Abstract
Konjac (Amorphophallus konjac K. Koch) is a well-known tuberous vegetable belonging to the important medicinal family Araceae, and the plant grows from an underground tuber. Here, we used a “one-step seedling regeneration” tissue culture system to improve the plantlet regeneration efficiency of konjac using young leaves as an explant source. In the current study, we used several sterilization methods for tuber sterilization. Moreover, various plant growth regulator combinations were applied to achieve efficient somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration. Our results showed that the optimal tuber sterilization was method C (75% alcohol for 15 s + 0.1% HgCl2 for 15 min + washing by double-sterilized water three times). Three types of embryogenic calli were induced on full-strength Murashige and Skoog (MS) basal medium supplemented with 0.5 mg/L of 6-benzylaminopurine (6-BA), 0.5 mg/L of naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA), 1.0 mg/L of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), and 30 g/L of sucrose. Of the three types of embryogenic calli, only type Ⅲ further regenerated plantlets, with a callus induction rate of 55.73% and a seedling induction rate of 92.73%. This suggests that the addition of the above hormones gives the optimal callus induction. The proliferation rate achieved was 38% on the MS basal medium containing 1.0 mg/L of 6-BA, 1.0 mg/L of indolebutyric acid (IBA), 0.2 mg/L of kinetin (KT), and 50 g/L of sucrose. The one-step seedling formation achieved in MS medium contained 2.0 mg/L of 6-BA, 0.5 mg/L of NAA, 0.1 mg/L of gibberellic acid (GA3), and 30 g/L of sucrose, and the number of regenerated shoots per explants was 6 ± 2. Therefore, we establish a one-step seedling regeneration system through indirect plant regeneration, which shortens the time for konjac in vitro regeneration, significantly increased the micropropagation efficiency, and decreased the cost of the konjac tissue culture.
1. Introduction
Konjac (Amorphophallus konjac K. Koch) is a perennial herbaceous plant that belongs to the family of Araceae and is mainly distributed in Southwest Asia [1]. In China, it is distributed in the southeastern provinces, Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, Sichuan basins, and other tropical and subtropical humid monsoon climate regions. Konjac has been used for a long time as a medicinal plant [1]. It is also utilized in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries, agriculture, and food sources because its tuber contains a high level of water-soluble glucomannan [2]. The economic organ of konjac is an underground tuber, which mainly contains glucomannan; more than 60% of konjac plants contain glucomannan. It is the only major economic crop that can provide large amounts of glucomannan in nature [3]. Glucomannan is a macromolecular polysaccharide with good physical and chemical properties such as water retention, thickening, rheology, emulsification, gelation, and film-formation [4]. In addition, konjac also contains starch, alkaloids, vitamins, various minerals, amino acids, flavonoids, and other active ingredients. It helps with weight loss, has laxative properties, lowers lipid content and blood pressure, helps with diabetes treatment, has anti-ageing properties, and boosts the intestinal microenvironment [3,5,6,7]. Therefore, konjac powder also has been widely used in the food and medical industries. At present, the safety and health benefits of konjac have been recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) and rated as one of the top ten healthy foods worldwide. In China, strong support for konjac processing industries has gradually emerged [7].
