Gels 2023, 9(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010011 - 25 Dec 2022
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2107
Abstract
This study reports a novel design of a moisturizing and antimicrobial hydrogel with injectable properties, using a green solvent (glycerol) as a cross-linking agent and gold nanoparticle reduced by Chlorella extract as an antimicrobial approach. We have synthesized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with environmentally
[...] Read more.
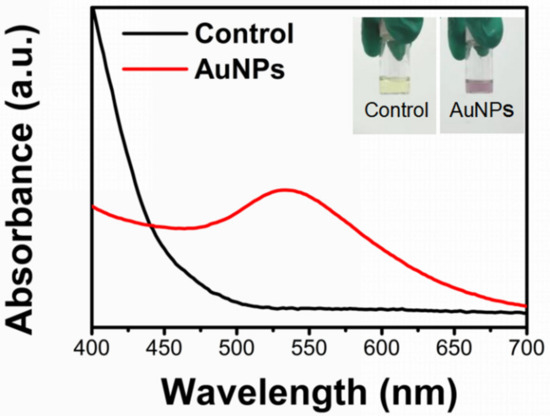
This study reports a novel design of a moisturizing and antimicrobial hydrogel with injectable properties, using a green solvent (glycerol) as a cross-linking agent and gold nanoparticle reduced by Chlorella extract as an antimicrobial approach. We have synthesized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with environmentally friendly and bio-safe properties using Chlorella aqueous extracts (AuNPs@Chlorella). Characterization of the nanoparticles by ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectrum, and transmission electron microscope (TEM) confirmed that spherical AuNPs with the particle size of 10–20 nm were successfully synthesized. An analysis of the enhancement of the stability of gelatin hydrogels by the addition of glycerol and AuNPs was performed by rheometry. In addition, we also used Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Escherichia coli (E. coli) to confirm the good antibacterial activity. Therefore, the as-prepared gelatin–glycerol hydrogels containing AuNPs@Chlorella are most likely promising alternatives for wound healing dressings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Gels in Medicine and Pharmacological Therapies)
►
Show Figures