An On-Demand Dissoluble Chitosan Hydrogel Containing Dynamic Diselenide Bond
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Diselenide Modified Chitosan
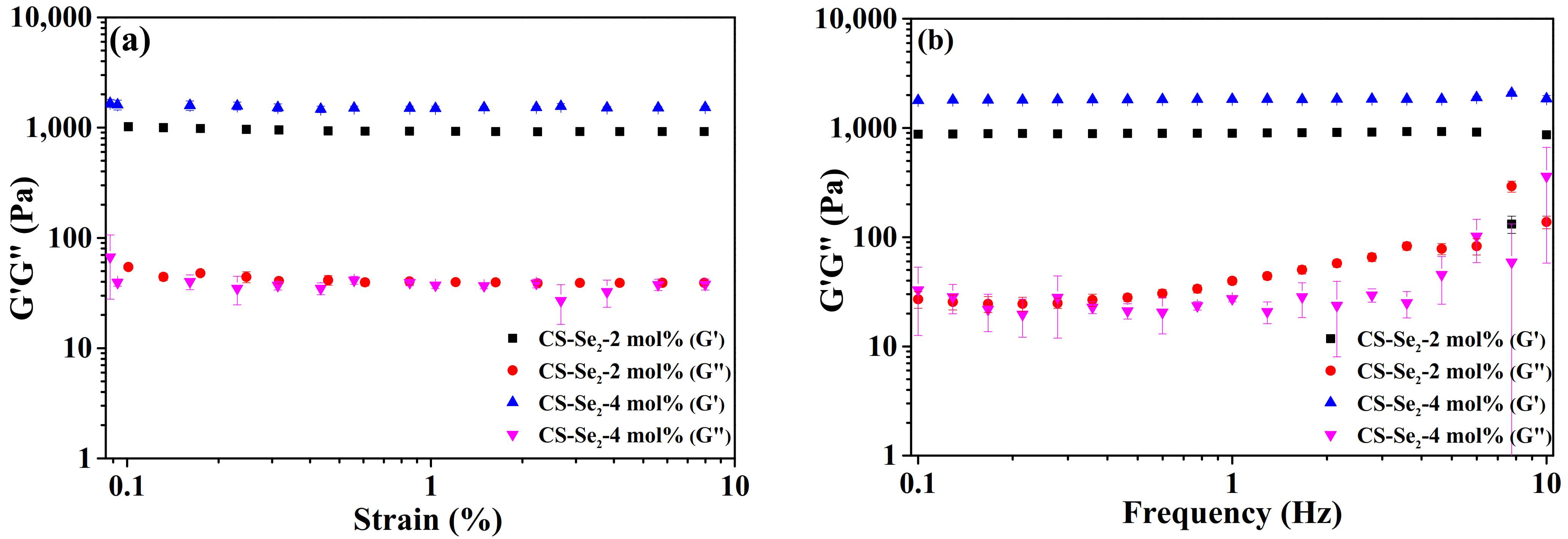
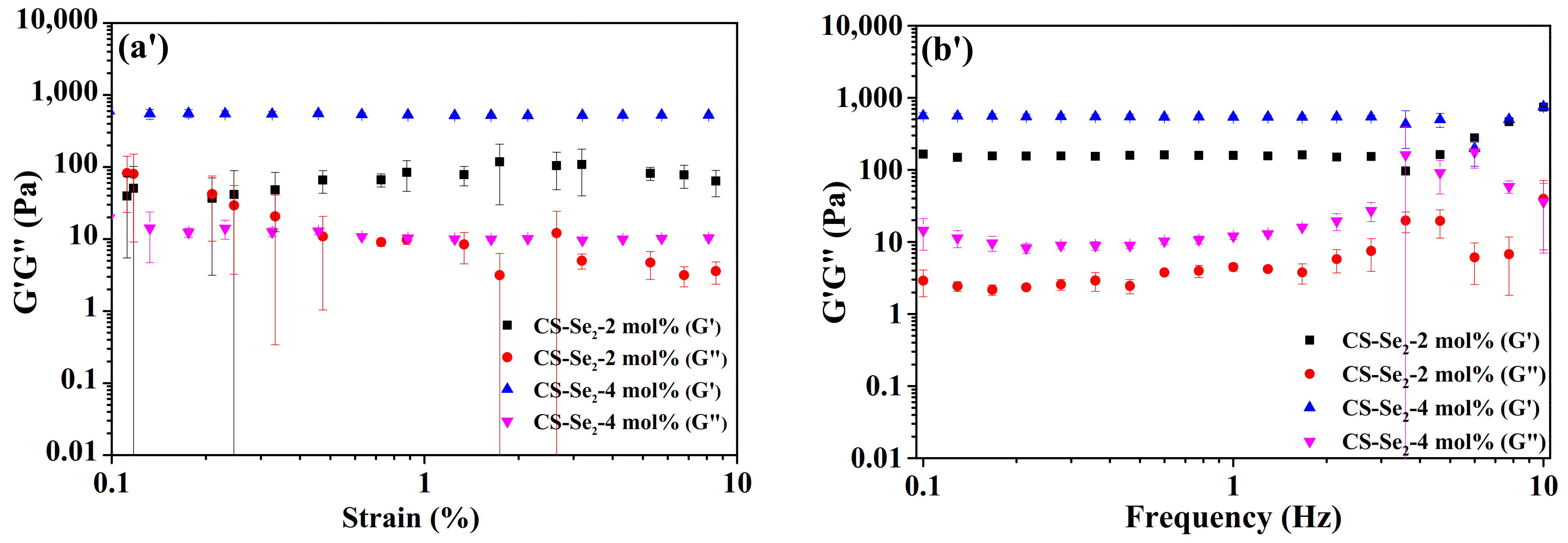
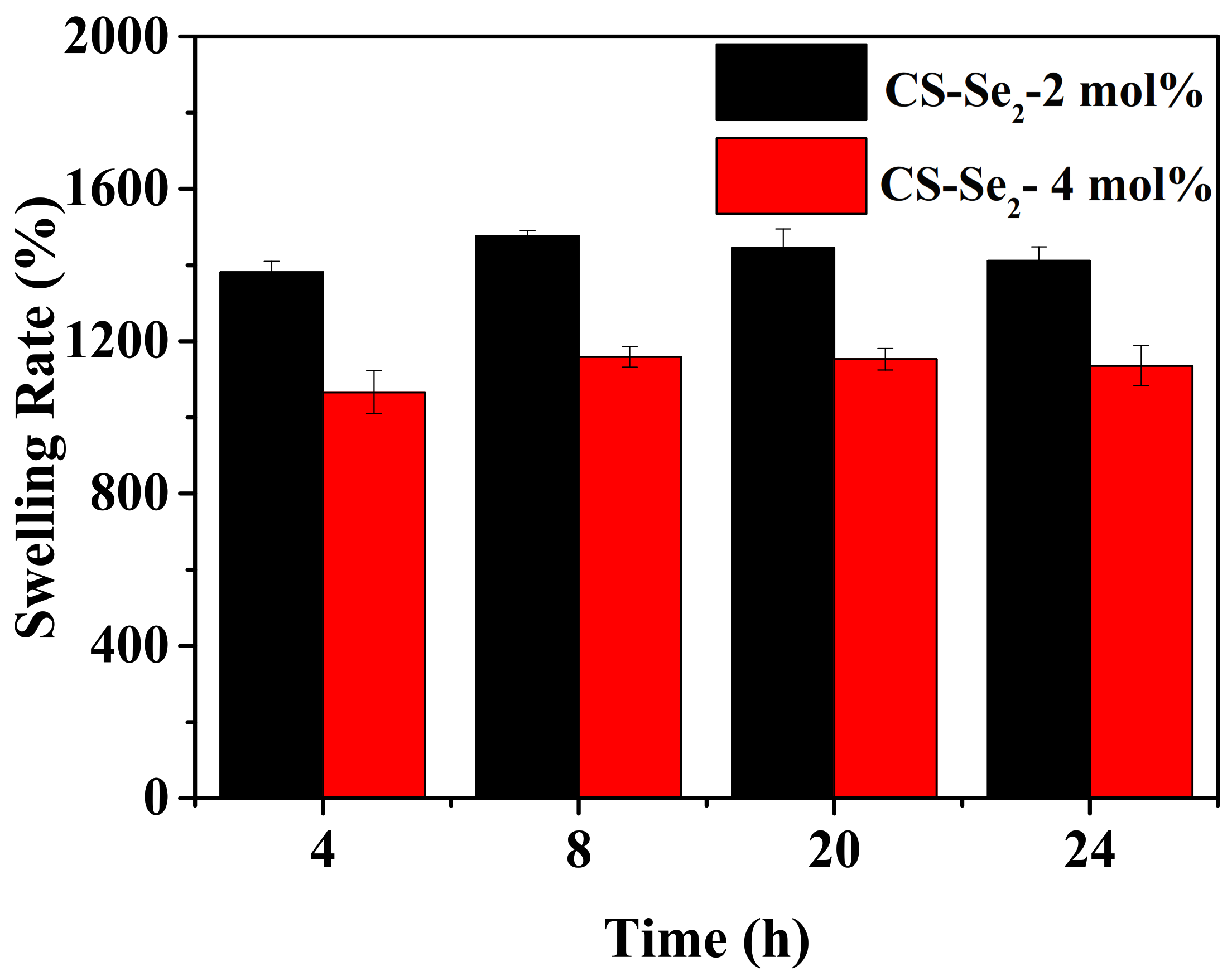
2.2. Rheological Property, Swelling Behaviour of Se-Containing CS-Se2 Hydrogels
2.3. On Demand Dissolution of CS-Se2 Hydrogels
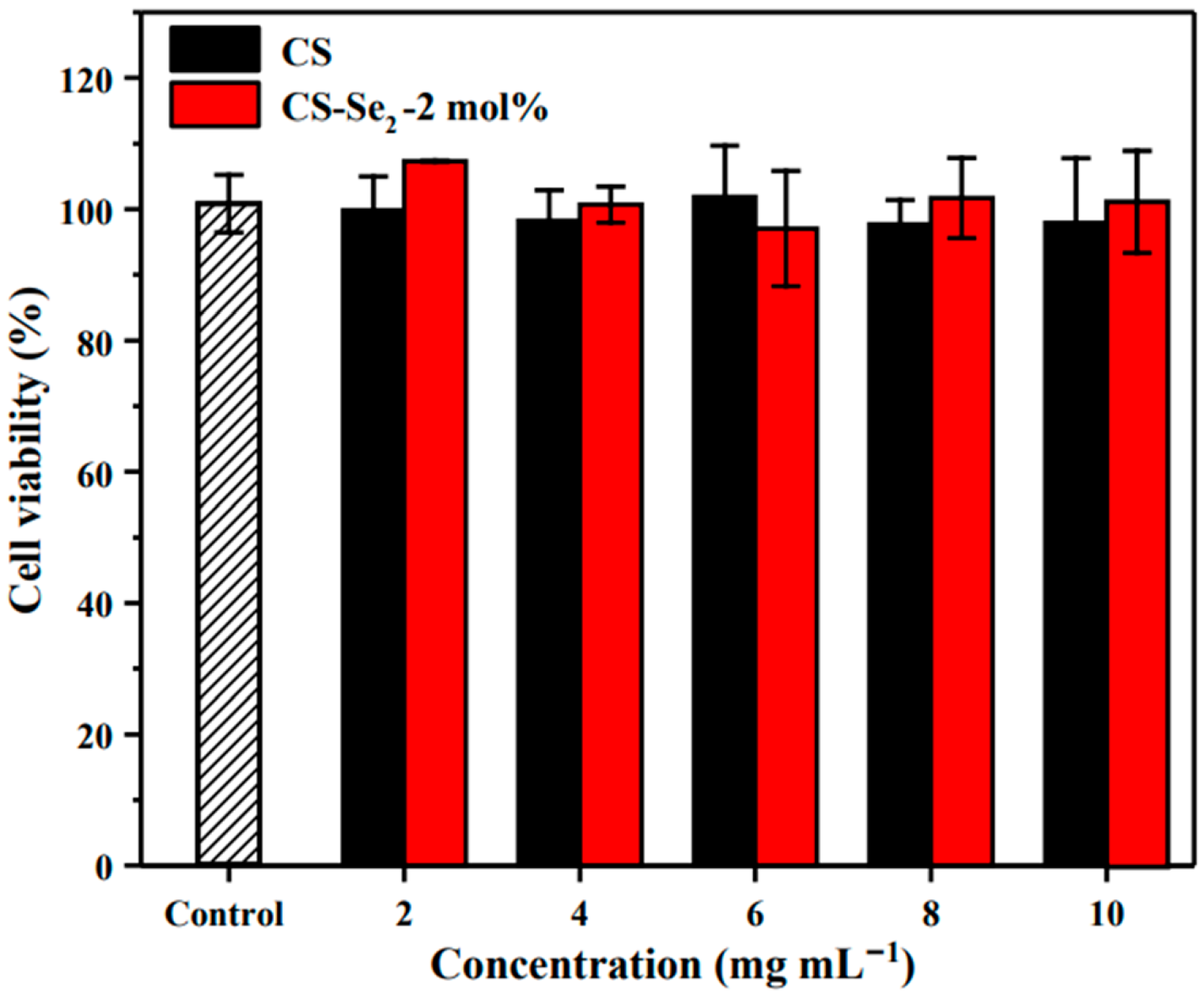
2.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies of the Hydrogel
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Se-Containing Chitosan Hydrogels
4.3. Structural Characterization of Se-Containing Chitosan Hydrogels
4.4. Rheology Characterization of Se-Containing Chitosan Hydrogels
4.5. Swelling Behavior of Se-Containing Chitosan Hydrogels
4.6. The Redox Responsive Behavior of Se-Containing Chitosan Hydrogels
4.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pillai, C.K.S.; Paul, W.; Sharma, C.P. Chitin and chitosan polymers: Chemistry, solubility and fiber formation. Prog. Poly. Sci. 2009, 34, 641–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braconnot, H. Sur la nature des champignons. Ann. Chim. Phys. 1811, 79, 265–304. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, K.; Aoki, H.; Nakamura, S.; Nakamura, S.; Takikawa, M.; Hanzawa, M.; Kishimoto, S.; Hattori, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Kiyosawa, T.; et al. Hydrogel blends of chitin/chitosan, fucoidan and alginate as healing-impaired wound dressings. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert-Viard, F.; Martin, A.; Chai, F.; Neut, C.; Tabary, N.; Martel, B.; Blanchemain, N. Chitosan finishing nonwoven textiles loaded with silver and iodide for antibacterial wound dressing applications. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 015023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Yuan, B.M.; Dong, X.M.; Duan, L.J.; Tian, H.Y.; He, C.L.; Chen, X.S. Injectable polysaccharide hybrid hydrogels as scaffolds for burn wound healing. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 94248–94256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aussel, A.; Thebaud, N.B.; Berard, X.; Brizzi, V.; Delmond, S.; Bareille, R.; Siadous, R.; James, C.; Ripoche, J.; Durand, M.; et al. Chitosan-based hydrogels for developing a small-diameter vascular graft: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 12, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, O.; Lyngstadaas, S.P.; Monjo, M.; Satue, M.; Ronold, H.J.; Petzold, C.; Wohlfahrt, J.C. Suture materials affect pen-implant bone healing and implant osseointegration. J. Oral Sci. 2015, 57, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, H.; Moradi, S.; Hudson, S.M.; Tonelli, A.E. Chitosan based hydrogels and their applications for drug delivery in wound dressings: A review. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 199, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatinia, Z. Carboxymethyl chitosan: Properties and biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1406–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, F.; Zhou, Y.N.; Wang, H.S.; Wan, T.; Zhong, C.; Chu, L.Q. Injectable self-healing carboxymethyl chitosan-zinc supramolecular hydrogels and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Liu, Y.; Song, S.; Tong, C.; Shi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hou, M. Influence of chitosan oligosaccharide on the gelling and wound healing properties of injectable hydrogels based on carboxymethyl chitosan/alginate polyelectrolyte complexes. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 205, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Tao, L.; Li, S.X.; Wei, Y. Synthesis of Multiresponsive and Dynamic Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Controlled Release of Bioactive Molecules. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2894–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; Yuan, J.G.; Shen, J.S.; Fan, X.R. Disulfide bond reconstruction: A novel approach for grafting of thiolated chitosan onto wool. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.W.; Liu, X.F.; Miller, A.L.; Cheng, Y.S.; Yeh, M.L.; Lu, L.C. Strengthening injectable thermo-sensitive NIPAAm-g-chitosan hydrogels using chemical cross-linking of disulfide bonds as scaffolds for tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobril, C.; Charoen, K.; Rodriguez, E.K.; Nazarian, A.; Grinstaff, M.W. A dendritic thioester hydrogel based on thiol-thioester exchange as a dissolvable sealant system for wound closure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 14070–14074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczynska, M.D.; Grinstaff, M.W. On-Demand Dissolution of Chemically Cross-Linked Hydrogels. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghizadeh, Z.; Karkhaneh, A.; Khojasteh, A. Self-crosslinking effect of chitosan and gelatin on alginate based hydrogels: Injectable in situ forming scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 89, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. On-Demand dissolvable self-healing hydrogel based on carboxymethyl chitosan and cellulose nanocrystal for deep partial thickness burn wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41076–41088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczynska, M.D.; Villa-Camacho, J.C.; Ghobril, C.; Perez-Viloria, M.; Tevis, K.M.; Blessing, W.A.; Nazarian, A.; Rodriguez, E.K.; Grinstaff, M.W. On-Demand Dissolution of a Dendritic Hydrogel-based Dressing for Second-Degree Burn Wounds through Thiol-Thioester Exchange Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9984–9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yuan, L.; Yu, X.Z.; Wu, C.Z.; He, D.F.; Deng, J. Recent Advances of On-Demand Dissolution of Hydrogel Dressings. Burns Trauma 2018, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cao, W.; Zhang, X. Selenium-containing polymers: Promising biomaterials for controlled release and enzyme mimics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayman, M.P. The importance of selenium to human health. Lancet 2000, 356, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomburg, L.; Schweizer, U.; Kohrle, J. Selenium and selenoproteins in mammals: Extraordinary, essential, enigmatic. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Berry, M.J. Selenium and selenoproteins in the brain and brain diseases. J. Neurochem. 2004, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquedano, Y.; Alcolea, V.; Toro, M.A.; Gutierrez, K.J.; Nguewa, P.; Font, M.; Moreno, E.; Espuelas, S.; Jimenez-Ruiz, A.; Palop, J.A.; et al. Novel Heteroaryl Selenocyanates and Diselenides as Potent Antileishmanial Agents. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 60, 3802–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, H.J.; Ryplida, B.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, G.; Ryu, J.H.; Park, S.Y. Diselenide-Bridged Carbon-Dot-Mediated Self-Healing, Conductive, and Adhesive Wireless Hydrogel Sensors for Label-Free Breast Cancer Detection. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8409–8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, W.; Huang, W.; Huo, F.; Xu, H. Selenium-Containing Polymer@Metal-Organic Frameworks Nanocomposites as an Efficient Multiresponsive Drug Delivery System. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepagan, V.G.; Kwon, S.; You, D.G.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Um, W.; Ko, H.; Lee, H.; Jo, D.-G.; Kang, Y.M.; Park, J.H. In Situ Diselenide-Crosslinked Polymeric Micelles for ROS-Mediated Anticancer Drug Delivery. Biomaterials 2016, 103, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; He, H.