Pathogen-Imprinted Organosiloxane Polymers as Selective Biosensors for the Detection of Targeted E. coli
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Handling
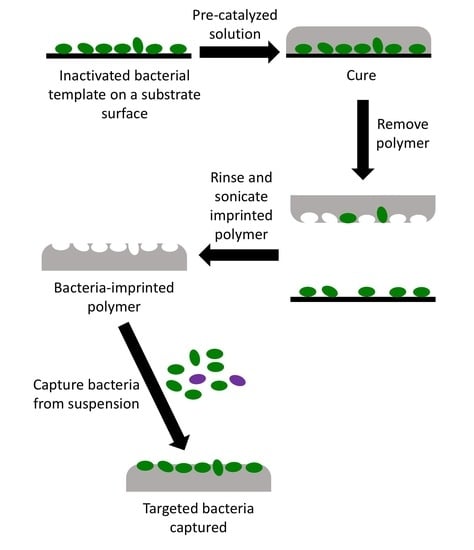
2.3. Template Preparation
2.4. Preparation of OSX and Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Polymers
2.5. Imprinting of OSX and PDMS Polymers
2.6. Bacterial Cell Capture
2.7. Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (DESI-MS) Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Organosiloxane (OSX) Polymers
3.2. Capture Selectivity and Sensitivity of Imprinted OSX Polymers
3.3. Non-Specific Adsorption of Targeted Bacteria on Non-Imprinted Areas of Imprinted OSX Polymers
3.4. Detection of Targeted Bacteria at Low Density
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Center for Strategic & International Studies. C2015. Available online: http://www.smartglobalhealth.org/issues/entry/infectious-diseases (accessed on 12 March 2017).
- Lazcka, O.; Del Campo, F.J.; Munoz, F.X. Pathogen detection: A perspective of traditional methods and biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivnitski, D.; Abdel-Hamid, I.; Atanasov, P.; Wilkins, E. Biosensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1999, 14, 599–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idil, N.; Mattiasson, B. Imprinting of microorganisms for biosensor applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, K.; Kraatz, H.B. Recent developments in biosensor technologies for pathogen detection in water. JSM Environ. Sci. Ecol. 2015, 3, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Wang, F.; Huang, Q.; Huang, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Yao, C.; Chen, Q.; Cai, G.; Fu, W. Detection of Staphylococcus epidermidis by a quartz crystal microbalance nucleic acid biosensor array using Au nanoparticle signal amplification. Sensors 2008, 8, 6453–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusak-Sochaczewski, E.; Luong, J.H.T.; Guilbault, G.G. Development of a piezoelectric immunosensor for the detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Enzyme Microbiol. Technol. 1990, 12, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, B.; Grätzel, M. Detection of viruses and bacteria with piezoelectric immunosensors. Anal. Lett. 1993, 26, 1567–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, R.E. Biosensor Platforms for Rapid Detection of E. coli Bacteria. In Recent Advances on Physiology, Pathogenesis and Biotechnological Applications; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 275–289. [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Molecular biosensors for electrochemical detection of infectious pathogens in liquid biopsies: current trends and challenges. Sensors 2017, 17, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenselau, C.; Demirev, P. Rapid Characterization of Microorganisms by Mass Spectrometry; Fenselau, C., Demirev, P., Eds.; ACS: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 1–4. ISBN 9780841226128. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C.; Andersson, H.S.; Andersson, L.I.; Ansell, R.J.; Kirsch, N.; Nicholls, I.A.; O’Mahony, J.; Whitcombe, M.J. Molecular imprinting science and technology: A survey of the literature for the years up to and including 2013. J. Mol. Recognit. 2006, 19, 106–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickert, F.L.; Hayden, O. Bioimprinting of polymers and sol-gel phases. Selective detection of yeasts with imprinted polymers. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mujahid, A.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Dickert, F.L. Chemical sensors based on molecularly imprinted sol-gel materials. Materials 2010, 3, 2196–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, O.; Dickert, F.L. Selective microorganism detection with cell surface imprinted polymers. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1480–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, T.; Starosvetsky, J.; Cheruti, U.; Armon, R. Whole cell imprinting in sol-gel thin films for bacterial recognition in liquids: Macromolecular fingerprinting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 1236–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starosvetsky, J.; Cohen, T.; Cheruti, U.; Dragoljub, D.; Armon, R. Effects of physical parameters on bacterial cell adsorption onto pre-imprinted sol-gel films. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 3, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diler, E.; Obst, U.; Schmitz, K.; Schwartz, T. A lysozyme and magnetic bead based method of separating intact bacteria. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirhagl, R.; Ren, K.; Zare, R.N. Surface-imprinted polymers in microfluidic devices. Sc. China Chem. 2012, 4, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Zare, R.N. Chemical recognition in cell-imprinted polymers. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4314–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Banaei, N.; Zare, R.N. Sorting inactivated cells using cell-imprinted polymer thin films. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6031–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooy, N.; Mohamed, K.; Pin, L.T.; Guan, O.S. A review of roll-to-roll nanoimprinting lithography. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.Y.; Krauss, P.R.; Renstrom, P.J. Imprint of sub-25 nm vias and trenches in polymers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 67, 3114–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, E.R.; Jeans, A.; Mei, P.; Taussig, C.P.; Elder, R.E.; Bell, C.; Howard, E.; Stowell, J.; O’Rourke, S. An enhanced flexible color filter via imprint lithography and inkjet deposition methods. J. Display Technol. 2011, 7, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.Y.; Krauss, P.R.; Renstrom, P.J. Nanoimprint lithography. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 1996, 14, 4129–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, A.E.; Hall, S.R.; Schnepp, Z. The evolution of ‘sol-gel’ chemistry as a technique for materials synthesis. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materials Safety Data Sheet, RTV615 Silicone Potting Compound; Momentive Performance Materials: Columbus, OH, USA, 2008–2011.
