Facile Synthesis of Sustainable Tannin/Sodium Alginate Composite Hydrogel Beads for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Tan/SA Beads
2.1.1. Morphology Analysis
2.1.2. Structure Analysis
2.1.3. Thermal Stability Analysis
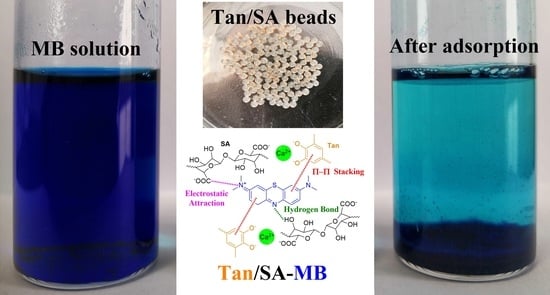
2.2. Adsorption Behavior of Tan/SA Hydrogel Beads
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics of Tan/SA Hydrogel Beads
2.4. Regeneration Behavior of Tan/SA Hydrogel Beads
2.5. Comparative Analysis of MB Adsorption
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Bio-Based Tan/SA Hydrogel Beads
4.3. Characterization
4.4. Adsorption Experiments
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghahehe, F.S.; Taghizadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Hatati, B.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Parastar, S. Clean synthesis of rock candy-like metal–organic framework biocomposite for toxic contaminants remediation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Taghizadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, A. Activated carbon/metal-organic framework composite as a bio-based novel green adsorbent: Preparation and mathematical pollutant removal modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Gupta, S.; Singh, A.K.; Sinha, S. Optimizing adsorption of crystal violet dye from water by magnetic nano composite using response surface modeling approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roosta, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Daneshfar, A.; Sahraei, R.; Asghari, A. Optimization of the ultrasonic assisted removal of methylene blue by gold nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon using experimental design methodology. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2014, 21, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadarin, A.; Collins, M.N.; Naushad, M.; Shirazian, S.; Walker, G.; Mangwandi, C. Activated lignin-chitosan extruded blends for efficient adsorption of methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrakchi, F.; Khanday, W.A.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H. Cross-linked chitosan/sepiolite composite for the adsorption of methylene blue and reactive orange 16. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscusi, G.; Lamberti, E.; Gorrasi, G. Design of sodium alginate/soybean extract beads loaded with hemp hurd and halloysite as novel and sustainable systems for methylene blue adsorption. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.D.; Lu, J.J.; Li, S.M.; Tong, Y.B.; Ye, B.C. Synthesis of magnetic microspheres with sodium alginate and activated carbon for removal of methylene blue. Materials 2017, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.F.; Mohsen, A.M.; Fouda, M.M. Comparative study of calcium alginate, activated carbon, and their composite beads on methylene blue adsorption. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 102, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Sang, Y.N.; Tang, M.; Hu, G.W.; Han, X.B.; Gao, J.; Ma, R. Facile synthesis of magnetic CS-g-SPSS microspheres via electron beam radiation for efficient removal of methylene blue. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.Q.; Li, G.F.; Wang, G.L.; Chen, W.; Wang, S.S. Preparation of acrylic acid modified alkalized MXene adsorbent and study on its dye adsorption performance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 632, 127730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.B.; Li, R.; Miao, P.P.; Gao, J.; Hu, G.W.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, T. Design, synthesis and adsorption evaluation of bio-based lignin/chitosan beads for congo red removal. Materials 2022, 15, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Liu, Q.Z.; Gao, T.T.; Dong, K.J.; Wei, G.; Yao, J.S. Facile preparation of tannic acid-poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate hydrogel beads for methylene blue removal from simulated solution. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 7523–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, B. Improving sodium alginate films properties by phenolic acid addition. Materials 2020, 13, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larosa, C.; Salerno, M.; Lima, J.S.; Meri, R.M.; Silva, M.F.; Carvalho, L.B.; Converti, A. Characterisation of bare and tannase-loaded calcium alginate beads by microscopic, thermogravimetric, FTIR and XRD analyses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulateefeh, S.R.; Taha, M.O. Enhanced drug encapsulation and extended release profiles of calcium-alginate nanoparticles by using tannic acid as a bridging cross-linking agent. J. Microencapsul. 2015, 32, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.S.; Liu, Z.; Hui, L.F.; Shang, Z.; Yuan, S.Y.; Dai, L.; Liu, P.T.; Liu, X.L.; Ni, Y.H. Lignin-containing cellulose nanocrystals/sodium alginate beads as highly effective adsorbents for cationic organic dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, W.J.; Mao, Q.H.; Bai, Y.S.; Ma, H.Z. Facile Synthesis of chitosan/gelatin filled with graphene bead adsorbent for orange II removal. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 144, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.J.; Brosse, N.; Hoppe, S.; Du, G.B.; Zhou, X.J.; Pizzi, A. One-step compatibilization of poly(lactic acid) and tannin via reactive extrusion. Mater. Des. 2020, 191, 108603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Hou, X.L.; Ma, B.M.; Xu, H.L.; Yang, Q.Y. Chitosan/gallnut tannins composite fifiber with improved tensile, antibacterial and flfluorescence properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 226, 115311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofomaja, A.E.; Ho, Y.S. Equilibrium sorption of anionic dye from aqueous solution by palm kernel fibre as sorbent. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 74, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Zhao, D.Q.