Although it has excellent potential for commercial application and offers favourable economic benefits, the poor disease resistance and low propagation efficiency of konjac hinder its production. Additionally, traditional konjac cultivation is limited by the seasons and by external environment conditions. The reproduction speed is slow, and the growth cycle is long. The quality of seedlings is uneven, and problems such as variety degradation and susceptibility to konjac soft rot occur during the cultivation procedure, which results in a decline in yield and in the quality of konjac [8]. In order to solve the problem of lacking high-quality seedlings in the production of konjac, an effective way to use konjac tissue culture technology is to establish a rapid propagation system. Plant in vitro culture technology has been applied to regenerate healthy seedlings for many crops, such as potato, corn, and wheat. The tissue culture technique could be an essential and efficient method in solving the problem in konjac processing industries [8,9]. Several kinds of research on in vitro cultures of konjac have been reported. These studies used various explant types of konjac, such as shoot tips and buds [8]. The leaves of konjac at different developmental stages were used as explants for in vitro culture and rapid propagation technology and resulted in the large-scale regeneration of konjac seedlings [10]. The petioles of konjac plants were used as explants to study the effect of PGRs on callus induction, callus proliferation, and adventitious bud formation [11]. In the above report, they established a rapid in vitro propagation system with the petiole of konjac, which requires four stages: callus induction, callus differentiation, rooting, seedling formation, and micro-corm regeneration in which the cultural production cycle is relatively long and time-consuming [11]. In addition, the konjac in in vitro plant regeneration studies was almost developed from direct organogenesis instead of indirect plant regeneration [9]. Plant indirect regeneration and somatic embryogenesis offer advantages over organogenesis since embryos contain both root and shoot meristems. Somatic embryos are single cells and clonal in origin. Somatic embryogenesis is a powerful tool for the genetic improvement of any plant species [12]. In addition, in most cases, the embryogenic cultures can be cryopreserved, making it possible to establish gene banks. Embryonic calli induction is an attractive target for genetic modification [13]. It is also an efficient method for clonal propagation of genetically stable regeneration in many species [14]. The embryogenic culture can be used to study the one-step seedling system formation of konjac plants, shortening the culture cycle of in vitro regenerated seedlings and highly improving the efficiency of seedling cultivation. In this study, the embryogenic callus of konjac was induced by the young leaves of konjac as explants. Three types of embryogenic calli were induced, and later, only the type III embryonic callus with strong differentiation ability and high proliferation efficiency was selected to regenerate seedlings. Studies on konjac micropropagation using a one-step seedling regeneration system has significant practical advantages in understanding the large-scale production of this plant. This technique facilitates the production of large quantities of elite plant materials. Among the series of procedures required for tissue culture sterilization and appropriate culture establishment includes a critical step for successful micropropagation. This ultimately helps in overcoming the problems associated with conventional culture methods. The application of in vitro plant propagation is vital to producing virus-free disease seedlings throughout the year.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Sterile Seedlings Preparation
The two-year-old konjac seed tubers were provided from the laboratory of cell engineering, Dalian Polytechnic University, Dalian city, China. Healthy konjac seed tubers were selected and rinsed in tap water, and the soil attached to the surface of tubers was gently wiped off with the help of a sponge brush and dried on four layers of filter paper. The tubers were chopped with a sharp knife into small pieces (about 0.5 × 0.5 × 0.5 cm) from the top buds as explants for seedling preparation. The surface bracts of the apical buds, peeled and sterilized with several sterilization agents, were then rinsed at least three times thoroughly in double-distilled water to remove chemical traces according to the methods shown in Table 1. The sterilized explants were kept on sterile filter paper to absorb the water from the surface of the corms and transferred to the culture medium. The corms were cultured in 250 mL culture jars poured with MS basal medium supplemented with 2.0 mg/L of 6-BA, 0.5 mg/L of NAA, 30 g/L of sucrose, and 0.4% agar. The pH of all media was adjusted to 5.8 ± 0.2 by 0.1 M NaOH and 0.1 M HCl and then were autoclaved at 121 °C for 20 min.

Table 1.
Different methods for tuber sterilization.
Moreover, 50 bottles were inoculated, and each bottle contained one explant. The culture bottles were incubated at 25 °C and 2000 Lx light intensity for 12 h. The corms contamination rate and survival rate were evaluated after two weeks, as follows:
Contamination rate % = Number of contaminated explants/Total number of explants * 100
Survival rate % = Number of surviving explants/Total number of inoculated explants * 100
2.2. Explant Inoculation and Embryogenic Callus Induction
The surviving and healthy explants were transferred to a new MS basal medium without PGRs and sub-cultured under the previous culture conditions. After 20 days, the explants produced cluster buds, and micro buds were cultured in separate bottles. Two to four konjac sterile buds with a bit of tuber portion were placed in a new medium. After two weeks, the sterile leaves from seedlings were unfolded and taken as leaf explants for callus induction. At the same time, the bottom of the tubers was cut after removing the leaves, cut into small pieces of about 0.5 × 0.5 × 0.5cm, and transferred to a new MS medium with the combination of PGRs. After 25 days, tubers were regenerated with new cluster buds. The above steps were repeated in order to obtain a large number of sterile konjac seedlings in the whole experimental procedure shown in (Figure 1).
