Biocompatibility Study of Purified and Low-Temperature-Sterilized Injectable Collagen for Soft Tissue Repair: Intramuscular Implantation in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sterility Test
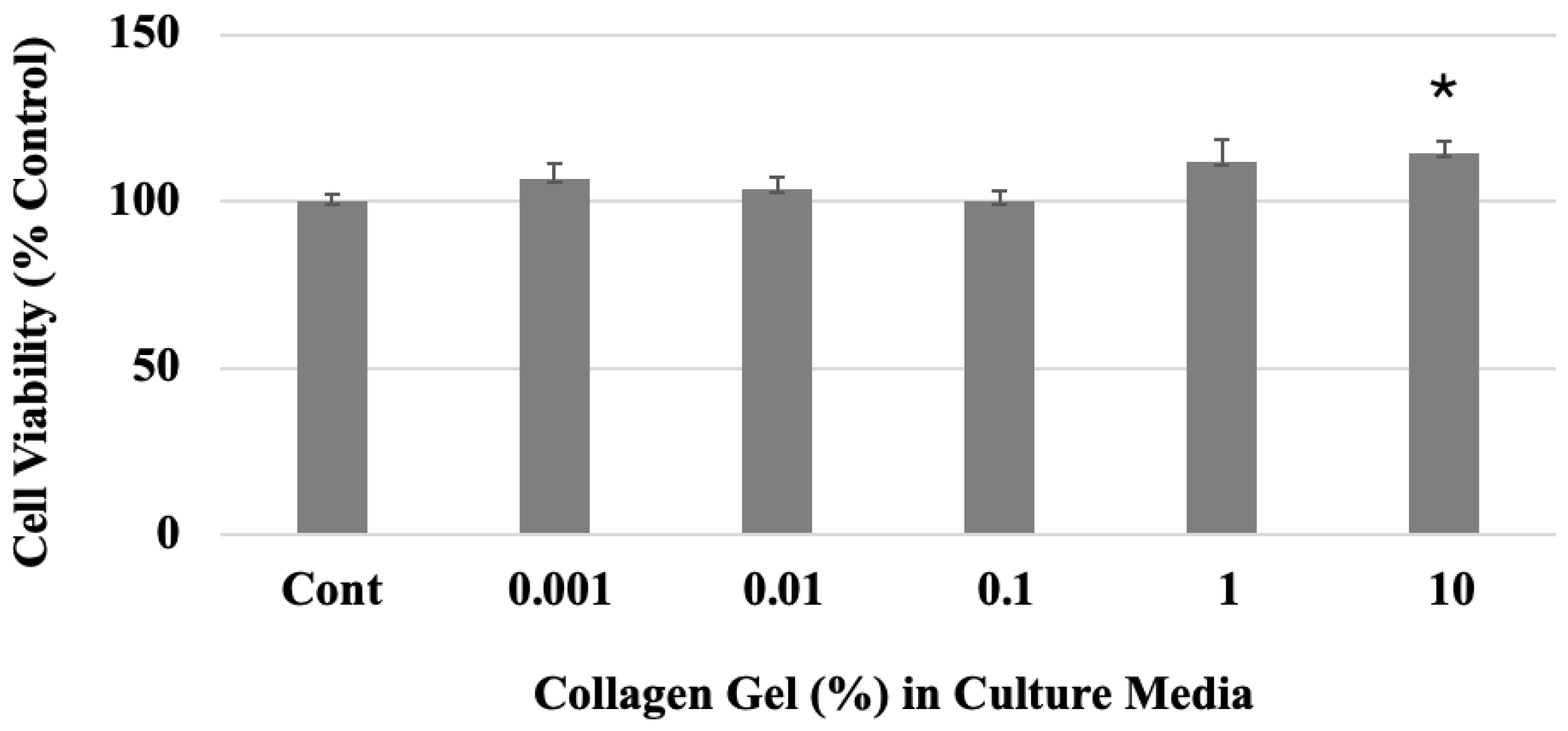
2.2. Cytotoxicity Test
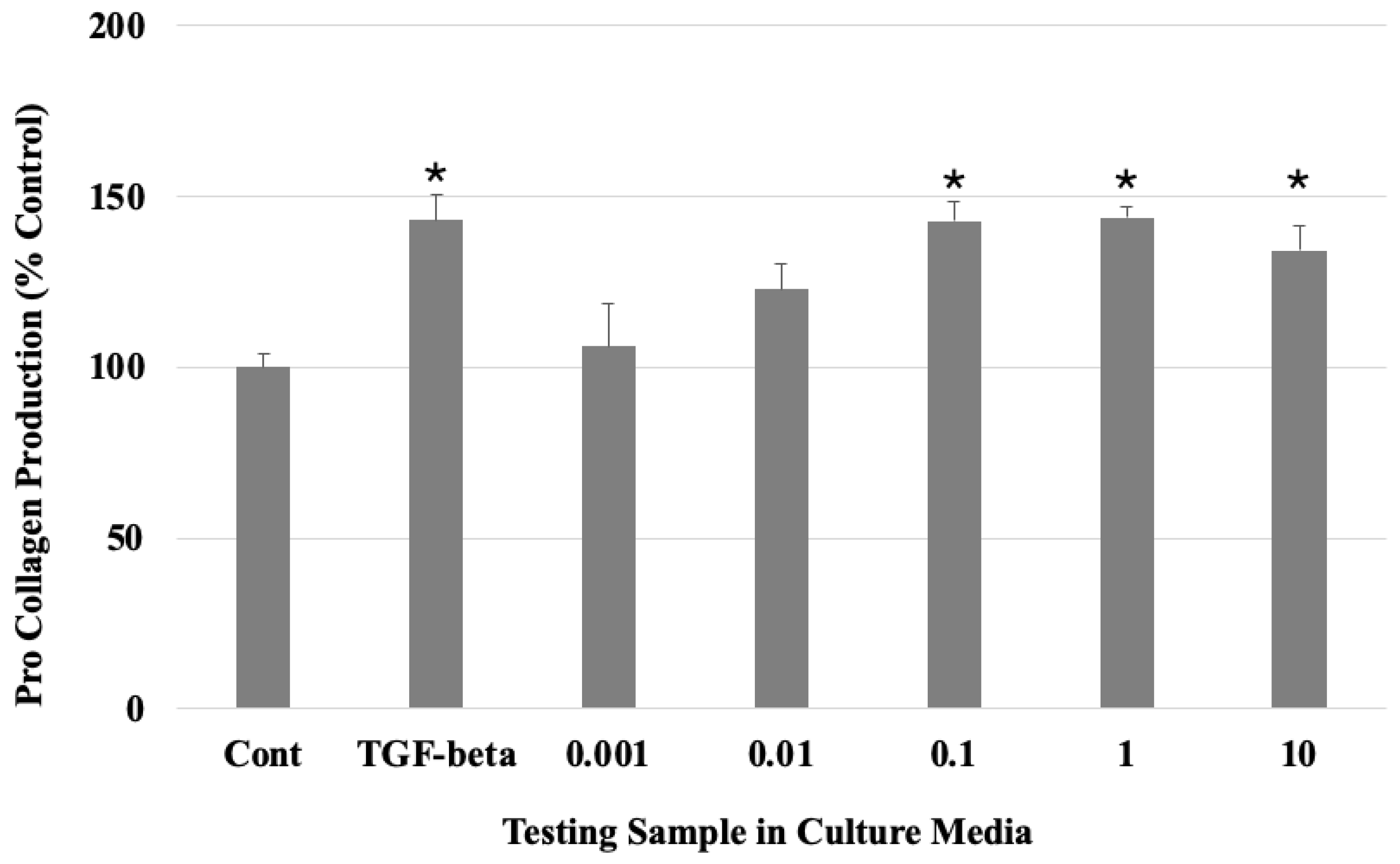
2.3. Collagen Expression
2.4. Gel Viscosity
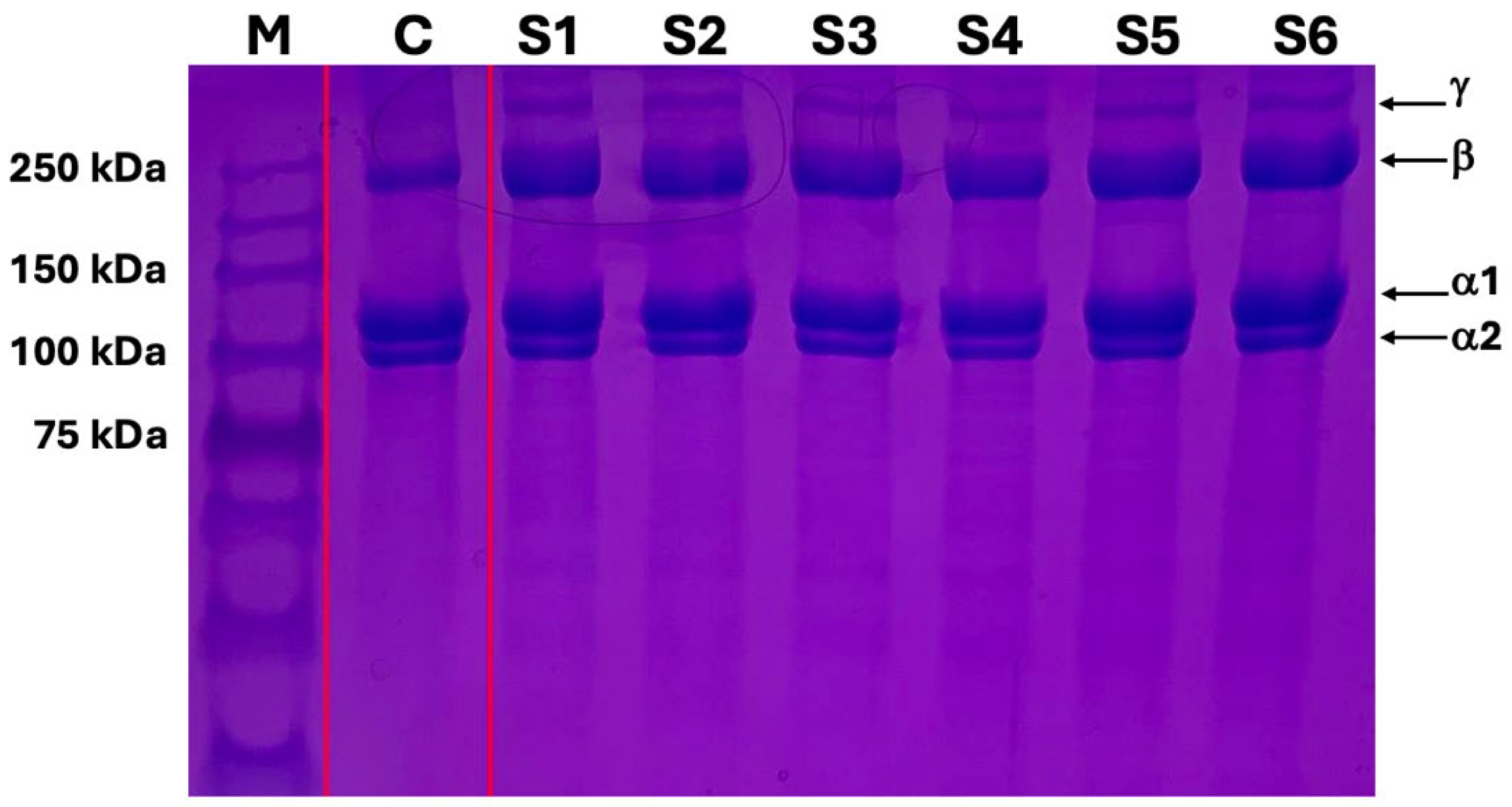
2.5. SDS-PAGE Gel Electrophoresis
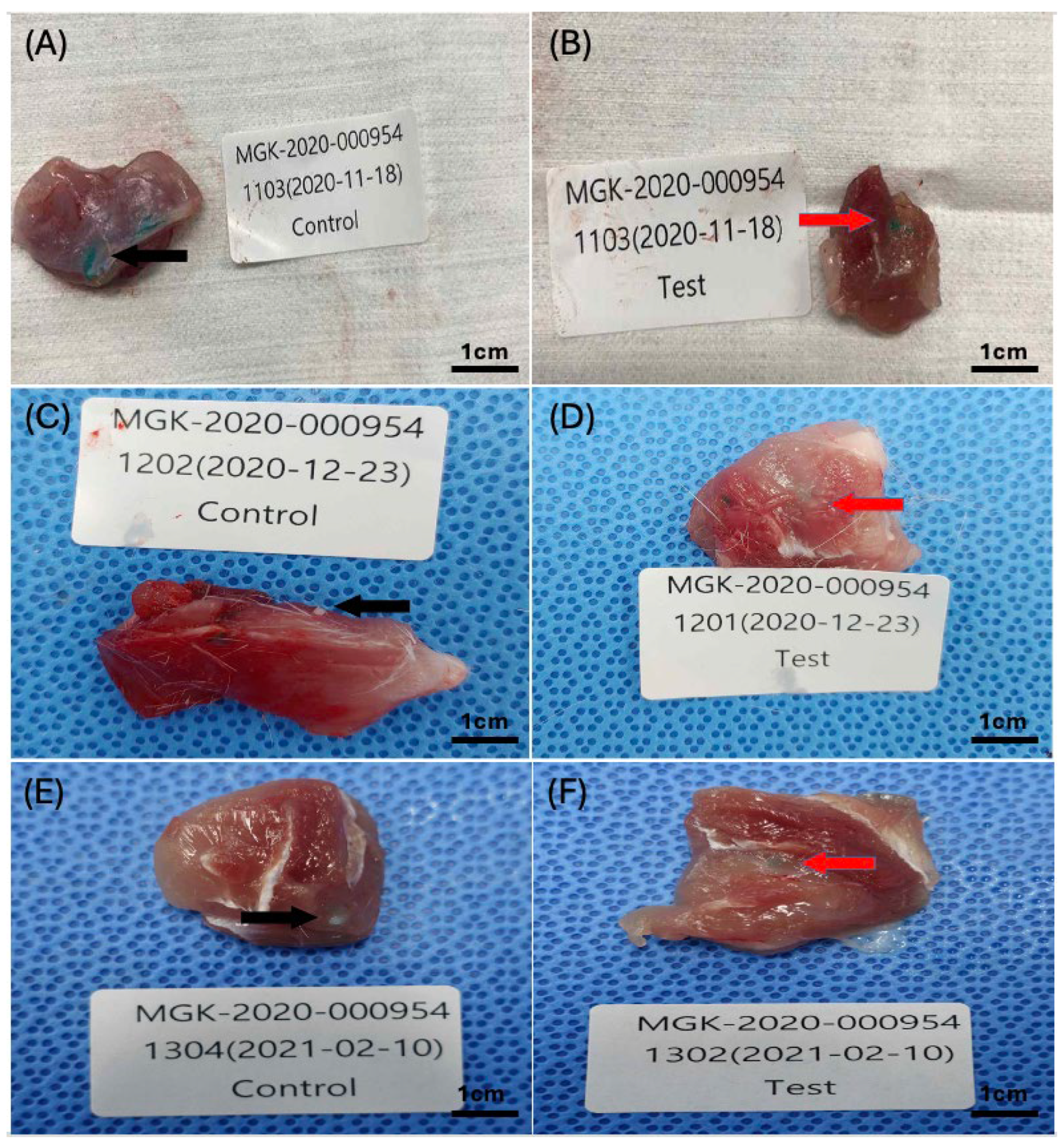
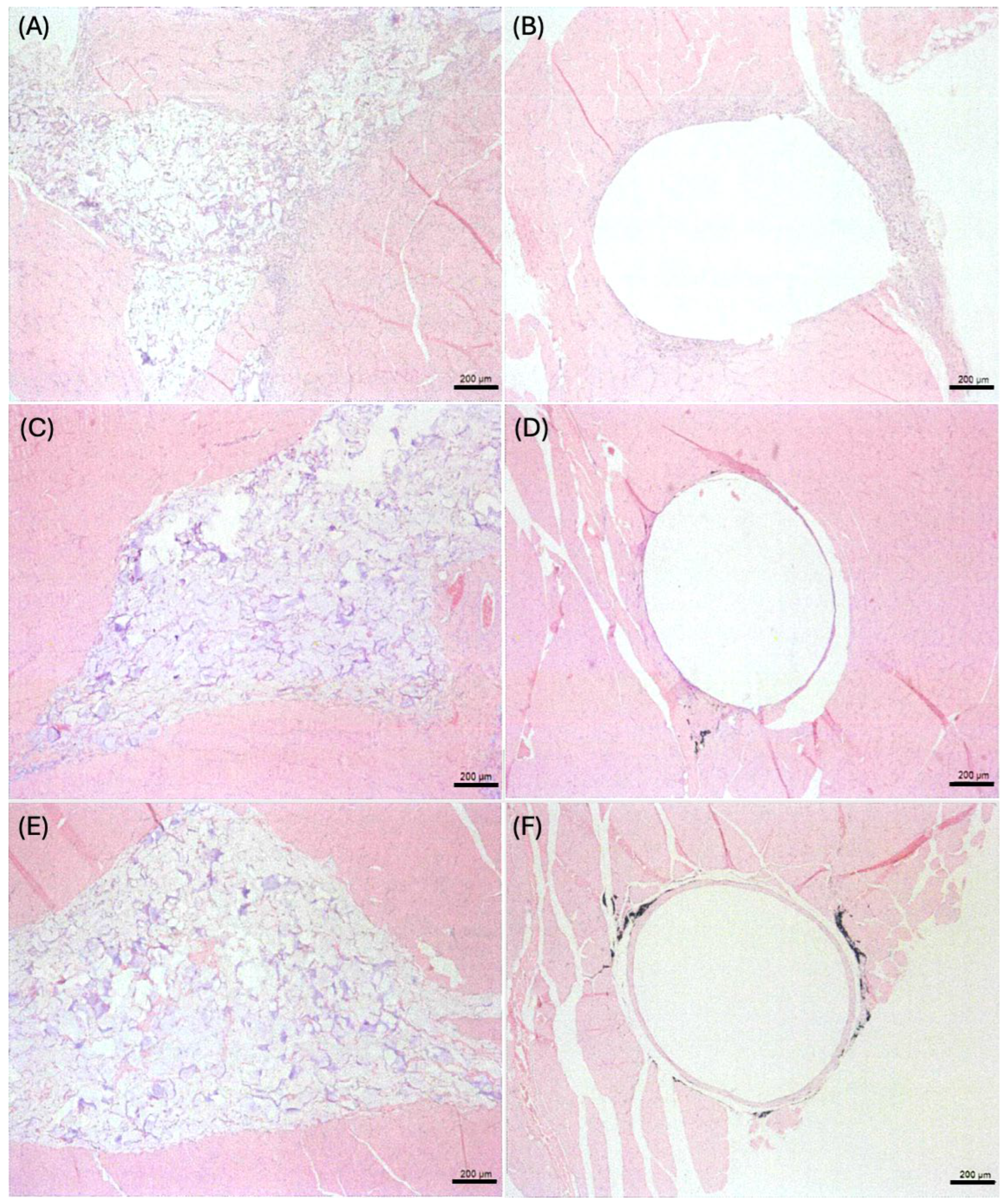
2.6. Microscopic Evaluations
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Test Samples
4.2. Preparation of Sterility Test
4.3. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Test
4.4. Quantitative Analysis of Collagen Expression
4.5. Viscosity Analysis of Collagen Gels
4.6. SDS-PAGE Analysis of Processed and Sterilized Collagen Gel
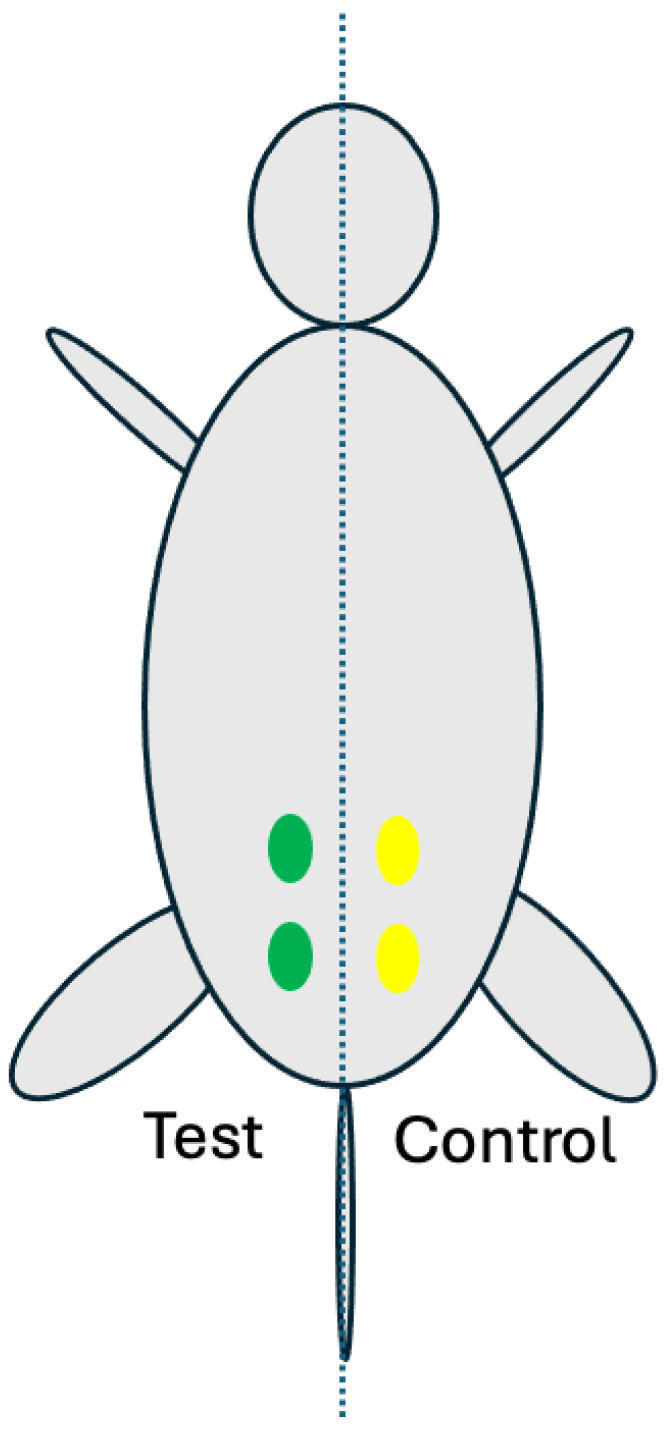
4.7. Rat Muscle Implantation Model
4.8. Microscopic Evaluation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Al-Atif, H. Collagen Supplements for Aging and Wrinkles: A Paradigm Shift in the Field of Dermatology and Cosmetics. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2022, 12, e2022018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Nikoo, M.; Boran, G.; Zhou, P.; Regenstein, J.M. Collagen and gelatin. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 527–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M. Processing of collagen-based biomaterials and the resulting materials properties. Biomed. Eng. Online 2019, 18, 