Plasticizers and Salt Concentrations Effects on Polymer Gel Electrolytes Based on Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) for Electrochemical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
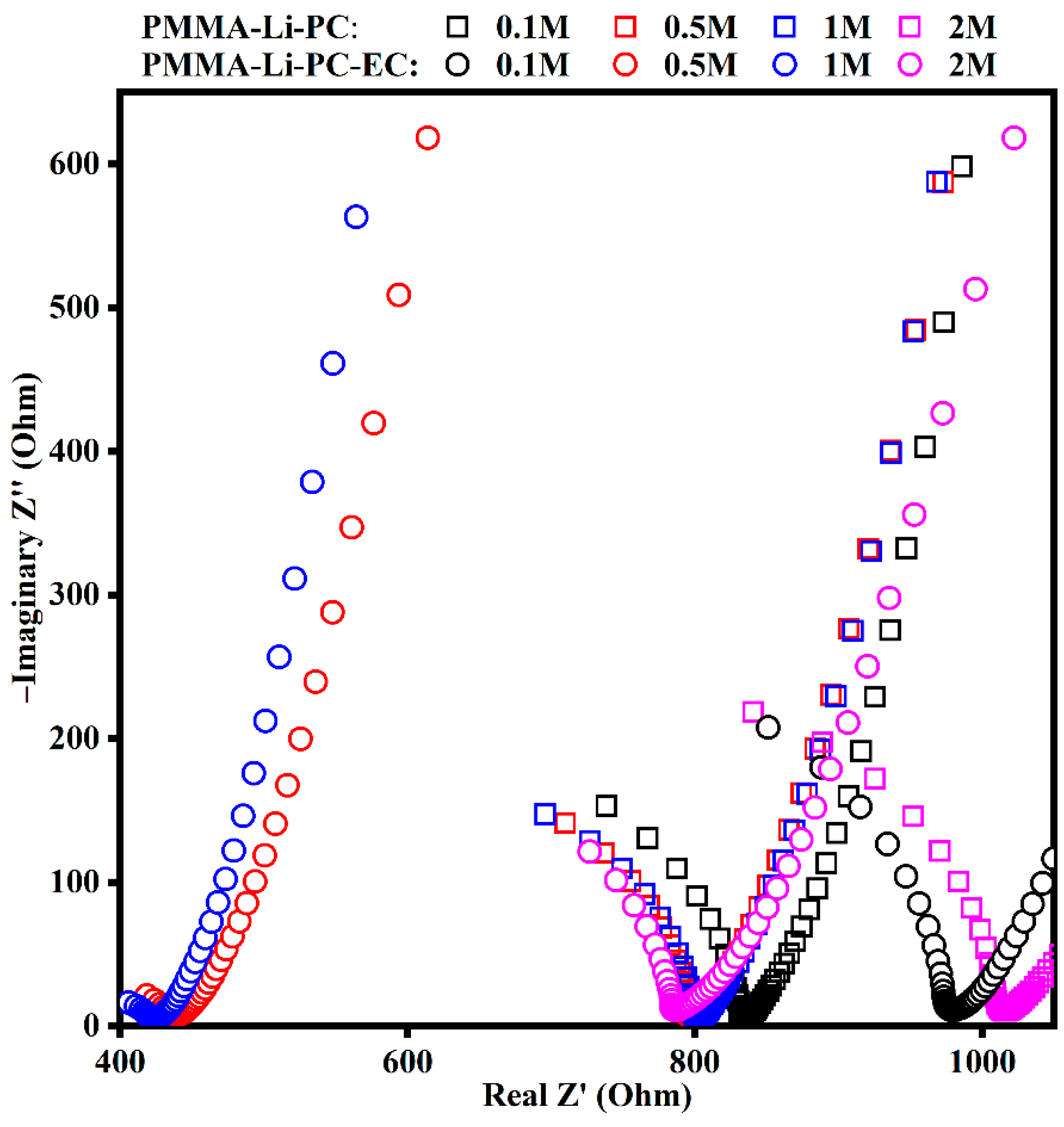
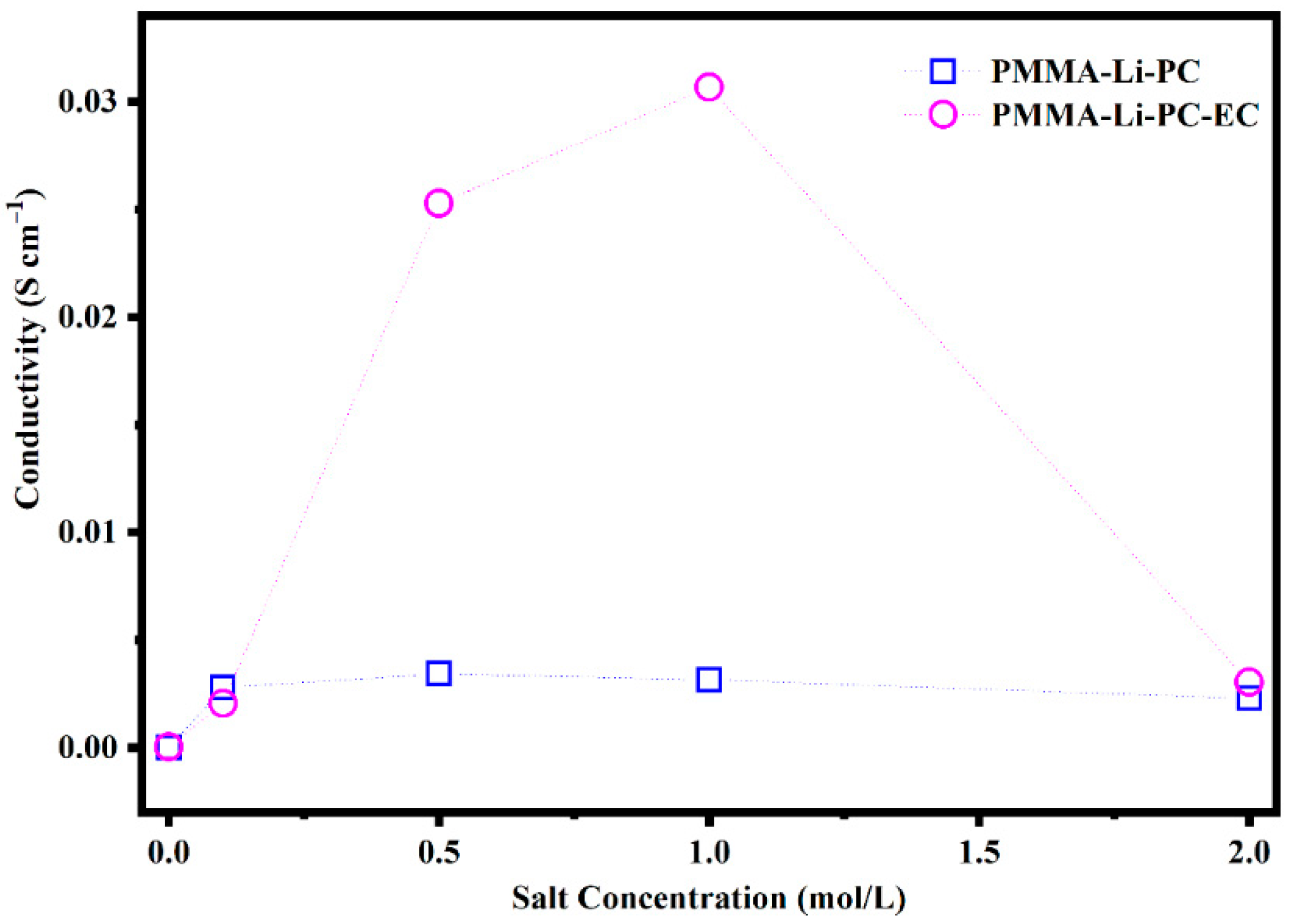
2.1. AC Impedance and Ionic Conductivities
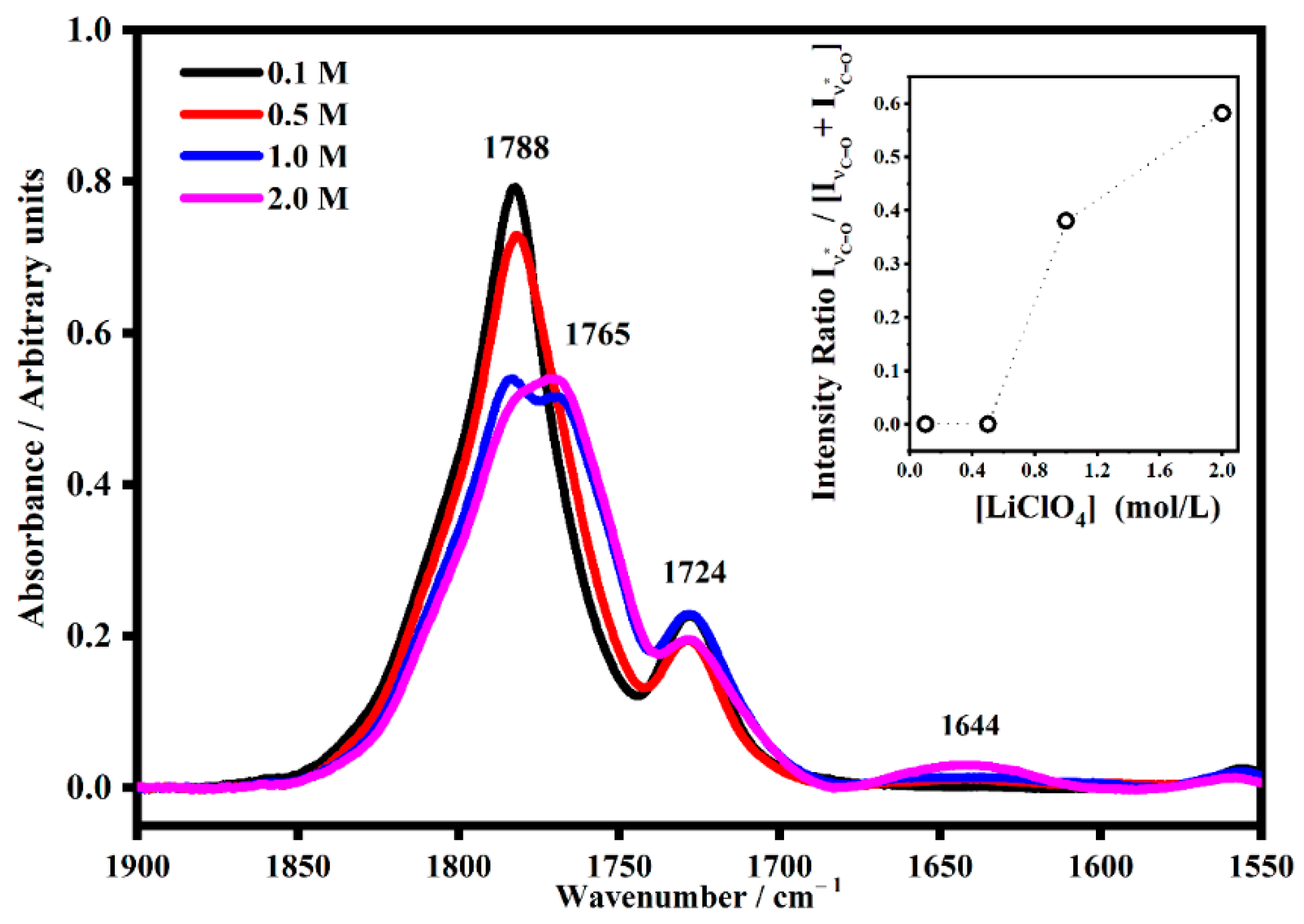
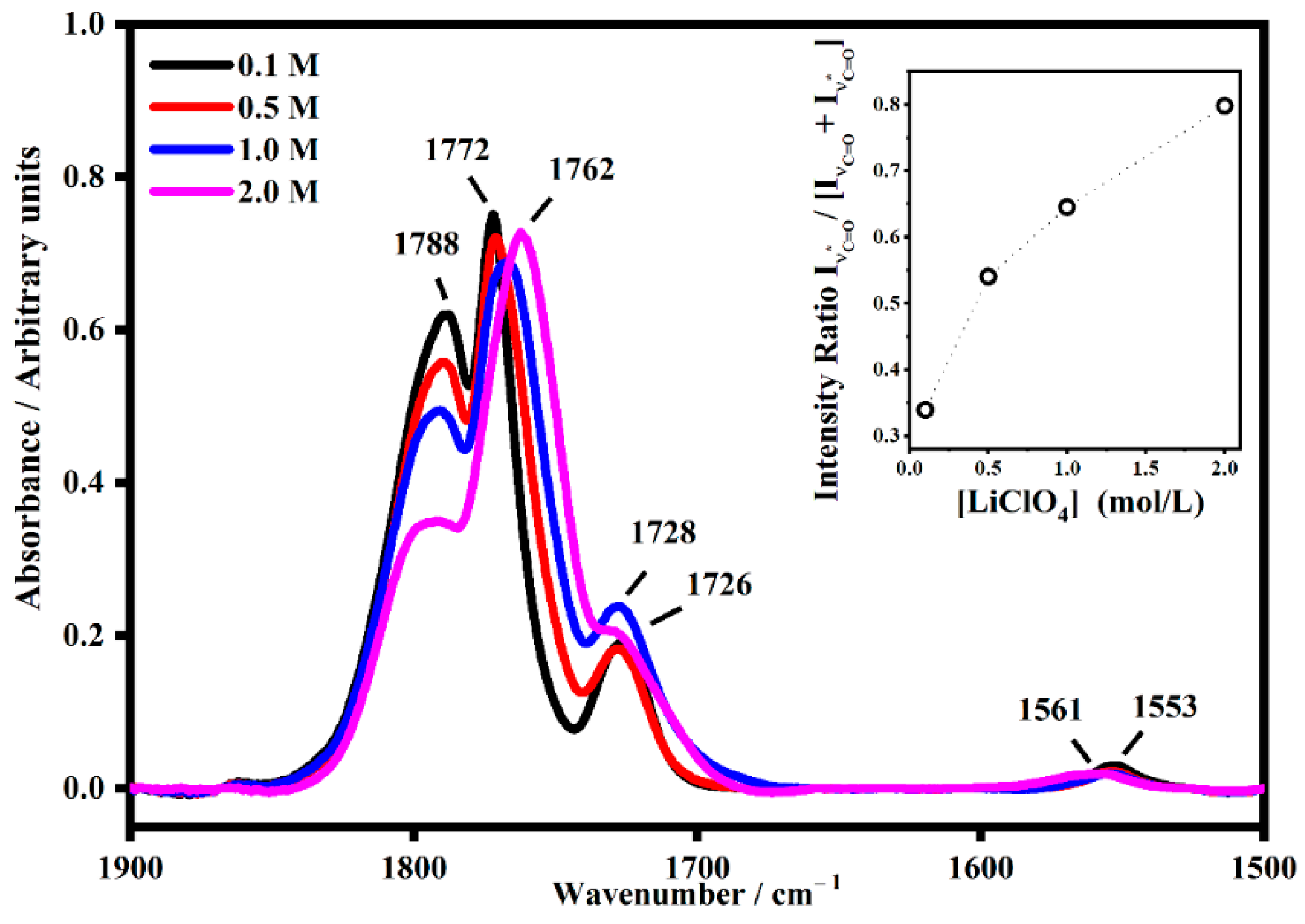
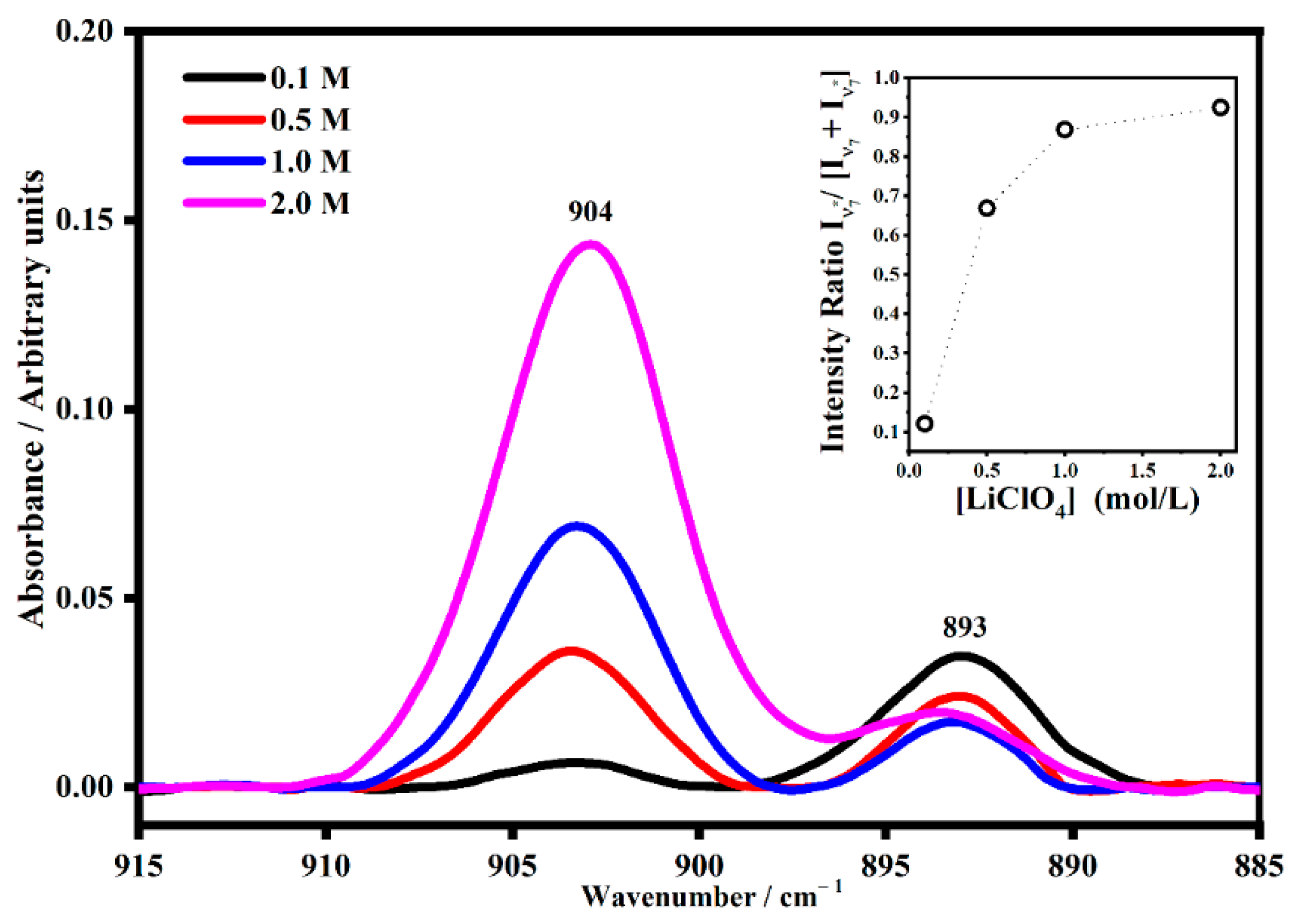
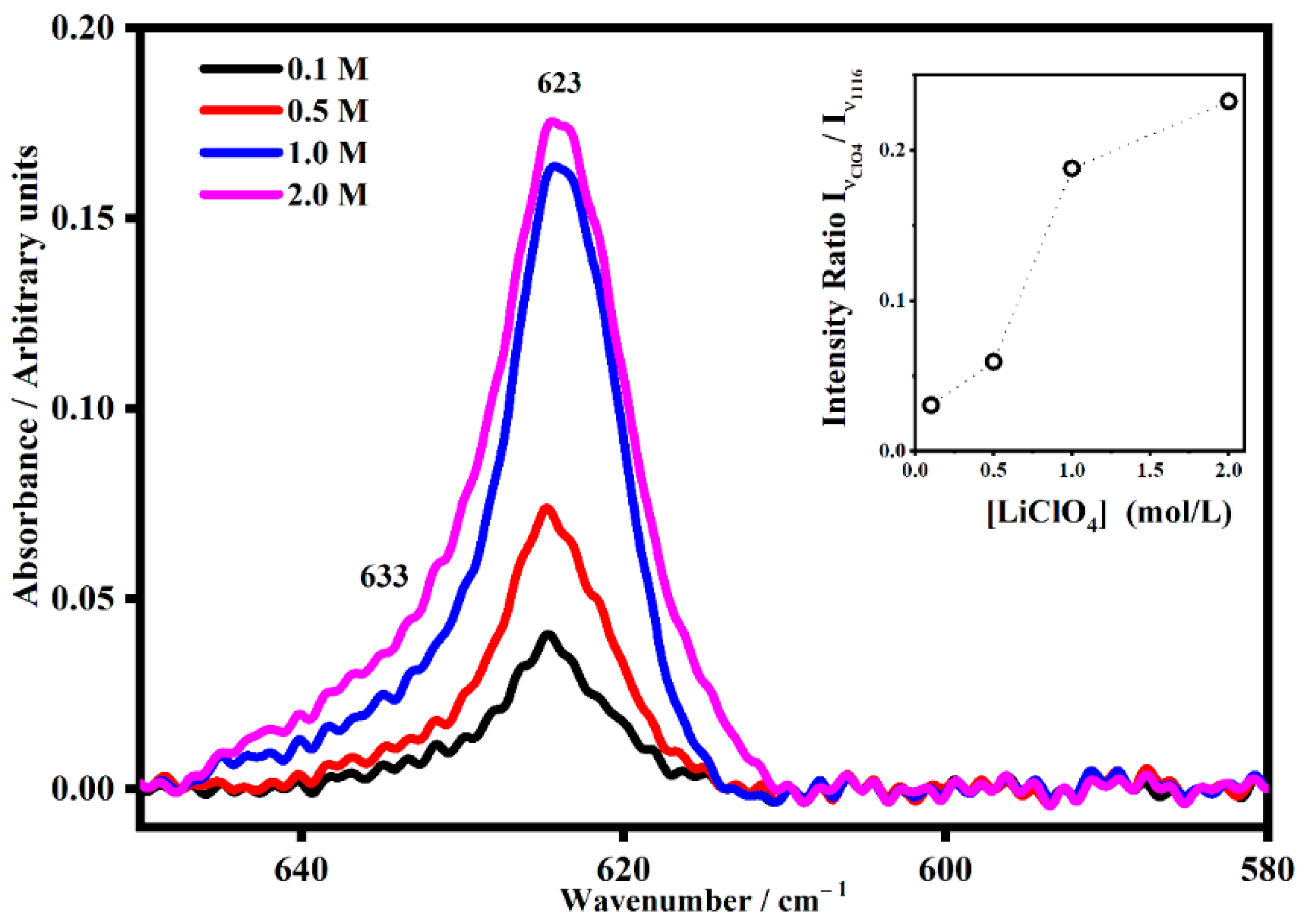
2.2. FT-IR Interactions and Ion Associations
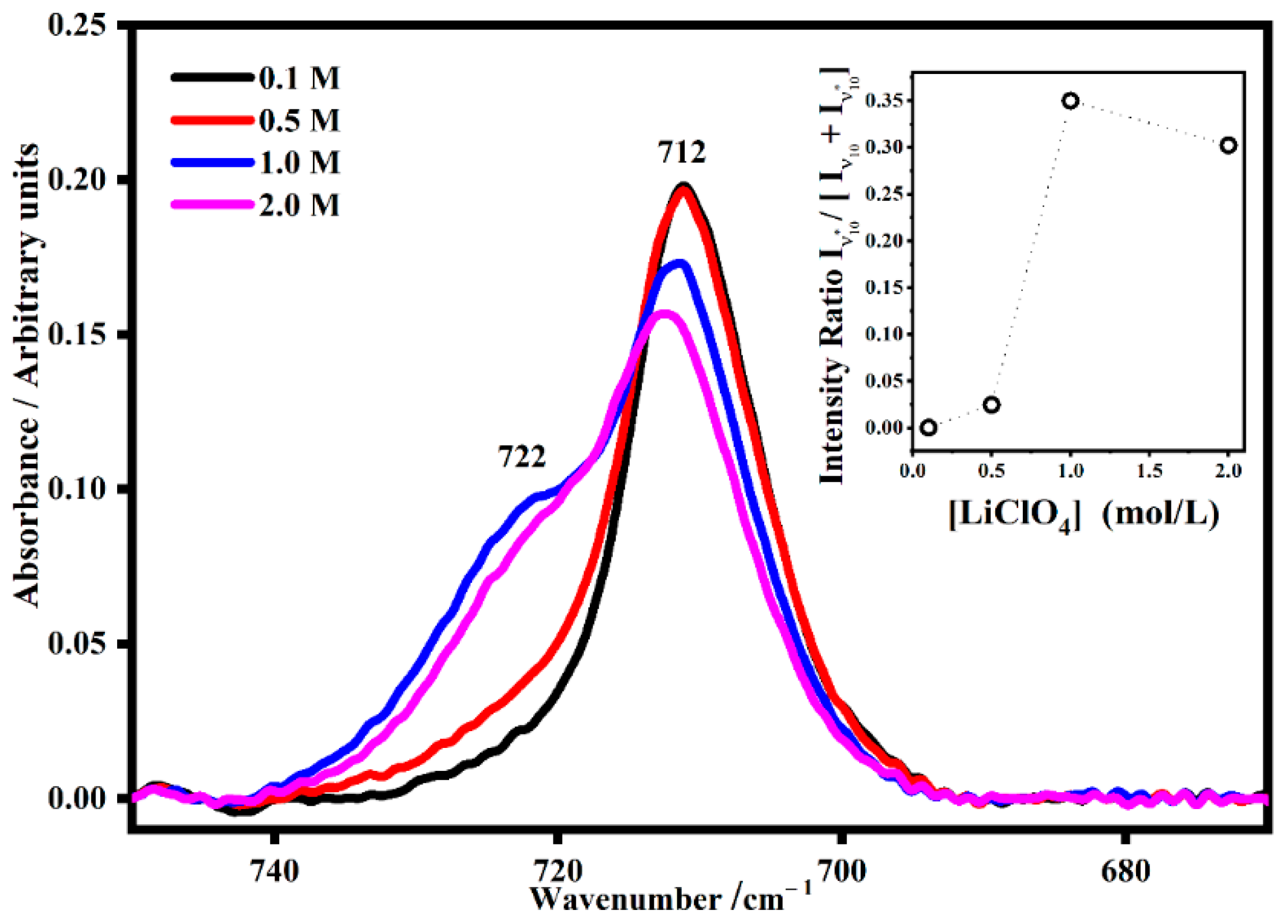
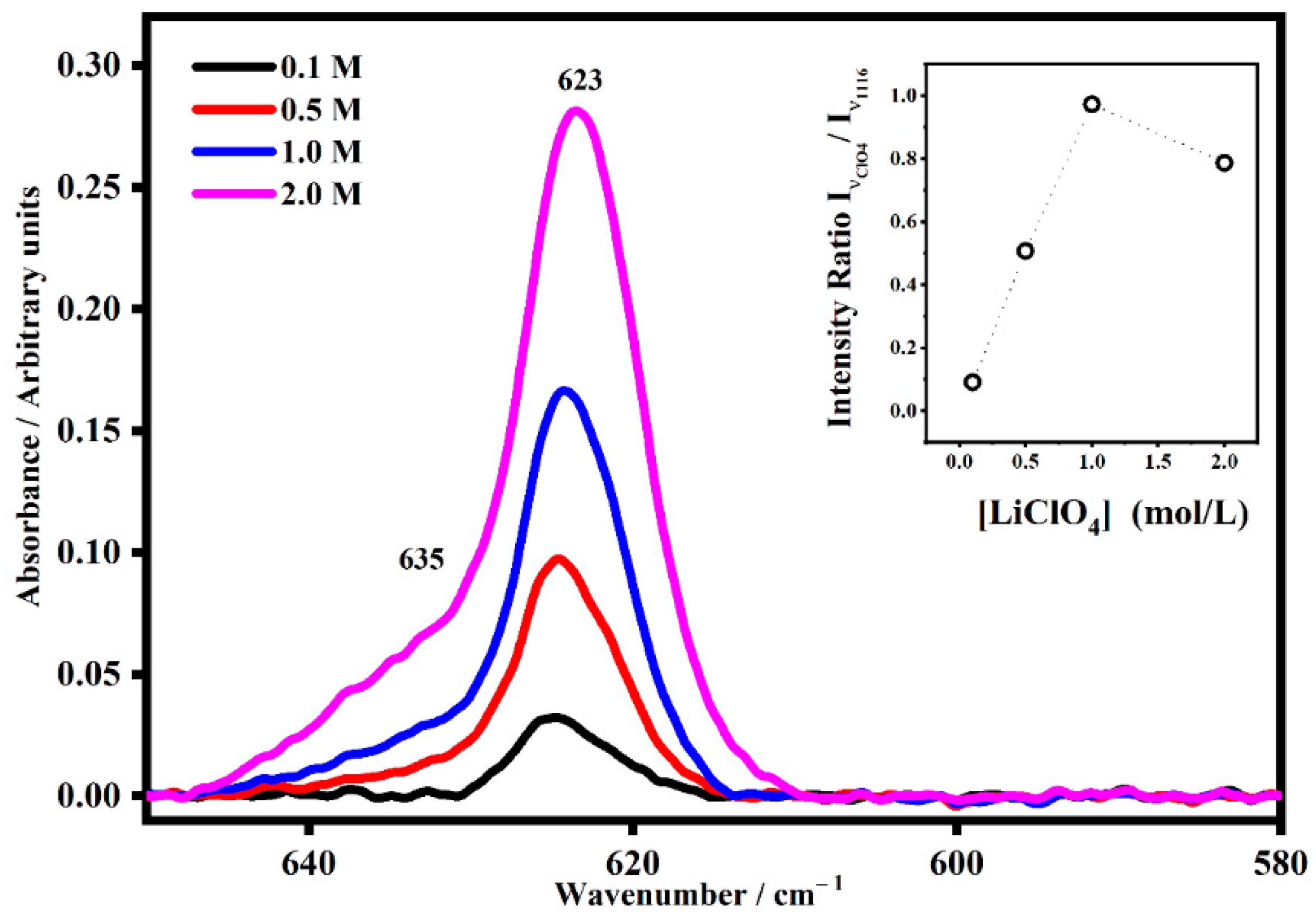
2.3. Ion Pairing
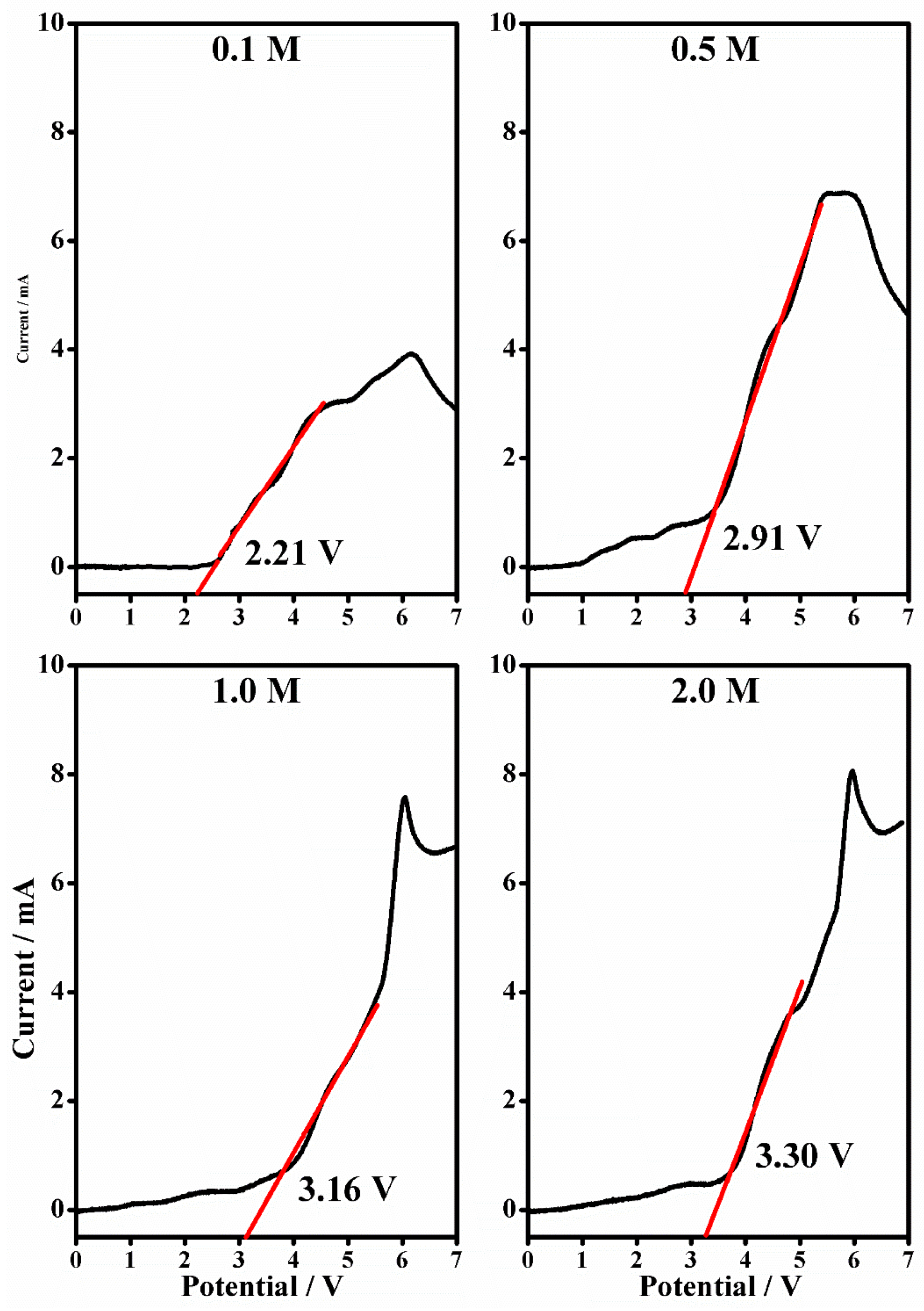
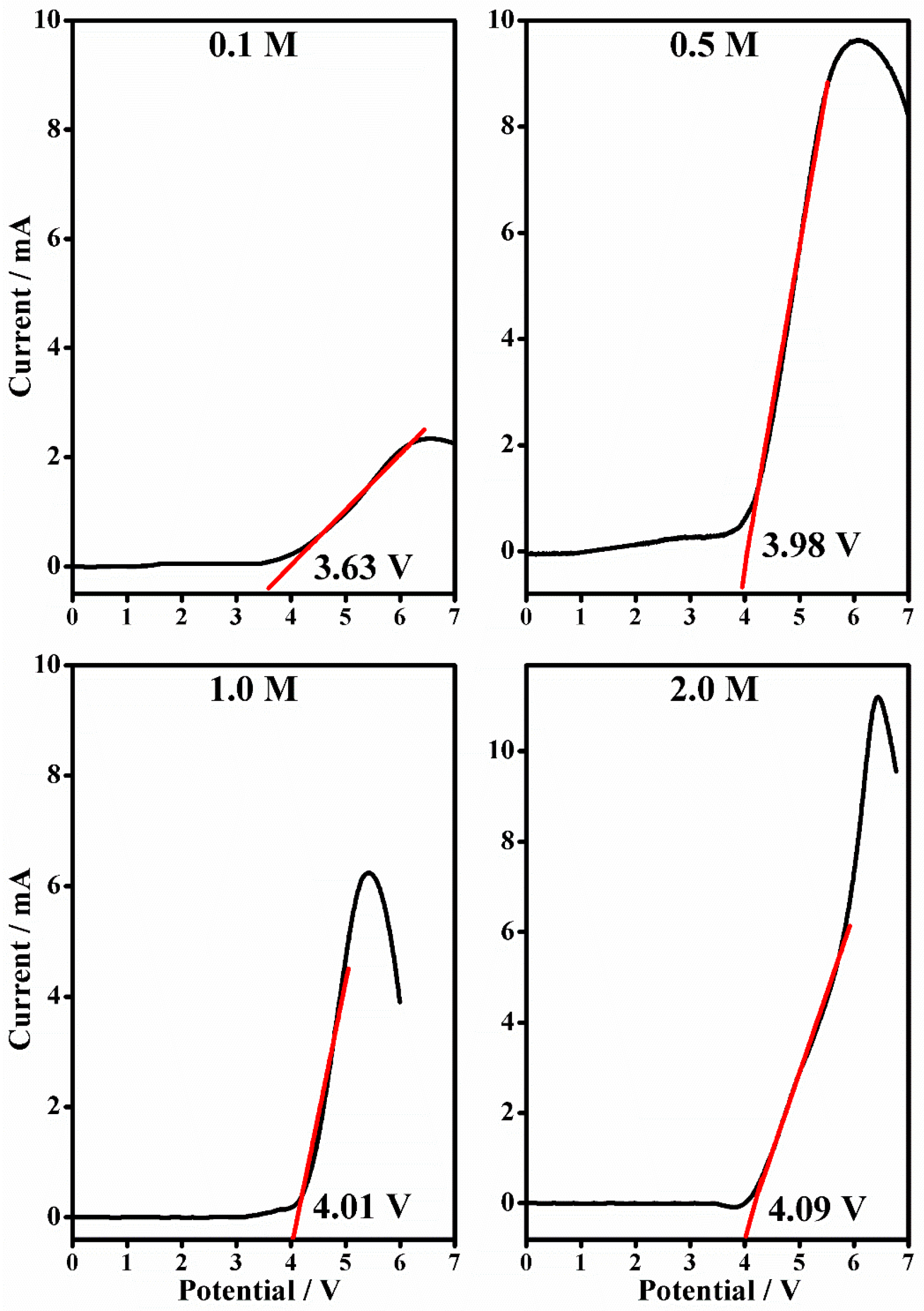
2.4. Linear Sweep Voltammetry
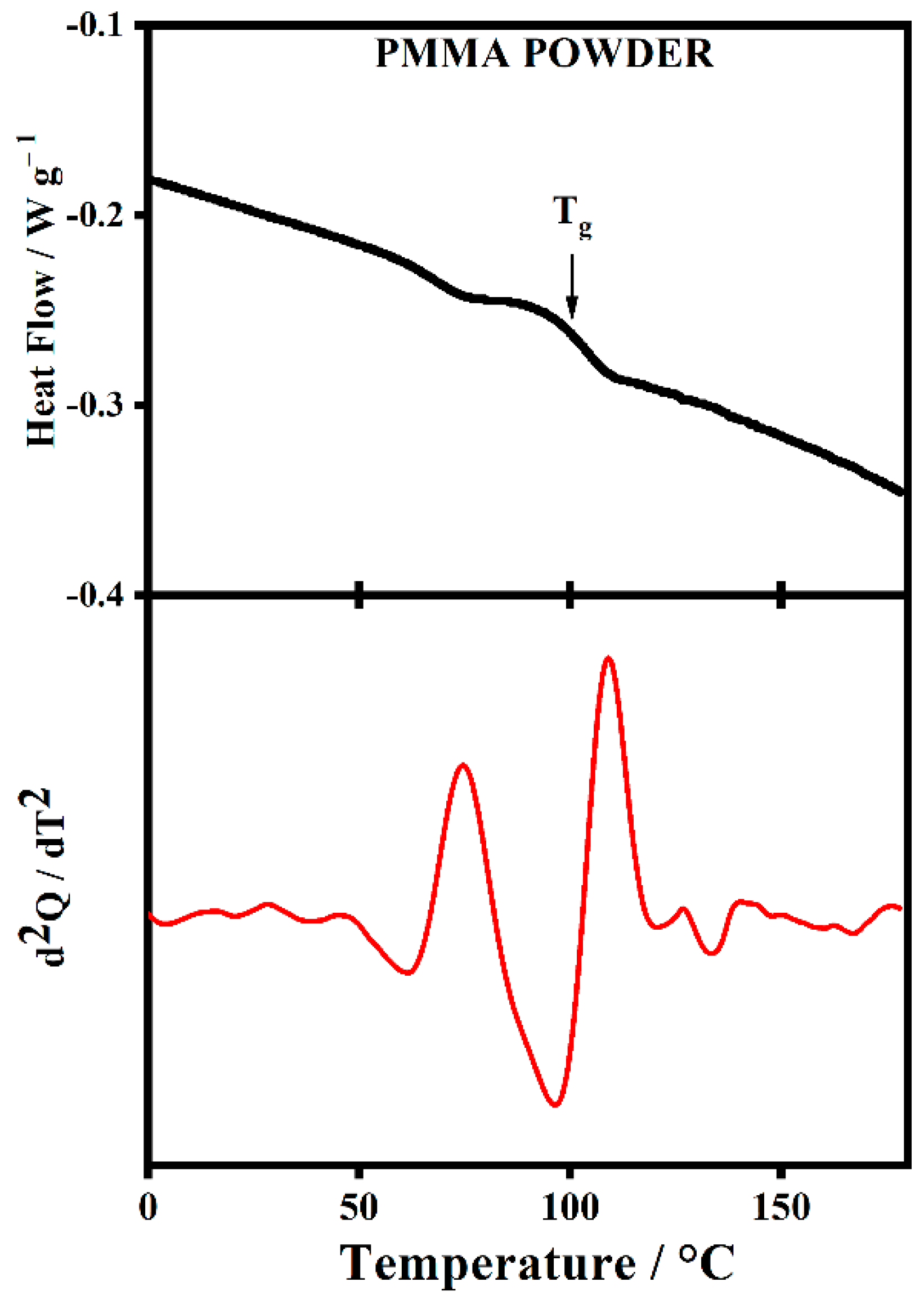
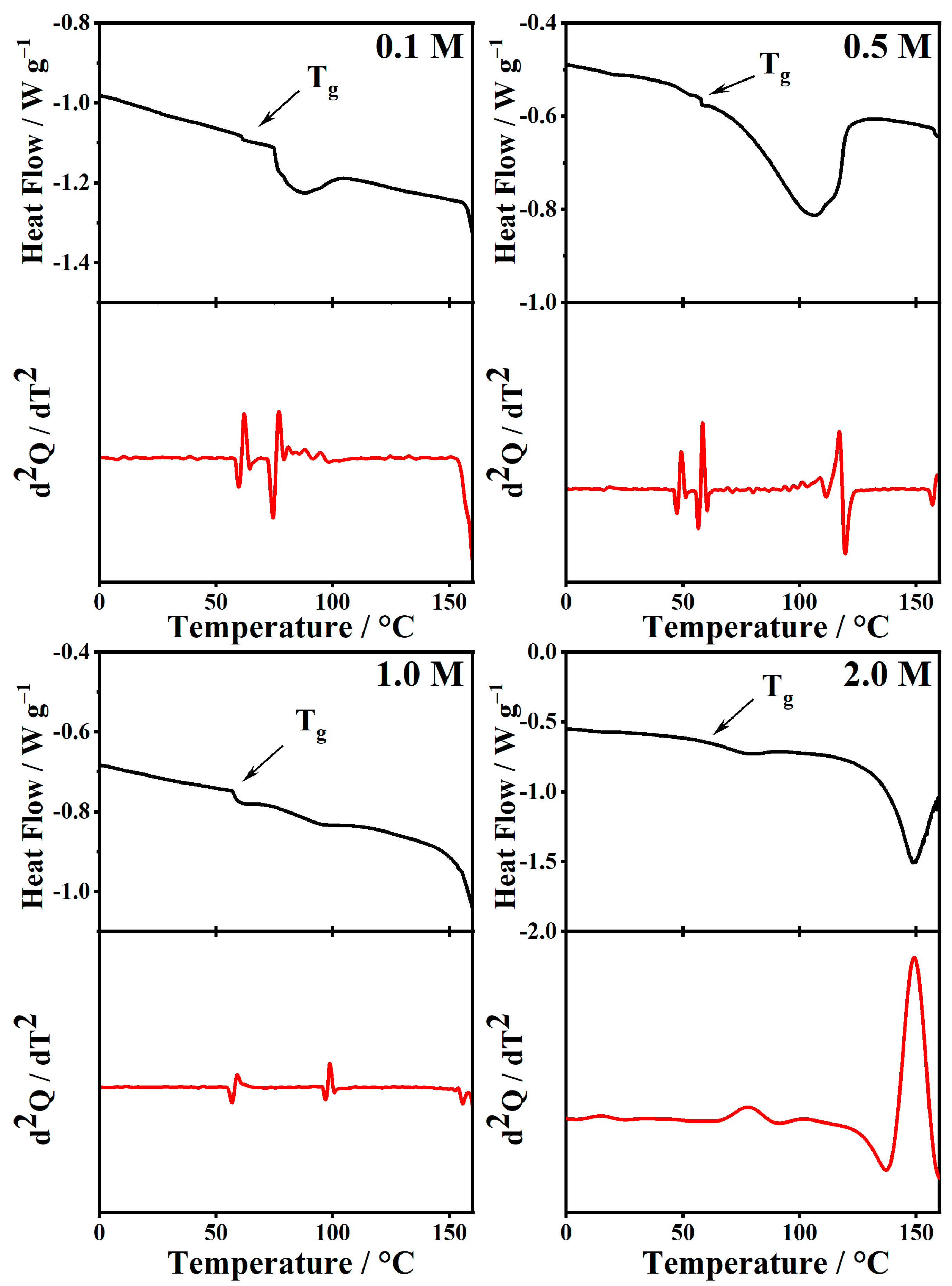
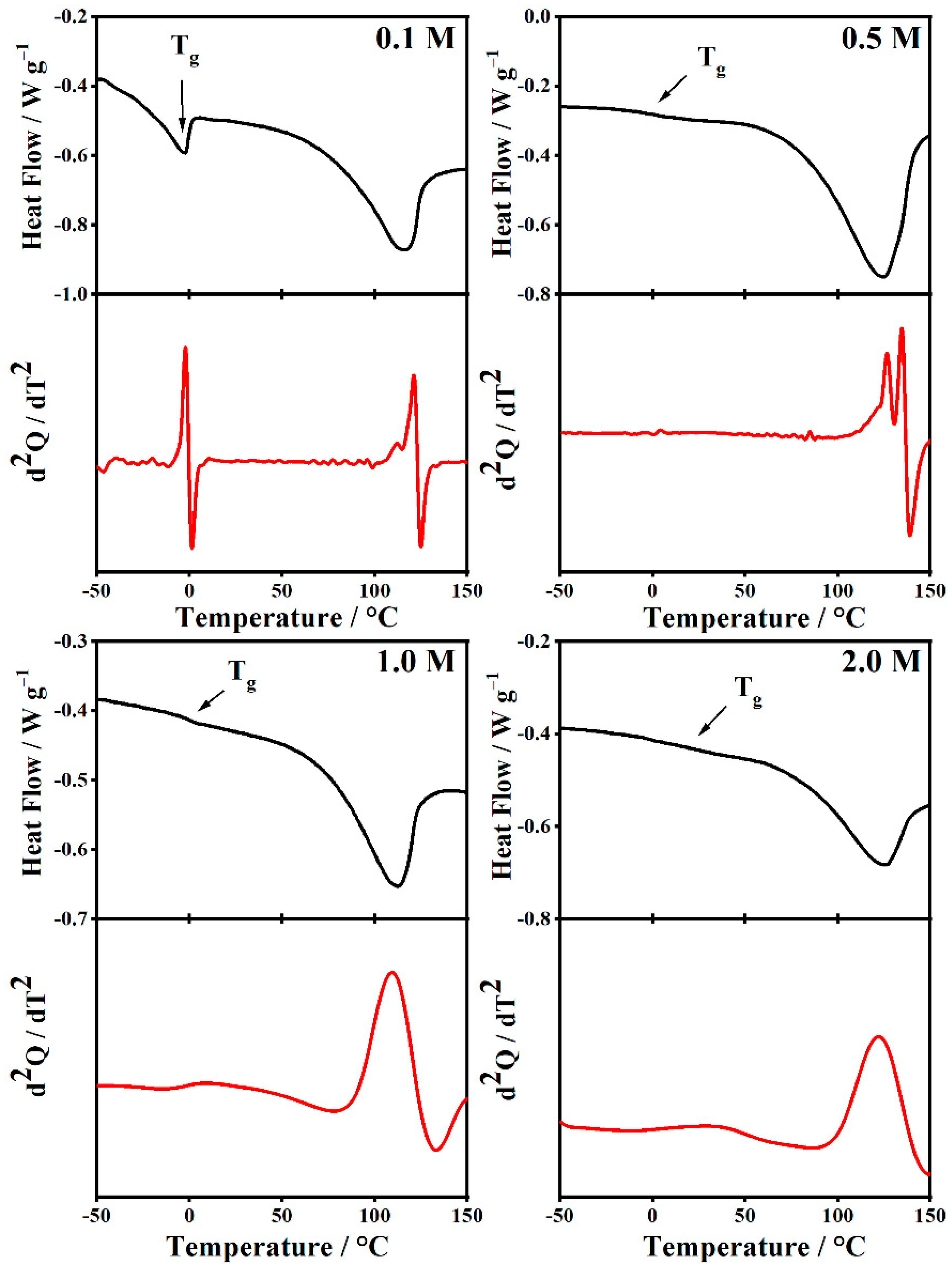
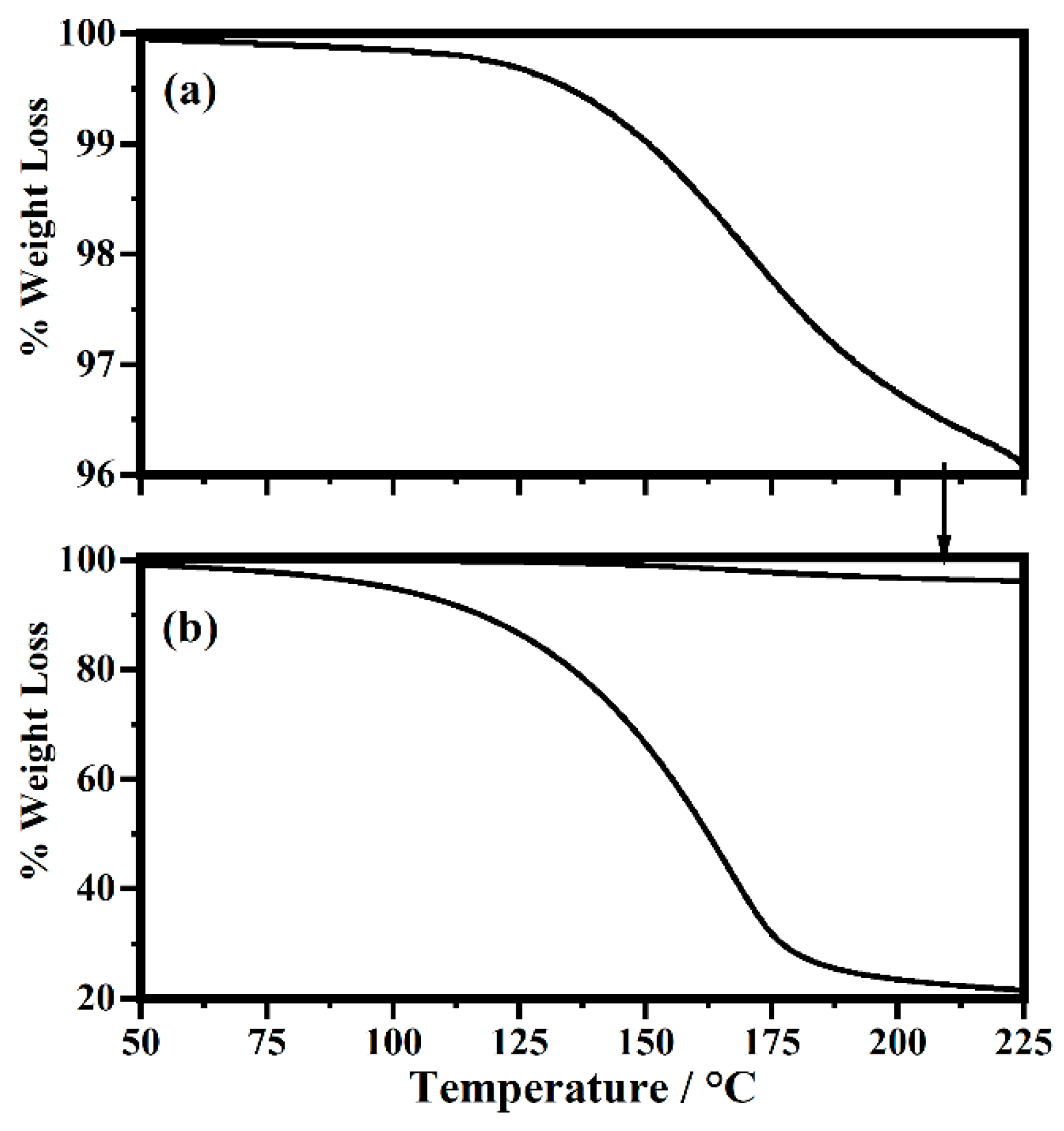
2.5. Thermal Analysis
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Liquid and Gel Polymer Electrolytes
4.3. Characterization of Gel Polymer Electrolytes
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thakur, V.K.; Ding, G.; Ma, J.; Lee, P.S.; Lu, X. Hybrid materials and polymer electrolytes for electrochromic device applications. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4071–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siczek, K.J. Chapter Seven–Electrolytes. In Next-Generation Batteries with Sulfur Cathodes, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 7, pp. 79–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K. Nonaqueous Liquid Electrolytes for Lithium-Based Rechargeable Batteries. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4303–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharski, M.; Łukaszewicz, T.; Mrozek, P. New electrolyte for electrochromic devices. