Quercetin/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex-Loaded Hydrogels for Accelerated Wound Healing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
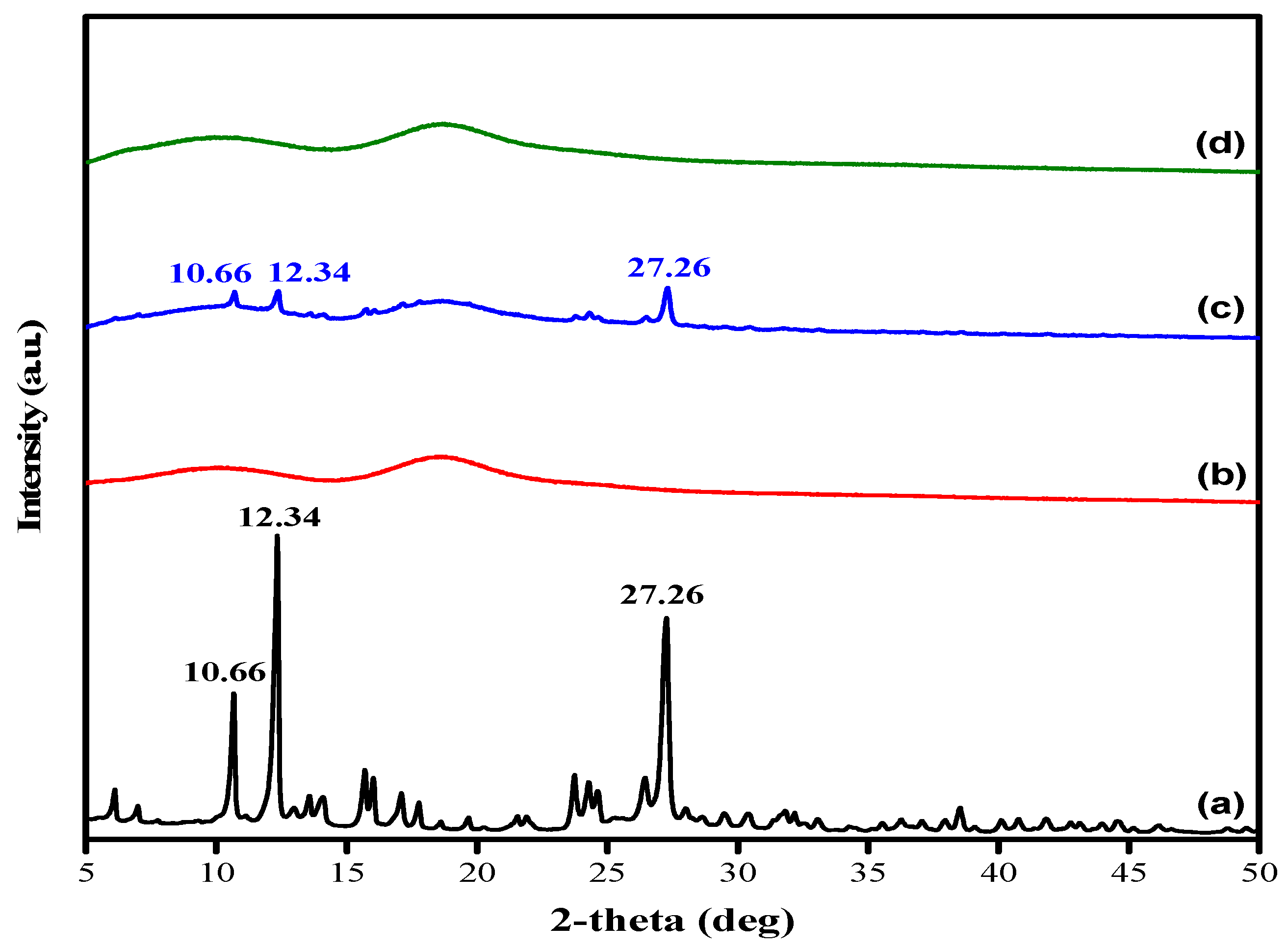
2.1. Characterization of Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex
2.2. Encapsulation Efficiency and Loading Capacity of Quercetin in the Inclusion Complex
2.3. Gelation of PVA Hydrogels Loaded with Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex
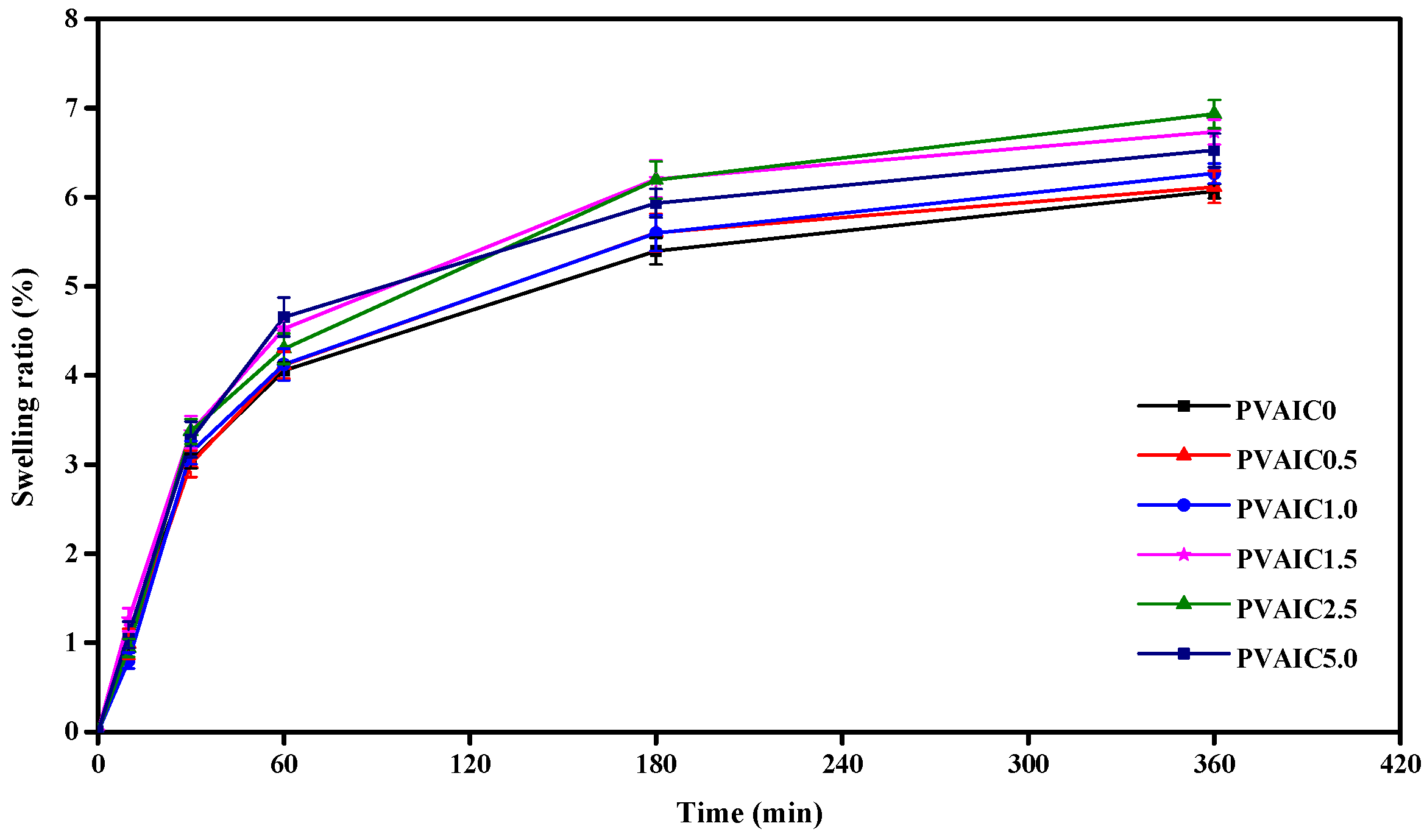
2.4. Swelling Ratio of PVA Hydrogels Loaded with Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex
2.5. Mechanical Test of PVA Hydrogels Loaded with Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex
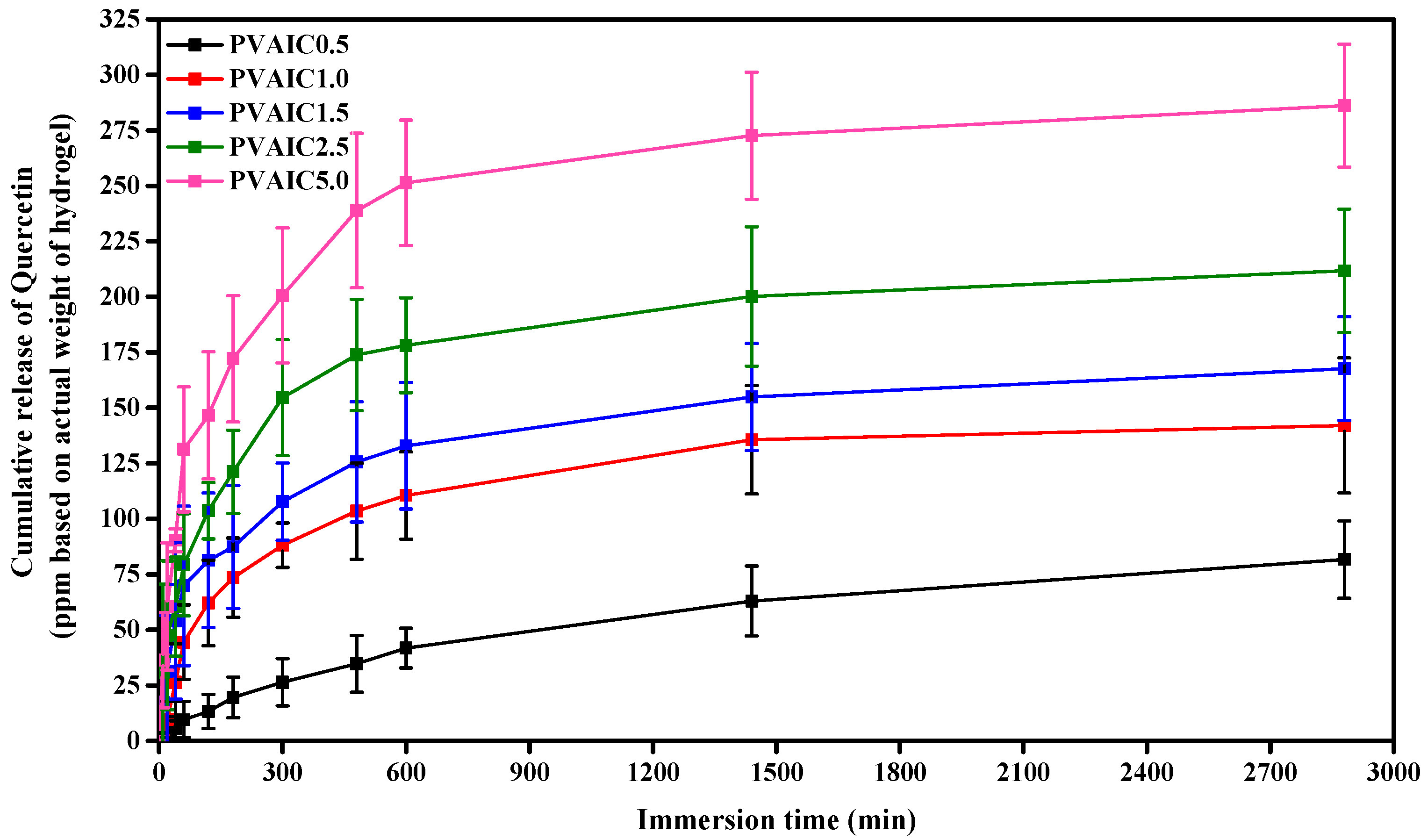
2.6. In Vitro PVA Hydrogels Loaded with Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex Dissolution and Release Kinetics Study
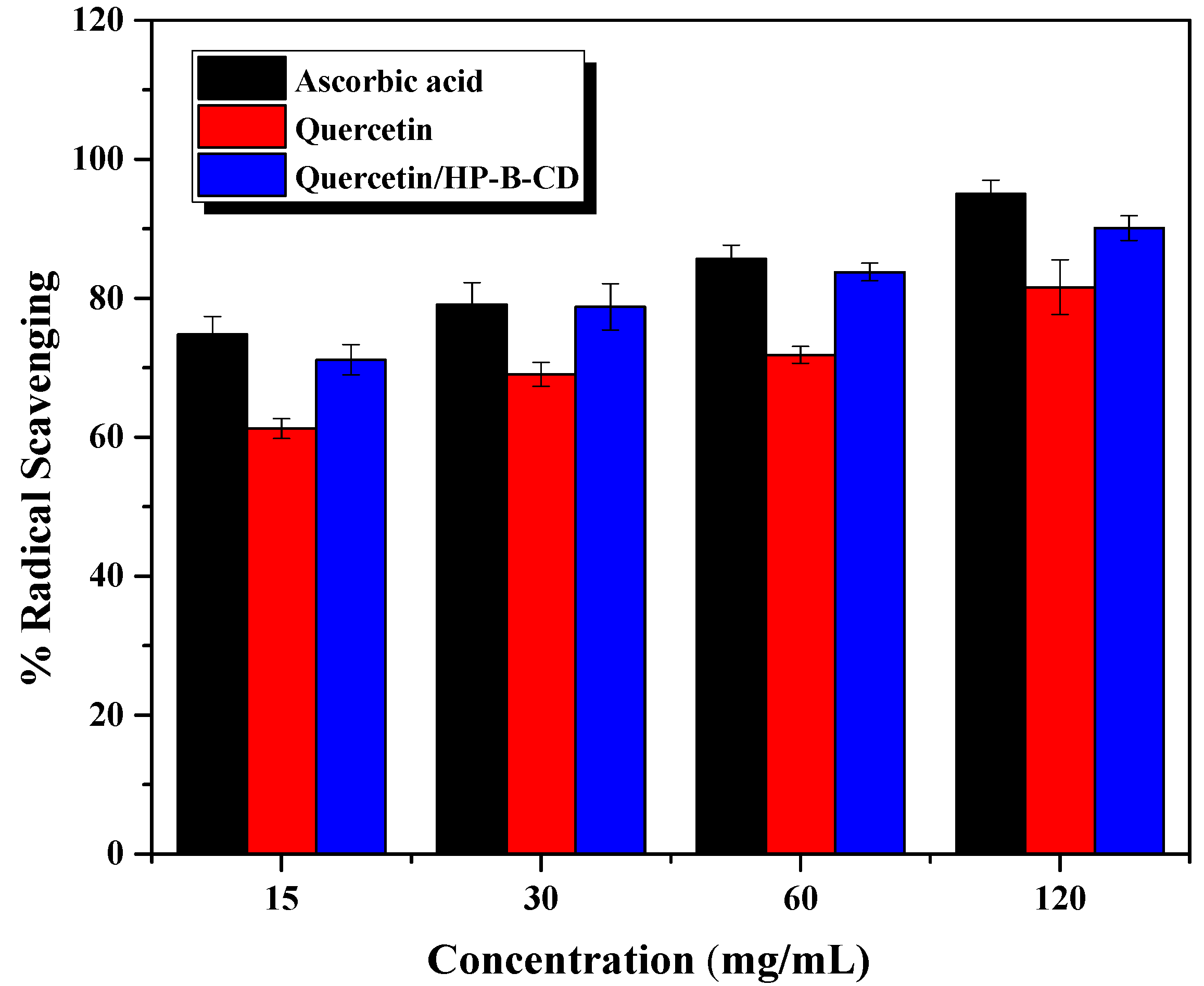
2.7. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity: DPPH-Radical Scavenging Ability Assay
2.8. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Formation of Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex
4.3. Characterization of Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex
4.4. Determination of Encapsulation Efficiency and Loading Capacity of Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex
4.5. Preparation of Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex-Loaded Hydrogels
4.6. Gelation of PVA Hydrogels Loaded with Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex
4.7. Swelling Ratio of PVA Hydrogels Loaded with Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex
4.8. Mechanical Test of PVA Hydrogels Loaded with Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex
4.9. In Vitro PVA Hydrogels Loaded with Quercetin/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex Dissolution and Release Kinetics Study
4.10. In Vitro Antioxidant Characterization
4.11. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDs | Cyclodextrins |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DPPH2 | 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| EE | Encapsulation efficiency |
| FT-IR | Fourier-transform infrared spectrometry |
| GR | Geraniol |
| HP-β-CD | Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin |
| IC | Quercetin/HP-β-CD inclusion complex |
