Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Yanbian Cattle Bone Gelatin Extracted Using Acid, Alkaline, and Enzymatic Hydrolysis Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Yield of Extraction
2.2. Physicochemical Properties
2.2.1. Moisture Content
2.2.2. Ash Content
2.2.3. Crude Protein Content
2.2.4. Hydroxyproline Content
2.2.5. Gel Strength
2.2.6. Viscosity
2.2.7. pH
2.2.8. Isoelectric Point
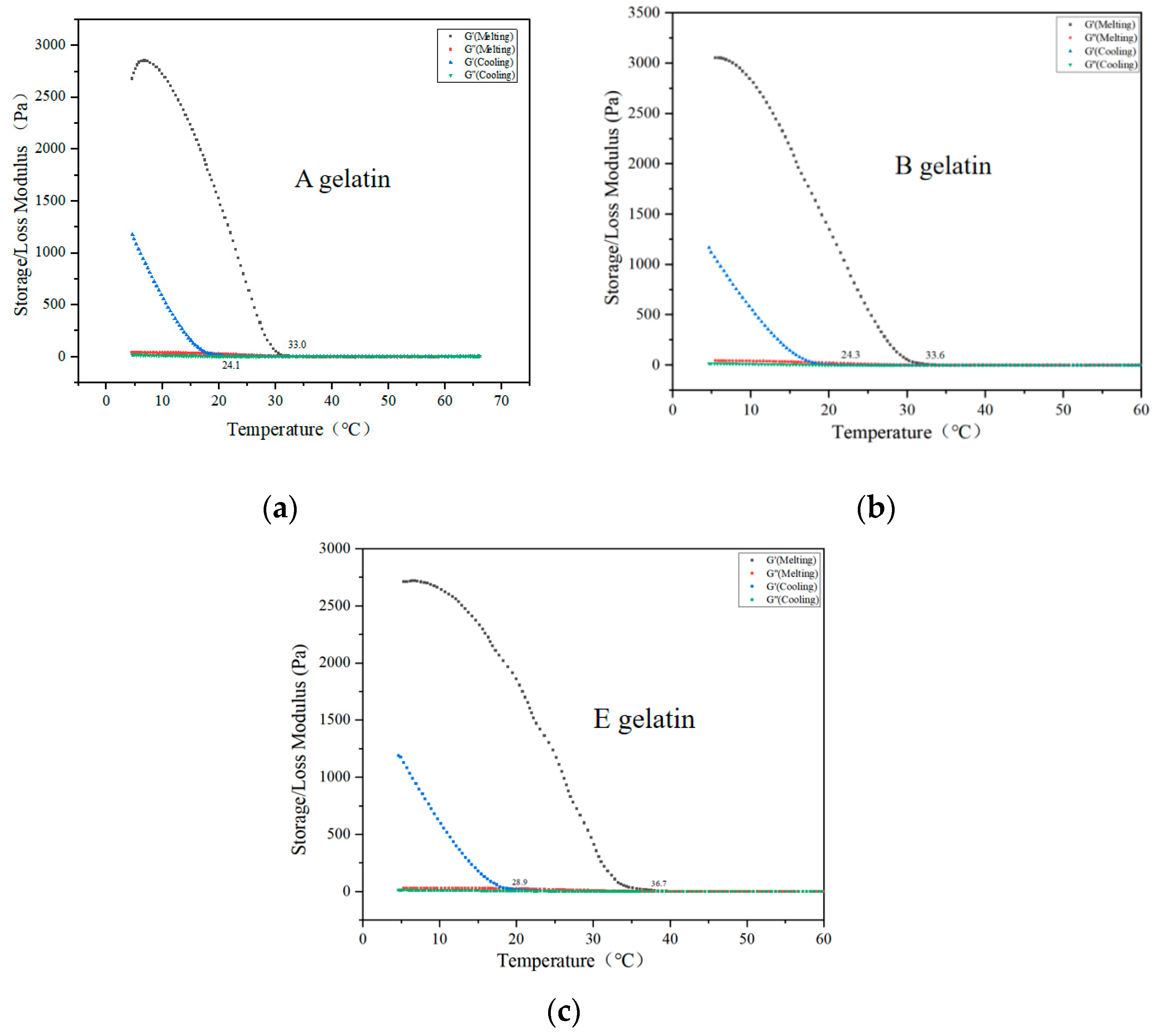
2.3. Rheological Properties of Gelatin
2.4. The Protein Structure of Gelatin
2.4.1. SDS-PAGE
2.4.2. GPC
2.5. Functional Groups of Gelatin
2.6. XRD Analysis
2.7. Amino Acid Composition of Gelatin
2.8. Circular Dichroism Spectrum of Gelatin
3. Conclusions
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Pretreatment
4.3. Gelatin Extraction
4.3.1. Enzymatic Extraction and Enzyme Selection
4.3.2. Acid Extraction and Determination of HCl Concentration
4.3.3. Alkaline Extraction and Determination of NaOH Concentration
4.4. Extraction Yield of Yanbian Cattle Bone Gelatin
4.5. Characterization of Yanbian Cattle Bone Gelatin
4.5.1. Chemical Properties
4.5.2. Hydroxyproline Content
4.5.3. Gel Strength
4.5.4. Viscosity
4.5.5. Measurement of ζ -Potential and pH
4.5.6. Rheological Properties
4.5.7. Electrophoresis Analysis of Gelatin (SDS-PAGE)
4.5.8. Molecular Weight Distribution (GPC)
4.5.9. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
4.5.10. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
4.5.11. Amino Acid Analysis
4.5.12. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
4.5.13. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alipal, J.; Pu’Ad, N.M.; Lee, T.; Nayan, N.; Sahari, N.; Basri, H.; Idris, M.; Abdullah, H. A review of gelatin: Properties, sources, process, applications, and commercialisation. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, M.A.; Tavassoli, M.; Salim, S.A.; Azizi-Lalabadi, M.; McClements, D.J. Development of green halochromic smart and active packaging materials: TiO2 nanoparticle- and anthocyanin-loaded gelatin/κ-carrageenan films. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesarinejad, M.A.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Rafe, A. Influence of gelatin/guar gum mixture on the rheological and textural properties of restructured ricotta cheese. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, W.; Min, C.; Qi, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H. pH-responsive color indicator film based on gelatin/chitosan cross-linking with anthocyanin-Fe2+ chelate for pork freshness monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 162, 110895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Parvar, S.H.; Keramat, J.; Kadivar, M.; Khanipour, E.; Motamedzadegan, A. Optimising conditions for enzymatic extraction of edible gelatin from the cattle bones using response surface methodology. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Feng, J.; Zhong, H.; Lou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, H.; Xia, G. Preparation, characterization and antioxidant effect of polypeptide mineral-chelate from Yanbian cattle bone. LWT 2023, 187, 115353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Abdullah, H.Z. The extraction of gelatin from black tilapia fish skins with different acid concentration. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1150, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, R.A.; Razali, U.H.M.; Noor, N.Q.I.M. Optimization of extraction conditions of gelatin from buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) skins using response surface methodology. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wei, G.; Li, T.; Hu, J.; Lu, N.