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.H.; Li, H.T.; Xie, J.H.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, H.K.; Liu, X.J.; Zhu, X.Y.; et al. A Graphene oxide modified cellulose nanocrystal/PNIPAAm IPN hydrogel for the adsorption of congo red and methylene blue. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 16679–16688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Fu, Y.Q.; Jiang, R.; Jiang, J.H.; Xiao, L.; Zeng, G.M.; Zhao, S.L.; Wang, Y. Adsorption removal of congo red onto magnetic cellulose/Fe3O4/activated carbon composite: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwegbe, C.A.; Ighalo, J.O.; Onyechi, K.K.; Onukwuli, O.D. Adsorption of Congo red and malachite green using H3PO4 and NaCl-modifed activated carbon from rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) seed shells. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwegbe, C.A.; Ighalo, J.O.; Ghosh, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Ugonabo, V.I. Pistachio (Pistacia vera) waste as adsorbent for wastewater treatment: A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.M.; Fu, K.X.; Yu, D.Y.; Hristovski, K.D.; Westerhoff, P.; Crittenden, J.C. Review of advances in engineering nanomaterial adsorbents for metal removal and recovery from water: Synthesis and microstructure impacts. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 623–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Chen, Z.Z.; Guo, W.; Zhu, C.W.; Zou, Y.J. Simple fabrication of chitosan/graphene nanoplates composite spheres for efficient adsorption of acid dyes from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Geng, J.; Li, M.L.; Chang, J.M.; Cui, Y. Synthesis of chitosan-ignosulfonate composite as an adsorbent for dyes and metal ions removal from wastewater. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 21421–21430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, Y.Q.; Freyburger, A.; Kunz, W.; Zollfrank, C. Lignin/chitin films and their adsorption characteristics for heavy metal ions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6965–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartape, A.S.; Mandhare, A.M.; Salvi, P.P.; Pawar, D.K.; Kolekar, S.S. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of the adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by wood apple shell activated carbon. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 4638–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yan, C.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Tang, C.H.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, R.; Duan, P. Synthesis of activated carbon-based amino phosphonic acid chelating resin and its adsorption properties for Ce(III) removal. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2168–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Characteristics of Elovich equation used for the analysis of adsorption kinetics in dye-chitosan systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeddou, N.; Bensmaili, A. Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by clay-wood sawdust mixture. Desalination 2005, 185, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljar, M.A.A.; Rashdan, S.; Fattah, A.A. Environmentally friendly polyvinyl alcohol-alginate/bentonite semi-interpenetrating polymer network nanocomposite hydrogel beads as an effificient adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Polymers 2021, 13, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, M.H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.L.; Ni, H.G. Surface functionalization of cellulose with hyperbranched polyamide for effificient adsorption of organic dyes and heavy metals. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Temperature (K) | K0 | ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | ΔH0 (kJ/mol) | ΔS0 (kJ/mol·k) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 288 | 0.36 | 2.44 | 80.80 | 0.27 |
| 298 | 0.69 | 0.92 | - | - |
| 308 | 2.53 | −2.38 | - | - |
| 318 | 8.25 | −5.58 | - | - |
| Kinetic Models | Coefficients | 60 mg/L | 80 mg/L | 100 mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | qe,cal (mg/g) | 9.7279 | 15.8790 | 27.4949 |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.0107 | 0.0139 | 0.0172 | |
| R2 | 0.9029 | 0.8050 | 0.9666 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | qe,cal (mg/g) | 86.81 | 116.55 | 144.93 |
| k2 (×10−3) (g/mg min) | 2.78 | 2.07 | 1.31 | |
| R2 | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | |
| Elovich model | α (mg/g min) | 3.14 × 106 | 5.87 × 106 | 2.89 × 105 |
| β (g/mg) | 0.219 | 0.166 | 0.110 | |
| R2 | 0.8147 | 0.7301 | 0.8463 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, T.; Hu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Han, X. Facile Synthesis of Sustainable Tannin/Sodium Alginate Composite Hydrogel Beads for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue. Gels 2022, 8, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080486
Gao J, Li Z, Wang Z, Chen T, Hu G, Zhao Y, Han X. Facile Synthesis of Sustainable Tannin/Sodium Alginate Composite Hydrogel Beads for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue. Gels. 2022; 8(8):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080486
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jie, Zhenzhen Li, Ziwen Wang, Tao Chen, Guowen Hu, Yuan Zhao, and Xiaobing Han. 2022. "Facile Synthesis of Sustainable Tannin/Sodium Alginate Composite Hydrogel Beads for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue" Gels 8, no. 8: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080486
APA StyleGao, J., Li, Z., Wang, Z., Chen, T., Hu, G., Zhao, Y., & Han, X. (2022). Facile Synthesis of Sustainable Tannin/Sodium Alginate Composite Hydrogel Beads for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue. Gels, 8(8), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080486