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2004, 12, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Sekhon, S.; Deepa, S.; Agnihotry, S.A. Solvent effect on gel electrolytes containing lithium salts. Solid State Ion. 2000, 136–137, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesanco, Y.; Viñuales, A.; Rodriguez, J.; Tena-Zaera, R. All-in-One Gel-Based Electrochromic Devices: Strengths and Recent Developments. Materials 2018, 11, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kotobuki, M. Chapter One-Polymer Electrolytes. In Polymer Electrolytes: Characterization Techniques and Energy Applications, 1st ed.; Winie, T., Arof, A.K., Thomas, S., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Wang, S.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y. Polymer electrolytes for lithium polymer batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 10038–10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.U.; Babu, R.; Rajendran, S. Conductivity Study on PVDF-HFP/PMMA Electrolytes for Lithium Battery Applications. Int. J. Chem Tech Res. 2013, 5, 1724–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, M.; Long, L.; Siyal, S.H.; Yang, X.; Sui, G. Recent advances in gel polymer electrolyte for high-performance lithium batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2019, 37, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicotera, I.; Oliviero, C.; Ranieri, G.; Spadafora, A.; Castriota, M.; Cazzanelli, E. Temperature evolution of thermoreversible polymer gel electrolytes LiClO4/ethyleneLiClO4/ethylene carbonate/poly(acrylonitrile). J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 7373–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Coppola, L.; Oliviero, C.; Castriota, M.; Cazzanelli, E. Investigation of ionic conduction and mechanical properties of PMMA–PVdF blend-based polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 2006, 177, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castriota, M.; Caruso, T.; Agostino, R.G.; Cazzanelli, E.; Henderson, W.A.; Passerini, S. Raman Investigation of the Ionic Liquid N-Methyl-N-propylpyrrolidinium Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide and Its Mixture with LiN(SO2CF3)2. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castriota, M.; Teeters, D. Impedance spectroscopy of PEO-lithium triflate confined in nanopores of alumina membranes. Ionics 2005, 11, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appetecchi, G.B.; Croce, F.; Scrosati, B. Kinetics and stability of the lithium electrode in poly(methylmethacrylate)-based gel electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 1995, 40, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnke, O.; Frand, G.; Rezrazi, M.; Rousselot, C.; Truche, C. Fast ion transport in new lithium electrolytes gelled with PMMA. 2. Influence of lithium salt concentration. Solid State Ion. 1993, 66, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnke, O.; Rousselot, C.; Gillet, P.A.; Truche, C. Gel Electrolyte for Solid-State Electrochromic Cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1992, 139, 1862–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frand, G.; Rousselot, C.; Bohnke, O. New solid electrolytes for electrochromic smart windows. SPIE-Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 1992, 1728, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Ghosh, A. Charge carrier dynamics in PMMA-LiClO4 based polymer electrolytes plasticized with different plasticizers. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallworth, P.E.; Greenbaum, S.G.; Croce, F.; Slane, S.; Salomon, M. Lithium-7 NMR and ionic conductivity studies of gel electrolytes based on poly(methylmethacrylate). Electrochim. Acta 1995, 40, 2137–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Mahbor, K. Investigation on PMMA-based gel electrolyte for electrochromic devices. In Solid State Ionics: Trends in the New Millennium; World Scientific: Singapore, 2002; pp. 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretera, M.; Reiter, J.; Vondrák, J.; Sedlaříková, M. Ionic Conductance of Lithium Salts in PMMA Gel Electrolytes. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference ABA, Chicago, IL, USA, 27–31 May 2005; University of Technology: Brno, Czech Republic, 2005; Volume 14686, p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, B.; Munteshari, O.; Lau, L.; Dunn, B.; Pilon, L. Physical Interpretations of Nyquist Plots for EDLC Electrodes and Devices. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, D.; Nazri, G.A.; Klassen, B.; Aroca, R. Vibrational Studies of Lithium Perchlorate in Propylene Carbonate Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 5826–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Qu, G. A Vibrational Spectroscopic Study of Ion Solvation in Lithium Perchlorate/Propylene Carbonate Electrolyte. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2001, 39, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, B.; Huang, H.; Chen, L.; Xue, R.; Wang, F. Infrared spectroscopic study of the interaction between lithium salt LiClO4 and the plasticizer ethylene carbonate in the polyacrylonitrile-based electrolyte. Solid State Ion. 1996, 85, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, M.; Xu, M.; Eyring, E.M.; Petrucci, S.J. Molecular Structure and Dynamics of LiClO4-Polyethylene Oxide-400 (Dimethyl Ether and Diglycol Systems) at 25 °C. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 8234–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, W.; Lipka, G.; Zukowska, G.; Wycislik, H. Ionic Interactions in Polymeric Electrolytes Based on Low Molecular Weight Poly(ethylene glycol)s. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 6968–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, A.V. Polymer electrolytes. Prog. Solid State Chem. 1987, 17, 145–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitaille, C.D.; Fauteux, D. Phase Diagrams and Conductivity Characterization of some PEO-LiX Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1986, 133, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridi, M.; Naji, L.; Kazemifard, S.; Pourali, N. Electrochemical Investigation of Gel Polymer Electrolytes Based on Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) and Dimethylacetamide for Application in Li-Ion Batteries. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 2289–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Karim, K.J.B.A.; Buang, N.A. A Review of the Properties and Applications of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA). Polym. Rev. 2015, 55, 678–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Kashiwagi, T.; Brown, J.E. Thermal and oxidative degradation of poly(methyl methacrylate): Weight loss. Macromolecules 1985, 18, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, E.A.; Durkan, R.; Koroglu, A.; Bagis, B. Comparative effect of different polymerization techniques on residual monomer and hardness properties of PMMA-based denture resins. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2014, 12, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, C.Y.K.; Darvell, B.W. Minimization of the inevitable residual monomer in denture base acrylic. Dent. Mater. 2005, 21, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nising, P.; Zeilmann, T.; Meyer, T. On the degradation and stabilization of poly (Methyl Methacrylate) in a continuous process. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2003, 26, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallittu, P.K.; Miettinen, V.; Alakuijala, P. Residual monomer content and its release into water from denture base materials. Dent. Mater. 1995, 11, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Brown, J.E.; Inaba, A.; Hatada, K.; Kitayama, T.; Masuda, E. Effects of Weak Linkages on the Thermal and Oxidative Degradation of Poly(methyl methacrylates). Macromolecules 1986, 19, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Bing, K.N. Conductivity, mechanical and thermal studies on poly(methyl methacrylate)-based polymer electrolytes complexed with lithium tetraborate and propylene carbonate. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Woo, T.J.