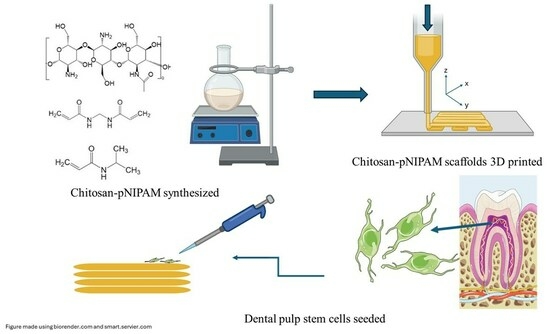
Development of 3D Printed pNIPAM-Chitosan Scaffolds for Dentoalveolar Tissue Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
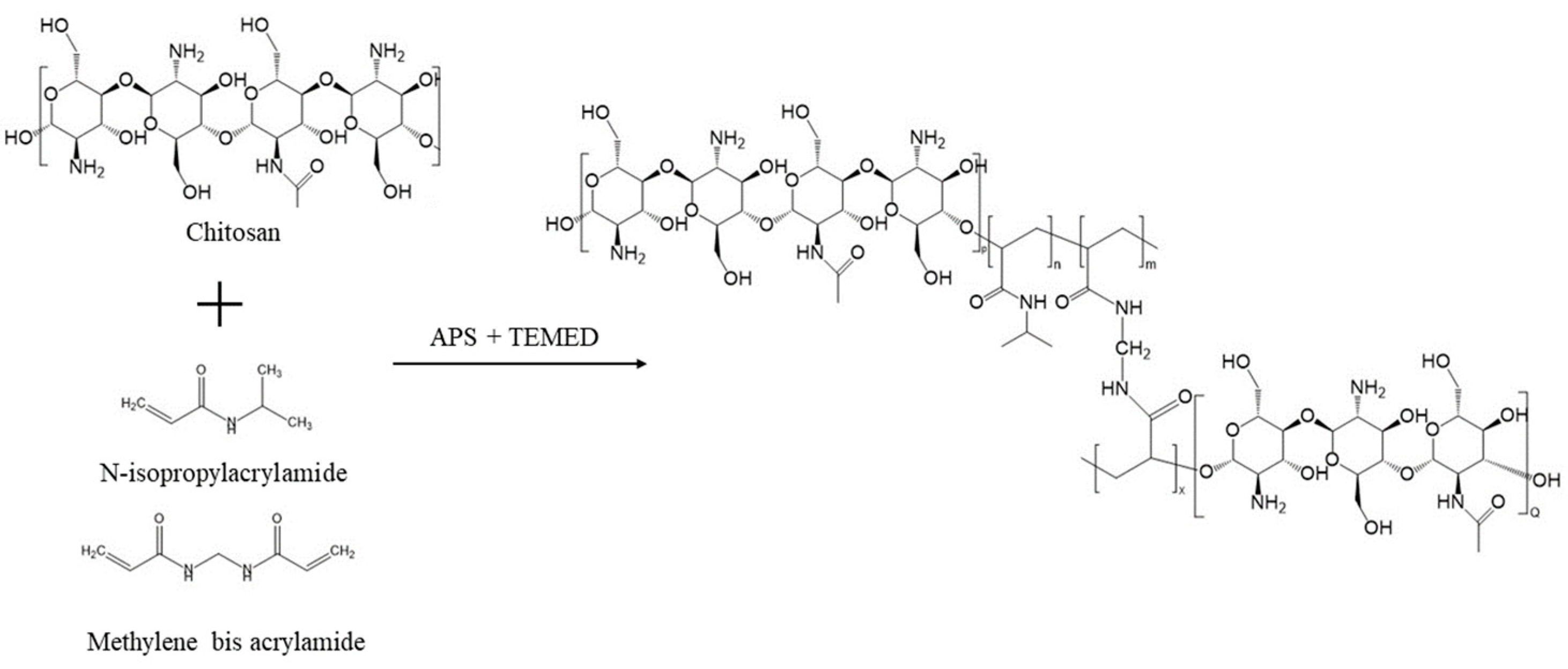
2.1. Sol-Gel Synthesis of pNIPAM-Chitosan Copolymer
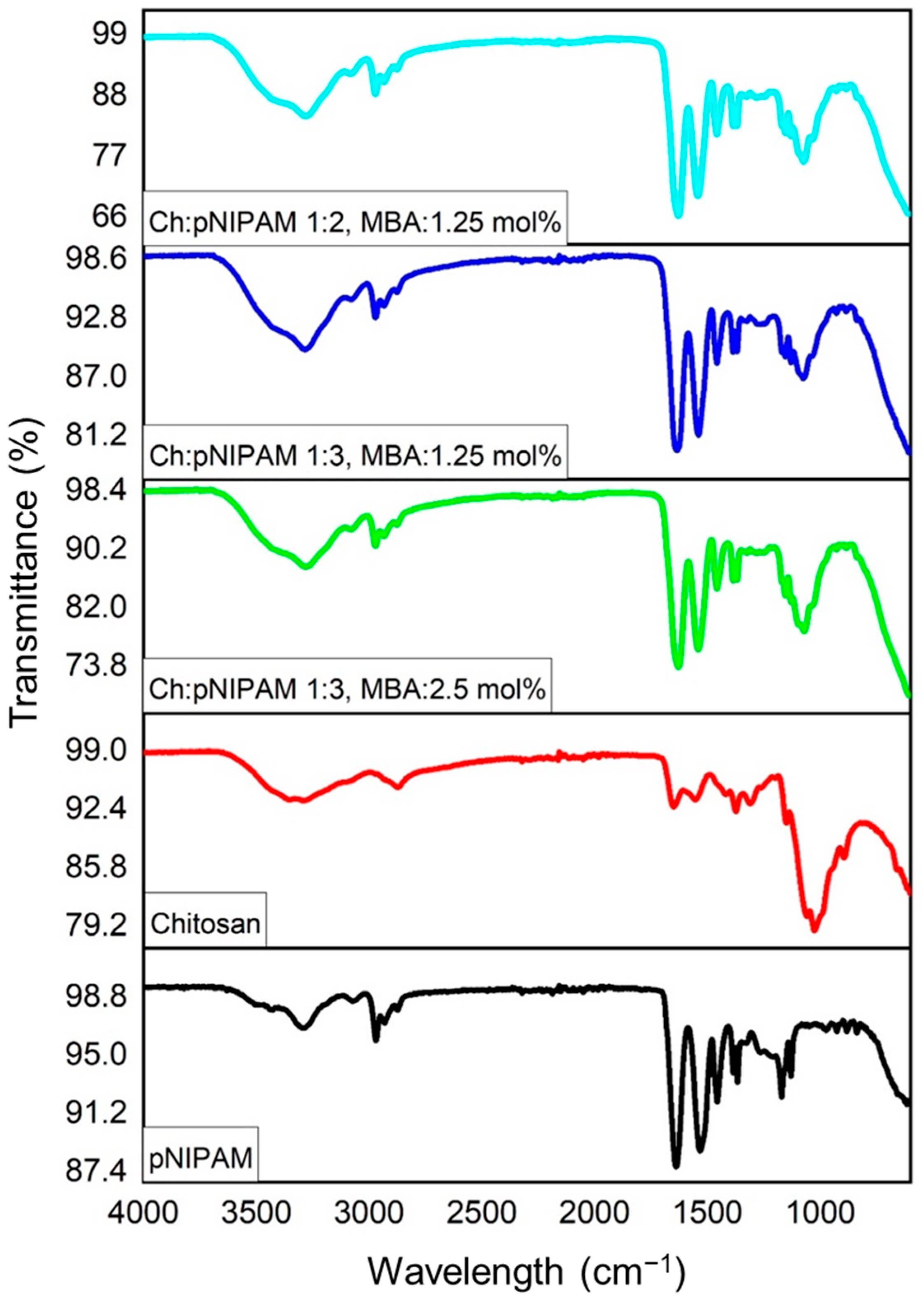
2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
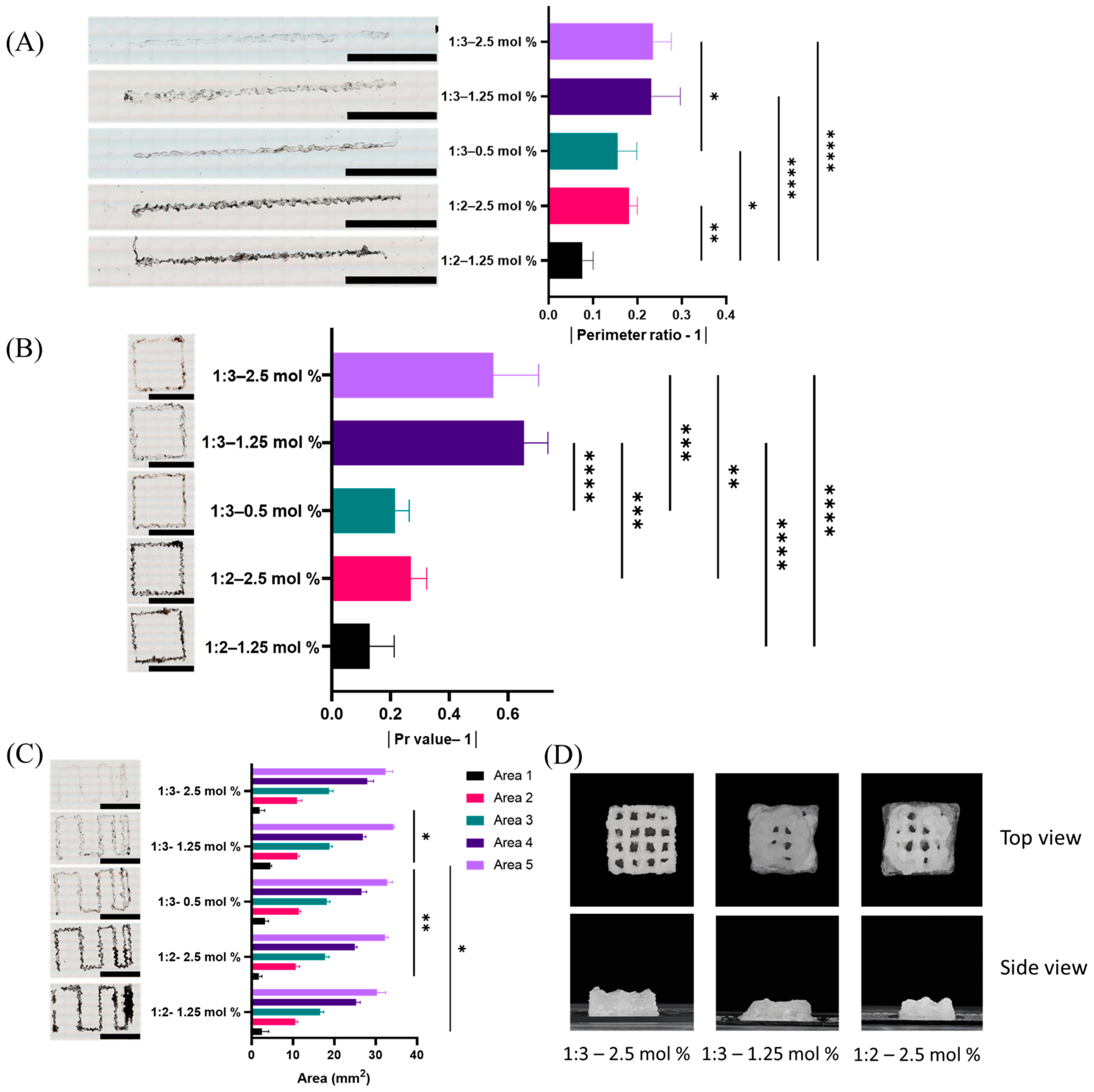
2.3. Evaluation of Printability
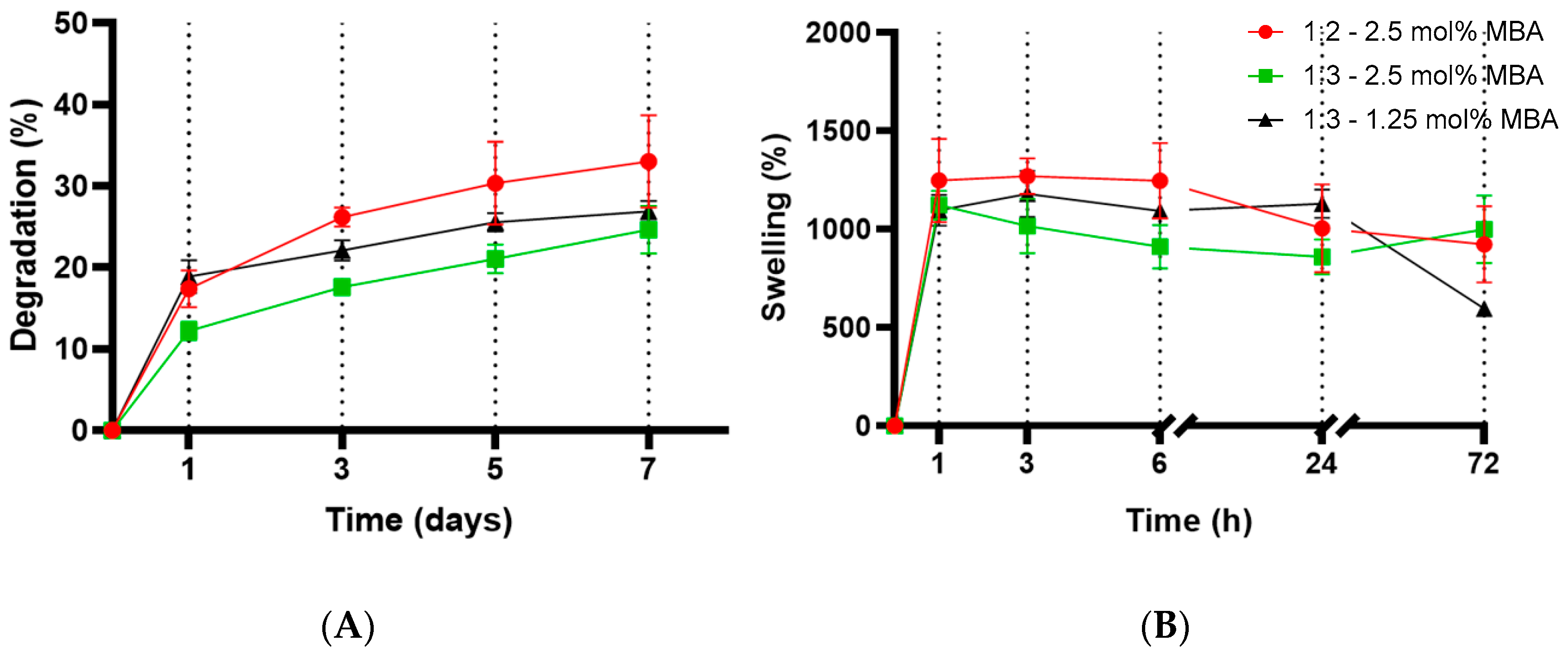
2.4. Evaluation of Degradation and Swelling
2.5. Evaluation of Surface Morphology
2.6. Cell Viability
2.7. Further Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Sol-Gel Synthesis of pNIPAM-Chitosan Copolymer
4.2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.2.3. 3D Printability of the Scaffolds
4.2.4. Evaluation of Degradation and Swelling
4.2.5. Evaluation of Surface Morphology
4.2.6. Cell Viability
4.2.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanif, A.; Qureshi, S.; Sheikh, Z.; Rashid, H. Complications in implant dentistry. Eur. J. Dent. 2017, 11, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EzEldeen, M.; Wyatt, J.; Al-Rimawi, A.; Coucke, W.; Shaheen, E.; Lambrichts, I.; Willems, G.; Politis, C.; Jacobs, R. Use of CBCT Guidance for Tooth Autotransplantation in Children. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, F.; Wang, W.; Ding, Y.; Li, D.; Jin, Y. Regeneration of dental pulp/dentine complex with a three-dimensional and scaffold-free stem-cell sheet-derived pellet. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakaram-Tafti, A.; Mehrabani, D.; Shaterzadeh-Yazdi, H.; Zamiri, B.; Omidi, M. Tissue Engineering in Maxillary Bone Defects. World J. Plast. Surg. 2018, 7, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Abou Neel, E.A.; Chrzanowski, W.; Salih, V.M.; Kim, H.-W.; Knowles, J.C. Tissue engineering in dentistry. J. Dent. 2014, 42, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.-M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; An, Y.; Chen, F.; Wu, Z.-F. A review on endogenous regenerative technology in periodontal regenerative medicine. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7892–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.R.; Lee, D.H.; Chung, P.