Thermosensitive Injectable Hydrogels for Intra-Articular Delivery of Etanercept for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
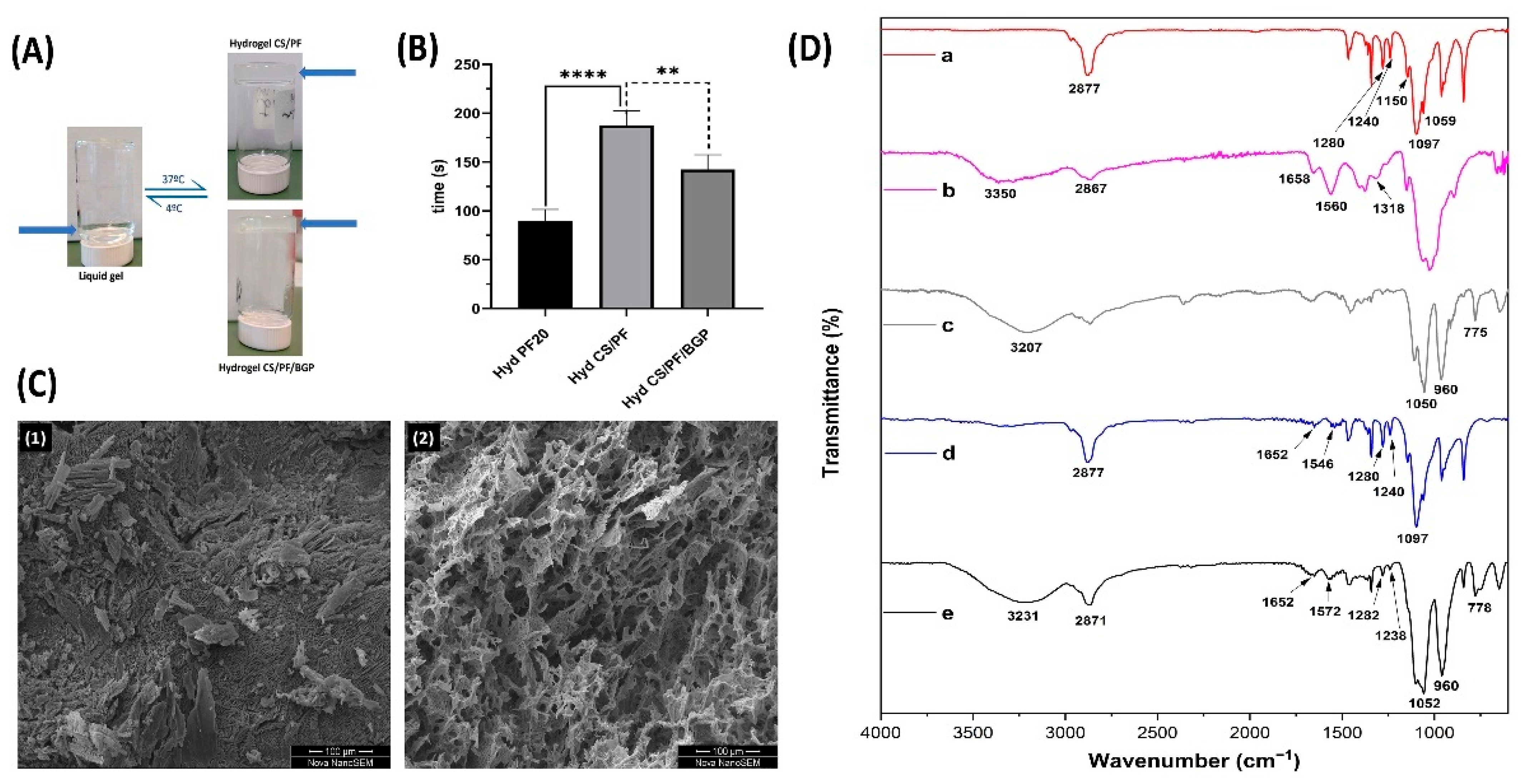
2.1. Hydrogel Preparation
2.1.1. Gelation Time
2.1.2. Morphological and Chemical Characterizations
2.2. In Vitro Experiments
2.2.1. ETA Release Study
2.2.2. Cell Viability and Proliferation
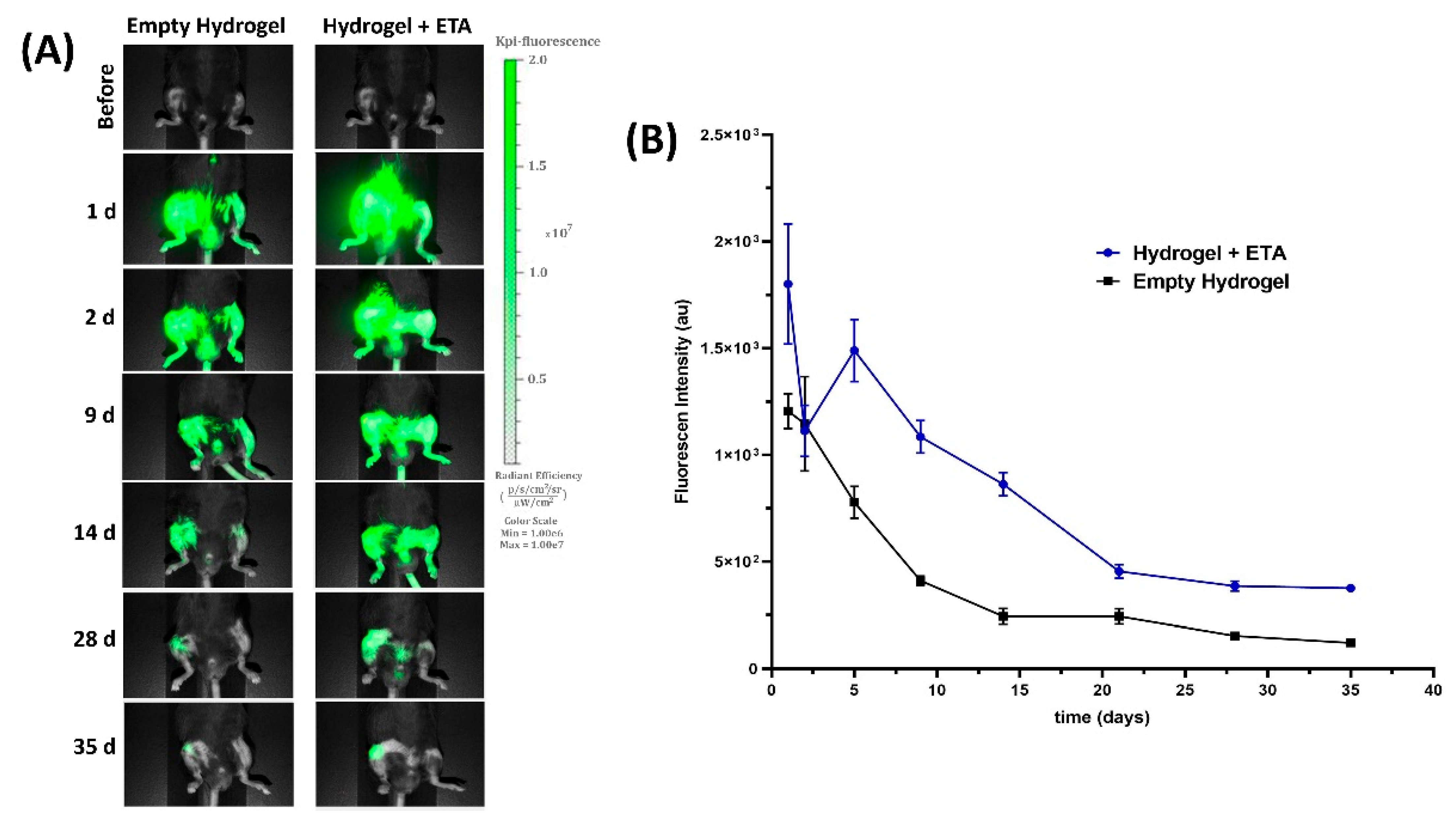
2.3. In Vivo ETA Release Study
2.4. Near-Infrared (NIR) Fluorescent Imaging
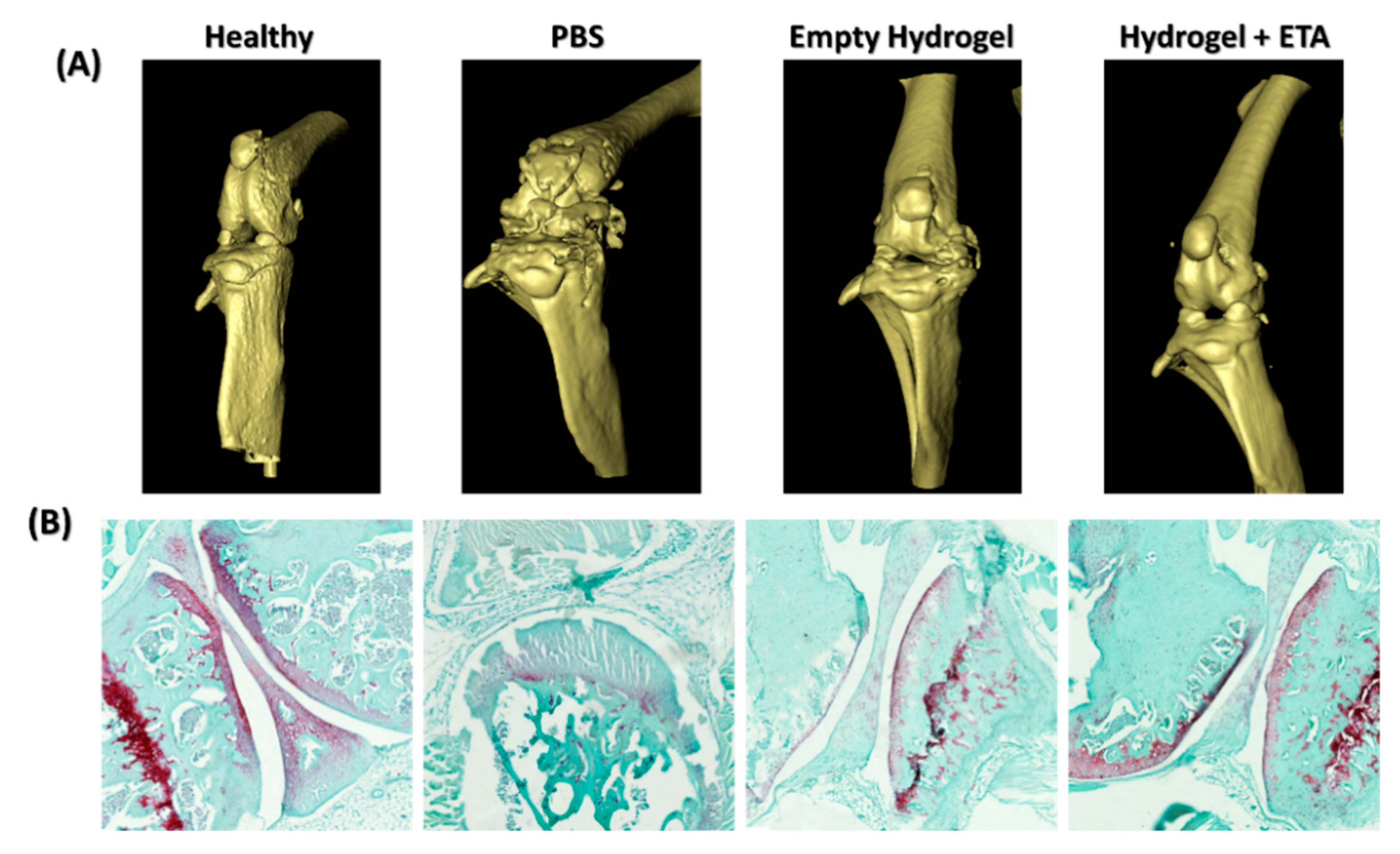
2.5. µ-CT and Histological Analysis
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Hydrogel Preparation
4.2. Hydrogel Characterization
4.2.1. Gelation Time
4.2.2. Morphological Characterization
4.2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.3. In Vitro Experiments
4.3.1. ETA Release Study
4.3.2. Hydrogel Cytocompatibility
4.3.3. LIVE/DEAD Staining on Hydrogels
4.4. In Vico and Ex Vivo Experiments
4.4.1. Animal Models
4.4.2. In Vivo ETA Release
4.4.3. In Vivo Imaging
4.4.4. Histological ANALYSIS
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oo, W.M.; Hunter, D.J. Repurposed and investigational disease-modifying drugs in osteoarthritis (DMOADs). Adv. Musculoskelet Dis. 2022, 14, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Lou, Z.; Zheng, S.; Wu, J.; Yao, Q.; Chen, R.; Kou, L.; Chen, D. Intra-articular drug delivery systems for osteoarthritis therapy: Shifting from sustained release to enhancing penetration into cartilage. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Lee, J.; Ghosh, T.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Dey, A.; Yoon, B.; Um, W.; Park, J.H. Polymeric Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery to Treat Arthritis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maudens, P.; Jordan, O.; Allémann, E. Recent advances in intra-articular drug delivery systems for osteoarthritis therapy. Drug Discov. 2018, 23, 1761–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Gad, S.F.; Chobisa, D.; Li, Y.; Yeo, Y. Local drug delivery systems for inflammatory diseases: Status quo, challenges, and opportunities. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 438–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I.; Glass, C.K. Anti-Inflammatory Therapy in Chronic Disease: Challenges and Opportunities. Science 2013, 339, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gao, H.; Ding, J.; He, Z. Intraarticular Injection of Infliximab-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogel Alleviates Pain and Protects Cartilage in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 3315–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouri, A.; Conaghan, P.G. Prospects for Therapies in Osteoarthritis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 109, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, W.M.; Little, C.; Duong, V.; Hunter, D.J. The Development of Disease-Modifying Therapies for Osteoarthritis (DMOADs): The Evidence to Date. Drug Des. Devel. 2021, 15, 2921–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yuan, S.