Abstract
Members of the family Tylenchidae are highly abundant in soil habitats, including agricultural settings, where they play key ecological roles. In the present study, we identified three Tylenchidae species, namely Basiria bhabi, Coslenchus acceptus, and Filenchus vulgaris, using integrative taxonomy. The detailed morphological and morphometric characteristics, distribution, and host associations of each species were also discussed. Phylogenetic analyses of these populations with other Tylenchidae nematodes indicated the presence of divergent lineages in Filenchus and Basiria, whereas Coslenchus appeared to be a monophyletic genus. Herein, we aim to grow awareness about this common but least studied group of nematodes. The species reported in this study are new records for Canada, revealing that the identified nematode diversity in our cultivated areas is relatively underrepresented. Our analyses also provided greater taxonomic resolution and captured rare taxa that might have been missed or misidentified in prior nematode inventory surveys. These findings will add to our understanding of the nematofauna of southern Alberta, thereby providing a more complete picture of existing nematode diversity present in the fields of this highly cultivated region.
1. Introduction
The nematode family Tylenchidae Örley [1] is exceptionally diverse in soil habitats. Members of this family have high ecological significance and prominence in both agricultural and natural systems [2,3,4]. Based on their life cycle strategies, Tylenchidae species have been given a colonizer–persister (cp) value of 2 [5]. Nematodes in the cp-2 category have ecological relevance as soil health indicators [5]. The taxonomic placement of Tylenchidae in terms of feeding behavior is controversial [6,7], since the feeding habits and food preferences of the majority of tylenchid genera are unknown. Thus, members of this family are either regarded as root hair/epidermal feeders [3], fungivores [8], or herbivores [9], or are generally referred to as plant associates [10].
The majority of Tylenchidae nematodes have similar general appearances, slender bodies, high intraspecific variation, and insufficient molecular data, posing great challenges to their classification and taxonomy [6]. Among plant-parasitic nematodes, Tylenchidae members have what is considered a “primitive morphology”, including weak stylets, weakly developed pharyngeal components, and long filiform tails. Subsequently, this family of nematodes has been preconceived to be economically insignificant and therefore often excluded from nematode surveillance and management programs [3,6,11]. In contrast, we believe that the identification of these nematodes is important, as they share a habitat with plant-parasitic nematodes [12,13]. Therefore, we focused on this neglected group of nematodes and found three species belonging to the genera Basiria Siddiqi [14], Coslenchus Siddiqi [15], and Filenchus Andrássy [16] from cultivated areas of southern Alberta, Canada.
Previous studies of the family Tylenchidae from Canada were limited to genus level identification of Basiria and Coslenchus [17,18], and to a few Filenchus species from high arctic areas [19,20,21]. This indicates that Tylenchidae nematodes are underrepresented and rarely documented in Canada. In the present study, we carefully examined the three Tylenchidae species found in southern Alberta and performed morphological and molecular analyses to confirm their identities. Detailed morphological examination revealed the presence of B. bhabi Siddiqi [22], C. acceptus Andrássy [23], and F. vulgaris (Brzeski) Lownsberry and Lownsberry [24,25]. Since all three species are first reports from Canada, the objectives of the present study were to (1) provide detailed morphometric and molecular characterizations of these species; (2) examine their phylogenetic relationships with related tylenchid nematodes; and (3) update the taxonomic records of these species from the new location of southern Alberta.
Our study provides increased taxonomic resolution and captures rare taxa that may have been missed or misidentified in prior nematode inventory surveys. Furthermore, our report will aid in filling the gaps of the virtually unknown nematofauna of southern Alberta, thereby providing a more complete picture of the existing nematode diversity present in the region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Morphological Studies
Continuing our wider program of uncovering soil nematofauna of southern Alberta, we collected several root and soil samples from the Vauxhall–Bow Island region. Nematodes were extracted from soil samples using the modified Cobb sieving and flotation-centrifugation method [26]. Basiria, Coslenchus, and Filenchus taxa were collected individually from the mixture of soil nematodes and assigned the population numbers 55, 60, and 70. For preliminary examinations, fresh adults of each species were transferred to a drop of distilled water, heat relaxed, and observed under a Zeiss Axioskope 40 microscope. For morphometric studies, nematodes were fixed, and permanent slides were prepared according to the methods of Seinhorst [27] and De Grisse [28]. Photomicrographs of each specimen were acquired using a Zeiss Axioskope 40 microscope equipped with a Zeiss Axiocam 208 camera (Carl Zeiss Microscopy, Jena, Germany). Measurements from the images were performed using ZEN blue 3.1 imaging software (Carl Zeiss Microscopy).
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Sequencing
After microscopic examination, a single nematode of each taxon was transferred to a 0.2 mL PCR tube, and DNA was extracted as described in Maria et al. [29]. Three sets of DNA primers (Integrated DNA Technologies, Coralville, IA, USA) were used to amplify the 18S (small subunit or SSU), 28S (large subunit or LSU), and ITS1 of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes. The partial 18S rRNA gene was amplified with 1813F and 2646R primers [30]. The 28S rRNA gene was amplified using D2A and D3B primers [31], and the ITS1 gene was amplified using F194 [32] and AB28-R primers [33]. For 18S, 28S, and ITS1 genes, the PCR conditions were as described in Holterman et al. [30], De Ley et al. [31], and Ferris et al. [32], respectively. Amplified PCR products were resolved by electrophoresis in 1% agarose gels and visualized by staining with GelRed (Biotium, Fremont, CA, USA). PCR products containing amplified DNA fragments of interest were sent to Genewiz, Inc. for DNA sequencing (South Plainfield, NJ, USA).