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Effects of alkaline pretreatments and acid extraction conditions on the acid-soluble collagen from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafazah, E.M.; Pranoto, Y.; Rohman, A. Extracting of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) fish skin gelatin as influenced by alkaline concentration and extraction times. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 139, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattrem, M.N.; Molnes, S.; Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I. Interfacial and rheological properties of gelatin based solid emulsions prepared with acid or alkali pretreated gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, H. Effects of calcium ion on gel properties and gelation of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) protein isolates processed with pH shift method. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samatra, M.Y.; Noor, N.Q.I.M.; Razali, U.H.M.; Bakar, J.; Shaarani, S.M. Bovidae-based gelatin: Extractions method, physicochemical and functional properties, applications, and future trends. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3153–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zeng, X.; Ma, X.; Yang, R.; Zhao, W. A simple and eco-friendly method of gelatin production from bone: One-step biocatalysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, S.Y. Changes in the Amino Acid Composition of Gelatin After Treatment of Bovine Collagen with Enzyme Preparations. Mosc. Univ. Chem. Bull. 2023, 78, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, E.; Mamboya, F. Papain, a plant enzyme of biological importance: A review. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 8, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samatra, M.Y.; Azmi, A.; Shaarani, S.M.; Hartina, U.; Razali, U.H.M. Characterisation of gelatin extracted from buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) bone using papain pre-treatment. J. Agric. Food Eng. 2020, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Verma, A.K.; Patel, R. Collagen extraction and recent biological activities of collagen peptides derived from sea-food waste: A review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 18, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Giménez, B.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Montero, M.P. Functional and bioactive properties of collagen and gelatin from alternative sources: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Xing, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, G. Structure and physical properties of gelatin from bovine bone collagen influenced by acid pretreatment and pepsin. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 121, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwate, B.W.; Kudre, T.G. Effect of various acids on physicochemical and functional characteristics of gelatin from swim bladder of rohu (Labeo rohita). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2540–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, I.; Hayes, M. Marine Gelatine from Rest Raw Materials. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwate, B.W.; Ballari, R.V.; Kudre, T.G. Influence of spray-drying, freeze-drying and vacuum-drying on physicochemical and functional properties of gelatin from Labeo rohita swim bladder. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthen, S.; Levasseur-Garcia, C.; Kleiber, D.; Violleau, F.; Vaca-Garcia, C.; Tsuchikawa, S.; Raynaud, C.D.; Daydé, J. Using near-infrared spectroscopy to determine moisture content, gel strength, and viscosity of gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Regenstein, J.M. Effect of EDTA, HCl, and Citric Acid on Ca Salt Removal from Asian (Silver) Carp Scales Prior to Gelatin Extraction. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, C426–C431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumaningrum, I.; Pranoto, Y.; Hadiwiyoto, S. Extraction optimization and characterization of gelatine from fish dry skin of Spanish mackerel (Scomberromorus commersoni). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 144, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Ismail, A.; Ahmad, S.A.; Khalil, K.A.; Kee, L.T.; Awad, E.A.; Sazili, A.Q. Physicochemical characteristics and molecular structures of gelatin extracted from bovine skin: Effects of actinidin and papain enzymes pretreatment. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyani, S.; Setyabudi, F.S.; Pranoto, Y.; Santoso, U. Physicochemical Properties of Gelatin Extracted from Buffalo Hide Pretreated with Different Acids. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2017, 37, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Kiick, K.L. Collagen-like peptides and peptide–polymer conjugates in the design of assembled materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 2998–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matinong, A.M.E.; Chisti, Y.; Pickering, K.L.; Haverkamp, R.G. Collagen Extraction from Animal Skin. Biology 2022, 11, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, G. Roles of dietary glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline in collagen synthesis and animal growth. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, Y.S.; Salgado, P.R.; Mauri, A.N. Smart edible films based on gelatin and curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Ishaq, A.; Mac Regenstein, J.; Sahar, A.; Aadil, R.M.; Sameen, A.; Khan, M.I.; Alam, A. Valorization of animal by-products for gelatin extraction using conventional and green technologies: A comprehensive review. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Benjakul, S.; Maqsood, S.; Kishimura, H. Isolation and characterisation of collagen extracted from the skin of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Food Chem. 2011, 124, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Mulvaney, S.J.; Regenstein, J.M. Properties of Alaska Pollock Skin Gelatin: A Comparison with Tilapia and Pork Skin Gelatins. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C313–C321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedinia, A.; Ariffin, F.; Huda, N.; Nafchi, A.M. Extraction and characterization of gelatin from the feet of Pekin duck (Anas platyrhynchos domestica) as affected by acid, alkaline, and enzyme pretreatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalesi, H.; Emadzadeh, B.; Kadkhodaee, R.; Fang, Y. Whey protein isolate-Persian gum interaction at neutral pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 59, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristaniemi, A.; Torniainen, J.; Stenroth, L.; Finnilä, M.; Paakkonen, T.; Töyräs, J.; Korhonen, R. Comparison of water, hydroxyproline, uronic acid and elastin contents of bovine knee ligaments and patellar tendon and their relationships with biomechanical properties. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 104, 103639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.E.; Gasek, N.; Hwang, J.; Weiss, D.J.; Lee, P.C. Effect of temperature on gelation and cross-linking of gelatin methacryloyl for biomedical applications. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 033102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Tian, H.