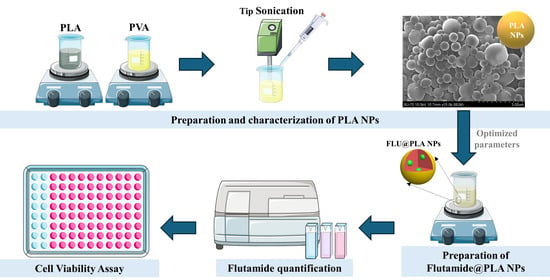
Optimized Synthesis of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanoparticles for the Encapsulation of Flutamide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Influence of PLA’s Molecular Weight
2.2. Influence of the Stirring Methodology
2.3. Influence of PLA Concentration
2.4. Influence of the PVA Concentration
2.5. Synthesis of the FLU@PLA NPs and Determination of the Encapsulation Efficiency
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Materials, and Cells
4.2. Preparation of PLA NPs
4.3. Preparation of FLU@PLA NPs
4.4. Characterization Methods
4.5. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. 84 Nat nanotech 2007 R Langer Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy.pdf. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, J.P.J.; Li, X. Role of Nanotechnology and Their Perspectives in the Treatment of Kidney Diseases. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayda, S.; Adeel, M.; Tuccinardi, T.; Cordani, M.; Rizzolio, F. The History of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: From Chemical–Physical Applications to Nanomedicine. Molecules 2019, 25, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, A.; Giuliano, E.; Venkateswararao, E.; Fresta, M.; Bulotta, S.; Awasthi, V.; Cosco, D. Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery to Solid Tumors. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 601626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M. Nanomaterials: Types, properties, recent advances, and toxicity concerns. In Current Opinion in Environmental Science and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 25, p. 100319. [Google Scholar]
- Thévenot, C.; Khoukh, A.; Reynaud, S.; Desbrières, J.; Grassl, B. Kinetic aspects, rheological properties and mechanoelectrical effects of hydrogels composed of polyacrylamide and polystyrene nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitta, S.K.; Numata, K. Biopolymer-based nanoparticles for drug/gene delivery and tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1629–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Ma, G.; Yuan, Z.; Qian, H.; Xu, L.; Sidransky, E.; Chen, S. Development of Zwitterionic Polypeptide Nanoformulation with High Doxorubicin Loading Content for Targeted Drug Delivery. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, M.C.; Jony, B.; Nandy, P.K.; Chowdhury, R.A.; Halder, S.; Kumar, D.; Ramakrishna, S.; Hassan, M.; Ahsan, A.; Hoque, E.; et al. Recent Advancement of Biopolymers and Their Potential Biomedical Applications. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Oluwafemi, O.S.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S.; Songca, S.P. Biopolymers—Application in Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. Recent Adv. Biopolym. 2016, 1, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- De Albuquerque, T.L.; Marques Júnior, J.E.; de Queiroz, L.P.; Ricardo, A.D.S.; Rocha, M.V.P. Polylactic acid production from biotechnological routes: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 933–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maduka, C.V.; Alhaj, M.; Ural, E.; Habeeb, O.M.; Kuhnert, M.M.; Smith, K.; Makela, A.V.; Pope, H.; Chen, S.; Hix, J.M.; et al. Polylactide Degradation Activates Immune Cells by Metabolic Reprogramming. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2304632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, F.; Ramezani Dana, H. Poly lactic acid (PLA) polymers: From properties to biomedical applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2021, 71, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hajleh, M.N.; AL-Samydai, A.; Al-Dujaili, E.A.S. Nano, micro particulate and cosmetic delivery systems of polylactic acid: A mini review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 2805–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefaniak, K.; Masek, A. Green Copolymers Based on Poly(Lactic Acid)—Short Review. Materials 2021, 14, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundel, R.; Thakur, T.; Chatterjee, M. Emerging uses of PLA–PEG copolymer in cancer drug delivery. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casalini, T.; Rossi, F.; Castrovinci, A.; Perale, G. A Perspective on Polylactic Acid-Based Polymers Use for Nanoparticles Synthesis and Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, E.; Orozco, V.H.; Hoyos, L.M.; Giraldo, L.F. Study of sonication parameters on PLA nanoparticles preparation by simple emulsion-evaporation solvent technique. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 173, 111307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.K.; Yun, Y.; Park, K. PLA micro- and nano-particles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, P.; Chen, C.; Hao, L.; Zhu, C.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Z. A novel sonication route to prepare anthracene nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2004, 39, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, S.; Niakousari, M.; Mohsenpour, Z. Production of tapioca starch nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation-sonication treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pencheva, D.; Bryaskova, R.; Kantardjiev, T. Polyvinyl alcohol/silver nanoparticles (PVA/AgNps) as a model for testing the biological activity of hybrid materials with included silver nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2048–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhujwalla, Z.; Krishnamachary, B.; Penet, M.F.; Glunde, K.; Serkova, N.J.; Eckhardt, S.G. Metabolic imaging to Assess Treatment Response to Cytotoxic and Cytostatic Agents. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 152. [Google Scholar]
- Kummar, S.; Gutierrez, M.; Doroshow, J.H.; Murgo, A.J. Drug development in oncology: Classical cytotoxics and molecularly targeted agents. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 62, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eitel, A.; Scherrer, M.; Kümmerer, K. Handling Cytostatic Drugs, a Practical Guide; Bristol-Myers-Squibb: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fossa, S.D.; Slee, P.T.; Brausi, M.; Horenblas, S.; Hall, R.R.; Hetherington, J.W.; de Prijck, A.L.; Collette, L. Flutamide versus Prednisone in Patients with Prostate Cancer Symptomatically Progressing After Androgen-Ablative Therapy: A Phase III Study of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Genitourinary Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanomaterials definition matters. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 193. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippov, S.K.; Khusnutdinov, R.; Murmiliuk, A.; Inam, W.; Zakharova, L.Y.A.; Zhang, H.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Dynamic light scattering and transmission electron microscopy in drug delivery: A roadmap for correct characterization of nanoparticles and interpretation of results. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 5354–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, E.; Sah, H. Recent trends in preparation of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles by mixing polymeric organic solution with antisolvent. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 794601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Shin, J.H.; Archer, L.A. Structure and rheology of nanoparticle–polymer suspensions. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 4097–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela-Noguera, V.; Alfonso, M.; Amorós, P.; Aznar, E.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Máñez, R. In-depth study of factors affecting the formation of MCM-41-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 363, 112840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Mäder, K.; Gohla, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—A review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, X.; Ding, T.; Sun, X.; Liu, D. Ultrasound effects on the degradation kinetics, structure and rheological properties of apple pectin. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2013, 20, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumitomo, S.; Koizumi, H.; Uddin, M.d.A.; Kato, Y. Comparison of dispersion behavior of agglomerated particles in liquid between ultrasonic irradiation and mechanical stirring. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2018, 40, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharana, T.; Mohanty, B.; Negi, Y.S. Preparation of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanoparticles and Optimization of the Particle Size. Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. Phys. Chem. 2010, 2, P100–P109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.N.; Brown, P.; Rogers, S.E.; Eastoe, J. Evidence for a Critical Micelle Concentration of Surfactants in Hydrocarbon Solvents. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3252–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazawa, T.; Itaya, M.; Burdeos, G.C.