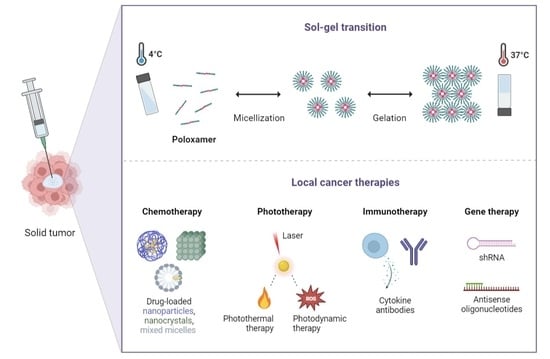
Injectable Poloxamer Hydrogels for Local Cancer Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
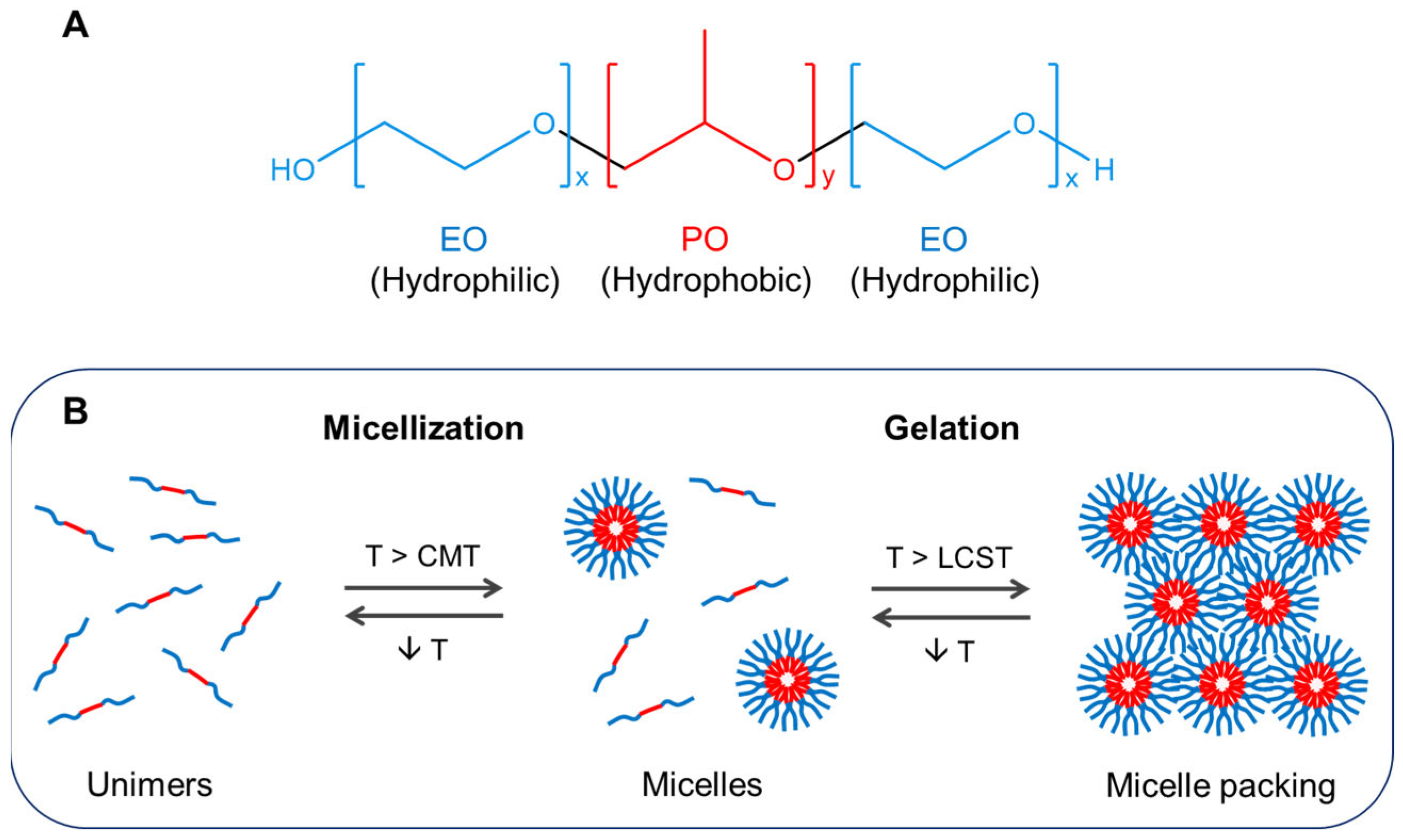
2. Poloxamer-Based Thermoresponsive Hydrogels
3. Characterization of Injectable Poloxamer Hydrogels
3.1. Gelation Temperature
3.2. Rheological Behavior, Mechanical Strength, and Injectability
3.3. Biocompatibility and Sterilization
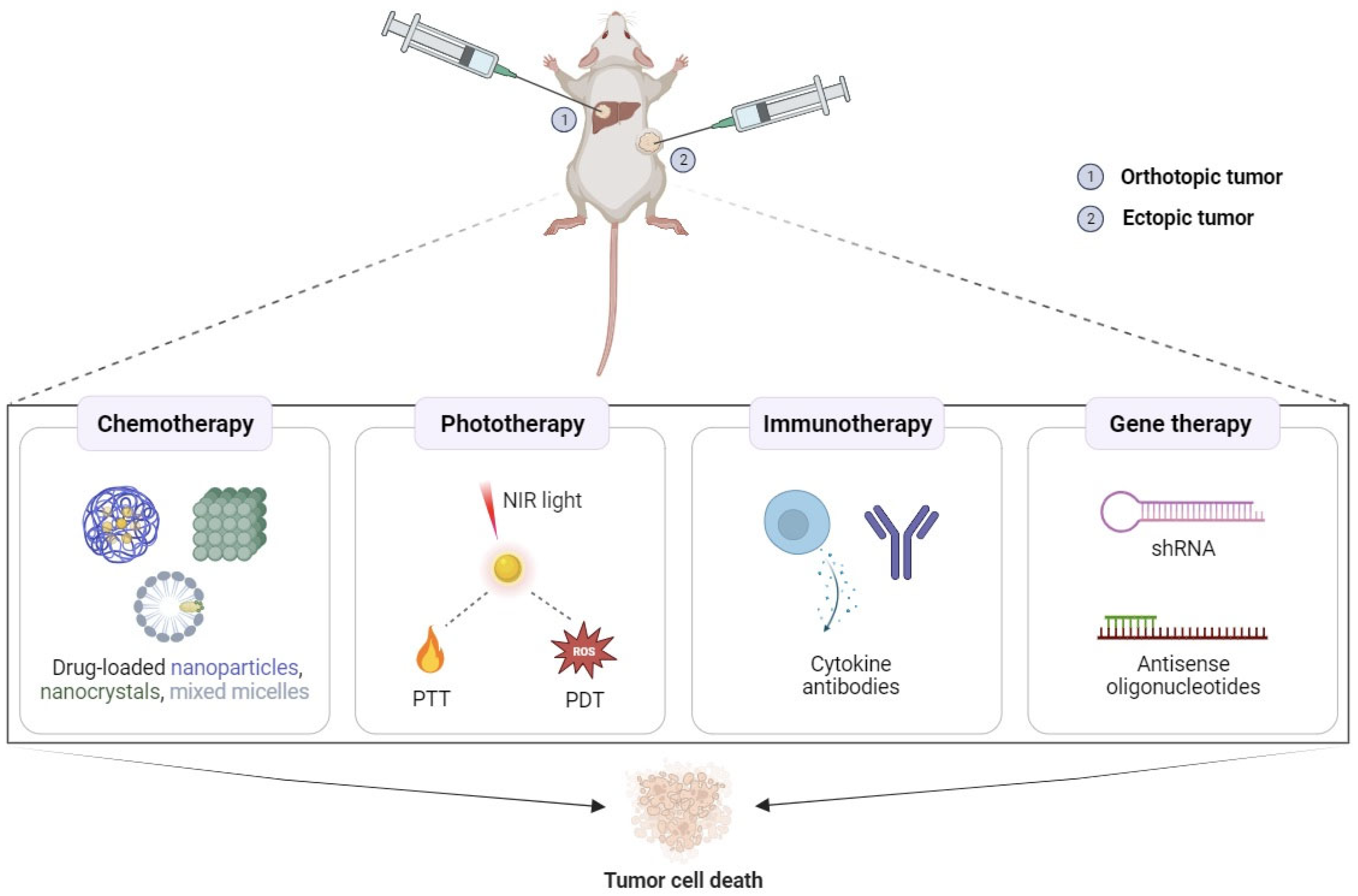
4. Local Tumor Administration of Poloxamer Hydrogels
4.1. Potential Applications in Cancer Chemotherapy
4.2. Potential Applications in Cancer Phototherapy
4.3. Potential Applications in Cancer Immunotherapy
4.4. Potential Applications in Cancer Gene Therapy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fakhari, A.; Subramony, J.A. Engineered in-situ depot-forming hydrogels for intratumoral drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 220, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.C.; Costa, P.J.; Velho, S.; Amaral, M.H. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels for intratumoral drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2397–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burris, H.A., 3rd; Vogel, C.L.; Castro, D.; Mishra, L.; Schwarz, M.; Spencer, S.; Oakes, D.D.; Korey, A.; Orenberg, E.K. Intratumoral cisplatin/epinephrine-injectable gel as a palliative treatment for accessible solid tumors: A multicenter pilot study. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1998, 118, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brachi, G.; Ruiz-Ramírez, J.; Dogra, P.; Wang, Z.; Cristini, V.; Ciardelli, G.; Rostomily, R.C.; Ferrari, M.; Mikheev, A.M.; Blanco, E.; et al. Intratumoral injection of hydrogel-embedded nanoparticles enhances retention in glioblastoma. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 23838–23850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Wang, L.L.; Chung, J.J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Atluri, P.; Burdick, J.A. Methods To Assess Shear-Thinning Hydrogels for Application As Injectable Biomaterials. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 3146–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thambi, T.; Li, Y.; Lee, D.S. Injectable hydrogels for sustained release of therapeutic agents. J. Control. Release 2017, 267, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.D.; Nath, L.K.; Chakraborty, P. Recent Progress in Smart Polymers: Behavior, Mechanistic Understanding and Application. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 57, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Weber, C.; Schubert, U.S.; Hoogenboom, R. Thermoresponsive polymers with lower critical solution temperature: From fundamental aspects and measuring techniques to recommended turbidimetry conditions. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Song, S.; Zheng, A. Thermosensitive Hydrogels and Advances in Their Application in Disease Therapy. Polymers 2022, 14, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragta, P.; Sidhu, R.K.; Jyoti, K.; Baldi, A.; Jain, U.K.; Chandra, R.; Madan, J. Intratumoral administration of carboplatin bearing poly (ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles amalgamated with in situ gel tendered augmented drug delivery, cytotoxicity, and apoptosis in melanoma tumor. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 166, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesoa, J.I.; Rico, M.J.; Rozados, V.R.; Scharovsky, O.G.; Luna, J.A.; Mengatto, L.N. Paclitaxel delivery system based on poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microparticles and chitosan thermo-sensitive gel for mammary adenocarcinoma treatment. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 70, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, Y.T.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, J.