-H.; Yang, H.-C. Distinct differentiation properties of human dental pulp cells on collagen, gelatin, and chitosan scaffolds. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2009, 108, e94–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grawish, M.E.; Grawish, L.M.; Grawish, H.M.; Grawish, M.M.; El-Negoly, S.A. Challenges of Engineering Biomimetic Dental and Paradental Tissues. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 17, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Zaky, S.; Ray, H.; Sfeir, C. Porous magnesium/PLGA composite scaffolds for enhanced bone regeneration following tooth extraction. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Ren, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhuang, C.; Wu, T.; Qin, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Qi, N. Improved osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in a layer-by-layer-modified gelatin scaffold. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 33, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Vazirzadeh, M.; Zohaib, S.; Najeeb, B.; Sefat, F. Potential of Electrospun Nanofibers for Biomedical and Dental Applications. Materials 2016, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groll, J.; Burdick, J.A.; Cho, D.W.; Derby, B.; Gelinsky, M.; Heilshorn, S.C.; Jüngst, T.; Malda, J.; Mironov, V.A.; Nakayama, K.; et al. A definition of bioinks and their distinction from biomaterial inks. Biofabrication 2018, 11, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaszczyńska, A.; Moczulska-Heljak, M.; Gradys, A.; Sajkiewicz, P. Advances in 3D Printing for Tissue Engineering. Materials 2021, 14, 3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabi, M.; McConnell, M.; Cabral, J.; Ali, M.A. Chitosan hydrogels in 3D printing for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, A.-V.; Khorsand, B.; Geary, S.M.; Salem, A.K. 3D Printing of Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1742–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubo-Mateo, N.; Rodríguez-Lorenzo, L.M. Design of Thermoplastic 3D-Printed Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: Influence of Parameters of “Hidden” Importance in the Physical Properties of Scaffolds. Polymers 2020, 12, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Feng, C.