Effect of Grape Seed Extract on Gelatin-Based Edible 3D-Hydrogels for Cultured Meat Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Features of GL-PC Porous Hydrogels
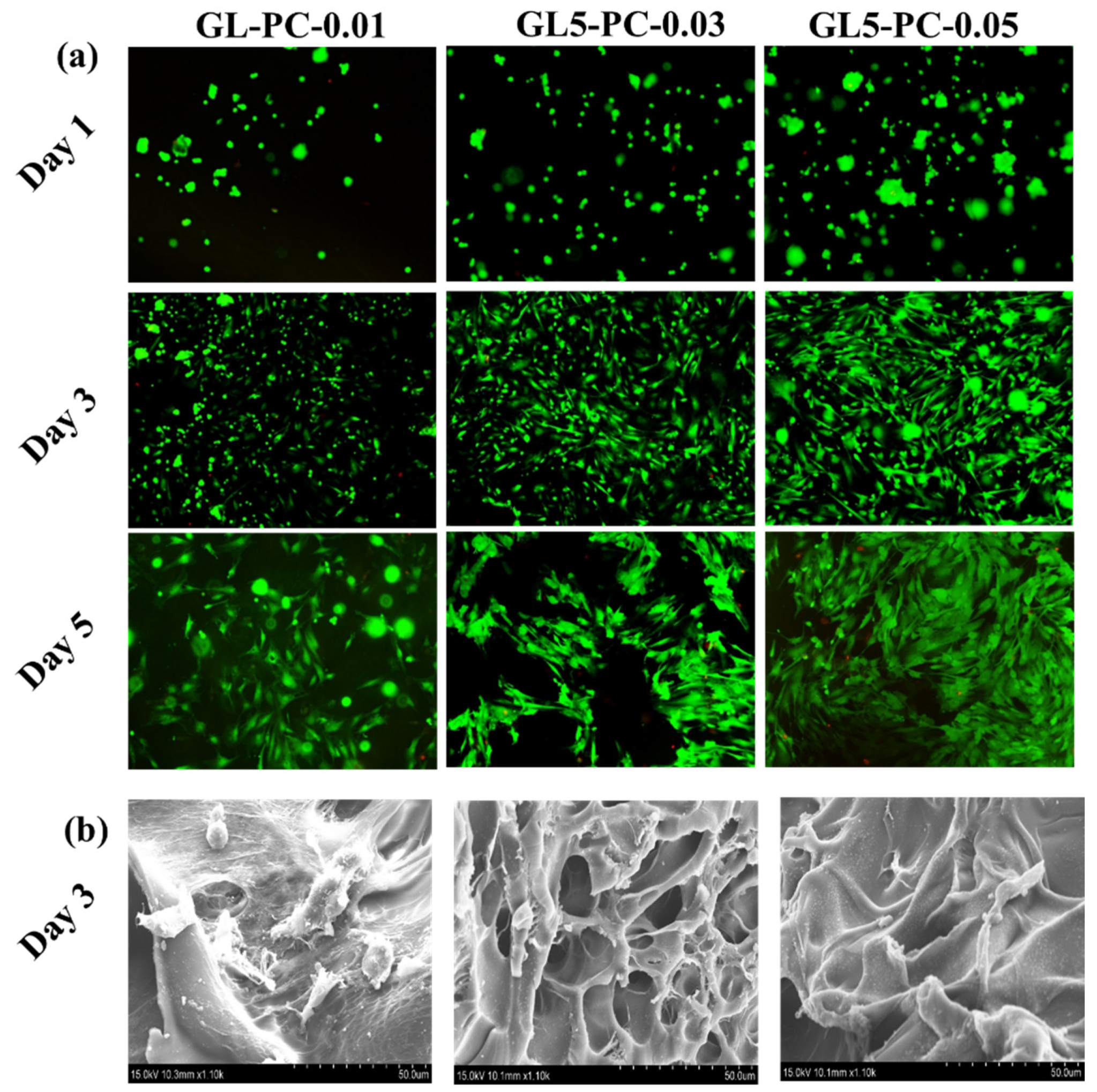
2.2. Biological Function of Porous Hydrogels with BSCs
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Fabrication of GL-PC Porous Hydrogels
4.3. Characterization
4.4. Cell Culture
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hubalek, S.; Post, M.J.; Moutsatsou, P. Towards resource-efficient and cost-efficient cultured meat. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 47, 100885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.K.; Shin, D.M.; Choi, J.; Do, J.T.; Han, S.G. Current issues and technical advances in cultured meat production: A review. Food. Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.; Kurisawa, M. Integrating biomaterials and food biopolymers for cultured meat production. Acta Biomater. 2021, 124, 108–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomkamp, C.; Skaalure, S.C.; Fernando, G.F.; Ben-Arye, T.; Swartz, E.W.; Specht, E.A. Scaffolding biomaterials for 3D cultivated meat: Prospects and challenges. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2102908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celikkin, N.; Rinoldi, C.; Costantini, M.; Trombetta, M.; Rainer, A.; Święszkowski, W. Naturally derived proteins and glycosaminoglycan scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 1277–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yaseen, M.; Zhao, X.; Coffey, P.; Pan, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Webster, J.; Lu, J.R. Gelatin modified ultrathin silk fibroin films for enhanced proliferation of cells. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Forsythe, S.; He, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xiong, G.; Wei, S.; Li, G.; Atala, A.; Skardal, A.; Zhang, Y. Tissue-specific extracellular matrix promotes myogenic differentiation of human muscle progenitor cells on gelatin and heparin conjugated alginate hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.W.; Huang, D.M.; Chang, W.H.; Huang, R.N.; Hsu, J.C. Evaluation of gelatin hydrogel crosslinked with various crosslinking agents as bioadhesives: In vitro study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 46, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, S.; Yen, F.C.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M. Scaffolding technologies for the engineering of cultured meat: Towards a safe, sustainable, and scalable production. Trends. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 126, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, A.H. Grapefruit Seed Extracts’ Antibacterial and Antiviral Activity: Anti-Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Impact. Arch. Pharm. Pract. 2022, 1, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Jaurequi, J.; Tang, B.W.; Nimni, M.E. Proanthocyanidin: A natural crosslinking reagent for stabilizing collagen matrices. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2003, 65, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Wang, J.; Cong, Y.; Fu, J. Recent progress in polymer hydrogel bioadhesives. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 59, 1312–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.J.; Novakofski, J.; Jenkins, W.K.; O’Brien, W.D. Young’s modulus measurements of soft tissues with application to elasticity imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1996, 43, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, A.; Nain, A.S. ECM in differentiation: A review of matrix structure, composition and mechanical properties. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 48, 1071–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suneetha, M.; Rao, K.M.; Han, S.S. Mussel-inspired cell/tissue-adhesive, hemostatic hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12647–12656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Guo, S.; Chang, R.; Zhang, D.; Ren, Y.; Guan, F.; Yao, M. Facile preparation of antibacterial hydrogel with multi-functions based on carboxymethyl chitosan and oligomeric procyanidin. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 20897–20905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, K.M.; Kim, H.J.; Won, S.; Choi, S.M.; Han, S.S. Effect of Grape Seed Extract on Gelatin-Based Edible 3D-Hydrogels for Cultured Meat Application. Gels 2023, 9, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010065
Rao KM, Kim HJ, Won S, Choi SM, Han SS. Effect of Grape Seed Extract on Gelatin-Based Edible 3D-Hydrogels for Cultured Meat Application. Gels. 2023; 9(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010065
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Kummara Madhusudana, Hyeon Jin Kim, Soyeon Won, Soon Mo Choi, and Sung Soo Han. 2023. "Effect of Grape Seed Extract on Gelatin-Based Edible 3D-Hydrogels for Cultured Meat Application" Gels 9, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010065
APA StyleRao, K. M., Kim, H. J., Won, S., Choi, S. M., & Han, S. S. (2023). Effect of Grape Seed Extract on Gelatin-Based Edible 3D-Hydrogels for Cultured Meat Application. Gels, 9(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010065








