; Reed, G.; Puri, R.; Khatri, J.K.; Kapadia, S.R. Left main percutaneous coronary intervention-Radial versus femoral access: A systematic analysis. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 95, E201–E213. [Google Scholar]
- Hamm, C.W.; Albrecht, A.; Bonzel, T.; Kelm, M.; Lange, H.; Schächinger, V.; Terres, W.; Voelker, W. Diagnostic heart catheterization. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2008, 97, 475–512. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnaird, T.; Anderson, R.; Gallagher, S.; Cockburn, J.; Sirker, A.; Ludman, P.; de Belder, M.; Copt, S.; Nolan, J.; Zaman, A.; et al. Vascular Access Site and Outcomes in 58,870 Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention with a Previous History of Coronary Bypass Surgery: Results From the British Cardiovascular Interventions Society National Database. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 11, 482–492. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, D.; Jahangir, A.; Singh, M.; Allaqaband, S.; Bajwa, T.K.; Mewissen, M.W. Access site complications after peripheral vascular interventions: Incidence, predictors, and outcomes. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 7, 821–828. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, W.D.; Malenka, D.J.; Ryan, T.J., Jr.; Shubrooks, S.J., Jr.; O’Connor, G.T.; Robb, J.F.; Farrell, K.L.; Corliss, M.S.; Hearne, M.J.; Kellett, M.A., Jr.; et al. Northern New England Cardiovascular Disease Study Group. Predicting vascular complications in percutaneous coronary interventions. Am. Heart J. 2003, 145, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar]
- van Kesteren, F.; van Mourik, M.S.; Vendrik, J.; Wiegerinck, E.M.A.; Henriques, J.P.S.; Koch, K.T.; Wykrzykowska, J.J.; de Winter, R.J.; Piek, J.J.; van Lienden, K.P.; et al. Incidence, Predictors, and Impact of Vascular Complications After Transfemoral Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation with the SAPIEN 3 Prosthesis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2018, 121, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Koreny, M.; Riedmüller, E.; Nikfardjam, M.; Siostrzonek, P.; Müllner, M. Arterial puncture closing devices compared with standard manual compression after cardiac catheterization: Systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2004, 291, 350–357. [Google Scholar]
- Mlekusch, W.; Haumer, M.; Mlekusch, I.; Dick, P.; Steiner-Boeker, S.; Bartok, A.; Sabeti, S.; Exner, M.; Wagner, O.; Minar, E.; et al. Prediction of iatrogenic pseudoaneurysm after percutaneous endovascular procedures. Radiology 2006, 240, 597–602. [Google Scholar]
- Etemad-Rezai, R.; Peck, D.J. Ultrasound-guided thrombin injection of femoral artery pseudoaneurysms. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2003, 54, 118–120. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatty, S.; Cooke, R.; Shetty, R.; Jovin, I.S. Femoral vascular access-site complications in the cardiac catheterization laboratory: Diagnosis and management. Interv. Cardiol. 2011, 3, 503–514. [Google Scholar]
- Schahab, N.; Kavsur, R.; Mahn, T.; Schaefer, C.; Kania, A.; Fimmers, R.; Nickenig, G.; Zimmer, S. Endovascular management of femoral access-site and access-related vascular complications following percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230535. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, P.; Al-Ani, A.; von Lueder, T.; Hoffmann, J.; Majak, P.; Hagen, O.; Loose, H.; Kløw, N.E.; Opdahl, A. Access site complications after transfemoral aortic valve implantation—a comparison of Manta and ProGlide. CVIR Endovasc. 2018, 1, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Van Mieghem, N.M.; El Faquir, N.; Rahhab, Z.; Rodríguez-Olivares, R.; Wilschut, J.; Ouhlous, M.; Galema, T.W.; Geleijnse, M.L.; Kappetein, A.P.; Schipper, M.E.; et al. Incidence and predictors of debris embolizing to the brain during transcatheter aortic valve implantation. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 8, 718–724. [Google Scholar]
- Stolt, M.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.; Herold, J. Do not underestimate the femoral pseudoaneurysm. Vasa 2018, 47, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, E.F.; Pulimi, S.; Coleman, C.; Florita, C.; Musat, D.; Tormey, D.; Fawzy, A.; Lee, S.; Herzog, E.; Coven, D.L.; et al. Increased vascular access complications in patients with renal dysfunction undergoing percutaneous coronary procedures using arteriotomy closure devices. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2010, 22, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Smilowitz, N.R.; Kirtane, A.J.; Guiry, M.; Gray, W.A.; Dolcimascolo, P.; Querijero, M.; Echeverry, C.; Kalcheva, N.; Flores, B.; Singh, V.P.; et al. Practices and complications of vascular closure devices and manual compression in patients undergoing elective transfemoral coronary procedures. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 110, 177–182. [Google Scholar]

