Engineered Magnetic-Functionalized Carbon Xerogels for Sustainable Arsenic Removal: Bridging Adsorption Efficiency with Regenerability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
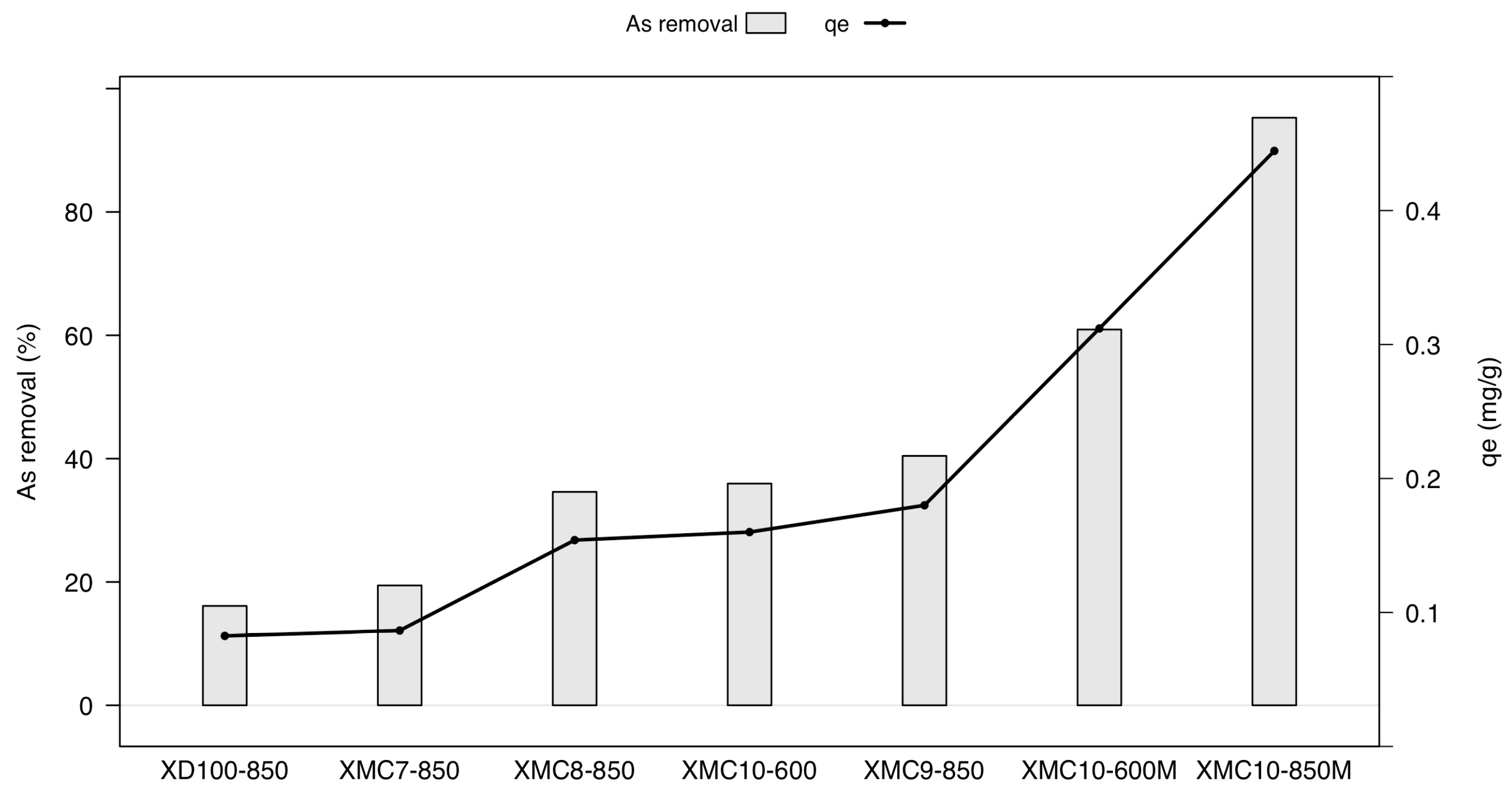
2.1. Effect of Fe Content and Carbonization Temperature on As(V) Adsorption in Magnetic-Functionalized Carbon Xerogel
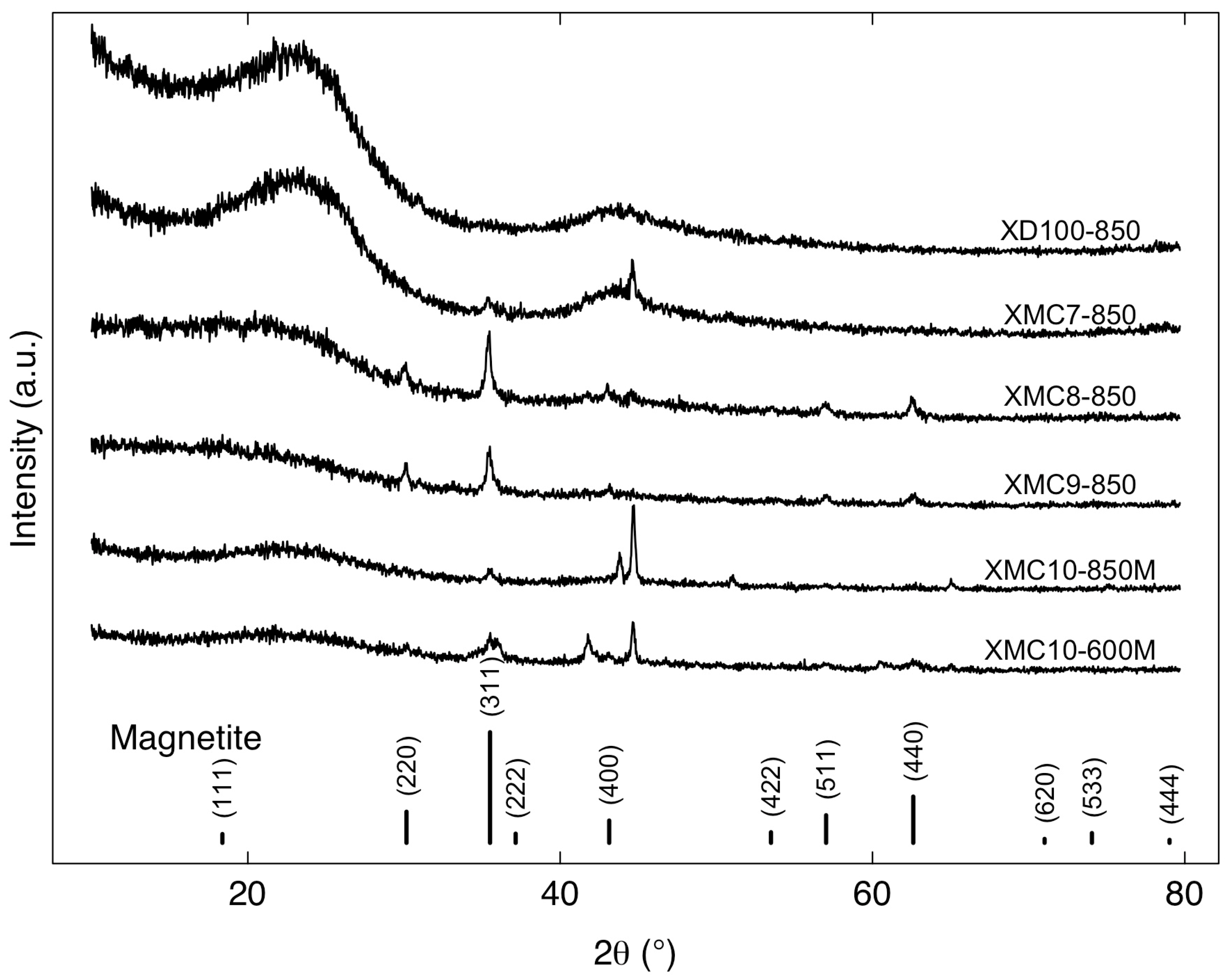
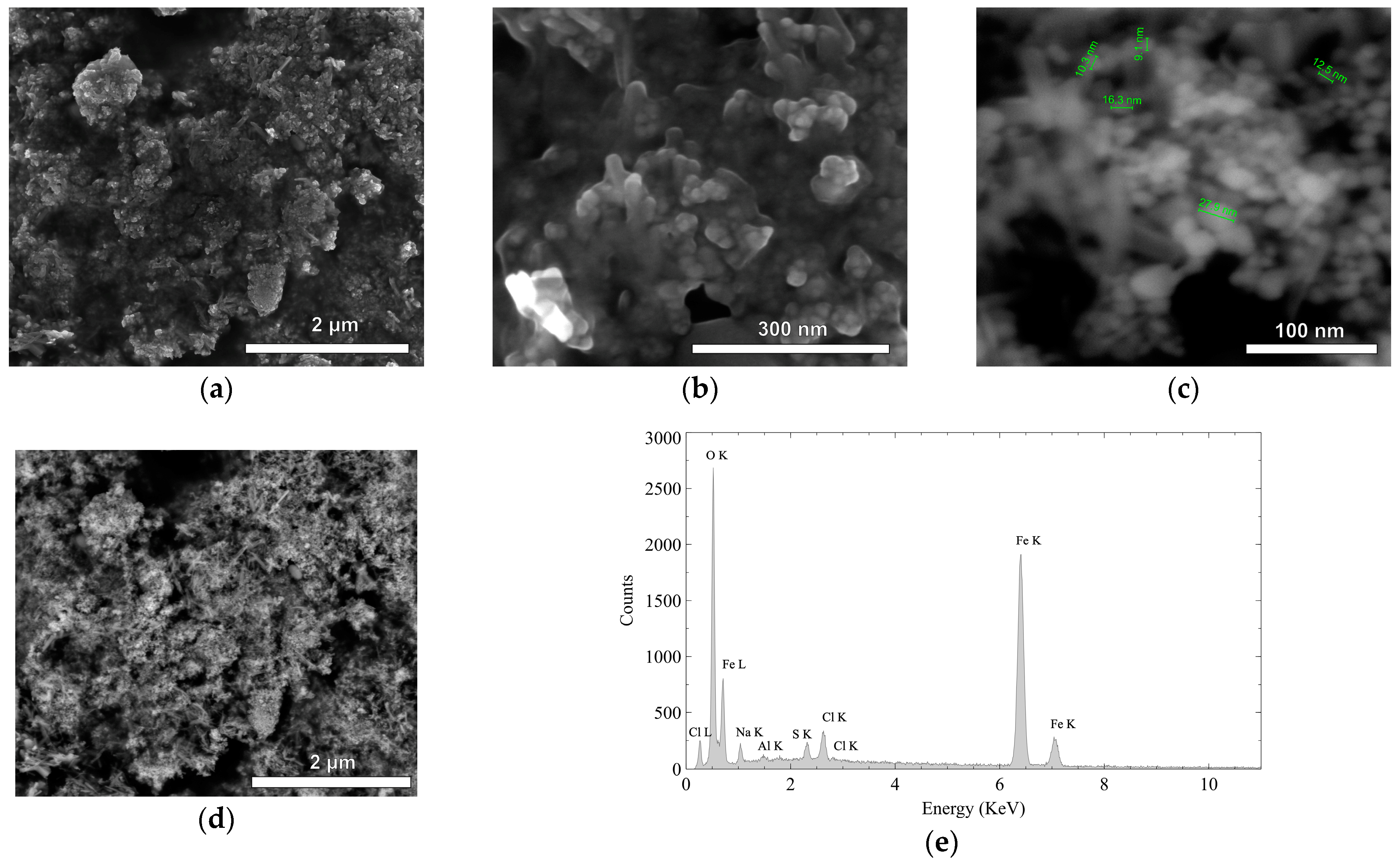
2.2. Characterization of Materials
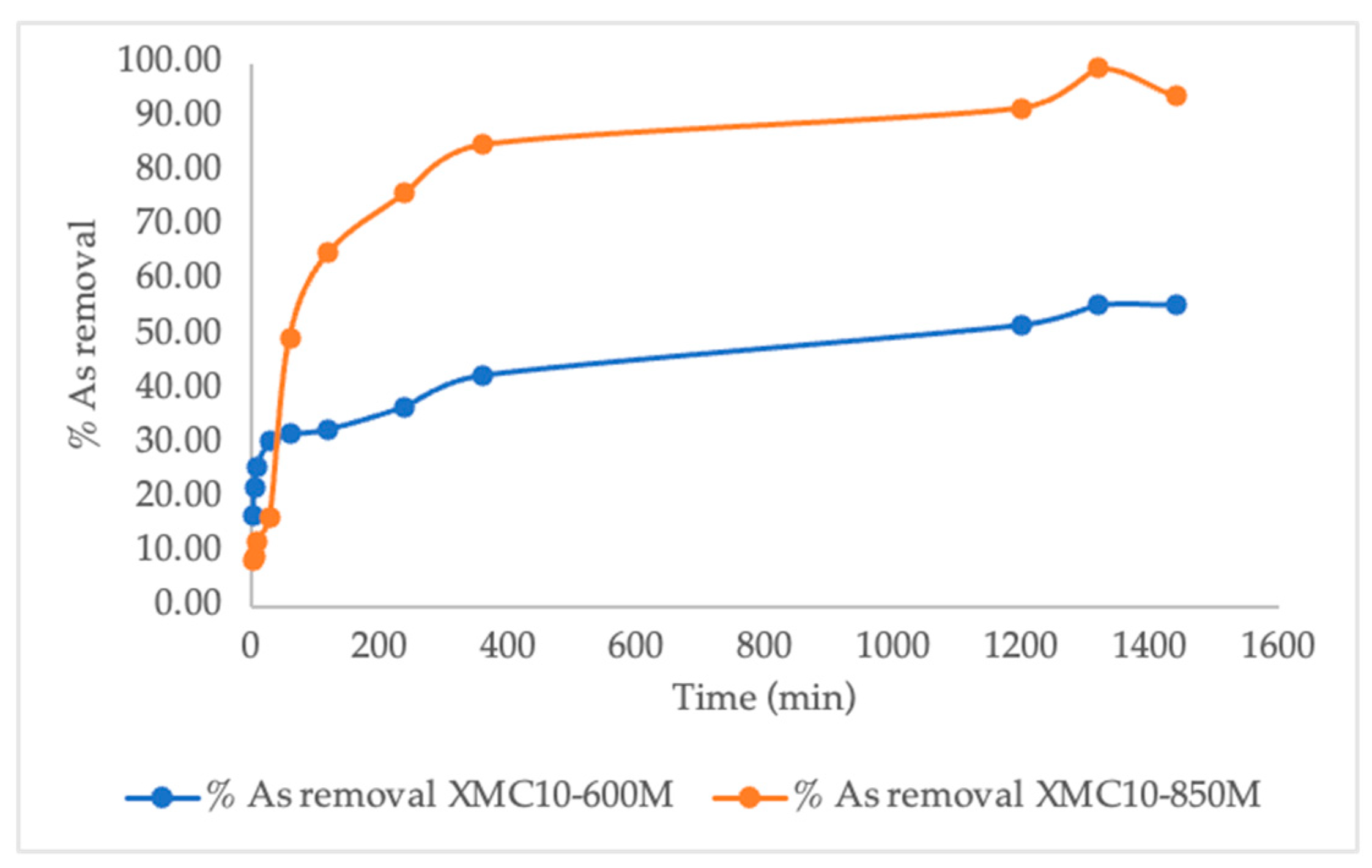
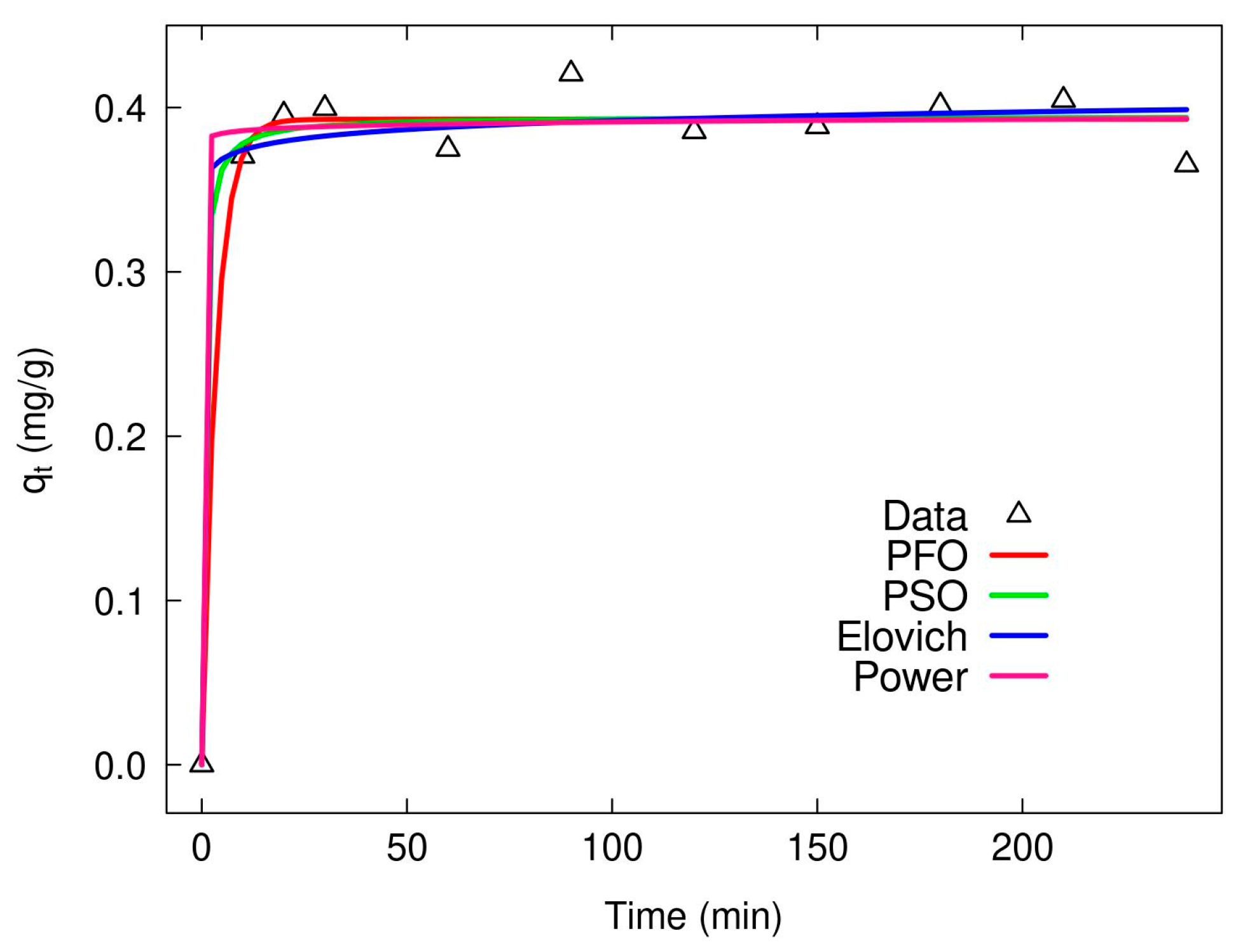
2.3. Kinetic As(V) Adsorption Analysis
2.4. Study of Acidic and Alkaline Regeneration Agents for Arsenic Desorption from Magnetic-Functionalized Carbon Xerogels
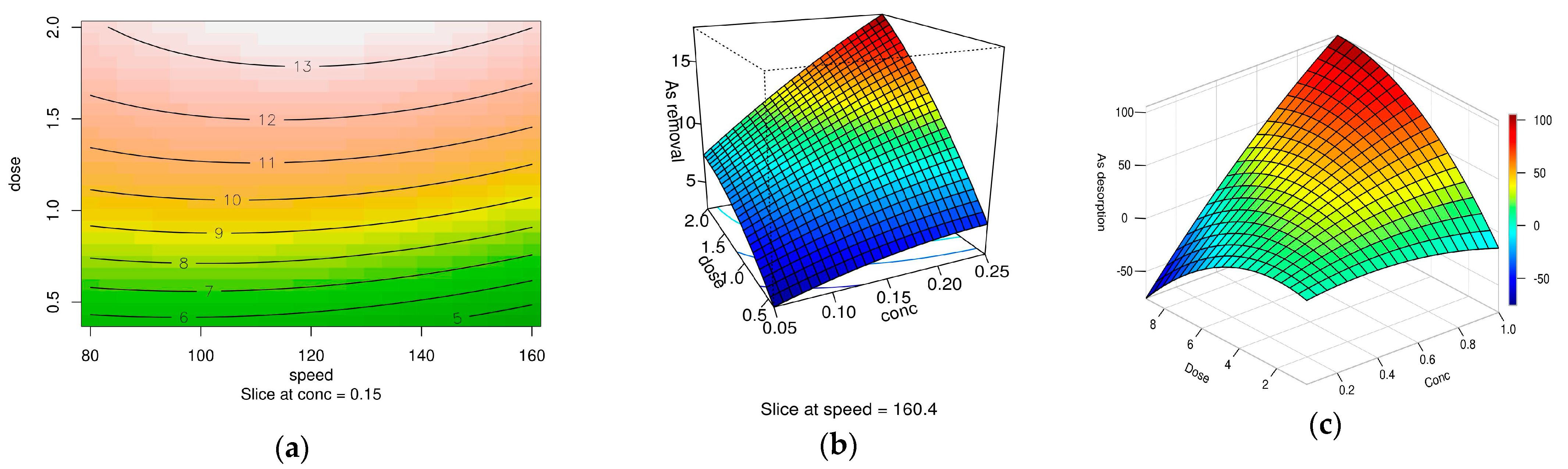
2.5. Optimizing Arsenic Desorption Using Response Surface Methodology
2.5.1. RSM Analysis for Arsenic Desorption Using XMC10-850M and HNO3
2.5.2. RSM Analysis for As(V) Desorption Using XMC10-850M and KOH
2.6. Kinetic Study of As(V) Desorption from XMC10-850M Carbon Xerogels
2.7. As(V) Adsorbent Regeneration
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Magnetic-Functionalized Xerogels and Variation in the M/R Ratio
4.2. Optimizing Conditions: The Role of Carbonization Temperature
4.3. Surface Modification Using H2O2 of Magnetic-Functionalized Carbon Xerogels
4.4. Characterization of Materials
4.5. The Kinetics of Arsenic Adsorption
4.6. Determining Optimal Conditions for Arsenate Desorption Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
4.7. Arsenic Adsorbent Regeneration
4.8. Arsenic Quantification
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valskys, V.; Hassan, H.R.; Wołkowicz, S.; Satkūnas, J.; Kibirkštis, G.; Ignatavičius, G. A Review on Detection Techniques, Health Hazards and Human Health Risk Assessment of Arsenic Pollution in Soil and Groundwater. Minerals 2022, 12, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alka, S.; Shahir, S.; Ibrahim, N.; Ndejiko, M.J.; Vo, D.V.N.; Manan, F.A. Arsenic Removal Technologies and Future Trends: A Mini Review. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 278, 123805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indah, S.; Helard, D.; Binuwara, A. Studies on Desorption and Regeneration of Natural Pumice for Iron Removal from Aqueous Solution. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 2017, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ccamerccoa, M.H.; Falcon, N.L.T.; Félix, L.L.; Pacheco-Salazar, D.G.; Aragón, F.F.H.