Polymeric Dural Biomaterials in Spinal Surgery: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanics and Evolution of Dural Adhesion
3. Natural-Hydrogel-Based Biomaterials
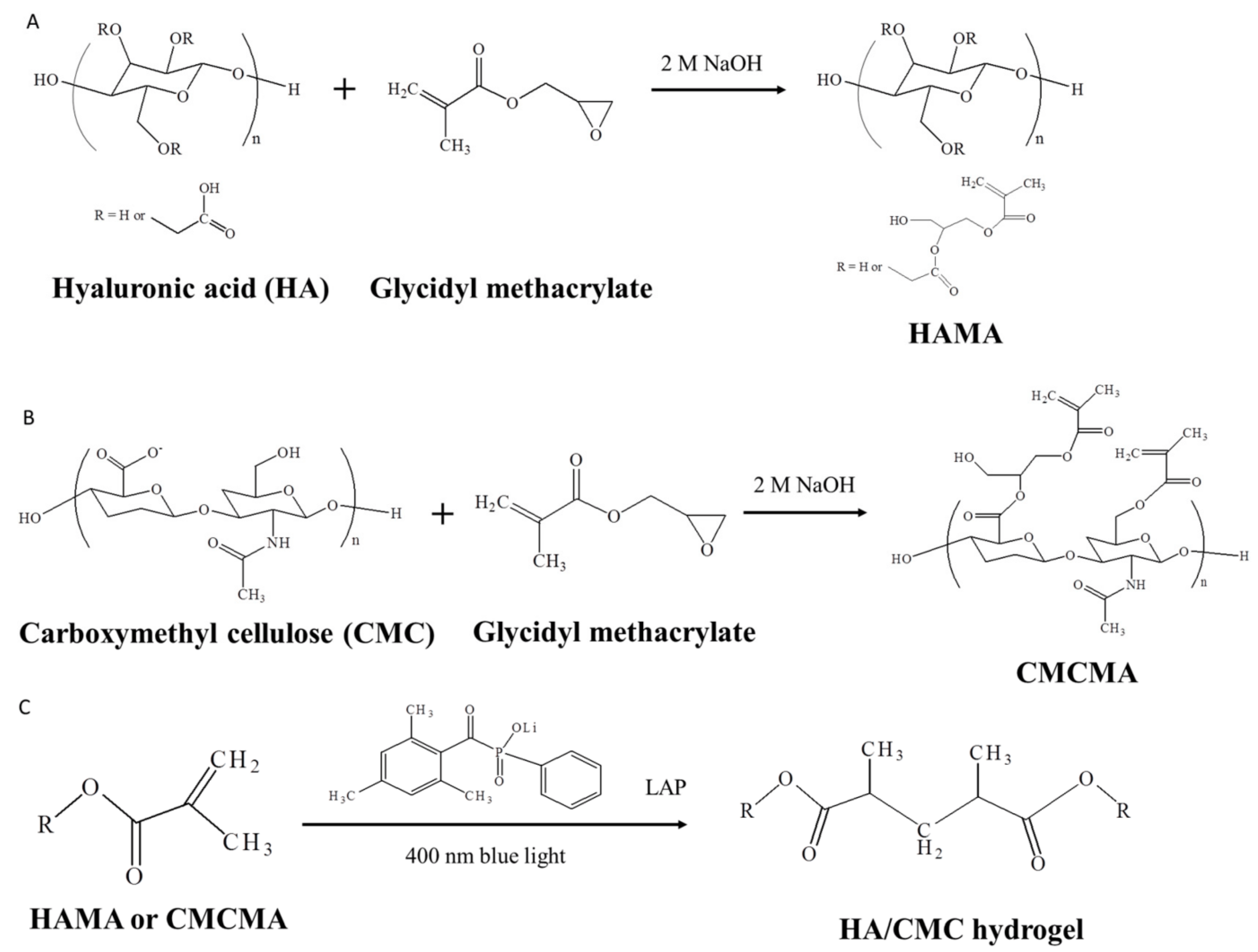
3.1. Hyaluronic Acid
3.2. Chitosan
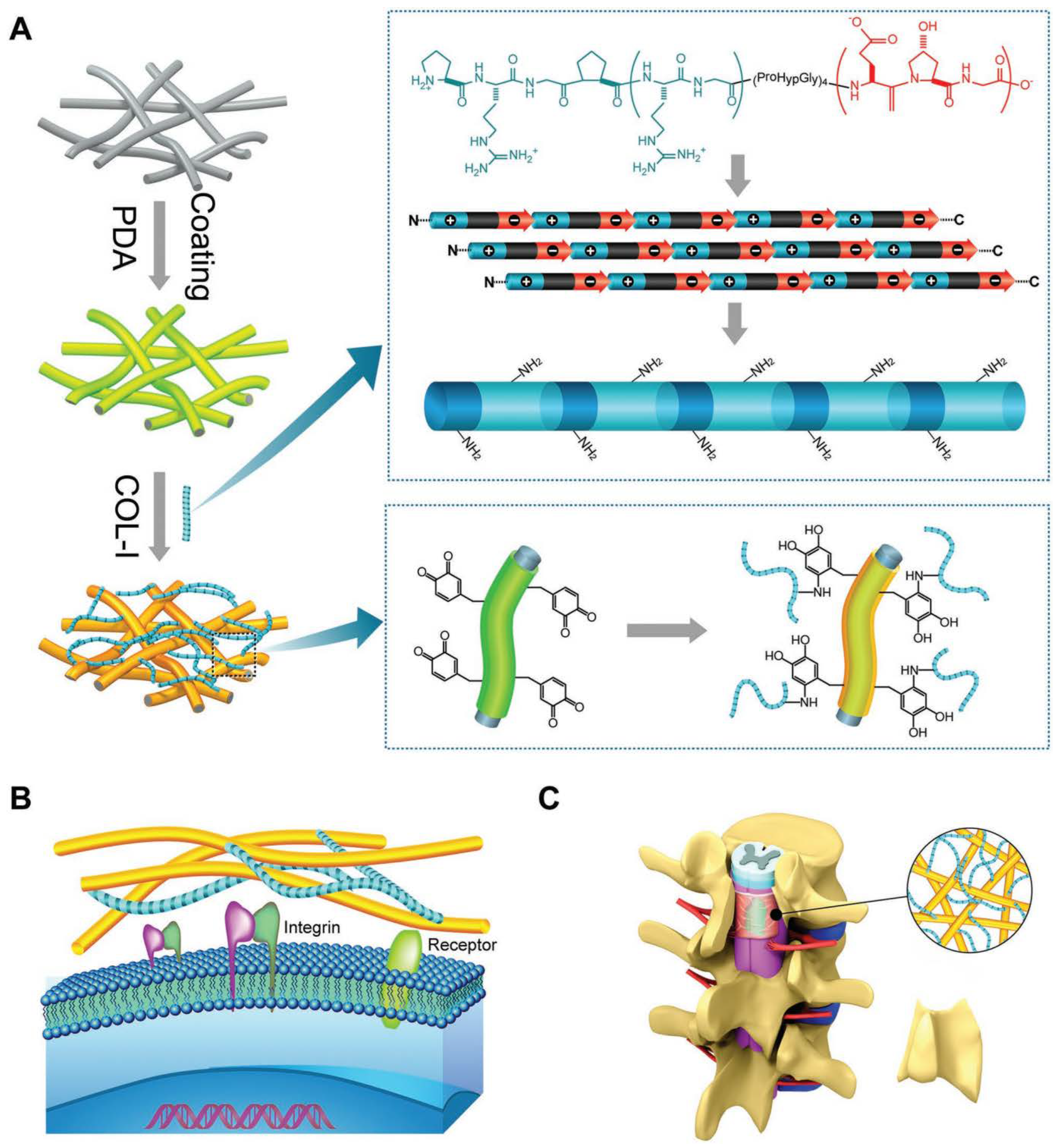
3.3. Collagen
4. Synthetic Polymer-Based Biomaterials
4.1. PLGA
4.2. PCL
4.3. PEG
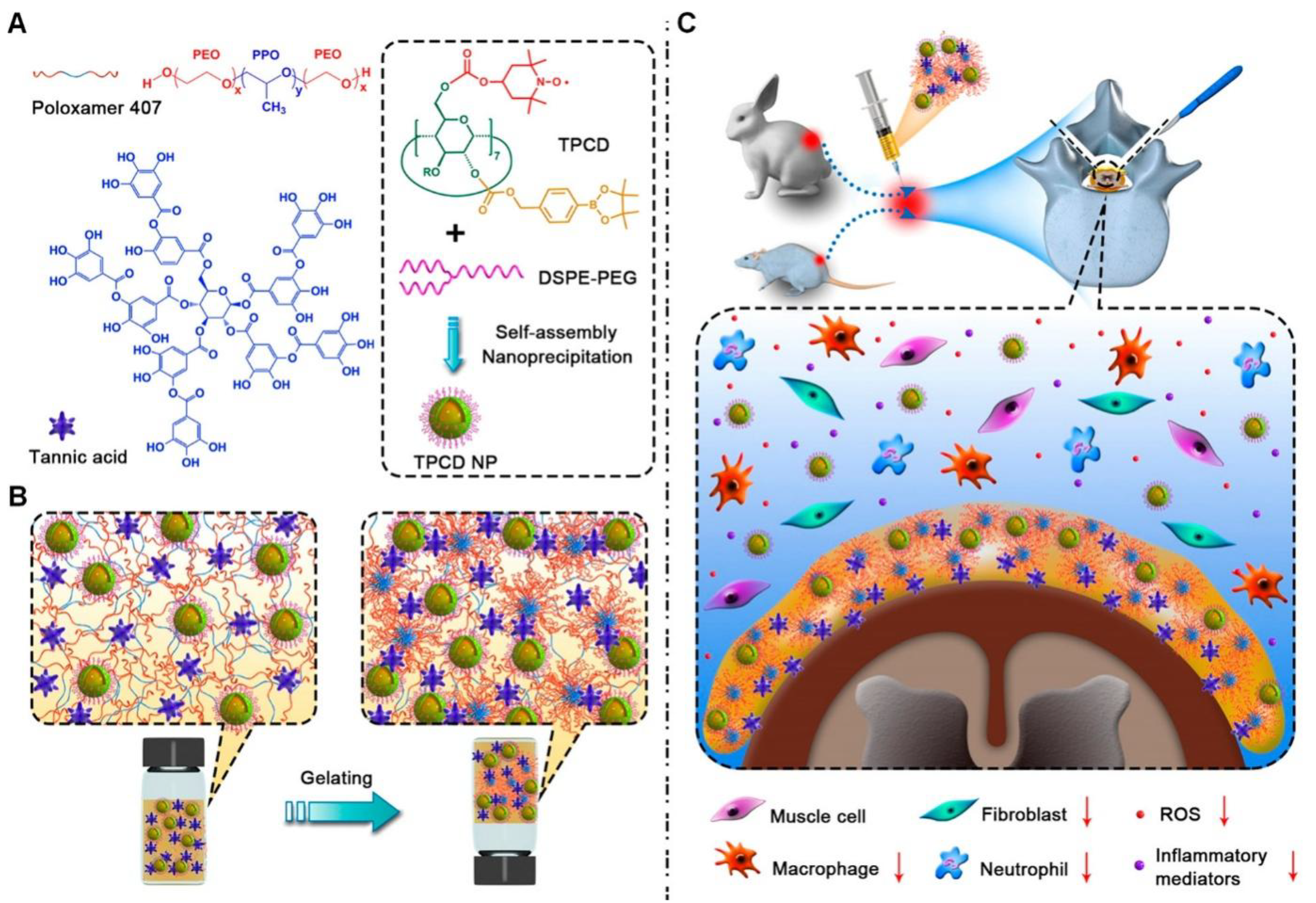
5. Other Strategies
6. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knezevic, N.N.; Candido, K.D.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S.; Van Zundert, J.; Cohen, S.P. Low back pain. Lancet 2021, 398, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, N.; Emanski, E.; Knaub, M.A. Acute and chronic low back pain. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 98, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijs, J.; Kosek, E.; Chiarotto, A.; Cook, C.; Danneels, L.A.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Hodges, P.W.; Koes, B.; Louw, A.; Ostelo, R.; et al. Nociceptive, neuropathic, or nociplastic low back pain? The low back pain phenotyping (BACPAP) consortium’s international and multidisciplinary consensus recommendations. Lancet Rheumatol. 2024, 6, e178–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.L.B.P. Global, regional, and national burden of low back pain, 1990–2020, its attributable risk factors, and projections to 2050: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e316–e329. [Google Scholar]
- Ghogawala, Z.; Dziura, J.; Butler, W.E.; Dai, F.; Terrin, N.; Magge, S.N.; Coumans, J.-V.C.; Harrington, J.F.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; Schwartz, J.S.; et al. Laminectomy plus Fusion versus Laminectomy Alone for Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1424–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.S.; Xu, A.; Ansari, K.; Hardacker, K.; Anderson, G.; Alsoof, D.; Daniels, A.H. Lumbar Disc Herniation: Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Med. 2023, 136, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.N.; Zimmerman, Z.E.; Mass, H.; Makhni, M.C. Diagnosis and Management of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Review. JAMA 2022, 327, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgeson, M.D.; Pisano, A.J.; Fredericks, D.R., Jr.; Wagner, S.C. What’s New in Spine Surgery. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2023, 105, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazard, R.G. Failed back surgery syndrome: Surgical and nonsurgical approaches. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2006, 443, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.F.; Chong, V.F. MRI findings in failed back surgery syndrome. Med. J. Malays. 1995, 50, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, H.; Liao, B.; Qian, J.; Yan, X. Comparative study on the technique and efficacy of microscope-assisted MI-TLIF and naked-eye MI-TLIF in lumbar revision surgery. