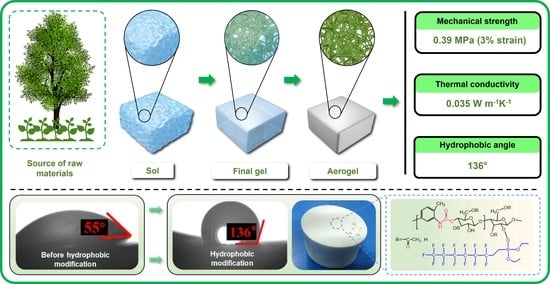
Hydrophobic Cellulose Acetate Aerogels for Thermal Insulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
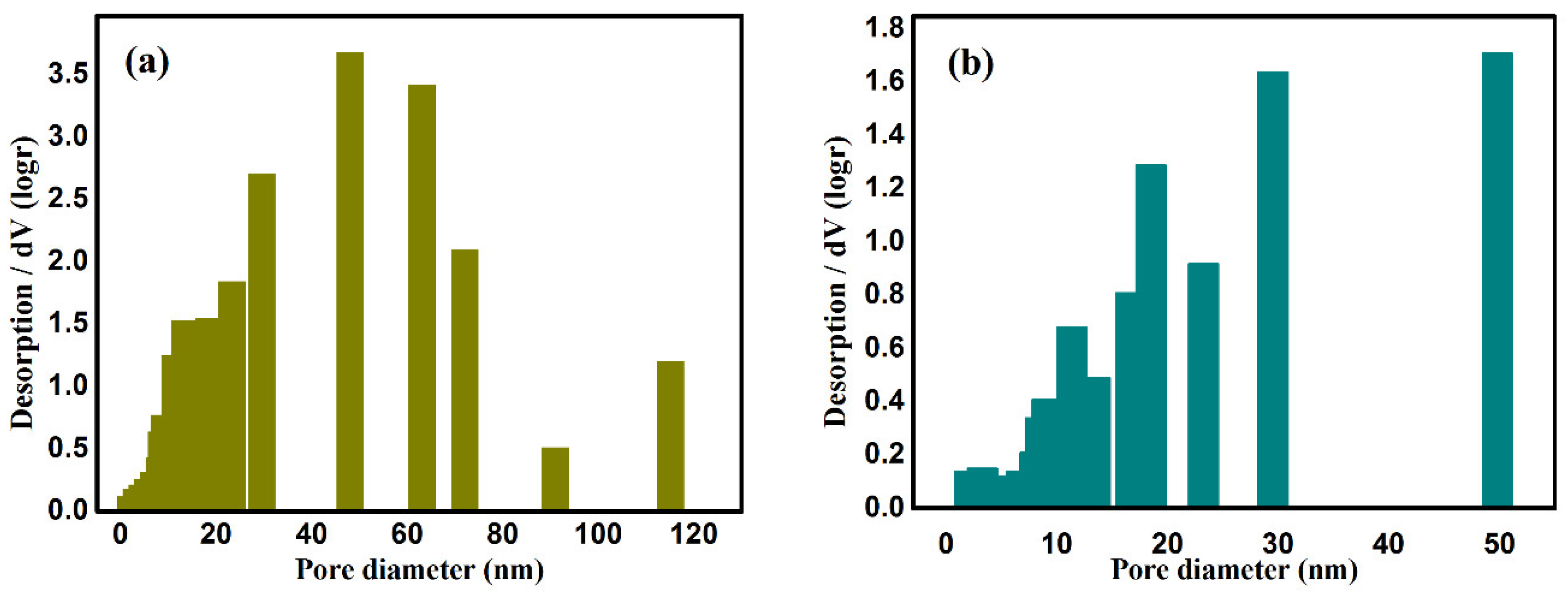
2.1. Microstructure Texture
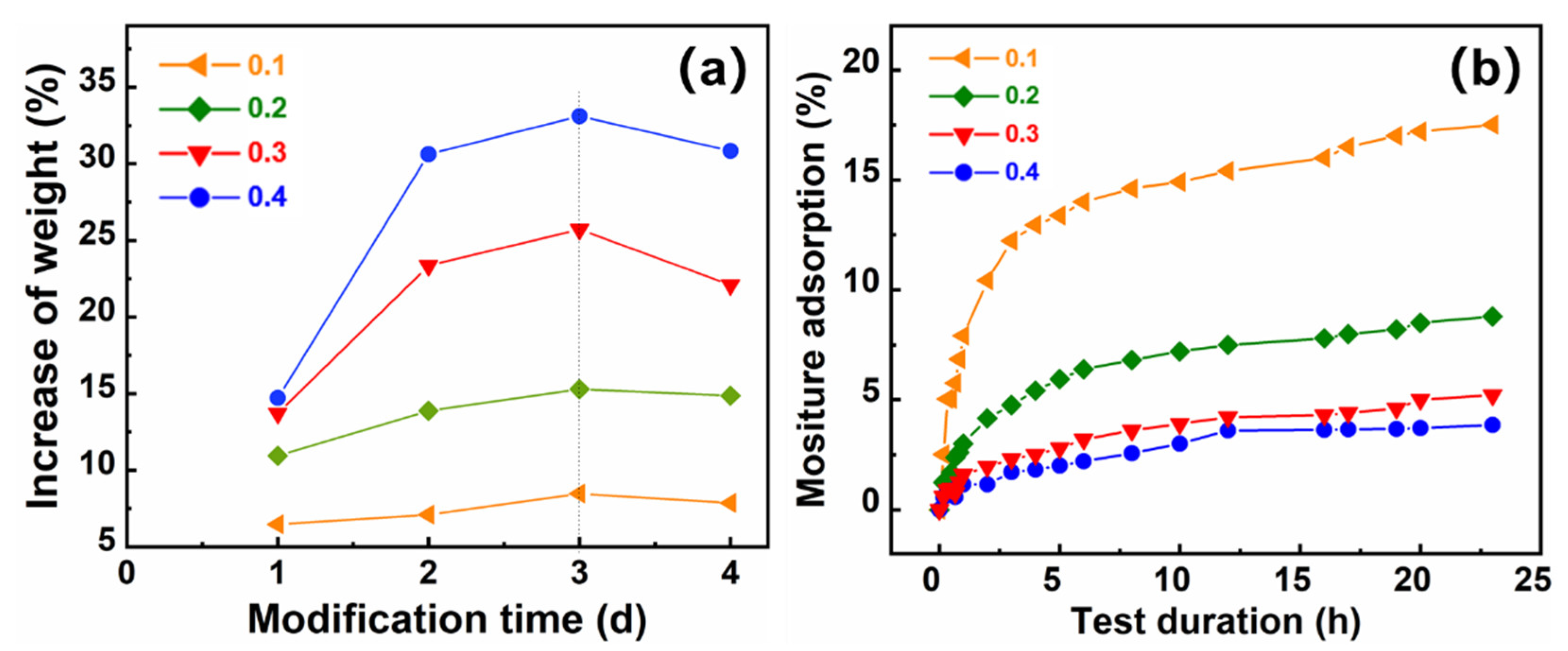
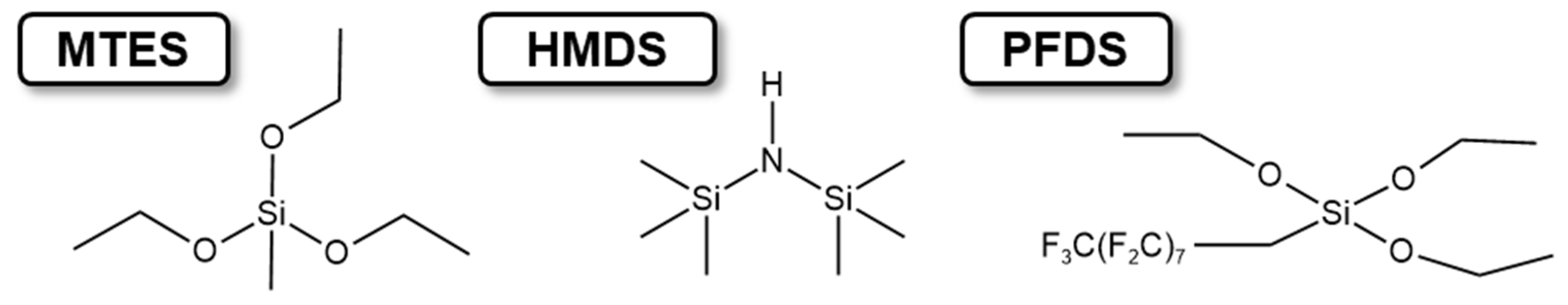
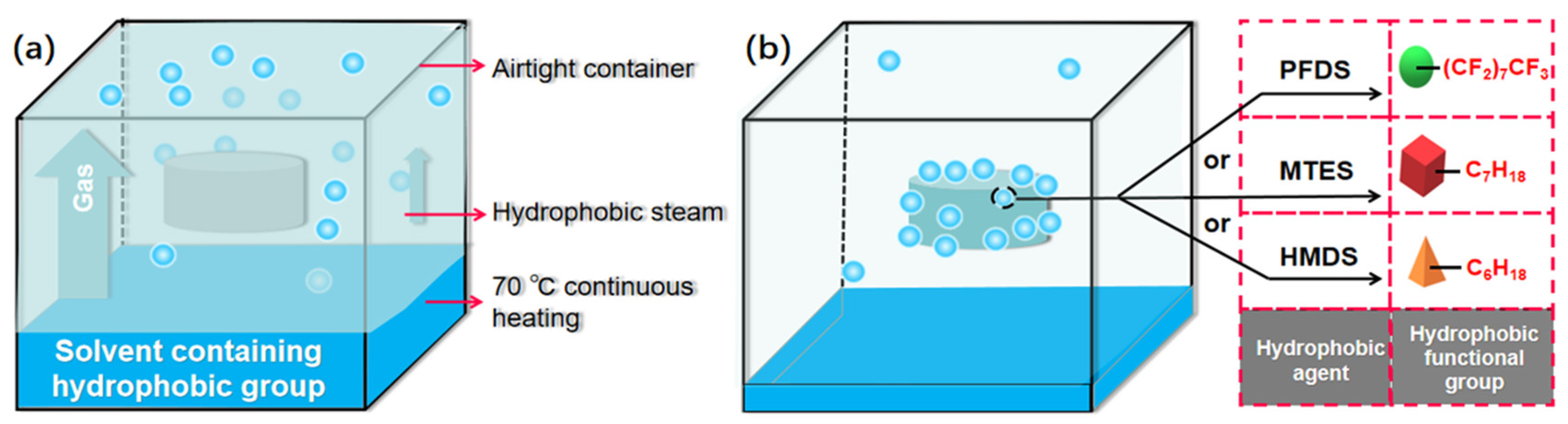
2.2. Cross-Linking Reaction and Hydrophobic Reaction
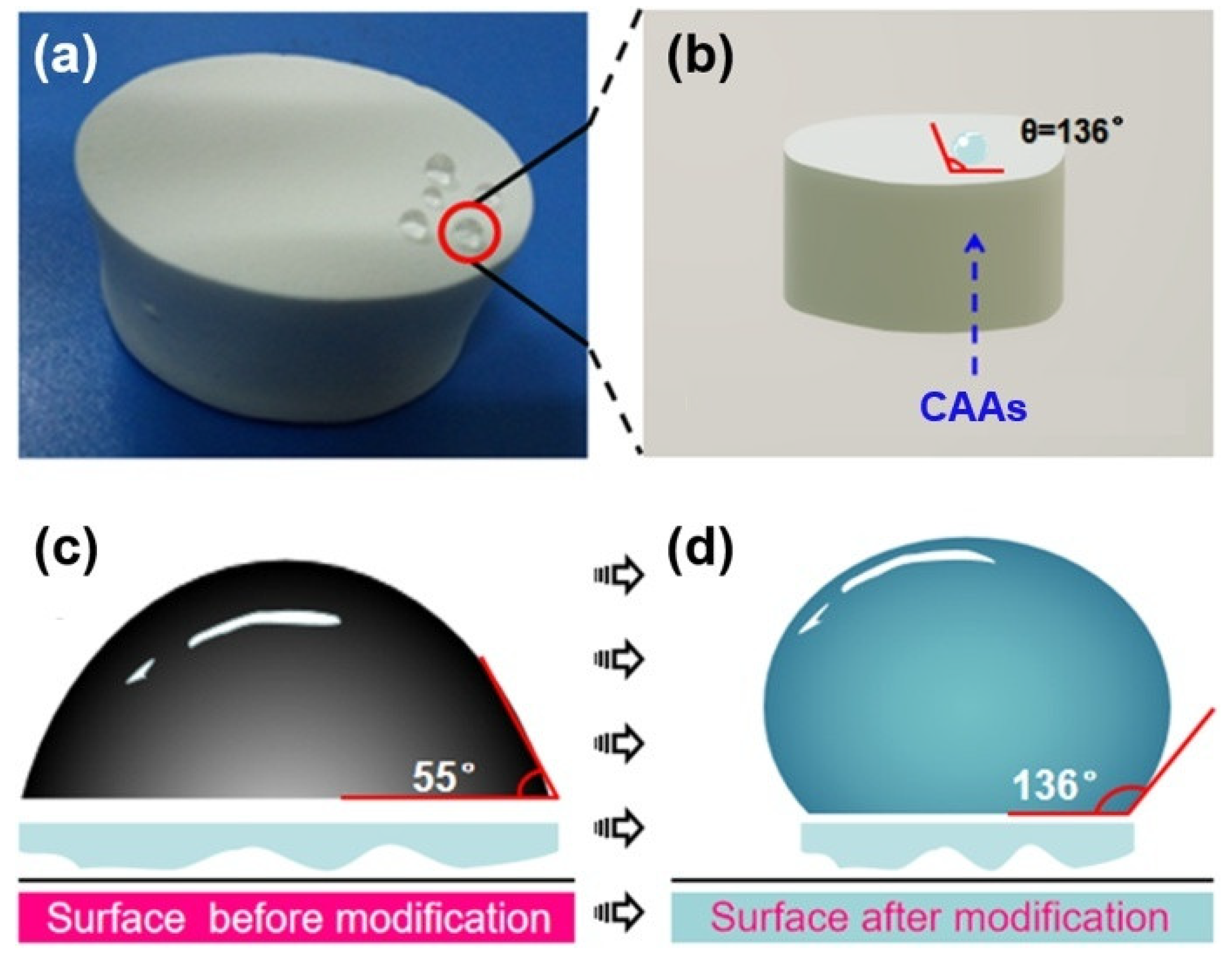
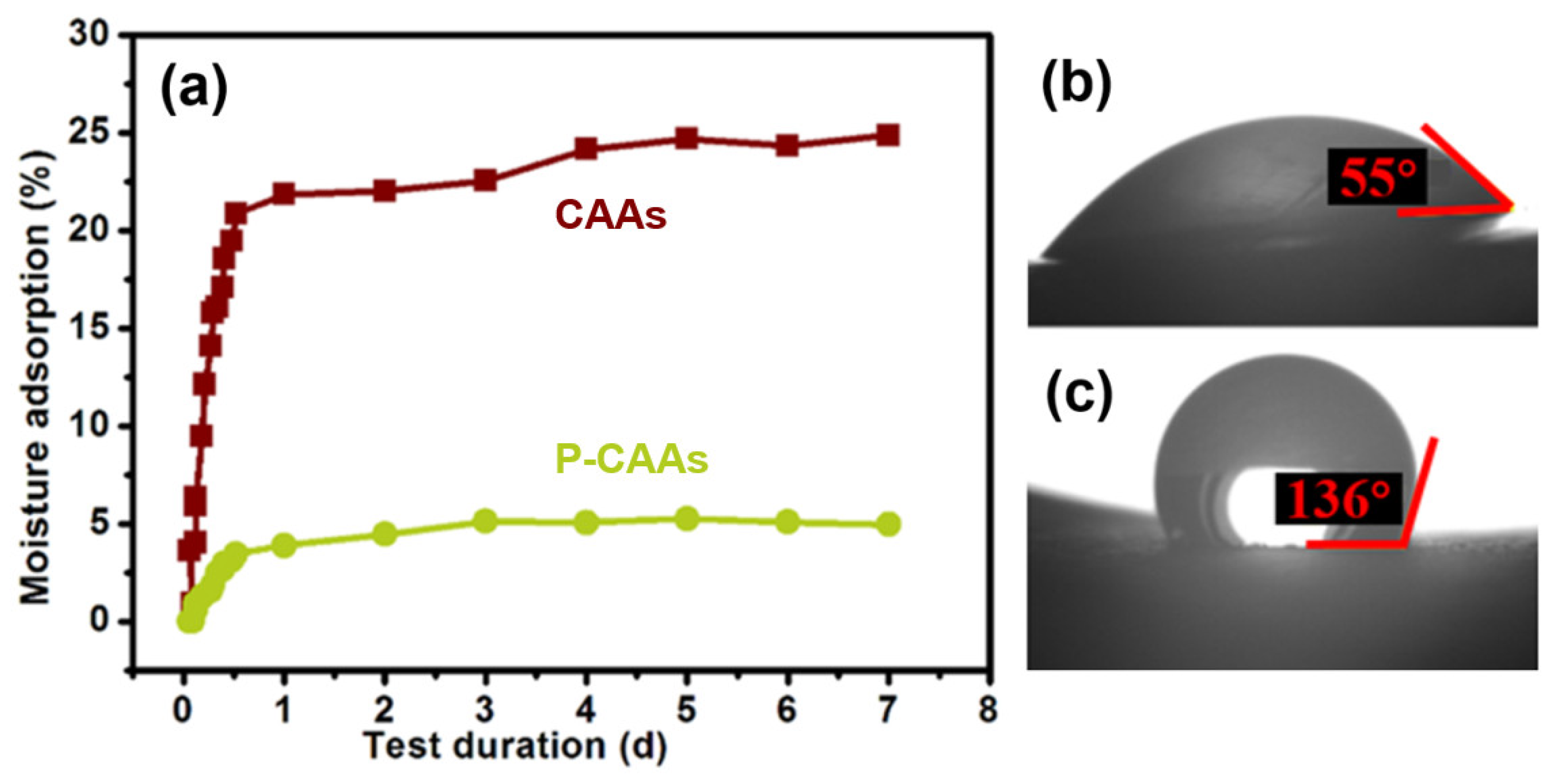
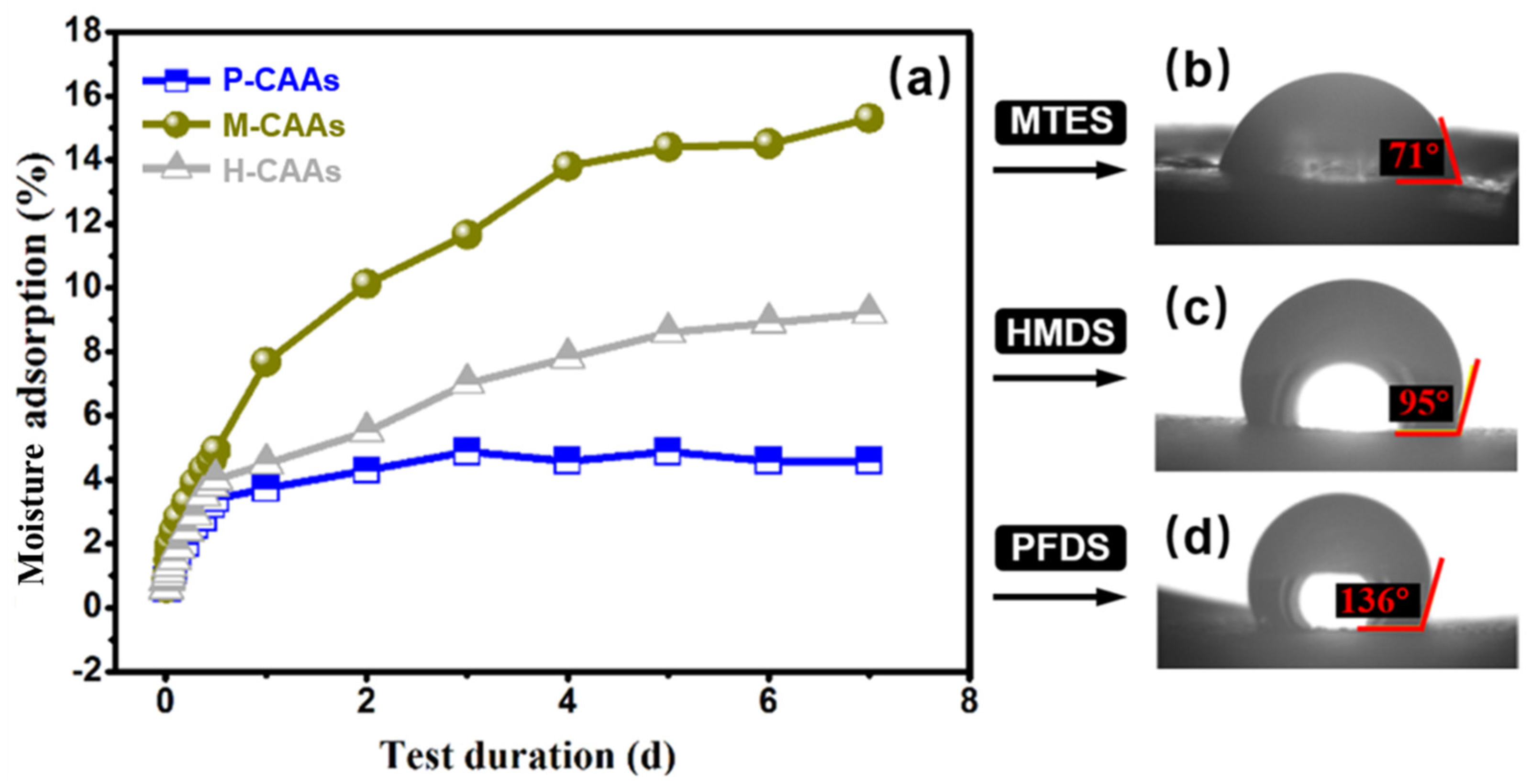
2.3. Hydrophobicity Evaluation
2.4. Thermal Conductivity Test
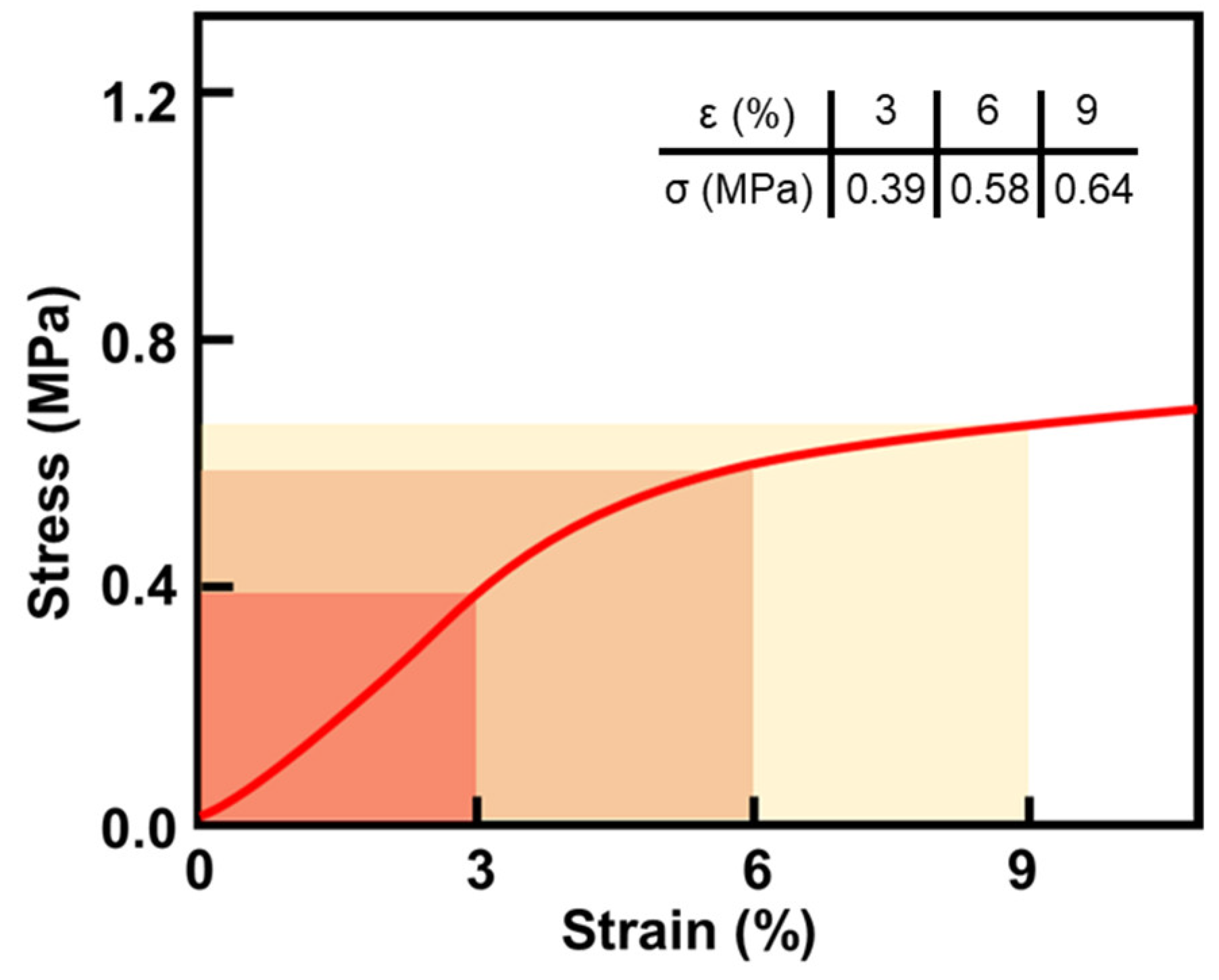
2.5. Compressive Strength and Its Analysis
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of Cellulose Acetate Aerogel
4.3. Hydrophobic Treatment
4.4. Characterizations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlo, A.; Tingting, W.; Tanja, Z.; Abderrahmane, K.; Marie-Jean, T.; Gustav, N.; Thomas, G. Ultra-porous nanocellulose foams: A facile and scalable fabrication approach. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1142. [Google Scholar]
- Long, L.-Y.; Weng, Y.-X.; Wang, Y.