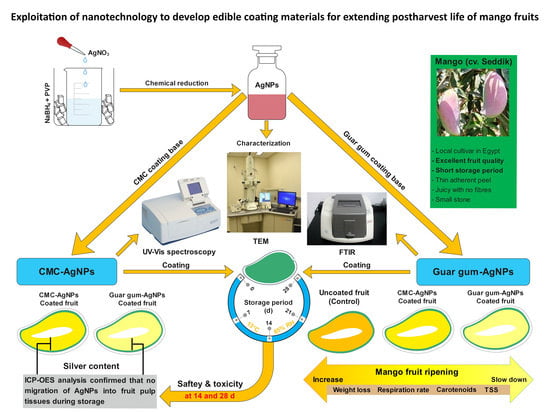
Storage Behavior of “Seddik” Mango Fruit Coated with CMC and Guar Gum-Based Silver Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of CMC and Guar Gum-Based Silver Nanoparticles Coatings
2.2.1. Preparation of Coating Base
2.2.2. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles
2.2.3. Preparation of CMC and Guar Gum-Based Silver Nanoparticle Coatings
2.3. Characterization of AgNPs and CMC and Guar Gum-Based Silver Nanoparticle Coatings
2.3.1. Ultraviolet (UV)/Visible Light (Vis) Spectroscopy
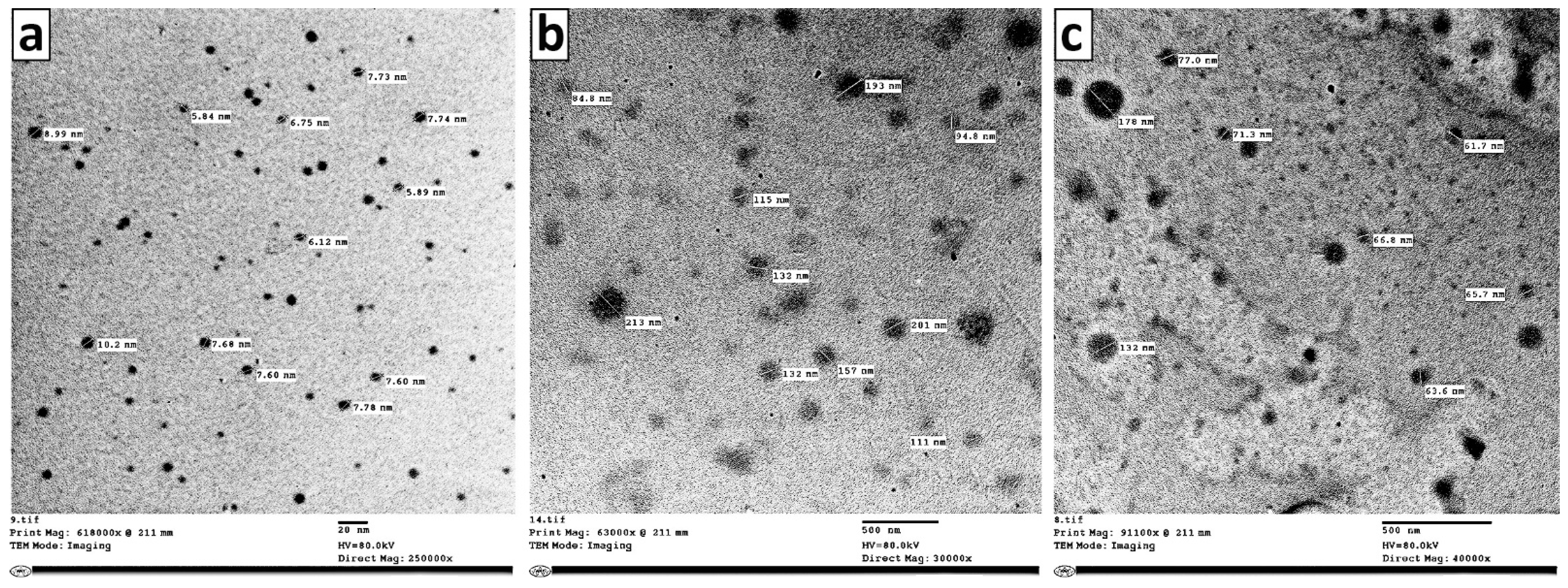
2.3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
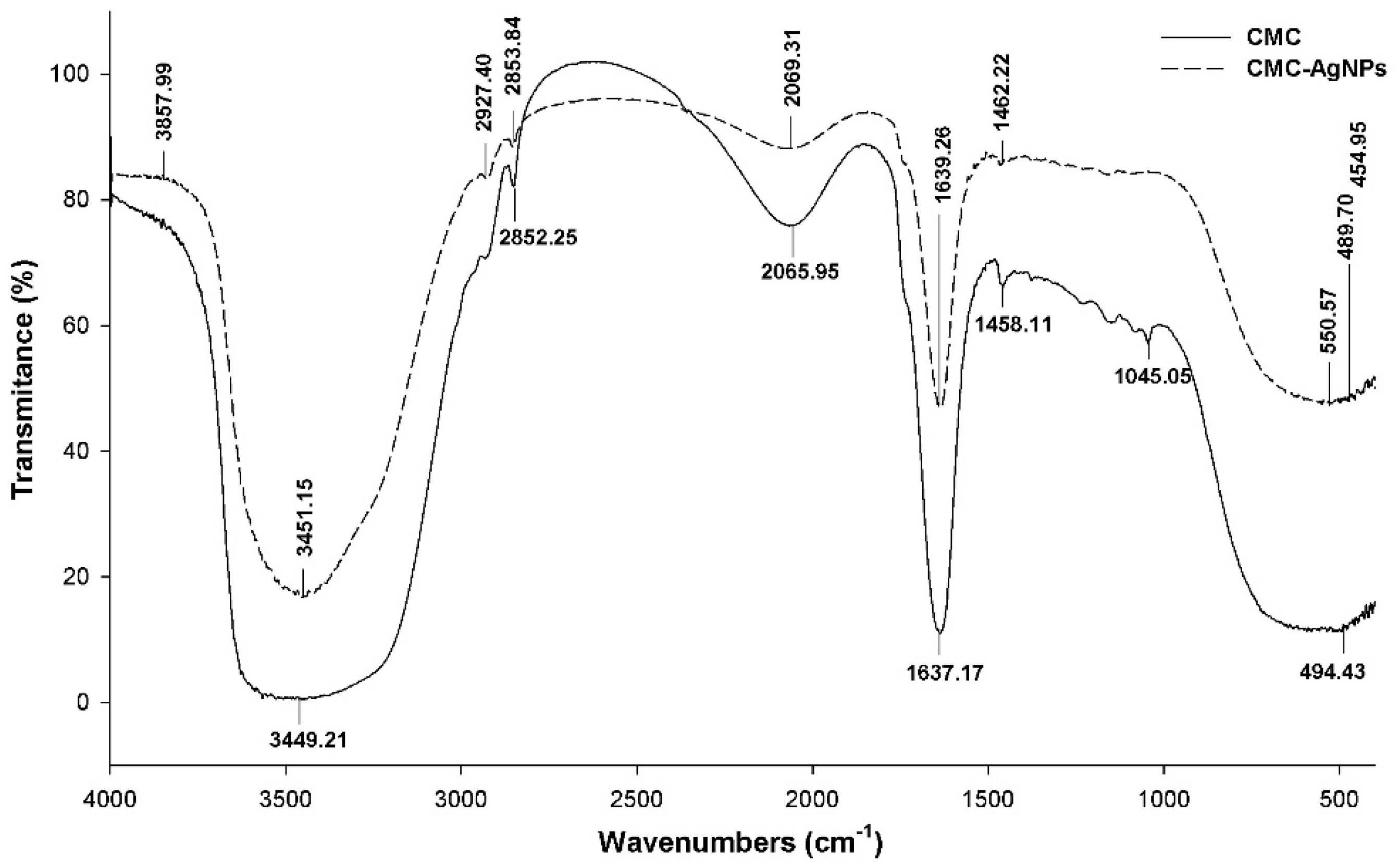
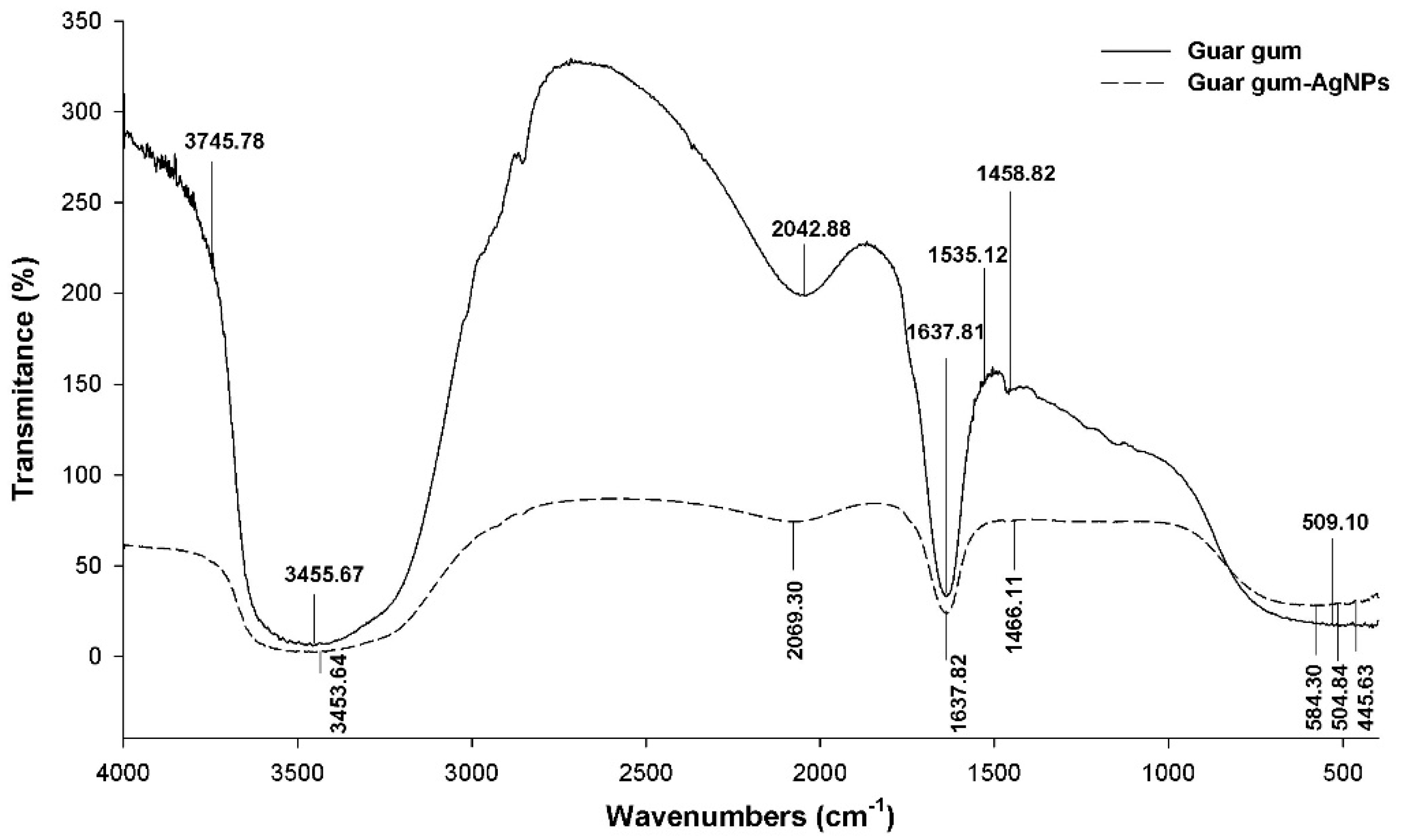
2.3.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR)
2.4. Fruit Material
2.5. Coating Application and Storage Conditions
2.6. Fruit Quality Attributes
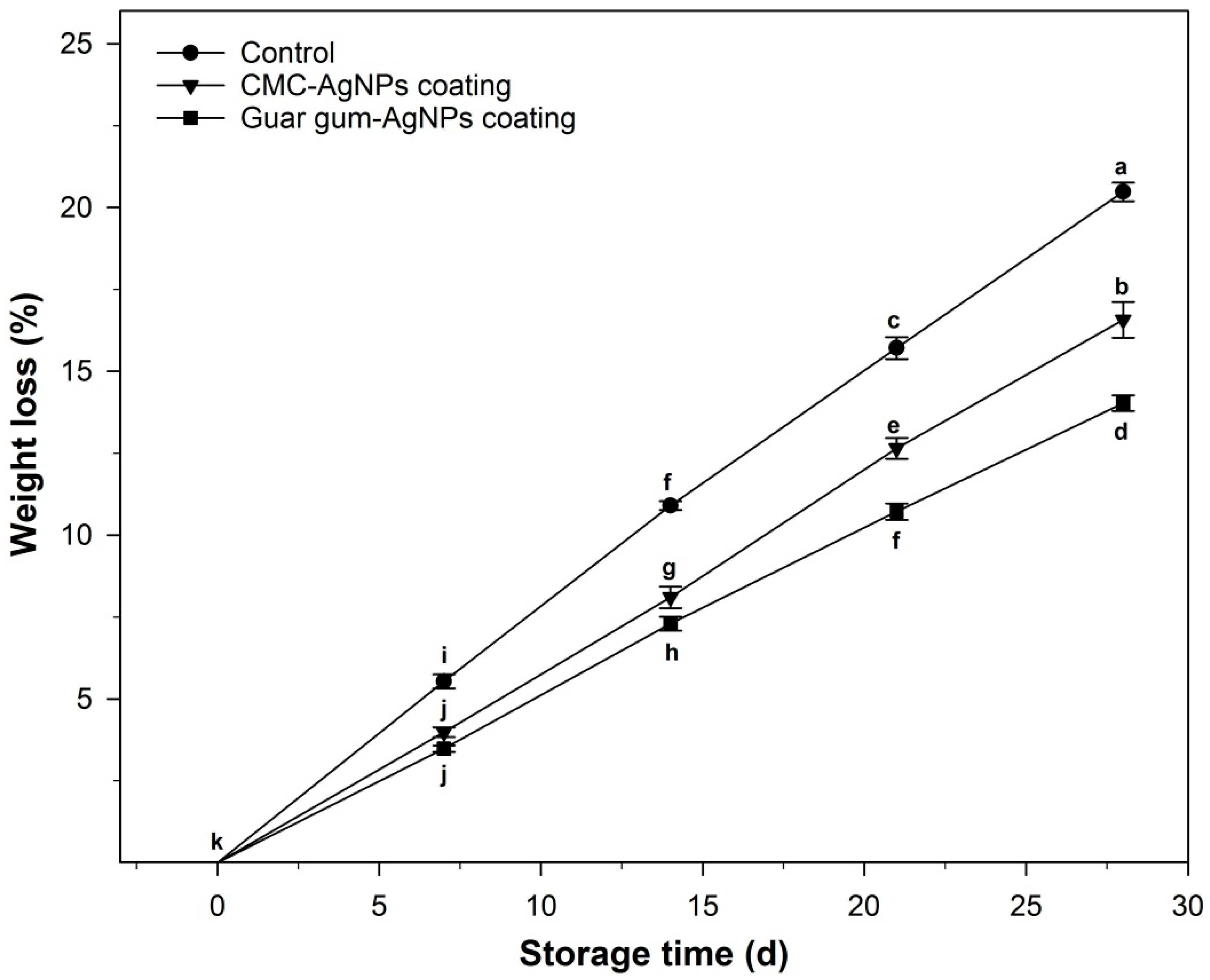
2.6.1. Weight Loss
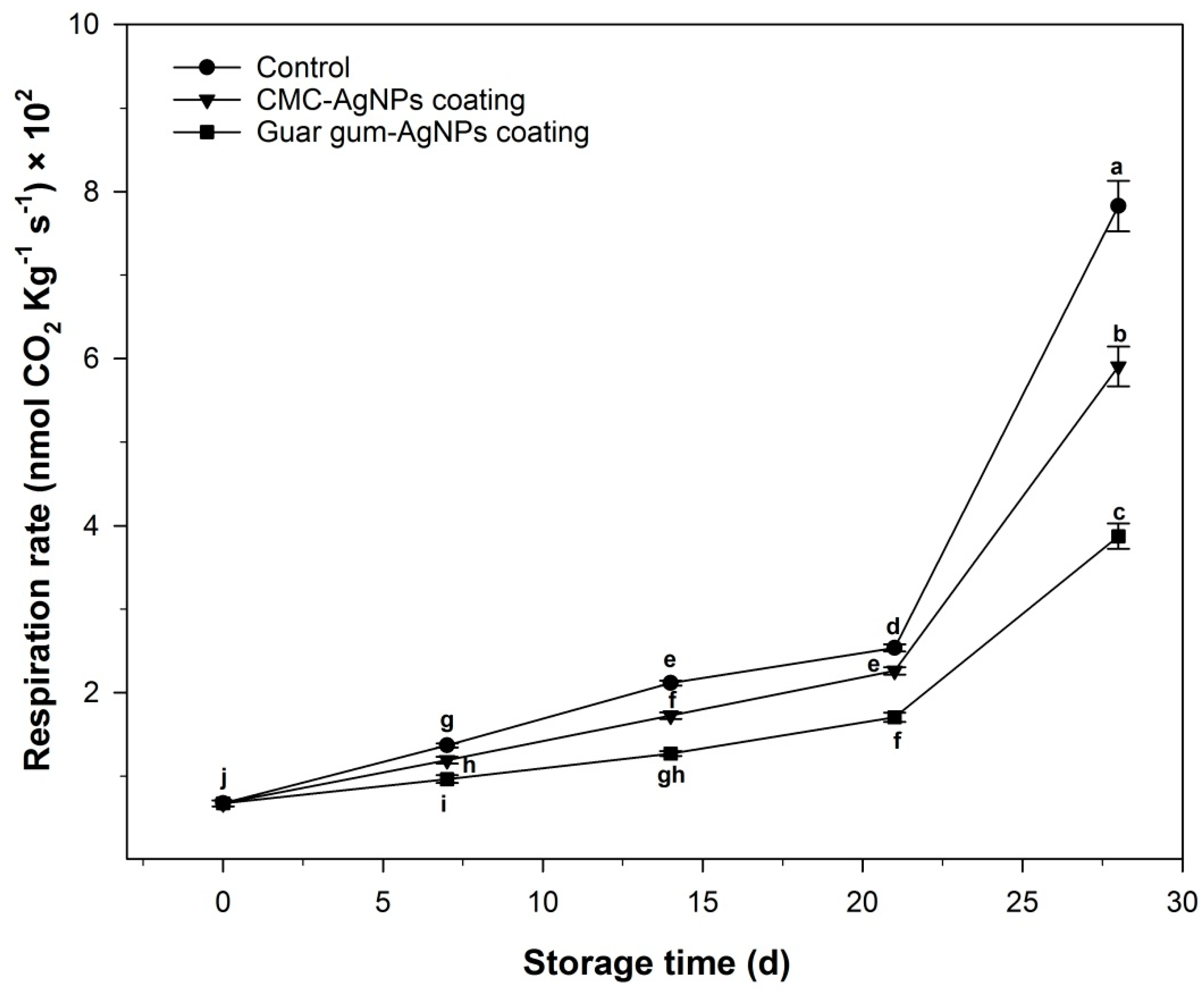
2.6.2. Respiration Rate
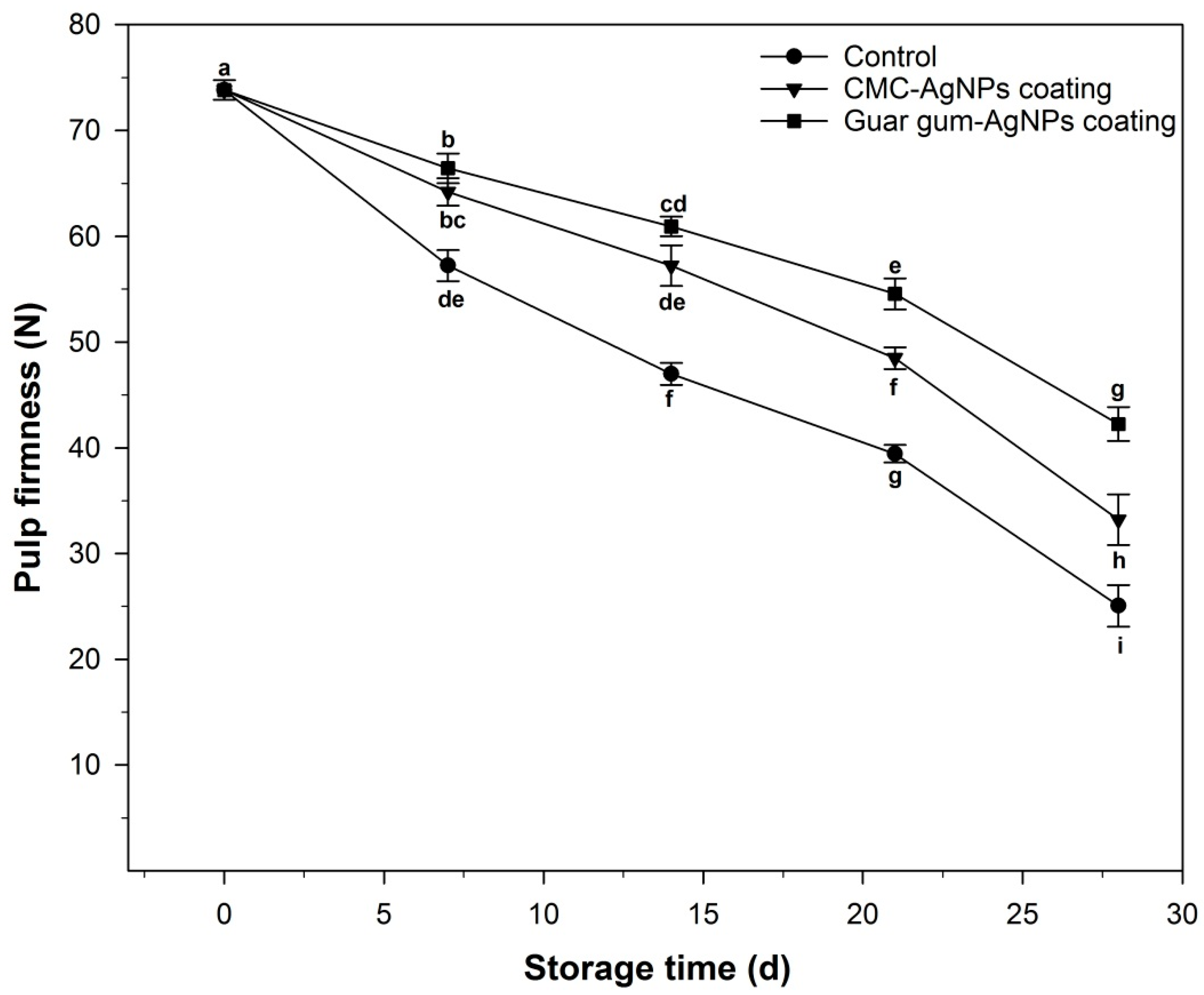
2.6.3. Fruit Pulp Firmness
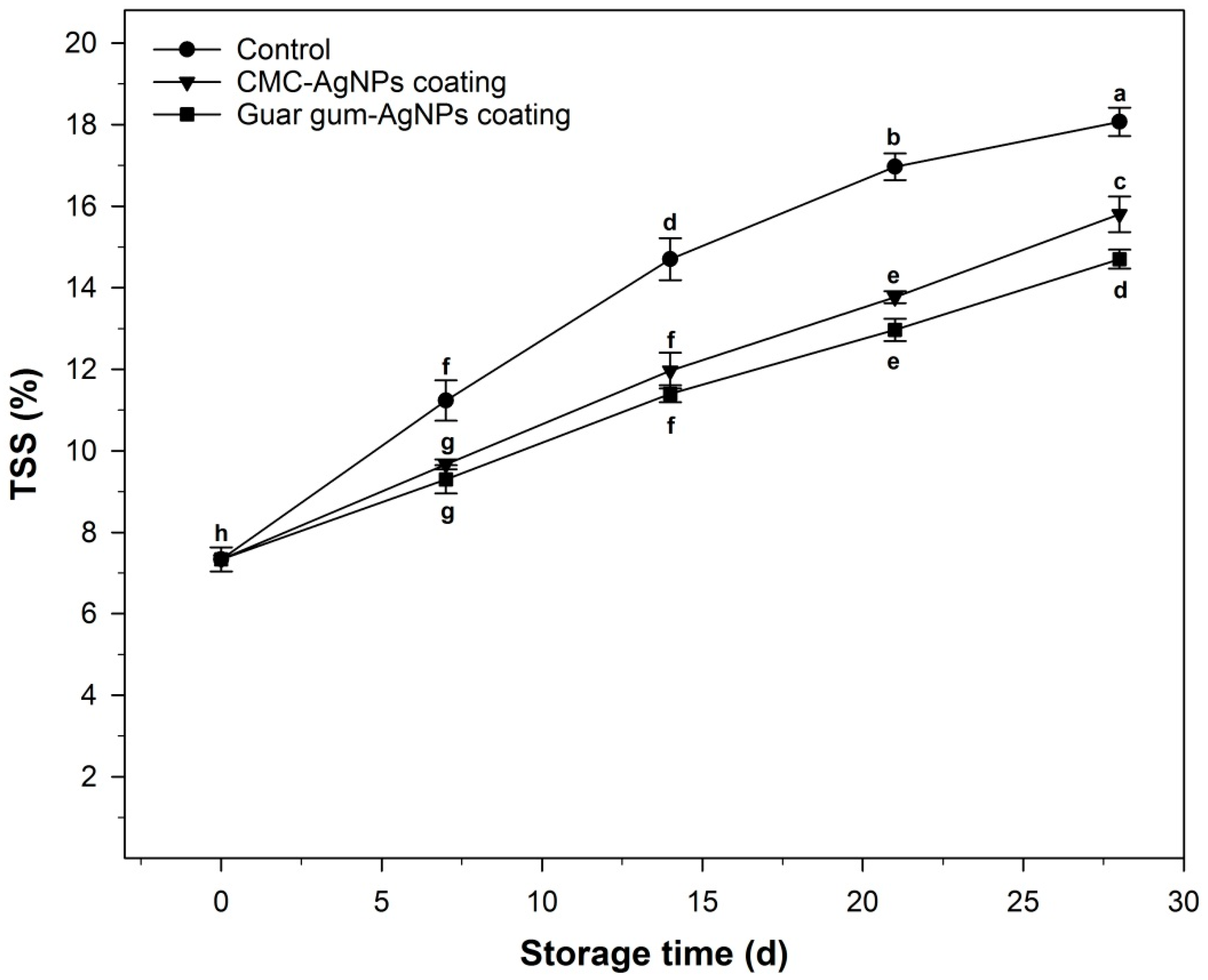
2.6.4. Total Soluble Solids (TSS), Titratable Acidity (TA), and TSS/TA Ratio
2.6.5. Total Sugar Content
2.6.6. Total Carotenoid Content
2.6.7. Determination of Total Silver Concentration
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of AgNPs and CMC and Guar Gum-Based Silver Nanoparticle Coatings
3.1.1. UV/Vis Spectroscopy
3.1.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.1.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared
3.2. Fruit Quality Attributes
3.2.1. Weight Loss
3.2.2. Respiration Rate
3.2.3. Fruit Pulp Firmness
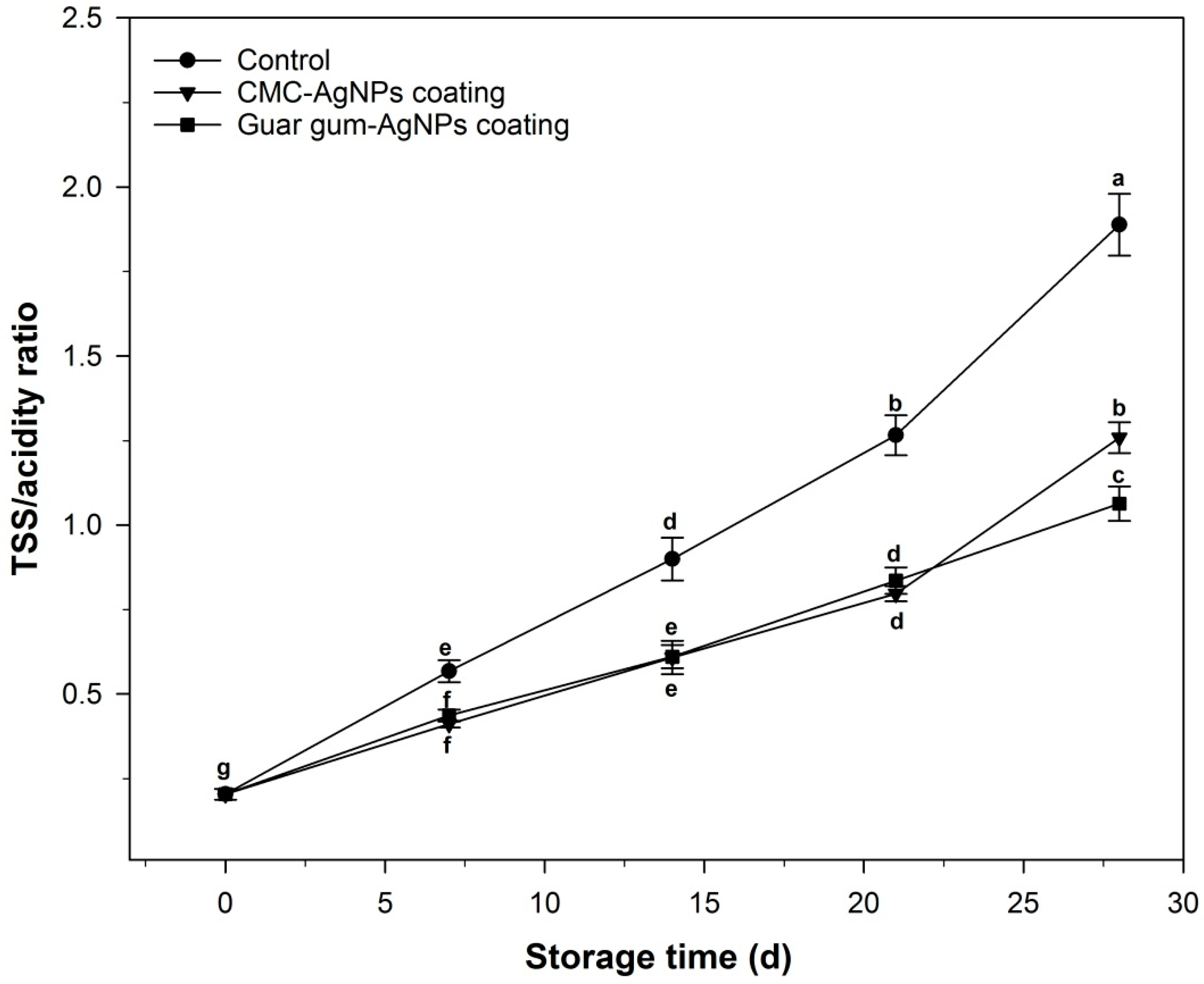
3.2.4. Total Soluble Solids (TSS), Titratable Acidity (TA), and TSS/TA Ratio
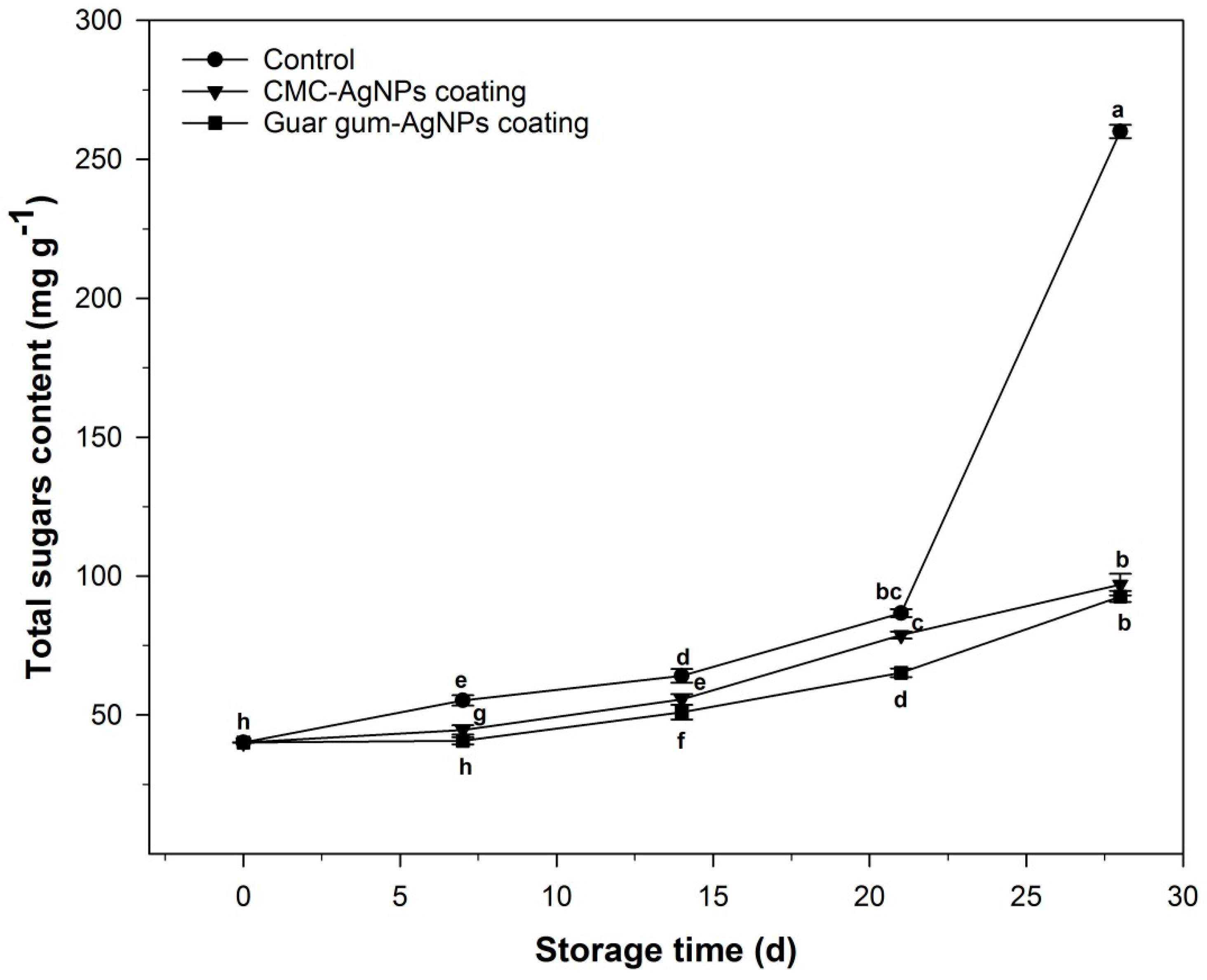
3.2.5. Total Sugar Content
3.2.6. Total Carotenoid Content
3.2.7. Determination of Total Silver Concentration
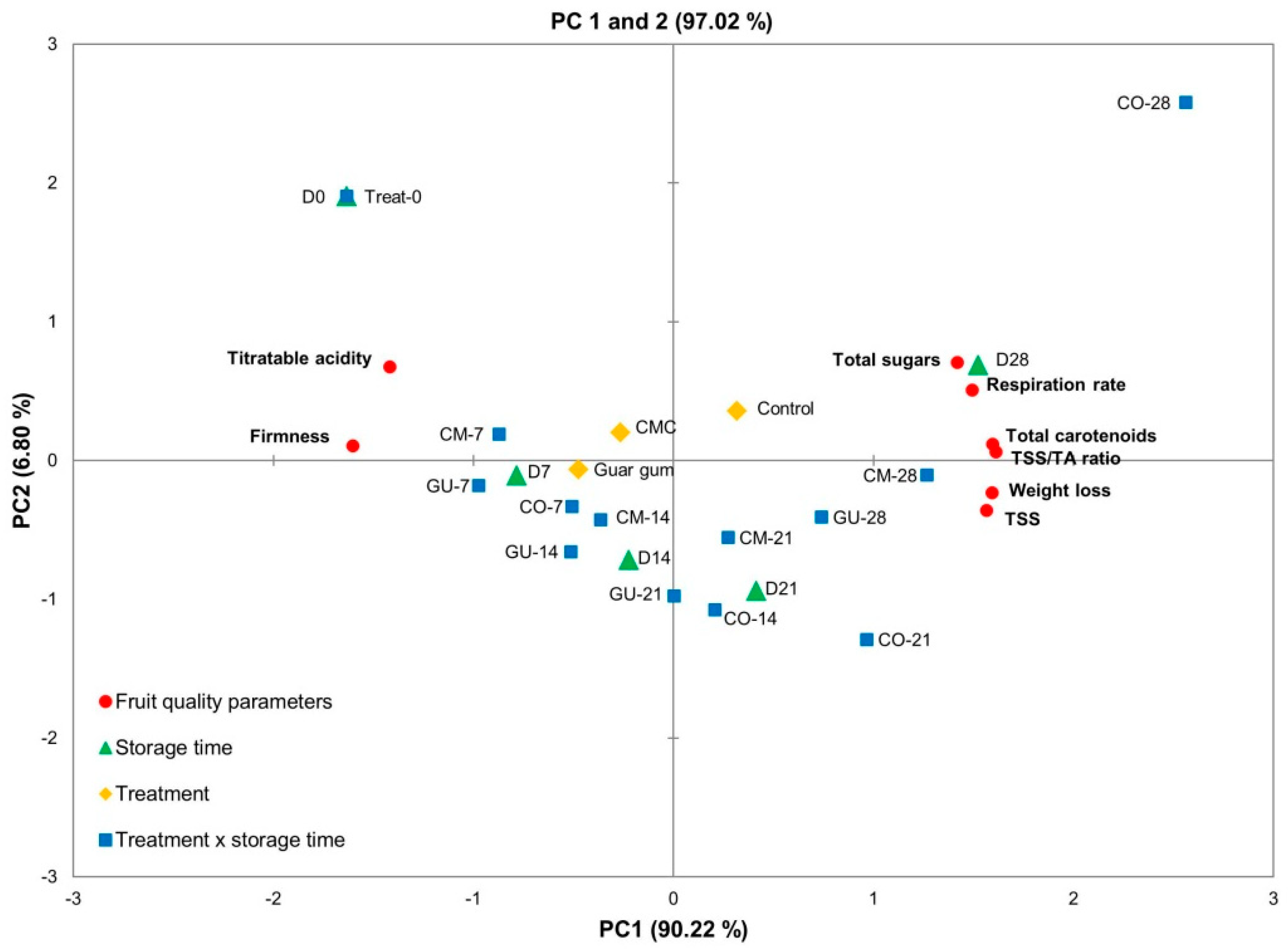
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sane, V.A.; Chourasia, A.; Nath, P. Softening in mango (Mangifera indica cv. Dashehari) is correlated with the expression of an early ethylene responsive, ripening related expansin gene, MiExpA1. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2005, 38, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.M.R.; Schieber, A. Bioactive compounds in mango (Mangifera indica L.). In Bioactive Foods in Promoting Health; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2010; pp. 