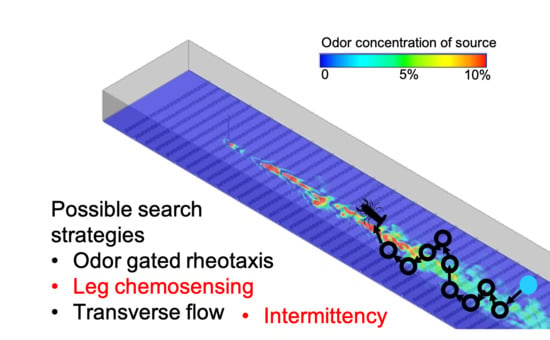
Interpreting the Spatial-Temporal Structure of Turbulent Chemical Plumes Utilized in Odor Tracking by Lobsters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Lobster Olfactory Search
2. Materials and Methods
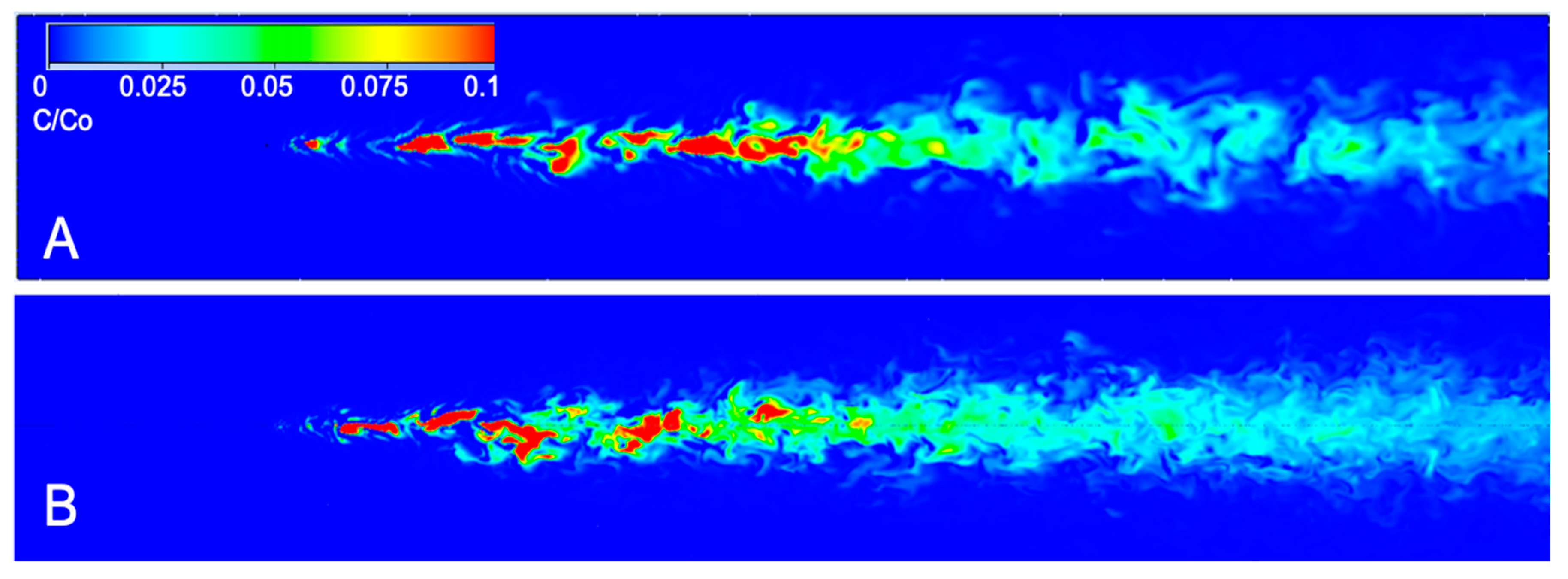
2.1. Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation
2.2. Search Algorithms
3. Results
3.1. CFD Plume Dynamics
3.2. Search Algorithms
3.3. Effect of Change in Source Concentration and Intermittency Threshold
4. Discussion
4.1. Odorant Dispersion in Turbulent Flows
4.2. Olfactory Search Strategies
4.3. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dittman, A.; Quinn, T. Homing in Pacific salmon: Mechanisms and ecological basis. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karavanich, C.; Atema, J. Olfactory Recognition of Urine Signals in Dominance Fights Between Male Lobster, Homarus Americanus. J. Behav. 1998, 135, 719–730. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, T.A.; Moore, P.A. Effects of ontogeny and odors on behavior: The influence of crayfish size and fish odors on crayfish movement. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 1999, 33, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, R.M.; Moore, P.A. The Role of the Major Chelae in the Localization and Sampling of Female Odours by Male Crayfish, Orconectes rusticus (Girard, 1852). Crustaceana 2009, 82, 653–668. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, P.A.; Atema, J. Spatial Information in the Three-Dimensional Fine Structure of an Aquatic Odor Plume. Biol. Bull. 1991, 181, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, D.R.; Weissburg, M.J. Chemosensory guidance cues in a turbulent chemical odor plume. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atema, J. Opening the chemosensory world of the lobster, Homarus americanus. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2018, 94, 479–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.M.; Aguiar, A.P.; Pascoal, A.M.S.; Martinoli, A. An Algorithm for Formation-Based Chemical Plume Tracing Using Robotic Marine Vehicles. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2016 MTS/IEEE Monterey, Monterey, CA, USA, 19–23 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hinow, P.; Strickler, J.R.; Yen, J. Olfaction in a viscous environment: The “color” of sexual smells in Temora longicornis. Sci. Nat. 2017, 104, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.J.; Hein, A.M.; Bobkov, Y.V.; Reidenbach, M.A.; Ache, B.W.; Principe, J.C. Neurally Encoding Time for Olfactory Navigation. PLoS. Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reidenbach, M.A.; Limm, M.; Hondzo, M.; Stacey, M.T. Effects of bed roughness on boundary layer mixing and mass flux across the sediment-water interface. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimaldi, J.P.; Wiley, M.B.; Koseff, J.R. The relationship between mean and instantaneous structure in turbulent passive scalar plumes. J. Turbul. 2002, 3, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissburg, M.J. The fluid dynamical context of chemosensory behavior. Biol. Bull. 2000, 198, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Yeoh, G.; Liu, C. Computational Fluid Dynamics a Practical Approach, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Waltham, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, D.R.; Volyanskyy, K.Y.; Weissburg, M.J. Bioinspired algorithm for autonomous sensor-driven guidance in turbulent chemical plumes. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2012, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webster, D.R.; Weissburg, M.J. The Hydrodynamics of Chemical Cues among Aquatic Organisms. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2009, 41, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergassola, M.; Villermaux, E.; Shraiman, B.I. “Infotaxis” as a strategy for searching without gradients. Nature 2007, 445, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, F.W.; Basil, J.A.; Atema, J. Toward the Convergence: Robot and Lobster Perspectives of Tracking Odors to Their Source in the Turbulent Marine Environment. