Poly(Vinylamine) Derived N-Doped C-Dots with Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of PVAm
2.3. Synthesis f CA:PVAm C-Dots
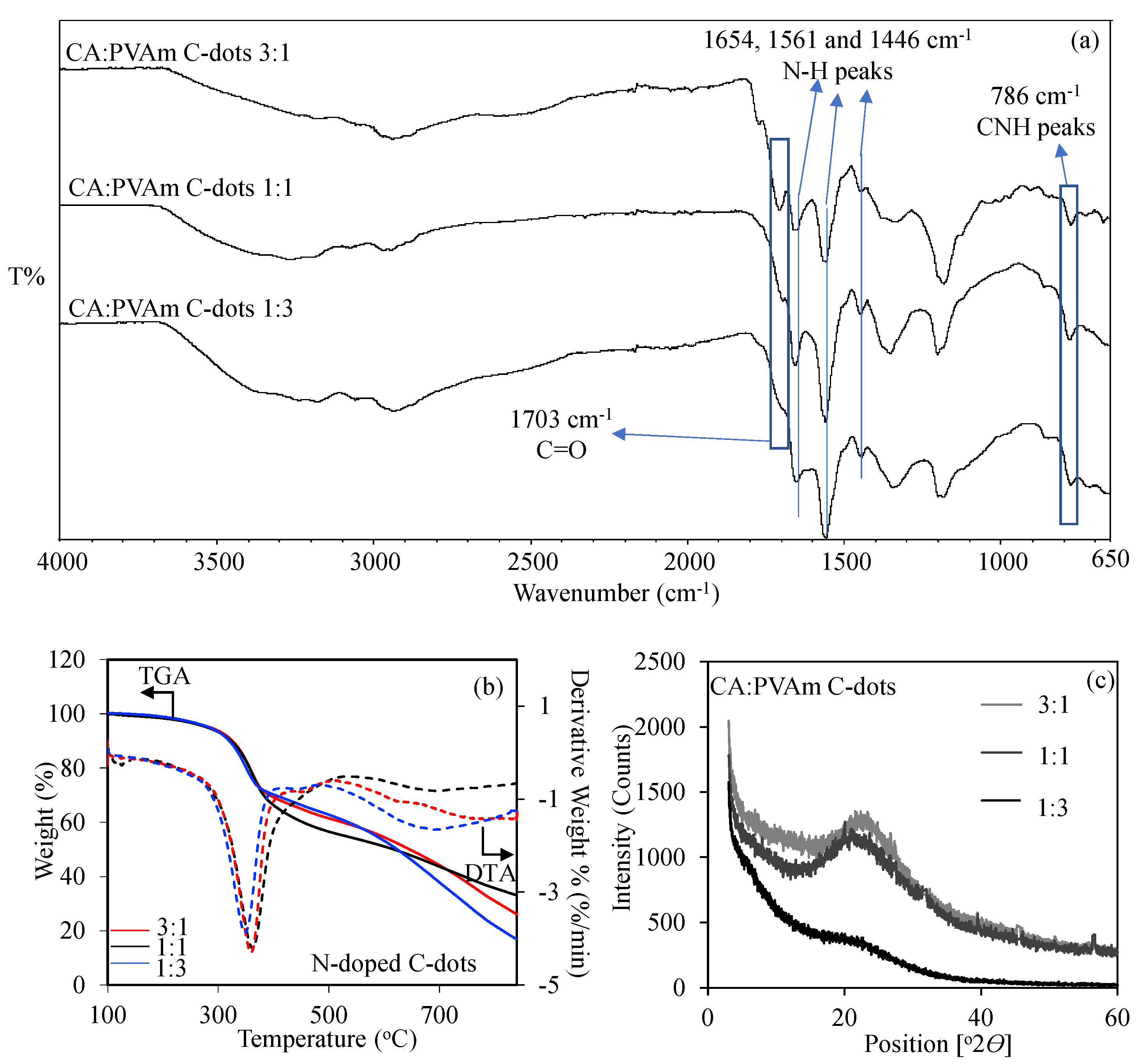
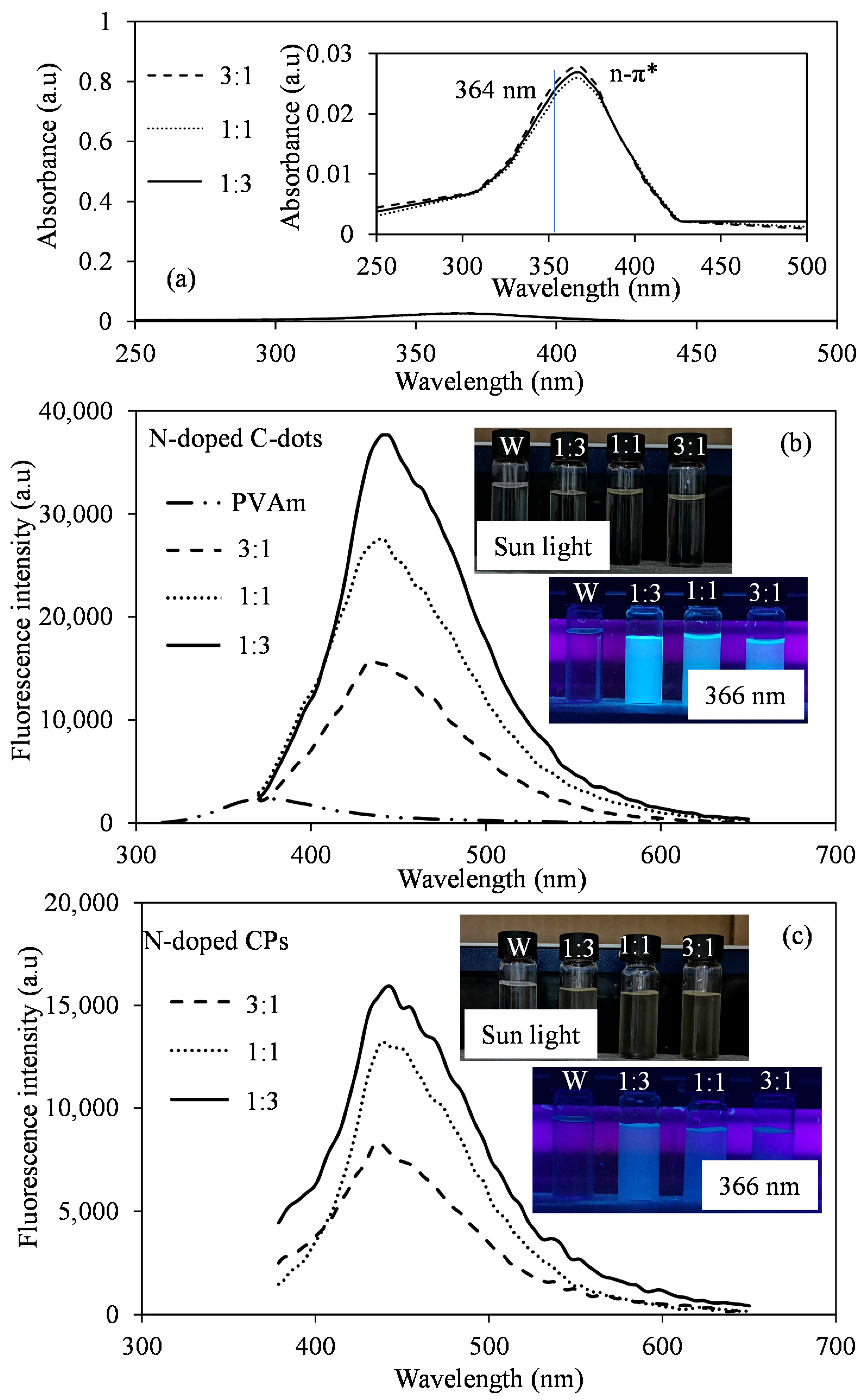
2.4. Characterization
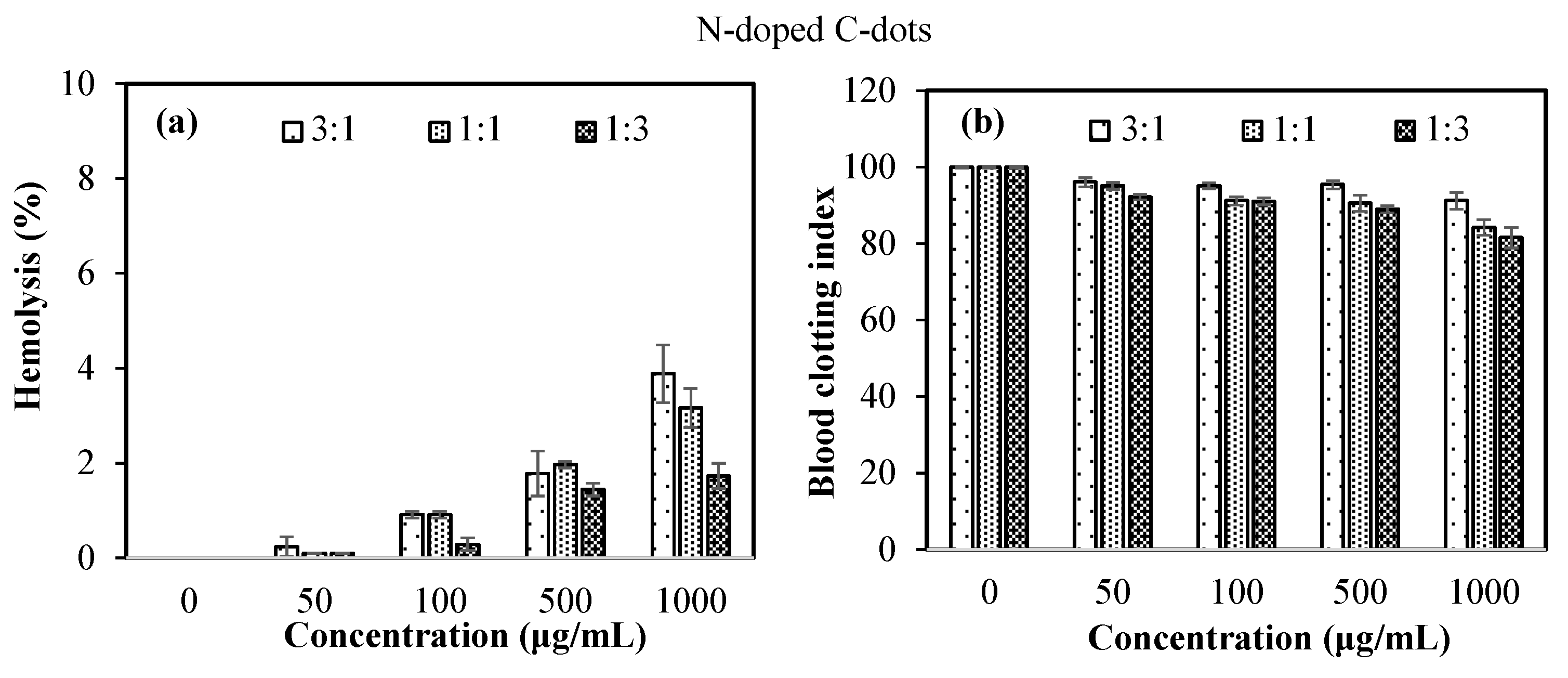
2.5. Blood Compatibility Analysis
2.6. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of N-Doped C-Dots
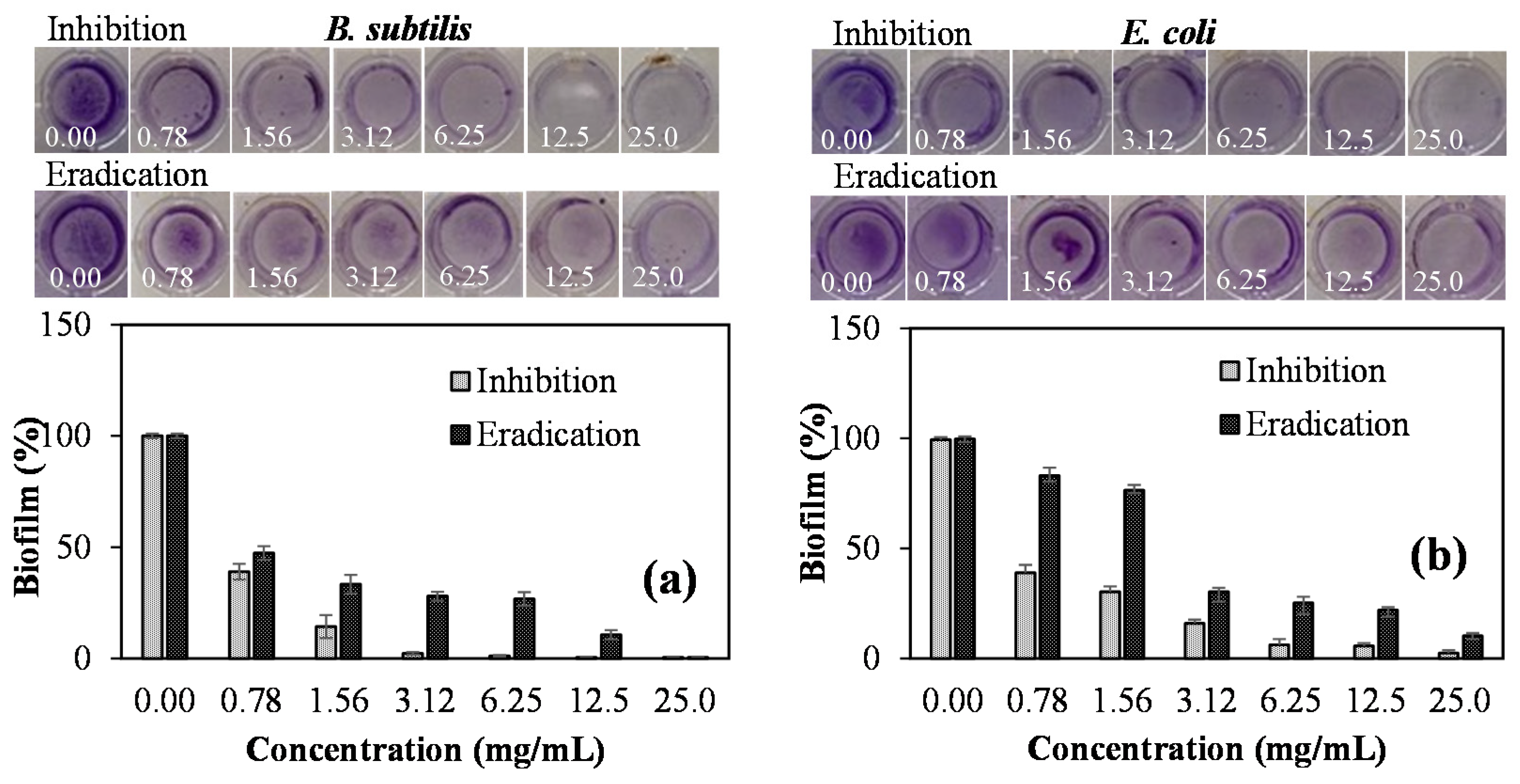
2.7. Biofilm Assays
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of CA:PVAm C-Dots
3.2. Blood Compatibility of N-Doped C-Dots
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity of N-Doped C-Dots
3.4. Antibiofilm Activity of CA:PVAm C-Dots
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, X.; Xiong, M.; Zhang, J.; He, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Kuang, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, Q. Carbon dots based on natural resources: Synthesis and applications in sensors. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon Dots: A New Type of Carbon-Based Nanomaterial with Wide Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Park, C.B. Photonic Carbon Dots as an Emerging Nanoagent for Biomedical and Healthcare Applications. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 6470–6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uriarte, D.; Vidal, E.; Canals, A.; Domini, C.E.; Garrido, M. Simple-to-use and portable device for free chlorine determination based on microwave-assisted synthesized carbon dots and smartphone images. Talanta 2021, 229, 122298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tam, T.; Hur, S.H.; Chung, J.S.; Choi, W.M. Novel paper- and fiber optic-based fluorescent sensor for glucose detection using aniline-functionalized graphene quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tian, F.; Wen, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, J. Selective determination of dopamine in pharmaceuticals and human urine using carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent probe. Processes 2021, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.Y.; Jayakumar, T.; Thanasekaran, P.; Lin, K.C.; Chen, H.M.; Veerakumar, P.; Sheu, J.R. Carbon dot nanoparticles exert inhibitory effects on human platelets and reduce mortality in mice with acute pulmonary thromboembolism. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashiya, N.; Padmini, N.; Ajilda, A.A.K.; Prabakaran, P.; Durgadevi, R.; Veera Ravi, A.; Ghosh, S.; Sivakumar, N.; Selvakumar, G. Inhibition of biofilm formation and quorum sensing mediated virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by marine sponge symbiont Brevibacterium casei strain Alu 1. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parastan, R.; Kargar, M.; Solhjoo, K.; Kafilzadeh, F. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: Structures, antibiotic resistance, inhibition, and vaccines. Gene Rep. 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.M.; Nguyen, M.T.H.; Bolhuis, A. Inhibition of biofilm formation by alpha-mangostin loaded nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Arora, N.; Chatrath, A.; Gangwar, R.; Pruthi, V.; Poluri, K.M.; Prasad, R. Delineating the biofilm inhibition mechanisms of phenolic and aldehydic terpenes against cryptococcus neoformans. ACS Omega 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, R.H.; Kalam Khan, F.A.; Jadhav, K.; Damale, M.; Akber Ansari, S.; Alkahtani, H.M.; Ali Khan, A.; Shinde, S.D.; Patil, R.; Sangshetti, J.N. Fungal biofilm inhibition by piperazine-sulphonamide linked Schiff bases: Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation. Arch. Der Pharm. 2018, 351, 1700354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Pan, J.; Tang, W.; Cao, W.; Zhou, J.; Gong, X.; Xing, X. Surface chemistry-dependent antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of polyamine-functionalized carbon quantum dots. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 16744–16757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harroun, S.G.; Lai, J.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Tsai, S.-K.; Lin, H.-J. Reborn from the Ashes: Turning Organic Molecules to Antimicrobial Carbon Quantum Dots. ACS Infect. Dis. 2017, 3, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Maruthapandi, M.; Das, P.; Ganguly, S.; Margel, S.; Luong, J.H.T.; Gedanken, A. Applications of N-Doped Carbon Dots as Antimicrobial Agents, Antibiotic Carriers, and Selective Fluorescent Probes for Nitro Explosives. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 8023–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Berkland, C. Acid-labile polyvinylamine micro- and nanogel capsules. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 4635–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.; Kwon, Y.S.; Moon, M.J.; Shon, M.Y.; Nam, S.E.; Park, Y.I. Poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(vinyl amine) blend membranes for isopropanol dehydration. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinskiy, S.N.; Danilovtseva, E.N.; Kandasamy, G.; Pal’Shin, V.A.; Shishlyannikova, T.A.; Krishnan, U.M.; Annenkov, V.V. Poly(vinyl amine) as a matrix for a new class of polymers. e-Polymers 2018, 18, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achari, A.E.; Coqueret, X.; Lablache-Combier, A.; Loucheux, C. Preparation of polyvinylamine from polyacrylamide: A reinvestigation of the hofmann reaction. Die Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1993, 194, 1879–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buys, H.C.W.M.; Vercauteren, F.F.; Van Elven, A.; Tinnernans, A.H.A. Molar fraction of VMAcm Acid hydrolysis of polymers and copolymers of N-vinyl-N-methylacetamide. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1081, 1088904, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Pelton, R. Polyvinylamine: A tool for engineering interfaces. Langmuir 2014, 30, 15373–15382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaiboonrod, S.; Cellesi, F.; Ulijn, R.V.; Saunders, B.R. One-step preparation of uniform cane-ball shaped water-swellable microgels containing poly (N-vinyl formamide). Langmuir 2012, 28, 5227–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illergård, J.; Wågberg, L.; Ek, M. Bacterial-growth inhibiting properties of multilayers formed with modified polyvinylamine. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henschen, J.; Larsson, P.A.; Illergård, J.; Ek, M.; Wågberg, L. Bacterial adhesion to polyvinylamine-modified nanocellulose films. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 151, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.D.; Deng, X.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, X.T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.L.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zheng, X.; et al. Layer-by-layer coating of polyvinylamine and dopamine-modified hyaluronic acid inhibits the growth of bacteria and tumor cell lines on the surface of materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 530, 147197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Zhu, S.; Hrymak, A.N. Acidic and basic hydrolysis of poly(N-vinylformamide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Zhu, S.; Hrymak, A.N.; Pelton, R.H. Kinetics and modeling of free radical polymerization of N-vinylformamide. Polymer 2001, 42, 3077–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Guo, S.; Xu, P.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, W.; Xue, M. Hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots with real-time live-cell imaging and blood-brain barrier penetration capabilities. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6325–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, S.; McNally, A.B.; Ayyala, R.S.; Lawson, L.B.; Sahiner, N. Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped carbon dots as fluorescent nanoprobes with antimicrobial properties and skin permeability. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, E.; Yahyaei, H.; Zamani, M.; States, U. Evaluation of the Mechanical properties and Blood compatibility of Polycarbonate Urethane and Fluorescent Self-colored Polycarbonate Urethane as Polymeric Biomaterials. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Chu, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Yao, C.; Zhou, N.; Shen, J. Insight into the effect of particle size distribution differences on the antibacterial activity of carbon dots. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 584, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, H.H.; Cheng, X.; Bao, Y.W.; Hua, X.W.; Gao, G.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Zhu, Y.-X.; Wu, F.-G. Multifunctional quaternized carbon dots with enhanced biofilm penetration and eradication efficiencies. J Mater Chem B 2019, 7, 5104–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, D.; Mao, H.; You, T. Multifunctional solid-state electrochemiluminescence sensing platform based on poly(ethylenimine) capped N-doped carbon dots as novel co-reactant. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, D.; Cao, Z.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G. Polymer dots of DASA-functionalized polyethyleneimine: Synthesis, visible light/pH responsiveness, and their applications as chemosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Dong, J.X.; Liu, S.G.; Li, N.; Lin, S.M.; Fan, Y.Z.; Lei, J.L.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. Carbon quantum dots prepared with polyethyleneimine as both reducing agent and stabilizer for synthesis of Ag/CQDs composite for Hg2+ ions detection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Pan, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, A.; Wu, S.; Shen, J. The carbonization of polyethyleneimine: Facile fabrication of N-doped graphene oxide and graphene quantum dots. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 105855–105861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Embrechts, H.; Damm, C.; Cadranel, A.; Strauss, V.; Distaso, M.; Hinterberger, V.; Guldi, D.M.; Peukert, W. Shedding light on the effective fluorophore structure of high fluorescence quantum yield carbon nanodots. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24771–24780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogi, T.; Aishima, K.; Permatasari, F.A.; Iskandar, F.; Tanabe, E.; Okuyama, K. Kinetics of nitrogen-doped carbon dot formation via hydrothermal synthesis. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 5555–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, H.S. Green synthesis of luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots from milk and its imaging application. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8902–8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudunkotuwa, I.A.; Grassian, V.H. Citric acid adsorption on TiO2 nanoparticles in aqueous suspensions at acidic and circumneutral pH: Surface coverage, surface speciation, and its impact on nanoparticle-nanoparticle interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14986–14994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Li, L.; Jin, W.J. Controlling speciation of nitrogen in nitrogen-doped carbon dots by ferric ion catalysis for enhancing fluorescence. Carbon 2017, 111, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, B.; Feng, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wu, P.; Zhao, D. Simple and Green Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Photoluminescent Carbonaceous Nanospheres for Bioimaging. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 8309–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, R.H.; Shan, D.; Fan, Y.R.; Zhang, X.J. Ethylenediamine-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for sensitive biosensing and bioimaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 218, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, K.A.S.; Sahu, S.; Liu, Y.; Lewis, W.K.; Guliants, E.A.; Jafariyan, A.; Wang, P.; Bunker, C.E.; Sun, Y.P. Carbon quantum dots and applications in photocatalytic energy conversion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8363–8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suner, S.S.; Sahiner, M.; Ayyala, R.S.; Bhethanabotla, V.R.; Sahiner, N. Nitrogen-Doped Arginine Carbon Dots and Its Metal Nanoparticle Composites as Antibacterial Agent. C J. Carbon Res. 2020, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yi, G.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C. A minireview on doped carbon dots for photocatalytic and electrocatalytic applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 13899–13906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holá, K.; Sudolská, M.; Kalytchuk, S.; Nachtigallová, D.; Rogach, A.L.; Otyepka, M.; Zbořil, R. Graphitic Nitrogen Triggers Red Fluorescence in Carbon Dots. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12402–12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, J.P.; Ray, A.R. Synthesis of blood compatible polyamide block copolymers. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-W.; Lee, H.-Y.; Kang, D.-H. Synergistic bactericidal effect of hot water with citric acid against Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilm formed on stainless steel. Food Microbiol. 2021, 95, 103676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Petterson, T.; Illergård, J.; Ek, M.; Wågberg, L. Influence of Cellulose Charge on Bacteria Adhesion and Viability to PVAm/CNF/PVAm-Modified Cellulose Model Surfaces. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Dai, X.; Gu, Z.; et al. Degradable Carbon Dots with Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 26936–26946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, W.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Zhou, N.; et al. Near-infrared carbon dot-based platform for bioimaging and photothermal/photodynamic/quaternary ammonium triple synergistic sterilization triggered by single NIR light source. Carbon 2021, 176, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malanovic, N.; Lohner, K. Gram-positive bacterial cell envelopes: The impact on the activity of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, L. One-step synthesis of blue–green luminescent carbon dots by a low-temperature rapid method and their high-performance antibacterial effect and bacterial imaging. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 155101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottenbos, B.; Grijpma, D.W.; Van Der Mei, H.C.; Feijen, J.; Busscher, H.J. Antimicrobial effects of positively charged surfaces on adhering Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 48, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, L.; Hartung, A.; Tramm, K.; Klinger-Strobel, M.; Jandt, K.D.; Makarewicz, O.; Pletz, M.W. MBEC Versus MBIC: The Lack of Differentiation between Biofilm Reducing and Inhibitory Effects as a Current Problem in Biofilm Methodology. Biol. Proced. Online 2019, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Du, S.; Tang, W.; Cao, W.; Zhou, J.; Gong, X.; Xing, X. Low-drug resistance carbon quantum dots decorated injectable self-healing hydrogel with potent antibiofilm property and cutaneous wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Zeta Potential (mV) | Particle Size (d.nm) | PDI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak 1 | %Int | Peak 2 | %Int | ||||