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
In the present study, we obtained DNA sequences for the 28S rRNA (D2–D3 domains), ITS1 rRNA, and 18S rRNA genes of three tylenchid populations. These sequences and additional Tylenchidae DNA sequences from GenBank were used for phylogenetic analysis. The selection of outgroup taxa for each dataset were based on previously published studies [34,35,36,37]. Multiple nucleotide sequence alignments for the different genes were performed using the heuristics progressive method FFT-NS-2 algorithm of MAFFT v.7.450 [38]. The BioEdit v7.2.5 program [39] was used for sequence alignment visualization. For alignment edition, we used Gblocks v0.91b [40] on the Castresana Laboratory server (available online: http://molevol.cmima.csic.es/castresana/Gblocks_server.html (accessed on 24 August 2021)) with options for a less stringent selection (minimum number of sequences for a conserved or a flanking position: 50% of the number of sequences + 1; maximum number of contiguous non-conserved positions: 8; minimum length of a block: 5; allowed gap positions: with half). Phylogenetic analyses were performed using Bayesian inference (BI) in MrBayes v3.1.2 [41]. The best-fit model of DNA evolution was achieved using JModelTest v2.1.7 [42] with the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC). Accordingly, the selected models were TIM2 + I + G, TIM3 + I + G, and GTR + G for the D2–D3 segments of the 28S rRNA, partial 18S, and ITS1, respectively. The best-fit model, base frequency, proportion of invariable sites, gamma distribution shape parameters, and substitution rates in the AIC were then used in MrBayes for the phylogenetic analyses, which ran with four chains for 4 × 106 generations in all datasets. A combined analysis of the three ribosomal genes was not undertaken due to several sequences not being available for all species. The sampling for Markov chains was carried out at intervals of 100 generations. For each analysis, two runs were conducted. After discarding burn-in samples of 30% and evaluating convergence, the remaining samples were retained for more in-depth analyses. The topologies were used to generate a 50% majority-rule consensus tree. On each appropriate clade, posterior probabilities (PP) were calculated. FigTree software v1.42 [43] was used for visualization of phylogenetic trees from all analyses.
3. Results
3.1. Description of Basiria bhabi
Female: Body shape slightly ventrally arcuate when heat relaxed. Cuticle finely annulated with lateral field having four lines, the outer lines not crenated. Lip region continuous, without striations, narrow with a weakly sclerotized framework. Stylet straight, slender, with fine lumen and small rounded knobs. Orifice of dorsal esophageal gland (DGO) close to stylet knobs. Median bulb oval and weakly developed, with inconspicuous valve plates situated at ca. 42–52% of pharyngeal length. Isthmus slender, surrounded with nerve ring gradually expanding into a cylindrical basal pharyngeal bulb. Excretory pore distinct, situated at the anterior region of pharyngeal bulb. Deirids present in the anterior region of basal pharyngeal bulb, only discernable in inverted specimen. Reproductive system mono-prodelphic, composed of a single, anteriorly outstretched gonad, with oocytes in one row; vulva smooth, vagina straight, weakly sclerotized; spermatheca not offset, irregular squarish-shaped, and mostly empty; post-vulval uterine sac shorter than vulval body diameter. Anus a minute pore, tail elongated and slender, ending in a rounded or clavate tip. Phasmid was not observed in any of the studied specimens (Figure 1, Table 1).
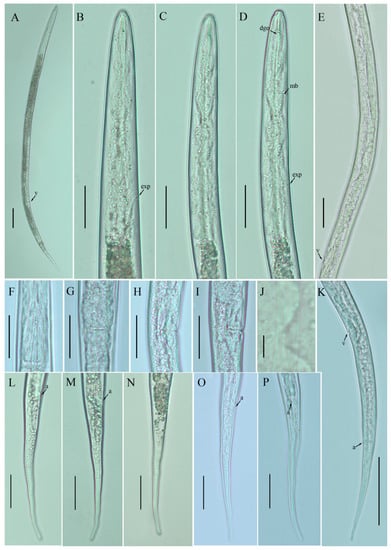
Figure 1.
Photomicrographs of Basiria bhabi female. (A) Entire body; (B–D) pharyngeal regions; (E) entire gonad; (F) basal pharyngeal bulb; (G) vulval region (ventral view); (H,I) vulval region (lateral view); (J) lateral lines; (K) posterior body to tail terminus; (L–O) tail regions (lateral view); (P) tail region (ventral view). Scale bars: (A,K) 50 µm; (B–I,L–P) 20 µm; (J) 5 µm. Arrowheads: (a) anus; (DGO) dorsal pharyngeal gland orifice; (exp) excretory pore; (mb) median bulb; (v) vulva.

Table 1.
Female morphometrics of Basiria bhabi from Canada and from the original description. All measurements are in µm and presented as mean ± standard deviation (range).
Male: Not found.
Juveniles: Present but not studied.
Remarks
Basiria bhabi was first described as B. indica by Bajaj and Bhatti in 1979 [44]; however, Siddiqi [22] recognized it as a junior homonym (i.e., a name for a taxon that is identical in spelling to another such name, which belongs to a different taxon) of B. indica described by Chawla et al. [45], and therefore renamed it B. bhabi. The species was described from India and was never reported outside of its type locality. The morphology and morphometry of the Canadian population agreed well with the original description of B. bhabi, except for the longer body length and longer tails. Since the original description of B. bhabi is based on the characteristics of a single specimen, we cannot precisely determine intraspecific variation. Consequently, we refer to the Canadian population of B. bhabi as the reference population for future studies, until topotypes of this species can be sequenced. The species was first discovered in the rhizosphere of Mangifera indica. In the present study this species was found in the rhizosphere of dandelion and grass growing on the headland of a cultivated potato field.
3.2. Description of Coslenchus acceptus
Female: Body open C-shaped to ventrally bent when heat relaxed. Cuticle widely annulated with 14 longitudinal ridges. Lateral field with four incisures. Lip region slightly offset, squarish, anteriorly flattened, with three to four annuli. Stylet straight, slender, with rounded knobs. Median bulb oval with refractive valve plates, situated at ca. 42–50% of pharyngeal length. Isthmus slender, encircled with nerve ring gradually expanding into a small pyriform basal pharyngeal bulb. Excretory pore at anterior end of basal bulb. Reproductive system mono-prodelphic, composed of an outstretched ovary with oocytes mostly in two rows, reflexed ovary was observed in some specimens; vulva sunken in body with large vulval flaps, vagina straight, weakly sclerotized; spermatheca irregular round-shaped, filled with few sperm; post-vulval uterine sac shorter than vulval body diameter. Anus a minute pore. Tail elongated, filiform, ending in a finely attenuated tip (Figure 2, Table 2).
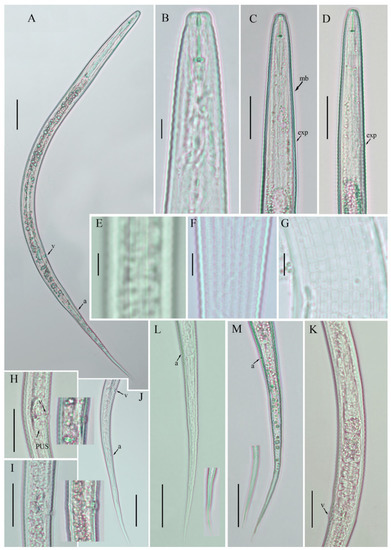
Figure 2.