-Z. Cellulose aerogels: Synthesis, applications, and prospects. Polymers 2018, 10, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, R.; Liu, G.; Wang, C.; Zhou, W.; Huang, L.; Deng, Y. Performance investigation of an exhaust thermoelectric generator for military SUV application. Coatings 2018, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, A.G.; Cooper, A.I. Function-led design of new porous materials. Science 2015, 348, 6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoyu, G.; Yixiang, W.; Zhigang, T.; Xiang, Z.; Lingyun, C. Controlled production of spruce cellulose gels using an environmentally “green” system. Cellulose 2014, 21, 1667. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, B.; Zhang, J.; Mi, Q.; Yu, J.; Song, R.; Zhang, J. Transparent cellulose—Silica composite aerogels with excellent flame retardancy via an in situ sol–gel process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 11117–11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuri, K.; Tsuguyuki, S.; Akira, I. Aerogels with 3D ordered nanofiber skeletons of liquid-crystalline nano-cellulose derivatives as tough and transparent insulators. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 10562–10565. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, F.V.; Otoni, C.G.; De France, K.J.; Barud, H.S.; Lona, L.M.; Cranston, E.D.; Rojas, O.J. Porous nanocellulose gels and foams: Breakthrough status in the development of scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater. Today 2020, 37, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhatat, A.; Al-Muhtaseb, S.A. Advances in tailoring resorcinol-formaldehyde organic and carbon gels. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2887–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourav, S.; Ajit, S.; Chandan, B.; Sangita, R.; Kamalakannan, K. Recent developments in biomass derived cellulose aerogel materials for thermal insulation application: A review. Cellulose 2022, 29, 4805–4833. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Jiang, R.; Zou, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G. Experimental research on an innovative sawdust biomass-based insulation material for buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, H.; Lazzaretto, A.; Manente, G.; Tong, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, N. The development history and prospects of biomass-based insulation materials for buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 912–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingyao, S.; Jungang, J.; Hengfei, Q.; Xueyong, R.; Feng, J. ACS applied materials & interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2020, 12, 45363–45372. [Google Scholar]
- Akira, I.; Tsuguyuki, S.; Hayaka, F. TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Illera, D.; Mesa, J.; Gomez, H.; Maury, H. Cellulose aerogels for thermal insulation in buildings: Trends and challenges. Coatings 2018, 8, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Gao, H.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J.; Dong, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, G. Vacuum-dried synthesis of low-density hydrophobic monolithic bridged silsesquioxane aerogels for oil/water separation: Effects of acid catalyst and its excellent flexibility. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzyb, B.; Hildenbrand, C.; Berthon-Fabry, S.; Bégin, D.; Job, N.; Rigacci, A.; Achard, P. Functionalisation and chemical characterisation of cellulose-derived carbon aerogels. Carbon 2010, 48, 2297–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, S.; Konishi, A.; Takebayashi, Y.; Yoda, S.; Otake, K. Aldehyde approach to hydrophobic modification of chitosan aerogels. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2172–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paksung, N.; Pfersich, J.; Arauzo, P.J.; Jung, D.; Kruse, A. Structural effects of cellulose on hydrolysis and carbonization behavior during hydrothermal treatment. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12210–12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-W.; Jeong, Y.G. Regenerated cellulose/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films with efficient electric heating performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Pang, Z.; Dong, C.; Liu, Z. Preparing cationic cotton linter cellulose with high substitution degree by ultrasonic treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, C.J.; Ismadji, S.; Aparamarta, H.W.; Gunawan, S. Hydrophobic modification of cellulose nano-crystals from bamboo shoots using rarasaponins. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20967–20975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.N.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wei, Y.H.; Si, J.Y.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Xie, J.; Bin, Y.; San-E, Z.; Lu, H.; et al. Robust, lightweight, hydrophobic, and fire-retarded polyimide/mxene aerogels for effective oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 40512–40523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Emily, D.C. Chemically cross-linked cellulose nanocrystal aerogels with shape recovery and super-absorbent properties. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 6016–6025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R. Silica aerogels having high flexibility and hydrophobicity prepared by sol-gel method. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 21262–21268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liang, W.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Biomimetic super-lyophobic and super-lyophilic materials applied for oil/water separation: A new strategy beyond nature. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 44, 336–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalludin, M.R.; Hubadillah, S.K.; Harun, Z.; Othman, M.H.D.; Yunos, M.Z.; Ismail, A.F.; Salleh, W.N.W. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic green ceramic hollow fiber membrane derived from waste sugarcane bagasse ash for oil/water separation. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 3558–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, C.; Edward, T.Y. Zeta potential dependent self-assembly for very large area nanosphere lithography. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 5090–5096. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Feng, J.; Qi, F.; E, D.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Xiong, S.; Feng, J. Thermal conductivities of cellulose diacetate based aerogels. Cellulose 2020, 27, 4555–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Lun, Z.; Gong, L.; Gao, M.; Zhang, H. “Robust–soft” anisotropic