| PCP n = 12,901 | Clinical Suspicion of ASC n = 2890 | Confirmed ASC n = 206 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coronary intervention, n (%) | 6118 (47.4) | 1277 (44.2) | 92 (1.5% of all coronary interventions) |
| Peripheral intervention, n (%) | 2474 (19.2) | 532 (18.4) | 37 (1.5% of all peripheral interventions) |
| Electrophysiological intervention, n (%) | 3843 (29.8) | 645 (22.3) | 46 (1.2% of all electrophysiological interventions) |
| TAVI/ valvular intervention, n (%) | 466 (3.6) | 436 (15.1) | 31 (6.7% of all TAVI/valvular interventions) |
| Characteristics | Total (n = 206) |
|---|---|
| Age in years, mean ± SD | 71.8 ± 12.7 |
| BMI in kg/m2, mean ± SD | 26.8 ± 5.0 |
| Male, n (%) | 119 (57.8) |
| Cardiovascular risk Factors and Comorbidities | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 44 (21.4) |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 29 (14.1) |
| Previous smoker, n (%) | 28 (13.6) |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 71 (34.5) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 139 (67.5) |
| CAD, n (%) | 104 (50.5) |
| PAD, n (%) | 47 (22.8) |
| CVD, n (%) | 14 (6.8) |
| Renal insufficiency 1, n (%) | 84 (41.8) |
| Renal replacement therapy, (%) | 5 (2.4) |
| Previous Medication | |
| Acetylsalicylic acid 100 mg, n (%) | 70 (34.0) |
| Clopidogrel, n (%) | 136 (66.0) |
| Vitamin-K-Anatgonists, n (%) | 57 (27.7) |
| Laboratory Results | |
| Creatinine in mg/dL, mean ± SD | 1.27 ± 1.16 |
| Glomerular filtration rate in mL/min/1.73 m2, mean ± SD | 64.8 ± 24.3 |
| Platelets in thousands/mL, mean ± SD | 216 ± 66 |
| International Normalized Ratio, mean ± SD | 1.47 ± 0.69 |
| Hemoglobin in g/dL, mean ± SD | 12.9 ± 1.9 |
| Procedural Characteristics | Total (n = 206) |
|---|---|
| Puncture site | |
| Left, n (%) | 63 (30.6) |
| Right, n (%) | 143 (69.4) |
| Punctured vessel | |
| Common femoral artery, n (%) | 137 (66.5) |
| Common femoral vein, n (%) | 40 (19.4) |
| Superficial femoral artery, n (%) | 22 (10.7) |
| Deep femoral artery, n (%) | 2 (1.0) |
| Indication n (%) | |
| Elective, n (%) | 182 (88.3) |
| Urgent, n (%) | 24 (11.7) |
| Sheath size in French, mean ± SD | 6.9 ± 3.1 |
| Vascular closure devices 1, n (%) | 117 (57.9) |
| Angio-Seal®, n (%) | 46 (39.3) # |
| FemoSealTM, n (%) | 22 (18.8) # |
| StarCloseTM, n (%) | 17 (14.5) # |
| Exoseal®, n (%) | 15 (12.8) # |
| ProstarTM, n (%) | 15 (12.8) # |
| Examination duration in min, mean ± SD | 82 ± 59 |
| Fluoroscopy time in seconds, mean ± SD | 873 ± 77 |
| Radiation dose in Gy, mean ± SD | 4248 ± 4657 |
| Contrast medium in mL, mean ± SD | 108 ± 82 |
| Hospital length of stay in days, mean ± SD | 10 ± 9 |
| Hemoglobin in g/dL, mean ± SD | 12.9 ± 1.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hetrodt, J.; Engelbertz, C.; Gebauer, K.; Stella, J.; Meyborg, M.; Freisinger, E.; Reinecke, H.; Malyar, N. Access Site Related Vascular Complications following Percutaneous Cardiovascular Procedures. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2021, 8, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8110136
Hetrodt J, Engelbertz C, Gebauer K, Stella J, Meyborg M, Freisinger E, Reinecke H, Malyar N. Access Site Related Vascular Complications following Percutaneous Cardiovascular Procedures. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2021; 8(11):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8110136
Chicago/Turabian StyleHetrodt, Johanna, Christiane Engelbertz, Katrin Gebauer, Jacqueline Stella, Matthias Meyborg, Eva Freisinger, Holger Reinecke, and Nasser Malyar. 2021. "Access Site Related Vascular Complications following Percutaneous Cardiovascular Procedures" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 8, no. 11: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8110136
APA StyleHetrodt, J., Engelbertz, C., Gebauer, K., Stella, J., Meyborg, M., Freisinger, E., Reinecke, H., & Malyar, N. (2021). Access Site Related Vascular Complications following Percutaneous Cardiovascular Procedures. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 8(11), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8110136