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, S. Interaction between fish gelatin and tremella polysaccharides from aqueous solutions to complex coacervates: Structure and rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 138, 108439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samatra, M.Y.; Razali, U.H.M.; Shaarani, S.M.; Roslan, J.; Ramli, R.A.; Izzreen, M.N.N.Q. Physicochemical and functional properties of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) bone gelatin extracted using acid pre-treatment. Futur. Foods 2024, 10, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammed, S.; Liu, F.; Wu, J. Effect of transglutaminase crosslinking on solubility property and mechanical strength of gelatin-zein composite films. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 116, 106649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, F.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Jahromi, M.; Petersen, H.O.; Sloth, J.J.; Eybye, K.L.; Kobbelgaard, S.; Jakobsen, G.; Jessen, F. Physico-chemical, structural and techno-functional properties of gelatin from saithe (Pollachius virens) skin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Yin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Sun, J. Physiochemical property and structure of gelatin obtained from Chinese soft-shelled turtle carapace by three pretreatment methods. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balti, R.; Jridi, M.; Sila, A.; Souissi, N.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Guillochon, D.; Nasri, M. Extraction and functional properties of gelatin from the skin of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) using smooth hound crude acid protease-aided process. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matmaroh, K.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Encarnacion, A.B.; Kishimura, H. Characteristics of acid soluble collagen and pepsin soluble collagen from scale of spotted golden goatfish (Parupeneus heptacanthus). Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintor, Đ.; Ninković, K.; Milošević, J.; Polović, N.Đ. Gaining insight into protein structure via ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 2024, 134, 103726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Ismail, A.; Ahmad, S.A.; Khalil, K.A.; Awad, E.A.; Akhtar, M.T.; Sazili, A.Q. Recovery of Gelatin from Bovine Skin with the Aid of Pepsin and Its Effects on the Characteristics of the Extracted Gelatin. Polymers 2021, 13, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedinia, A.; Nafchi, A.M.; Sharifi, M.; Ghalambor, P.; Oladzadabbasabadi, N.; Ariffin, F.; Huda, N. Poultry gelatin: Characteristics, developments, challenges, and future outlooks as a sustainable alternative for mammalian gelatin. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 104, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, C.; Wang, S.; Iglesia, E.; Liu, H. Acid Catalysis Mediated by Aqueous Hydronium Ions Formed by Contacting Zeolite Crystals with Liquid Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 35185–35198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meutter, J.; Goormaghtigh, E. Evaluation of protein secondary structure from FTIR spectra improved after partial deuteration. Eur. Biophys. J. 2021, 50, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Ismail, A.; Ahmad, S.A.; Khalil, K.A.; Kee, L.T.; Awad, E.A.; Sazili, A.Q. Extraction, characterization and molecular structure of bovine skin gelatin extracted with plant enzymes bromelain and zingibain. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3772–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamian, S.; Lu, T.; Kruse, H.; Emamian, H. Exploring Nature and Predicting Strength of Hydrogen Bonds: A Correlation Analysis Between Atoms-in-Molecules Descriptors, Binding Energies, and Energy Components of Symmetry-Adapted Perturbation Theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2019, 40, 2868–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Lorente, Á.I.; Mizaikoff, B. Mid-infrared spectroscopy for protein analysis: Potential and challenges. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 2875–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, S.A.; Ianoul, A.; Mix, G.; Boyden, M.N.; Karnoup, A.; Diem, M.; Schweitzer-Stenner, R. Dihedral ψ Angle Dependence of the Amide III Vibration: A Uniquely Sensitive UV Resonance Raman Secondary Structural Probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 11775–11781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Vuppu, S. A sustainable approach for conversion of leather trimming wastes into non-edible gelatine and its physicochemical analysis, optimization, FTIR, XRD characterization, and statistical study. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 25, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhou, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, B. Collagen and its derivatives: From structure and properties to their applications in food industry. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Piaggi, P.M.; Invernizzi, M.; Parrinello, M. Molecular dynamics simulations of liquid silica crystallization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5348–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rather, J.A.; Akhter, N.; Ashraf, Q.S.; Mir, S.A.; Makroo, H.A.; Majid, D.; Barba, F.J.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Dar, B. A comprehensive review on gelatin: Understanding impact of the sources, extraction methods, and modifications on potential packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.Q.I.M.; Razali, R.S.; Ismail, N.K.; Ramli, R.A.; Razali, U.H.M.; Bahauddin, A.R.; Zaharudin, N.; Rozzamri, A.; Bakar, J.; Shaarani, S.M. Application of Green Technology in Gelatin Extraction: A Review. Processes 2021, 9, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venupriya, V.; Krishnaveni, V.; Ramya, M. Effect of acidic and alkaline pretreatment on functional, structural and thermal properties of gelatin from waste fish scales. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 10533–10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, M.; Nishikawa, Y.; Shigenobu, Y.; Ambe, D.; Morita, T.; Morioka, K.; Adachi, K. Correlation of proline, hydroxyproline and serine content, denaturation temperature and circular dichroism analysis of type I collagen with the physiological temperature of marine teleosts. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 126775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, V.; Dutta, A.; Muthuswami, R. CD Spectroscopy to Study DNA-Protein Interactions. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 180, e63147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 17th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, T.; Ismail, A.; Ahmad, S.A.; Khalil, K.A.; Awad, E.A.; Leo, T.K.; Imlan, J.C.; Sazili, A.Q. Characterization of gelatin from bovine skin extracted using ultrasound subsequent to bromelain pretreatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthusamran, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Characteristics and gel properties of gelatin from skin of seabass (Lates calcarifer) as influenced by extraction conditions. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amertaning, D.; Bachrudin, Z.; Chin, K.B.; Erwanto, Y. Characteristics of Gelatin Extracted from Indonesian Local Cattle Hides Using Acid and Base Curing. Pak. J. Nutr. 2019, 18, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of Gelatin | Hydroxyproline Content (g/100 g) | Moisture (%) | Ash (%) | Crude Protein (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A gelatin | 11.51 ± 0.20 c | 7.67 ± 0.29 a | 0.94 ± 0.07 a | 77.57 ± 0.46 c |
| B gelatin | 13.48 ± 0.35 b | 7.47 ± 0.26 a | 1.00 ± 0.06 a | 84.16 ± 0.42 b |