-P. Intratumoral Delivery of Doxorubicin on Folate-Conjugated Graphene Oxide by In-Situ Forming Thermo-Sensitive Hydrogel for Breast Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; He, X.; Shi, K.; Yuan, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ming, Y.; Yi, C.; Qian, Z. Injectable Thermosensitive Hydrogel Containing Erlotinib-Loaded Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Localized Drug Delivery System for NSCLC Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Davoodi, J.; Dehghan, R.; Zahiri, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Thermosensitive composite hydrogel incorporated with curcumin-loaded nanopolymersomes for prolonged and localized treatment of glioma. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Villa, C. Poloxamer Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giuliano, E.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Mucosal Applications of Poloxamer 407-Based Hydrogels: An Overview. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soliman, K.A.; Ullah, K.; Shah, A.; Jones, D.S.; Singh, T.R. Poloxamer-based in situ gelling thermoresponsive systems for ocular drug delivery applications. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodratti, A.M.; Alexandridis, P. Formulation of Poloxamers for Drug Delivery. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenzuela-Oses, J.K.; García, M.C.; Feitosa, V.A.; Pachioni-Vasconcelos, J.A.; Gomes-Filho, S.M.; Lourenço, F.R.; Cerize, N.N.; Bassères, D.S.; Rangel-Yagui, C.O. Development and characterization of miltefosine-loaded polymeric micelles for cancer treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 81, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, F.U.; Sharma, R.; Shaikh, S.; Ray, D.; Aswal, V.K.; Pathak, C. Pluronic micelles encapsulated curcumin manifests apoptotic cell death and inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines in human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Rep. 2018, 2, e1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotta, S.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Nair, A.B.; Kaleem, M.; Dalhat, M.H. Thermosensitive Hydrogels Loaded with Resveratrol Nanoemulsion: Formulation Optimization by Central Composite Design and Evaluation in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Gels 2022, 8, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Xu, J.; Zheng, X.; Hui, J. Preparation of Injectable Composite Hydrogels by Blending Poloxamers with Calcium Carbonate-Crosslinked Sodium Alginate. Chemistryopen 2020, 9, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Naghib, S.M.; Garshasbi, H.R.; Ghorbanzadeh, S.; Zhang, W. Smart stimuli-responsive injectable gels and hydrogels for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications: A review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1104126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Shi, X.; Lin, X.; Yao, C.; Shen, L.; Feng, Y. Poloxamer-based in situ hydrogels for controlled delivery of hydrophilic macromolecules after intramuscular injection in rats. Drug Deliv. 2014, 22, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beard, M.C.; Cobb, L.H.; Grant, C.S.; Varadarajan, A.; Henry, T.; Swanson, E.A.; Kundu, S.; Priddy, L.B. Autoclaving of Poloxamer 407 hydrogel and its use as a drug delivery vehicle. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B: Appl. Biomater. 2020, 109, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhari, A.; Corcoran, M.; Schwarz, A. Thermogelling properties of purified poloxamer 407. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wei, G.; Lu, W. Amino-functionalized poloxamer 407 with both mucoadhesive and thermosensitive properties: Preparation, characterization and application in a vaginal drug delivery system. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Ma, K.; He, B.; Dai, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. Novel thermo-sensitive hydrogel system with paclitaxel nanocrystals: High drug-loading, sustained drug release and extended local retention guaranteeing better efficacy and lower toxicity. J. Control. Release 2014, 174, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, S.; Fu, S.; Yang, X.; Li, B. Intratumoral Administration of Thermosensitive Hydrogel Co-Loaded with Norcantharidin Nanoparticles and Doxorubicin for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 4073–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Mou, Y.; Hu, M.; Dong, W.; Su, X.; Wu, R.; Zhang, P. Evaluation of micelles incorporated into thermosensitive hydrogels for intratumoral delivery and controlled release of docetaxel: A dual approach for in situ treatment of tumors. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, D.S.; Shaker, M.A.; Klingner, A.; Hanafy, M.S. In situ thermosensitive Tamoxifen citrate loaded hydrogels: An effective tool in breast cancer loco-regional therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 35, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiji, M.M.; Lai, P.-K.; Shenoy, D.B.; Rao, M. Intratumoral Administration of Paclitaxel in an In Situ Gelling Poloxamer 407 Formulation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2002, 7, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sguizzato, M.; Valacchi, G.; Pecorelli, A.; Boldrini, P.; Simelière, F.; Huang, N.; Cortesi, R.; Esposito, E. Gallic acid loaded poloxamer gel as new adjuvant strategy for melanoma: A preliminary study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shastri, D.H.; Prajapati, S.T.; Patel, L.D. Design and Development of Thermoreversible Ophthalmic In Situ Hydrogel of Moxifloxacin HCl. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Meng, M.; Cui, N.; Dai, C.-Y.; Jia, Q.; Lee, E.-S.; Jiang, H.-B. An Overview on Thermosensitive Oral Gel Based on Poloxamer 407. Materials 2021, 14, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.-S.; Park, W.; Park, H.; Lee, D.-K.; Na, K. Thermo-sensitive injectable hydrogel based on the physical mixing of hyaluronic acid and Pluronic F-127 for sustained NSAID delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. Understanding the burst release phenomenon: Toward designing effective nanoparticulate drug-delivery systems. Ther. Deliv. 2021, 12, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswani, G.; Chablani, L.; Gupta, U.; Sahoo, R.K.; Nakhate, K.T.; Taksande, A.G. Ajazuddin Exploration of hemocompatibility and intratumoral accumulation of paclitaxel after loco-regional administration of thermoresponsive hydrogel composed of poloxamer and xanthan gum: An application to dose-dense chemotherapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Wu, H.-C.; Sun, J.-S.; Dong, G.-C.; Wang, T.-W. Injectable and Thermoresponsive Self-Assembled Nanocomposite Hydrogel for Long-Term Anticancer Drug Delivery. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3721–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turabee, H.; Jeong, T.H.; Ramalingam, P.; Kang, J.H.; Ko, Y.T. N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan embedded in situ Pluronic F127 hydrogel for the treatment of brain tumor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 203, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sabbagh, C.; Seguin, J.; Agapova, E.; Kramerich, D.; Boudy, V.; Mignet, N. Thermosensitive hydrogels for local delivery of 5-fluorouracil as neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy in colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 157, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, C.; Sun, J.; Zi, P.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C. Thermosensitive Micelles–Hydrogel Hybrid System Based on Poloxamer 407 for Localized Delivery of Paclitaxel. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 2707–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, H.; Duffy, G.; Rossi, S.; Hastings, C. A Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel for Intratumoral Administration as a Treatment in Solid Tumor Cancers. WO2019092049A1, 7 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Phogat, K.; Ghosh, S.B.; Bandyopadhyay-Ghosh, S. Recent advances on injectable nanocomposite hydrogels towards bone tissue rehabilitation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 140, e53362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, G.; Yadav, K.S. High encapsulation efficiency of poloxamer-based injectable thermoresponsive hydrogels of etoposide. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 19, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.M.; Murray, T.E.; Cassidy, J.; Lee, M.J.; Kelly, H.M. A Custom Radiopaque Thermoresponsive Chemotherapy-Loaded Hydrogel for Intratumoural Injection: An In Vitro and Ex Vivo Assessment of Imaging Characteristics and Material Properties. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 42, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, M.; Firouzi, J.; Sodeifi, N.; Ebrahimi, M.; Miller, D.W. Salinomycin-loaded injectable thermosensitive hydrogels for glioblastoma therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 598, 120316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.K.; Fransen, M.F.; van der Maaden, K.; Campos, Y.; García-Couce, J.; Kralisch, D.; Chan, A.; Ossendorp, F.; Cruz, L.J. Thermosensitive hydrogels as sustained drug delivery system for CTLA-4 checkpoint blocking antibodies. J. Control. Release 2020, 323, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, S. Thermosensitive Hydrogel System With Paclitaxel Liposomes Used in Localized Drug Delivery System for In Situ Treatment of Tumor: Better Antitumor Efficacy and Lower Toxicity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galante, R.; Pinto, T.D.J.A.; Colaco, R.; Serro, A.P. Sterilization of hydrogels for biomedical applications: A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 106, 2472–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.; Marques, A.C.; Costa, P.C.; Amaral, M.H. Effects of Steam Sterilization on the Properties of Stimuli-Responsive Polymer-Based Hydrogels. Gels 2023, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burak, J.; Grela, K.P.; Pluta, J.; Karolewicz, B.; Marciniak, D.M. Impact of sterilisation conditions on the rheological properties of thermoresponsive pluronic F-127-based gels for the ophthalmic use. Acta Pol. Pharm.—Drug Res. 2018, 75, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Liu, L.; Morin, E.E.; Liu, M.; Schwendeman, A. Survey of Clinical Translation of Cancer Nanomedicines—Lessons Learned from Successes and Failures. Accounts Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2445–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L. A temperature-sensitive phase-change hydrogel of topotecan achieves a long-term sustained antitumor effect on retinoblastoma cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 6069–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, C.K.; García-Couce, J.; Campos, Y.; Kralisch, D.; Bierau, K.; Chan, A.; Ossendorp, F.; Cruz, L.J. Doxorubicin Loaded Poloxamer Thermosensitive Hydrogels: Chemical, Pharmacological and Biological Evaluation. Molecules 2020, 25, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Nie, S.; Hsiao, W.W.; Pam, W. Thermoreversible Pluronic® F127-based hydrogel containing liposomes for the controlled delivery of paclitaxel: In vitro drug release, cell cytotoxicity, and uptake studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, C.; Tang, Z.; Tang, X.; Xu, H. Intratumoral injection of gels containing losartan microspheres and (PLG-g-mPEG)-cisplatin nanoparticles improves drug penetration, retention and anti-tumor activity. Cancer Lett. 2018, 442, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Hao, D.; Wei, P.; Zhou, L.; Liu, G. Evaluation of TPGS-modified thermo-sensitive Pluronic PF127 hydrogel as a potential carrier to reverse the resistance of P-gp-overexpressing SMMC-7721 cell lines. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 140, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lin, Z.; He, B.; Dai, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. A novel localized co-delivery system with lapatinib microparticles and paclitaxel nanoparticles in a peritumorally injectable in situ hydrogel. J. Control. Release 2015, 220, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Rodríguez, P.; Landin, M. Smart design of intratumoral thermosensitive β-lapachone hydrogels by Artificial Neural Networks. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 433, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, S.; Díaz-Rodríguez, P.; Sendon-Lago, J.; Gallego, R.; Perez-Fernandez, R.; Landin, M. Administration of the optimized β-Lapachone–poloxamer–cyclodextrin ternary system induces apoptosis, DNA damage and reduces tumor growth in a human breast adenocarcinoma xenograft mouse model. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhan, H.-J.; Liu, J.-J.; Chen, Y.-C.; Liu, D.-Z.; Sheu, M.-T.; Ho, H.-O. Novel injectable thermosensitive hydrogels for delivering hyaluronic acid–doxorubicin nanocomplexes to locally treat tumors. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, M.-T.; Jhan, H.-J.; Su, C.-Y.; Chen, L.-C.; Chang, C.-E.; Liu, D.-Z.; Ho, H.-O. Codelivery of doxorubicin-containing thermosensitive hydrogels incorporated with docetaxel-loaded mixed micelles enhances local cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Q. A novel mixed micelle gel with thermo-sensitive property for the local delivery of docetaxel. J. Control. Release 2009, 135, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, K.; Bao, X.; Chu, Q.; He, Y.; Tian, Y. Preparation and characterization of curcumin thermosensitive hydrogels for intratumoral injection treatment. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 40, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Deng, X.; Wu, Q.; Cao, X.; Ye, T.; Wang, S. Liposome-loaded thermo-sensitive hydrogel for stabilization of SN-38 via intratumoral injection: Optimization, characterization, and antitumor activity. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 23, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, J.; Miranda, A.; Nunes, S.; Cova, T.; Sousa, J.; Vitorino, C.; Pais, A. Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery Nanosystems for the Treatment of Brain Tumors. Gels 2018, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, M.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Sun, Y.; Han, B.-S.; Duan, Y.-R. Preparation of a Thermosensitive Gel Composed of a mPEG-PLGA-PLL-cRGD Nanodrug Delivery System for Pancreatic Tumor Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20530–20537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.-H.; Ge, M.; Peng, J.-B.; Jiang, X.-R.; Wang, D.-S.; Ji, L.-Q.; Ying, Y.; Wang, Z. In-vivo anti-tumor activity of a novel poloxamer-based thermosensitive in situ gel for sustained delivery of norcantharidin. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 24, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Filho, M.S.S.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Martínez-Pacheco, R.; Landin, M. Temperature-Sensitive Gels for Intratumoral Delivery of β-Lapachone: Effect of Cyclodextrins and Ethanol. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 126723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jhan, H.J.; Ho, H.O.; Sheu, M.T.; Shen, S.C.; Ho, Y.S.; Liu, J.J. Thermosensitive Injectable Hydrogel for Drug Delivery. U.S. Patent 9,364,545, 14 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Emami, J.; Rezazadeh, M.; Akbari, V.; Amuaghae, E. Preparation and characterization of an injectable thermosensitive hydrogel for simultaneous delivery of paclitaxel and doxorubicin. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Pan, H.; Qiao, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Pan, W. The utilization of low molecular weight heparin-poloxamer associated Laponite nanoplatform for safe and efficient tumor therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, N. Thermosensitive Hydrogel Co-loaded with Gold Nanoparticles and Doxorubicin for Effective Chemoradiotherapy. AAPS J. 2015, 18, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Shen, J.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Polymer-based hydrogels with local drug release for cancer immunotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overchuk, M.; Weersink, R.A.; Wilson, B.C.; Zheng, G. Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapies: Synergy Opportunities for Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 7979–8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.-J.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Li, S.-P.; Zhang, L.-M.; Lin, Z.-X.; Liang, L.; Qin, A.-P.; Yu, X.-Y. CuS Nanodot-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Anticancer Photothermal Therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4621–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wu, B.; Wei, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Du, L. Prussian blue nanosphere-embedded in situ hydrogel for photothermal therapy by peritumoral administration. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 9, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tao, J.; Zhang, M.; Lu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Song, P.; Wang, T.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, X. Iota carrageenan gold-silver NPs photothermal hydrogel for tumor postsurgical anti-recurrence and wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 298, 120123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhu, C.; Peng, T.; Ma, Q.; Gao, S. Injectable and Temperature-Sensitive Titanium Carbide-Loaded Hydrogel System for Photothermal Therapy of Breast Cancer. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 791891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Qu, D.; Xue, L.; Mo, R.; Zhang, C. Nanocomposite hydrogel incorporating gold nanorods and paclitaxel-loaded chitosan micelles for combination photothermal–chemotherapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 497, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Ling, G.; Peng, F.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, S.; He, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, P. Black phosphorus nanosheets and gemcitabine encapsulated thermo-sensitive hydrogel for synergistic photothermal-chemotherapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ma, Z.; Sun, C.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Yan, Q.; Liu, C.; Hou, B.; Zhang, C. An injectable thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with a theranostic nanoprobe for synergistic chemo–photothermal therapy for multidrug-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2828–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, J.H.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Pimenta, S.; Dong, T.; Yang, Z. Photodynamic Therapy Review: Principles, Photosensitizers, Applications, and Future Directions. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Y.; He, Z.; Tian, X.; Battaglia, G. Thermosensitive nanocomposite gel for intra-tumoral two-photon photodynamic therapy. J. Control. Release 2019, 298, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Shan, L.; Yao, Y.; Peng, F.; Jiang, S.; Yang, D.; Ling, G.; Zhang, P. Black phosphorus nanosheets and docetaxel micelles co-incorporated thermoreversible hydrogel for combination chemo-photodynamic therapy. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, K.; Roudaia, L.; Buhlaiga, N.; Del Rincon, S.V.; Papneja, N.; Miller, W.H., Jr. A Review of Cancer Immunotherapy: From the Past, to the Present, to the Future. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 27 (Suppl. S2), S87–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.S.; June, C.H.; Langer, R.; Mitchell, M.J. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhari, A.; Nugent, S.; Elvecrog, J.; Vasilakos, J.; Corcoran, M.; Tilahun, A.; Siebenaler, K.; Sun, J.; Subramony, J.A.; Schwarz, A. Thermosensitive Gel–Based Formulation for Intratumoral Delivery of Toll-Like Receptor 7/8 Dual Agonist, MEDI9197. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-C.; Chou, H.-Y.; Chuang, S.-H.; Lai, J.-Y.; Chen, Y.-S.; Wen, Y.-H.; Yu, L.-Y.; Lo, C.-L. Preparation of Immunotherapy Liposomal-Loaded Thermal-Responsive Hydrogel Carrier in the Local Treatment of Breast Cancer. Polymers 2019, 11, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.-S.; Choi, D.-S.; Ko, M.; Kim, D.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, S.; Lee, A.Y.; Kang, S.G.; Kim, S.H.; Jung, Y.; et al. Extracellular pH modulating injectable gel for enhancing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. J. Control. Release 2019, 315, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Archer, P.A.; Manspeaker, M.P.; Avecilla, A.R.; Pollack, B.P.; Thomas, S.N. Sustained release hydrogel for durable locoregional chemoimmunotherapy for BRAF-mutated melanoma. J. Control. Release 2023, 357, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, A.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, M.; Ou, W.-B.; Qi, N.; Wu, Y. Insights Into Dendritic Cells in Cancer Immunotherapy: From Bench to Clinical Applications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 686544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemdani, K.; Seguin, J.; Lesieur, C.; Al Sabbagh, C.; Doan, B.-T.; Richard, C.; Capron, C.; Malafosse, R.; Boudy, V.; Mignet, N. Mucoadhesive thermosensitive hydrogel for the intra-tumoral delivery of immunomodulatory agents, in vivo evidence of adhesion by means of non-invasive imaging techniques. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.-D.; Xu, C.-X.; Quan, J.-S.; Song, C.-K.; Jin, H.; Kim, D.-D.; Choi, Y.-J.; Cho, M.-H.; Cho, C.-S. Synergistic anti-tumor activity of paclitaxel-incorporated conjugated linoleic acid-coupled poloxamer thermosensitive hydrogel in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4777–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.-D.; Hong, S.-H.; Jiang, H.-L.; Minai-Tehrani, A.; Kim, J.-E.; Shin, J.-Y.; Jiang, T.; Kim, Y.-K.; Choi, Y.-J.; Cho, C.-S.; et al. Synergistic effects of Akt1 shRNA and paclitaxel-incorporated conjugated linoleic acid-coupled poloxamer thermosensitive hydrogel on breast cancer. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2272–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Song, H.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Gao, X.; Zhu, X.; Chen, D. Novel facile thermosensitive hydrogel as sustained and controllable gene release vehicle for breast cancer treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 134, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hemelryck, S.; Dewulf, J.; Niekus, H.; van Heerden, M.; Ingelse, B.; Holm, R.; Mannaert, E.; Langguth, P. In vitro evaluation of poloxamer in situ forming gels for bedaquiline fumarate salt and pharmacokinetics following intramuscular injection in rats. Int. J. Pharm. X 2019, 1, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.M.; del Olmo, J.A.; Gonzalez, R.P.; Saez-Martinez, V. Injectable Hydrogels: From Laboratory to Industrialization. Polymers 2021, 13, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Dai, C.