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; Garnier, J.; Vera-Gonzales, C. High Efficiency of Magnetite Nanoparticles for the Arsenic Removal from an Aqueous Solution and Natural Water Taken from Tambo River in Peru. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisticò, R. A Synthetic Guide toward the Tailored Production of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Bol. Soc. Esp. Ceram. Y Vidr. 2021, 60, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, E.; Okuthe, G.E. Engineered Nanoparticles in Aquatic Systems: Toxicity and Mechanism of Toxicity in Fish. Emerg. Contam. 2023, 9, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, C.; Pinsino, A. Nanomaterial Ecotoxicology in the Terrestrial and Aquatic Environment: A Systematic Review. Toxics 2022, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadallah-F, A.; Al-Muhtaseb, S.A. Novel Controlled Synthesis of Nanoporous Carbon Nanorods from Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Xerogels. Mater. Lett. 2017, 201, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Torres, S.; Jirglová, H.; Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. Influence of Electrostatic Interactions during the Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Polymerization on the Characteristics of Mo-Doped Carbon Gels. Processes 2020, 8, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Using the Sol–Gel Approach: Adjusting Architecture and Composition for Novel Applications. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselov, G.B.; Vedyagin, A.A. Resorcinol–Formaldehyde-Derived Carbon Xerogels: Preparation, Functionalization, and Application Aspects. Materials 2023, 16, 6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Muhtaseb, S.A.; Ritter, J.A. Preparation and Properties of Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Organic and Carbon Gels. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu Prabhu, S.; Rane, N.R.; Li, X.; Otari, S.V.; Girawale, S.D.; Palake, A.R.; Kodam, K.M.; Park, Y.K.; Ha, Y.H.; Kumar Yadav, K.; et al. Magnetic Nanostructured Adsorbents for Water Treatment: Structure-Property Relationships, Chemistry of Interactions, and Lab-to-Industry Integration. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143474. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta, M.E.; Ocampo, S.; Funes, I.G.; Medina, F.O.; Parolo, M.E.; Carlos, L. Nanomaterials with Tailored Magnetic Properties as Adsorbents of Organic Pollutants from Wastewaters. Inorganics 2020, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudhoo, A.; Sillanpää, M. Magnetic Nanoadsorbents for Micropollutant Removal in Real Water Treatment: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 4393–4413. [Google Scholar]