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. 3D-printed bioceramic scaffolds: From bone tissue engineering to tumor therapy. Acta Biomater. 2018, 79, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.-W. Emerging properties of hydrogels in tissue engineering. J. Tissue Eng. 2018, 9, 2041731418768285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisken, C.; Kalyon, D.M.; Zhou, J.; Kim, S.G.; Mao, J.J. Viscoelastic Properties of Dental Pulp Tissue and Ramifications on Biomaterial Development for Pulp Regeneration. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, M.B.; Cereceres, S.N.; Luong, P.T.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E.M. Determination of the in vivo degradation mechanism of PEGDA hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 102, 4244–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoleru, E.; Dumitriu, R.P.; Ailiesei, G.-L.; Yilmaz, C.; Brebu, M. Synthesis of Bioactive Materials by In Situ One-Step Direct Loading of Syzygium aromaticum Essential Oil into Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Gels 2022, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarandona, I.; Bengoechea, C.; Álvarez-Castillo, E.; de la Caba, K.; Guerrero, A.; Guerrero, P. 3D Printed Chitosan-Pectin Hydrogels: From Rheological Characterization to Scaffold Development and Assessment. Gels 2021, 7, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salar Amoli, M.; Anand, R.; EzEldeen, M.; Amorim, P.A.; Geris, L.; Jacobs, R.; Bloemen, V. The development of a 3D printable chitosan-based copolymer with tunable properties for dentoalveolar regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 289, 119441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-L.; Jung, G.-Y.; Yoon, J.-H.; Han, J.-S.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, D.-G.; Zhang, M.; Kim, D.-J. Preparation and characterization of nano-sized hydroxyapatite/alginate/chitosan composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 54, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-Y.; Luo, L.