Photomicrographs of Coslenchus acceptus female. (A) Entire body; (B) lip region; (C,D) pharyngeal regions; (E) lateral lines; (F,G) cuticular ridges; (H,I) vulval region; (J) posterior body to tail terminus; (K) entire gonad; (L,M) tail region. Scale bars: (A,J) 50 µm; (C,D; H,I; K–M) 20 µm; (B,E–G) 5 µm. Arrowheads: (a) anus; (exp) excretory pore; (mb) median bulb; (PUS) post-vulval uterine sac; (v) vulva.

Table 2.
Female morphometrics of Coslenchus acceptus from Canada and from the original description. All measurements are in µm and presented as mean ± standard deviation (range).
Male: Not found.
Juveniles: Present but not studied.
Remarks
This species was first described by Andrássy [23] from California, USA, in the rhizosphere of strawberry. The same author reported it from two other localities, namely Colorado, USA, and Újszentmargita, Hungary, in the rhizosphere of Carex sp. and Artemisia sp. Here, we found C. acceptus in the rhizosphere of grass growing on the headland of a cultivated potato field. To the best of our knowledge, after the formal description, the species was never reported again. The apparent morphology and morphometry of the C. acceptus original description agree well with the Canadian population except for the longer tail length (100–128 vs. 92–105 µm) and the presence (vs. absence) of a post-vulval uterine sac (PUS). In fresh specimens of the Canadian population, we were not able to observe any PUS; however, in permanent mounts we observed a small rudimentary PUS. The absence of a PUS in the original description could be related to the fixation technique used on specimens [23]. As for the longer tail of Canadian specimens, we agree with Brzeski [46], who stated that tail length in tylenchid nematodes cannot be accepted as a specific character because the filiform portion of the tail is attenuated and could easily break off during handling and processing of specimens.
3.3. Description of Filenchus vulgaris
Female: Body slightly ventrally arcuate when heat relaxed. Cuticle finely annulated with four lateral lines. Lip region hemispherical anteriorly flattened, continuous with body contour. Stylet straight, delicate, with rounded knobs. Median bulb oval with refractive valve plates, situated at ca. 39–45% of pharyngeal length. Isthmus slender, encircled with nerve ring gradually expanding into a small pyriform basal pharyngeal bulb. Excretory pore at anterior end of basal bulb. Reprod+uctive system mono-prodelphic, composed of an outstretched ovary with oocytes mostly in a single row; vulva smooth, vagina straight to slightly inclined anteriorly; spermatheca offset, irregular rounded shaped filled with few sperm; post-vulval uterine sac shorter than vulval body diameter. Anus a minute pore. Tail elongated, filiform, ending in a finely attenuated tip (Figure 3, Table 3).
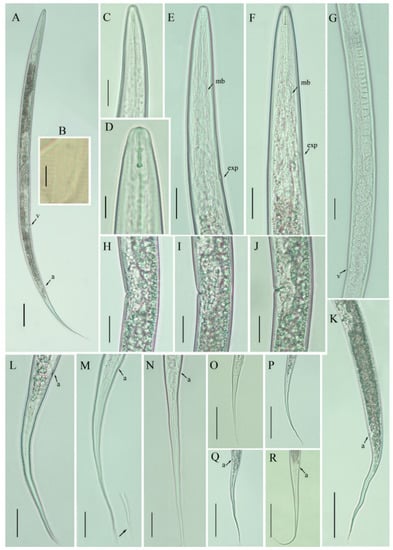
Figure 3.
Photomicrographs of Filenchus vulgaris female. (A) Entire body; (B) lateral lines; (C,D) lip regions; (E,F) pharyngeal regions; (G) entire gonad; (H–J) vulval regions; (K) posterior body till tail terminus; (L–R) tail regions. Scale bars: (A,K,O–R) 50 µm; (C,E–J,L–N) 20 µm; (B,D) 5 µm. Arrowheads: (a) anus; (exp) excretory pore; (mb) median bulb; (v) vulva.
Male: Not found.
Juveniles: Present but not studied.
Remarks
This species was described by Brzeski [24] in the rhizosphere of a vegetable crop from Poland. Filenchus vulgaris is considered to be a cosmopolitan species; it has been reported from Belgium, Germany, Iran, Korea, Poland, Russia, Slovakia, and the USA [9,24,25,47,48,49,50]. In the present study, the Canadian population of F. vulgaris was recovered from the rhizosphere of dandelion and grass growing on the headland of a cultivated potato field. Because of the widespread distribution of F. vulgaris, it has a broad host association. The species is known to occur in various biotypes, e.g., agricultural and forest soils and rhizospheres of grasses and vegetables [46,49]. Because F. vulgaris is a common species, morphometric studies were not always performed for the detected populations of this nematode (Table 3). Based on the available data, the morphological and morphometric details of the Canadian population are within the species boundaries of F. vulgaris.

Table 3.
Female morphometrics of Filenchus vulgaris from Canada and retrieved from the original and subsequent published descriptions. All measurements are in µm and presented as mean ± standard deviation (range).
Table 3.
Female morphometrics of Filenchus vulgaris from Canada and retrieved from the original and subsequent published descriptions. All measurements are in µm and presented as mean ± standard deviation (range).
