Mesoporous Starch Cryoaerogel Material as an Emerging Platform for Oral Drug Delivery: Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Drug Loading
2.2. SEM Analysis
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4. XRD Analysis
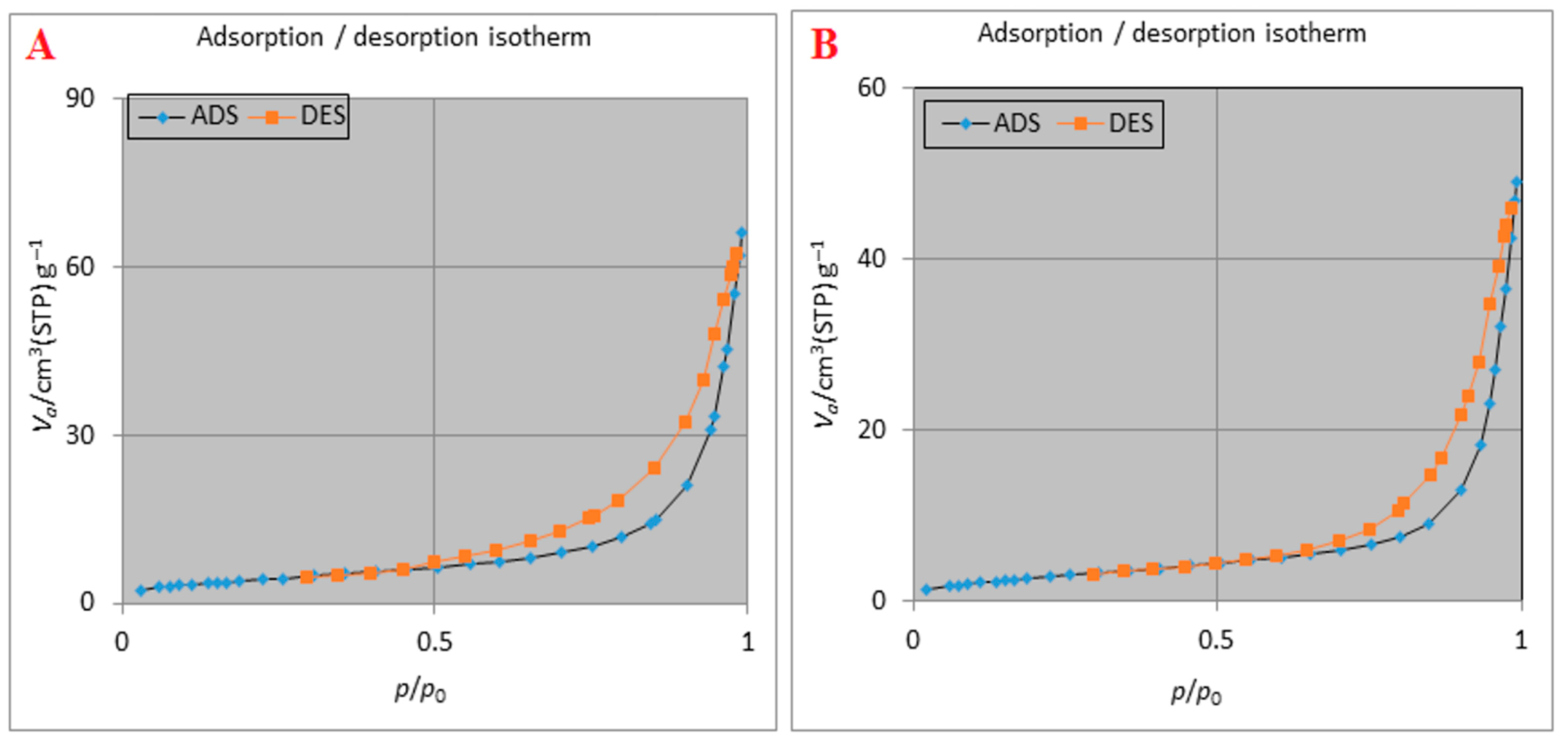
2.5. Surface Area Determination
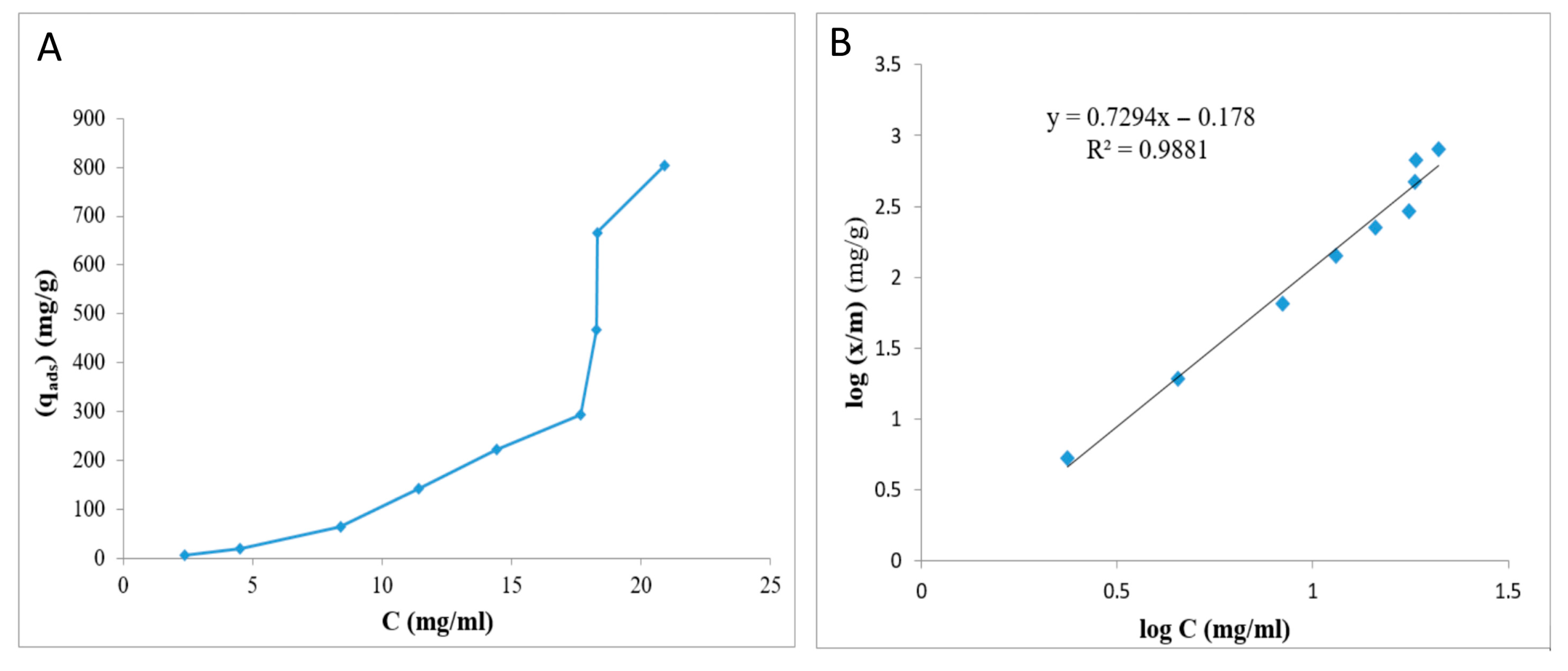
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms
2.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis
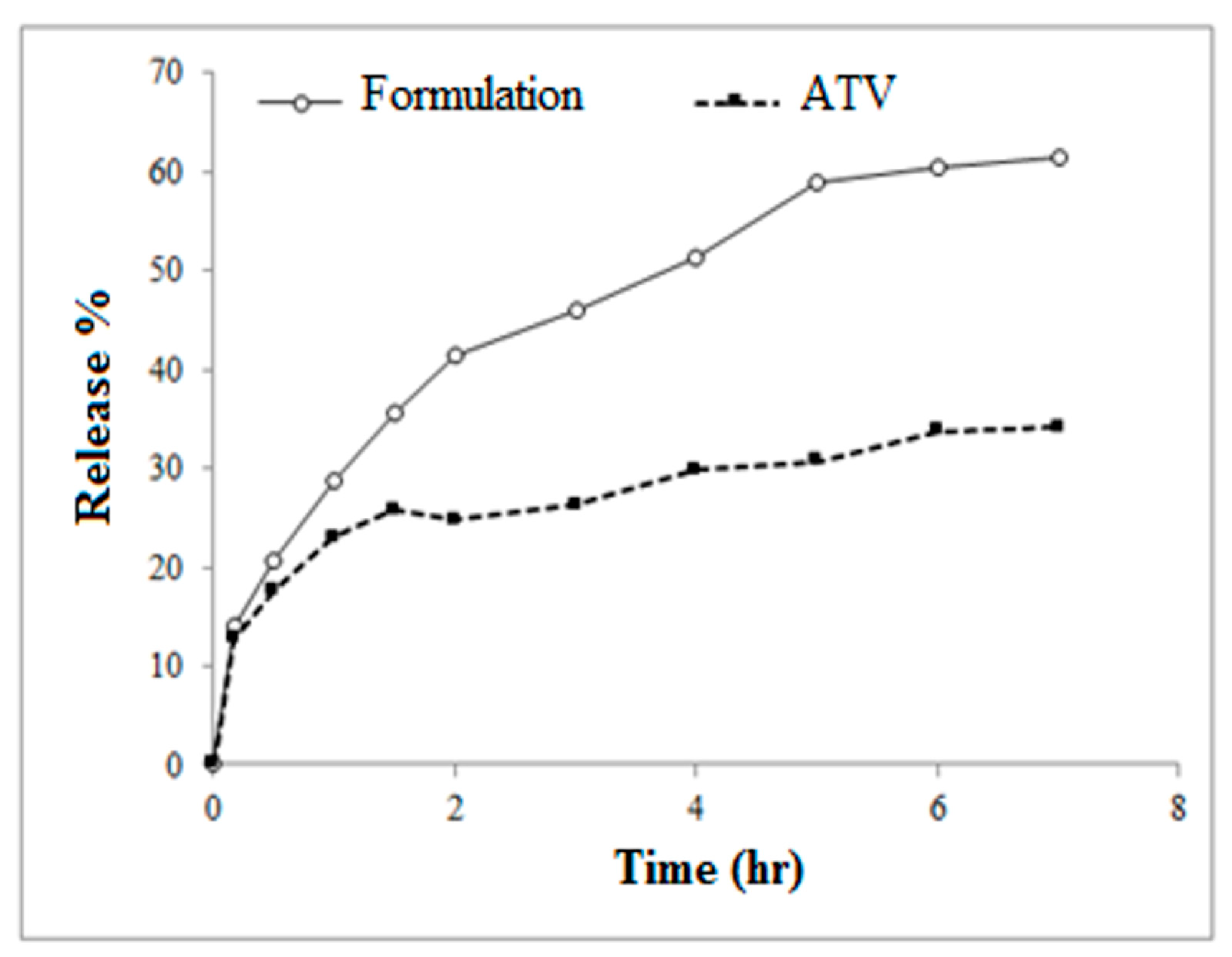
2.8. In Vitro Drug Release
2.9. Cytotoxicity Assessment
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Starch Cryoaerogel Preparation
4.3. Cryoaerogel Drug Loading
4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.6. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
4.7. BET Analysis
4.8. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4.9. In Vitro Drug Release
4.10. Cytotoxicity Assay
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maleki, A.; Hamidi, M. Dissolution enhancement of a model poorly water-soluble drug, atorvastatin, with ordered mesoporous silica: Comparison of MSF with SBA-15 as drug carriers. Expert. Opin. Drug. Deliv. 2016, 13, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldırım, Y.; İnce, İ.; Gümüştaş, B.; Vardar, Ö.; Yakar, N.; Munjaković, H.; Özdemir, G.; Emingil, G. Development of doxycycline and atorvastatin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles for local delivery in periodontal disease. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 82, 104322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilvel, C.K.; Karuppaiyan, K.; Pothumani, A.; Vedharethinam, A.; Jose, A.W.; Muthu Mohamed, J.M.; Sherbiny, M.E.; Ebrahim, H.A.; Shafey, M.E.; Dejene, M. Development of atorvastatin calcium biloaded capsules for oral administration of hypercholesterolemia. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 4995508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, S.H.; Rashidijahanabad, Z.; Ramadan, S.; Kauffman, N.; Parameswaran, N.; Zinn, K.R.; Qian, C.; Arora, R.; Agnew, D.; Huang, X. Effective atherosclerotic plaque inflammation inhibition with targeted drug delivery by hyaluronan conjugated atorvastatin nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 9541–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Jin, F.; Liu, D.; Shu, G.; Wang, X.; Qi, J.; Sun, M.; Yang, P.; Jiang, S.; Ying, X.; et al. ROS-responsive nano-drug delivery system combining mitochondria-targeting ceria nanoparticles with atorvastatin for acute kidney injury. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soorbaghi, F.P.; Isanejad, M.; Salatin, S.; Ghorbani, M.; Jafari, S.; Derakhshankhah, H. Bioaerogels: Synthesis approaches, cellular uptake, and the biomedical applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Xiu, K.; Wang, Z.; Hu, N.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, H.; Kong, F.; Xiao, J.; Cheng, L.; Bi, X. Multifunctional wearable humidity and pressure sensors based on biocompatible graphene/bacterial cellulose bioaerogel for wireless monitoring and early warning of sleep apnea syndrome. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, C.A.; Uy, J.J.; Alnaief, M.; Smirnova, I. Preparation of tailor-made starch-based aerogel microspheres by the emulsion-gelation method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Lee, D.; Shin, Y.; Park, J. Recent progress in polysaccharide aerogels: Their synthesis, application, and future outlook. Polymers 2021, 13, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubeyitogullari, A.; Ciftci, O.N. Formation of nanoporous aerogels from wheat starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkalec, G.; Knez, Ž.; Novak, Z. Fast production of high-methoxyl pectin aerogels for enhancing the bioavailability of low-soluble drugs. J. Supercrit Fluids 2015, 106, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sánchez-Soto, M.; Abt, T. Properties of bio-based gum Arabic/clay aerogels. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 91, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.G.; Tran, C.H.; Wang, M.; Varyambath, A.; Kim, J.; Kim, I. Efficient synthesis of folate-conjugated hollow polymeric capsules for accurate drug delivery to cancer cells. Biomacromolecules 2020, 22, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroppel, L.; Schultz-Fademrecht, T.; Cebulla, M.; Blech, M.; Marhöfer, R.J.; Selzer, P.M.; Garidel, P. Antimicrobial Preservatives for Protein and Peptide Formulations: An Overview. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Tian, Y.; Ye, F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, G. Fabrication and application of starch-based aerogel: Technical strategies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; Dai, H.; Wu, W. Nanocellulose/gelatin composite cryogels for controlled drug release. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng 2019, 7, 6381–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagri, L.P.; Bajpai, J.; Bajpai, A.K. Evaluation of starch based cryogels as potential biomaterials for controlled release of antibiotic drugs. Bull. Mat. Sci. 2011, 34, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, S.; Göktürk, D.; Demir, D.; Damla Özdemir, M.; Bölgen, N. Comparison of additive effects on the PVA/starch cryogels: Synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity, and genotoxicity studies. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2018, 67, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, I.; Reverchon, E. Starch aerogel loaded with poorly water-soluble vitamins through supercritical CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 119, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Moghaddas, J. Mesoporous tablet-shaped potato starch aerogels for loading and release of the poorly water-soluble drug celecoxib. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 1778–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Moghaddas, J.S. Mesoporous starch aerogels production as drug delivery matrices: Synthesis optimization, ibuprofen loading, and release property. Turk. J. Chem. 2020, 44, 614–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fan, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D. The synthesis of hierarchical porous iron oxide with wood templates. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 85, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.; Ahmad, A.; Hameed, B. Adsorption isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and desorption studies of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol on oil palm empty fruit bunch-based activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.K.; Kim, W.H.; Park, J.; Cho, J.; Jeong, T.Y.; Park, P.K. Application of Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms to predict adsorbate removal efficiency or required amount of adsorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 28, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, B.E.; Matsumoto, M.R. Modeling cadmium adsorption by activated carbon using the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm expressions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, I.; Guiochon, G. Derivation and application of a Jovanovic–Freundlich isotherm model for single-component adsorption on heterogeneous surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 183, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, H.; Hamed, M.M.; Eldahab, H.A.; Moustafa, M.; El-Reefy, S. Radiation-induced grafting copolymerization of resin onto the surface of silica extracted from rice husk ash for adsorption of gadolinium. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 231, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukmar, T.; Maver, U.; Planinšek, O.; Kaučič, V.; Gaberšček, M.; Godec, A. Understanding controlled drug release from mesoporous silicates: Theory and experiment. J. Control. Release 2011, 155, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Formulation | Cryoaerogel (mg) | ATV (mg) | DL % ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500 | 100 | 0.60 ± 0.27 |
| 2 | 500 | 200 | 3.66 ± 0.52 |
| 3 | 500 | 300 | 6.97 ± 0.61 |
| 4 | 500 | 400 | 15.17 ± 1.17 |
| 5 | 500 | 500 | 17.59 ± 2.45 |
| 6 | 500 | 600 | 25.53 ± 1.71 |
| 7 | 500 | 700 | 35.72 ± 0.64 |
| 8 | 500 | 800 | 38.60 ± 3.49 |
| Samples | WDH (nm) | SBET (m2/g) | Vt (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AEO | 27.565 | 10.723 | 0.07 |
| ATV/AEO | 25.997 | 15.394 | 0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jafari, S.; Khodaensaf, F.; Delattre, C.; Bazargan, V.; Lukova, P. Mesoporous Starch Cryoaerogel Material as an Emerging Platform for Oral Drug Delivery: Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation. Gels 2023, 9, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080623
Jafari S, Khodaensaf F, Delattre C, Bazargan V, Lukova P. Mesoporous Starch Cryoaerogel Material as an Emerging Platform for Oral Drug Delivery: Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation. Gels. 2023; 9(8):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080623
Chicago/Turabian StyleJafari, Samira, Farzaneh Khodaensaf, Cédric Delattre, Vahid Bazargan, and Paolina Lukova. 2023. "Mesoporous Starch Cryoaerogel Material as an Emerging Platform for Oral Drug Delivery: Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation" Gels 9, no. 8: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080623
APA StyleJafari, S., Khodaensaf, F., Delattre, C., Bazargan, V., & Lukova, P. (2023). Mesoporous Starch Cryoaerogel Material as an Emerging Platform for Oral Drug Delivery: Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation. Gels, 9(8), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080623









