Efficient Adsorption and Utilisation of Methylene Blue by NaOH-Modified Nanocellulose–Polyacrylamide Interpenetrating Network Gels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
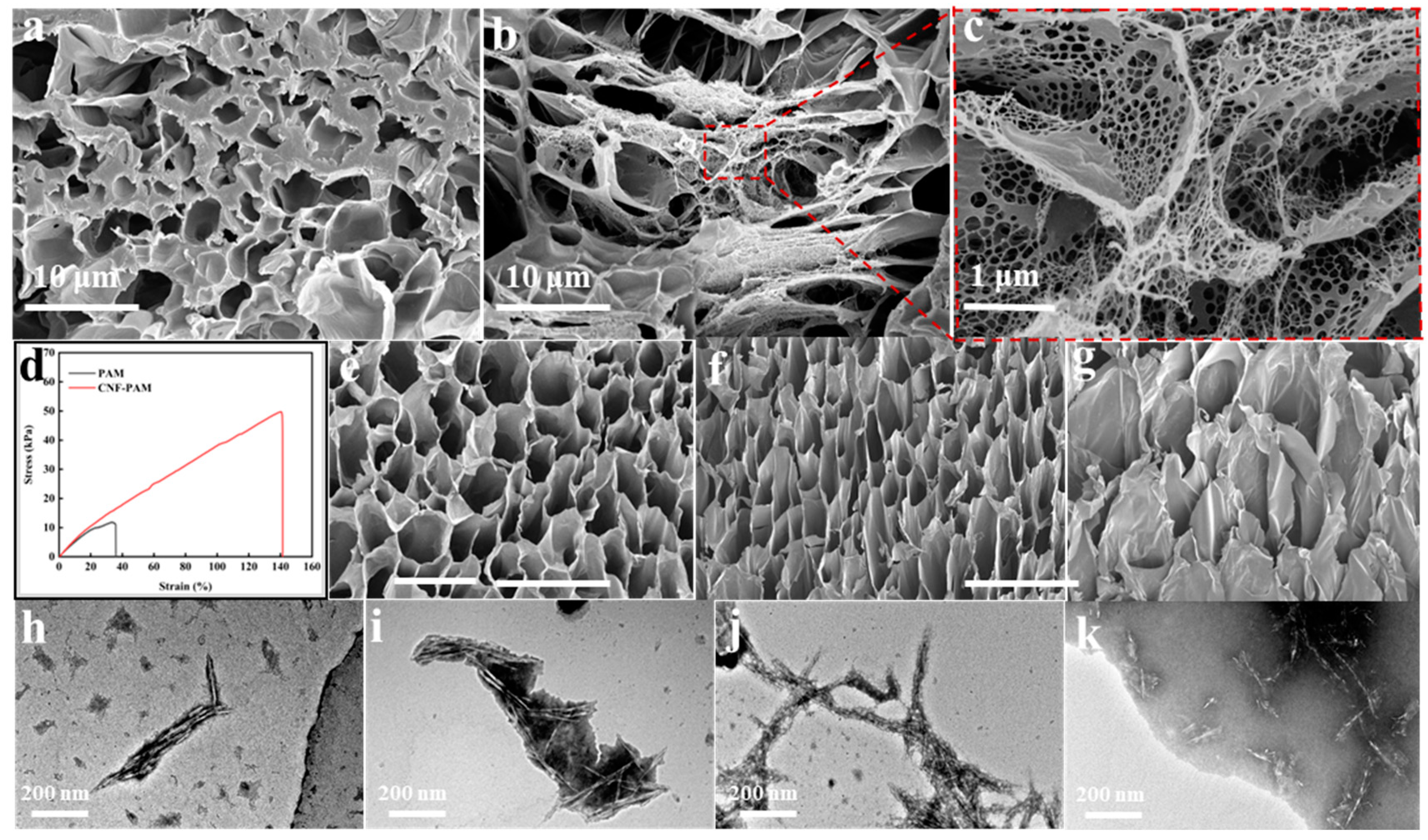
2.1. Characterisation of Gels
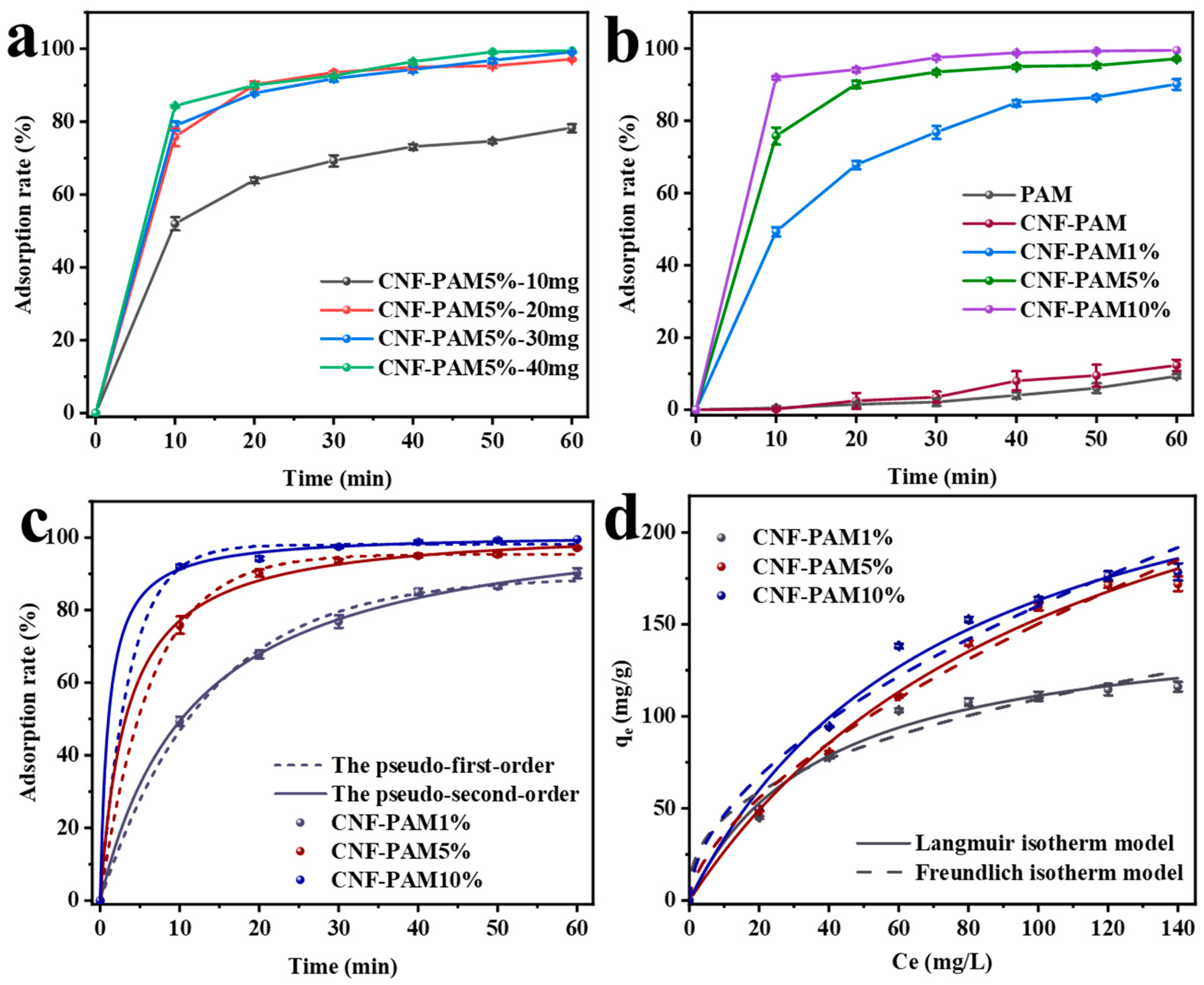
2.2. Adsorption Kinetics Analysis
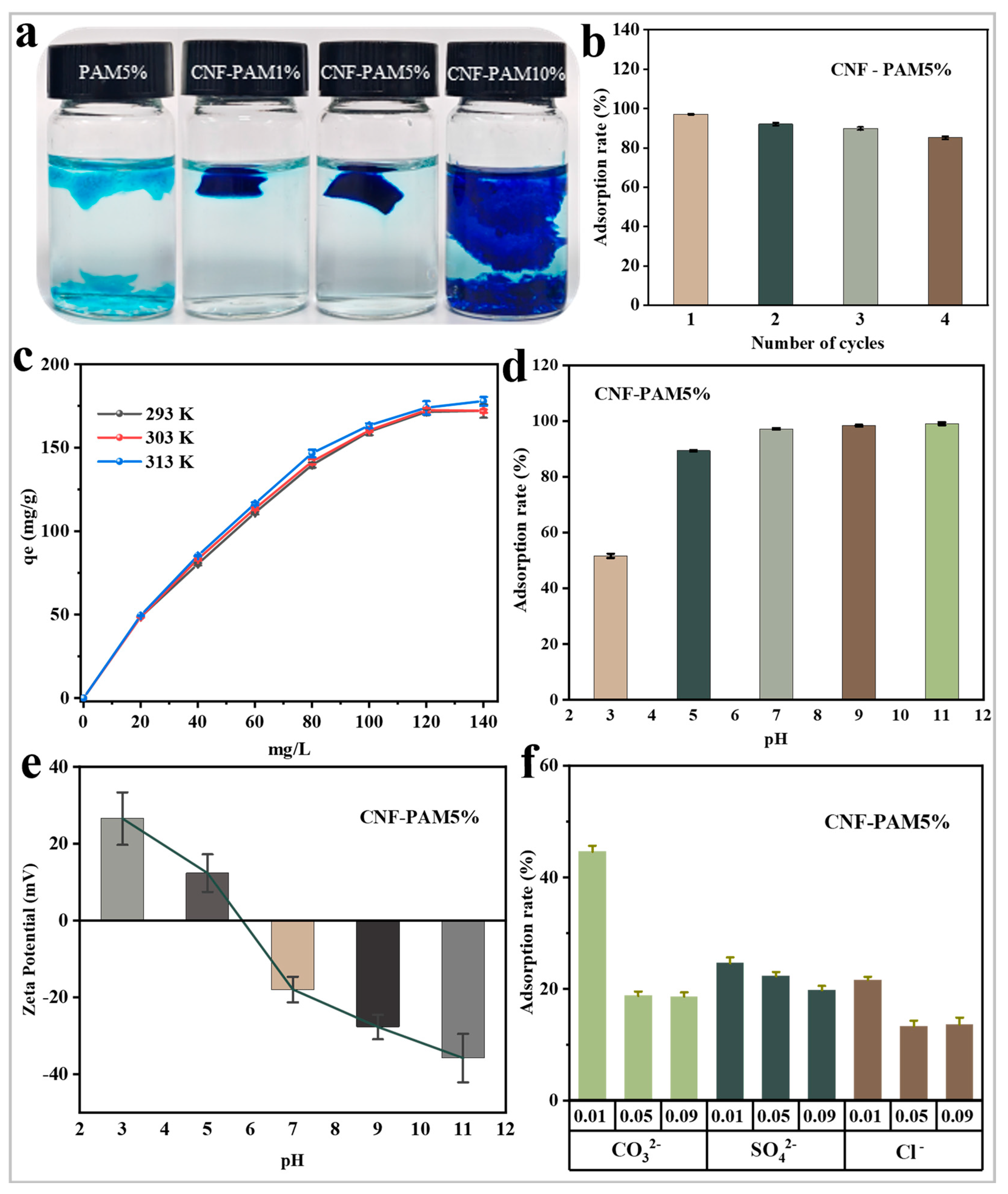
2.3. Effect of Different Factors on Adsorption Performance
2.4. Adsorption Mechanism Analysis
2.5. Toxicity Analysis of the Gels
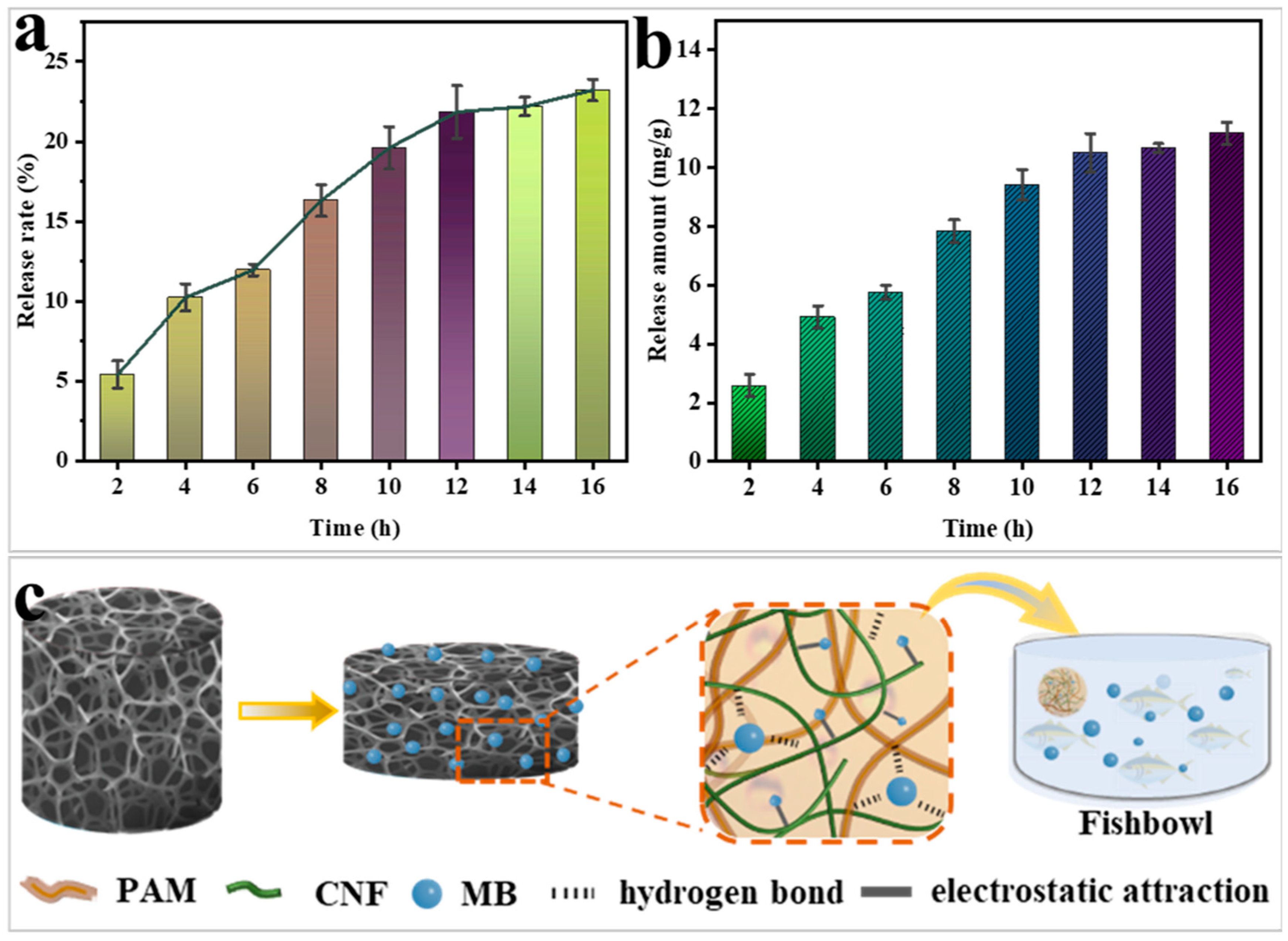
2.6. Prospects for the Application of Gel-Releasing MB as a Fish Fungicide
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
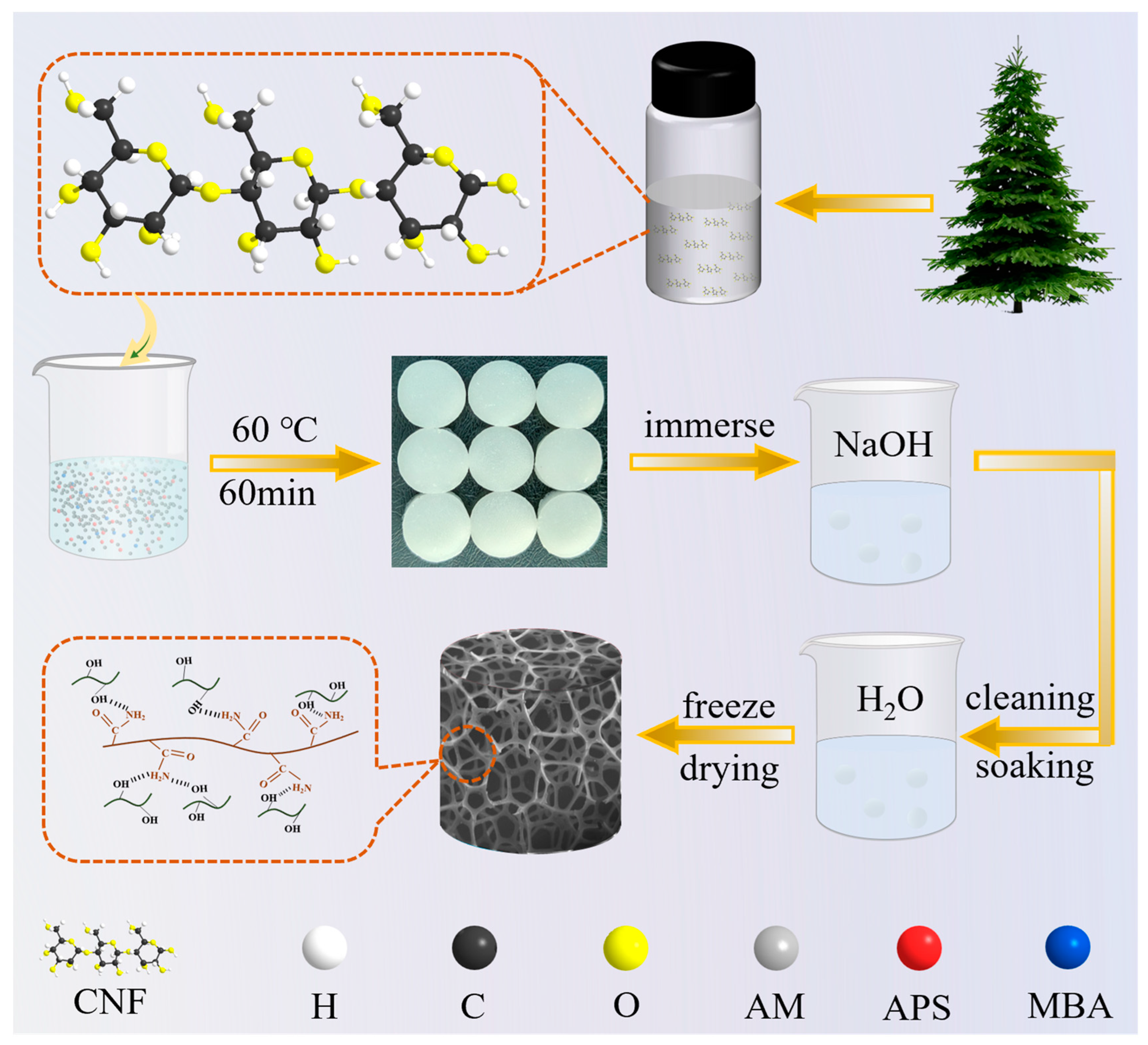
4.2. Preparation Methods
4.3. Characterisation and Testing of Gels
4.4. Adsorption Rate and Adsorption Capacity Tests
4.5. Release Rate Test
4.6. Kinetic Modelling and Isothermal Curve Fitting
4.7. Toxicity Test of the Gel on Living Cells
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wan, X.; Rong, Z.; Zhu, K.; Wu, Y. Chitosan-based dual network composite hydrogel for efficient adsorption of methylene blue dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarce, E.; Cantero-López, P.; Roa, K.; Boulett, A.; Yáñez, O.; Santander, P.; Pizarro, G.d.C.; Sánchez, J. Removal of highly concentrated methylene blue dye by cellulose nanofiber biocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 238, 124045. [Google Scholar]
- Sudarshan, S.; Harikrishnan, S.; RathiBhuvaneswari, G.; Alamelu, V.; Aanand, S.; Rajasekar, A.; Govarthanan, M. Impact of textile dyes on human health and bioremediation of textile industry effluent using microorganisms: Current status and future prospects. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxac064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Budarin, V.L.; Clark, J.H.; North, M.; Wu, X. Rapid and efficient adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by hierarchically porous, activated starbons®: Mechanism and porosity dependence. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129174. [Google Scholar]
