Evaluation of Carrageenan, Xanthan Gum and Depolymerized Chitosan Based Coatings for Pineapple Lily Plant Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Culture and Treatment
2.2. Measurement of Growth Parameters
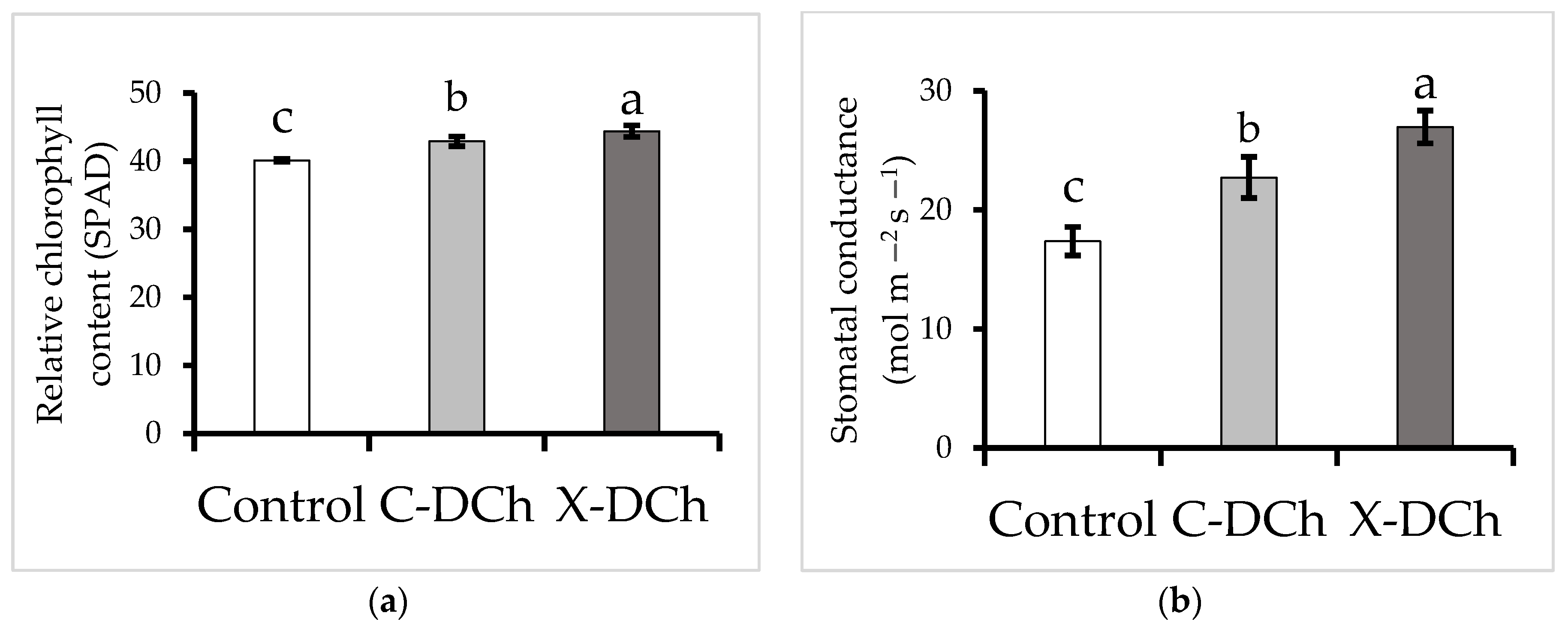
2.3. Measurement of Physiological Parameters
2.4. Total N, P, K, and Total Sugar Content in Bulb Determination
2.5. L-Ascorbic Acid, Total Polyphenol Content, and Antioxidant Activity Determination
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, A.; Mor, V.S.; Tokas, J.; Punia, H.; Malik, S.; Malik, K.; Sangwan, S.; Tomar, S.; Singh, P.; Singh, N.; et al. Biostimulant-Treated Seedlings under Sustainable Agriculture: A Global Perspective Facing Climate Change. Agronomy 2021, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobek, M.; Frąc, M.; Cybulska, J. Plant Biostimulants: Importance of the Quality and Yield of Horticultural Crops and the Improvement of Plant Tolerance to Abiotic Stress—A Review. Agronomy 2019, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Biostimulants in Agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, F.; Casadesús, A.; Brockman, H.; Munné-Bosch, S. An Overview of Plant-Based Natural Biostimulants for Sustainable Horticulture with a Particular Focus on Moringa Leaf Extracts. Plant Sci. 2020, 295, 110194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocira, A.; Lamorska, J.; Kornas, R.; Nowosad, N.; Tomaszewska, M.; Leszczyńska, D.; Kozłowicz, K.; Tabor, S. Changes in Biochemistry and Yield in Response to Biostimulants Applied in Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elarroussia, H.; Elmernissia, N.; Benhimaa, R.; El Kadmiria, I.M.; Bendaou, N.; Smouni, A.; Wahbya, I. Microalgae polysaccharides a promising plant growth biostimulant. J. Algal Biomass Utln. 2016, 7, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Shen, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wang, P.; Jiang, X. Growth Stimulation Activity of Alginate-Derived Oligosaccharides with Different Molecular Weights and Mannuronate/Guluronate Ratio on Hordeum vulgare L. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Yin, H. Preparation of alginate oligosaccharides and their biological activities in plants: A review. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 494, 108056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salachna, P. Effects of Depolymerized Gellan with Different Molecular Weights on the Growth of Four Bedding Plant Species. Agronomy 2020, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.S.; Borza, T.; Critchley, A.T.; Prithiviraj, B. Carrageenans from Red Seaweeds as Promoters of Growth and Elicitors of Defense Response in Plants. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.B.M.; Khan, M.M.A.; Siddiqui, H.; Jahan, A. Chitosan and Its Oligosaccharides, a Promising Option for Sustainable Crop Production-a Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Rahman, M.; Khan, M.A.R.; Bhowmik, P.; Mahmud, N.U.; Tanveer, M.; Islam, T. Mechanism of Plant Growth Promotion and Disease Suppression by Chitosan Biopolymer. Agriculture 2020, 10, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Morishita, S.; Suda, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Hosoki, T. Effects of Chitosan Soil Mixture Treatment in the Seedling Stage on the Growth and Flowering of Several Ornamental Plants. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2004, 73, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Hernández, H.; Juárez-Maldonado, A.; Benavides-Mendoza, A.; Ortega-Ortiz, H.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Sánchez-Aspeytia, D.; González-Morales, S. Chitosan-PVA and Copper Nanoparticles Improve Growth and Overexpress the SOD and JA Genes in Tomato Plants under Salt Stress. Agronomy 2018, 8, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malerba, M.; Cerana, R. Chitin- and Chitosan-Based Derivatives in Plant Protection against Biotic and Abiotic Stresses and in Recovery of Contaminated Soil and Water. Polysaccharides 2020, 1, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALKahtani, M.D.F.; Attia, K.A.; Hafez, Y.M.; Khan, N.; Eid, A.M.; Ali, M.A.M.; Abdelaal, K.A.A. Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters and Antioxidant Defense System Can Display Salt Tolerance of Salt Acclimated Sweet Pepper Plants Treated with Chitosan and Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.E.; Yuan, S.; Liu, H.M.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, H.Y. A combination of chitosan and chemical fertilizers improves growth and disease resistance in Begonia × hiemalis Fotsch. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2016, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elansary, H.O.; Abdel-Hamid, A.M.; Yessoufou, K.; Al-Mana, F.A.; El-Ansary, D.O.; Mahmoud, E.A.; Al-Yafrasi, M.A. Physiological and molecular characterization of water-stressed Chrysanthemum under robinin and chitosan treatment. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2020, 42, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byczyńska, A. Chitosan improves growth and bulb yield of pineapple lily (Eucomis bicolor Baker) an ornamental and medicinal plant. World Sci. News 2018, 110, 159–171. [Google Scholar]
- Salachna, P.; Zawadzińska, A. Effect of chitosan on plant growth, flowering and corms yield of potted freesia. J. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 15, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Krupa-Małkiewicz, M.; Fornal, N. Application of chitosan in vitro to minimize the adverse effects of salinity in Petunia × atkinsiana D. Don. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malerba, M.; Cerana, R. Recent advances of chitosan applications in plants. Polymers 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Miniawy, S.M.; Ragab, M.E.; Youssef, S.M.; Metwally, A.A. Response of strawberry plants to foliar spraying of chitosan. Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 366–372. [Google Scholar]
- Algam, S.A.E.; Xie, G.; Li, B.; Yu, S.; Su, T.; Larsen, J. Effects of Paenibacillus Strains and Chitosan on Plant Growth Promotion and Control of Ralstonia Wilt in Tomato. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 92, 593–600. [Google Scholar]
- Muhmed, S.A.; Nor, N.A.M.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F.; Othman, M.H.D.; Rahman, M.A.; Aziz, F.; Yusof, N. Emerging Chitosan and Cellulose Green Materials for Ion Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell: A Review. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2020, 5, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Winnicka, K. Stability of chitosan—a challenge for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1819–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowiak, A.; Startek, L.; Salachna, P.; Zurawik, P. Method of Hydrogel Coating Formation on the Surface of Plant Organs. Pat. No PL 2008, 197101, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Salachna, P.; Grzeszczuk, M.; Soból, M. Effects of Chitooligosaccharide Coating Combined with Selected Ionic Polymers on the Stimulation of Ornithogalum saundersiae Growth. Molecules 2017, 22, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Startek, L.; Bartkowiak, A.; Salachna, P.; Kaminska, M.; Mazurkiewicz-Zapalowicz, K. The influence of new methods of corm coating on freesia growth, development and health. Acta Hortic. 2005, 673, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, J.; Castro, J.; Contreras, R.A.; González, A.; Moenne, A. Oligo-carrageenans induce a long-term and broad-range protection against pathogens in tobacco plants (Var. Xanthi). Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 79, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, L.V.; Aurigue, F.B.; Relleve, L.S.; Montefalcon, D.R.V.; Lopez, G.E.P. Characterization of low molecular weight fragments from gamma irradiated κ-carrageenan used as plant growth promoter. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016, 118, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanegas, J.S.; Torres, G.R.; Campos, B.B. Characterization of a κ-Carrageenan Hydrogel and Its Evaluation as a Coating Material for Fertilizers. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.; Jahan, A.; Sadiq, Y.; Shabbir, A.; Jaleel, H.; Khan, M.M.A. Radiation-Mediated Molecular Weight Reduction and Structural Modification in Carrageenan Potentiates Improved Photosynthesis and Secondary Metabolism in Peppermint (Mentha piperita L.). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akalin, G.O.; Pulat, M. Controlled Release Behavior of Zinc-Loaded Carboxymethyl Cellulose and Carrageenan Hydrogels and Their Effects on Wheatgrass Growth. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo, S.; González, A.; Gómez, M.; Contreras, R.A.; Laporte, D.; Sáez, C.A.; Zúñiga, G.; Moenne, A. Oligo-Carrageenan Kappa Increases Glucose, Trehalose and TOR-P and Subsequently Stimulates the Expression of Genes Involved in Photosynthesis, and Basal and Secondary Metabolisms in Eucalyptus globulus. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San, P.T.; Khanh, C.M.; Khanh, H.H.N.; Khoa, T.A.; Hoang, N.; Nhung, L.T.; Trinh, N.T.K.; Nguyen, T.-D. k-Oligocarrageenan Promoting Growth of Hybrid Maize: Influence of Molecular Weight. Molecules 2020, 25, 3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rao, K.M.; Han, S.S. Application of xanthan gum as polysaccharide in tissue engineering: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiz, C.; Schauffler, G.P.; Lemos-Blainski, J.M.; Rosa, D.J.; Di Piero, R.M. Mechanisms of action of aloe polysaccharides and xanthan gum for control of black rot in cauliflower. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 200, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Binh, N.; Diep, T.B.; Sang, H.D.; Thao, H.P.; Thom, N.T.; Quynh, T.M. Low Molecular Weight Xanthan Prepared by Gamma Irradiation and Its Effects on Development of Seedlings. RAD Conf. Proc. 2016, 1, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Jang, H.Y.; Ahn, S.J.; Kim, E. β-Glucan-and Xanthan Gum-Based Biopolymer Stimulated the Growth of Dominant Plant Species in the Korean Riverbanks. Ecol. Resilient Infrastruct. 2019, 6, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R.; Babbar, S.B. Xanthan gum: An economical substitute for agar in plant tissue culture media. Plant Cell Rep. 2006, 25, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, A.S.; Dole, J.M. Postharvest handling recommendations for cut pineapple lily. HortTechnology 2014, 24, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, A.S.; Dole, J.M. Determining Optimal Bulb Storage and Production Methods for Successful Forcing of Cut Pineapple Lily. HortTechnology 2015, 25, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salachna, P.; Grzeszczuk, M.; Meller, E.; Soból, M. Oligo-Alginate with Low Molecular Mass Improves Growth and Physiological Activity of Eucomis autumnalis under Salinity Stress. Molecules 2018, 23, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masondo, N.A.; Finnie, J.F.; Van Staden, J. Pharmacological potential and conservation prospect of the genus Eucomis (Hyacinthaceae) endemic to southern Africa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salachna, P.; Grzeszczuk, M.; Wilas, J. Total phenolic content, photosynthetic pigment concentration and antioxidant activity of leaves and bulbs of selected Eucomis L’Hér. taxa. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 4220–4225. [Google Scholar]
- Salachna, P.; Mizielińska, M.; Soból, M. Exopolysaccharide Gellan Gum and Derived Oligo-Gellan Enhance Growth and Antimicrobial Activity in Eucomis Plants. Polymers 2018, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salachna, P.; Zawadzińska, A. Effect of nitric oxide on growth, flowering and bulb yield of Eucomis autumnalis. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1201, 635–640. [Google Scholar]
- Salachna, P.; Zawadzińska, A. Comparison of morphological traits and mineral content in Eucomis autumnalis (Mill.) Chitt. plants obtained from bulbs treated with fungicides and coated with natural polysaccharides. J. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 16, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowska, A.; Gawliński, S.; Szczubiałka, Z. Methods for Analyzing and Assessing the Properties of Soil and Plants; Instytut Ochrony Środowiska: Warsaw, Poland, 1991; pp. 1–333. [Google Scholar]
- Salachna, P.; Mikiciuk, M.; Zawadzińska, A.; Piechocki, R.; Ptak, P.; Mikiciuk, G.; Pietrak, A.; Łopusiewicz, Ł. Changes in Growth and Physiological Parameters of ×Amarine Following an Exogenous Application of Gibberellic Acid and Methyl Jasmonate. Agronomy 2020, 10, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1990.
