Cognitive Impairment in Acute Heart Failure: Narrative Review
Abstract
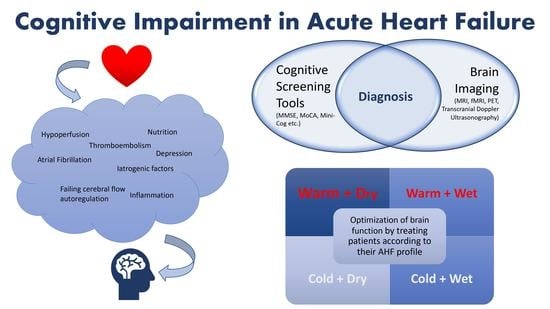
:1. Introduction
2. Cognitive Screening Tools
3. Epidemiology
4. Pathophysiology
5. Trajectory of CI over the Time Course of HF
6. Role of Brain Imaging Modalities
7. Therapeutic Strategy
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bueno, H.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Falk, V.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Harjola, V.P.; Jankowska, E.A.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2129–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmani, S.; Squire, I. Acute Heart Failure: Definition, Classification and Epidemiology. Curr. Hear. Fail. Rep. 2017, 14, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arrigo, M.; Jessup, M.; Mullens, W.; Reza, N.; Shah, A.M.; Sliwa, K.; Mebazaa, A. Acute heart failure. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnenberg, L.; Givertz, M.M. Acute heart failure. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 30, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alla, F.; Zannad, F.; Filippatos, G. Epidemiology of acute heart failure syndromes. Hear. Fail. Rev. 2007, 12, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Albert, N.M.; Allen, L.A.; Bluemke, D.A.; Butler, J.; Fonarow, G.C.; Ikonomidis, J.S.; Khavjou, O.; Konstam, M.A.; Maddox, T.M.; et al. Forecasting the impact of heart failure in the United States: A policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weintraub, N.L.; Collins, S.P.; Pang, P.S.; Levy, P.D.; Anderson, A.S.; Arslanian-Engoren, C.; Gibler, W.B.; McCord, J.K.; Parshall, M.B.; Francis, G.S.; et al. Acute heart failure syndromes: Emergency department presentation, treatment, and disposition: Current approaches and future aims: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 122, 1975–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ambrosy, A.P.; Fonarow, G.C.; Butler, J.; Chioncel, O.; Greene, S.J.; Vaduganathan, M.; Nodari, S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Sato, N.; Shah, A.N.; et al. The global health and economic burden of hospitalizations for heart failure: Lessons learned from hospitalized heart failure registries. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjola, V.-P.; Mullens, W.; Banaszewski, M.; Bauersachs, J.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Chioncel, O.; Collins, S.P.; Doehner, W.; Filippatos, G.S.; Flammer, A.J.; et al. Organ dysfunction, injury and failure in acute heart failure: From pathophysiology to diagnosis and management. A review on behalf of the Acute Heart Failure Committee of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherbakov, N.; Doehner, W. Heart–brain Interactions in Heart Failure. Card. Fail. Rev. 2018, 4, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havakuk, O.; King, K.; Grazette, L.; Yoon, A.J.; Fong, M.; Bregman, N.; Elkayam, U.; Kloner, R.A. Heart Failure-Induced Brain Injury. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardiogenic Dementia. Lancet 1977, 1, 27–28. [CrossRef]
- Alagiakrishnan, K.; Mah, D.; Ahmed, A.; Ezekowitz, J. Cognitive decline in heart failure. Hear. Fail. Rev. 2016, 21, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C. Mild Cognitive Impairment and Mild Dementia: A Clinical Perspective. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uthamalingam, S.; Gurm, G.S.; Daley, M.; Flynn, J.; Capodilupo, R. Usefulness of Acute Delirium as a Predictor of Adverse Outcomes in Patients >65 Years of Age with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 108, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, L.A.; Kilian, S.; Firek, A.; Kashner, T.M.; Firek, C.J.; Silvet, H. Cognitive impairment and medication adherence in outpatients with heart failure. Hear. Lung 2012, 41, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alosco, M.L.; Spitznagel, M.B.; van Dulmen, M.; Raz, N.; Cohen, R.; Sweet, L.H.; Colbert, L.H.; Josephson, R.; Hughes, J.; Rosneck, J.; et al. Cognitive Function and Treatment Adherence in Older Adults With Heart Failure. Psychosom. Med. 2012, 74, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Currie, K.; Rideout, A.; Lindsay, G.; Harkness, K. The Association Between Mild Cognitive Impairment and Self-care in Adults With Chronic Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2015, 30, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cameron, J.; Worrall-Carter, L.; Page, K.; Riegel, B.; Lo, S.K.; Stewart, S. Does cognitive impairment predict poor self-care in patients with heart failure? Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2010, 12, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harkness, K.; Heckman, G.; Akhtar-Danesh, N.; Demers, C.; Gunn, E.; McKelvie, R.S. Cognitive function and self-care management in older patients with heart failure. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2014, 13, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjelm, C.M.; Broström, A.; Riegel, B.; Årestedt, K.; Strömberg, A. The association between cognitive function and self-care in patients with chronic heart failure. Hear. Lung 2015, 44, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.P.; Kinugawa, K.; Nakayama, E.; Tsuji, T.; Kumagai, Y.; Imamura, T.; Maki, H.; Shiga, T.; Hatano, M.; Yao, A.; et al. Insufficient Self-Care Is an Independent Risk Factor for Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Japanese Patients With Heart Failure. Int. Hear. J. 2013, 54, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelow, J.M.; Mudd, J.O.; Chien, C.V.; Lee, C.S. Usefulness of Cognitive Dysfunction in Heart Failure to Predict Cardiovascular Risk at 180 Days. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuccalà, G.; Pedone, C.; Cesari, M.; Onder, G.; Pahor, M.; Marzetti, E.; Monaco, R.L.; Cocchi, A.; Carbonin, P.; Bernabei, R. The effects of cognitive impairment on mortality among hospitalized patients with heart failure. Am. J. Med. 2003, 115, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.K.; Davidson, K.W.; Krist, A.H.; Barry, M.J.; Cabana, M.; Caughey, A.B.; Doubeni, C.A.; Epling, J.W., Jr.; Kubik, M.; Landefeld, C.S.; et al. Screening for Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2020, 323, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leto, L.; Feola, M. Cognitive impairment in heart failure patients. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2014, 11, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardiotis, E.; Giamouzis, G.; Mastrogiannis, D.; Vogiatzi, C.; Skoularigis, J.; Triposkiadis, F.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M. Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.K.; Allen, J.K. Identifying cognitive impairment in heart failure: A review of screening measures. Hear. Lung 2013, 42, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, L.C.; Johnson, J.K.; Pozehl, B.J. Cognition in heart failure: An overview of the concepts and their measures. J. Am. Acad. Nurse Pract. 2011, 23, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, R.C.; Lopez, O.; Armstrong, M.J.; Getchius, T.S.; Ganguli, M.; Gloss, D.; Gronseth, G.S.; Marson, D.; Pringsheim, T.; Day, G.S.; et al. Practice guideline update summary: Mild cognitive impairment: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2018, 90, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohani, Z.N.; Samaan, Z. Does depression impact cognitive impairment in patients with heart failure? Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 524325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, J.C.; Moore, T.M.; Stein, D.J.; Pretorius, A.; Zingela, Z.; Nagdee, M.; Ngqengelele, L.; Campbell, M.; Sibeko, G.; King, M.C.; et al. Adaptation and validation of a computerized neurocognitive battery in the Xhosa of South Africa. Neuropsychology 2021, 35, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devenney, E.; Hodges, J.R. The Mini-Mental State Examination: Pitfalls and limitations. Pract. Neurol. 2017, 17, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athilingam, P.; King, K.B.; Burgin, S.W.; Ackerman, M.; Cushman, L.A.; Chen, L. Montreal Cognitive Assessment and Mini-Mental Status Examination compared as cognitive screening tools in heart failure. Hear. Lung 2011, 40, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, J.; Kure, C.E.; Pressler, S.J.; Ski, C.F.; Clark, A.M.; Thompson, D.R. Diagnostic Accuracy of Cognitive Screening Instruments in Heart Failure: A Systematic Review. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2016, 31, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, J.; Gallagher, R.; Pressler, S.J. Detecting and Managing Cognitive Impairment to Improve Engagement in Heart Failure Self-Care. Curr. Hear. Fail. Rep. 2017, 14, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Parikh, R.; Howell, E.H.; Hsich, E.; Landers, S.H.; Gorodeski, E.Z. Mini-cog performance: Novel marker of post discharge risk among patients hospitalized for heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2015, 8, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borson, S.; Scanlan, J.; Brush, M.; Vitaliano, P.; Dokmak, A. The mini-cog: A cognitive ‘vital signs’ measure for dementia screening in multi-lingual elderly. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2000, 15, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.; Nyenhuis, D.; Black, S.E.; Law, L.S.; Lo, E.S.; Kwan, P.W.; Au, L.; Chan, A.Y.; Wong, L.K.; Nasreddine, Z.; et al. Montreal Cognitive Assessment 5-Minute Protocol Is a Brief, Valid, Reliable, and Feasible Cognitive Screen for Telephone Administration. Stroke 2015, 46, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cameron, J.D.; Gallagher, R.; Pressler, S.J.; McLennan, S.N.; Ski, C.F.; Tofler, G.; Thompson, D.R. Sensitivity and Specificity of a Five-Minute Cognitive Screening Test in Patients With Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2016, 22, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.C.; LeResche, L.; Niaz, U.; Von Korff, M.R.; Folstein, M.F. Limits of the ‘Mini-Mental State’ as a screening test for dementia and delirium among hospital patients. Psychol. Med. 1982, 12, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’connor, D.W.; Pollitt, P.A.; Hyde, J.B.; Fellows, J.L.; Miller, N.D.; Brook, C.P.B.; Reiss, B.B. The reliability and validity of the Mini-Mental State in a British community survey. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1989, 23, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayne, C. The mini-mental state examination, will we be using it in 2001? Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 1998, 13, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naugle, R.I.; Kawczak, K. Limitations of the Mini-Mental State Examination. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 1989, 56, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.J. A meta-analysis of the accuracy of the mini-mental state examination in the detection of dementia and mild cognitive impairment. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2009, 43, 411–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M. Mini-mental and son. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 1998, 13, 290–294. [Google Scholar]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A Brief Screening Tool For Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, Z.; Rajji, T.K.; Shulman, K.I. Brief cognitive screening instruments: An update. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2010, 25, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.; Mathias, J.; Brennan, L.; Stewart, S. Validity of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) as a Screening Test for Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) in a Cardiovascular Population. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2011, 24, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coen, R.F.; Cahill, R.; Lawlor, B.A. Things to watch out for when using the Montreal cognitive assessment (MoCA). Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2011, 26, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, J.; Worrall-Carter, L.; Page, K.N.; Stewart, S.; Ski, C. Screening for mild cognitive impairment in patients with heart failure: Montreal Cognitive Assessment versus Mini Mental State Exam. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2013, 12, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, M.A.; Gathright, E.C.; Gunstad, J.; Dolansky, M.A.; Redle, J.D.; Josephson, R.; Moore, S.M.; Hughes, J.W. The MoCA and MMSE as screeners for cognitive impairment in a heart failure population: A study with comprehensive neuropsychological testing. Hear. Lung 2014, 43, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindenfeld, J.; Albert, N.M.; Boehmer, J.P.; Collins, S.P.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Givertz, M.M.; Katz, S.D.; Klapholz, M.; Moser, D.K.; Rogers, J.G.; et al. HFSA 2010 Comprehensive Heart Failure Practice Guideline. J. Card. Fail. 2010, 16, e1–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, O.P.; Tamai, S. Congestive heart failure and cognitive functioning amongst older adults. Arq. De Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2001, 59, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccalà, G.; Marzetti, E.; Cesari, M.; Monaco, M.R.L.; Antonica, L.; Cocchi, A.; Carbonin, P.; Bernabei, R. Correlates of cognitive impairment among patients with heart failure: Results of a multicenter survey. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debette, S.; Bauters, C.; Leys, D.; Lamblin, N.; Pasquier, F.; de Groote, P. Prevalence and Determinants of Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Heart Failure Patients. Congest. Hear. Fail. 2007, 13, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, J.A.; Truong, T.-T.N.; Towle, V.R.; Kerins, G.; Chaudhry, S.I. Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults with Heart Failure: Prevalence, Documentation, and Impact on Outcomes. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huynh, Q.; Negishi, K.; Blizzard, L.; Saito, M.; De Pasquale, C.; Hare, J.L.; Leung, D.; Stanton, T.; Sanderson, K.; Venn, A.J.; et al. Mild cognitive impairment predicts death and readmission within 30 days of discharge for heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 221, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, M.R.; Safford, M.M.; Goggins, K.; Nwosu, S.K.; Schildcrout, J.S.; A Wallston, K.; Mixon, A.S.; Rothman, R.L.; Kripalani, S. Numeracy, Health Literacy, Cognition, and 30-Day Readmissions among Patients with Heart Failure. J. Hosp. Med. 2018, 13, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, K.S.; Kazim, R.; Xu, J.; Borson, S.; Taffet, G.E. Unrecognized Cognitive Impairment and Its Effect on Heart Failure Readmissions of Elderly Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2016, 64, 2296–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajduk, A.M.; Lemon, S.C.; McManus, D.D.; Lessard, D.M.; Gurwitz, J.H.; A Spencer, F.; Goldberg, R.J.; Saczynski, J.S. Cognitive impairment and self-care in heart failure. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 5, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levin, S.N.; Hajduk, A.M.; McManus, D.D.; Darling, C.E.; Gurwitz, J.H.; Spencer, F.A.; Goldberg, R.J.; Saczynski, J.S. Cognitive status in patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure. Am. Hear. J. 2014, 168, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holm, H.; Bachus, E.; Jujic, A.; Nilsson, E.D.; Wadström, B.; Molvin, J.; Minthon, L.; Fedorowski, A.; Nägga, K.; Magnusson, M. Cognitive test results are associated with mortality and rehospitalization in heart failure: Swedish prospective cohort study. ESC Hear. Fail. 2020, 7, 2948–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruñén, J.M.G.; Echeverria, M.P.; Díez-Manglano, J.; Manzano, L.; Trullàs, J.C.; Requena, J.M.R.; Bautista, M.P.S.; Franco, Á.G.; Rodrigo, J.M.C.; Montero-Pérez-Barquero, M.; et al. Cognitive impairment in patients hospitalized for congestive heart failure: Data from the RICA Registry. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastva, A.M.; Hugenschmidt, C.E.; Kitzman, D.W.; Nelson, M.B.; Brenes, G.A.; Reeves, G.R.; Mentz, R.J.; Whellan, D.J.; Chen, H.; Duncan, P.W. Cognition, Physical Function, and Quality of Life in Older Patients With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2021, 27, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, O.B.; Strandgaard, S.; Edvinsson, L. Cerebral autoregulation. Cerebrovasc. Brain Metab. Rev. 1990, 2, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vavilala, M.S.; A Lee, L.; Lam, A.M. Cerebral blood flow and vascular physiology. Anesthesiol. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 20, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sila, C.A. Cognitive impairment in chronic heart failure. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2007, 74, S132–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, D.; Sievert, M.; Cencetti, S.; Uhlmann, F.; Krivokuca, M.; Zierz, S.; Werdan, K. Cerebrovascular reactivity is impaired in patients with cardiac failure. Eur. Hear. J. 2000, 21, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraser, K.S.; Heckman, G.A.; McKelvie, R.S.; Harkness, K.; Middleton, L.E.; Hughson, R.L. Cerebral hypoperfusion is exaggerated with an upright posture in heart failure: Impact of depressed cardiac output. JACC Heart Fail. 2015, 3, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loncar, G.; Bozic, B.; Lepić, T.; Dimkovic, S.; Prodanovic, N.; Radojicic, Z.; Cvorovic, V.; Markovic, N.; Brajović, M.; Despotovic, N.; et al. Relationship of reduced cerebral blood flow and heart failure severity in elderly males. Aging Male 2011, 14, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-R.; Kim, J.S.; Yang, Y.J.; Park, K.-M.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, Y.-H.; Hong, M.-K.; Song, J.-K.; Park, S.-W.; Park, S.-J.; et al. Factors Associated With Decreased Cerebral Blood Flow in Congestive Heart Failure Secondary to Idiopathic Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghiade, M.; Abraham, W.T.; Albert, N.M.; Greenberg, B.H.; O’Connor, C.M.; She, L.; Stough, W.G.; Yancy, C.W.; Young, J.B.; Fonarow, G.C.; et al. Systolic Blood Pressure at Admission, Clinical Characteristics, and Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized With Acute Heart Failure. JAMA 2006, 296, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuccala, G.; Onder, G.; Pedone, C.; Carosella, L.; Pahor, M.; Bernabei, R.; Cocchi, A. Hypotension and cognitive impairment: Selective association in patients with heart failure. Neurology 2001, 57, 1986–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoth, K.F.; Poppas, A.; Moser, D.J.; Paul, R.H.; Cohen, R.A. Cardiac Dysfunction and Cognition in Older Adults With Heart Failure. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 2008, 21, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, R.F.; Grega, M.A.; Bailey, M.M.; Zeger, S.L.; Baumgartner, W.A.; McKhann, G.M.; Selnes, O.A. Association between hypotension, low ejection fraction and cognitive performance in cardiac patients. Behav. Neurol. 2010, 22, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, R.A.; Starling, R.C.; Myerowitz, P.D.; Haas, G.J. Neuropsychological function in patients with end-stage heart failure before and after cardiac transplantation. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1995, 91, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, D.D.; Kubo, S.H.; Ormaza, S.; Francis, G.S.; Bank, A.J.; Shumway, S.J. Memory improvement following cardiac transplantation. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 1997, 19, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bommel, R.J.; Marsan, N.A.; Koppen, H.; Delgado, V.; Borleffs, C.J.; Ypenburg, C.; Bertini, M.; Schalij, M.J.; Bax, J.J. Effect of cardiac resynchronization therapy on cerebral blood flow. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 106, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, N.K.; Vazquez, L.D.; Cross, N.J.; Kuhl, E.A.; Serber, E.R.; Kovacs, A.; Dede, D.E.; Conti, J.B.; Sears, S.F. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy: A Pilot Study Examining Cognitive Change in Patients Before and After Treatment. Clin. Cardiol. 2010, 33, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, A.L.; Poppas, A.; Paul, R.H.; Cohen, R.A. Systemic hypoperfusion is associated with executive dysfunction in geriatric cardiac patients. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajagopalan, B.; Raine, A.E.; Cooper, R.; Ledingham, J.G. Changes in cerebral blood flow in patients with severe congestive cardiac failure before and after captopril treatment. Am. J. Med. 1984, 76, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruhn, N.; Larsen, F.S.; Boesgaard, S.; Knudsen, G.M.; Mortensen, S.A.; Thomsen, G.; Aldershvile, J. Cerebral Blood Flow in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure Before and After Heart Transplantation. Stroke 2001, 32, 2530–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alosco, M.L.; Brickman, A.M.; Spitznagel, M.B.; Garcia, S.L.; Narkhede, A.; Griffith, E.Y.; Raz, N.; Cohen, R.; Sweet, L.H.; Colbert, L.H.; et al. Cerebral perfusion is associated with white matter hyperintensities in older adults with heart failure. Congest. Hear. Fail. 2013, 19, E29–E34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madhavan, M.; Graff-Radford, J.; Piccini, J.P.; Gersh, B.J. Cognitive dysfunction in atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Torre, J.C. Hemodynamic Instability in Heart Failure Intensifies Age-Dependent Cognitive Decline. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 76, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alosco, M.L.; Brickman, A.M.; Spitznagel, M.B.; van Dulmen, M.; Raz, N.; Cohen, R.; Sweet, L.H.; Colbert, L.H.; Josephson, R.; Hughes, J.; et al. The independent association of hypertension with cognitive function among older adults with heart failure. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 323, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tchistiakova, E.; Anderson, N.; Greenwood, C.E.; MacIntosh, B. Combined effects of type 2 diabetes and hypertension associated with cortical thinning and impaired cerebrovascular reactivity relative to hypertension alone in older adults. NeuroImage Clin. 2014, 5, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strachan, M.W.J.; Deary, I.J.; E Ewing, F.M.; Frier, B.M. Is Type II Diabetes Associated With an Increased Risk of Cognitive Dysfunction?: A critical review of published studies. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.W.; Serebrisky, D.; Castaldelli-Maia, J.M. Smoking and Cognition. Curr. Drug Abus. Rev. 2016, 9, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knecht, K.M.; Alosco, M.L.; Spitznagel, M.B.; Cohen, R.; Raz, N.; Sweet, L.; Colbert, L.H.; Josephson, R.; Hughes, J.; Rosneck, J.; et al. Sleep Apnea and Cognitive Function in Heart Failure. Cardiovasc. Psychiatry Neurol. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hjelm, C.; Broström, A.; Dahl, A.; Johansson, B.; Fredrikson, M.; Strömberg, A. Factors Associated With Increased Risk for Dementia in Individuals Age 80 Years or Older With Congestive Heart Failure. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2014, 29, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de la Torre, J.C. Are Major Dementias Triggered by Poor Blood Flow to the Brain? Theoretical Considerations. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, S.; Al-Ahmad, A.J.; Gassmann, M.; Ogunshola, O.O. Hypoxia selectively disrupts brain microvascular endothelial tight junction complexes through a hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) dependent mechanism. J. Cell Physiol. 2014, 229, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampadu, J.; Morley, J.E. Heart failure and cognitive dysfunction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 178, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immink, R.V.; Born, B.