| LC | Loading capacity |
| m | Mass |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| MTT | 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide |
| NCTC 929 | Connective mouse tissue (L cell, L-929, derivative of Strain L) |
| NSCS | N–succinyl chitosan |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PVAc | Polyvinyl acetate |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| TCPS | Tissue-culture polystyrene |
| W | Weight |
| XRD | X-ray powder diffraction |
References
- Cuzzell, J. Choosing a wound dressing. Geriatr. Nurs. 1997, 18, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhivya, S.; Padma, V.V.; Santhini, E. Wound dressings—A review. BioMedicine 2015, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maver, T.; Kurecic, M.; Smrke, D.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Maver, U. Plant-derived medicines with potential use in wound treatment. In Herbal Medicine, 1st ed.; Builders, P., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 121–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedoeva, A.; Leavesley, D.; Upton, Z.; Fan, C. Wound Healing and the Use of Medicinal Plants. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 2684108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, K.; Flora, S.J.S. Oral co-administration of α-lipoic acid, quercetin and captopril prevents gallium arsenide toxicity in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 28, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinonen, I.M.; Meyer, A.S. Antioxidants in fruits, berries and vegetables. In Fruit and Vegetable Processing, 1st ed.; Jongen, W., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, OH, USA, 2002; pp. 23–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathiya, S.; Durga, M.; Devasena, T. Quercetin, encapsulated quercetin and its application—A review. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Razmara, R.S.; Daneshfar, A.; Sahraei, R. Solubility of Quercetin in Water + Methanol and Water + Ethanol from (292.8 to 333.8) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 3934–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Dong, L.; Chen, A.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, B. Inclusion complexes of quercetin with three β-cyclodextrins derivatives at physiological pH: Spectroscopic study and antioxidant activity. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 115, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kumar, S. Chapter 2—Microbial enzyme in food biotechnology. In Enzymes in Food Biotechnology, 1st ed.; Kuddus, M., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Del Valle, E.M.M. Cyclodextrins and their uses: A review. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfoury, M.; Hădărugă, N.G.; Hădărugă, D.I.; Fourmentin, S. 4—Cyclodextrins as encapsulation material for flavors and aroma. In Encapsulations; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 127–192. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Keddie, D.J.; Kannappan, V.; Gibson, H.; Khalil, I.R.; Kowalczuk, M.; Martin, C.; Shuai, X.; Radecka, I. Production and characterisation of bacterial cellulose hydrogels loaded with curcumin encapsulated in cyclodextrins as wound dressings. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 118, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilpour, D.; Hussein, A.A.; Almalki, F.A.; Shityakov, S.; Bordbar, A.K. Probing inclusion complexes of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin with mono-amino mono-carboxylic acids: Physicochemical specification, characterization and molecular modeling. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, X. Alginate hydrogel dressings for advanced wound management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonkaew, B.; Barber, P.M.; Rengpipat, S.; Supaphol, P.; Kempf, M.; He, J.; John, V.T.; Cuttle, L. Development and Characterization of a Novel, Antimicrobial, Sterile Hydrogel Dressing for Burn Wounds: Single–Step Production with Gamma Irradiation Creates Silver Nanoparticles and Radical Polymerization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3244–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, C.; Weller, C.; Team, V. 4—Interactive dressings and their role in moist wound management. In Advanced Textiles for Wound Care, 2nd ed.; Rajendran, S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 105–134. [Google Scholar]
