Bio-Chemical Fertilizer Improves the Oil Yield, Fatty Acid Compositions, and Macro-Nutrient Contents in Nigella sativa L.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Characteristics and the Region Weather Data
2.2. Soil Preparation and Sowing
2.3. Design and Measurements
2.4. Treatments
2.5. Application of Biofertilizers
2.6. Measurement of Morphological Traits
2.7. Estimation of Fatty Acid Content
2.8. Nitrogen Content
2.9. Estimation of Phosphorus Content
2.10. Estimation of Potassium Content
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
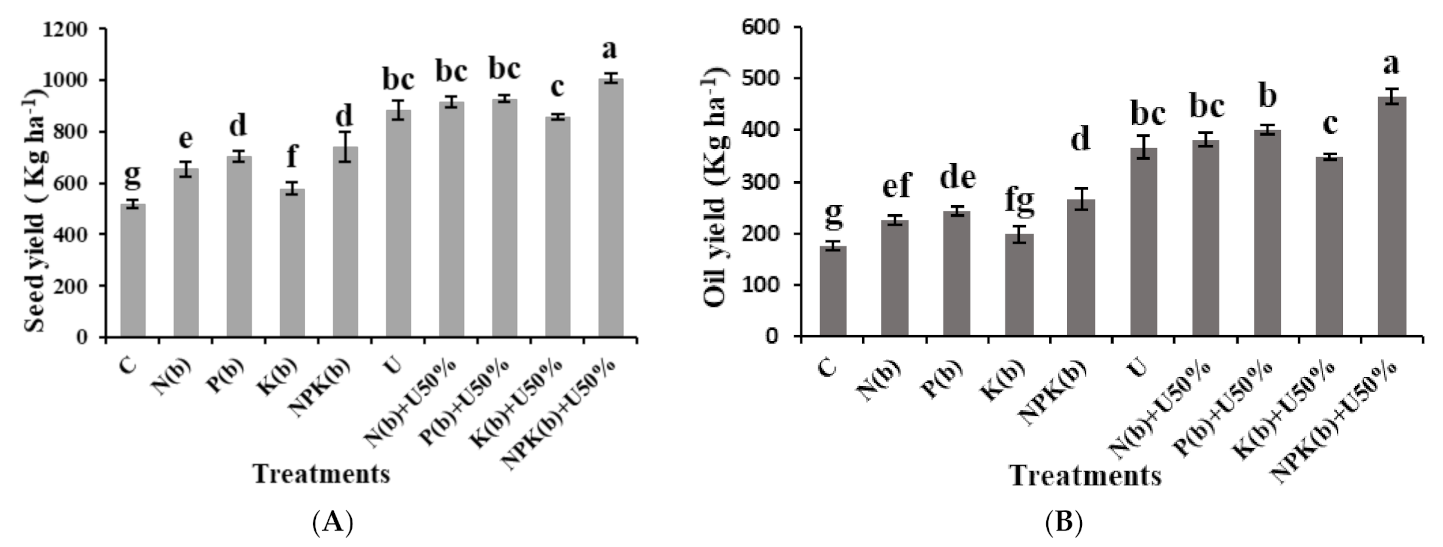
3.1. Seed Yield per Hectare
3.2. Oil Yield
3.3. Oil Percentage
3.4. Fatty Acid Profile of Seeds
3.4.1. Oleic Acid
3.4.2. Linoleic Acid
3.4.3. Linolenic Acid
3.4.4. Myristic Acid
3.4.5. Palmitic Acid
3.4.6. Stearic Acid
3.4.7. Graph of Unsaturated to Saturated Fatty Acid
3.5. The Accumulation of Macronutrients (NPK) in N. sativa Seeds
3.5.1. Seed N Content
3.5.2. Seed P Content
3.5.3. Seed K Content
4. Discussion
4.1. Seed Yield per Hectare
4.2. Oil Yield
4.3. Oil Percentage
4.4. Fatty Acid Profile of Seeds
4.5. The Accumulation of Macronutrients (NPK) in N. sativa Seeds
4.5.1. Seed N Percentage
4.5.2. Seed P Content
4.5.3. Seed K Content
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griffe, P.; Metha, S.; Shankar, D. Organic Production of Medicinal, Aromatic and Dye-Yielding Plants (MADPs): Forward, Preface and Introduction; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hamid, B.; Zaman, M.; Farooq, S.; Fatima, S.; Sayyed, R.; Baba, Z.; Sheikh, T.; Reddy, M.; El Enshasy, H.; Gafur, A.; et al. Bacterial Plant Biostimulants: A Sustainable Way towards Improving Growth, Productivity, and Health of Crops. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabborova, D.; Sayyed, R.; Azimov, A.; Jabbarov, Z.; Matchanov, A.; Enakiev, Y.; Baazeem, A.; EL Sabagh, A.; Danish, S.; Datta, R. Impact of mineral fertilizers on mineral nutrients in the ginger rhizome and on soil enzymes activities and soil properties. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 5268–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, S.; Bhat, R.; Kannan, C.; Balasimha, D. Impact of intercropping of medicinal and aromatic plants with organic farming approach on resource use efficiency in arecanut (Areca catechu L.) plantation in India. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2010, 33, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.; Lenzen, M.; Dey, C.; Lundie, S. A comparative study of some environmental impacts of conventional and organic farming in Australia. Agric. Syst. 2006, 89, 324–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majnoon Hosseini, N.; Davazdahemami, S. Cultivation and Production of Certain Herbs and Spices; Uni Tehran Press: Tehran, Iran, 2007; p. 300. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Kıralan, M. Changes in volatile compounds of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) seed oil during thermal oxidation. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Muhammad, Z.; Ahmad, H.; Hayat, S.S.S.; Inayat, N.; Siyyar, S. Nigella sativa L.: Uses in traditional and contemporary medicines–An overview. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 2020, 41, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Husain, A.; Mujeeb, M.; Khan, S.A.; Najmi, A.K.; Siddique, N.A.; Anwar, F. Review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa: A miracle herb. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grundy, S.M. What is the desirable ratio of saturated, polyunsaturated, and monounsaturated fatty acids in the diet? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 988S–990S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Hwang, Y.S.; Kim, S.T.; Yoon, W.B.; Han, W.Y.; Kang, I.K.; Choung, M.G. Seed coat color and seed weight con-tribute differential responses of targeted metabolites in soybean seeds. