Molecular Simulation of Interactions between High-Molecular-Polymer Flocculation Gel for Oil-Based Drilling Fluid and Clay Minerals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
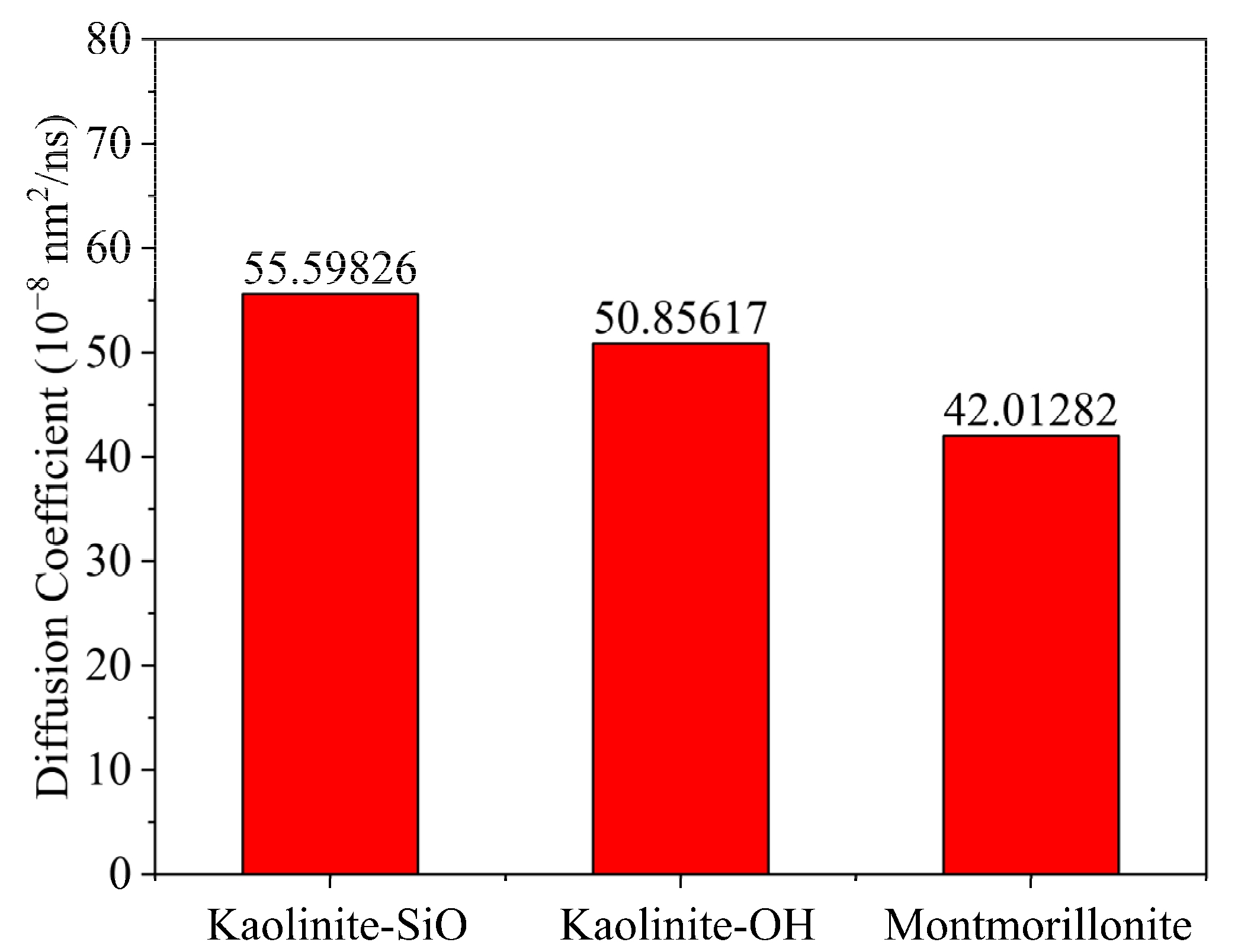
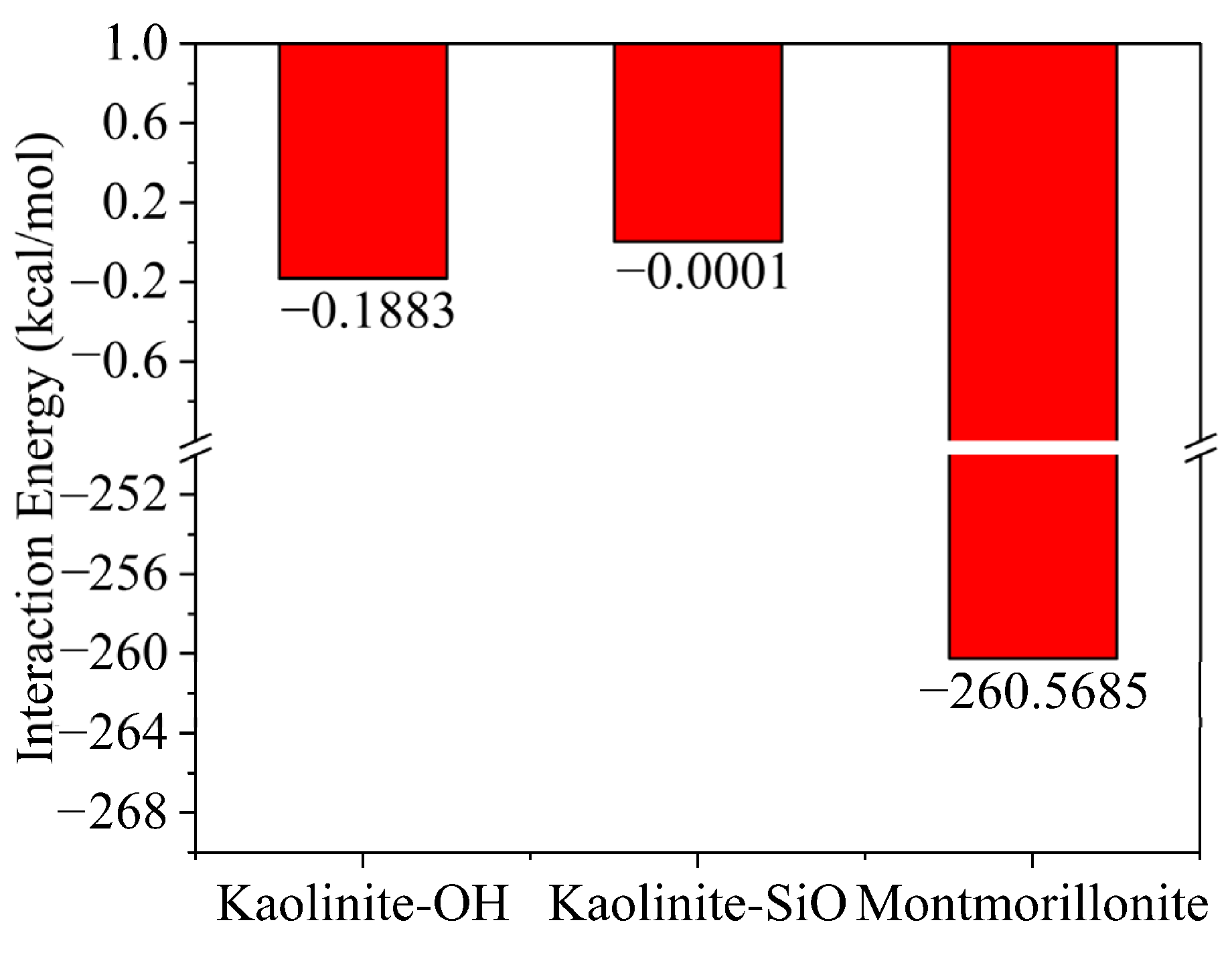
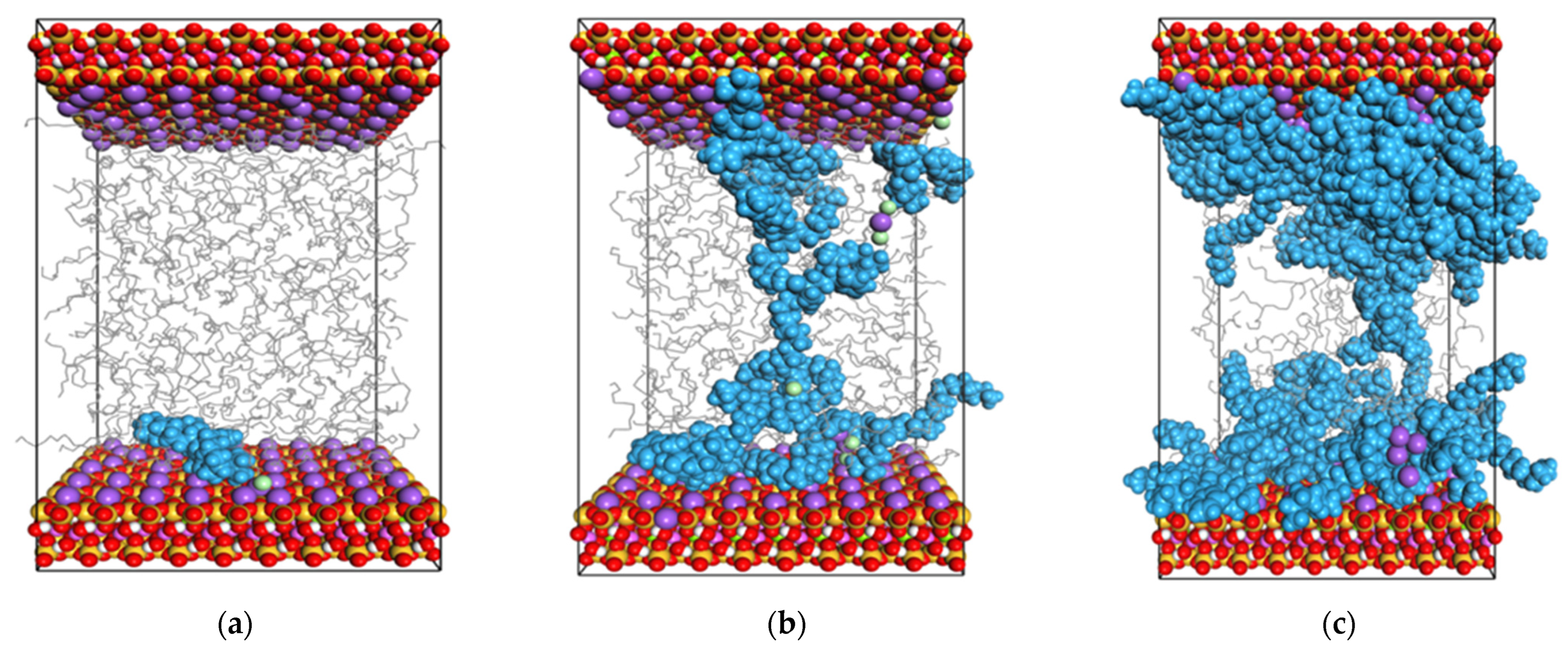