| Brzeski [24] | Raski and Geraert [48] | Karegar and Geraert [49] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | Canadian Population | Poland | Colorado | Belgium | Korea | Iran |
| n * | 15 | 25 | 5 | 51 | 11 | 5 |
| Body length | 779.1 ± 61.8 (677.0–870.0) | 520–810 | 650–690 | 490–750 | 560–740 | 580–730 |
| a | 29.9 ± 2.8 (25.3–36.5) | 29–42 | 36–40 | 24–42.5 | – | 31.6–37.2 |
| b | 6.0 ± 0.3 (5.4–6.5) | 4.7–7.0 | 5.6–5.9 | 4.7–6.4 | 5.1–6.9 | 5.9–6.4 |
| c | 5.3 ± 0.4 (4.7–6.2) | 4.2–5.7 | 4.2–4.9 | 3.4–5.3 | 4.6–5.3 | 3.9–4.5 |
| c’ | 9.7 ± 1.0 (8.2–11.7) | 13 | 12–15 | – | – | 13.4–17.4 |
| V | 61.2 ± 1.4 (59.0–64.0) | 53–65 | 58–61 | 53–64 | 60–65 | 54.6–60.2 |
| MB | 41.2 ± 1.4 (39.7–45.1) | 44 | 40–43 | 40–48 | 39–44.5 | 38.1–45.8 |
| Lip height | 3.2 ± 0.3 (3.0–4.0) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Lip width | 6.5 ± 0.4 (6.0–7.0) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Stylet length | 10.5 ± 1.0 (9.0–12.0) | 10–12 | 10–11 | 9–12 | 9.5–10.5 | 8.1–10.5 |
| Dorsal pharyngeal gland orifice (DGO) | 1.5 ± 0.2 (1.0–2.0) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Median bulb length | 12.4 ± 0.9 (11.0–14.0) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Median bulb width | 7.7 ± 0.7 (7.0–9.0) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Pharynx length | 129.4 ± 5.8 (120.0–141.0) | 114 | 111–123 | 89–123 | 98–124 | 96–115 |
| Anterior end to excretory pore | 98.9 ± 6.8 (87.0–110.0) | 92–102 | 84–94 | – | – | – |
| Maximum body width | 26.3 ± 2.4 (22.0–30.0) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Vulva body width | 24.4 ± 1.9 (21.5–27.5) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Post-vulval uterine sac (PUS) length | 14.1 ± 1.8 (12.0–17.0) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Distance from vulva to anus | 149.3 ± 12.4 (125.0–166.0) | – | – | – | – | 105–122 |
| Anal body width | 15.3 ± 1.2 (13.0–17.0) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Tail length | 146.9 ± 12.0 (133.0–175.0) | 135 | 137–157 | 111–165 | 114–150 | 145–172 |
* Abbreviations: n, number of specimens on which measurements are based; a, body length/greatest body diameter; b, body length/distance from anterior end to pharyngo-intestinal junction; c, body length/tail length; c’, tail length/tail diameter at anus; V, distance from body anterior end to vulva expressed as percentage (%) of the body length; MB, distance between anterior end of body and center of median pharyngeal bulb expressed as percentage (%) of the pharynx length.
3.4. Molecular Characterization and Phylogenetic Relationship of Basiria bhabi, Coslenchus acceptus, and Filenchus vulgaris with Related Tylenchidae Species
The three Tylenchidae species recovered in this study were molecularly characterized using partial 18S, 28S, and ITS1 sequences. The newly obtained sequences were edited and submitted to NCBI under the following accession numbers: partial 18S (MZ959113 for C. acceptus); D2–D3 of 28S (MZ959290–MZ959292 for B. bhabi; MZ959293–MZ959294 for C. acceptus; MZ959295 for F. vulgaris); and ITS1 (MZ959284 for B. bhabi; MZ959285–MZ959286 for C. acceptus; MZ959287–MZ959288 for F. vulgaris).
In the 28S tree (Figure 4), B. bhabi clustered with species of subfamily Boleodorinae Khan [51] in a highly supported molecular clade (PP = 1.00). This clade further divided into two subclades where B. bhabi has a sister relationship with B. ritteri (Baqri and Jairajpuri) Bernard [52,53] (from China), and grouped with Discopersicus iranicus (Ghaemi, Pourjam, Atighi, Pedram, and Karssen) Yaghoubi et al. [54,55], Boleodorus volutus Lima and Siddiqi [56], and Boleodorus thylactus Thorne [57].
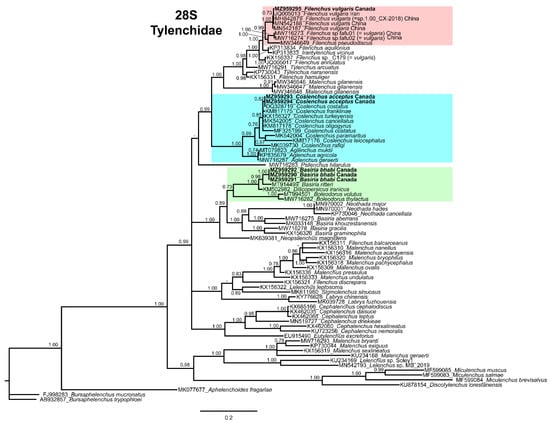
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic relationships of Basiria bhabi, Coslenchus acceptus, and Filenchus vulgaris within Tylenchidae. Bayesian 50% majority rule consensus tree as inferred from D2–D3 expansion domains of the 28S rRNA sequence alignment under the transition model with invariable sites and a gamma-shaped distribution (TIM2 + I + G). Posterior probabilities of greater than 0.70 are given for appropriate clades. Sequences produced in this study are shown in bold, and colored boxes indicate the clade association of each species detected in this study.
This clade further grouped with other species of Basiria (such as B. aberrans (Thorne) Siddiqi [58,59], B. gracilis (Thorne) Siddiqi [58,59], B. graminophila Siddiqi [14], B. khouzestanensis Eisvand, Farrokhi-Nejad, and Azimi [60]), Neothada Khan [61], and Neopsilenchus Thorne and Malek [62]. Our results support previous findings of Yaghoubi et al. [55] that monodelphic genera of Boleodorinae are monophyletic. Although B. bhabi is in the Boleodorinae clade, it grouped distantly from other Basiria species. The sequence identity of our B. bhabi with available Basiria species was 81–95% (38–149 nucleotide differences), with 0–6% indels.
In subfamily Atylenchinae Skarbilovich [63], the 28S-rRNA gene has been sequenced only for Coslenchus and Aglenchus Andrássy [16]. In our 28S tree, C. acceptus grouped with C. cancellatus (Cobb) Siddiqi [15,64]; C. costatus (de Man) Siddiqi [15,65]; C. franklinae Siddiqi [66]; C. leiocephalus Brzeski [67]; C. oligogyrus Brzeski [68]; C. paramaritus Hosseinvand, Eskandari, and Ghaderi [36]; C. turkeyensis Siddiqi [66]; C. rafiqi (Siddiqui and Khan) Siddiqi [22,69] and A. agricola (de Man) Andrássy [16,70]; A. geraerti Mizukubo [71]; and A. muktii Phukan and Sanwal [72]. The sequence identity of C. acceptus with the species of Coslenchus was 87–99%, with 87–99 nucleotide differences and 0–2% indels, whereas the identity with Aglenchus species was 90%, with 71–73 nucleotide difference and 2% indels.