- Tsou, Y.-H.; Khoneisser, J.; Huang, P.-C.; Xu, X. Hydrogel as a bioactive material to regulate stem cell fate. Bioact. Mater. 2016, 1, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa-Pizano, M.D.; Vélaz, I.; Martínez-Barbosa, M.E. A Freeze-Thawing Method to Prepare Chitosan-Poly(vinyl alcohol) Hydrogels without Crosslinking Agents and Diflunisal Release Studies. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 155, e59636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, C.; Peppas, N. Structure and Morphology of Freeze/Thawed PVA Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catauro, M.; Papale, F.; Bollino, F.; Piccolella, S.; Marciano, S.; Nocera, P.; Pacifico, S. Silica/quercetin sol-gel hybrids as antioxidant dental implant materials. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Júnior, W.F.; Bezerra de Menezes, D.L.; de Oliveira, L.C.; Koester, L.S.; Oliveira de Almeida, P.D.; Lima, E.S.; de Azevedo, E.P.; da Veiga Júnior, V.F.; Neves de Lima, Á.A. Inclusion Complexes of β and HPβ-Cyclodextrin with α, β Amyrin and In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Q.; Di, D.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Gao, Y.; Chang, D.; Jiang, T. Chitosan-N-acetylcysteine modified HP-β-CD inclusion complex as a potential ocular delivery system for anti-cataract drug: Quercetin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.A.; Silva, M.A.; Barroca, J.M.; Marques, M.P.M.; Braga, S.S. Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Action and Practical Application in Fresh Cheese of the Solid Inclusion Compound γ-Cyclodextrin•quercetin, in Comparison with β-Cyclodextrin•quercetin. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Ipek, S.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Antioxidant electrospun zein nanofibrous web encapsulating quercetin/cyclodextrin inclusion complex. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Han, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xin, S.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z. Solubility Enhancement of Myricetin by Inclusion Complexation with Heptakis-O-(2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-Cyclodextrin: A Joint Experimental and Theoretical Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, R.; Niu, Y. Encapsulation of l-menthol in hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and release characteristics of the inclusion complex. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2016, 18, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J. Study of flavonoid/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes by UV-Vis, FT-IR, DSC, and X-Ray diffraction analysis. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 25, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, R.; Qi, L.; Zou, Y.; Zou, J.; Luo, Z.; Shao, P.; Tamer, T.M. Preparation and structural properties of amylose complexes with quercetin and their preliminary evaluation in delivery application. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1445–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Pang, Y.; Vara Prasad, C.; Wang, B. Formation of inclusion complex of enrofloxacin with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pralhad, T.; Rajendrakumar, K. Study of freeze-dried quercetin–cyclodextrin binary systems by DSC, FT-IR, X-ray diffraction and SEM analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2004, 34, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, C.P.; Mandal, A.; Dutta, A.; Sarkar, R.; Kundu, A.; Saha, S. Delineating the behavior of Berberis anthocyanin/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex in vitro: A molecular dynamics approach. LWT 2022, 157, 113090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choipang, C.; Buntum, T.; Chuysinuan, P.; Techasakul, S.; Supaphol, P.; Suwantong, O. Gelatin scaffolds loaded with asiaticoside/2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex for use as wound dressings. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qubaisi, M.S.; Rasedee, A.; Flaifel, M.H.; Eid, E.E.M.; Hussein-Al-Ali, S.; Alhassan, F.H.; Salih, A.M.; Hussein, M.Z.; Zainal, Z.; Sani, D.; et al. Characterization of thymoquinone/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex: Application to anti-allergy properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 133, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadian, Z.; Maleki, M.; Abdi, K.; Atyabi, F.; Mohammadi, A.; Khaksar, R. Preparation and Characterization of Nanoparticle β-Cyclodextrin:Geraniol Inclusion Complexes. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Afshar, M.; Dini, G.; Vaezifar, S.; Mehdikhani, M.; Movahedi, B. Preparation and characterization of sodium alginate/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel containing drug-loaded chitosan nanoparticles as a drug delivery system. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-F.; Woodrow, K.A. Relationships between mechanical properties and drug release from electrospun fibers of PCL and PLGA blends. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 65, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, X.; He, G.; Liu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Cai, W.; Fan, L.; Fardim, P. Preparation and properties of polyvinyl alcohol/N–succinyl chitosan/lincomycin composite antibacterial hydrogels for wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, L.; Rimm, E.; Hollman, P.C.; de Vries, J.H.; Katan, M.B. Flavonol and flavone intakes in US health professionals. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2002, 102, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Engqvist, H.; Bredenberg, S. Development and evaluation of a tampering resistant transdermal fentanyl patch. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 488, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanyacharoen, T.; Chuysinuan, P.; Techasakul, S.; Nooeaid, P.; Ummartyotin, S. Development of a gallic acid-loaded chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel composite: Release characteristics and antioxidant activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalini, T.; Basha, S.K.; Sadiq, A.M.; Kumari, V.S. In vitro cytocompatibility assessment and antibacterial effects of quercetin encapsulated alginate/chitosan nanoparticle. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, G.K.; Alonso-Alonso, M.L.; Fernandez-Bueno, I.; Garcia-Gutierrez, M.T.; Rull, F.; Medina, J.; Coco, R.M.; Pastor, J.C. Comparison between direct contact and extract exposure methods for PFO cytotoxicity evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiras, A.; Carvalho, R.A.; Ribeiro, L.; Torres-Labandeira, J.J.; Veiga, F.J.B. Solid-state characterization and dissolution profiles of the inclusion complexes of omeprazole with native and chemically modified β-cyclodextrin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Dias, R.; Ghorpade, V. Freeze dried multicomponent inclusion complexes of quercetin: Physicochemical evaluation and pharmacodynamic study. Marmara Pharm. J. 2019, 23, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Deng, J.; Xiao, Z.; Kou, X.; Zhu, G.; Liu, M.; Liu, S. Preparation and slow release kinetics of apple fragrance/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 143, 3775–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.; Farooq, M.A. Therapeutic potential of green synthesized silver nanoparticles loaded PVA hydrogel patches for wound healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 101308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Garnier, G. Characterisation of hydrogels: Linking the nano to the microscale. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 274, 102044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, M. Shape memory polyacrylamide/gelatin hydrogel with controllable mechanical and drug release properties potential for wound dressing application. Polymer 2021, 226, 123786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuysinuan, P.; Thanyacharoen, T.; Thongchai, K.; Techasakul, S.; Ummartyotin, S. Preparation of chitosan/hydrolyzed collagen/hyaluronic acid based hydrogel composite with caffeic acid addition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1937–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, E. Reaktionsgeschwindigkeit in heterogenen Systemen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1904, 47, 56–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasetti-Escargueil, C.; Grangé, V. Pharmacokinetic profiles of two tablet formulations of piroxicam. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 295, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.N.; Marchetti, J.M. Nimesulide PLA microspheres as a potential sustained release system for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 295, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staedler, D.; Idrizi, E.; Kenzaoui, B.H.; Juillerat-Jeanneret, L. Drug combinations with quercetin: Doxorubicin plus quercetin in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 68, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudłacik-Kramarczyk, S.; Drabczyk, A.; Głąb, M.; Alves-Lima, D.; Lin, H.; Douglas, T.E.L.; Kuciel, S.; Zagórska, A.; Tyliszczak, B. Investigations on the impact of the introduction of the Aloe vera into the hydrogel matrix on cytotoxic and hydrophilic properties of these systems considered as potential wound dressings. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2021, 123, 111977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample | Gelation (%) | Mass Content (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC | PVA | ||