-J. Chitosan-g-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) copolymers as delivery carriers for intracameral pilocarpine administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 113, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Li, L.; Leong, W.C.; Gan, L.H. Thermo-Responsive Association of Chitosan-graft-Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) in Aqueous Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 10666–10673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Witt, H.; Oswald, T.A.; Tarantola, M. Adhesion of Epithelial Cells to PNIPAm Treated Surfaces for Temperature-Controlled Cell-Sheet Harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 33516–33529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapeyre, V.; Ancla, C.; Catargi, B.; Ravaine, V. Glucose-responsive microgels with a core–shell structure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 327, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelle, A.R.; Horner, C.B.; Low, K.; Ico, G.; Nam, J. Electrospun thermosensitive hydrogel scaffold for enhanced chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2018, 66, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.A.; Martins, M.V.S.; Bressiani, A.H.; Bressiani, J.C.; Leyva, M.E.; de Queiroz, A.A.A. Electrochemical preparation and characterization of PNIPAM-HAp scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 81, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gialouri, A.; Saravanou, S.F.; Loukelis, K.; Chatzinikolaidou, M.; Pasparakis, G.; Bouropoulos, N. Thermoresponsive Alginate-Graft-pNIPAM/Methyl Cellulose 3D-Printed Scaffolds Promote Osteogenesis In Vitro. Gels 2023, 9, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patenaude, M.; Hoare, T. Injectable, Degradable Thermoresponsive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogels. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patras, G.; Qiao, G.G.; Solomon, D.H. On the mechanism of background silver staining during sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Jung, M.C.; Park, H.D.; Park, K.D.; Ryu, G.H. Synthesis and characterization of thermosensitive chitosan copolymer as a novel biomaterial. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2004, 15, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Cheng, T.