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control (ISIC) held jointly with IEEE International Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Robotics and Automation (CIRA) Intell, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 17 September 1998; pp. 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Page, J.L.; Dickman, B.D.; Webster, D.R.; Weissburg, M.J. Staying the course: Chemical signal spatial properties and concentration mediate cross-stream motion in turbulent plumes. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, J.L.; Dickman, B.D.; Webster, D.R.; Weissburg, M.J. Getting ahead: Context-dependent responses to odorant filaments drive along-stream progress during odor tracking in blue crabs. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 1498–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozlowski, C.; Voigt, R.; Moore, P.A. Changes in odour intermittency influence the success and search behaviour during orientation in the crayfish (Orconectes rusticus). Mar. Freshwat. Behav. Physiol. 2003, 36, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.A.; Ferrante, P.A.; Bergner, J.L. Chemical orientation strategies of the crayfish are influenced by the hydrodynamics of their native environment. Am. Midl. Nat. 2015, 173, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.A.; Grills, J.L. Chemical orientation to food by the crayfish Orconectes rusticus: Influence of hydrodynamics. Animal Behav. 1999, 58, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, F.W.; Basil, J.A. How lobsters, crayfishes, and crabs locate sources of odor: Current perspectives and future directions. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2002, 12, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravin, S.; Reidenbach, M.A. Simultaneous sampling of flow and odorants by crustaceans can aid searches within a turbulent plume. Sensors 2013, 13, 16591–16610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gleeson, R.A.; Carr, W.E.S.; Trapido-Rosenthal, H.G. Morphological characteristics facilitating stimulus access and removal in the olfactory organ of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus: Insight from the design. Chem. Senses 1993, 18, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steullet, P.; Krützfeldt, D.R.; Hamidani, G.; Flavus, T.; Ngo, V.; Derby, C.D. Dual antennular chemosensory pathways mediate odor-associative learning and odor discrimination in the Caribbean spiny lobster Panulirus argus. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 851–867. [Google Scholar]
- Devine, D.V.; Atema, J. Function of chemoreceptor organs in spatial orientation of the lobster, Homarus americanus: Differences and overlap. Biol. Bull. 1982, 163, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehl, M.A.R. The Fluid Mechanics of Arthropod Sniffing in Turbulent Odor Plumes. Chem. Senses 2006, 31, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, A. Functional Roles of Crustacean Dual Antennular Chemosensory Pathways in Odor Mediated Behaviors. Ph.D. Thesis, Georgia State University, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M. Identification of putative neuroblasts at the base of adult neurogenesis in the olfactory midbrain of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 503, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Derby, C.D. Non-olfactory chemoreceptors in asymmetric setae activate antennular grooming behavior in the Caribbean spiny lobster Panulirus argus. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stacey, M.T.; Mead, K.S.; Koehl, M.A.R. Molecule capture by olfactory antennules: Mantis shrimp. J. Math. Biol. 2002, 44, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pravin, S.; Mellon, D.; Reidenbach, M.A. Micro-scale fluid and odorant transport to antennules of the crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2012, 198, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, G. Electrophysiological recordings from olfactory receptor cells in adult mice. Brain Res. 1986, 397, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frings, S.; Lindemann, B. Odorant response of isolated olfactory receptor cells is blocked by amiloride. J. Membr. Biol. 1988, 105, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisert, J.; Matthews, H.R. Response properties of isolated mouse olfactory receptor cells. J. Physiol. 2001, 530, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisert, J.; Matthews, H.R. Responses to prolonged odour stimulation in frog olfactory receptor cells. J. Physiol. 2001, 534, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holy, T.E.; Dulac, C.; Meister, M. Responses of Vomeronasal Neurons to Natural Stimuli. Science 2000, 289, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arnson, H.A.; Holy, T.E. Chemosensory burst coding by mouse vomeronasal sensory neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 106, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ukhanov, K.; Bobkov, Y.; Ache, B.W. Imaging ensemble activity in arthropod olfactory receptor neurons in situ. Cell Calcium 2011, 49, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bobkov, Y.V.; Ache, B.W. Intrinsically bursting olfactory receptor neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Bobkov, Y.; Ache, B.; Principe, J. Intermittency Coding in the Primary Olfactory System: A Neural Substrate for Olfactory Scene Analysis. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reidenbach, M.A.; Koehl, M.A.R. The spatial and temporal patterns of odors sampled by lobsters and crabs in a turbulent plume. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 3138–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Major, R.; Jeffs, A. Orientation and food search behaviour of a deep sea lobster in turbulent versus laminar odour plumes. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2017, 71, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adedoyin, A.; Walters, D.; Bhushan, S. Investigation of turbulence model and numerical scheme combinations for practical finite-volume large eddy simulations. Eng. Appl Comput. Fluid Mech. 2015, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reidenbach, M.A. Tracking odorant plumes. In Olfactory Receptors: Methods and Protocols; Simoes de Souza, F.M., Antunes, G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 251–263. ISBN 978-1-4939-8608-8. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, J.; Weissburg, M.J.; Doall, M.H. The fluid physics of signal perception by mate-tracking copepods. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. B 1998, 353, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weissburg, M.J. Chemo- and Mechanosensory Orientation by Crustaceans in Laminar and Turbulent flows: From Odor Trails to Vortex Streets. In Orientation and Communication in Arthropods; Lehrer, M., Ed.; EXS.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 1997; pp. 215–246. ISBN 978-3-0348-8878-3. [Google Scholar]
- Reidenbach, M.A.; George, N.; Koehl, M.A.R. Antennule morphology and flicking kinematics facilitate odor sampling by the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 2849–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pravin, S.; Mellon, D.; Berger, E.J.; Reidenbach, M.A. Effects of sensilla morphology on mechanosensory sensitivity in the crayfish. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 036006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, G.; Voigt, R.; Atema, J. Frequency filter properties of lobster chemoreceptor cells determined with high-resolution stimulus measurement. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1994, 174, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, G.; Atema, J. Temporal resolution in olfaction II: Time course of recovery from adaptation in lobster chemoreceptor cells. J. Neurophysiol. 