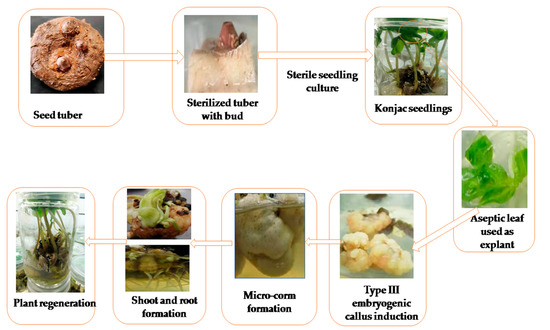
Figure 1.
Proposed universal protocol for regeneration of the konjac plant from leaves as an explant. Starting from seed tuber sterilization in method C, seedling regeneration in MS medium, embryogenic callus induction in M1-5 medium, micro-corm regeneration in M2-9 medium, and seedling formation in M3-9 medium.
At the initial stage, the unfolded young leaves were taken from the sterile seedlings, cut into 0.5 × 0.5 cm pieces, and used as explants for callus induction, with five replications in each treatment. The explants were cultured in MS basal medium combined with the different concentrations of 2,4-D (0.5–2 mg/L), 6-BA (0.1–1.0 mg/L), and NAA (0.1–1.0 mg/L) used. The cultures were incubated in the dark at 25 °C and 60% relative humidity, and the media were visualized regularly. The different PGR combination-induced embryogenic calli are shown in (Table 2).

Table 2.
Effect of different types of detergents on tuber sterilization.
2.3. Adventitious Shoot Induction from the Callus
The compact tumour-like, pink or light green, embryogenic callus type III was selected and sub-cultured in the shoot induction medium. This type of embryogenic callus was able to induce adventitious shoots. The type III embryonic callus was cut into 0.5 g pieces and sub-cultured in the same medium. The cultured medium was incubated under a light intensity of 1000 Lx, a photoperiod of 16 h/8 h, and a temperature of 25 °C. Based on different treatments, an orthogonal experimental design was used to screen the medium effects on adventitious shoot formation. The differentiated somatic embryogenic calli in culture medium supplemented with various hormone ratios are shown in (Table 3), with five replications in each treatment.

Table 3.
Effect of PGRs on embryogenic callus induction from konjac leaves.
2.4. One-Step Seedling Formation System
The induced konjac micro-corm was cut into small pieces of about 1.0 g of plant tissue measured on an aseptic electronic balance, then transferred to the seedling culture medium, and cultured under light conditions of 2000 Lx light intensity and 25 °C in MS medium. An orthogonal experimental design method was applied to screen hormone formulas. The concentration of PGRs and experimental schemes are shown in (Table 4). Each experiment had four parallel replications.

Table 4.
Differentiation responses of somatic embryo to various PGR combinations and plant regeneration.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
For callus and somatic embryogenesis induction, each experiment was performed at least with four replications. Data were recorded with Excel 2016 software and analysed using an analysis of variance (ANOVA). The average value is displayed as a standard error. SPSS 21.0 software was used to determine significant differences at the 1% level using Duncan’s multiple range test.