1–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghatge, A.S.; Ghatge, S.B. The Effectiveness of Injectable Hyaluronic Acid in the Improvement of the Facial Skin Quality: A Systematic Review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Yu, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yao, Z. Clinical efficacy and safety of targeted injection of PRP with skin booster in the treatment of aging face. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.N.; Choi, S.; Lee, Y.I.; Suk, J.; Lee, J.H. The efficacy of intradermal hyaluronic acid filler as a skin quality booster: A prospective, single-center, single-arm pilot study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, G.; Arora, S.; Sadoughifar, R.; Batra, N. Biorevitalization of the skin with skin boosters: Concepts, variables, and limitations. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 20, 2458–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Winayanuwattikun, W.; Kim, S.; Wan, J.; Vachatimanont, V.; Putri, A.I.; Hidajat, I.J.; Yogya, Y.; Pamela, R. Skin boosters: Definitions and varied classifications. Ski. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, e13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayatollahi, A.; Firooz, A.; Samadi, A. Evaluation of safety and efficacy of booster injections of hyaluronic acid in improving the facial skin quality. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 2267–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.I.A.; Barroso, L.G.R.; Sánchez, M.L. Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2017, 17, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Sanchez, A.C.; Tantry, E.K.; Burns, E.K.; Perez, V.M.; Prabhu, S.; Katta, R.; Skin, H. Nail Supplements: Marketing and Labeling Concerns. Cureus 2020, 12, e12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skin Boosters Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Type (Mesotherapy, Micro-needle), By Gender (Female, Male), by End-Use (Dermatology Clinics, Medspa), by Region, and Segment Forecasts, 2024–2030; Grand View Research: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2023; p. 108.
- Salvatore, L.; Natali, M.L.; Brunetti, C.; Sannino, A.; Gallo, N. An Update on the Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Collagen Injectables for Aesthetic and Regenerative Medicine Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuska, A.M.; McFetridge, P.S. The effect of terminal sterilization on structural and biophysical properties of a decellularized collagen-based scaffold; implications for stem cell adhesion. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 103, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvikas-Peltonen, E.; Hakoinen, S.; Celikkayalar, E.; Laaksonen, R.; Airaksinen, M. Incorrect aseptic techniques in medicine preparation and recommendations for safer practices: A systematic review. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2016, 24, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elson, M.L. Injectable Collagen and Autoimmune Disease. J. Dermatol. Surg. Oncol. 