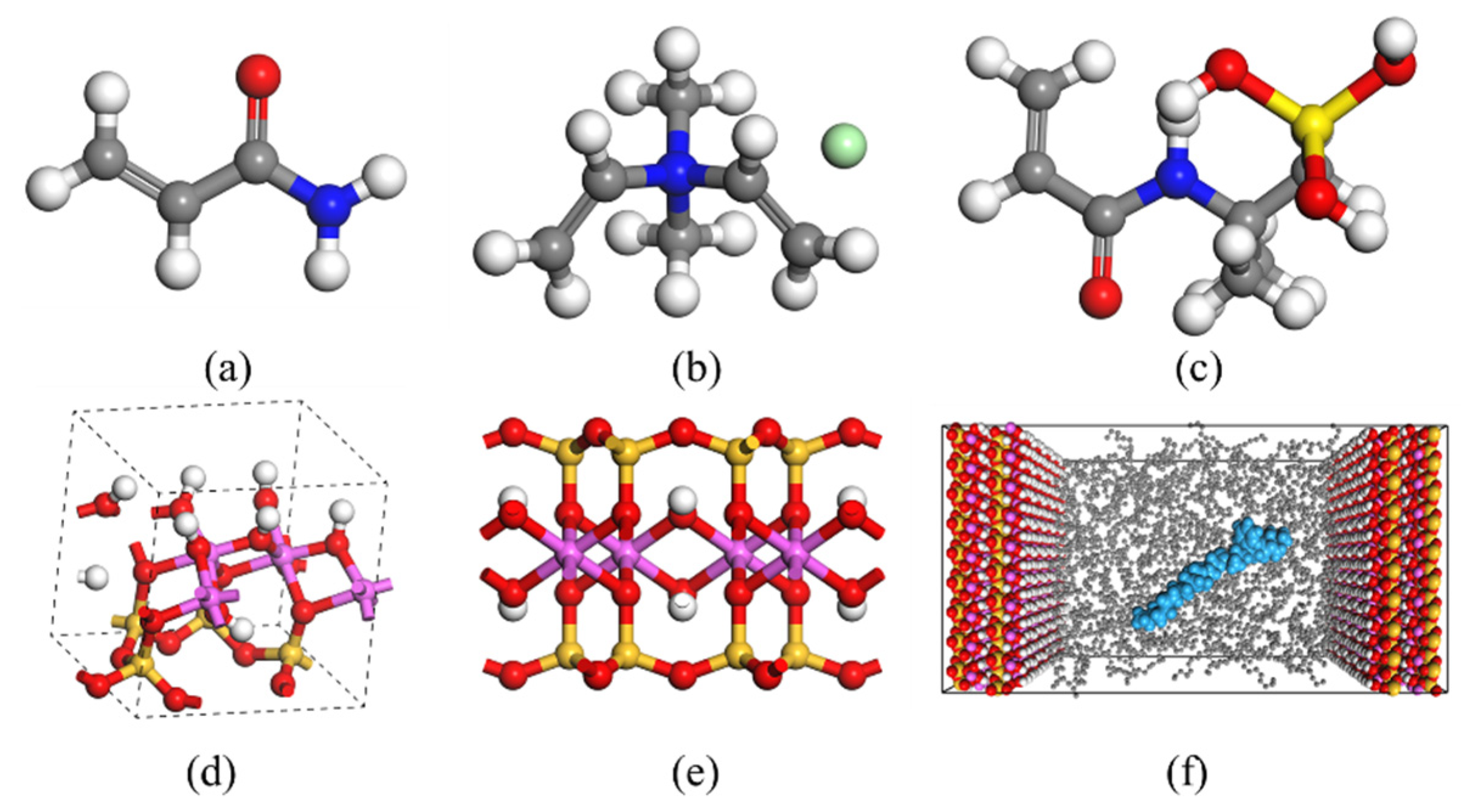
2.1. Simulation of Selective Flocculation of Rock Cuttings
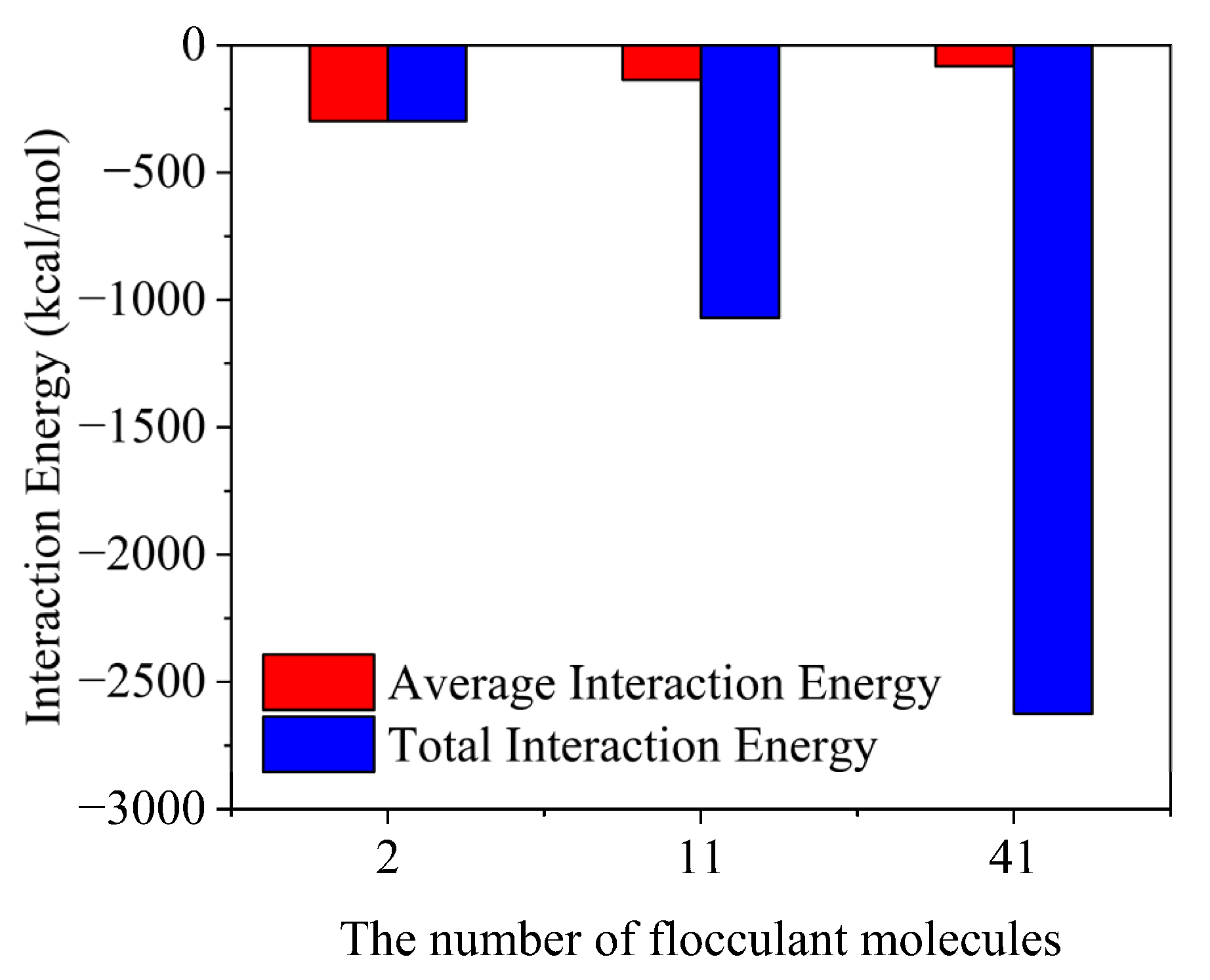