nanofibrillated cellulose aerogels with superior mechanical, flame-retardant, and thermal insulating properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 27458–27470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Wan, C.; Qiang, T.; Li, J. Synthesis of superhydrophobic ultralight aerogels from nano-fibrillated cellulose isolated from natural reed for high-performance adsorbents. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Feng, J.; Qi, F.; E, D.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Xiong, S.; Feng, J. Structure, compression and thermally insulating properties of cellulose diacetate-based aerogels. Mater. Des. 2020, 189, 108502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Si, Z.; Cai, D.; Teng, X.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Qin, P. High-hydrophobic CF3 groups within PTFPMS membrane for enhancing the furfural pervaporation performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 235, 116144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakellis, P.; Gogolides, E. Hydrophobic and superhydrophobic surfaces fabricated using atmospheric pressure cold plasma technology: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 254, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Shen, H. Ultralight, hydrophobic, sustainable, cost-effective and floating kapok/microfibrillated cellulose aerogels as speedy and recyclable oil superabsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 406, 124758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Lai, Y. Advanced functional materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1707415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; He, J.; Feng, J.; Xiong, S.; Li, Z. Hydrophobic Cellulose Acetate Aerogels for Thermal Insulation. Gels 2022, 8, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100671
Zhang S, Yang Z, Huang X, Wang J, Xiao Y, He J, Feng J, Xiong S, Li Z. Hydrophobic Cellulose Acetate Aerogels for Thermal Insulation. Gels. 2022; 8(10):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100671
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Sizhao, Zhouyuan Yang, Xing Huang, Jing Wang, Yunyun Xiao, Junpeng He, Jian Feng, Shixian Xiong, and Zhengquan Li. 2022. "Hydrophobic Cellulose Acetate Aerogels for Thermal Insulation" Gels 8, no. 10: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100671
APA StyleZhang, S., Yang, Z., Huang, X., Wang, J., Xiao, Y., He, J., Feng, J., Xiong, S., & Li, Z. (2022). Hydrophobic Cellulose Acetate Aerogels for Thermal Insulation. Gels, 8(10), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100671