1993, 19, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, J.M.; Townes, A.S.; Kang, A.H. Collagen Autoimmune Arthritis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1984, 2, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiyoshi, T.; Cheng, K.-C.; Krug, M.S.; Yoo, T.-J. Molecular Basis of Type II Collagen Autoimmune Disease: Observations of Arthritis, Auricular Chondritis and Tympanitis in Mice. ORL 1997, 59, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlman, R.L.; McClung, S.J.W.; Schlesinger, T. Introduction to soft tissue fillers. Dermatol. Rev. 2023, 4, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Açil, Y.; Springer, I.N.; Niehoff, P.; Gaßling, V.; Warnke, P.H.; Açmaz, S.; Sönmez, T.T.; Kimmig, B.; Lefteris, V.; Wiltfang, J. Proof of Direct Radiogenic Destruction of Collagen in Vitro. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2007, 183, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, J.; Wauk, L.; Chu, S.; DeLustro, F. Clinical use of injectable bovine collagen: A decade of experience. Clin. Mater. 1992, 9, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. A Review of the Effects of Collagen Treatment in Clinical Studies. Polymers 2021, 13, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. The extracellular matrix in myocardial injury, repair, and remodeling. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1600–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matinong, A.M.E.; Chisti, Y.; Pickering, K.L.; Haverkamp, R.G. Collagen Extraction from Animal Skin. Biology 2022, 11, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Shen, Y.; Gong, S.; Li, M.; Sun, L. Improving the Sustainability of Processing By-Products: Extraction and Recent Biological Activities of Collagen Peptides. Foods 2023, 12, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneke, E. Managing complications of fillers: Rare and not-so-rare. J. Cutan. Aesthetic Surg. 2015, 8, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galante, R.; Pinto, T.J.; Colaco, R.; Serro, A.P. Sterilization of hydrogels for biomedical applications: A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 2472–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirrah, I.N.; Lokanathan, Y.; Zulkiflee, I.; Wee, M.F.M.R.; Motta, A.; Fauzi, M.B. A Comprehensive Review on Collagen Type I Development of Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering: From Biosynthesis to Bioscaffold. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, L.M.; Pandit, A.; Zeugolis, D.I. Influence of sterilisation methods on collagen-based devices stability and properties. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2014, 11, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šupová, M.; Suchý, T.; Chlup, H.; Šulc, M.; Kotrč, T.; Šilingová, L.; Žaloudková, M.; Rýglová, Š.; Braun, M.; Chvátil, D.; et al. The electron beam irradiation of collagen in the dry and gel states: The effect of the dose and water content from the primary to the quaternary levels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Puig, D.; Costa-Larrión, E.; Rubio-Rodríguez, N.; Gálvez-Martín, P. Collagen Supplementation for Joint Health: The Link between Composition and Scientific Knowledge. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rýglová, Š.; Braun, M.; Suchý, T. Collagen and Its Modifications-Crucial Aspects with Concern to Its Processing and Analysis. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.I.; Koo, T.H.; Chen, P.; D’Lima, D.D. Subcutaneous toxicity of a dual ionically cross-linked atelocollagen and sodium hyaluronate gel: Rat in vivo study for biological safety evaluation of the injectable hydrogel. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, S.; Kaur, S.; David, S.A.W.; Kenney, J.L.; McCormick, W.M.; Gupta, R.K. Evaluation of growth based rapid microbiological methods for sterility testing of vaccines and other biological products. Vaccine 2011, 29, 8012–8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tungtasana, H.; Shuangshoti, S.; Shuangshoti, S.; Kanokpanont, S.; Kaplan, D.L.; Bunaprasert, T.; Damrongsakkul, S. Tissue response and biodegradation of composite scaffolds prepared from Thai silk fibroin, gelatin and hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10993-6:2016; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 6: Tests for Local Effects after Implantation. ISO/TC 194. 3rd ed. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–29.

| Media | Test Samples | D-0 | D+7 | D+14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSA | #01 | No growth | No growth | No growth |
| #02 | No growth | No growth | No growth | |
| #03 | No growth | No growth | No growth | |
| Negative control | No growth | No growth | No growth | |
| Positive control | No growth | Growth | Growth | |
| Positive control in TSA: Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Clostridium sporogenes | ||||
| FTM | Test Samples | D-0 | D+7 | D+14 |
| #01 | No growth | No growth | No growth | |
| #02 | No growth | No growth | No growth | |
| #03 | No growth | No growth | No growth | |
| Negative control | No growth | No growth | No growth | |
| Positive control | No growth | Growth | Growth | |
| Positive control in FTM: Bacillus subtilis, Candida albicans, and Aspergillus niger | ||||
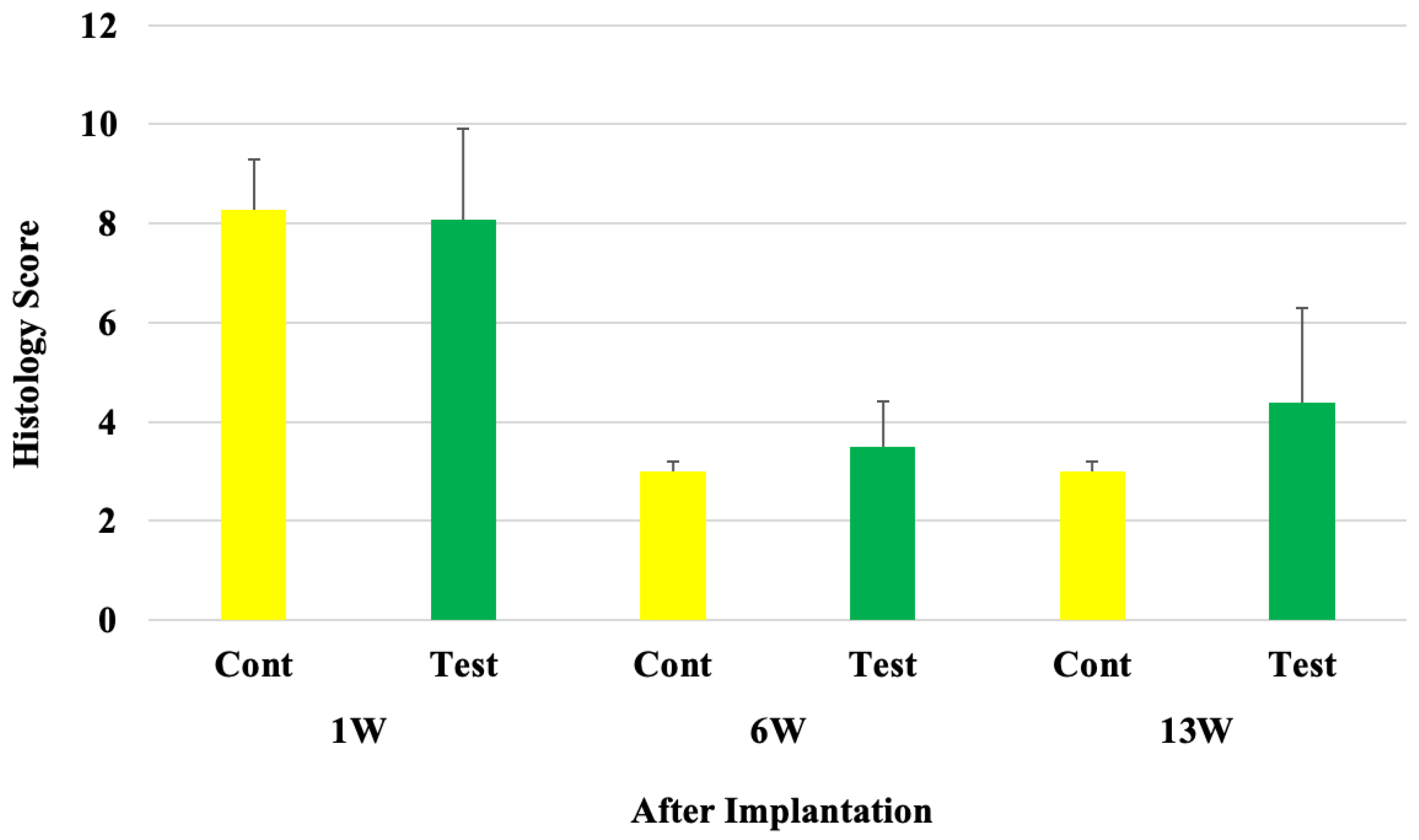
| Implantation Period | Mean Score (Control) | Mean Score (Test) | Mean Score Difference (Test−Control) | Bio-Reactivity Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 week | 8.3 | 8.1 | 8.1 − 8.3 = −0.2 (Considered as 0.0) | Minimal or No Reaction |
| 6 weeks | 3.0 | 3.5 | 3.5 − 3.0 = 0.5 | Minimal or No Reaction |
| 13 weeks | 3.0 | 4.4 | 4.4 − 3.0 = 1.4 | Minimal or No Reaction |
| Category | Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Leukocyte | 0 | Rare, 1–5/phf * | 5–10/phf | Heavy infiltrate | Packed |
| Lymphocytes | 0 | Rare, 1–5/phf | 5–10/phf | Heavy infiltrate | Packed |
| Macrophages | 0 | Rare, 1–5/phf | 5–10/phf | Heavy infiltrate | Packed |
| Neo-vascularization | 0 | Minimal capillary proliferation, focal, 1–3 buds | Groups of 4–7 capillaries with supporting fibroblastic structures | Broad band of capillaries with supporting structures | Extensive band of capillaries with supporting fibroblastic structures |