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of Surface Sterilization Treatments on Percentage of Aseptic Culture
Successful micropropagation of all plants depends on the initial material conditions to remove the contaminating exogenous and endogenous microorganisms. Fungi and bacteria are the most common microorganisms found on/in a plant. Establishing a sterile in vitro culture is the first and most crucial step to success in the commercial micropropagation of plants. An explant’s survival rate and contamination rate are two important indicators for measuring the sterilization effect of explants. A reasonable sterilization method achieves a balance between the two indicators, that is, it obtains a higher explant survival rate under the lowest contamination rate. We used 2-year-old expanded healthy tubers as the starting material for sterilization and in vitro culture. Later on, the sterilized explants were cultured on MS medium for 14 days; the contamination rate of the explants is given in Table 2. After 60 days, a sterile plant with micro-corms and leaf regenerates after the sterilization procedure is shown in Figure 2. The contamination rate of group C is 0, and the survival rate is 82%, while the contamination rates in groups A and B were 39 and 20%, the death rate was 20%, and the survival rates were recorded as 40% and 20%, respectively. Considering the given data in (Table 2), the method of group C recorded the best explant sterilization method for establishing a sterile konjac tuber culture followed by groups B and A. Group C indicates that washing with 0.1% mercury chloride (HgCl2) for 15 min gives the best sterilization result in (Table 1).
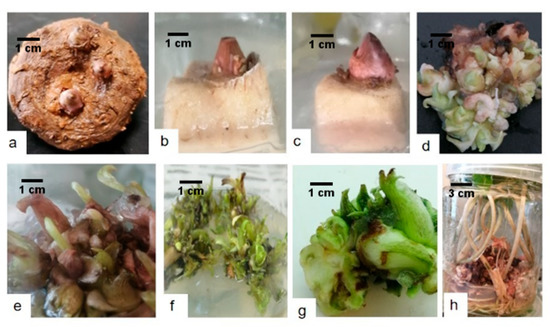
Figure 2.
The procedure for konjac aseptic seedlings induction. (a) Two-year-old konjac tuber. (b) Corm with apical bud. (c) Corm with apical bud inoculated after 14 days. (d) Buds differentiated after 35 days of culture. (e) The different buds that grew (after 45 days). (f) Seedling formation and development (g). Seedling regenerated (f). Tiny seedlings zoomed in, cut, and transferred to a new medium. (h) Seedling growth and development after 60 days of sub-culture.
3.2. Effect of PGRs on Embryogenic Callus Induction
By optimizing the combination of the three plant hormones 6-BA, NAA, and 2,4-D, callus surfaces appeared at 25 days of culture. After ten days, the leaf edge began to swell and thicken, and the colour of the leaf became pale pink or light yellow-greenish. Three types of embryogenic calli were successfully induced, as shown in (Figure 3g–i). Type I calli formed after 28 days of culture, and the callus looks transparent, brittle, and undifferentiable (Figure 3g). Type II calli formed after 28 days of inoculation; the calli appeared yellow-white, had a loose structure, and was granular and compact (Figure 3h). In 20 days, the expanded leaf entered the somatic embryogenic formation stage. It had a granular and rounded shape (Figure 3i), forming many embryogenic calli after 28 days. As shown in (Table 3), when the amounts of 6-BA and NAA are equal and at a lower concentration, the induction rate of embryogenic calli decreases. When the contents of the two hormones are equal but exceed 0.5 mg/L, the induction rate of the embryogenic calli was significantly reduced by more than the concentrations of the two hormones.
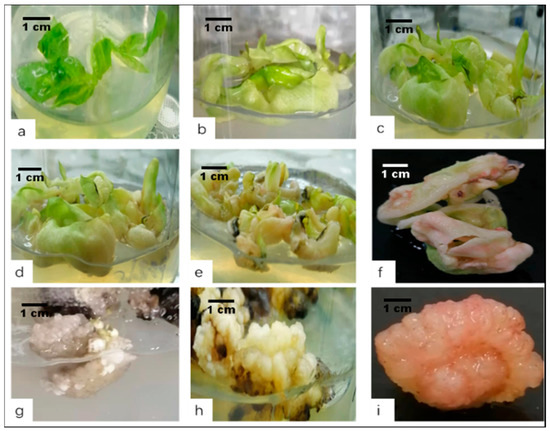
Figure 3.