2.2. Effect of Flocculation Gel Concentrations on Flocculation Performance
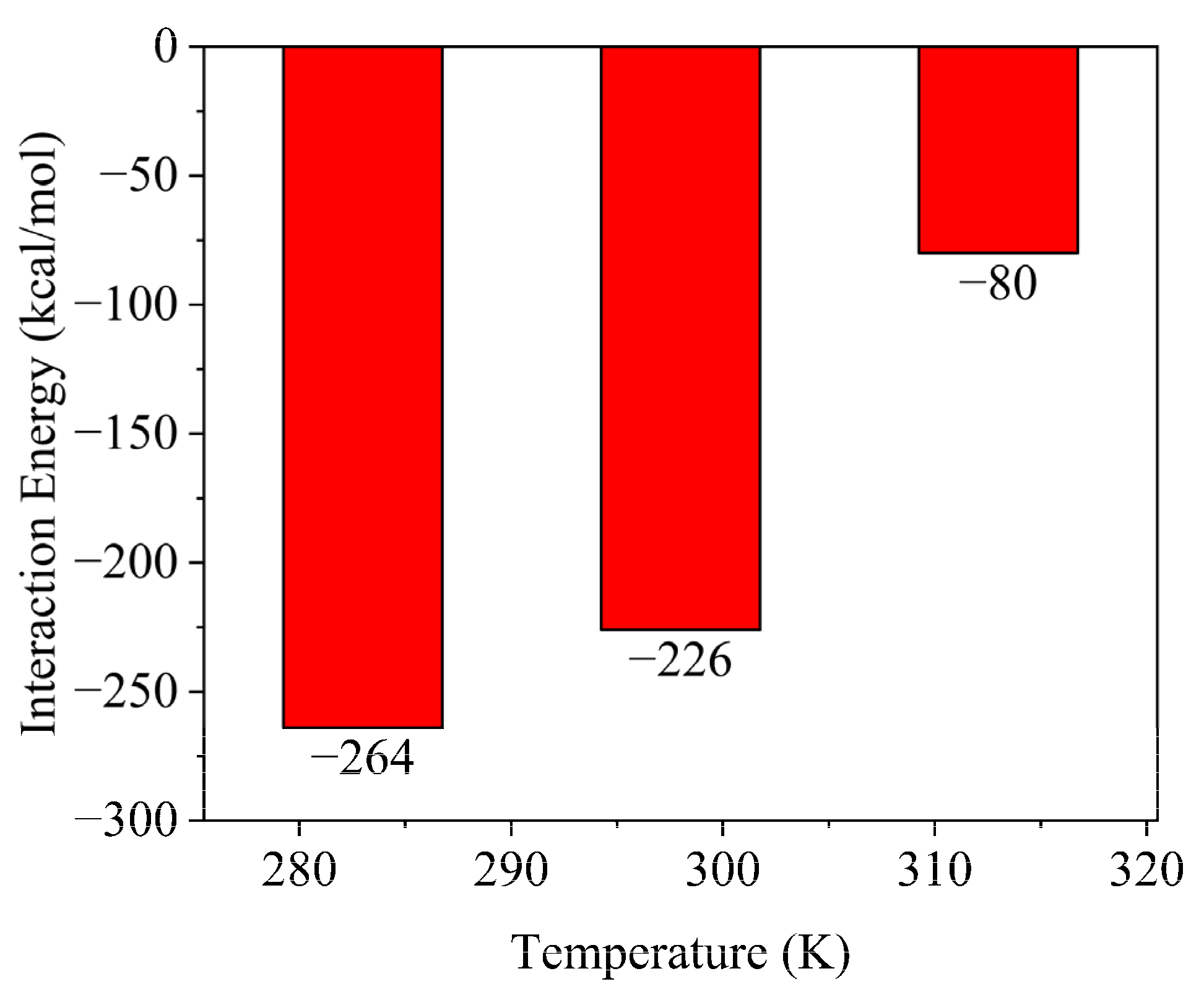
2.3. Effect of Flocculation Gel Concentration on Flocculation Performance
3. Conclusions
- The flocculation gel for oil-based drilling fluid selectively flocculates rock cuttings, and it is highly effective for flocculating electrically negative cuttings components, but it is ineffective for uncharged cuttings components.