| PVAIC0 | 97.40 ± 0.62 | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| PVAIC0.5 | 94.36 ± 0.80 | 4.67 | 95.24 |
| PVAIC1.0 | 92.29 ± 0.71 | 9.09 | 90.91 |
| PVAIC1.5 | 89.88 ± 0.83 | 13.04 | 86.96 |
| PVAIC2.5 | 85.59 ± 0.95 | 20.00 | 80.00 |
| PVAIC5.0 | 74.52 ± 0.86 | 33.33 | 66.67 |
| Sample | Stiffness (N/m) | Compressive Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| PVAIC0 | 27,318 ± 831 | 1.19 ± 0.07 |
| PVAIC0.5 | 26,199 ± 1275 | 1.12 ± 0.08 |
| PVAIC1.0 | 24,878 ± 758 | 1.09 ± 0.10 |
| PVAIC1.5 | 24,011 ± 941 | 0.99 ± 0.06 |
| PVAIC2.5 | 21,817 ± 1001 | 0.92 ± 0.04 |
| PVAIC5.0 | 19,520 ± 1066 | 0.88 ± 0.04 |
| Sample | Release Kinetic Models | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Order | Korsmeyer–Peppas | |||
| k | r2 | n | r2 | |
| PVAIC0.5 | 0.78 | 0.7953 | 1.31 | 0.995 |
| PVAIC1.0 | 0.67 | 0.9127 | 0.77 | 0.9671 |
| PVAIC1.5 | 1.10 | 0.844 | 0.68 | 0.9526 |
| PVAIC2.5 | 1.49 | 0.7033 | 0.58 | 0.9748 |
| PVAIC5.0 | 2.31 | 0.6468 | 0.77 | 0.9535 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wangsawangrung, N.; Choipang, C.; Chaiarwut, S.; Ekabutr, P.; Suwantong, O.; Chuysinuan, P.; Techasakul, S.; Supaphol, P. Quercetin/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex-Loaded Hydrogels for Accelerated Wound Healing. Gels 2022, 8, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8090573
Wangsawangrung N, Choipang C, Chaiarwut S, Ekabutr P, Suwantong O, Chuysinuan P, Techasakul S, Supaphol P. Quercetin/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex-Loaded Hydrogels for Accelerated Wound Healing. Gels. 2022; 8(9):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8090573
Chicago/Turabian StyleWangsawangrung, Nutsarun, Chasuda Choipang, Sonthaya Chaiarwut, Pongpol Ekabutr, Orawan Suwantong, Piyachat Chuysinuan, Supanna Techasakul, and Pitt Supaphol. 2022. "Quercetin/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex-Loaded Hydrogels for Accelerated Wound Healing" Gels 8, no. 9: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8090573
APA StyleWangsawangrung, N., Choipang, C., Chaiarwut, S., Ekabutr, P., Suwantong, O., Chuysinuan, P., Techasakul, S., & Supaphol, P. (2022). Quercetin/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex-Loaded Hydrogels for Accelerated Wound Healing. Gels, 8(9), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8090573