In the 28S tree, members of subfamily Tylenchinae Örley [1] did not form a monophyletic group; species of Filenchus, Discotylenchus Siddiqi [73], Malenchus Andrássy [74], and Miculenchus Andrássy [75] were independently grouped at various positions of the tree. However, the Canadian population of F. vulgaris formed a clade with the sequences of F. vulgaris from the NCBI database and a few other species of Filenchus (namely, F. pseudodiscus Mortatazavi, Heydari, Abolafia, Castillo, and Pedram [37], F. aquilonius Wu [20], F. annulatus (Siddiqui and Khan) Siddiqi [22,69], F. hamuliger Brzeski [67] Tylenchus Bastian [76], and Malenchus as well. The tree also revealed that the sequence of Filenchus sp. deposited in the NCBI database under F. xuelouensis sp. n. (not published) is 99% identical (7 nucleotide difference) to the Canadian population of F. vulgaris; consequently, we refer to this as a population of F. vulgaris. In addition, the Canadian population of F. vulgaris showed 99% sequence identity (5–7 nucleotide difference and 0% indels) with F. vulgaris populations from China and Iran. The other supposed F. vulgaris populations from China (recovered from the rhizosphere of vegetables) showed 93% sequence identity (44 nucleotide difference and 1% indels) with our Canadian population of F. vulgaris. These sequences were deposited under F. vulgaris; however, no morphological or morphometric information is available to confirm their identity. Based on our results, we believe a detailed re-evaluation based on integrative taxonomy should be performed to determine the exact status of these species, which could have been previously misidentified.
The majority of studies conducted to understand the phylogenetic relationships of the family Tylenchidae is based on D2–D3 domains of the 28S gene. In contrast, very few Tylenchidae members were characterized by ITS1 sequences. Notably, no ITS1 sequence was found for the genus Basiria, and only a single ITS1 sequence was available for each of Filenchus and Coslenchus species. We constructed the ITS tree (Figure 5) with the available ITS sequences of Cephalenchus Goodey [77] and the Canadian populations of tylenchid nematodes. Basiria bhabi appeared independently and occupied a basal position in the tree, whereas C. acceptus clustered with C. rhombus, and F. vulgaris finally grouped with the F. vulgaris from China, initially identified as sp1 CX-2018. Due to the lack of ITS1 sequences, prediction of the phylogenetic relationships is uncertain; therefore, we omitted calculation of the sequence identity of the Canadian populations of tylenchid nematodes with related species.
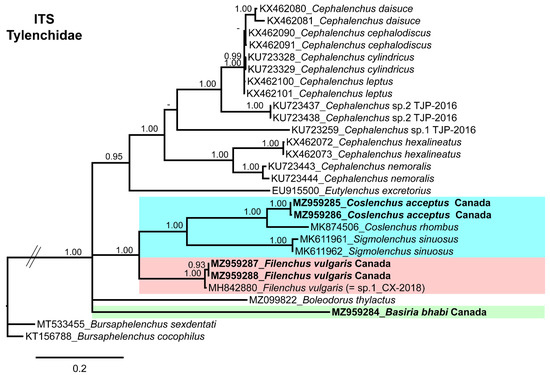
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic relationships of Basiria bhabi, Coslenchus acceptus, and Filenchus vulgaris within Tylenchidae. Bayesian 50% majority rule consensus tree as inferred from the ITS1 rRNA sequence alignment under the general time-reversible model and a gamma-shaped distribution (GTR + G). Posterior probabilities of more than 0.70 are given for appropriate clades. Sequences produced in this study are shown in bold, and colored boxes indicate clade association of each species detected in this study.
An 18S tree was constructed with the single sequence of C. acceptus and related Tylenchidae species sequences (Figure 6). As with the 28S and ITS trees, C. acceptus grouped within the Coslenchus clade. The sequence identity of C. acceptus with the Coslenchus clade species was 99%, with 4–9 nucleotide differences and 0–1% indels.
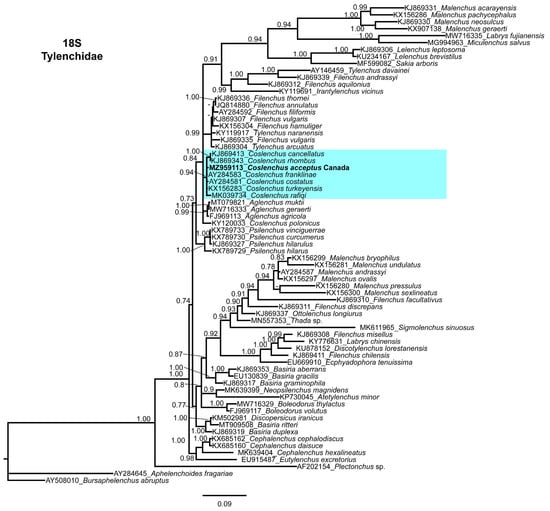
Figure 6.
Phylogenetic relationships of Coslenchus acceptus within Tylenchidae. Bayesian 50% majority rule consensus tree as inferred from the 18S rRNA sequence alignment under the transition model with invariable sites and a gamma-shaped distribution (TIM3 + I + G). Posterior probabilities of more than 0.70 are given for appropriate clades. Sequences produced in this study are shown in bold, and colored box indicate clade association of Coslenchus species.
The Canadian populations of B. bhabi, C. acceptus, and F. vulgaris obtained in this study were identified using an integrative taxonomical approach. Hence, the sequences of these populations could serve as reference sequences for future studies, until topotype specimens of these species can be sequenced.
4. Discussion
Members of the family Tylenchidae are highly abundant in agricultural soil, representing at least 30% of soil nematofauna in any given sample [6]. In the present study, the Canadian populations of B. bhabi, C. acceptus, and F. vulgaris were present at higher densities in headland vegetation (grasses and flowering plants) than those in field soils. The lower densities of these nematodes in field samples may be due to sampling depth, as Tylenchidae nematodes dominated in the upper 10 cm of soil, with their numbers declining with depth [78]. Another reason may simply be that these nematodes have adapted better to the headland vegetation because the headland area is less disturbed—not vigorously tilled as are the cultivated fields.