The procedure for embryogenic callus induction from konjac leaves as an explant. (a) Leaf explants were taken from sterile seedlings. (b) Ten days after culture, the explants faded and thickened. The embryogenic callus induction preparation period. (c) Fourteen days after culture, the edge was further enlarged and thickened. (d) The leaves became light red after 20 days of culture in a culture medium. (e) The colour became darker after 25 days of culture, and the surface appears granular. (f) A zoomed-in image from (e). (g) Type I calli formed after 28 days of culture and were transparent, brittle, and undifferentiable. (h) Type II calli formed after 28 days of culture and were yellow-white, loose, granular, compact in structure, and differentiable. (i) Type Ⅲ callus formed after 28 days of inoculation and culture; were greenish or pink, compact in structure, granular, and highly differentiable; and had a high conversion rate.
Nevertheless, when the amounts of 6-BA and NAA in the M1-1 treatment are equal and at a lower concentration, the proportion of type II calli increased along with the increases in the concentration of 2,4-D in the M1-6 treatment (Table 3). When the amounts of the two hormones equal to 0.5 mg/L, the type Ⅲ callus increased proportionally with an increase in 2,4-D concentration in the M1-5 combination (0.5 mg/L of 6-BA, 0.5 mg/L of NAA, and 1.0 mg/L of 2,4-D). The embryogenic callus induction rate of leaf tissue reached 92.73%, and the proportion of type III callus reached 55.73% (Table 3). Both induction rates of the embryogenic calli and type III calli were the highest. Therefore, the hormone ratio in the M1-5 treatment was selected as the proliferation medium in which embryogenic callus induction can increase the subsequent regeneration rate of konjac micropropagation.
3.3. Shoot Induction
The embryogenic calli transferred to a new MS medium containing different concentrations of the three PGRs 6-BA (0.1–1.0 mg/L), IBA (0.1–1.0 mg/L), and KT (0.1–0.5 mg/L). An orthogonal design experiment was conducted to screen the best hormone ratios for plant regeneration. The statistical analysis results are shown in Table 4. After ten days of the transfer, the type Ⅲ callus volume began to swell and increase. It gradually became the bud-like structure in a differentiating medium, and the colour gradually changed from pink to light white; after 30 days, buds formed. The type Ⅲ calli were transferred to the M2-9 medium, the number of buds was exceeded, and the rate of the ball reached about 60%, as shown in (Table 4). Thus, the above hormone ratio combination was chosen for konjac indirect plant regeneration.
3.4. One-Step Seedling Formation
The type Ⅲ embryogenic callus was cultured as a starting material to achieve one-step seedling formation through hormone optimization. Three PGR combinations, 6-BA (1–2 mg/L), NAA (0.1–0.5 mg/L), and GA3 (0.05–0.1 mg/L), were selected for protocol optimization, and the best hormone ratios for one-step seedling formation were visualized. The compact calli, about 0.5 × 0.5 × 0.5 CM in size, were transferred to culture mediums (Table 5) and incubated at 25 °C, 2000 Lx light conditions; green shoots appeared within 23 days after culture, and the calli regenerated with a plant height of about 1–2 CM, bearing well-formed tubers produced after 30 days. The M3-9 (2.0 mg/L of 6-BA, 0.5 mg/L of NAA, and 0.1 mg/L of GA3) culture medium was the most suitable medium for plant development, as shown in (Figure 4). The calli simultaneously grew 6–10 adventitious roots, developing into robust plants after 45 days. Using the M3-9 hormone combination, the preparation time of the tissue-cultured seedlings was shortened. The proliferation ratio of the callus to seedlings is relatively high, so this hormone ratio is suitable for differentiating micro-corms into seedlings.

Table 5.
PGR combinations for one-step seedling and regeneration time.

Figure 4.