- Dariani, R.S.; Esmaeili, A.; Mortezaali, A.; Dehghanpour, S. Photocatalytic reaction and degradation of methylene blue on TiO2 nano-sized particles. Optik 2016, 127, 7143–7154. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.; Makhado, E.; Kim, S.; Kang, M. Recent developments of polysaccharide based superabsorbent nanocomposite for organic dye contamination removal from wastewater—A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 217, 114909. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; Wang, X.; Ding, M.; Tang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Z. The role of lateral size of MXene nanosheets in membrane filtration of dyeing wastewater: Membrane characteristic and performance. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, A.; Rai, B.N.; Singh, R.S.; Jaiswal, R.P. A comprehensive review on the integration of advanced oxidation processes with biodegradation for the treatment of textile wastewater containing azo dyes. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 617–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Guo, M. Porous spherical Cu2O supported by wood-based biochar skeleton for the adsorption-photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 611, 155744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Chang, P.R.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, F.; Ma, X. Fabrication of ultra-light graphene-based gels and their adsorption of methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 240, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Han, X.; Song, J.; Huang, L. Removal of methylene blue and lead(ii) via PVA/SA double-cross-linked network gel beads loaded with Fe3O4@KHA nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 5605–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Qi, Y.; Sun, W.; Men, Y. Preparation of κ-carrageenan/graphene oxide gel beads and their efficient adsorption for methylene blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 506, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madkour, T.M.; Elsayed, R.E.; Azzam, R.A. Environmentally Friendly Nanoporous Polymeric Gels for Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Gels 2024, 10, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, X.; Zhao, S.; Du, Q.; Pi, X.; Jing, Z.; Jin, Y. Green preparation of polydopamine-modified multiwalled carbon nanotube/calcium alginate composite aerogels for effective adsorption of methylene blue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazani, A.; Oveisi, M.; Sheikhi, M.; Gouranlou, F. Natural polymers as environmental friendly adsorbents for organic pollutants such as dyes removal from colored wastewater. Curr. Org. Chem. 2018, 22, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, A.; Lv, W.; Wang, Y.; Geng, H.; Wang, J.; Qin, M. Fabrication of cellulose self-assemblies and high-strength ordered cellulose films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Hou, L.; Ching, Y.C.; Ching, K.Y.; Hai, N.D.; Chuah, C.H. A review of recent advances of cellulose-based intelligent-responsive hydrogels as vehicles for controllable drug delivery system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, L.; Wei, G. Recent Advances in the Fabrication and Environmental Science Applications of Cellulose Nanofibril-Based Functional Materials. Materials 2021, 14, 5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouzeid, R.E.; Owda, M.E.; Dacrory, S. Effective adsorption of cationic methylene blue dye on cellulose nanofiber/graphene oxide/silica nanocomposite: Kinetics and equilibrium. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52377. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Qin, F.; Fang, Z.; Li, G.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, X. Mechanically stable core-shell cellulose nanofibril/sodium alginate hydrogel beads with superior cu(II) removal capacity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, A.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Ismail, N.; Khalil, N.A.; Balakrishnan, V.; Zulkifli, M.; Yahaya, A.N.A. Isolation and Characterization of Magnetic Oil Palm Empty Fruits Bunch Cellulose Nanofiber Composite as a Bio-Sorbent for Cu(II) and Cr(VI) Removal. Polymers 2020, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zeng, J.; Li, P.; Hu, F.J.S.; Technology, P. A preassembled framework nanocellulose hydrogel inspired by biological systems in nature and ion-imprinted polymers for efficient removal of Cu (II). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 340, 126703. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroiwa, T.; Takada, H.; Shogen, A.; Saito, K.; Kobayashi, I.; Uemura, K.; Kanazawa, A. Cross-linkable chitosan-based hydrogel microbeads with pH-responsive adsorption properties for organic dyes prepared using size-tunable microchannel emulsification technique. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 514, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Ohemeng-Boahen, G.; Sewu, D.D.; Osei, B.A.; Woo, S.H. Improved adsorption of Congo red from aqueous solution using alkali-treated goethite impregnated chitosan hydrogel capsule. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Long, L.