Construction of Engineered Muscle Tissue Consisting of Myotube Bundles in a Collagen Gel Matrix
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
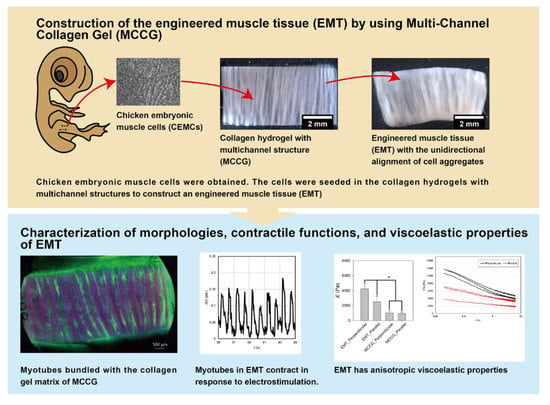
2.1. Construction Method of the EMT Using MCCG
2.2. Hierarchical Structures of the EMT
2.3. Contractile Functions of Myotubes in the EMT
2.4. Stress–Strain Curves of EMT
2.5. Stress Relaxation Behaviors of EMT
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qazi, T.H.; Mooney, D.J.; Pumberger, M.; Geissler, S.; Duda, G.N. Biomaterials based strategies for skeletal muscle tissue engineering: Existing technologies and future trends. Biomaterials 2015, 53, 502–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Ito, A.; Kato, M.; Kawabe, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Fujita, H.; Nagamori, E.; Kamihira, M. Preparation of artificial skeletal muscle tissues by a magnetic force-based tissue engineering technique. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2009, 108, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levenberg, S.; Rouwkema, J.; Macdonald, M.; Garfein, E.S.; Kohane, D.S.; Darland, D.C.; Marini, R.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Mulligan, R.C.; D'Amore, P.A.; et al. Engineering vascularized skeletal muscle tissue. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzener, L.; Verzijden, K.E.; Buijs, A.J.; Post, M.J.; Flack, J.E. Cultured beef: From small biopsy to substantial quantity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.H.; Louis, F.; Liu, H.; Shimoda, H.; Nishiyama, Y.; Nozawa, H.; Kakitani, M.; Takagi, D.; Kasa, D.; Nagamori, E.; et al. Engineered whole cut meat-like tissue by the assembly of cell fibers using tendon-gel integrated bioprinting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M.; Morimoto, Y.; Shima, A.; Nakamura, F.; Ishikawa, H.; Takeuchi, S. Formation of contractile 3D bovine muscle tissue for construction of millimetre-thick cultured steak. NPJ Sci. Food 2021, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Cvetkovic, C.; Uzel, S.G.; Platt, R.J.; Sengupta, P.; Kamm, R.D.; Bashir, R. Optogenetic skeletal muscle-powered adaptive biological machines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2016, 113, 3497–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, A.W. Biological Soft Robotics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 17, 243–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Onoe, H.; Takeuchi, S. Biohybrid robot powered by an antagonistic pair of skeletal muscle tissues. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaat4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Shimizu, T.; Nakayama, M.; Yamato, M.; Okano, T. The use of anisotropic cell sheets to control orientation during the self-organization of 3D muscle tissue. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7372–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Nakamoto, T.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Engineering multi-layered skeletal muscle tissue by using 3D microgrooved collagen scaffolds. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, K.; Sato, S.; Masumoto, J.; Hanazaki, Y.; Maki, Y.; Dobashi, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Fukui, A.; Sasaki, N. Studies on the formation mechanism and the structure of the anisotropic collagen gel prepared by dialysis-induced anisotropic gelation. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemoto, J.; Maki, Y.; Koh, I.; Furusawa, K.; Annaka, M. Formation of Multi-Channel Collagen Gels Investigated Using Particle Tracking Microrheology. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 3819–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, A.R.; Lieber, R.L. Structure and function of the skeletal muscle extracellular matrix. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, Y.; Wagatsuma, A.; Hoshino, T.; Mabuchi, K. Simple micropatterning method for enhancing fusion efficiency and responsiveness to electrical stimulation of C2C12 myotubes. Biotechnol. Prog. 2015, 31, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, K.; Kawashima, T.; Sekine, S.; Ido, Y.; Kanzaki, M.; Nishizawa, M. Spatiotemporally controlled contraction of micropatterned skeletal muscle cells on a hydrogel sheet. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Black, B.L.; Derynck, R. TGF-beta inhibits muscle differentiation through functional repression of myogenic transcription factors by Smad3. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2950–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, S.; Alzhanov, D.; Knollman, P.; Kuninger, D.; Rotwein, P. TGF-beta inhibits muscle differentiation by blocking autocrine signaling pathways initiated by IGF-II. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaffe, D.; Saxel, O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature 1977, 270, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.; Braun, T.; Buchberger, A.; Jurs, S.; Winter, B.; Arnold, H.H. Transcription of the muscle regulatory gene Myf4 is regulated by serum components, peptide growth factors and signaling pathways involving G proteins. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 115, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iyo, T.; Maki, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Nakata, M. Anisotropic viscoelastic properties of cortical bone. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, P.; Coles, D.; Peckham, M. Preferential adhesion to and survival on patterned laminin organizes myogenesis in vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 230, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocalan, M.; Goodman, S.L.; Kuhl, U.; Hauschka, S.D.; von der Mark, K. Laminin alters cell shape and stimulates motility and proliferation of murine skeletal myoblasts. Dev. Biol. 1988, 125, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, K.; Narazaki, Y.; Tomita, N.; Dobashi, T.; Sasaki, N.; Yamamoto, T. Effect of pH on anisotropic gelation of DNA induced by aluminum cations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 13923–13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.J.; Larsen, J.; Krasieva, T.B.; Lyubovitsky, J.G. Effect of genipin crosslinking on the optical spectral properties and structures of collagen hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2579–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furusawa, K.; Kawahana, Y.; Miyashita, R. Construction of Engineered Muscle Tissue Consisting of Myotube Bundles in a Collagen Gel Matrix. Gels 2023, 9, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9020141
Furusawa K, Kawahana Y, Miyashita R. Construction of Engineered Muscle Tissue Consisting of Myotube Bundles in a Collagen Gel Matrix. Gels. 2023; 9(2):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9020141
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurusawa, Kazuya, Yuuki Kawahana, and Ryoya Miyashita. 2023. "Construction of Engineered Muscle Tissue Consisting of Myotube Bundles in a Collagen Gel Matrix" Gels 9, no. 2: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9020141
APA StyleFurusawa, K., Kawahana, Y., & Miyashita, R. (2023). Construction of Engineered Muscle Tissue Consisting of Myotube Bundles in a Collagen Gel Matrix. Gels, 9(2), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9020141