1996, 76, 1340–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer-Faust, R.K. Chemical Signal-to-Noise Detection by Spiny Lobsters. Biol. Bull. 1991, 181, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, A.J.; Weissburg, M.J.; Derby, C.D. Dual antennular chemosensory pathways can mediate orientation by Caribbean spiny lobsters in naturalistic flow conditions. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 3785–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, T.A.; Weissburg, M.J. Effects of Odor Flux and Pulse Rate on Chemosensory Tracking in Turbulent Odor Plumes by the Blue Crab, Callinectes sapidus. Biol. Bull. 2004, 207, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, M.C.; Voigt, R.; Moore, P.A. Spatial Arrangement of Odor Sources Modifies the Temporal Aspects of Crayfish Search Strategies. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voges, N.; Chaffiol, A.; Lucas, P.; Martinez, D. Reactive Searching and Infotaxis in Odor Source Localization. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroni, P.F.; Atema, J. Adaptation in chemoreceptor cells. J. Comp. Physiol. 1988, 164, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, G.; Atema, J. Temporal resolution in olfaction: Stimulus integration time of lobster chemoreceptor cells. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, P.A. A model of the role of adaptation and disadaptation in olfactory receptor neurons: Implications for the coding of temporal and intensity patterns in odor signals. Chem. Senses 1994, 19, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.A.; Shao, K. An electrical circuit model of chemoreceptor cells based on adaptation and disadaptation time constants: Implications for temporal filtering. Mater. Sci. and Eng. C 1999, 7, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garm, A.; Shabani, S.; Høeg, J.T.; Derby, C.D. Chemosensory neurons in the mouthparts of the spiny lobsters Panulirus argus and Panulirus interruptus (Crustacea: Decapoda). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2005, 314, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenning, M.; Lehmann, P.; Lindström, M.; Harzsch, S. Heading which way? Y-maze chemical assays: Not all crustaceans are alike. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2015, 69, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniel, P.C.; Fox, M.; Mehta, S. Identification of Chemosensory Sensilla Mediating Antennular Flicking Behavior in Panulirus argus, the Caribbean Spiny Lobster. Biol. Bull. 2008, 215, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissburg, M.J.; Ferner, M.C.; Pisut, D.P.; Smee, D.L. Ecological Consequences of Chemically Mediated Prey Perception. J. Chem. Ecol. 2002, 28, 1953–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjos, K.; Grasso, F.; Atema, J. Antennule Use by the American Lobster, Homarus americanus, During Chemo-orientation in Three Turbulent Odor Plumes. Biol. Bull. 1999, 197, 249–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.A. Fluid Dynamic Design of Lobster Olfactory Organs: High Speed Kinematic Analysis of Antennule Flicking by Panulirus argus. Chem. Senses 2001, 26, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kraus-Epley, K.E.; Lahman, S.E.; Moore, P.A. Behaviorally-selective chemoreceptor lesions reveal two different chemically mediated orientation strategies in the rusty crayfish, Orconectes rusticus. J. Crust. Biol. 2015, 35, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michaelis, B.T.; Leathers, K.W.; Bobkov, Y.V.; Ache, B.W.; Principe, J.C.; Baharloo, R.; Park, I.M.; Reidenbach, M.A. Odor tracking in aquatic organisms: The importance of temporal and spatial intermittency of the turbulent plume. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Inlet Velocity (cm·s−1) | Outlet Velocity (cm·s−1) | u* (cm/s) | Re* | η (cm) | ε (m2·s−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.0 | 9.2 | 0.21 | 23.5 | 0.12 | 1.66 × 10−4 |