- Sinko, K. Influence of chemical conditions on the nanoporous structure of silicate aerogels. Materials 2010, 3, 704–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J. Porous inorganic materials. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 1996, 1, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.N. Sol-gel Processing, Ceramic Processing and Sintering; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Hayase, G.; Kanamori, K.; Fukuchi, M.; Kaji, H.; Nakanishi, K. Facile synthesis of marshmallow-like macroporous gels usable under harsh conditions for the separation of oil and water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1986–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozuka, H. Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–37. ISBN 978-3-319-19454-7. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, R.; Yin, Q.; Guo, X.; Tong, X.; Wang, X. Evolution of mesoporous TiO2 during fast sol-gel synthesis. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 6433–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell Genome Institute. Genomes: Microorganisms. Available online: http://genome.wustl.edu/genomes/category/microorganisms/ (accessed on 12 January 2018).
- Rajput, D.; Costa, L.; Lansford, K.; Terekhov, A.; Hofmeister, W. Solution-cast high-aspect-ratio polymer structures from direct-write templates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, Y.; Zhang, T. Optimization of fixation methods for observation of bacterial cell morphology and surface ultrastructures by atomic force microscopy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meetani, M.A.; Shin, Y.S.; Zhang, S.; Mayer, R.; Basile, F. Desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of intact bacteria. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 42, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbunova, O.V.; Baklanova, O.N.; Gulyaeva, T.I.; Trenikhin, M.V.; Drozdov, V.A. Poly(ethylene glycol) as structure directing agent in sol-gel synthesis of amorphous silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 190, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnfinnsdottir, N.B.; Ottesen, V.; Lale, R.; Sletmoen, M. The design of simple bacterial microarrays: development towards immobilizing single living bacteria on predefined micro-sized spots on patterned surfaces. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, M.L.; Gaido, L. Laboratory diagnosis of urinary tract infections in adult patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Polymer | Silane(s) | [HCl] (M) | Additive | Reaction T (°C) | H2O:Si Molar Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSX-A | MTMS:DMDMS (2:1, v/v) | 0.12 | None | 65 | 1.32 |
| OSX-B | MTMS:DMDMS (2:1, v/v) | 0.012 | None | 65 | 1.32 |
| OSX-C | MTMS | 0.12 | PEG-10 | 25 | 1.32 |
| OSX-D | MTMS | 0.12 | PEG-10 | 25 | 1.83 |
| Polymer | Imprint Bacteria | Total E. coli Captured | Total S. typhimurium Captured | Selectivity Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSX-A | E. coli (heat fixed) | 120 ± 40 | 17 ± 4 | 7.1 ± 1.5 |
| OSX-B | E. coli (heat fixed) | 108 ± 20 | 38 ± 10 | 2.8 ± 2.0 |
| OSX-C | E. coli (glutaraldehyde inactivated) | 136 ± 25 | 5 ± 1 | 27.2 ± 5.2 |
| OSX-D | E. coli (glutaraldehyde inactivated) | 281 ± 42 | 26 ± 11 | 10.8 ± 7.4 |
| PDMS | E. coli (glutaraldehyde inactivated) | 80 ± 13 | 8 ± 2 | 10.0 ± 4.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dulay, M.T.; Zaman, N.; Jaramillo, D.; Mody, A.C.; Zare, R.N. Pathogen-Imprinted Organosiloxane Polymers as Selective Biosensors for the Detection of Targeted E. coli. C 2018, 4, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4020029
Dulay MT, Zaman N, Jaramillo D, Mody AC, Zare RN. Pathogen-Imprinted Organosiloxane Polymers as Selective Biosensors for the Detection of Targeted E. coli. C. 2018; 4(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleDulay, Maria T., Naina Zaman, David Jaramillo, Alison C. Mody, and Richard N. Zare. 2018. "Pathogen-Imprinted Organosiloxane Polymers as Selective Biosensors for the Detection of Targeted E. coli" C 4, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4020029
APA StyleDulay, M. T., Zaman, N., Jaramillo, D., Mody, A. C., & Zare, R. N. (2018). Pathogen-Imprinted Organosiloxane Polymers as Selective Biosensors for the Detection of Targeted E. coli. C, 4(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4020029