The family Tylenchidae is notorious for its complicated taxonomy and morphology, whereby phenotypic convergence of morphologically similar but genetically distant genera cause problems in the delimitation of taxa [6,35]. However, implementation of molecular tools allows nematologists to better study the characters and utilize them to distinguish the species [6,7,11,34,35,79]. In our phylogenetic analysis, B. bhabi exhibited a sister relationship with B. ritteri and clustered distant from the other species of Basiria. Such divergent phylogenetic placement suggests that Basiria is not a monophyletic genus. Currently, the genus contains over 40 nominal species [21,80], and the molecular information is only available for few species. In our view, genus-wide sequencing is needed to validate the true positioning and phylogenetic relationships of Basiria. Andrássy [23] did a thorough review of Coslenchus and concluded that the genus is homogenous. This close morphological affinity is also reflected in several phylogenetic studies [7,36,81] where all the Coslenchus species form a monophyletic clade. Our results are also in line with these studies, i.e., the Canadian population of C. acceptus was nested within the Coslenchus clade with very little sequence divergence. Filenchus is one of the most diverse genera in the subfamily Tylenchinae, currently representing over 90 species [21]. Phylogenetic studies have indicated the presence of divergent lineages in Filenchus; therefore, superficial observation of morphologically similar species can lead to misidentifications [82]. We also observed questionable sequences of F. vulgaris deposited in the NCBI database. Moreover, no morphological or morphometric details were associated with these supposed sequences. Therefore, future studies are well advised to meticulously examine species morphological characters and use the same specimen for morphological and molecular studies. Nevertheless, molecular studies of Tylenchidae genera are important to expand our knowledge of these microscopic, morphologically-reduced organisms [6].
The feeding habits of the majority of Tylenchidae nematodes are barely known; the species we detected in this study were all isolated from the rhizosphere of plants. We did not observe significant root damage or mycelial growths at the time of sampling, which suggests that Canadian populations of B. bhabi, C. acceptus, and F. vulgaris are plant-feeding rather than plant-parasitic nematodes. The detection of these species in our cultivated areas updates the biogeography of these nematodes; however, there is still lack of knowledge on the diversity of tylenchid species from southern Alberta, Canada. It is likely that tylenchid species not directly implicated in plant diseases will remain undocumented for years to come.
5. Conclusions
In southern Alberta, the presence of phytoparasitic nematodes has been examined in several studies [12,13,83], but detection and identification of Tylenchidae-related nematodes had never been addressed. As a result, we know almost nothing about insignificant or mild parasitic nematodes that share the same habitat with economically important plant-parasitic nematodes. Herein, we aim to grow awareness about a less studied group of nematodes. We believe that including more species in nematode surveillance programs is both a step forward in understanding the nematofauna of agro-ecosystems and an essential component for the assessment of soil biodiversity in any management plan. It is also a promising direction for both taxonomy and education. In addition, our results suggest that the nematode diversity in our cultivated areas is underrepresented, since the species reported in this study are all new records for Canada. This study updates the biogeography of B. bhabi, C. acceptus, and F. vulgaris from Canada.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M., D.P.Y. and P.C.; methodology, M.M., D.P.Y. and P.C.; software, M.M., D.P.Y. and P.C.; validation, M.M., D.P.Y. and P.C.; formal analysis, M.M. and P.C.; investigation, M.M. and D.P.Y.; resources, M.M., D.P.Y. and P.C.; data curation, M.M. and P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M. and D.P.Y.; writing—review and editing, M.M., D.P.Y. and P.C.; visualization, M.M. and P.C.; supervision, M.M. and D.P.Y.; project administration, D.P.Y.; funding acquisition, D.P.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Potato Early Dying Complex project funded by the University of Lethbridge Research Operating Fund, and the Canadian Potato Early Dying Network project funded by the Canadian Agri-Science Cluster for Horticulture 3 grant to D.P.Y., in collaboration with the Potato Growers of Alberta (Taber, AB, Canada), McCain Foods Canada Ltd. (Chin, AB, Canada), Cavendish Farms Corp. (Lethbridge, AB, Canada), and Lamb Weston Inc (Purple Springs, AB, Canada).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank potato growers in Alberta, Canada, for providing access to their fields, and Mariana Vetrici and Atta Ur Rahman (University of Lethbridge, AB, Canada) for the collection of soil samples. We also thank Carolina Cantalapiedra-Navarrete (Institute for Sustainable Agriculture (IAS), CSIC, Córdoba, Spain), for the excellent technical assistance in molecular analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Örley, L. Monograph of the Anguillulids. Természetrajzi Füzetek 1880, 4, 16–150. [Google Scholar]
- Geraert, E. Tylenchidae in agricultural soils. In Manual of Agricultural Nematology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1991; pp. 795–826. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, M. Tylenchida Parasites of Plants and Insects; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2000; p. 833. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, M.; Qing, X.; Qiao, K.; Ning, X.; Xiao, S.; Cheng, X.; Liu, G. Mitochondrial COI gene is valid to delimitate Tylenchidae (Nematoda: Tylenchomorpha) species. J. Nematol. 2020, 52, e2020-38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bongers, T.; Bongers, M. Functional diversity of nematodes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1998, 10, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Bert, W. Family Tylenchidae (Nematoda): An overview and perspectives. Org. Divers. Evol. 2019, 19, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahandeh, Y.; Pourjam, E.; Pedram, M. Data on some species of the genus Coslenchus Siddiqi, 1978 (Rhabditida, Tylenchidae) from Iran. J. Nematol. 2016, 48, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, H.; Harada, H.; Kadota, I. Fungal-feeding habits of six nematode isolates in the genus Filenchus. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čerevková, A.; Miklisová, D.; Bobuľská, L.; Renčo, M. Impact of the invasive plant Solidago gigantea on soil nematodes in a semi-natural grassland and a temperate broadleaved mixed forest. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSorley, R.; Frederick, J. Nematode population fluctuations during decomposition of specific organic amendments. J. Nematol. 