Embryogenic callus differentiation and shoot regeneration by one-step seedling formation system. (a) Type Ⅲ embryogenic callus. (b) Fifteen days after transfer, the volume of the embryogenic callus increased. (c) Micro-corm formation after 30 days. (d) Micro-corm germination after 45 days. (e) Multiple shoots formed on the surface of the micro-corm, and adventitious roots began to grow after 50 days. (f) Plants increased after 55 days of culture. (g) Zoomed-in view showing many adventitious roots in the lower part of the micro-corms. (h,i) Clusters after 65 days and 70 days of culture, respectively.
4. Discussion
Studies have shown that embryogenic callus induction is affected by various factors such as explants, PGRs, and media. PGRs can significantly regulate cell differentiation and in vitro plant culture [15,16]. Through totipotency, plant cells can form new plants from the somatic embryo via exposure to multiple explants in an appropriate growth regulator combination that can induce in vitro somatic embryos [17]. Our findings show that the hormone ratio plays a crucial role in embryogenic callus induction in the konjac plant. In particular, the balance of auxins and cytokinins is vital for shoot and root formation. Similar results were also observed by [18]. They suggested that, when the amounts of 6-BA and NAA are similar, it significantly affects embryogenic callus induction while a large amount of 6-BA compared with that of NAA is beneficial for bud differentiation. Qin et al. [19] found that, when the amounts of 6-BA to NAA are similar, the callus induction rate of Amorphophallus konjac was higher. They suggested that 0.5 mg/L of 6-BA and 0.5 mg/L of NAA are suitable for callus induction. Our results showed that calli could be induced with different firmness and colours under various combinations of 6-BA and NAA concentrations with leaves as explants (Figure 3). Non-embryogenic calli appeared soft and milky white, while embryogenic calli appeared compact, light, and brownish-yellow. The highest induction and proliferation rates for embryogenic calli were found for 2 mg/L of 2,4-D with 0.5 mg/L of 6-BA and NAA (Table 3), suggesting that 2,4-D plays a dominant role in the process of induction or proliferation of the konjac embryogenic callus. At the same time, NAA functions as a negative regulator. Likewise, Hu [20] used konjac coleoptile as explant materials and found that other hormones combined with 2,4-D can induce callus. In many plants, auxin promotes the initiation and proliferation of callus and pro-embryogenic mass. Embryo initiation was mainly due to the irregular distribution of auxin in plants [21]. After applying 2,4-D in rice, embryogenic calli from mature seeds were successfully induced [22]. In addition, we also found that the hormone combination M1-5 (0.5 mg/L of 6-BA, 0.5 mg/L of NAA, and 1.0 mg/L of 2, 4-D) was the most optimal ratio for embryogenic callus induction. The induction rate achieved was more than 90%, of which type Ⅲ callus constituted 55.73%, followed by type I and type II callus (Table 3). Our findings also show that the balance between 6-BA and NAA plant hormones has a significant promotional effect on the induction of embryogenic calli in konjac plant. In low concentrations of 6-BA and NAA with an increase in 2,4-D concentration, a synergistic effect is required to induce embryogenic calli. When the ratio between 6-BA and NAA hormones equal in high concentrations, the induction rate of embryogenic calli decreased significantly (Table 3). In this study, the type Ⅲ callus was used to regenerate konjac micro-tubers. This callus has a compact structure and consists of being small, having a dense cytoplasm, and having tightly arranged cells. It belongs to the conservative division type and has a strong organ differentiation ability [23]. The induced type Ⅲ callus was transferred to the plant regeneration medium.