| E gelatin | 19.13 ± 0.13 a | 7.40 ± 0.11 a | 1.00 ± 0.09 a | 87.54 ± 0.40 a |
| Type of Gelatin | Gel Strength (g) | Viscosity (cP) | pH | Isoelectric Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A gelatin | 197.33 ± 13.58 c | 484.33 ± 5.13 b | 5.31 ± 0.01 c | 7.44 ± 0.22 b |
| B gelatin | 207.67 ± 11.59 b | 482.67 ± 6.81 b | 7.41 ± 0.01 a | 5.42 ± 0.06 c |
| E gelatin | 259.00 ± 10.54 a | 521.67 ± 7.37 a | 6.44 ± 0.01 b | 8.5 ± 0.14 a |
| Type of Gelatin | Wavenumber (cm−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amide A | Amide B | Amide I | Amide II | Amide III | |
| A gelatin | 3390.86 | 3064.89 | 1643.35 | 1550.77 | 1238.30 |
| B gelatin | 3435.22 | 2935.66 | 1641.42 | 1529.55 | 1242.16 |
| E gelatin | 3348.42 | 2931.80 | 1629.85 | 1462.04 | 1247.94 |
| Assignment | Corresponds to the N–H stretching vibration | Corresponds to another mode of N–H stretching vibration | Primarily arises from the C=O stretching vibration | Mainly composed of N–H bending vibration and C–N stretching vibration | Results from a combination of C–N stretching and N–H bending vibrations |
| Amino Acid | A Gelatin | B Gelatin | E Gelatin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asp | 3.06 ± 0.37 | 5.01 ± 0.41 | 5.06 ± 0.33 |
| Thr | 1.03 ± 0.58 | 1.90 ± 0.83 | 1.95 ± 0.78 |
| Ser | 2.46 ± 0.26 | 3.43 ± 0.11 | 3.36 ± 0.16 |
| Glu | 6.23 ± 0.27 | 8.65 ± 0.22 | 8.27 ± 0.17 |
| Gly | 33.25 ± 0.48 | 37.40 ± 0.51 | 36.55 ± 0.41 |
| Ala | 13.19 ± 0.35 | 14.08 ± 0.21 | 14.09 ± 0.28 |
| Cys | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Val | 1.96 ± 0.80 | 2.46 ± 0.74 | 2.42 ± 0.79 |
| Met | 0.29 ± 0.55 | 0.75 ± 0.32 | 0.54 ± 0.27 |
| Ile | 1.06 ± 0.58 | 1.37 ± 0.62 | 1.36 ± 0.63 |
| Leu | 2.17 ± 0.21 | 2.97 ± 0.12 | 3.01 ± 0.11 |
| Tyr | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 0.29 ± 0.42 | 0.31 ± 0.35 |
| Phe | 1.37 ± 0.34 | 1.49 ± 0.51 | 1.54 ± 0.44 |
| Lys | 2.46 ± 0.15 | 3.03 ± 0.11 | 3.16 ± 0.25 |
| NH3 | 3.15 ± 0.08 | 3.83 ± 0.22 | 3.78 ± 0.18 |
| His | 0.47 ± 0.21 | 0.59 ± 0.31 | 0.61 ± 0.23 |
| Arg | 4.83 ± 0.18 | 5.54 ± 0.25 | 5.52 ± 0.22 |
| Imino Acid (Pro + Hyp) | 12.26 ± 0.11 | 16.44 ± 0.12 | 22.31 ± 0.07 |
| Type of Gelatin | α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | Unordered Coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A gelatin | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 25.5 ± 0.1 | 28.2 ± 0.1 | 44.9 ± 0.2 |
| B gelatin | 8.7 ± 0.2 | 20.2 ± 0.3 | 35.5 ± 0.3 | 35.6 ± 0.1 |
| E gelatin | 14.4 ± 0.1 | 27.1 ± 0.2 | 35.2 ± 0.2 | 23.3 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zhao, D.; Yin, L.; Wang, R.; Jin, Z.; Xu, H.; Xia, G. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Yanbian Cattle Bone Gelatin Extracted Using Acid, Alkaline, and Enzymatic Hydrolysis Methods. Gels 2025, 11, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030186
Zhang S, Zhao D, Yin L, Wang R, Jin Z, Xu H, Xia G. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Yanbian Cattle Bone Gelatin Extracted Using Acid, Alkaline, and Enzymatic Hydrolysis Methods. Gels. 2025; 11(3):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030186
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Song, Duanduan Zhao, Lu Yin, Ruixuan Wang, Zhiyan Jin, Hongyan Xu, and Guangjun Xia. 2025. "Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Yanbian Cattle Bone Gelatin Extracted Using Acid, Alkaline, and Enzymatic Hydrolysis Methods" Gels 11, no. 3: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030186
APA StyleZhang, S., Zhao, D., Yin, L., Wang, R., Jin, Z., Xu, H., & Xia, G. (2025). Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Yanbian Cattle Bone Gelatin Extracted Using Acid, Alkaline, and Enzymatic Hydrolysis Methods. Gels, 11(3), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030186