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahurul, M.H.A.; Zaidul, I.S.M.; Ghafoor, K.; Al-Juhaimi, F.Y.; Nyam, K.L.; Norulaini, N.A.N.; Sahena, F.; Omar, A.M. Mango (Mangifera indica L.) by-products and their valuable components: A review. Food Chem. 2015, 183, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, A.A. Quality and safety factors: Definition and evaluation for fresh horticultural crops. In Postharvest Technology of Horticultural Crops, 3rd ed.; Kader, A.A., Ed.; University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources: Davis, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Lalel, H.J.D.; Singh, Z.; Tan, S.C.; Agustí, M. Maturity stage at harvest affects fruit ripening, quality and biosynthesis of aroma volatile compounds in ‘Kensington Pride’ mango. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2003, 78, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, D.; Jiang, Y.; Yahia, E.M. Maintaining mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit quality during the export chain. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Coronel, W.G.; Velez-de la Rocha, R.; Siller-Cepeda, J.H.; Osuna-Enciso, T.; Muy-Rangel, M.D.; Sañudo-Barajas, J.A. Changes in the composition of starch, pectin and hemicellulose during ripening of mango (Mangifera indica cv. Kent). Rev. Chapingo Ser. Hortic. 2012, 18, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Lopez, A.; Ramirez-Bustamante, F.; Valdez-Torres, J.B.; Rojas-Villegas, R.; Yahia, E.M. Ripening and quality changes in mango fruit as affected by coating with an edible film. J. Food Qual. 2000, 23, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, T.T.; Ducamp, M.N.; Lebrun, M.; Baldwin, E.A. Effect of different coating treatments on the quality of mango fruit. J. Food Qual. 2002, 25, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridoutt, B.G.; Juliano, P.; Sanguansri, P.; Sellahewa, J. The water footprint of food waste: Case study of fresh mango in Australia. J. Clean Prod. 2010, 18, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Mora, L.I.; Gutiérrez-Martínez, P.; Bautista-Baños, S.; Jiménez-García, L.F.; Zavaleta-Mancera, H.A. Evaluation of antifungal activity of chitosan in Alternaria alternata and in the quality of ‘Tommy Atkins’ mango during storage. Rev. Chapingo Ser. Hortic. 2013, 19, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, B.