| N-doped C-dots | 3:1 | 27.4 ± 0.5 | 168 ± 10 | 91.6 | 31.8 ± 7 | 8.4 | 0.329 |
| 1:1 | 27.2 ± 0.6 | 148 ± 10 | 80.1 | 6.6 ± 3 | 19.9 | 0.258 | |
| 1:3 | 29.7 ± 0.1 | 12.6 ± 6 | 100 | - | - | 0.309 | |
| CPs | 3:1 | 26.4 ± 0.4 | 1422 ± 40 | 0.447 | |||
| 1:1 | 8.4 ± 0.1 | 951 ± 4 | 0.608 | ||||
| 1:3 | 35 ± 0.5 | 1218 ± 72 | 0.714 | ||||
| % | Ratio | CA:PVAm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-Doped C-Dots | CPs | ||
| QY | 3:1 | 20.1 ± 1.3 | 9.6 ± 0.8 |
| 1:1 | 33.8 ± 2.1 | 13.2 ± 1.1 | |
| 1:3 | 47.5 ± 1.9 | 17.8 ± 1.3 | |
| N-Doped C-Dots | B. subtilis | S. aureus | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (mg/mL) | MBC (mg/mL) | MIC (mg/mL) | MBC (mg/mL) | |
| CA | 0.75 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 3.12 |
| PVAm | 0.31 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 3.12 |
| 3:1 | 25.0 | N.D. | 25.0 | N.D. |
| 1:1 | 3.12 | 6.25 | 1.56 | 6.25 |
| 1:3 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 1.56 | 3.12 |
| Gentamicin | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| N-Doped C-Dots | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (mg/mL) | MBC (mg/mL) | MIC (mg/mL) | MBC (mg/mL) | |
| CA | 1.56 | 3.12 | 1.56 | 3.12 |
| PVAm | 3.12 | 12.5 | 1.56 | 3.12 |
| 3:1 | 25.0 | N.D. | 25.0 | N.D. |
| 1:1 | 1.56 | 6.25 | 1.56 | 3.12 |
| 1:3 | 1.56 | 3.12 | 1.56 | 3.12 |
| Gentamicin | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.004 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sutekin, S.D.; Sahiner, M.; Suner, S.S.; Demirci, S.; Güven, O.; Sahiner, N. Poly(Vinylamine) Derived N-Doped C-Dots with Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities. C 2021, 7, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7020040
Sutekin SD, Sahiner M, Suner SS, Demirci S, Güven O, Sahiner N. Poly(Vinylamine) Derived N-Doped C-Dots with Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities. C. 2021; 7(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7020040
Chicago/Turabian StyleSutekin, Semiha Duygu, Mehtap Sahiner, Selin Sagbas Suner, Sahin Demirci, Olgun Güven, and Nurettin Sahiner. 2021. "Poly(Vinylamine) Derived N-Doped C-Dots with Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities" C 7, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7020040
APA StyleSutekin, S. D., Sahiner, M., Suner, S. S., Demirci, S., Güven, O., & Sahiner, N. (2021). Poly(Vinylamine) Derived N-Doped C-Dots with Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities. C, 7(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7020040