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, J.A.; Ford, L.T. Experimental intervertebral-disc lesions. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1948, 30, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRocca, H.; Macnab, I. The laminectomy membrane. Studies in its evolution, characteristics, effects and prophylaxis in dogs. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1974, 56, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.T. Role of peridural fibrosis in the failed back: A review. Eur. Spine J. 1996, 5 (Suppl. S1), S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.; Kwon, W.K.; Kim, J.H.; Park, Y.K.; Yoon, W.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, T.H.; Moon, H.J. Inflammation by activated macrophage-like THP-1 cells increases human dura mater cell adhesion with alteration of integrin alpha(2) beta(1) and matrix metalloproteinase. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmez, H.; Kardes, O.; Dogulu, F.; Kurt, G.; Memis, L.; Baykaner, M.K. Role of antifibrotic cytokine interferon-gamma in the prevention of postlaminectomy peridural fibrosis in rats. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 1351–1357; discussion 1357–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswell, M.V.; Trescot, A.M.; Datta, S.; Schultz, D.M.; Hansen, H.C.; Abdi, S.; Sehgal, N.; Shah, R.V.; Singh, V.; Benyamin, R.M.; et al. Interventional techniques: Evidence-based practice guidelines in the management of chronic spinal pain. Pain. Physician 2007, 10, 7–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Shen, W.; Qiao, C.; Ambrosio, F.; Lavasani, M.; Nozaki, M.; Branca, M.F.; Huard, J. Relationships between transforming growth factor-beta1, myostatin, and decorin: Implications for skeletal muscle fibrosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 25852–25863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, S.; Liu, B.; Wu, N.; Cao, X. The effect of 10-hydroxycamptothecine in preventing fibroblast proliferation and epidural scar adhesion after laminectomy in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 593, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ni, B.; Liu, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, W. Application of liposome-encapsulated hydroxycamptothecin in the prevention of epidural scar formation in New Zealand white rabbits. Spine J. 2011, 11, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Stenzel, W.; Ebel, H.; Wedekind, C.; Ernestus, R.-I.; Klug, N. Mitomycin C in preventing spinal epidural fibrosis in a laminectomy model in rats. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Stenzel, W.; Löhr, M.; Stützer, H.; Ernestus, R.-I.; Klug, N. The role of mitomycin C in reducing recurrence of epidural fibrosis after repeated operation in a laminectomy model in rats. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2006, 4, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y. Pirfenidone inhibits fibroblast proliferation, migration or adhesion and reduces epidural fibrosis in rats via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 547, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Pan, G.; Liu, G.; Neves, J.D.; Song, S.; Chen, S.; Cheng, B.; Sun, Z.; Sarmento, B.; Cui, W.; et al. Electrospun fibrous membranes featuring sustained release of ibuprofen reduce adhesion and improve neurological function following lumbar laminectomy. J. Control Release 2017, 264, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yan, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, D.; Zhu, G.; Liang, Y. Methotrexate prevents epidural fibrosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 796, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, V.; Kancherla, Y.; Igram, C.M.; Pugely, A.J.; Salem, A.K.; Shin, K.; Lim, T.-H.; Seol, D. Pharmacotherapies to prevent epidural fibrosis after laminectomy: A systematic review of in vitro and in vivo animal models. Spine J. 2023, 23, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, J.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Wu, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, P. First-Aid Hydrogel Wound Dressing with Reliable Hemostatic and Antibacterial Capability for Traumatic Injuries. Adv. Health Mater. 2023, 12, e2300312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabaharan, M.; Mano, J.F. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels based on polysaccharides incorporated with thermo-responsive polymers as novel biomaterials. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 991–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunamaker, E.A.; Kipke, D.R. An alginate hydrogel dura mater replacement for use with intracortical electrodes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 95, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Hydrogel-Based Biomaterials Engineered from Natural-Derived Polysaccharides and Proteins for Hemostasis and Wound Healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 780187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tang, X.; Jia, Y.; Ho, C.-T.; Huang, Q. Applications and delivery mechanisms of hyaluronic acid used for topical/transdermal delivery—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 578, 119127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdick, J.A.; Prestwich, G.D. Hyaluronic acid hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, H41–H56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jeong, H.; Han, S.; Beack, S.; Hwang, B.W.; Shin, M.; Oh, S.S.; Hahn, S.K. Hyaluronate and its derivatives for customized biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2017, 123, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.E.; Cui, H.; Ballios, B.G.; Ing, S.; Yan, P.; Wolfer, J.; Wright, T.; Dang, M.; Gan, N.Y.; Cooke, M.J.; et al. Stable oxime-crosslinked hyaluronan-based hydrogel as a biomimetic vitreous substitute. Biomaterials 2021, 271, 120750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ke, H.; Lei, X.; Zhang, J.; Wen, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, H.; Yao, J.; Wang, X.; Wei, Z.; et al. Controlled-release hydrogel loaded with magnesium-based nanoflowers synergize immunomodulation and cartilage regeneration in tendon-bone healing. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 36, 62–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Liu, Z.-H.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-P. Photo-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite Hydrogel as a Dural Substitute to Prevent Post-Surgical Adhesion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwapiszewska, G.; Gungl, A.; Wilhelm, J.; Marsh, L.M.; Puthenparampil, H.T.; Sinn, K.; Didiasova, M.; Klepetko, W.; Kosanovic, D.; Schermuly, R.T.; et al. Transcriptome profiling reveals the complexity of pirfenidone effects in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Peng, H.-H.; Chen, M.-H.; Sun, J.-S.; Chang, C.-J.; Liu, T.-Y.; Chen, M.-H. Ibuprofen-conjugated hyaluronate/polygalacturonic acid hydrogel for the prevention of epidural fibrosis. J. Biomater. Appl. 2016, 30, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, T.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, R.; Wan, Q.; Xu, R. Design and Fabrication of Nanofibrous Dura Mater with Antifibrosis and Neuroprotection Effects on SH-SY5Y Cells. Polymers 2022, 14, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zha, L.; Jin, L.; Zhang, L. Nanofiber Hydrogel Drug Delivery System for Prevention of Postsurgical Intestinal Adhesion. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 3164–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajiv, S.; Drilling, A.; Bassiouni, A.; Harding, M.; James, C.; Robinson, S.; Moratti, S.; Wormald, P.-J. Chitosan Dextran gel as an anti adhesion agent in a postlaminectomy spinal sheep model. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 40, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; So, J.; Min, K. Anti-adhesive effect of poloxamer-based thermo-sensitive sol-gel in rabbit laminectomy model. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, J.; Li, C.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y. A hydrogel spinal dural patch with potential anti-inflammatory, pain relieving and antibacterial effects. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 14, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vediappan, R.S.; Mascarenhas, A.; Nguyen-Hoang, A.; Fong, S.A.; Jukes, A.; Richter, K.; Bassiouni, A.; Patel, S.; Chryssidis, S.; Otto, S.; et al. Prevention of peridural adhesions in spinal surgery: Assessing safety and efficacy of Chitogel with Deferiprone in a sheep model. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 72, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monica, F.; Campora, S.; Ghersi, G. Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Chronic Skin Wound Treatment. Gels 2024, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Li, L.; Bian, Q.; Xue, B.; Jin, J.; Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Li, H. Cartilage-like protein hydrogels engineered via entanglement. Nature 2023, 618, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itai, S.; Onoe, H. Flexibly Deformable Collagen Hydrogel Tube Reproducing Immunological Tissue Deformation of Blood Vessels as a Pharmacokinetic Testing Model. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2101509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; He, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Yuan, T.; Xiao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X. Icariin conjugated hyaluronic acid/collagen hydrogel for osteochondral interface restoration. Acta Biomater. 2018, 74, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Gu, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, B.; Chen, L. Hierarchical Micro/Nanofibrous Bioscaffolds for Structural Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Li, S.; Xi, K.; Tang, J.; Shen, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Zhang, N.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. ECM-engineered electrospun fibers with an immune cascade effect for inhibiting tissue fibrosis. Acta Biomater. 2023, 171, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
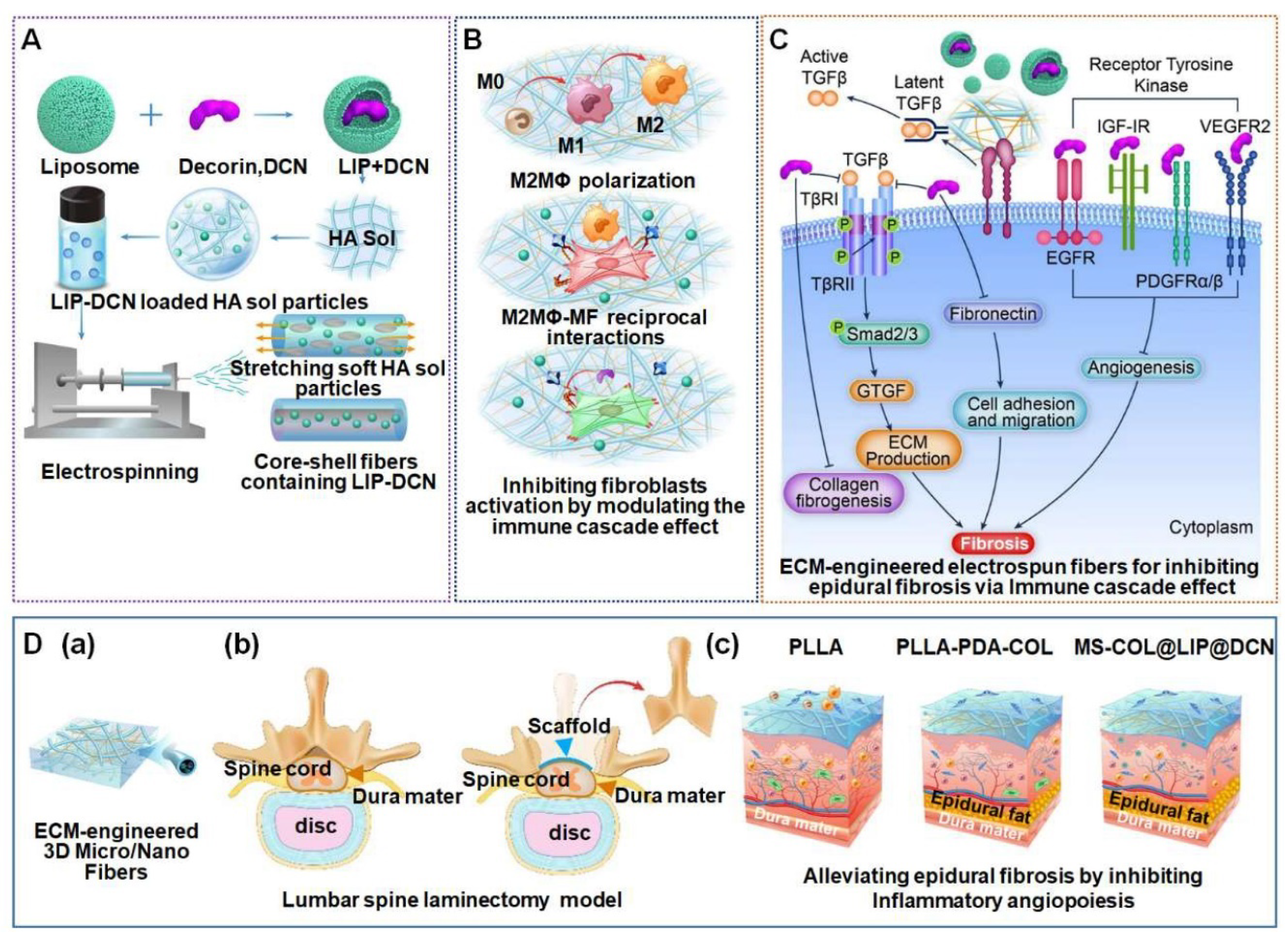
- Ding, Q.; Wei, Q.; Sheng, G.; Wang, S.; Jing, S.; Ma, T.; Zhang, R.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Tang, X.; et al. The Preventive Effect of Decorin on Epidural Fibrosis and Epidural Adhesions After Laminectomy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 774316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.; Corrigan, N.; Wong, E.H.H.; Boyer, C. Bioactive Synthetic Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amani, H.; Kazerooni, H.; Hassanpoor, H.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Pazoki-Toroudi, H. Tailoring synthetic polymeric biomaterials towards nerve tissue engineering: A review. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3524–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiryaghoubi, N.; Fathi, M.; Pesyan, N.N.; Samiei, M.; Barar, J.; Omidi, Y. Bioactive polymeric scaffolds for osteogenic repair and bone regenerative medicine. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 1833–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhudaithi, S.S.; Kalam, M.A.; Binobaid, L.; Ali, R.; Almutairi, M.M.; Qamar, W.; Bin Hithlayn, H.; Almutairi, A.; Alshememry, A.K. Sorafenib and Piperine co-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: Development, characterization, and anti-cancer activity against hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Saudi Pharm. J. 2024, 32, 102064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.V.; Gonçalves, V.; da Silva, M.C.; Bañobre-López, M.; Gallo, J. PLGA-Based Composites for Various Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Rachid, O.; Alkawareek, M.Y.; Billa, N.; Daou, A.; Murphy, C.J. PLGA-Gold Nanocomposite: Preparation and Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Wu, H.; Kong, Q. Superhydrophilic PLGA-Graft-PVP/PC Nanofiber Membranes for the Prevention of Epidural Adhesion. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 1423–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Yin, J.; Cui, L.; Chen, Z. The prevention effect of poly (L-glutamic acid)/chitosan on spinal epidural fibrosis and peridural adhesion in the post-laminectomy rabbit model. Eur. Spine J. 2014, 23, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Hu, B.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Cao, P.; Wu, X.; Liang, L.; Zang, F.; et al. Continuous release of mefloquine featured in electrospun fiber membranes alleviates epidural fibrosis and aids in sensory neurological function after lumbar laminectomy. Mater. Today Bio. 2022, 17, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Gould, M.; Ali, M.A. Fabrication and characterisation of melt-extruded chitosan/keratin/PCL/PEG drug-eluting sutures designed for wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 120, 111696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, K.S.; Costello, K.E.; O’Brien, L.; Wijdicks, C.A.; Laprade, R.F. A historical perspective of PCL bracing. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2013, 21, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrychowski, J.; Frontczak-Baniewicz, M.; Sulejczak, D.; Kowalczyk, T.; Chmielewski, T.; Czernicki, Z.; Kowalewski, T.A. Nanofiber nets in prevention of cicatrization in spinal procedures. Experimental study. Folia Neuropathol. 2013, 51, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Gong, M.; Tian, W.; Zhang, L. Effective delivery of mitomycin-C and meloxicam by double-layer electrospun membranes for the prevention of epidural adhesions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2020, 108, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shi, R.; Gong, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Song, Q.; Wu, C.; Tian, W. Icariin-loaded electrospun PCL/gelatin sub-microfiber mat for preventing epidural adhesions after laminectomy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4831–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.; Ajazuddin Khan, J.