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Hussain, A.I.; Zia, K.M.; Akhtar, N. Recent advances on polysaccharides, lipids and protein based edible films and coatings: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, M.S.; Saxena, A.; Kaur, C. Effect of chitosan and alginate based coatings enriched with pomegranate peel extract to extend the postharvest quality of guava (Psidium guajava L.). Food Chem. 2018, 240, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maftoonazad, N.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Marcotte, M. Shelf-life extension of peaches through sodium alginate and methyl cellulose edible coatings. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazón, P.; Velazquez, G.; Ramírez, J.A.; Vázquez, M. Polysaccharide-based films and coatings for food packaging: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 68, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Peng, X.; Zeng, R.; Wan, C.; Chen, M.; Chen, J. Physiological and biochemical responses in cold-stored citrus fruits to carboxymethyl cellulose coating containing ethanol extract of Impatiens balsamina L. stems. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e12999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahirad, S.; Naghshiband-Hassani, R.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Zaare-Nahandi, F.; Mahna, N. Shelf life quality of plum fruits (Prunus domestica L.) improves with carboxymethylcellulose-based edible coating. HortScience 2019, 54, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, C.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Miranda, C. Optimization of edible coating composition to retard strawberry fruit senescence. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2007, 44, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Candido, R.G.; Gonçalves, A.R. Synthesis of cellulose acetate and carboxymethylcellulose from sugarcane straw. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmiri, H.J.; Osman, A.; Tan, C.P.; Abdul Rahman, R. Developing a new antimicrobial edible coating formulation based on carboxymethylcellulose-silver nanoparticles for tropical fruits and an in vitro evaluation of its antimicrobial properties. Acta Hortic. 2013, 1012, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, P.B.; Gol, N.B.; Rao, T.R. Postharvest quality maintenance of papaya fruit using polysaccharide-based edible coatings. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2014, 14, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, H.; Granit, R.; Porat, R.; Poverenov, E. Development of polysaccharides-based edible coatings for citrus fruits: A layer-by-layer approach. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.T. The physiological and rheological effects of foods supplemented with guar gum. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombare, N.; Jha, U.; Mishra, S.; Siddiqui, M.Z. Guar gum as a promising starting material for diverse applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruelas-Chacon, X.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Montañez, J.; Aguilera-Carbo, A.F.; Reyes-Vega, M.L.; Peralta-Rodriguez, R.D.; Sanchéz-Brambila, G. Guar gum as an edible coating for enhancing shelf-life and improving postharvest quality of roma tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naeem, A.; Abbas, T.; Ali, T.M.; Hasnain, A. Effect of guar gum coatings containing essential oils on shelf life and nutritional quality of green-unripe mangoes during low temperature storage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, B.; Golding, J.B.; Marques, J.R.; Pristijono, P.; Chockchaisawasdee, S.; Scarlett, C.J.; Stathopoulos, C.E. Application of biocomposite edible coatings based on pea starch and guar gum on quality, storability and shelf life of ‘Valencia’ oranges. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 137, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Tang, J. Physical, chemical and microbiological changes in stored green asparagus spears as affected by coating of silver nanoparticles-PVP. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; McClements, D.J. Food-grade microemulsions and nanoemulsions: Role of oil phase composition on formation and stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Kaur, P.; Devgan, K.; Attkan, A.K. Shelf life prolongation of cherry tomato using magnesium hydroxide reinforced bio-nanocomposite and conventional plastic films. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammariello, D.; Conte, A.; Buonocore, G.G.; Del Nobile, M.A. Bio-based nanocomposite coating to preserve quality of Fior di latte cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 5298–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.Y.; et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.; Sim, S.J.; Gu, M.B.; Yi, J.; Lee, J. Eco-toxicity of commercial silver nanopowders to bacterial and yeast strains. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2009, 14, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azeredo, H.M. Nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.W.A.; Jahangir, M.; Qaisar, M.; Khan, S.A.; Mahmood, T.; Saeed, M.; Farid, A.; Liaquat, M. Storage stability of kinnow fruit (Citrus reticulata) as affected by CMC and guar gum-based silver nanoparticle