1999, 31, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira, T.J.; Baldwin, J.G. Contrasting evolutionary patterns of 28S and ITS rRNA genes reveal high intragenomic variation in Cephalenchus (Nematoda): Implications for species delimitation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 98, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, M.; Yevtushenko, D.P.; Castillo, P. Integrative taxonomy, distribution, and host associations of Geocenamus brevidens and Quinisulcius capitatus from southern Alberta, Canada. J. Nematol. 2021, 53, e2021-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, M.; Yevtushenko, D.P.; Palomares-Rius, J.E.E.; Castillo, P. Species diversity of pin nematodes (Paratylenchus spp.) from potato growing regions of southern Alberta, Canada. Plants 2021, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, M.R. Basiria graminophila ng, n. sp. (Nematoda: Tylenchinae) found associated with grassroots in Aligarh India. Nematologica 1959, 4, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, M.R. The unusual position of the phasmids in Coslenchus costatus (de Man, 1921) gen. n., comb. n. and other Tylenchidae (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Nematologica 1978, 24, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrássy, I. Revision der Gattung Tylenchus Bastian, 1865 (Tylenchidae, Nematoda). Acta Zool. Hung 1954, 1, 5–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lumactud, R.A. Spatial Distribution of Soil Nematodes in the Sub-Arctic Environment of Churchill, Manitoba. Master’s Thesis, The University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, F.G. Survey of plant-parasitic nematodes in pulse crop fields of the Canadian prairies. Master’s Thesis, The University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.-Y. Dactylotylenchus crassacuticulus, a new genus and new species (Tylenchinae: Nematoda). Can. J. Zool. 1968, 46, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-Y. Five new species of Tylenchus Bastian, 1865 (Nematoda: Tylenchidae) from the Canadian high Arctic. Can. J. Zool. 1969, 47, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraert, E. The Tylenchidae of the World: Identification of the Family Tylenchidae (Nematoda); Academia Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, M. Tylenchida Parasites of Plants and Insects; Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux Farnham Royal: Slough, UK, 1986; 646p. [Google Scholar]
- Andrássy, I. The genera and species of the family Tylenchidae Örley, 1880 (Nematoda): The genus Coslenchus Siddiqi, 1978. Acta Zool. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1982, 28, 193–232. [Google Scholar]
- Brzeski, M. Tylenchus ditissimus sp. n., a new nematode from Poland (Nematoda, Tylenchidae). Bulletin de l’Academie Polonaise des Sciences. Cl. II Ser. Sci. Biol. 1963, 11, 537–540. [Google Scholar]
- Lownsbery, J.; Lownsbery, B. Plant-parasitic nematodes associated with forest trees in California. Hilgardia 1985, 53, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jenkins, W. A rapid centrifugal-flotation technique for separating nematodes from soil. Plant. Dis. Rep. 1964, 48, 692. [Google Scholar]
- Seinhorst, J. A rapid method for the transfer of nematodes from fixative to anhydrous glycerin. Nematologica 1959, 4, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Grisse, A.T. Redescription ou modifications de quelques technique utilis [a] es dan l’etude des n [a] ematodes phytoparasitaires. Meded. Rijksfakulteit Landbowwetenschappen Gent. 1969, 34, 351–369. [Google Scholar]
- Maria, M.; Powers, T.; Tian, Z.; Zheng, J. Distribution and description of criconematids from Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China. J. Nematol. 2018, 50, 183–206. [Google Scholar]
- Holterman, M.; van der Wurff, A.; van den Elsen, S.; van Megen, H.; Bongers, T.; Holovachov, O.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ley, P.; Felix, M.-A.; Frisse, L.; Nadler, S.; Sternberg, P.; Thomas, W.K. Molecular and morphological characterisation of two reproductively isolated species with mirror-image anatomy (Nematoda: Cephalobidae). Nematology 1999, 1, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, V. Variation in spacer ribosomal DNA in some cyst-forming species of plant parasitic nematodes. Fundam. Appl. Nematol. 1993, 16, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Curran, J.; Driver, F.; Ballard, J.; Milner, R. Phylogeny of Metarhizium: Analysis of ribosomal DNA sequence data. Mycol. Res. 1994, 98, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.J.; Qing, X.; Chang, K.F.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Cares, J.E.; Ragsdale, E.J.; Nguyen, C.N.; Baldwin, J.G. Phylogeny and biogeography of the genus Cephalenchus (Tylenchomorpha, Nematoda). Zool. Scr. 2017, 46, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Decraemer, W.; Claeys, M.; Bert, W. Molecular phylogeny of Malenchus and Filenchus (Nematoda: Tylenchidae). Zool. Scr. 2017, 46, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinvand, M.; Eskandari, A.; Ghaderi, R. Morphological and molecular characterization of Coslenchus paramaritus n. sp. and C. cancellatus (Cobb, 1925) Siddiqi, 1978 (Nematoda: Tylenchidae) from Iran. J. Nematol. 2019, 51, e2019-59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortazavi, P.; Heydari, F.; Abolafia, J.; Castillo, P.; Pedram, M. Morphological and molecular characterization of Filenchus pseudodiscus n. sp. from east Golestan province, north Iran; with an updated phylogeny of Malenchus Andrássy, 1968 (Tylenchomorpha: Tylenchidae). J. Nematol. 2021, 53, e2021-69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, T. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1. 4.2, a Graphical Viewer of Phylogenetic Trees. 2014. Available online: https://github.com/rambaut/figtree (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Bajaj, H.; Bhatti, D. Two new species of Basiria Siddiqi, 1959 (Tylenchida) from Haryana, India. Indian J. Nematol. 1979, 8, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, M.; Prasad, S.; Khan, E.; Nand, S. Two new species of the genus Tylenchus Bastian, 1865 (Nematoda: Tylenchidae) from Utter Pradesh, India. Labdev. J. Sci. Technol. 1969, 4, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Brzeski, M. Redescription of some species of the genus Filenchus Andrássy, 1954 (Nematoda, Tylenchidae). Miscel Lània Zoològica 1997, 20, 45–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kazachenko, I. New nematode species of the family Tylenchidae Örley, 1880, form litters of coniferous forests. Biol. Pochviennovo Inst. Novaya Ceriya Vladivostok 1975, 26, 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Raski, D.; Geraert, E. Review of the genus Filenchus Andrássy, 1954 and descriptions of six new species (Nemata: Tylenchidae). Nematologica 1986, 32, 265–311. [Google Scholar]
- Karegar, A.; Geraert, E. The Genus Filenchus Andrássy, 1954 (Nemata: Tylenchidae) from Iran. Belg. J. Zool. 1995, 125, 363–382. [Google Scholar]