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, N.; Ding, C. New Trends in Pharmacological Treatments for Osteoarthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 645842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Jeong, S.; Kim, H.; Kang, D.; Lee, J.; Kang, S.-B.; Kim, J.-H. Disease-modifying therapeutic strategies in osteoarthritis: Current status and future directions. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloppenburg, M.; Ramonda, R.; Bobacz, K.; Kwok, W.-Y.; Elewaut, D.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Kroon, F.P.B.; Punzi, L.; Smolen, J.S.; Vander Cruyssen, B.; et al. Etanercept in patients with inflammatory hand osteoarthritis (EHOA): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Mysler, E.; Moots, R.J. Etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunotherapy 2018, 10, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtori, S.; Orita, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Eguchi, Y.; Ochiai, N.; Kishida, S.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Aoki, Y.; Nakamura, J.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Efficacy of Direct Injection of Etanercept into Knee Joints for Pain in Moderate and Severe Knee Osteoarthritis. Yonsei Med. J. 2015, 56, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.L.; Im, G.-I. Drug delivery systems for intra-articular treatment of osteoarthritis. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Tsao, C.T.; Kyomoto, M.; Zhang, M. Injectable Natural Polymer Hydrogels for Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2101479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.M.; Fernandes, D.C.; Cengiz, I.F.; Reis, R.L.; Oliveira, J.M. Hydrogels in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: Drug delivery systems and artificial matrices for dynamic in vitro models. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2021, 32, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçüktürkmen, B.; Öz, U.C.; Bozkir, A. In Situ Hydrogel Formulation for Intra-Articular Application of Diclofenac Sodium-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 14, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Han, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. ECM based injectable thermo-sensitive hydrogel on the recovery of injured cartilage induced by osteoarthritis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.H.M.; Franco, M.K.K.D.; Yokaichyia, F.; de Paula, E.; Lombello, C.B.; de Araujo, D.R. Hyaluronic acid in Pluronic F-127/F-108 hydrogels for postoperative pain in arthroplasties: Influence on physico-chemical properties and structural requirements for sustained drug-release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, A.; da Silva, D.C.; de Mello, J.C.; de Moraes, V.W.R.; Cavalcanti, L.P.; Franco, M.K.K.D.; Alkschbirs, M.I.; Fraceto, L.F.; Yokaichiya, F.; Rodrigues, T.; et al. Pluronics F-127/L-81 Binary Hydrogels as Drug-Delivery Systems: Influence of Physicochemical Aspects on Release Kinetics and Cytotoxicity. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13689–13698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, B.; Hu, C.; Zhao, J. An overview of hydrogel-based intra-articular drug delivery for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 154, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comblain, F.; Rocasalbas, G.; Gauthier, S.; Henrotin, Y. Chitosan: A promising polymer for cartilage repair and viscosupplementation. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2017, 28, S209–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Xiao, S.; Sun, R.; Bao, S.; Yao, Q.; Chen, R. Biomaterial-engineered intra-articular drug delivery systems for osteoarthritis therapy. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Q.; He, W.; Feng, Q.; Yu, B. A novel thermo-sensitive hydrogel based on thiolated chitosan/hydroxyapatite/beta-glycerophosphate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 110, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Stegemann, J.P. Thermogelling chitosan and collagen composite hydrogels initiated with β-glycerophosphate for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P.R.; Jain, N.J.; Sharma, R.K.; Bahadur, P. Effect of additives on the micellization of PEO/PPO/PEO block copolymer F127 in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 178, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacucina, G.; Spina, M.; Misici-Falzi, M.; Cespi, M.; Pucciarelli, S.; Angeletti, M.; Palmieri, G.F. Effect of hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin on the self-assembling and thermogelation properties of Poloxamer 407. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 32, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Couce, J.; Tomás, M.; Fuentes, G.; Que, I.; Almirall, A.; Cruz, L.J. Chitosan/Pluronic F127 Thermosensitive Hydrogel as an Injectable Dexamethasone Delivery Carrier. Gels 2022, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Jiang, L.J.; Cao, P.P.; Li, J.B.; Chen, X.G. Glycerophosphate-based chitosan thermosensitive hydrogels and their biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, D. Synthesis and characterization of a chitosan based nanocomposite injectable hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skwarczynska, A.; Kaminska, M.; Owczarz, P.; Bartoszek, N.; Walkowiak, B.; Modrzejewska, Z. The structural (FTIR, XRD, and XPS) and biological studies of thermosensitive chitosan chloride gels with β-glycerophosphate disodium. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, A.; Yang, Y.; Diao, L.; Wang, L.; Cai, D.; Hu, Y. Injectable Chitosan-Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel/Nanoparticle-Loaded System for Local Delivery of Vancomycin in the Treatment of Osteomyelitis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5855–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, R.; de Bruijn, J.D. Biocompatibility and gelation of chitosan–glycerol phosphate hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2008, 86A, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Lei, T.; Bi, W.; Sun, S.; Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Du, H. Chitosan Hydrogel Supplemented with Metformin Promotes Neuron–like Cell Differentiation of Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Vimalraj, S.; Thanikaivelan, P.; Banudevi, S.; Manivasagam, G. A review on injectable chitosan/beta glycerophosphate hydrogels for bone tissue regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, Q.L.; Choong, C. Three-Dimensional Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications: Role of Porosity and Pore Size. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2013, 19, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenzi, P.; Malfatti, L.; Piccinini, M.; Marcelli, A. Evaporation-Induced Crystallization of Pluronic F127 Studied in Situ by Time-Resolved Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, C.; Khouzami, K.; Wanderlingh, U.; D’Angelo, G. Effect of intercalated chitosan/clay nanostructures on concentrated pluronic F127 solution: A FTIR-ATR, DSC and rheological study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 517, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankongadisak, P.; Suwantong, O. Enhanced properties of injectable chitosan-based thermogelling hydrogels by silk fibroin and longan seed extract for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyamao, P.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Sirisa-ard, P.; Charumanee, S. Injectable Thermosensitive Chitosan/Pullulan-Based Hydrogels with Improved Mechanical Properties and Swelling Capacity. Polymers 2020, 12, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.J.; Faneca, H.; Lima, M.P.; Gil, M.H.; Figueiredo, M.M. In Situ Forming Chitosan Hydrogels Prepared via Ionic/Covalent Co-Cross-Linking. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3275–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, A.; Kang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S. Enhanced gelation of chitosan/β-sodium glycerophosphate thermosensitive hydrogel with sodium bicarbonate and biocompatibility evaluated. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiz-Fernández, S.; Guaresti, O.; Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Gabilondo, N.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. β-Glycerol phosphate/genipin chitosan hydrogels: A comparative study of their properties and diclofenac delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 248, 116811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-García, D.; Guerra-Contreras, A.; Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Palestino, G. Role of porous silicon/hydrogel composites on drug delivery. Open Mater. Sci. 2016, 3, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Metters, A.T. Hydrogels in controlled release formulations: Network design and mathematical modeling. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1379–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertz, A.; Wöhl-Bruhn, S.; Miethe, S.; Tiersch, B.; Koetz, J.; Hust, M.; Bunjes, H.; Menzel, H. Encapsulation of proteins in hydrogel carrier systems for controlled drug delivery: Influence of network structure and drug size on release rate. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 163, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mooney, D.J. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigata, M.; Meinert, C.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Bock, N. Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of Current Characterization and Evaluation Techniques. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, D.; Nayak, S.K.; Maji, S.; Anis, A.; Kim, D.; Pal, K. Environment sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 120, 109220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccavo, D. An overview on the mathematical modeling of hydrogels’ behavior for drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 560, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.I. Kinetics of drug release from hydrogel matrices. J. Control. Release 1985, 2, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Narasimhan, B. Mathematical models in drug delivery: How modeling has shaped the way we design new drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10993-5; 2009-Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices-Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Tateiwa, D.; Yoshikawa, H.; Kaito, T. Cartilage and Bone Destruction in Arthritis: Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategy: A Literature Review. Cells 2019, 8, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qi, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, Q. Spatiotemporal regulation of endogenous MSCs using a functional injectable hydrogel system for cartilage regeneration. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camplejohn, K.L.; Allard, S.A. Limitations of safranin ‘O’ staining in proteoglycan-depleted cartilage demonstrated with monoclonal antibodies. Histochemistry 1988, 89, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibegović, A.; Blagus, R.; Martinez, I.Z. Safranin O without fast green is the best staining method for testing the degradation of macromolecules in a cartilage extracellular matrix for the determination of the postmortem interval. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2020, 16, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiji, A.; Sohrabi, A.; Hungerford, D.S.; Frondoza, C.G. Chitosan supports the expression of extracellular matrix proteins in human osteoblasts and chondrocytes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 51, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprenyeszk, F.; Sanchez, C.; Dubuc, J.-E.; Maquet, V.; Henrist, C.; Compère, P.; Henrotin, Y. Chitosan Enriched Three-Dimensional Matrix Reduces Inflammatory and Catabolic Mediators Production by Human Chondrocytes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprenyeszk, F.; Chausson, M.; Maquet, V.; Dubuc, J.E.; Henrotin, Y. Protective effect of a new biomaterial against the development of experimental osteoarthritis lesions in rabbit: A pilot study evaluating the intra-articular injection of alginate-chitosan beads dispersed in a hydrogel. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, E.; Yaghmour, K.M.; Khan, W.S. The effects of TNF-alpha inhibition on cartilage: A systematic review of preclinical studies. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020, 28, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catrina, A.I.; Lampa, J.; Ernestam, S.; af Klint, E.; Bratt, J.; Klareskog, L.; Ulfgren, A.K. Anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α therapy (etanercept) down-regulates serum matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3 and MMP-1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.-M.; Simmons, K.L.; Gutowska, A.; Jeong, B. Sol−Gel Transition Temperature of PLGA-g-PEG Aqueous Solutions. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T. Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J. Pharm. Sci. 1963, 52, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Sahlin, J.J. A simple equation for the description of solute release. III. Coupling of diffusion and relaxation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nguyen, D.T.; Yang, G.; Anesi, J.; Kelly, J.; Chai, Z.; Ahmady, F.; Charchar, F.; Golledge, J. A Modified MTS Proliferation Assay for Suspended Cells to Avoid the Interference by Hydralazine and β-Mercaptoethanol. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2021, 19, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | CS/PF | CS/PF/BGP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Parameters | ||
| Higuchi | K | 31 ± 1 | 19 ± 2 |
| R2 | 0.9555 | 0.7655 | |
| Korsmeyer-Peppas | K | 35 ± 2 | 23 ± 2 |
| n | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.06 | |
| R2 | 0.9762 | 0.8531 | |
| Peppas-Sahlin | K1 | 44 ± 3 | 33 ± 4 |
| K2 | −7 ± 1 | −7 ± 2 | |
| n | 0.56 ± 0.04 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | |
| R2 | 0.9864 | 0.8902 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Couce, J.; Schomann, T.; Chung, C.K.; Que, I.; Jorquera-Cordero, C.; Fuentes, G.; Almirall, A.; Chan, A.; Cruz, L.J. Thermosensitive Injectable Hydrogels for Intra-Articular Delivery of Etanercept for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Gels 2022, 8, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080488
García-Couce J, Schomann T, Chung CK, Que I, Jorquera-Cordero C, Fuentes G, Almirall A, Chan A, Cruz LJ. Thermosensitive Injectable Hydrogels for Intra-Articular Delivery of Etanercept for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Gels. 2022; 8(8):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080488
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Couce, Jomarien, Timo Schomann, Chih Kit Chung, Ivo Que, Carla Jorquera-Cordero, Gastón Fuentes, Amisel Almirall, Alan Chan, and Luis J. Cruz. 2022. "Thermosensitive Injectable Hydrogels for Intra-Articular Delivery of Etanercept for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis" Gels 8, no. 8: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080488
APA StyleGarcía-Couce, J., Schomann, T., Chung, C. K., Que, I., Jorquera-Cordero, C., Fuentes, G., Almirall, A., Chan, A., & Cruz, L. J. (2022). Thermosensitive Injectable Hydrogels for Intra-Articular Delivery of Etanercept for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Gels, 8(8), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080488