-H. Thermo-Responsive Chitosan-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Injectable Hydrogel for Cultivation of Chondrocytes and Meniscus Cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheaburu-Yilmaz, C.N.; Yilmaz, O.; Aydin Kose, F.; Bibire, N. Chitosan-Graft-Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)/PVA Cryogels as Carriers for Mucosal Delivery of Voriconazole. Polymers 2019, 11, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, F.; Zheng, D.; Jia, L.; Feng, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, K.; Wang, F.; et al. Chitosan-g-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) based nanogels for tumor extracellular targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 409, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, M.; Li, G.; Yu, N.; Meng, Y.; Liu, X. Synthesis of thermo-sensitive polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles from CS-g-PNIPAM and SA-g-PNIPAM for controlled drug release. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslahi, N.; Abdorahim, M.; Simchi, A. Smart Polymeric Hydrogels for Cartilage Tissue Engineering: A Review on the Chemistry and Biological Functions. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3441–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, G.; Shen, J.; Duan, P.; Xia, X.; Chen, R.; Jin, B. Temperature-Sensitive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/Konjac Glucomannan/Graphene Oxide Composite Membranes with Improved Mechanical Property, Swelling Capability, and Degradability. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 7906747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, R.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, M. Regulating the degradation rate of silk fibroin films through changing the genipin crosslinking degree. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 109, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimida, S.; Barca, A.; Cancelli, N.; De Benedictis, V.; Raucci, M.G.; Demitri, C. Effects of Genipin Concentration on Cross-Linked Chitosan Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: Structural Characterization and Evidence of Biocompatibility Features. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 2017, 8410750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.V.; Molina, M.; Barbero, C.A. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Cross-Linked Gels as Intrinsic Amphiphilic Materials: Swelling Properties Used to Build Novel Interphases. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 9038–9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felfel, R.M.; Gideon-Adeniyi, M.J.; Zakir Hossain, K.M.; Roberts, G.A.F.; Grant, D.M. Structural, mechanical and swelling characteristics of 3D scaffolds from chitosan-agarose blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 204, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.; Salar Amoli, M.; Huysecom, A.-S.; Amorim, P.A.; Agten, H.; Geris, L.; Bloemen, V. A tunable gelatin-hyaluronan dialdehyde/methacryloyl gelatin interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel for additive tissue manufacturing. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 17, 045027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, Q.L.; Choong, C. Three-dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: Role of porosity and pore size. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2013, 19, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, D.; Gerlach, G. Studies on porosity in poly($N$-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels for fast-responsive piezoresistive microsensors. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2021, 10, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.-P.; Wang, Y.-J.; Ren, L.; Wu, G.; Caridade, S.G.; Fan, J.-B.; Wang, L.-Y.; Ji, P.-H.; Oliveira, J.M.; Oliveira, J.T.; et al. Genipin-cross-linked collagen/chitosan biomimetic scaffolds for articular cartilage tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 95, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Xiao, W.; Sun, J.; Zhong, M.; Guo, L.; Fan, H.; Zhang, X. A biocompatible hydrogel with improved stiffness and hydrophilicity for modular tissue engineering assembly. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2753–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanzari, I.; Buratti, E.; Huang, R.; Tusan, C.G.; Dinelli, F.; Evans, N.D.; Prodromakis, T.; Bertoldo, M. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) based thin microgel films for use in cell culture applications. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Tian, T.; Ma, Q.; Xue, C.; Lin, S.; Cai, X. Stiffness regulates the proliferation and osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells via the WNT signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilkens, P.; Gervois, P.; Fanton, Y.; Vanormelingen, J.; Martens, W.; Struys, T.; Politis, C.; Lambrichts, I.; Bronckaers, A. Effect of isolation methodology on stem cell properties and multilineage differentiation potential of human dental pulp stem cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2013, 353, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Chitosan/NIPAM Weightratio | APS (mol%) | MBA (mol%) | TEMED (μL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 4 | 0.5 | 25 |
| 1:2 | 4 | 0.5 | 25 |
| 1:3 | 4 | 0.5 | 25 |
| 1:1 | 4 | 1.25 | 25 |
| 1:2 | 4 | 1.25 | 25 |
| 1:3 | 4 | 1.25 | 25 |
| 1:1 | 4 | 2.45 | 25 |
| 1:2 | 4 | 2.45 | 25 |
| 1:3 | 4 | 2.45 | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salar Amoli, M.; Anand, R.; EzEldeen, M.; Geris, L.; Jacobs, R.; Bloemen, V. Development of 3D Printed pNIPAM-Chitosan Scaffolds for Dentoalveolar Tissue Engineering. Gels 2024, 10, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10020140
Salar Amoli M, Anand R, EzEldeen M, Geris L, Jacobs R, Bloemen V. Development of 3D Printed pNIPAM-Chitosan Scaffolds for Dentoalveolar Tissue Engineering. Gels. 2024; 10(2):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10020140
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalar Amoli, Mehdi, Resmi Anand, Mostafa EzEldeen, Liesbet Geris, Reinhilde Jacobs, and Veerle Bloemen. 2024. "Development of 3D Printed pNIPAM-Chitosan Scaffolds for Dentoalveolar Tissue Engineering" Gels 10, no. 2: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10020140
APA StyleSalar Amoli, M., Anand, R., EzEldeen, M., Geris, L., Jacobs, R., & Bloemen, V. (2024). Development of 3D Printed pNIPAM-Chitosan Scaffolds for Dentoalveolar Tissue Engineering. Gels, 10(2), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10020140