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Yin, L. Serum-resistant, reactive oxygen species (ROS)-potentiated gene delivery in cancer cells mediated by fluorinated, diselenide-crosslinked polyplexes. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anugrah, D.S.B.; Ramesh, K.; Kim, M.; Hyun, K.; Lim, K.T. Near-infrared light-responsive alginate hydrogels based on diselenide-containing cross-linkage for on demand degradation and drug release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; An, X.; Pang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, J.; Du Prez, F.E.; Pan, X. Dynamic diselenide-containing polyesters from alcoholysis/oxidation of γ-butyroselenolactone. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 4044–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.W.; Aguirresarobe, R.H.; Irusta, L.; Ruiperez, F.; Matxain, J.M.; Pan, X.Q.; Aramburu, N.; Mecerreyes, D.; Sardon, H.; Zhu, J. Aromatic diselenide crosslinkers to enhance the reprocessability and self-healing of polyurethane thermosets. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3641–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.W.; Lu, W.H.; Pang, M.L.; Zhang, Z.B.; Zhu, X.L.; Zhu, J.; Pan, X.Q. One-pot cascade polymerization based on the addition reactions of electrophilic selenium reagents to alkenes. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Vergaelen, M.; Pan, X.; Du Prez, F.E.; Hoogenboom, R.; De Clerck, K. In Situ Cross-Linked Nanofibers by Aqueous Electrospinning of Selenol-Functionalized Poly(2-oxazoline)s. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 6149–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Xu, X.; Imbernon, L.; Zhu, J.; Hoogenboom, R.; Du Prez, F.E.; Pan, X. On-Demand Dissoluble Diselenide-Containing Hydrogel. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 3308–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Driessen, F.; Zhu, X.; Du Prez, F.E. Selenolactone as a building block toward dynamic diselenide-containing polymer architectures with controllable topology. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kats, L. Catalysis of Reduction of Disulfide by Selenol. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 232, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.; Koul, V.; Dinda, A.K. In vitro and in vivo investigational studies of a nanocomposite-hydrogel-based dressing with a silver-coated chitosan wafer for full-thickness skin wounds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Cao, W.; Yi, Y.; Geng, W.; Sun, Z.; Xu, H. Selenium-platinum coordination compounds as novel anticancer drugs: Selectively killing cancer cells via a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated apoptosis route. Chem. Asian J. 2014, 9, 2295–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.T.; Huang, W.; Zhou, L.Z.; Huang, P.; Pang, Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Yan, D.Y. PEGylated poly(diselenide-phosphate) nanogel as efficient self-delivery nanomedicine for cancer therapy. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 6498–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashida, H.; Nakayama, A.; Kaname, M. A New One-Pot Synthetic Method for Selenium-Containing Medium-Sized α, β-Unsaturated Cyclic Ketones. Synthesis 2008, 2008, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



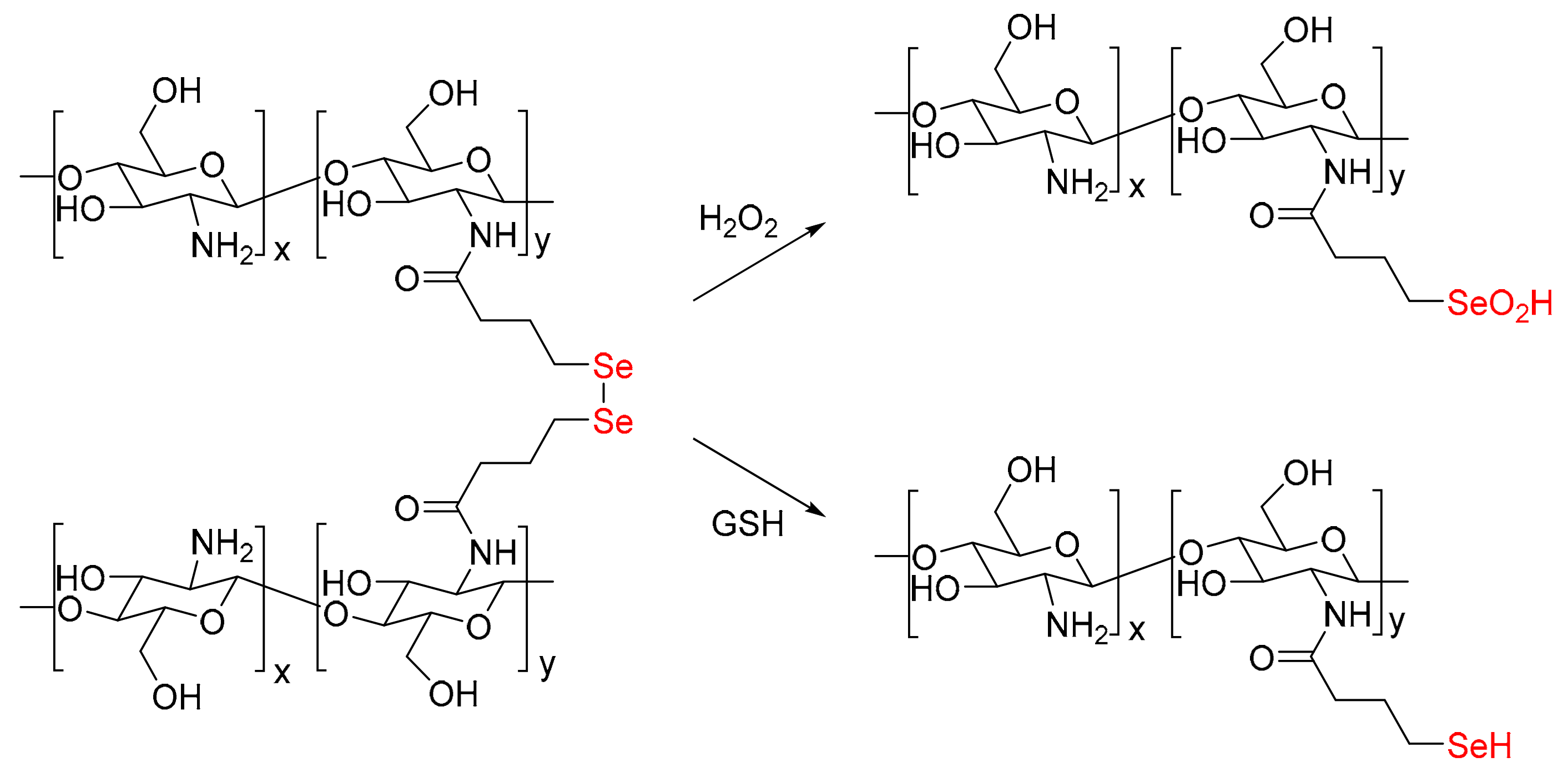
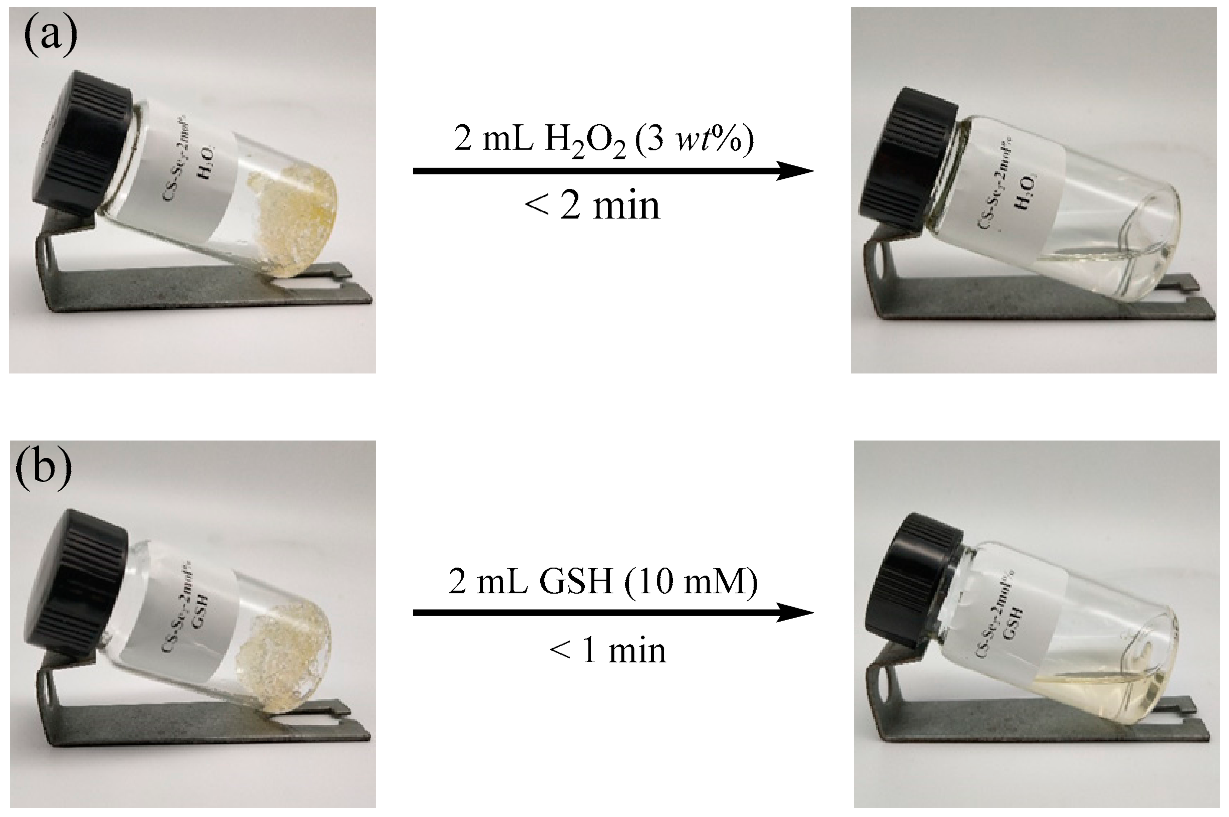
| Selenium Content (mol%) | H2O2 (3 wt%) | GSH (10 mM) | Degradation Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 mL | – | <2 |
| 4 | 2 mL | – | <4.5 |
| 2 | – | 2 mL | <1 |
| 4 | – | 2 mL | <1.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Lu, W.; Zhu, J.; Pan, X.; Zhu, X. An On-Demand Dissoluble Chitosan Hydrogel Containing Dynamic Diselenide Bond. Gels 2021, 7, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7010021
Xu X, Lu W, Zhu J, Pan X, Zhu X. An On-Demand Dissoluble Chitosan Hydrogel Containing Dynamic Diselenide Bond. Gels. 2021; 7(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xingxia, Weihong Lu, Jian Zhu, Xiangqiang Pan, and Xiulin Zhu. 2021. "An On-Demand Dissoluble Chitosan Hydrogel Containing Dynamic Diselenide Bond" Gels 7, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7010021
APA StyleXu, X., Lu, W., Zhu, J., Pan, X., & Zhu, X. (2021). An On-Demand Dissoluble Chitosan Hydrogel Containing Dynamic Diselenide Bond. Gels, 7(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7010021