-J.H.V.D.; van Montfrans, G.A.; Koopmans, R.P.; Karemaker, J.M.; van Lieshout, J.J. Impaired Cerebral Autoregulation in Patients With Malignant Hypertension. Circulation 2004, 110, 2241–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skinhoj, E.; Strandgaard, S. Pathogenesis of hypertensive encephalopathy. Lancet 1973, 1, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, C.J.; Lee, K. Hyperperfusion Syndromes: Insight into the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Hypertensive Encephalopathy. CNS Spectr. 2007, 12, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, E.T.; Strandgaard, S.; I Graham, D.; Jones, J.V.; Harper, A.M.; Farrar, J.K. Effects of acutely induced hypertension in cats on pial arteriolar caliber, local cerebral blood flow, and the blood-brain barrier. Circ. Res. 1976, 39, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auer, L. The Sausage-String Phenomenon in Acutely Induced Hypertension—Arguments Against the Vasospasm Theory in the Pathogenesis of Acute Hypertensive Encephalopathy. Eur. Neurol. 1978, 17, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B. Regional Cerebral Blood Flow in Acute Experimental Hypertension. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1974, 50, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulop, G.A.; Tarantini, S.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Molnar, A.; Prodan, C.I.; Kiss, T.; Csipo, T.; Lipecz, A.; Balasubramanian, P.; Farkas, E.; et al. Role of age-related alterations of the cerebral venous circulation in the pathogenesis of vascular cognitive impairment. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2019, 316, H1124–H1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.-H.; Lee, C.-W.; Wang, P.-N.; Lee, H.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Chung, C.-P. Cognitive functions and jugular venous reflux in severe mitral regurgitation: A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0207832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulop, G.A.; Ahire, C.; Csipo, T.; Tarantini, S.; Kiss, T.; Balasubramanian, P.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Farkas, E.; Toth, A.; Nyúl-Tóth, Á.; et al. Cerebral venous congestion promotes blood-brain barrier disruption and neuroinflammation, impairing cognitive function in mice. GeroScience 2019, 41, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.-J. Heart and Brain Interconnection—Clinical Implications of Changes in Brain Function During Heart Failure. Circ. J. 2015, 79, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doehner, W.; Ural, D.; Haeusler, K.G.; Čelutkienė, J.; Bestetti, R.; Cavusoglu, Y.; Peña-Duque, M.A.; Glavas, D.; Iacoviello, M.; Laufs, U.; et al. Heart and brain interaction in patients with heart failure: Overview and proposal for a taxonomy. A position paper from the Study Group on Heart and Brain Interaction of the Heart Failure Association. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2017, 20, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Athilingam, P.; A Moynihan, J.; Chen, L.; D’Aoust, R.; Groer, M.; E Kip, K. Elevated Levels of Interleukin 6 and C-Reactive Protein Associated With Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure. Congest. Hear. Fail. 2013, 19, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAfoose, J.; Baune, B. Evidence for a cytokine model of cognitive function. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, X.; Bu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Suo, H.; Yang, L.; Shi, Y.; et al. Increases in the Risk of Cognitive Impairment and Alterations of Cerebral β-amyloid Metabolism in Mouse Model of Heart Failure. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanninen, S.A.; Darling, P.B.; Sole, M.J.; Barr, A.; Keith, M.E. The Prevalence of Thiamin Deficiency in Hospitalized Patients With Congestive Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calingasan, N.Y.; Chun, W.J.; Park, L.C.; Uchida, K.; Gibson, G.E. Oxidative Stress Is Associated with Region-Specific Neuronal Death During Thiamine Deficiency. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 58, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlais, P.J.; Savage, L.M. Thiamine deficiency in rats produces cognitive and memory deficits on spatial tasks that correlate with tissue loss in diencephalon, cortex and white matter. Behav. Brain Res. 1995, 68, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, B.B.; Cankurtaran, M.; Haznedaroglu, I.C.; Halil, M.; Ulger, Z.; Altun, B.; Ariogul, S. Iron deficiency can cause cognitive impairment in geriatric patients. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2012, 16, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parissis, J.T.; Adamopoulos, S.; Rigas, A.; Kostakis, G.; Karatzas, D.; Venetsanou, K.; Kremastinos, D.T. Comparison of circulating proinflammatory cytokines and soluble apoptosis mediators in patients with chronic heart failure with versus without symptoms of depression. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 94, 1326–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, G.; Metra, M.; Davison, B.A.; Jondeau, G.; Cleland, J.G.; Bourge, R.C.; Milo, O.; O’Connor, C.M.; Parker, J.D.; Torre-Amione, G.; et al. Systolic blood pressure reduction during the first 24 h in acute heart failure admission: Friend or foe? Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2017, 20, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleutjens, F.A.; Janssen, D.J.; Ponds, R.W.; Dijkstra, J.B.; Wouters, E.F. COgnitive-pulmonary disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 697825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowak, K.L.; Yaffe, K.; Orwoll, E.S.; Ix, J.H.; You, Z.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Hoffman, A.R.; Chonchol, M. Serum Sodium and Cognition in Older Community-Dwelling Men. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Brunner, E.; Fuhrer, R. Minireview: Mechanisms by Which the Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes Impair Memory. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Boil. Sci. Med. Sci. 2000, 55, B228–B232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pulignano, G.; Del Sindaco, D.; Di Lenarda, A.; Tinti, M.D.; Tarantini, L.; Cioffi, G.; Tolone, S.; Pero, G.; Minardi, G. Chronic renal dysfunction and anaemia are associated with cognitive impairment in older patients with heart failure. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 15, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjihambi, A.; Arias, N.; Sheikh, M.; Jalan, R. Hepatic encephalopathy: A critical current review. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shinohara, M.; Yamada, M. Drug-induced Cognitive Impairment. Brain Nerve 2016, 68, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, M.R.; Jannat-Khah, D.; Bryan, J.; Banerjee, S.; McClure, L.A.; Wadley, V.G.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Levitan, E.B.; Goyal, P.; Peterson, J.C.; et al. The Prevalence of Cognitive Impairment Among Adults With Incident Heart Failure: The “Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke” (REGARDS) Study. J. Card. Fail. 2019, 25, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, C.A.; Blades, N.J.; Chaudhry, S.I.; Dodson, J.A.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Heckbert, S.R.; Psaty, B.M.; Arnold, A.M.; Dublin, S.; Sitlani, C.M.; et al. Long-Term Cognitive Decline After Newly Diagnosed Heart Failure: Longitudinal Analysis in the CHS (Cardiovascular Health Study). Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e004476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwerdt, J.; Edwards, J.D.; Athilingam, P.; O’Connor, M.L.; Valdes, E. Longitudinal Differences in Cognitive Functioning Among Older Adults With and Without Heart Failure. J. Aging Health 2013, 25, 1358–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelm, C.; Dahl, A.; Broström, A.; Mårtensson, J.; Johansson, B.; Strömberg, A. The influence of heart failure on longitudinal changes in cognition among individuals 80 years of age and older. J. Clin. Nurs. 2011, 21, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, O.P.; Beer, C.; Lautenschlager, N.T.; Arnolda, L.; Alfonso, H.; Flicker, L. Two-year course of cognitive function and mood in adults with congestive heart failure and coronary artery disease: The Heart-Mind Study. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2012, 24, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijts, M.; Van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Duits, A.; Burkard, T.; Muzzarelli, S.; Maeder, M.T.; Schindler, R.; Pfisterer, M.E.; Rocca, H.-P.B.-L. Cognitive impairment in heart failure: Results from the Trial of Intensified versus standard Medical therapy in Elderly patients with Congestive Heart Failure (TIME-CHF) randomized trial. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2013, 15, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanek, K.M.; Gunstad, J.; Paul, R.H.; Poppas, A.; Jefferson, A.L.; Sweet, L.H.; Hoth, K.F.; Haley, A.P.; Forman, D.E.; Cohen, R.A. Longitudinal cognitive performance in older adults with cardiovascular disease: Evidence for improvement in heart failure. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2009, 24, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kindermann, I.; Fischer, D.; Karbach, J.; Link, A.; Walenta, K.; Barth, C.; Ukena, C.; Mahfoud, F.; Köllner, V.; Kindermann, M.; et al. Cognitive function in patients with decompensated heart failure: The Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure (CogImpair-HF) study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.; Fazekas, F.; Offenbacher, H.; Dusleag, J.; Lechner, H. Brain magnetic resonance imaging and neuropsychologic evaluation of patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Stroke 1991, 22, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woo, M.A.; Ogren, J.A.; Abouzeid, C.M.; Macey, P.; Sairafian, K.G.; Saharan, P.S.; Thompson, P.; Fonarow, G.; Hamilton, M.A.; Harper, R.M.; et al. Regional hippocampal damage in heart failure. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2015, 17, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Woo, M.A.; Birrer, B.V.; Macey, P.M.; Fonarow, G.C.; Hamilton, M.A.; Harper, R.M. Mammillary bodies and fornix fibers are injured in heart failure. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 33, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Nguyen, H.D.; Ogren, J.A.; Macey, P.; Thompson, P.; Fonarow, G.; Hamilton, M.A.; Harper, R.M.; Woo, M.A. Global and regional putamen volume loss in patients with heart failure. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2011, 13, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Yadav, S.K.; Palomares, J.A.; Park, B.; Joshi, S.H.; Ogren, J.A.; Macey, P.M.; Fonarow, G.C.; Harper, R.M.; Woo, M.A. Reduced Regional Brain Cortical Thickness in Patients with Heart Failure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, O.P.; Garrido, G.J.; Etherton-Beer, C.; Lautenschlager, N.T.; Arnolda, L.; Flicker, L. Cognitive and brain changes associated with ischaemic heart disease and heart failure. Eur. Hear. J. 2012, 33, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, T.C.; Rays, J.; Fráguas, R., Jr.; Wajngarten, M.; Meneghetti, J.C.; Prando, S.; Busatto, G.F. Localized cerebral blood flow reductions in patients with heart failure: A study using 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT. J. Neuroimaging 2005, 15, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, T.C.D.T.F.; Busatto, G.F. Regional cerebral blood flow reductions, heart failure and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Res. 2006, 28, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Woo, M.A.; Macey, P.; Fonarow, G.; Hamilton, M.A.; Harper, R.M. Brain axonal and myelin evaluation in heart failure. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 307, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Lu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, B.; Xu, Q.; Han, X.; Li, T.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, W.; et al. Dynamic Changes in Brain Glucose Metabolism and Neuronal Structure in Rats with Heart Failure. Neuroscience 2019, 424, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, L.; Bisdas, S. The diagnostic value of FDG and amyloid PET in Alzheimer’s disease—A systematic review. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 94, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alongi, P.; Sardina, D.S.; Coppola, R.; Scalisi, S.; Puglisi, V.; Arnone, A.; Di Raimondo, G.; Munerati, E.; Alaimo, V.; Midiri, F.; et al. 18F-Florbetaben PET/CT to Assess Alzheimer’s Disease: A new Analysis Method for Regional Amyloid Quantification. J. Neuroimaging 2019, 29, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, A.; Dervenoulas, G.; Politis, M. Magnetic resonance imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Warner Stevenson, L.; Ahmad, T.; Amin, V.J.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Davis, L.L.; Drazner, M.H.; Kirkpatrick, J.N.; Peterson, P.N.; et al. 2019 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Risk Assessment, Management, and Clinical Trajectory of Patients Hospitalized With Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1966–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Screening Tool | Scoring System | Usual Cut-Off Point | Administration Time (min) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) [35,43,44,45,46,47,48,49] | 0–30 | <24 | 5–10 |
|
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) [50,51,52,53] | 0–30 | <26 | 10 |
|
| Mini-Cog Test [39,40] | Composite score: 5
| ≤2 | 3 |
|
| MoCA 5-min protocol (Mini-MoCA) [41,42] | 12 | ≤9 | 5 |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ventoulis, I.; Arfaras-Melainis, A.; Parissis, J.; Polyzogopoulou, E. Cognitive Impairment in Acute Heart Failure: Narrative Review. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2021, 8, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8120184
Ventoulis I, Arfaras-Melainis A, Parissis J, Polyzogopoulou E. Cognitive Impairment in Acute Heart Failure: Narrative Review. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2021; 8(12):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8120184
Chicago/Turabian StyleVentoulis, Ioannis, Angelos Arfaras-Melainis, John Parissis, and Eftihia Polyzogopoulou. 2021. "Cognitive Impairment in Acute Heart Failure: Narrative Review" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 8, no. 12: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8120184
APA StyleVentoulis, I., Arfaras-Melainis, A., Parissis, J., & Polyzogopoulou, E. (2021). Cognitive Impairment in Acute Heart Failure: Narrative Review. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 8(12), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8120184