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, H.R.; Isaac, A.; Malcher-Lopes, R.; Diaz, B.L.; Trevenzoli, I.H.; de Melo Reis, R.A. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and endocannabinoids in health and disease. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 21, 695–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zárate, R.; El Jaber-Vazdekis, N.; Tejera, N.; Pérez, J.A.P.; Rodríguez, C. Significance of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in human health. Clin. Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinagaran, S.; Sridhar, S.; Eganathan, P. Chemical composition and antioxidant activities of black seed oil (Nigella sativa L.). Int. J. Pharmac. Sci. Res. 2016, 7, 4473. [Google Scholar]
- Moradzadeh, S.; Siavash Moghaddam, S.; Rahimi, A.; Pourakbar, L.; Sayyed, R.Z. Combined bio-chemical fertilizers ameliorate agro-biochemical attributes of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, L. Dairy products and plasma cholesterol levels. Food Nutr. Res. 2010, 54, 5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Da Costa, A.R.F.C.; Rolim, M.M.; Bonfim-Silva, E.M.; Neto, D.E.S.; Pedrosa, E.; e Silva, Ê.F.F. Accumulation of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in sugarcane cultivated under different types of water management and doses of nitrogen. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 2016, 10, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djajadi; Syaputra, R.; Hidayati, S.N. Effect of NPK fertilizer, biofertilizer containing N fixer and P solubilizer, and green manure of C. juncea on nutrients uptake and growth of sugarcane. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 418, 012068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, P.; Qalavand, A.; Moddares Sanavi, S. The effect of the application of different nutritional systems (organic, chemical, and integrated) and biofertilizer in grain yield and other agronomic traits of sunflower. Iran. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 1–10. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Hazarika, D.K.; Talukdar, N.C.; Phookan, A.K.; Saikia, U.N.; Das, B.C.; Deka, P.C. Influence of vesicular arbascular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on nursery establishment and growth of tea seeding in Assam. In Proceedings of the 17th World Congress of Soil Science, Bangkok, Thailand, 14–21 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jadid Soleimandarabi, M.; Hashemabadi, D.; Zaredost, F. The effect of potassium biofertilizer and chemical fertilizer on quantitative and qualitative traits of periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus cv. ‘Acillata’). J. Ornamen. Plants 2017, 7, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Vessey, J.K. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant. Soil 2003, 255, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.; Devaraj, P. Biomass and nutrient distribution and their return of Casuarina equisetifolia inoculated with biofertilizers in farm land. Biomass Bioenergy 2004, 26, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.S.; Lee, K.D. Effect of co-inoculation with phosphate and potassium solubilizing bacteria on mineral uptake and growth of pepper and cucumber. Plant. Soil. Environ. 2006, 52, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darakeh, S.A.S.S.; Weisany, W.; Diyanat, M.; Ebrahimi, R. Bio-organic fertilizers induce biochemical changes and affect seed oil fatty acids composition in black cumin (Nigella sativa Linn). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 164, 113383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedi, S.M.; Khajeh-Hosseini, M.J.; Moghaddam, P.R.; Shahandeh, H. Effects of phosphorus and seed priming on seed vigor, fatty acids composition and heterotrophic seedling growth of black seed (Nigella sativa L.) grown in a calcareous soil. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 74, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.M.; Villarreal, M.; Juarez, M.D.; Samman, N.C. Nitrogen contents in food: A comparison between the Kjeldahl and Hach methods. An. Asoc. Química Argent. 2004, 92, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Walinga, I.; Van der Lee, J.J.; Houba, V.J.G.; Van Vark, W.; Nomozamsky, I. Plant. Analysis Manual; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yasari, E.; Patwardhan, A.M. Effects of (Azotobacter and Azospirillum) inoculants and chemical fertilizers on growth and productivity of canola (Brassica napus L.). Asian J. Plant. Sci. 2007, 6, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhtar, M.; Siddiqui, Z. Effects of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms and Rhizobium sp. on the growth, nodulation, yield and root-rot disease complex of chickpea under field condition. Afr. J. Biotech. 2009, 8, 3489–3496. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, M.S.; Riaz, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Yasmeen, T.; Akhtar, M.J.; Riaz, M.A.; Buttler, A. Associative interplay of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa QS40) with nitrogen fertilizers improves sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) productivity and fertility of aridisol. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2016, 108, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, C.; Liang-Gang, Z.; Jun, X.; Qian, Z.; Yan, Z. Effects of biofertilizer on organically cultured cucumber growth and soil biological characteristics. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2010, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, R.S.; Namvar, A.; Sharifi, R.S. Grain filling and fatty acid composition of safflower fertilized with integrated nitrogen fertilizer and biofertilizers. Pesqui. Agr. Brasil 2017, 52, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefan, M.; Munteanu, N.; Stoleru, V.; Mihasan, M. Effects of inoculation with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on photosynthesis, antioxidant status and yield of runner bean. Rom. Biotech. Lett. 2013, 18, 8132–8143. [Google Scholar]
- Piras, A.; Rosa, A.; Marongiu, B.; Porcedda, S.; Falconieri, D.; Dessì, M.A.; Ozcelik, B.; Koca, U. Chemical composition and in vitro bioactivity of the volatile and fixed oils of Nigella sativa L. extracted by supercritical carbon dioxide. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 46, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Thelen, K.D.; Min, D.-H.; Smith, S.; Hao, X.; Gehl, R. Effects of Manure and Fertilizer Applications on Canola Oil Content and Fatty Acid Composition. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M. Effect of vermicompost and chemical fertilizers on growth, yield and quality of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) in a semi-arid tropical climate. J. Spices Arom. Crops 2012, 20, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, E.; Polat, T.; Sezek, M. The Effect of Sowing Date and Nitrogen Fertilizer form on Growth, Yield and Yield Components in sunflower. Turk. J. Field Crop. 2017, 22, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, P.; Ghalavand, A.; Sanavy, A.M.; AghaAlikhani, M.; Kalkhoran, S. Comparison of different nutritional levels and the effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on the grain yield and quality of sunflower. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 2011, 5, 1570. [Google Scholar]