- Sturhan, D.; Hohberg, K. Nematodes of the order Tylenchida in Germany–the non-phytoparasitic species. Soil Org. 2016, 88, 19–41. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, E. Boleodorus mirus n. sp. (Tylenchida: Boleodorinae n. subfam.) from Kufri, Simla (HP) India, with a key to the species of the genus Boleodorus Thorne, 1941. Zool. Anz. 1964, 173, 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Baqri, Q.H.; Jairajpuri, M.S. Two known and three new species of nematodes associated with fibrous crops in India. Ann. Zool. Ecol. Anim. 1969, 1, 327–337. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, E. Ditylenchus intermedius (De Man) Filipjev (Nematoda: Anguinidae) and Basiria hiberna, n. sp. (Nematoda: Psilenchidae) from Tennessee. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1980, 93, 303–310. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaemi, R.; Pourjam, E.; Atighi, M.R.; Pedram, M.; Karssen, G. First record of the genus Discotylenchus Siddiqi, 1980 (Nematoda: Tylenchidae) from Iran, with description of one new and data on two known species. Zootaxa 2012, 3493, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubi, A.; Pourjam, E.; Alvarez-Ortega, S.; Liebanas, G.; Atighi, M.R.; Pedram, M. Discopersicus n. gen., a new member of the family Tylenchidae Örley, 1880 with detailed SEM study on two known species of the genus Discotylenchus Siddiqi, 1980 (Nematoda; Tylenchidae) from Iran. J. Nematol. 2016, 48, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, M.; Siddiqi, M.R. Boleodorus volutus n. sp. (Nematoda: Nothotylenchinae) found in soil about grass roots in England. Nematologica 1963, 9, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, G. Some nematodes of the family Tylenchidae which do not possess a valvular median esophageal bulb. Great Basin Nat. 1941, 2, 37–85. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, G. On the classification of the Tylenchida, new order (Nematoda, Phasmidia). Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1949, 16, 37–73. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, M.R. Four new species of the genus Tylenchus Bastian, 1865 (Nematoda) from North India. Z. Für Parasitenkd. 1963, 23, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisvand, P.; Nejad, R.F.; Azimi, S. Description of Basiria khouzestanensis n. sp. (Nematoda: Tylenchidae) from Iran and its phylogenetic relationships with other species in the family. Zootaxa 2019, 4563, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S. On the proposal for Neothada n. gen.(Nematoda: Tylenchinae). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. India Biol. Sci. 1973, 43, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, G.; Malek, R.B. Nematodes of the northern Great Plains. Part I. Tylenchida (Nemata: Secernentea). Tech. Bull. S. Dakota Agric. Exp. Stn. 1968, 31, 1–111. [Google Scholar]
- Skarbilovich, T. On the structure of systematics of nematodes order Tylenchida Thorne, 1949. Acta Parasitol. Pol. 1959, 7, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, N. Biological relationships of the mathematical series 1, 2, 4, etc., with a description of a new nema, Tylenchus Cancellatus. Contrib. A Sci. Nematol. 1925, 15, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- de Man, J.C. Nouvelles recherches sur les nématodes libres terricoles de la Hollande. Capita Zool. 1921, 1, 3–62. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, M.R. Six new species of Coslenchus Siddiqi, 1978 (Nematoda: Tylenchidae). Nematologica 1980, 26, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzeski, M.W. Nematodes of Tylenchina in Poland and Temperate Europe; Muzeum i Instytutu Zoologii, Polska Akademia Nauk (MiIZ PAN): Warsaw, Poland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Brzeski, M.W. Taxonomic Notes on Coslenchus Siddiqi, 1978 (Nematoda: Tylenchidae). Ann. Zool. 1987, 40, 417–436. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, A.; Khan, E. Taxonomic studies on tylenchidae (nematoda) of India. II. Descriptions of two new sp. of Cosaglenghus gen. n. alongwith proposition of a new sub-family aglenchinae. Indian J. Nematol. 1982, 12, 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- de Man, J.G. Die, Frei in der Reinen Erde und Im Süssen Wasser Lebenden Nematoden der Niederländischen Fauna: Eine Systematisch-Faunistische Monographie; EJ Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1884; Volume 1, p. 206. [Google Scholar]
- Mizukubo, T. Aglenchus ainakamurae n. sp. and records of Cephalenchus leptus and Lelenchus leptosoma from Japan (Tylenchida: Tylenchidae). Jpn. J. Nematol. 1989, 19, 18–31. [Google Scholar]
- Phukan, P.; Sanwal, K. Two new species of Aglenchus and record of Cephalenchus leptus (Tylenchidae: Nematoda) from Assam. Indian J. Nematol 1980, 10, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, M.R. Two new nematode genera, Safianema (Anguinidae and Discotylenchus (Tylenchidae), with descriptions of three new species. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1980, 47, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Andrássy, I. Fauna Paraguayensis. 2. Nematoden aus den Galeriewäldern des Acaray-Flusses. Opusc. Zool. Bp. 1968, 8, 167–312. [Google Scholar]
- Andrássy, I. Freilebende nematoden aus Rumänien. Annales Universitatis Scientiarum Budapestinensis de Rolando Eotvos Nominatae. Sect. Biol. 1959, 2, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Bastian, H.C., II. Monograph on the Anguillulidæ, or Free Nematoids, Marine, Land, and Freshwater; with Descriptions of 100 New Species. Trans. Linn. Soc. Lond. 1865, 25, 73–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodey, J. Tylenchus (Cepha-lenchus) megacephalus n. sbg., n. sp. Nematologica 1962, 7, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschoor, B.C.; de Goede, R.G.; de Hoop, J.-W.; de Vries, F.W. Seasonal dynamics and vertical distribution of plant-feeding nematode communities in grasslands. Pedobiologia 2001, 45, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Bert, W. Redefinition of genus Malenchus Andrássy, 1968 (Tylenchomorpha: Tylenchidae) with additional data on ecology. J. Nematol. 2017, 49, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azimi, S. Description of Basiria iranica sp. nov. (Nematoda: Tylenchidae) from southwestern Iran and its phylogenetic relationships. Ann. Zool. 2021, 71, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, K.; Bai, M.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiao, S.; Cheng, X.; Liu, G.; Braun-Miyara, S.; Qing, X. Description of Labrys fuzhouensis sp. n. and first record of Coslenchus rafiqi (Nematoda: Tylenchidae) from China. Nematology 2019, 21, 693–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Pereira, T.J.; Slos, D.; Couvreur, M.; Bert, W. A new species of Malenchus (Nematoda: Tylenchomorpha) with an updated phylogeny of the Tylenchidae. Nematology 2018, 20, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forge, T.A.; Larney, F.J.; Kawchuk, L.M.; Pearson, D.C.; Koch, C.; Blackshaw, R.E. Crop rotation effects on Pratylenchus neglectus populations in the root zone of irrigated potatoes in southern Alberta. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2015, 37, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).