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Yang, G.; Shen, F.; Liu, Y. Alkali-treated yttrium-containing chitosan-based hydrogels for phosphate recover with highly selective in wide pH aqueous solution. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 45, 103851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Tran, H.N.; Godfred, O.-B.; Woo, S.H. Supersorption Capacity of Anionic Dye by Newer Chitosan Hydrogel Capsules via Green Surfactant Exchange Method. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3604–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moztahida, M.; Lee, D.S. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue with P25/graphene/polyacrylamide hydrogels: Optimization using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Lai, K.; Rasco, B.A.; Fan, Y. Analysis of trace methylene blue in fish muscles using ultra-sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Food Control 2016, 65, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Rahman, M.; Foysal, M.; Hossain, M. Determination of lethal concentration and antibacterial activity of commonly used disinfectants. Int. J. Nat. Sci. 2011, 1, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaikambo, L.Y.; Ansell, M.P. Chemical modification of hemp, sisal, jute, and kapok fibers by alkalization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 84, 2222–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, H.; Qi, D.; Wang, R. Wood Functional Modification Based on Deposition of Nanometer Copper Film by Magnetron Sputtering. For. Prod. J. 2020, 70, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, C.; Miyamoto, H.; Hayakawa, D.; Ueda, K. Folded-chain structure of cellulose II suggested by molecular dynamics simulation. Carbohydr. Res. 2013, 379, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Q. A novel polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogel reinforced with natural chitosan nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Cai, L.; Zhu, G.; Chen, L.; Xie, X.; Guo, J. Nanocellulose and multi-walled carbon nanotubes reinforced polyacrylamide/sodium alginate conductive hydrogel as flexible sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 677, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Guo, M.; Chen, X.; Lu, Y. Construction of a non-toxic interpenetrating network hydrogel drug carrier supported by carbon microspheres and nanocellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 350, 123035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Wang, C.; Jia, C.; Kuang, Y.; Pastel, G.; Chen, C.; Chen, G.; He, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Muscle-Inspired Highly Anisotropic, Strong, Ion-Conductive Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1801934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Fang, L.; Li, D. Reinforcement of cellulose nanofibers in polyacrylamide gels. Cellulose 2017, 24, 5487–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Karsani, K.S.M.; Al-Muntasheri, G.A.; Sultan, A.S.; Hussein, I.A. Impact of salts on polyacrylamide hydrolysis and gelation: New insights. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 41185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, Z.; Yuan, B.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Thang Nguyen, T.; Guo, M.; Guo, Z. Fluorescent carbon dots crosslinked cellulose Nanofibril/Chitosan interpenetrating hydrogel system for sensitive detection and efficient adsorption of Cu (II) and Cr (VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenaga, S.; Osada, M. Self-Sustaining Cellulose Nanofiber Hydrogel Produced by Hydrothermal Gelation without Additives. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanaeishoar, H.; Sabbaghan, M.; Argyropoulos, D.S. Ultrasound assisted polyacrylamide grafting on nano-fibrillated cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, I.A.W.; Ahmad, A.L.; Hameed, B.H. Adsorption of basic dye on high-surface-area activated carbon prepared from coconut husk: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; He, C.; Li, H.; Yan, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.-N. A novel hydrophilic–hydrophobic magnetic interpenetrating polymer networks (IPNs) and its adsorption towards salicylic acid from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, I.D.; Srivastava, V.C.; Agarwal, N.K. Removal of Orange-G and Methyl Violet dyes by adsorption onto bagasse fly ash—Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 69, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L. The investigation of synergistic and competitive interaction between dye Congo red and methyl blue on magnetic MnFe2O4. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 246, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu Demirezen, D.; Demirezen Yılmaz, D.; Yıldız, Y.Ş. Magnetic chitosan/calcium alginate double-network hydrogel beads: Preparation, adsorption of anionic and cationic surfactants, and reuse in the removal of methylene blue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Zhang, K.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Fei, X.; Tian, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y. Neural network inspired bionic ordered structure polyaniline gel for wearable sensor. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 217, 113314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, Y.; Feng, S.; Li, L.; You, R. Silk Nanofibers/Carbon Nanotube Conductive Aerogel. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2024, 46, e2400702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,exp (mg·g−1) | qe,c (mg·g−1) | k1 (h−1) | R2 | qe,c (mg·g−1) | k2 × 104 (g·mg−1·h−1) | R2 | |