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Ahmed, H.M. A conceptual review on polymer electrolytes and ion transport models. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2018, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.P.; Cecchin, D.; Soares, R.G.; Botelho, A.L.; Takahashi, J.M.F.K.; Mazzetto, M.O.; Mesquita, M.F. Evaluation of Vickers hardness of different types of acrylic denture base resins with and without glass fibre reinforcement. Gerodontology 2012, 29, e155–e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, W.J. Flexural strength of microwave-cured denture baseplates. In Gen. Dent.; 1986; 34, pp. 367–371. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3464529 (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Kedjarune, U.; Charoenworaluk, N.; Koontongkaew, S. Release of methyl methacrylate from heat-cured and autopolymerized resins: Cytotoxicity testing related to residual monomer. Aust. Dent. J. 1999, 44, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, D.J.; Ellis, B.; Priestley, D. The effects of process variables on levels of residual monomer in autopolymerizing dental acrylic resin. J. Dent. 1983, 11, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lai, Y.L.; Hsu, T.S. Influence of polymerization conditions on monomer elution and microhardness of autopolymerized polymethyl methacrylate resin. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2002, 110, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

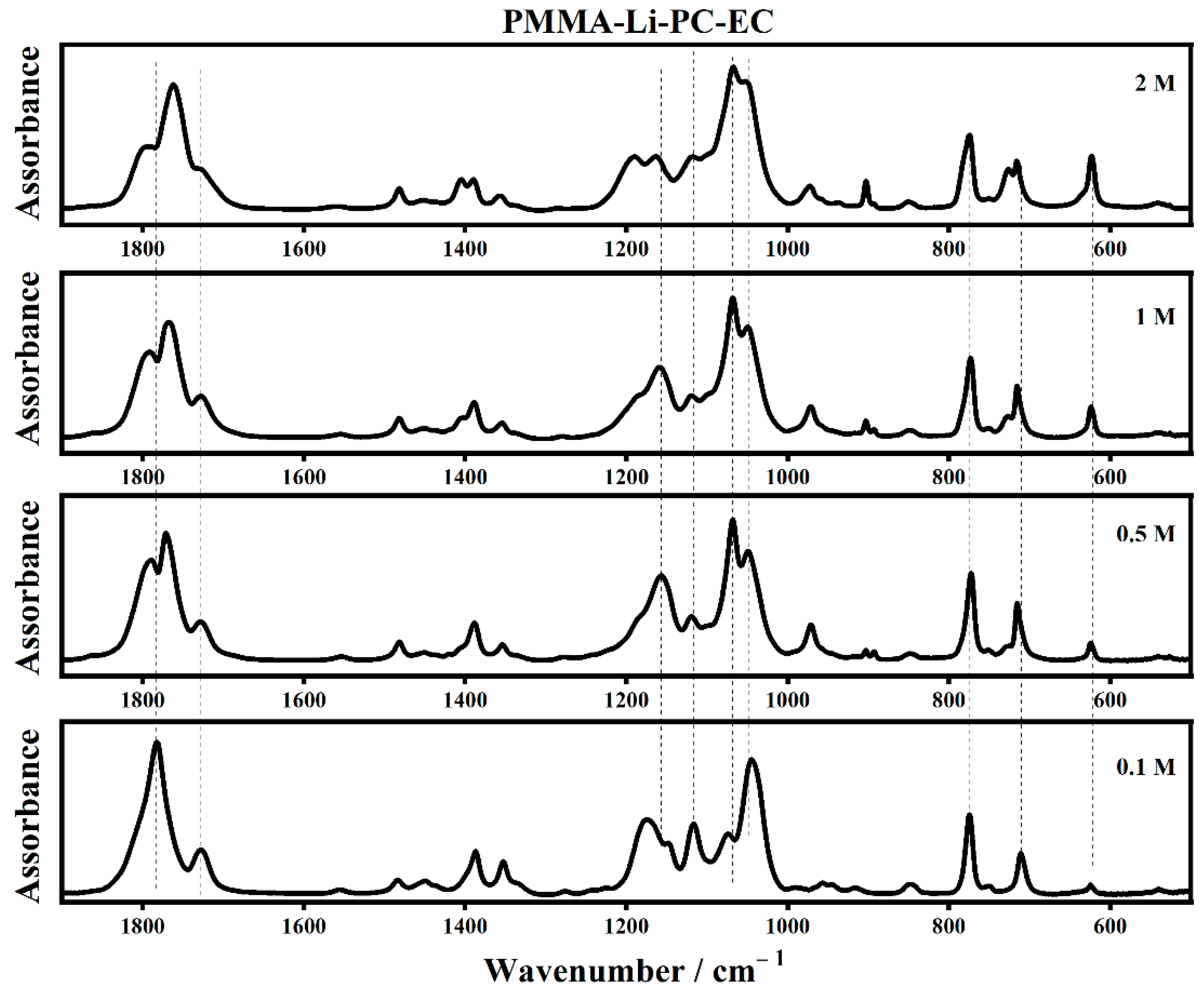
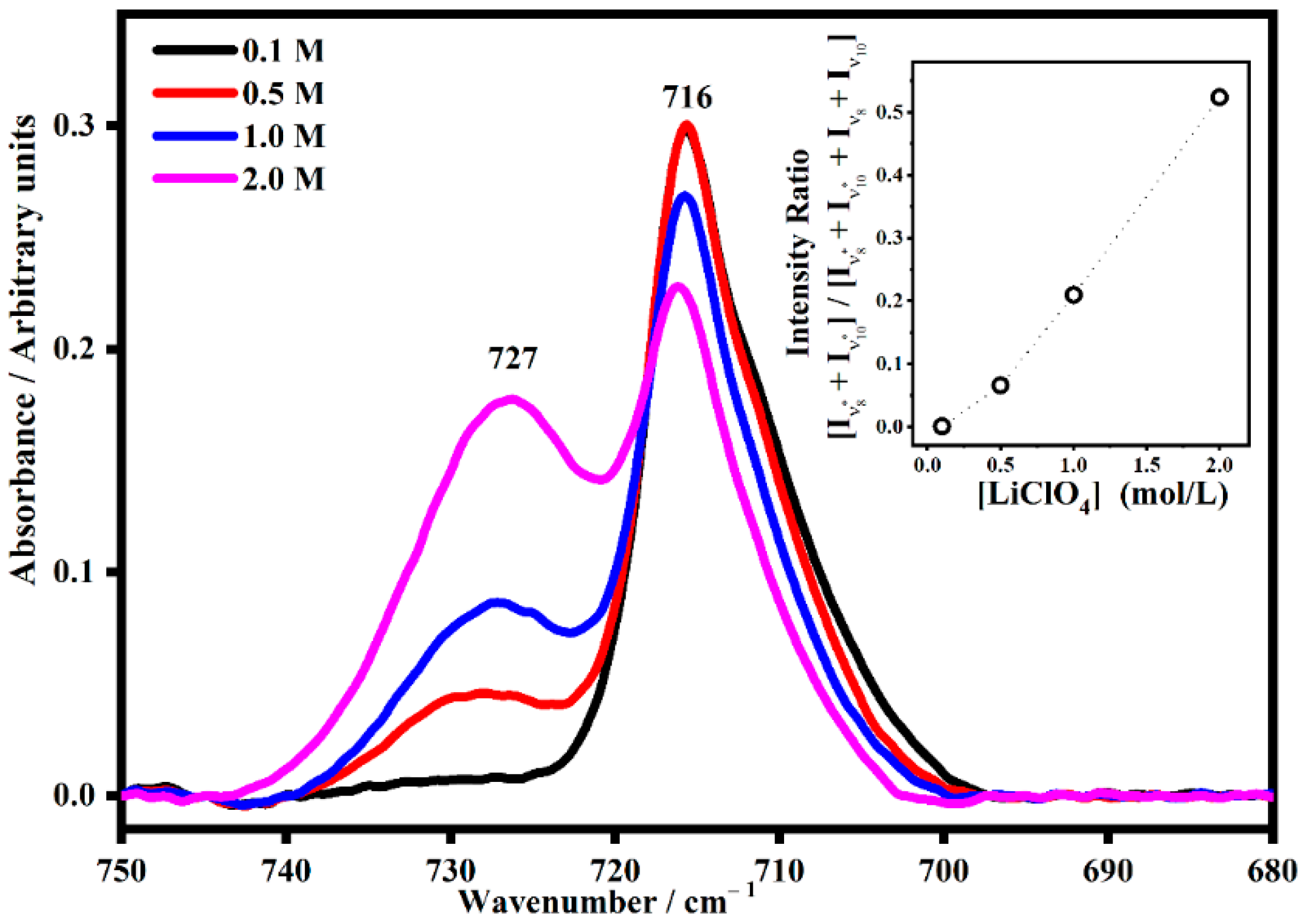
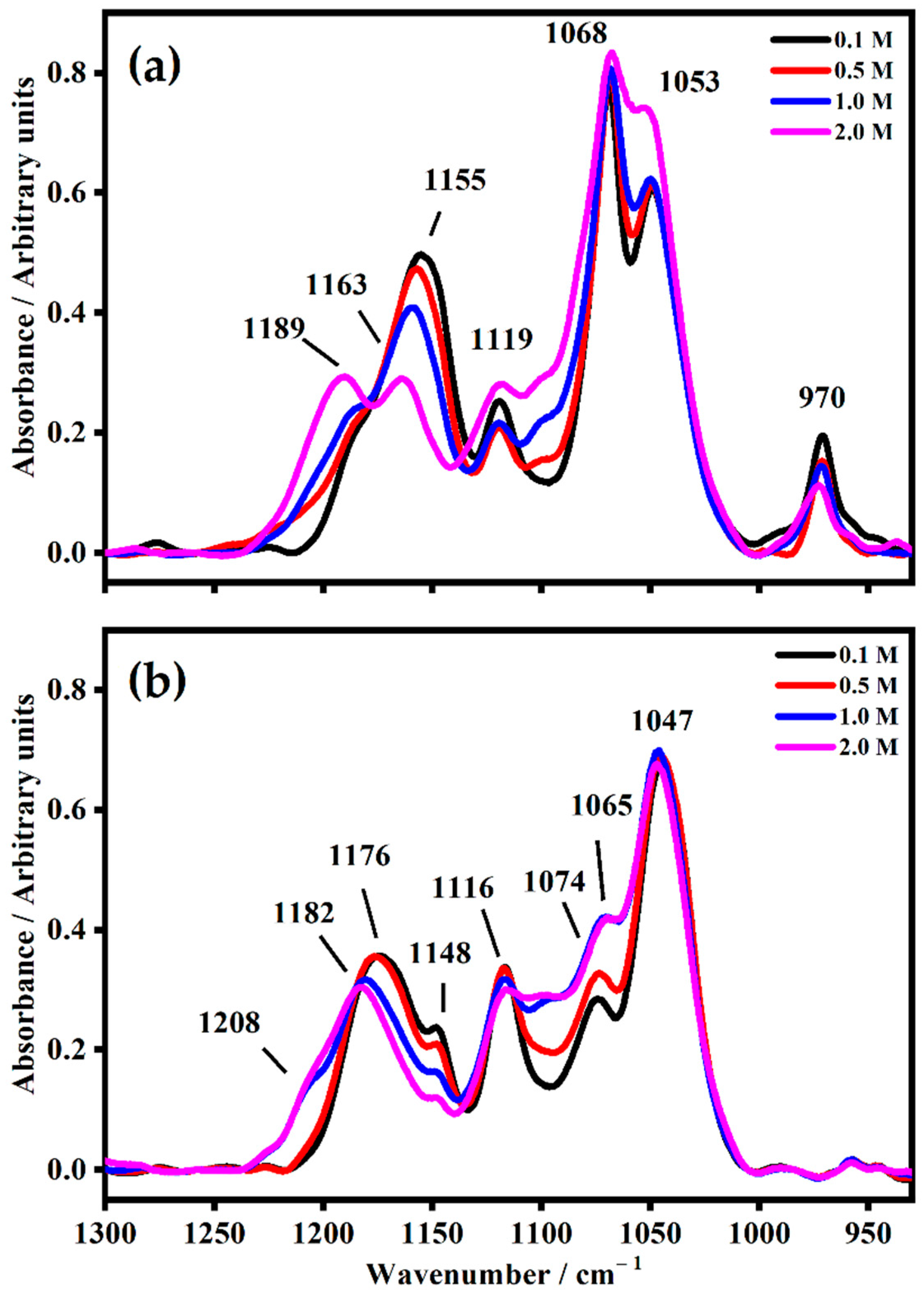
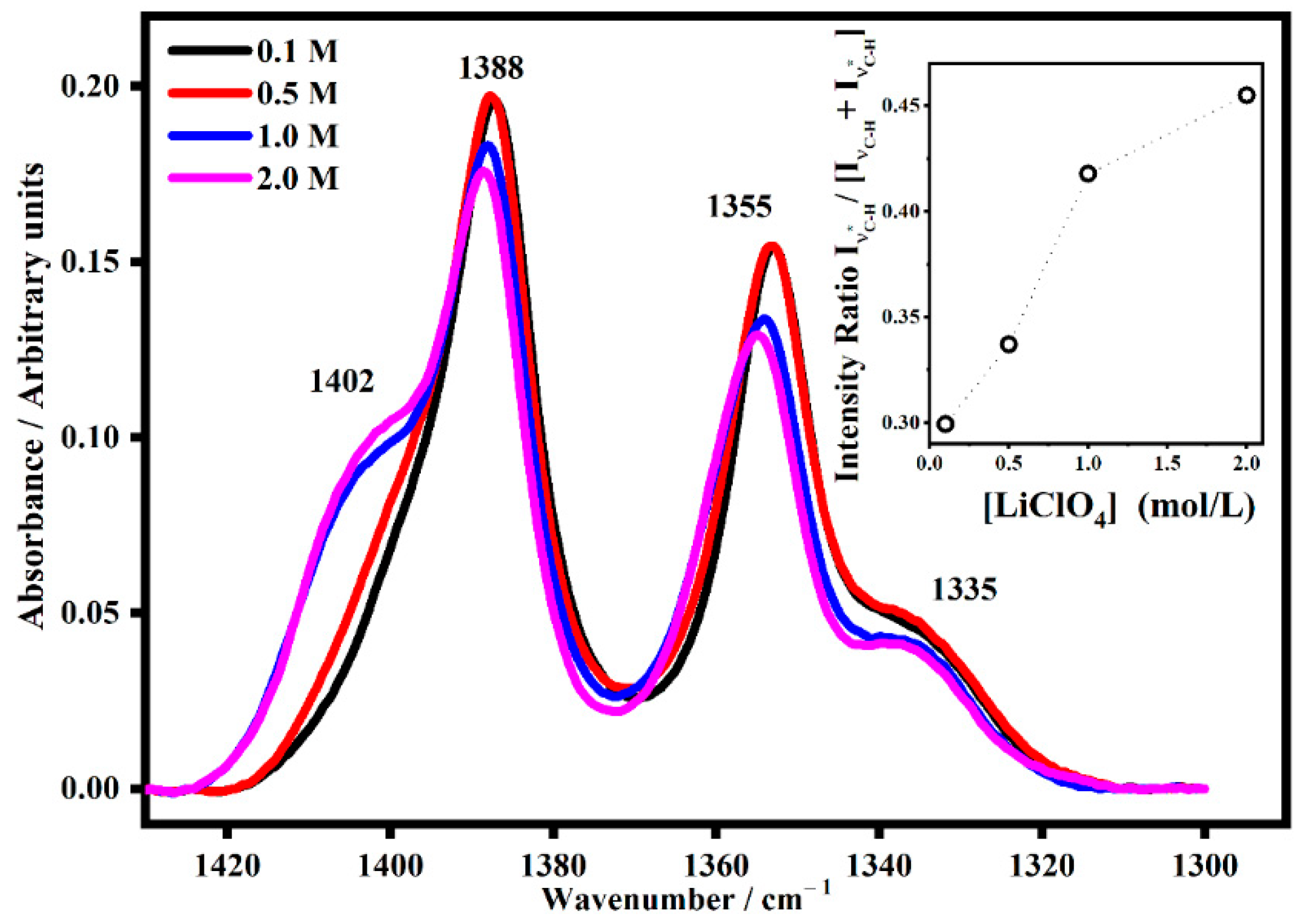
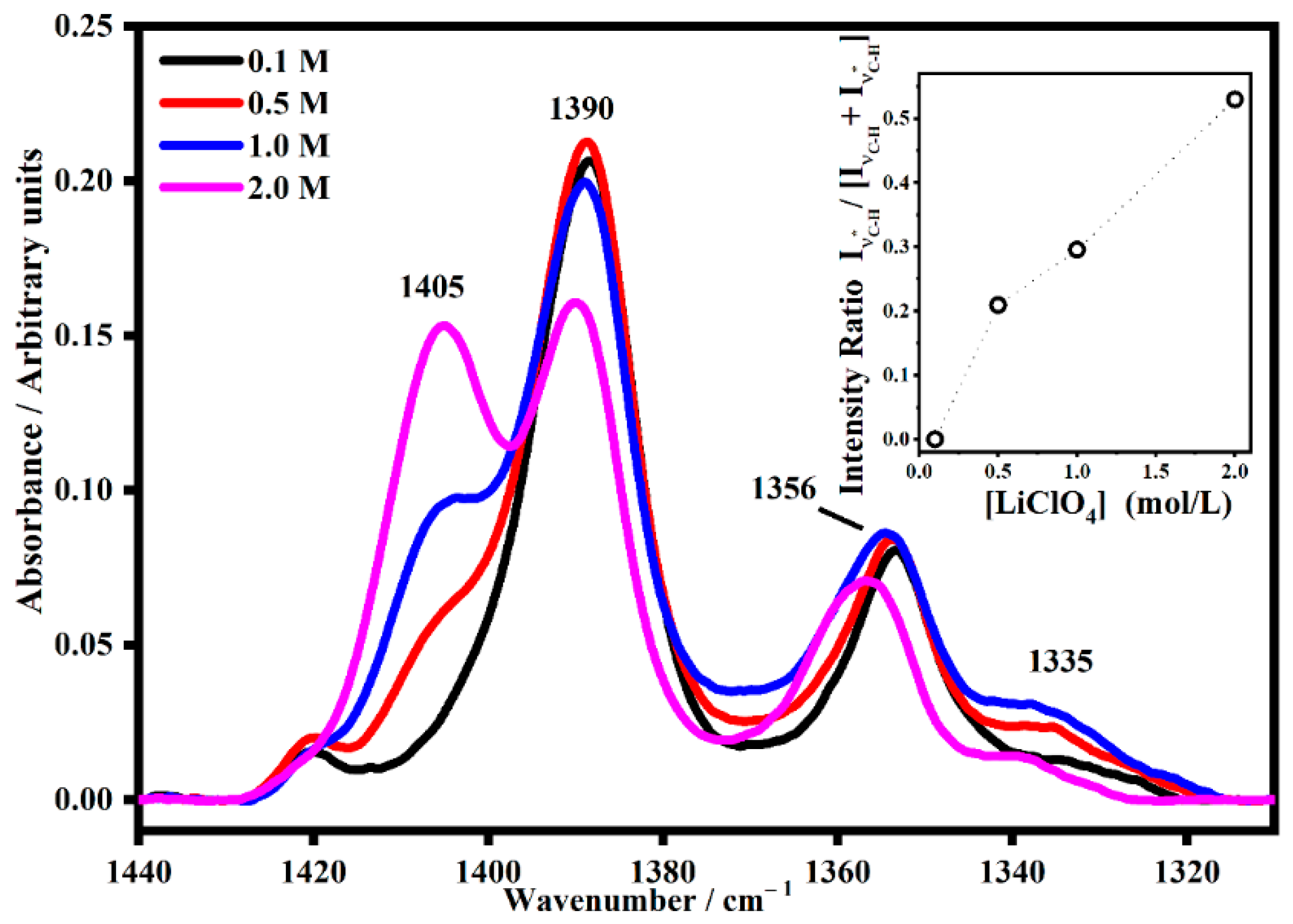
| ETHYLENE CARBONATE | ||
|---|---|---|
| Wavenumber/cm−1 | Assignments | Mode |
| 714 | Ring bending | ν8 |
| 770 | Rocking in-phase of CH2 | ν22 |
| 892 | Skeletal ring breathing | ν7 |
| 970 | Symmetric skeletal stretching | ν4 |
| 1007 | Rocking out of phase of CH2 | ν11 |