- Shehata, M.M.; El-Khawas, S.A. Effect of two biofertilizers on growth parameters, yield characters, nitrogenous compo-nents, nucleic acids content, minerals, oil content, protein profiles and DNA banding pattern of sunflower (Helianthus annus L. cv. Vedock) yield. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2003, 6, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.-T.; Duan, Y.; Guo, T.-W.; Zhang, P.-L.; He, P.; Majumdar, K. Sunflower response to potassium fertilization and nutrient requirement estimation. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2802–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaie-Chiyaneh, E.; Amirnia, R.; Machiani, M.A.; Javanmard, A.; Maggi, F.; Morshedloo, M.R. Intercropping fennel (Foeniculum vulgare L.) with common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as affected by PGPR inoculation: A strategy for improving yield, essential oil and fatty acid composition. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, K.A.; Ross, S.A.; El-Sohly, M.A.; Khalafalla, M.M.; Abdel-Halim, O.B.; Ikegami, F. Effect of different fertilizers on the amino acid, fatty acid, and essential oil composition of Nigella sativa seeds. Saudi Pharm. J. 2000, 8, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Anandham, R.; Sridar, R.; Nalayini, P.; Poonguzhali, S.; Madhaiyan, M.; Sa, T. Potential for plant growth promotion in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cv. ALR-2 by co-inoculation of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and Rhizobium. Microbiol. Res. 2007, 162, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raei, Y.; Shariati, J.; Veisani, V. Effect of biological fertilizers on oil percentage, yield and yield components of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) in different levels of irrigation. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 25, 65–84. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Silva, L.R.; Pereira, M.J.; Azevedo, J.; Mulas, R.; Velazquez, E.; González-Andrés, F.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B. Inoculation with Bradyrhizobium japonicum enhances the organic and fatty acids content of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) seeds. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3636–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölzl, G.; Dörmann, P. Chloroplast Lipids and Their Biosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2019, 70, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, G.H.; Singhal, R.; Kachroo, A.; Kachroo, P. Fatty acid–and lipid-mediated signaling in plant defense. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 505–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aid, F. Plant lipid metabolism. In Lipid Metabolism; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li-Beisson, Y.; Shorrosh, B.; Beisson, F.; Andersson, M.X.; Arondel, V.; Bates, P.D.; Franke, R.B. Acyl-lipid metabolism. Arab. Book Am. Soc. Plant. Biol. 2013, 11, e0161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeidi, M.; Yaghoub, R.A.E.I.; Amini, R.; Taghizadeh, A.; Pasban-Eslam, B. Changes in Fatty Acid and Protein of Safflower as Response to Biofertilizers and Cropping System. Turk. J. Field Crop. 2018, 23, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, N.; Kumar, V.; Behl, R.K.; Deubel, A.; Gransee, A.; Merbach, W. Effect of P-solubilizing Azotobacter chroococcum on N, P, K uptake in P-responsive wheat genotypes grown under greenhouse conditions. J. Plant. Nut. Soil. Sci. 2000, 163, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.F.T.A.B.; Ashraf, M.; Asad, S.A.; Farooq, M. Effect of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms on phosphorus uptake, yield and yield traits of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in rainfed area. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2005, 7, 207–209. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, M.D.; Tiwari, D.D.; Chaudhari, S.K.; Biswas, D.R.; Narjary, B.; Meena, A.L.; Meena, R.B. Effect of biofertilizer and nutrient levels on yield and nutrient uptake by maize (Zea mays L.). Anna. Agri-Bio. Res. 2013, 18, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, K.K.; Tilak, V.B.R.; Saxena, A.K.; Dey, R.; Singh, C.S. Suppression of maize root diseases caused by Macrophomia phaseolina, Fusarium moniliforme and (Fusarium graminaerum) caused by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Microbiol. Res. 2001, 156, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeel, A.M.; Naglaa, S.A.T.; Sadek, A.A. Effect of bio-fertilizers on the growth, volatile oil yield and chemical composition of Ocimum basilicum L. Plant. Ann. Agr. Sci. Ain. Shams. Uni. Cairo 2002, 47, 351–371. [Google Scholar]