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyazawa, T. A critical review of the use of surfactant-coated nanoparticles in nanomedicine and food nanotechnology. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 3937–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibowski, S.; Paszkiewicz, M.; Krupa, M. Investigation of the influence of the polyvinyl alcohol adsorption on the electrical properties of Al2O3–solution interface, thickness of the adsorption layers of PVA. Powder Technol. 2000, 107, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleimann, J.; Gehin-Delval, C.; Auweter, H.; Borkovec, M. Super-stoichiometric charge neutralization in particle-polyelectrolyte systems. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3688–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.C.L.; Al-Jamal, W.T. Sterically stabilized liposomes production using staggered herringbone micromixer: Effect of lipid composition and PEG-lipid content. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, N.; Hornok, V.; Janovák, L.; Dékány, I.; Csapó, E. The effect of synthesis conditions and tunable hydrophilicity on the drug encapsulation capability of PLA and PLGA nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 176, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miraj, S.; Saeed, H.; Iqtedar, M.; Albekairi, N.A.; Ahmed, N.; Danish, M.Z.; Islam, M.; Rasool, M.F.; Deen, K.M.; Rathore, H.A. Docetaxel-Loaded Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-poly (L-lactic Acid) Nanoparticles for Breast Cancer: Synthesis, Characterization, Method Validation, and Cytotoxicity. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Lueje, A.; Peña, C.; Núñez-Vergara, L.J.; Squella, J.A. Electrochemical Study of Flutamide, an Anticancer Drug, and Its Polarographic, UV Spectrophotometric and HPLC Determination in Tablets. Electroanalysis 1998, 10, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Turnbull, T.; Sebastian, S.; Kempson, I. The mtt assay: Utility, limitations, pitfalls, and interpretation in bulk and single-cell analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riss, T.L.; Moravec, R.A.; Niles, A.L.; Duellman, S.; Benink, H.A.; Worzella, T.J.; Minor, L. Cell Viability Assays. In The Assay Guidance Manual; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Sun, C.; Xue, Y.; Liu, C.; Qiu, D.; Cui, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, H.; Zeng, H. Tannic acid-based nanopesticides coating with highly improved foliage adhesion to enhance foliar retention. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27096–27104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Sample | Diameter (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA TS | 538 ± 265 | 0.243 | −26.0 ± 1.3 | 6.15 |
| PLA UT | 365 ± 137 | 0.141 | −10.1 ± 0.2 | 6.47 |
| Sample | Diameter (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA1 | 287 ± 9 | 0.218 | −18.4 ± 1.7 | 6.50 |
| PLA10 | 267 ± 1 | 0.089 | −13.4 ± 0.4 | 6.17 |
| PLA50 | 295 ± 1 | 0.147 | −12.6 ± 0,3 | 6.20 |
| Sample | Diameter (nm) | PDI | Ζeta Potential (mV) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA0.1 | 482 ± 26 | 0.374 | −25.7 ± 0.4 | 6.45 |
| PVA2.5 | 336 ± 2 | 0.161 | −14.0 ± 0.3 | 6.38 |
| PVA10 | 502 ± 6 | 0.209 | −17.0 ± 0.2 | 6.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeida, D.; Dias, M.; Teixeira, B.; Frazão, C.; Almeida, M.; Gonçalves, G.; Oliveira, M.; Pinto, R.J.B. Optimized Synthesis of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanoparticles for the Encapsulation of Flutamide. Gels 2024, 10, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040274
Almeida D, Dias M, Teixeira B, Frazão C, Almeida M, Gonçalves G, Oliveira M, Pinto RJB. Optimized Synthesis of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanoparticles for the Encapsulation of Flutamide. Gels. 2024; 10(4):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040274
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeida, Duarte, Mariana Dias, Beatriz Teixeira, Carolina Frazão, Mónica Almeida, Gil Gonçalves, Miguel Oliveira, and Ricardo J. B. Pinto. 2024. "Optimized Synthesis of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanoparticles for the Encapsulation of Flutamide" Gels 10, no. 4: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040274
APA StyleAlmeida, D., Dias, M., Teixeira, B., Frazão, C., Almeida, M., Gonçalves, G., Oliveira, M., & Pinto, R. J. B. (2024). Optimized Synthesis of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanoparticles for the Encapsulation of Flutamide. Gels, 10(4), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040274