PGRs act synergistically at different stages of somatic embryos [24]. Auxin and cytokinin combinations work together to promote the initiation of somatic embryos [25]. Our study observed that embryogenic callus budding initiated within 22 days of inoculation and that seedlings formed at 45 days after culture. Different hormone ratios can affect konjac plant regeneration during micro-corm formation from somatic embryos calli. Treatment with combinations of IBA and 6-BA showed a much higher induction rate of micro-corms than the application of KT, suggesting that a certain ratio of 6-BA and IBA could play a significant role in the differentiation process and that PGRs are necessary for the maintenance of konjac plant regeneration. The combined beneficial effect of auxin and cytokinins is consistent with reports in date palm leaves as explants [26]. It has been reported that a defined medium supplemented with low doses of 6-BA can directly stimulate somatic embryos in Spathoglottis plicata [27]. Micro-corm formation from calli was achieved using 6-BA and NAA treatments and subsequently induced seedlings in a medium containing GA3. Altogether, our results showed that the mechanism of somatic embryogenesis is different between the ratios of hormone dependence, varying with indirect plant regeneration. The adventitious buds obtained by transferring the somatic embryo to the differentiation medium thrive and simultaneously developed micro-corms shoot and root in the differentiation medium. The micro-corms formed from the callus could be used to achieve the “one-step seedling formation”. However, indirect plant regeneration undergoes embryogenic callus induction and proliferation steps, which are more suitable for mass production and industrialized seedling production.
5. Conclusions
In some studies, the tissue culture of konjac adopts multiple procedures such as explants for callus formation, differentiation of calli to seedlings, rooting induction from seedling cultures, of which the cycle is relatively long. The one-step seedling formation system of konjac can shorten the konjac tuberization and shoot formation. The seedling cultivation cycle improves the culture efficiency of konjac micro-corms and provides a technical guarantee for multiple shoot production of konjac micro-corm. In addition, konjac micropropagation is a kind of micro metamorphic reproductive organ with the advantages of having a small size, having convenient storage, and providing transportation and is expected to replace konjac in vitro faster than plantlet propagation technology. Therefore, research on the one-step seedling formation of konjac has significant commercial value and developmental potential.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Q. and Z.Z.; data curation, D.L. and M.A.M.; formal analysis, D.L.; funding acquisition, Z.Z.; investigation and methodology, D.L. and M.A.M.; project administration, Z.Z.; software, D.L. and M.A.M.; supervision, Y.Q. and Z.Z.; writing—original draft, D.L. and M.A.M.; writing—review and editing, Y.Q. and Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Dalian’s Science and Technology Innovation Fund (grant no. 2020JJ27SN107), the Science and Technology Program of Fujian Province (2019N5008), and Guangxi Distinguished Experts Fellowship.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank all colleagues at our lab for providing valuable discussions and technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| 2,4-D | 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid |
| 6-BA | 6-benzyladenine |
| GA3 | gibberellic acid |
| IAA | indole-3-acetic acid |
| IBA | indole-3-butyric acid |
| Kn | kinetin |
| MS | Murashige and Skoog (1962) medium |
| NAA | α-naphthaleneacetic acid |
| PGRs | plant growth regulators |
References
- Hetterscheid, W.; Ittenbach, S. Everything you always wanted to know about Amorphophallus, but were afraid to stick your nose into. Aroideana 1996, 19, 7–131. [Google Scholar]
- Cescutti, P.; Campa, C.; Delben, F.; Rizzo, R. Structure of the oligomers obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis of the glucomannan produced by the plant Amorphophallus konjac. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 2505–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Wu, P. Variations of Konjac glucomannan (KGM) from Amorphophallus konjac and its refined powder in China. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Cheng, J.; Lan, G.; Lu, F. A cellulose/Konjac glucomannan–based macroporous antibacterial wound dressing with synergistic and complementary effects for accelerated wound healing. Cellulose 2021, 28, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Yan, D. The effects of konjac oligosaccharides on decreasing blood lipid. Chin. J. Bio-Chem. Pharm. 2002, 23, 181–182. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Xia, N.; Shang, J.; Tran, V.; Guo, K. Preparation and Properties of Oriented Cotton Stalk Board with Konjac Glucomannan-Chitosan-Polyvinyl Alcohol Blend Adhesive. Bioresources 2015, 10, 3736–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.-T.; Chen, H.