coatings. Molecules 2015, 20, 22645–22661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelissari, F.M.; Andrade-Mahecha, M.M.; do Amaral Sobral, P.J.; Menegalli, F.C. Nanocomposites based on banana starch reinforced with cellulose nanofibers isolated from banana peels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibolla, H.; Pelissari, F.M.; Martins, J.T.; Vicente, A.A.; Menegalli, F.C. Cellulose nanofibers produced from banana peel by chemical and mechanical treatments: Characterization and cytotoxicity assessment. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.; Hashmi, M.S. Chitosan–aloe vera gel coating delays postharvest decay of mango fruit. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pristijono, P.; Golding, J.B.; Bowyer, M.C. Postharvest UV-C treatment, followed by storage in a continuous low-level ethylene atmosphere, maintains the quality of ‘Kensington pride’ mango fruit stored at 20 °C. Horticulturae 2019, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Huang, H.; Huber, D.J.; Pan, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Z. Delay of ripening and softening in ‘Guifei’ mango fruit by postharvest application of melatonin. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 163, 111136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, G.; Mohamed, M.T.M.; Ali, A.; Ding, P.; Ghazali, H.M. Effect of gum arabic coating combined with calcium chloride on physico-chemical and qualitative properties of mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit during low temperature storage. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 190, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A. Chlorophylls and carotenoids. In Handbook of Phycological Methods: Physiological and Biochemical Methods; Hellebust, J.A., Craigie, J.S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1978; pp. 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Altundag, H.; Tuzen, M. Comparison of dry, wet and microwave digestion methods for the multi element determination in some dried fruit samples by ICP-OES. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2800–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kong, F.; Vardhanabhuti, B.; Mustapha, A.; Lin, M. Detection of engineered silver nanoparticle contamination in pears. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10762–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.B. Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 1955, 11, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, B.C.G.; Madhavan, J.; Santhanam, A. Cytotoxic effect of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Padina tetrastromatica on breast cancer cell line. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shousha, W.G.; Aboulthana, W.M.; Salama, A.H.; Saleh, M.H.; Essawy, E.A. Evaluation of the biological activity of Moringa oleifera leaves extract after incorporating silver nanoparticles, in vitro study. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bar, H.; Bhui, D.K.; Sahoo, G.P.; Sarkar, P.; De, S.P.; Misra, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using latex of Jatropha curcas. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 339, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayagam, V.; Gabriel, M.; Palanisamy, K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by Coccinia grandis and Phyllanthus emblica: A comparative comprehension. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvert, P.Y.; Herrera-Urbina, R.; Tekaia-Elhsissen, K. Preparation of colloidal silver dispersions by the polyol process. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abidin, Z.H.Z.; Arof, A.K. Influence of silver ion reduction on electrical modulus parameters of solid polymer electrolyte based on chitosan-silver triflate electrolyte membrane. Express Polym. Lett. 2010, 4, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasekara, R.; Harding, I.; Bowater, I.; Christie, G.B.Y.; Lonergan, G.T. Preparation, surface modification and characterisation of solution cast starch PVA blended films. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, A.M.; Brennan, M.E.; Blau, W.J.; Kellya, J.M. Enhanced third-order optical nonlinearity of silver nanoparticles with a tunable surface plasmon resonance. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004, 4, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Duan, B.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L. Superabsorbent hydrogels based on cellulose for smart swelling and controllable delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fu, S.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X. Hydrogel beads based on carboxymethyl cellulose for removal heavy metal ions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Goswami, G.K.; Nanda, K.K. Green synthesis of biopolymer–silver nanoparticle nanocomposite: An optical sensor for ammonia detection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.M.C.; Silva, W.B.; Medeiros, D.B.; Salvador, A.R.; Cordeiro, M.H.M.; da Silva, N.M.; Santana, D.B.; Mizobutsi, G.P. The chitosan affects severely the carbon metabolism in mango (Mangifera indica L. cv. Palmer) fruit during storage. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, R.; Golding, J. Postharvest: An Introduction to the Physiology and Handling of Fruit and Vegetables, 6th ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2016; 293p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawab, A.; Alam, F.; Hasnain, A. Mango kernel starch as a novel edible coating for enhancing shelf-life of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardesh, A.S.K.; Badii, F.; Hashemi, M.; Ardakani, A.Y.; Maftoonazad, N.; Gorji, A.M. Effect of nanochitosan based coating on climacteric behavior and postharvest shelf-life extension of apple cv. Golab Kohanz. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 70, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Maqbool, M.; Ramachandran, S.; Alderson, P.G. Gum arabic as a novel edible coating for enhancing shelf-life and improving postharvest quality of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2010, 58, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheshetawy, H.E.; Mossad, A.; Elhelew, W.K.; Farina, V. Comparative study on the quality characteristics of some Egyptian mango cultivars used for food processing. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2016, 61, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Z.; Jung, J.; Simonsen, J.; Zhao, Y. Cellulose nanomaterials emulsion coatings for controlling physiological activity, modifying surface morphology, and enhancing storability of postharvest bananas (Musa acuminate). Food Chem. 2017, 232, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, R.K.; Rao, T.R.; Nandane, A.S. Improvement of post-harvest quality of pear fruit with optimized composite edible coating formulations. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3917–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Song, S.; Luo, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Qin, Y. Effect of PLA nanocomposite films containing bergamot essential oil, TiO2 nanoparticles, and Ag nanoparticles on shelf life of mangoes. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 249, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittur, F.S.; Saroja, N.; Tharanathan, R. Polysaccharide-based composite coating formulations for shelf-life extension of fresh banana and mango. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001, 213, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Ahmed, A.; Shah, S.W.A.; Mehmood, T.; Abbasi, K.S. Effect of silver nanoparticle coatings on physicochemical and nutraceutical properties of loquat during postharvest storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gol, N.B.; Chaudhari, M.L.; Rao, T.V.R. Effect of edible coatings on quality and shelf life of carambola (Averrhoa carambola L.) fruit during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista-Silva, W.; Nascimento, V.L.; Medeiros, D.B.; Nunes-Nesi, A.; Ribeiro, D.M.; Zsögön, A.; Araújo, W.L. Modifications in organic acid profiles during fruit development and ripening: Correlation or causation? Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Abbasi, N.A.; Shafique, M.; Qureshi, A.A. Influence of edible coatings on biochemical fruit quality and storage life of bell pepper cv. “Yolo Wonder”. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvaraj, Y.; Kumar, R.; Pal, D.K. Changes in sugars, organic acids, amino acids, lipid constituents and aroma characteristics of ripening mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1989, 26, 308–313. [Google Scholar]
- Osorio, S.; Scossa, F.; Fernie, A. Molecular regulation of fruit ripening. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Li, F.; Wang, L.; Sheng, J.; Xin, Z.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, Q. Effect of nano-packing on preservation quality of Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill. var. inermis (Bunge) Rehd). Food Chem. 2009, 114, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hmmam, I.; Zaid, N.; Mamdouh, B.; Abdallatif, A.; Abd-Elfattah, M.; Ali, M. Storage Behavior of “Seddik” Mango Fruit Coated with CMC and Guar Gum-Based Silver Nanoparticles. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030044
Hmmam I, Zaid N, Mamdouh B, Abdallatif A, Abd-Elfattah M, Ali M. Storage Behavior of “Seddik” Mango Fruit Coated with CMC and Guar Gum-Based Silver Nanoparticles. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(3):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030044
Chicago/Turabian StyleHmmam, Ibrahim, Ne’ma Zaid, Bahaaaldin Mamdouh, Abdou Abdallatif, Mohamed Abd-Elfattah, and Mohamed Ali. 2021. "Storage Behavior of “Seddik” Mango Fruit Coated with CMC and Guar Gum-Based Silver Nanoparticles" Horticulturae 7, no. 3: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030044
APA StyleHmmam, I., Zaid, N., Mamdouh, B., Abdallatif, A., Abd-Elfattah, M., & Ali, M. (2021). Storage Behavior of “Seddik” Mango Fruit Coated with CMC and Guar Gum-Based Silver Nanoparticles. Horticulturae, 7(3), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030044