- Stamford, N.P.; Santos, P.R.D.; Moura, A.M.M.F.D.; Freitas, A.D.S.D. Biofertilzers with natural phosphate, sulphur and Acidithiobacillus in a siol with low available-P. Sci. Agr. 2003, 60, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.A.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Khalifa, Y.A.M. Efficiency of biofertilization on growth, yield, alkaloids content and chemical constitutes of Lupinus termis L. plants. Aust. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. 2012, 6, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Das, K.; Dang, R.; Shivananda, T.N. Influence of bio-fertilizers on the availability of nutrients (N, P and K) in soil in relation to growth and yield of Stevia rebaudiana grown in South India. Int. J. Appl. Res. Nat. Pro. 2008, 1, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Larbi, A.; Morales, F.; Abadía, A.; Gogorcena, Y.; Lucena, J.J.; Abadia, J. Effects of Cd and Pb in sugar beet plants grown in nutrient solution: Induced Fe deficiency and growth inhibition. Funct. Plant. Biol. 2002, 29, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, M.A.; El-Magd, M.A.; Hassan, H.A.; El-Sharky, M.F.Z. Effect of biofertilization, nitrogen sources, nitrogen levels and their interaction on the vegetative growth, chemical content and oil yield of sweet fennel. Egy. J. Appl. Sci. 2005, 20, 567–591. [Google Scholar]







| Month | Total Monthly Precipitation (mm) | Average Monthly Temperature (°C) | Average Monthly Relative Humidity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| March | 31.3 | 7.2 | 60.1 |
| April | 57.9 | 12.3 | 54.7 |
| May | 42.8 | 16.6 | 57.3 |
| June | 28.7 | 20.6 | 51.4 |
| July | 5.5 | 24.4 | 42.1 |
| Measured Trait | Soil of Study Site before Urea Application |
|---|---|
| Sampling depth (cm) | 0–30 |
| Salinity (dS/m) | 1.31 |
| Soil texture | Loam-clay |
| Acidity (pH) | 7.72 |
| Lime % (TNV) | 16.78 |
| Clay (%) | 44 |
| Silt (%) | 35 |
| Sand (%) | 21 |
| Organic carbon (%) | 0.91 |
| Nitrogen (%) | 0.03 |
| Phosphorous (mg/kg) | 10.33 |
| Potassium (mg/kg) | 398 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moradzadeh, S.; Siavash Moghaddam, S.; Rahimi, A.; Pourakbar, L.; El Enshasy, H.A.; Sayyed, R.Z. Bio-Chemical Fertilizer Improves the Oil Yield, Fatty Acid Compositions, and Macro-Nutrient Contents in Nigella sativa L. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7100345
Moradzadeh S, Siavash Moghaddam S, Rahimi A, Pourakbar L, El Enshasy HA, Sayyed RZ. Bio-Chemical Fertilizer Improves the Oil Yield, Fatty Acid Compositions, and Macro-Nutrient Contents in Nigella sativa L. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(10):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7100345
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoradzadeh, Samira, Sina Siavash Moghaddam, Amir Rahimi, Latifeh Pourakbar, Hesham A. El Enshasy, and R. Z. Sayyed. 2021. "Bio-Chemical Fertilizer Improves the Oil Yield, Fatty Acid Compositions, and Macro-Nutrient Contents in Nigella sativa L." Horticulturae 7, no. 10: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7100345
APA StyleMoradzadeh, S., Siavash Moghaddam, S., Rahimi, A., Pourakbar, L., El Enshasy, H. A., & Sayyed, R. Z. (2021). Bio-Chemical Fertilizer Improves the Oil Yield, Fatty Acid Compositions, and Macro-Nutrient Contents in Nigella sativa L. Horticulturae, 7(10), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7100345