| 1060 | Symmetric skeletal stretching (ring breathing) | ν5 |
| 1150 | Stretching of (C–O) + Wagging of C–H | ν10 |
| 1217 | Twisting out-of-phase of CH2 | ν21 |
| 1231 | Twisting in-phase of CH2 | ν19 + ν8 |
| 1391 | Wagging out-of-phase of CH2 | ν4 |
| 1420 | Wagging in-phase of CH2 | ν15 |
| 1486 | Bending of CH2 | ν2, ν14 |
| 1553 | Overtone of 770 cm−1 band | 2 ν22 |
| 1682 | Overtone of 970 cm−1 and 714 cm−1 bands | ν4 + ν8 |
| 1789 | Stretching of C=O | 2 ν7 |
| PROPYLENE CARBONATE | ||
| 711 | Symmetric ring deformation | ν10 |
| 774 | Ring deformation | ν18 |
| 848 | Stretching of CH3 + Ring (Ring breathing) | ν9 |
| 917 | Rocking of CH3 | ν32 |
| 948 | Rocking of CH3 | ν31 |
| 957 | Ring Stretching + Bending of CH3 | ν8 |
| 1043 | Asym. Ring Stretch. + Bend. of C–H + Twist. of C–C | ν6 |
| 1075 | Asymmetric Ring Stretching | ν7 |
| 1116 | Wagging of C–H + Bending of C–H | ν20 |
| 1172 | Stretching of O–C + Wagging of C–H | ν5 |
| 1353 | Symmetric bending of C–H | ν16 |
| 1387 | Wagging of C–H + Bending of C–H | ν30 |
| 1450 | Bending of C–C-H in CH3 | ν29 |
| 1484 | Umbrella of C–H in CH3 | ν15 |
| 1779 | Stretching of C=O | ν1 |
| PERCHLORATE | ||
| 625 | Free ClO4− | ν4 |
| 944 | ClO4 | ν1 |
| 1089 | Pure LiClO4 | ν3 |
| PMMA | ||
| 750 | Asymmetric rocking of CH2 (skeletal mode) | – |
| 840 | Symmetric rocking of CH2 | – |
| 968 | Rocking of (α-CH3) | – |
| 987 | Rocking of (O–CH3) | – |
| 1063 | Stretching of C–C (skeletal mode)) | – |
| (1142–1191) | Stretching of C–O–C | – |
| (1239–1266) | Stretching of C–O bond or the C–C–O (ν4) | – |
| 1387 | Symmetric bending of C–H in (α-CH3) | – |
| 1433 | Symmetric bending of (C–H) of O–CH3 | – |
| 1447– | Asymmetric bending of (C–H) in (α-CH3) | – |
| 1479 | Scissoring of CH2 | – |
| 1721 | Symmetric stretching of C=O | – |
| [LiClO4] (mol/L) | Anodic Stability (V) | |
|---|---|---|
| PMMA-Li-PC | PMMA-Li-PC-EC | |
| 0.1 | 2.21 | 3.36 |
| 0.5 | 2.91 | 3.98 |
| 1.0 | 3.16 | 4.01 |
| 2.0 | 3.30 | 4.09 |