- Wojdyło, A.; Oszmiański, J.; Czemerys, R. Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds in 32 selected herbs. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, G.C.; Chen, H.Y. Antioxidant activity of various tea extracts in relation to their antimutagenicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Giussani, E.; Morelli, R.; Scalzo, R.; Nani, R.C.; Torreggiani, D. Effect of fruit blanching on phenolics and radical scavenging activity of highbush blueberry juice. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y. Seed coating with beneficial microorganisms for precision agriculture. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniazzi, N.; Deschamps, C.; Bach, E.E. Effect of xanthan gum and allicin as elicitors against Bipolaris sorokiniana on barley in field experiments. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2008, 115, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademacher, W. Plant growth regulators: Backgrounds and uses in plant production. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 34, 845–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Synergistic biostimulatory action: Designing the next generation of plant biostimulants for sustainable agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, J.L.; Benard, C.; Robin, C.; Bourgaud, F.; Adamowicz, S. The ‘trade-off’ between synthesis of primary and secondary compounds in young tomato leaves is altered by nitrate nutrition: Experimental evidence and model consistency. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 4301–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caretto, S.; Linsalata, V.; Colella, G.; Mita, G.; Lattanzio, V. Carbon Fluxes between Primary Metabolism and Phenolic Pathway in Plant Tissues under Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26378–26394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H.; Jaafar, H.Z.E.; Rahmat, A.; Rahman, Z.A. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilization on Synthesis of Primary and Secondary Metabolites in Three Varieties of Kacip Fatimah (Labisia pumila Blume). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5238–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Type of Coatings | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | C-DCh | X-DCh | |
| Plant height (cm) | 32.6 ± 0.96 c z | 35.1 ± 0.59 b | 37.7 ± 1.07 a |
| Plant diameter (cm) | 25.7 ± 1.61 b | 35.8 ± 1.86 a | 36.0 ± 1.17 a |
| Fresh weight of the aboveground part (g) | 107 ± 1.91 c | 183 ± 4.10 b | 209 ± 4.07 a |
| Length of inflorescence (cm) | 16.5 ± 1.70 b | 21.7 ± 1.19 a | 20.7 ± 0.72 a |
| Number of florets | 72.6 ± 3.39 b | 78.6 ± 1.46 a | 79.2 ± 1.15 a |
| Days to anthesis | 161 ± 2.08 a | 144 ± 3.21 b | 148 ± 2.52 b |
| Parameter | Type of Coatings | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | C-DCh | X-DCh | |
| Fresh weight of bulbs (g) | 31.0 ± 1.87 c z | 43.0 ± 2.61 b | 50.0 ± 4.95 a |
| Number of daughter bulbs | 0.75 ± 0.15 c | 0.93 ± 0.07 b | 1.11 ± 0.10 a |
| Total N content (% DW) | 0.39 ± 0.03 c | 0.58 ± 0.02 b | 0.64 ± 0.02 a |
| Total P content (% DW) | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a |
| Total K content (% DW) | 0.44 ± 0.02 c | 0.64 ± 0.03 b | 0.69 ± 0.02 a |
| Total sugar content (% FW) | 6.66 ± 0.39 b | 7.47 ± 0.15 a | 7.76 ± 0.16 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salachna, P.; Pietrak, A. Evaluation of Carrageenan, Xanthan Gum and Depolymerized Chitosan Based Coatings for Pineapple Lily Plant Production. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7020019
Salachna P, Pietrak A. Evaluation of Carrageenan, Xanthan Gum and Depolymerized Chitosan Based Coatings for Pineapple Lily Plant Production. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalachna, Piotr, and Anna Pietrak. 2021. "Evaluation of Carrageenan, Xanthan Gum and Depolymerized Chitosan Based Coatings for Pineapple Lily Plant Production" Horticulturae 7, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7020019
APA StyleSalachna, P., & Pietrak, A. (2021). Evaluation of Carrageenan, Xanthan Gum and Depolymerized Chitosan Based Coatings for Pineapple Lily Plant Production. Horticulturae, 7(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7020019