- The flocculation gel for oil-based drilling fluid is ineffective for cuttings with strong hydrophilicity, while exerting almost no flocculation effect on cuttings with weak hydrophilicity.
- Within a limited concentration range, the flocculation effect becomes better with increasing flocculation gel concentrations, but the interaction between a single flocculation gel molecule and the cuttings will be diminished.
- The performance of the flocculation gel declines as the environmental temperature increases.
4. Methods
4.1. Modeling and Simulation Methods
4.2. Settings of Force Field and Cutoff Radius
4.3. Calculation Parameters
4.3.1. Density Distribution Function
4.3.2. Interaction Energy
4.3.3. Mean Square Displacement and Diffusion Coefficient
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, D.; Zou, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, G. Progress and prospects of shale gas exploration and development in China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Xingang, Z.; Jiaoli, K.; Bei, L. Focus on the development of shale gas in China—Based on SWOT analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Huang, W.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Xue, H.; Wang, W.; Cai, X. Classification and evaluation criteria of shale oil and gas resources: Discussion and application. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2012, 39, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonglou, G.U.O. Key geological issues and main controls on accumulation and enrichment of Chinese shale gas. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 349–359. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, R.; Yang, H.; Yang, H. Understanding and research on the drilling fluid technology for shale gas horizontal wells in south Sichuan, China. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, 13 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, L.B.; Sad, C.M.S.; Castro, E.V.; Filgueiras, P.R.; Lacerda, V. Environmental impacts related to drilling fluid waste and treatment methods: A critical review. Fuel 2022, 310, 122301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Han, X. Particular pollutants, human health risk and ecological risk of oil-based drilling fluid: A case study of Fuling shale gas field. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, E.; Garcia, F.A.P.; Ferreira, P.; Blanco, A.; Negro, C.; Rasteiro, M. Modelling PCC flocculation by bridging mechanism using population balances: Effect of polymer characteristics on flocculation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 3798–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, D. Model of Relationship between Molecular Weight and Flocculant Concentration of Chitosan. Res. Environ. Sci. 2003, 16, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Quezada, G.R.; Jeldres, M.; Toro, N.; Robles, P.; Toledo, P.G.; Jeldres, R.I. Understanding the flocculation mechanism of quartz and kaolinite with polyacrylamide in seawater: A molecular dynamics approach. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 608, 125576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S. Investigation of the interaction between xanthate and kaolinite based on experiments, molecular dynamics simulation, and density functional theory. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, G.R.; Rozas, R.E.; Toledo, P.G. Polyacrylamide adsorption on (101) quartz surfaces in saltwater for a range of pH values by molecular dynamics simulations. Miner. Eng. 2021, 162, 106741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.P.; Jeldres, R.I.; Quezada, G.R.; Concha, F.; Toledo, P.G. Zeta potential and viscosity of colloidal silica suspensions: Effect of seawater salts, pH, flocculant, and shear rate. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 538, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cygan, R.T.; Liang, J.; Kalinichev, A.G. Molecular Models of Hydroxide, Oxyhydroxide, and Clay Phases and the Development of a General Force Field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- And, M.G.M.; Siepmann, J.I. Transferable Potentials for Phase Equilibria. 1. United-Atom Description of n-Alkanes. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 2569–2577. [Google Scholar]