| [LiClO4] (mol/L) | PMMA | PMMA-Li-PC | PMMA-Li-PC-EC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tg (°C) | Tg (°C) | Tg (°C) | |
| 0.0 | 101.5 | - | - |
| 0.1 | - | 61.9 | −1.94 |
| 0.5 | - | 58.3 | 4.41 |
| 1.0 | - | 59.0 | 7.80 |
| 2.0 | - | 78.1 | 36.3 |
| [LiClO4] (mol/L) | PMMA-Li-PC | PMMA-Li-PC-EC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tg (°C) | Ionic Conductivity (S/cm) | Anodic Stability (V) | Tg (°C) | Ionic Conductivity (S/cm) | Anodic Stability (V) | |
| 0.1 | 61.9 | 0.00278 | 2.1 | −1.94 | 0.00206 | 3.63 |
| 0.5 | 58.3 | 0.00343 | 2.91 | 4.41 | 0.02527 | 3.98 |
| 1.0 | 59.0 | 0.00314 | 3.16 | 7.80 | 0.03068 | 4.01 |
| 2.0 | 78.1 | 0.00229 | 3.30 | 36.3 | 0.00304 | 4.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizzuto, C.; Teeters, D.C.; Barberi, R.C.; Castriota, M. Plasticizers and Salt Concentrations Effects on Polymer Gel Electrolytes Based on Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) for Electrochemical Applications. Gels 2022, 8, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060363
Rizzuto C, Teeters DC, Barberi RC, Castriota M. Plasticizers and Salt Concentrations Effects on Polymer Gel Electrolytes Based on Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) for Electrochemical Applications. Gels. 2022; 8(6):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060363
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizzuto, Carmen, Dale C. Teeters, Riccardo C. Barberi, and Marco Castriota. 2022. "Plasticizers and Salt Concentrations Effects on Polymer Gel Electrolytes Based on Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) for Electrochemical Applications" Gels 8, no. 6: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060363
APA StyleRizzuto, C., Teeters, D. C., Barberi, R. C., & Castriota, M. (2022). Plasticizers and Salt Concentrations Effects on Polymer Gel Electrolytes Based on Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) for Electrochemical Applications. Gels, 8(6), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060363