- Perez Mora, B.; Bellú, S.; Mangiameli, M.F.; Frascaroli, M.I.; González, J.C. Response Surface Methodology and Optimization of Arsenic Continuous Sorption Process from Contaminated Water Using Chitosan. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, U.K.; Mahapatra, S.S.; Patel, R.K. Application of Box–Behnken Design in Response Surface Methodology for Adsorptive Removal of Arsenic from Aqueous Solution Using CeO2/Fe2O3/Graphene Nanocomposite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 207, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugushe, A.S.; Nqombolo, A.; Nomngongo, P.N. Application of Response Surface Methodology and Desirability Function in the Optimization of Adsorptive Remediation of Arsenic from Acid Mine Drainage Using Magnetic Nanocomposite: Equilibrium Studies and Application to Real Samples. Molecules 2019, 24, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz Letechipia, J.; González-Trinidad, J.; Júnez-Ferreira, H.E.; Bautista-Capetillo, C.; Robles-Rovelo, C.O.; Contreras Rodríguez, A.R.; Dávila-Hernández, S. Aqueous Arsenic Speciation with Hydrogeochemical Modeling and Correlation with Fluorine in Groundwater in a Semiarid Region of Mexico. Water 2022, 14, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahidul Hassan, H. A Review on Different Arsenic Removal Techniques Used for Decontamination of Drinking Water. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2023, 35, 2165964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devrajani, S.K.; Ahmed, Z.; Qambrani, N.A.; Kanwal, S.; Sundaram, U.M.; Mubarak, N.M. Mechanism of Arsenic Removal Using Brown Seaweed Derived Impregnated with Iron Oxide Biochar for Batch and Column Studies. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, K. Defluoridation Behavior of Layered Fe-Mg-Zr Hydroxides and Its Continuous Purification of Groundwater. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 578, 123640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo-Cisneros, R.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R.; Nava, J.L.; Larios-Durán, E.R.; Chazaro-Ruiz, L.F. Influence of Surface Chemistry of Activated Carbon Electrodes on Electro-Assisted Adsorption of Arsenate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizal, A.N.M.; Zaini, M.A.A. Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Carbon Gels Adsorption: A Commentary. Acta Chem. Iasi 2019, 27, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xiao, F.; Xie, X.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; You, X.; Gai, Y.; et al. Adsorption and Desorption of Hg(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Magnetic Fe3O4@PPy Composite Microspheres. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2021, 11, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptaszkowska-Koniarz, M.; Goscianska, J.; Bazan-Wozniak, A.; Pietrzak, R. Amine-Modified Carbon Xerogels as Effective Carbon-Based Adsorbents of Anionic Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2022, 15, 5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaminger, S.P.; Bauer, D.; Fraga-García, P.; Wagner, F.E.; Berensmeier, S. Oxidation of Magnetite Nanoparticles: Impact on Surface and Crystal Properties. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaefferer, S.; Habler, G. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Electron Backscatter Diffraction. Eur. Mineral. Union. Notes Mineral. 2017, 16, 37–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesús Ruíz-Baltazar, Á.; Reyes-López, S.Y.; de Lourdes Mondragón-Sánchez, M.; Robles-Cortés, A.I.; Pérez, R. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Evaluation of Their Catalytic Activity in Methylene Blue Degradation by Kinetic Adsorption Models. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N. Functional Biocompatible Magnetite-Cellulose Nanocomposite Fibrous Networks: Characterization by Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy, X-Ray Powder Diffraction and Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 1450–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elashmawi, I.S.; Alhusaiki-Alghamdi, H.M. Fabrication, Characterization, Spectroscopic, and Magnetic Properties of Polyaniline/Magnetite (PANi/Fe3O4) Nanocomposites. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2024, 56, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodewald, J.; Thien, J.; Ruwisch, K.; Pohlmann, T.; Hoppe, M.; Schmalhorst, J.; Küpper, K.; Wollschläger, J. Structure-Related Electronic and Magnetic Properties in Ultrathin Epitaxial NixFe3−xO4 Films on MgO(001). Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, P.; Horszczaruk, E.; Cendrowski, K.; Mijowska, E. The Influence of Nano-Fe3O4 on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cementitious Composites. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Miao, P.; Liang, J.; Wang, X. Effects of Carbonization Temperature on Structure and Mechanical Strength of Electrospun Carbon Nanofibrous Mats. Mater. Lett. 2020, 273, 127962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamkure, S.; Bustos-Terrones, V.; Torrecilla-Valle, A.; Gamero-Melo, P.; Reyes-Rosas, A.; Vargas-Gutiérrez, G.; Garrido-Hoyos, S.E. Optimization Study for Desorption of Arsenic and Regeneration Performance on Magnetic Carbon Xerogels for Environmental Sustainability †. Eng. Proc. 2023, 37, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Hansda, K.M.; Mahata, N. Tuning of Pore Texture of Carbon Xerogels Synthesized Using Resorcinol and Paraformaldehyde as Precursors. J. Indian. Chem. Soc. 2020, 97, 743–747. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas, S.; Heryanto; Abdullah, B.; Tahir, D. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis of Nanocomposite Fe3O4/Activated Carbon by Williamson–Hall and Size-Strain Plot Methods. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2019, 20, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Levin, B.D.A.; Schmidt, M.P.; Guzman, J.J.L.; Enders, A.; Martínez, C.E.; Muller, D.A.; Angenent, L.T.; Lehmann, J. Simultaneous Quantification of Electron Transfer by Carbon Matrices and Functional Groups in Pyrogenic Carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8538–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, S.M.; Abdelfatah, M.S.; Mossad, M.M. Conduction Mechanism and Dielectric Properties of Pure and Composite Resorcinol Formaldehyde Aerogels Doped with Silver. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 869, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, P.; Khraisheh, M.; Kandasubramanian, B. Nanofibers of Resorcinol–Formaldehyde for Effective Adsorption of As (III) Ions from Mimicked Effluents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11729–11745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Li, Y.; Ke, Y.; Shi, M.; Chai, L.; Xue, K. Fe-FeS2 Adsorbent Prepared with Iron Powder and Pyrite by Facile Ball Milling and Its Application for Arsenic Removal. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Mora, M.S.; Alfaro-Cuevas-Villanueva, R.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Hernández-Cristóbal, O.; Cortés-Martínez, R. Removal of As(V) from Aqueous Solutions Using Calcium-Alginate Microspheres with Encapsulated Iron Nanoparticles. Water Supply 2022, 22, 2896–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, U.K.; Mandal, S.; Sahu, S.; Gouda, N.; Patel, R.K. Preparation and Characterization of Mesoporous Cerium Oxide for Toxic As(V) Removal: Performance and Mechanistic Studie. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2022, 30, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, N.; Li, G. A Critical Review on Arsenic Removal from Water Using Iron-Based Adsorbents. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 39545–39560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaika, A.; Morawa Eblagon, K.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. The Impact of Surface Chemistry of Carbon Xerogels on Their Performance in Phenol Removal from Wastewaters via Combined Adsorption-Catalytic Process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 511, 145467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Lin, W.; Fan, L. Novel Method for the Arsenic Removal Experiment and Mechanism Analysis. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 35893–35903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antić, K.; Onjia, A.; Vasiljević-Radović, D.; Veličković, Z.; Tomić, S.L. Removal of Nickel Ions from Aqueous Solutions by 2-Hydroxyethyl Acrylate/Itaconic Acid Hydrogels Optimized with Response Surface Methodology. Gels 2021, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayuo, J.; Rwiza, M.J.; Choi, J.W.; Sillanpää, M.; Mtei, K.M. Optimization of Desorption Parameters Using Response Surface Methodology for Enhanced Recovery of Arsenic from Spent Reclaimable Activated Carbon: Eco-Friendly and Sorbent Sustainability Approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 280, 116550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, F.S.; Izanloo, H.; Heidari, H.; Vaezi, N.; Zamanzadeh, M.; Nadali, A.; Aali, R.; Asadi-Ghalhari, M. Modeling and Optimization of Arsenic (III) Removal from Aqueous Solutions by GFO Using Response Surface Methodology. Pollution 2020, 6, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, C.; Reis, F.D.A.A. Interplay of Adsorption and Surface Mobility in Tracer Diffusion in Porous Media. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 022120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Flores, H.; Pariona, N.; Herrera-Trejo, M.; Hdz-García, H.M.; Mtz-Enriquez, A.I. Concrete/Maghemite Nanocomposites as Novel Adsorbents for Arsenic Removal. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1171, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamkure, S.; Gamero-Melo, P.; Garrido-Hoyos, S.E.; Reyes-Rosas, A.; Pacheco-Catalán, D.E.; López-Martínez, A.M. The Development of Fe3O4-Monolithic Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Carbon Xerogels Using Ultrasonic-Assisted Synthesis for Arsenic Removal of Drinking Water. Gels 2023, 9, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamkure, S.; Garrido-Hoyos, S.E.; Gamero-Melo, P.; Reyes-Rosas, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Xerogel Monolith as an Adsorbent for As(V) Removal from Groundwater. Processes 2021, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embaby, M.A.; Abdel Moniem, S.M.; Fathy, N.A.; El-kady, A.A. Nanocarbon Hybrid for Simultaneous Removal of Arsenic, Iron and Manganese Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.K.; Khare, P.; Verma, N. Synthesis of Iron-Doped Resorcinol Formaldehyde-Based Aerogels for the Removal of Cr(VI) from Water. Green. Process. Synth. 2015, 4, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Magnetic Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticle Synthesis and Applications for Lead (Pb2+) and Chromium (Cr6+) Removal from Water. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2016, 468, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, G.; Scarfone, A.M.; Evangelista, L.R. The Kinetics of Sorption–Desorption Phenomena: Local and Non-Local Kinetic Equations. Molecules 2022, 27, 7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Luna, J.; Ramírez-Montes, L.E.; Martinez-Vargas, S.; Martínez, A.I.; Mijangos-Ricardez, O.F.; González-Chávez, M.D.C.A.; Carrillo-González, R.; Solís-Domínguez, F.A.; Cuevas-Díaz, M.d.C.; Vázquez-Hipólito, V. Linear and Nonlinear Kinetic and Isotherm Adsorption Models for Arsenic Removal by Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, L.A.; Salimi, L.; Nabi-Bidhendi, G.; Gafourian, H.; Baghdadi, M. Removal of Cadmium Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Nickel Metal-Organic Framework: Isotherm, Kinetic Studies, Optimization, and Modeling by Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 227, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

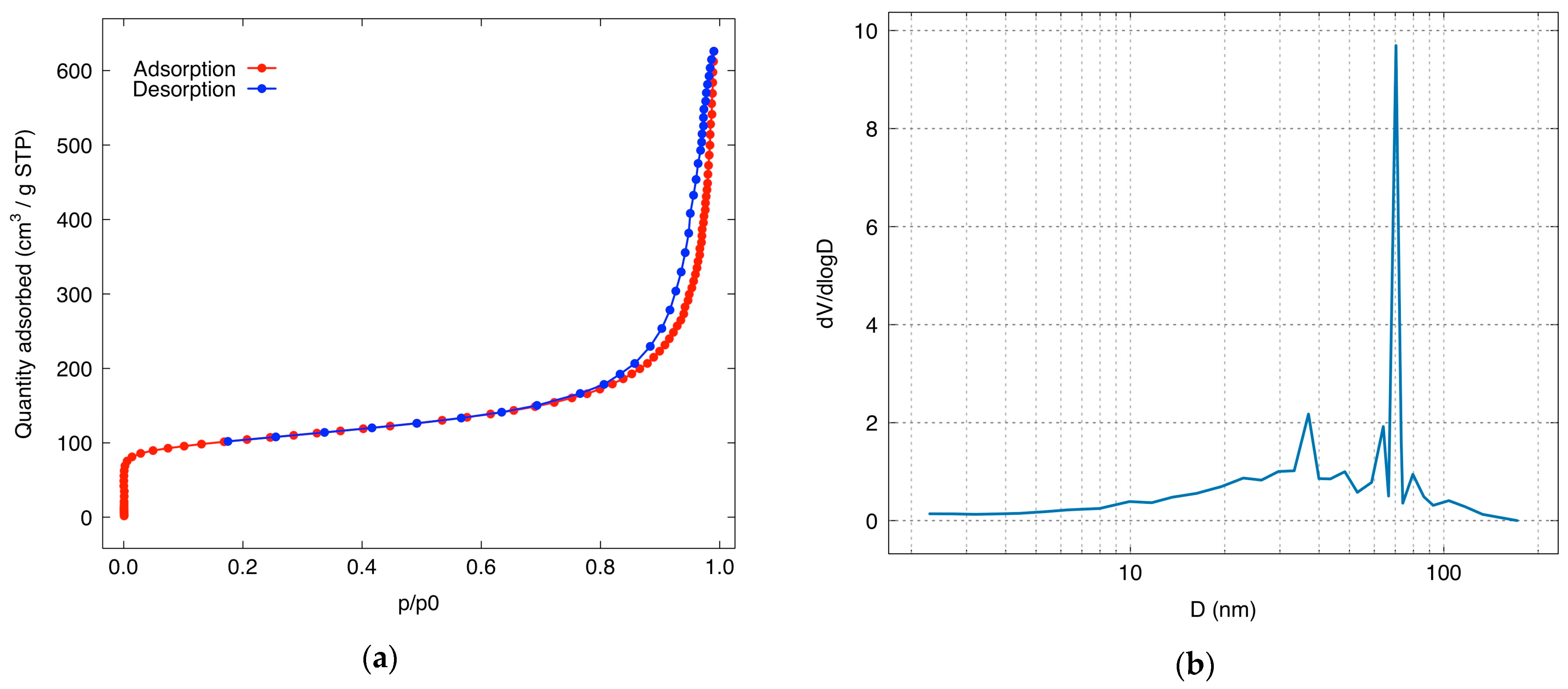
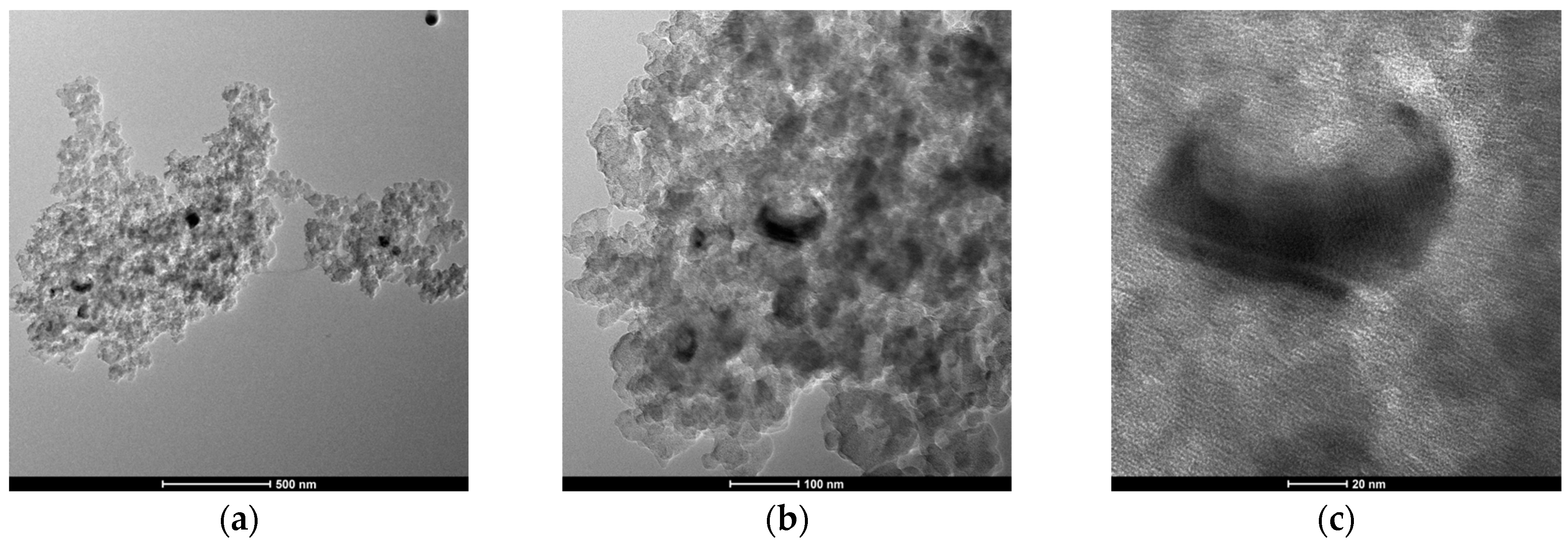
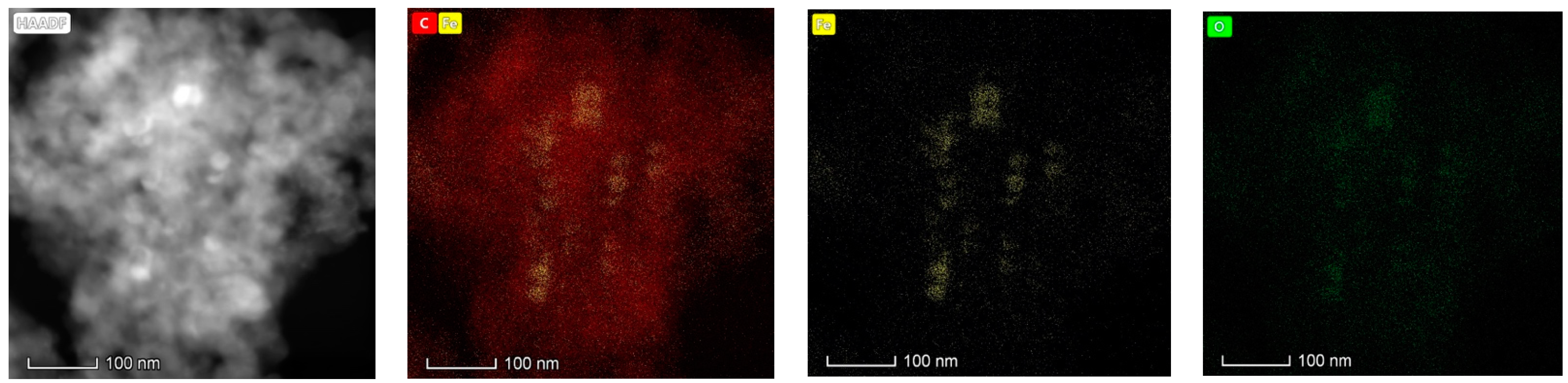

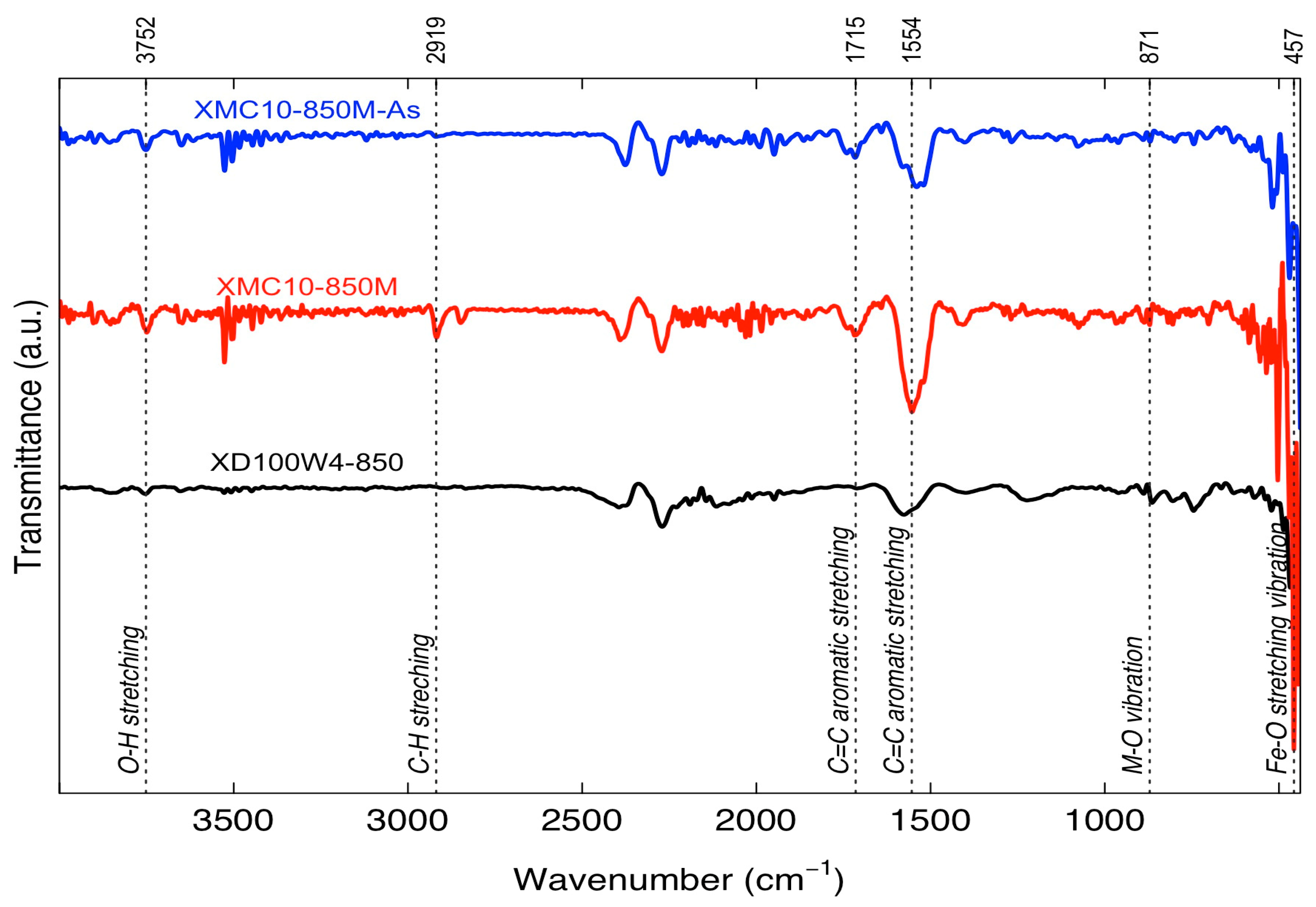


| Pore Size Range (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2.00–10.00 | 0.13751 | 15.22 |
| 10.00–20.00 | 0.09271 | 10.26 |
| 20.00–50.00 | 0.18482 | 20.45 |
| >50.00 | 0.48856 | 54.07 |
| Kinetic Models | Parameters and Correlation Coefficients | XMC10-600M | XMC10-850M |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-First-Order equation (PFO) | k1 | 0.2837 | 0.0046 |