-Y.; Mao, X.; Lv, X.; Gu, Y.; Lee, E.-S.; Jiang, H.-B.; Sun, Y. Poloxamer-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review. Gels 2022, 8, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Han, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. ECM based injectable thermo-sensitive hydrogel on the recovery of injured cartilage induced by osteoarthritis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.-C.; Su, C.-Y.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hoang, T.C.; Tsou, Y.-S.; Fang, H.-W. Investigation and Characterization of Factors Affecting Rheological Properties of Poloxamer-Based Thermo-Sensitive Hydrogel. Polymers 2022, 14, 5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, P.; Su, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, C. Drug-grafted DNA as a novel chemogene for targeted combinatorial cancer therapy. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cancer Therapy | Injection Type | Hydrogel Composition | Cancer Cell (In Vitro) | Cancer (In Vivo) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | IT | P407, Topotecan | - | Retinoblastoma (Y79) | [54] |
| Chemotherapy | - | P407, DOX | MC-38 (colon) | - | [55] |
| Chemotherapy | IT | P407, Salinomycin | U251 | GBM | [47] |
| Chemotherapy | IT | P407, CDDP NP, LP microspheres | - | Melanoma (B16) | [57] |
| Chemotherapy | IT | P407, P188, SN-38 liposomes | - | HCC (H22) | [66] |
| Chemotherapy | IT | P407, P188, DTX micelles | - | Colon (HT-29) | [30] |
| Chemotherapy | IT | P407, P188, HPMC, NCTD | - | HCC (H22) | [69] |
| Chemotherapy | IT | P407, DOX, NCTD NP | HepG2 | HCC (H22) | [29] |
| Chemotherapy | IT | P407, HA, HPMC K4M, DOX, PTX micelles | - | - | [72] |
| Chemotherapy | IT | P407, P188, Alginate, 5-FU | - | Colon (CT26-luc) | [41] |
| Chemotherapy | IT | P407, P188, Xanthan gum, PTX NP | MCF-7 | Breast | [38] |
| Chemotherapy | PT | Heparin-P407, DOX laponite NP | S180 | Sarcoma | [73] |
| PTT | PT | P407, CuS nanodots | 4T1 | Breast | [77] |
| PTT | PT | P407, Prussian blue nanospheres | 4T1 | Breast | [78] |
| PTT | IT | P407, CA-AuAg NP | 4T1 B16F10 | Breast Melanoma | [79] |
| PTT | IT | P407, Ti3C2 NP | 4T1 | Breast | [80] |
| PTT + Chemotherapy | IT | P407, BP nanosheets, Gemcitabine | - | Breast (4T1) | [82] |
| PDT | IT | P407, T1 and PPa co-encapsulated micelles | 4T1 | Breast | [85] |
| PDT + Chemotherapy | IT | P407, P188, BP nanosheets, DTX micelles | - | Breast (4T1) | [86] |
| Immunotherapy | IT | P407, Imiquimod liposomes | 4T1 | Breast | [90] |
| Immunotherapy | PT | P407, CTLA-4 Ab | MC-38 (colon) | Colon (CT26) | [48] |
| Immunotherapy | IT | P407, NaHCO3 | - | Colon (MC-38) | [91] |
| Immunotherapy | IT | P407-g-gelatin, Vemurafenib, PD-1 mAb | D4M B16F10 | Melanoma | [92] |
| Immunotherapy | IT | P407, Xanthan gum, GM-CSF, HKMT | B16 CT26 3LL (Lewis lung carcinoma) | Colon (CT26) | [94] |
| Gene therapy | IT | P407, Sur-ASON, PHB-b-PDMAEMA | MCF-7/PDR | Breast | [97] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marques, A.C.; Costa, P.C.; Velho, S.; Amaral, M.H. Injectable Poloxamer Hydrogels for Local Cancer Therapy. Gels 2023, 9, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070593
Marques AC, Costa PC, Velho S, Amaral MH. Injectable Poloxamer Hydrogels for Local Cancer Therapy. Gels. 2023; 9(7):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070593
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarques, Ana Camila, Paulo Cardoso Costa, Sérgia Velho, and Maria Helena Amaral. 2023. "Injectable Poloxamer Hydrogels for Local Cancer Therapy" Gels 9, no. 7: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070593
APA StyleMarques, A. C., Costa, P. C., Velho, S., & Amaral, M. H. (2023). Injectable Poloxamer Hydrogels for Local Cancer Therapy. Gels, 9(7), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070593