| Strategy | Behavior | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | If one antennule (A1 or A2) senses odor concentration above threshold, the lobster moves upstream diagonally towards that antennule. If both antennules sense odor, the lobster moves directly upstream. If neither antennule senses odor, the lobster moves transversely to its left or right in random fashion. | A1, A2 |
| Intermittency | The rules of the Concentration strategy apply, except intermittency, I, is used when neither antennule senses odor at the present time. If neither antennule senses odor, then the lobster moves in the direction that has the lowest I (I1 or I2) measured by time since last odor encounter within the previous 5 s. If neither antennule sensed odor within the last five seconds, the lobster moves transversely, as in the concentration strategy | A1, A2, I1, I2 |
| Concentration + leg sensors | The rules of the Concentration strategy apply except if odor is not detected by either A1 or A2 and at least one of two leg chemosensors (L1 or L2) senses above threshold odor, the lobster moves in the direction of whichever leg senses a concentration or directly upstream if both legs sense odor. If only one antennule senses an above threshold concentration and both legs sense odor, then the lobster moves directly forward, as it is likely still within the plume. | A1, A2, L1, L2 |
| Intermittency + leg sensors | This strategy is the same as concentration + leg sensors except if neither antennules nor leg chemosensors sense odor in the present time, the intermittency strategy is used. | A1, A2, L1, L2, I1, I2 |
| Concentration + transverse flow | The rules of the concentration strategy apply except movements are adjusted in the case that a single antennule senses odor above threshold. If the left antennule senses odor and transverse flow, V1, above 1 cm s−1 towards the lobster body from the left side, the lobster moves diagonally as normal and takes an additional step to its left beyond its normal movement over a total of two seconds. The lobster uses the same process if its right antennule senses odor and transverse flow, V2, in the direction of the lobster body above 1 cm s−1. | A1, A2, V1, V2 |
| Intermittency + transverse flow | The rules of the intermittency strategy apply except when just one of A1 or A2 senses odor, the transverse flow strategy is used. | A1, A2, V1, V2, I1, I2 |
| Contrast | Num DF | Den DF | Chi-Square | Pr > ChiSq | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intermittency vs. Concentration | 1 | 5994 | 10.01 | 0.0016 | LR |
| Intermittency and Leg Search vs. Intermittency | 1 | 5994 | 455.27 | <0.0001 | LR |
| Concentration and Leg Search vs. Concentration | 1 | 5994 | 1189.15 | <0.0001 | LR |
| Intermittency and Flow Search vs. Intermittency | 1 | 5994 | 2.21 | 0.1368 | LR |
| Concentration and Flow Search vs. Concentration | 1 | 5994 | 21.85 | <0.0001 | LR |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leathers, K.W.; Michaelis, B.T.; Reidenbach, M.A. Interpreting the Spatial-Temporal Structure of Turbulent Chemical Plumes Utilized in Odor Tracking by Lobsters. Fluids 2020, 5, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5020082
Leathers KW, Michaelis BT, Reidenbach MA. Interpreting the Spatial-Temporal Structure of Turbulent Chemical Plumes Utilized in Odor Tracking by Lobsters. Fluids. 2020; 5(2):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5020082
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeathers, Kyle W., Brenden T. Michaelis, and Matthew A. Reidenbach. 2020. "Interpreting the Spatial-Temporal Structure of Turbulent Chemical Plumes Utilized in Odor Tracking by Lobsters" Fluids 5, no. 2: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5020082
APA StyleLeathers, K. W., Michaelis, B. T., & Reidenbach, M. A. (2020). Interpreting the Spatial-Temporal Structure of Turbulent Chemical Plumes Utilized in Odor Tracking by Lobsters. Fluids, 5(2), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5020082