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S. Poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) based thermosensitive injectable hydrogels for biomedical applications. J. Control Release 2013, 172, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Kunduru, K.R.; Doppalapudi, S.; Domb, A.J.; Khan, W. Poly(lactic acid) based hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Dong, A.; Song, J.; Chen, X. Injectable thermosensitive hydrogel systems based on functional PEG/PCL block polymer for local drug delivery. J. Control Release 2019, 297, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simińska-Stanny, J.; Nicolas, L.; Chafai, A.; Jafari, H.; Hajiabbas, M.; Dodi, G.; Gardikiotis, I.; Delporte, C.; Nie, L.; Podstawczyk, D.; et al. Advanced PEG-tyramine biomaterial ink for precision engineering of perfusable and flexible small-diameter vascular constructs via coaxial printing. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 36, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, E.; Aydin, H.A.; Kalayci, M.; Işik, E.; Özgen, U.; Şimşek, K.; Baklaci, D.; Gökçe, M. The histopathological effects of reabsorbable polyethylene glycol hydrogel (Coseal) on epidural fibrosis in an experimental postlaminectomy model in rats. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, L.; Lin, H.; Cao, L.; Cheng, J.; Dong, J.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. Efficacy of Poly(D,L-Lactic Acid-co-Glycolic acid)-Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Poly(D,L-Lactic Acid-co-Glycolic Acid) Thermogel As a Barrier to Prevent Spinal Epidural Fibrosis in a Postlaminectomy Rat Model. Clin. Spine Surg. 2017, 30, E283–E290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Lin, T.-C.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Wey, S.-L.; Lin, F.-H.; Yang, K.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Hu, M.-H. Antifibrotic Effect of Bletilla striata Polysaccharide-Resveratrol-Impregnated Dual-Layer Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Sponge for The Prevention of Epidural Fibrosis after Laminectomy. Polymers 2021, 13, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Pu, W.; Huang, B.; Wen, X.; Cao, X.; et al. Multifunctional Supramolecular Hydrogel for Prevention of Epidural Adhesion after Laminectomy. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8202–8219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, K.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X. Effect of surface microstructure on the anti-fibrosis/adhesion of hydroxyapatite ceramics in spinal repair of rabbits. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 2629–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, L.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, W.; Ou, Y.; Quan, Z.; Jiang, D. Clinical Use of a New Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Polyamide66 Composite Artificial Lamina in Spinal Decompression Surgery: More Than 4 Years’ Follow-Up. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 5573–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andia, I.; Abate, M. Platelet-rich plasma: Underlying biology and clinical correlates. Regen. Med. 2013, 8, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, C. Application of platelet-rich plasma in spinal surgery. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1138255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelak, A.; Hnydka, A.; Higuchi, J.; Michalak, A.; Tarczynska, M.; Gaweda, K.; Klimek, K. Recent Achievements in the Development of Biomaterials Improved with Platelet Concentrates for Soft and Hard Tissue Engineering Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Du, W.; Ding, Z.; Liu, J.; Ding, Y. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy combined with platelet-rich plasma injection for lumbar disc herniation: Analysis of clinical and imaging outcomes. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keser, N.; Is, M.; Ceman, D.; Somay, A. Locally Used Antibiotics for Spinal Infection Prophylaxis and Their Effects on Epidural Fibrosis: An Experimental Laminectomy Study in Rats Using Rifamycin and Gentamycin. Inflammation 2019, 42, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkurt, I.; Bakar, B.; Dincel, G.C.; Yıldıran, F.A.B.; Ogden, M.; Nursoy, E.; Sari, E. Effectiveness of the Biophysical Barriers to the Peridural Fibrosis in Rat Laminectomy Model. J. Investig. Surg. 2019, 32, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Dong, Y. Reconstruction of Epidural Fat to Prevent Epidural Fibrosis After Laminectomy in Rabbits. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2022, 28, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Liu, T.-Y.; Chen, M.-H.; Sun, J.-S.; Chen, M.-H. An injectable extracellular matrix for the reconstruction of epidural fat and the prevention of epidural fibrosis. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 11, 035010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, T.; Cheng, J.; He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Polymeric Dural Biomaterials in Spinal Surgery: A Review. Gels 2024, 10, 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10090579
Yan T, Cheng J, He Q, Wang Y, Zhang C, Huang D, Liu J, Wang Z. Polymeric Dural Biomaterials in Spinal Surgery: A Review. Gels. 2024; 10(9):579. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10090579
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Taoxu, Junyao Cheng, Qing He, Yifan Wang, Chuyue Zhang, Da Huang, Jianheng Liu, and Zheng Wang. 2024. "Polymeric Dural Biomaterials in Spinal Surgery: A Review" Gels 10, no. 9: 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10090579
APA StyleYan, T., Cheng, J., He, Q., Wang, Y., Zhang, C., Huang, D., Liu, J., & Wang, Z. (2024). Polymeric Dural Biomaterials in Spinal Surgery: A Review. Gels, 10(9), 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10090579