| qt (µg/g) | 211.23 | 459.4 | |
| R2 | 0.218 | 0.846 | |
| RMSE | 45.73 | 65.23 | |
| Pseudo-Second-Order equation (PSO) | k2 | 0.0018 | 0.00001 |
| qt (µg/g) | 220.9 | 497.7 | |
| R2 | 0.3319 | 0.8977 | |
| RMSE | 42.29 | 53.25 | |
| Elovich | β | 0.0476 | 0.0102 |
| α | 2795.3 | 8.048 | |
| R2 | 0.7375 | 0.9396 | |
| RMSE | 26.51 | 40.90 | |
| Power | β | 0.1190 | 0.3483 |
| α | 111.5 | 39.07 | |
| R2 | 0.8037 | 0.9443 | |
| RMSE | 22.92 | 39.30 |
| Factors | Coding Factors | Desorbing Agent | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNO3 | KOH | ||||||
| Low | Center | High | Low | Center | High | ||
| (−1) | 0 | −1 | (−1) | 0 | −1 | ||
| Desorbing solution concentration (M) | x1 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 |
| Agitation speed (rpm) | x2 | 80 | 120 | 160 | 80 | 120 | 160 |
| Dose of used adsorbent (g/L) | x3 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khamkure, S.; Gamero-Melo, P.; Reyes-Rosas, A.; Zermeño-González, A.; Álvarez-Cruz, J.L.; Albiter Escobar, E.; Moeller-Chávez, G.E.; Bustos-Terrones, V. Engineered Magnetic-Functionalized Carbon Xerogels for Sustainable Arsenic Removal: Bridging Adsorption Efficiency with Regenerability. Gels 2025, 11, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050323
Khamkure S, Gamero-Melo P, Reyes-Rosas A, Zermeño-González A, Álvarez-Cruz JL, Albiter Escobar E, Moeller-Chávez GE, Bustos-Terrones V. Engineered Magnetic-Functionalized Carbon Xerogels for Sustainable Arsenic Removal: Bridging Adsorption Efficiency with Regenerability. Gels. 2025; 11(5):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050323
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhamkure, Sasirot, Prócoro Gamero-Melo, Audberto Reyes-Rosas, Alejandro Zermeño-González, José Luis Álvarez-Cruz, Elim Albiter Escobar, Gabriela Eleonora Moeller-Chávez, and Victoria Bustos-Terrones. 2025. "Engineered Magnetic-Functionalized Carbon Xerogels for Sustainable Arsenic Removal: Bridging Adsorption Efficiency with Regenerability" Gels 11, no. 5: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050323
APA StyleKhamkure, S., Gamero-Melo, P., Reyes-Rosas, A., Zermeño-González, A., Álvarez-Cruz, J. L., Albiter Escobar, E., Moeller-Chávez, G. E., & Bustos-Terrones, V. (2025). Engineered Magnetic-Functionalized Carbon Xerogels for Sustainable Arsenic Removal: Bridging Adsorption Efficiency with Regenerability. Gels, 11(5), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050323