| CNF-PAM1% | 45.08 | 89.14192 | 0.07433 | 0.99607 | 108.17313 | 0.000776841 | 0.99925 |
| CNF-PAM5% | 48.58 | 95.40894 | 0.15557 | 0.99874 | 103.07561 | 0.00287 | 0.99911 |
| CNF-PAM10% | 49.75 | 98.04909 | 0.27116 | 0.99752 | 101.02541 | 0.00928 | 0.99941 |
| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg g−1) | kL (L mg−1) | R2 | n | kF (L mg−1) | R2 | |
| CNF-PAM1% | 116.08 | 0.02614 | 0.95173 | 2.58906 | 18.47327 | 0.94484 |
| CNF-PAM5% | 172.08 | 0.00892 | 0.98491 | 1.62024 | 8.76337 | 0.98246 |
| CNF-PAM10% | 178.50 | 0.0133 | 0.96972 | 1.86043 | 13.47115 | 0.96474 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhong, H.; Guo, M.; Li, J. Efficient Adsorption and Utilisation of Methylene Blue by NaOH-Modified Nanocellulose–Polyacrylamide Interpenetrating Network Gels. Gels 2025, 11, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040252
Wang Y, Lu Y, Zhong H, Guo M, Li J. Efficient Adsorption and Utilisation of Methylene Blue by NaOH-Modified Nanocellulose–Polyacrylamide Interpenetrating Network Gels. Gels. 2025; 11(4):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040252
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yanan, Yanan Lu, Hao Zhong, Minghui Guo, and Jingkui Li. 2025. "Efficient Adsorption and Utilisation of Methylene Blue by NaOH-Modified Nanocellulose–Polyacrylamide Interpenetrating Network Gels" Gels 11, no. 4: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040252
APA StyleWang, Y., Lu, Y., Zhong, H., Guo, M., & Li, J. (2025). Efficient Adsorption and Utilisation of Methylene Blue by NaOH-Modified Nanocellulose–Polyacrylamide Interpenetrating Network Gels. Gels, 11(4), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040252