-L. Effects of Konjac Glucomannan on Putative Risk Factors for Colon Carcinogenesis in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, X.; Cailian, W.; Mei, S.; Qiufang, C. Shoot tips culture and plant regeneration in Amorphophallus konjac in vitro. Shengwu Jishu Biotechnol. 1994, 4, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Long, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Z. A tissue culture and plant regeneration system of Amorphophallus konjac in Guizhou. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2012, 7, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Thach, B.D.; Linh, N.K.; Duy, T.T.B.; Giang, T.T.L.; Uyen, N.P.A.; Suong, N.K.; Van Du, N. Preliminary selection and in vitro propagation of amorphophallus species with high content of gluco-mannan distributed in vietnam. Eur. J. Adv. Res. Biol. Life Sci. 2016, 4, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.B.; Liu, J.; Yan, H.B.; Xie, C.H. Histological observations of morphogenesis in petiole derived callus of Amorphophallus rivieri Durieu in vitro. Plant Cell Rep. 2005, 24, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vibha, J.B.; Choudhary, K.; Singh, M.; Rathore, M.S.; Shekhawat, N.S. An efficient somatic embryogenesis system for velvet bean [Mucuna pruriens (L.) DC.]: A source of anti Parkinson’s drug. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2009, 99, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Arnold, S.; Sabala, I.; Bozhkov, P.; Dyachok, J.; Filonova, L. Developmental pathways of somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2002, 69, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikuła, A.; Rybczyński, J.J. Somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana genus I. The effect of the preculture treatment and primary explant origin on somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana cruciata (L.), G. pannonica (Scop.), and G. tibetica (King). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2001, 23, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourguillon, L.; Gondet, L.; Lobstein, A. Effects of explant type, culture media and growth regulators for callus induction of a potential bioactive halophyte: Armeria maritima (Plumbaginaceae). Planta Med. 2016, 81, S1–S381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.-M.; Xu, C.; Kim, C.-H.; Um, Y.-C.; Bah, A.A.; Guo, D.-P. Effects of explant type, culture media and growth regulators on callus induction and plant regeneration of Chinese jiaotou (Allium chinense). Sci. Hortic. 2009, 123, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, A.; Bemer, M.; Boutilier, K. A transcriptional view on somatic embryogenesis. Regeneration 2017, 4, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Guo, X.; Hu, X. Multi-factor orthogonal test for callus induction of konjac. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2016, 55, 3479–3481. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y. Establishment of in vitro regeneration system of konjac flower. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2015, 54, 6054–6057. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X. Research on Callus Induction from Coleoptile Explants of Amorphophallus. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Márquez-López, R.E.; Pérez-Hernández, C.; Ku-González, Á.; Galaz-Ávalos, R.M.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M. Localization and transport of indole-3-acetic acid during somatic embryogenesis in Coffea canephora. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.I.; Johan, N.S.; Wagiran, A. Effect of 2,4-D on Embryogenic Callus Induction of Malaysian indica Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars MR123 and MR127. J. Teknol. 2013, 64, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Yan, H.; Xie, C. Different types of calluses and differentiation ability of Konjac. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2004, 23, 654–658. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Singh, D.; Saroj, P. Callus induction, somatic embryogenesis, in vitro plantlet development and ex vitro transplantation of two date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) cultivars. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2020, 8, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botini, N.; Almeida, F.A.; Cruz, K.Z.C.M.; Reis, R.S.; Vale, E.M.; Garcia, A.B.; Santa-Catarina, C.; Silveira, V. Stage-specific protein regulation during somatic embryo development of Carica papaya L. ‘Golden’. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2021, 1869, 140561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baharan, E.; Pour Mohammadi, P. Induction of direct somatic embryogenesis and callogenesis in date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) using leaf explants. Biotechnology 2018, 99, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, W.; Sun, M. Characterization and expression pattern analysis of DcNAC gene in somatic embryos of Dendrobium candidum Wall Ex Lindl. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2011, 107, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).