- Vajihinejad, V.; Gumfekar, S.P.; Bazoubandi, B.; Najiafabadi, Z.R.; Soares, J.B. Water soluble polymer flocculants: Synthesis, characterization, and performance assessment. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šolc, R.; Gerzabek, M.H.; Lischka, H.; Tunega, D. Wettability of kaolinite (001) surfaces—Molecular dynamic study. Geoderma 2011, 169, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Liao, B.; Kong, Z.Y.; Sun, Z.G.; Li, Q.; Wang, D.S. Oscillating Electric Field Effects on Adsorption of the Methane-Water System on Kaolinite Surface. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 11440–11451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Xue, Q.; Yan, K.; Gao, X.; Li, Q.; Hao, L. Effect of chemisorption on the interfacial bonding characteristics of carbon nanotube–polymer composites. Polymer 2008, 49, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Edwards, S.A.; Gräter, F. A new transferable forcefield for simulating the mechanics of CaCO3 crystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 20067–20075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; He, X.; Qiu, N.X.; Yang, X.; Tian, Z.-Y.; Li, M.-J.; Xue, Y. Molecular simulation of CH4, CO2, H2O and N2 molecules adsorption on heterogeneous surface models of coal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.M.; Shi, J.Q.; Sun, X.; Shen, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B. Supercritical CO2 selective extraction inducing wettability alteration of oil reservoir. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 113, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Kang, J.; Kang, T. Effect of water on methane adsorption on the kaolinite (0 0 1) surface based on molecular simulations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, J. DFT simulation of the adsorption of sodium silicate species on kaolinite surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 370, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futera, Z.; English, N.J. Electric-Field Effects on Adsorbed-Water Structural and Dynamical Properties at Rutile- and Anatase-TiO2 Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 19603–19612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Atom | Mass (g/mol) | ε (kcal/mol) | σ (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Montmorillonite | |||
| O | 15.999400 | 0.1554164124 | 3.1655200879 |
| H | 1.007970 | 0 | 0 |
| Si | 28.085500 | 0.0000018402 | 3.3019566252 |
| Al | 26.981540 | 0.0000013297 | 4.2713219316 |
| Mg | 24.305000 | 0.0000009030 | 5.2643258688 |
| White oil | |||
| C | 12.011150 | 0.0389999952 | 3.8754094636 |
| H | 1.007970 | 0.0380000011 | 2.4499714540 |
| Flocculation gel | |||
| C | 12.011150 | 0.0389999952 | 3.8754094636 |
| O | 15.999400 | 0.2280000124 | 2.8597848722 |
| H | 1.007970 | 0.0380000011 | 2.4499714540 |
| N | 14.006700 | 0.1669999743 | 3.5012320066 |
| Cl | 35.453000 | 0.1070000050 | 4.4462973121 |
| Kaolinite | |||
| Al | 26.981540 | 0.0000013297 | 4.2713219316 |
| Si | 28.085500 | 0.0000018402 | 3.3019566252 |
| O | 15.999400 | 0.1554164124 | 3.1655200879 |
| H | 1.007970 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Wang, J.; Liao, B.; Bai, Y.; Shao, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Molecular Simulation of Interactions between High-Molecular-Polymer Flocculation Gel for Oil-Based Drilling Fluid and Clay Minerals. Gels 2022, 8, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070442
He Z, Wang J, Liao B, Bai Y, Shao Z, Huang X, Wang Q, Li Y. Molecular Simulation of Interactions between High-Molecular-Polymer Flocculation Gel for Oil-Based Drilling Fluid and Clay Minerals. Gels. 2022; 8(7):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070442
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zhijun, Jintang Wang, Bo Liao, Yujing Bai, Zihua Shao, Xianbin Huang, Qi Wang, and Yiyao Li. 2022. "Molecular Simulation of Interactions between High-Molecular-Polymer Flocculation Gel for Oil-Based Drilling Fluid and Clay Minerals" Gels 8, no. 7: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070442
APA StyleHe, Z., Wang, J., Liao, B., Bai, Y., Shao, Z., Huang, X., Wang, Q., & Li, Y. (2022). Molecular Simulation of Interactions between High-Molecular-Polymer Flocculation Gel for Oil-Based Drilling Fluid and Clay Minerals. Gels, 8(7), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070442