| Fibrosis | 0 | Narrow band | Moderately thick band | Thick band | Extensive band |
| Bio-Reactivity Rating | Mean Score (Animal Score) |
|---|---|
| Minimal or no reaction | 0.0–2.9 |
| Slight reaction | 3.0–8.9 |
| Moderate reaction | 9.0–15.0 |
| Severe reaction | >15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koo, T.-H.; Lee, J.K.; Grogan, S.P.; Ra, H.J.; D’Lima, D.D. Biocompatibility Study of Purified and Low-Temperature-Sterilized Injectable Collagen for Soft Tissue Repair: Intramuscular Implantation in Rats. Gels 2024, 10, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100619
Koo T-H, Lee JK, Grogan SP, Ra HJ, D’Lima DD. Biocompatibility Study of Purified and Low-Temperature-Sterilized Injectable Collagen for Soft Tissue Repair: Intramuscular Implantation in Rats. Gels. 2024; 10(10):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100619
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoo, Tae-Hoon, Jason K. Lee, Shawn P. Grogan, Ho Jong Ra, and Darryl D. D’Lima. 2024. "Biocompatibility Study of Purified and Low-Temperature-Sterilized Injectable Collagen for Soft Tissue Repair: Intramuscular Implantation in Rats" Gels 10, no. 10: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100619
APA StyleKoo, T.-H., Lee, J. K., Grogan, S. P., Ra, H. J., & D’Lima, D. D. (2024). Biocompatibility Study of Purified and Low-Temperature-Sterilized Injectable Collagen for Soft Tissue Repair: Intramuscular Implantation in Rats. Gels, 10(10), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100619







