High NH4+/NO3− Ratio Inhibits the Growth and Nitrogen Uptake of Chinese Kale at the Late Growth Stage by Ammonia Toxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Treatments
2.3. Parameter Measurements
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
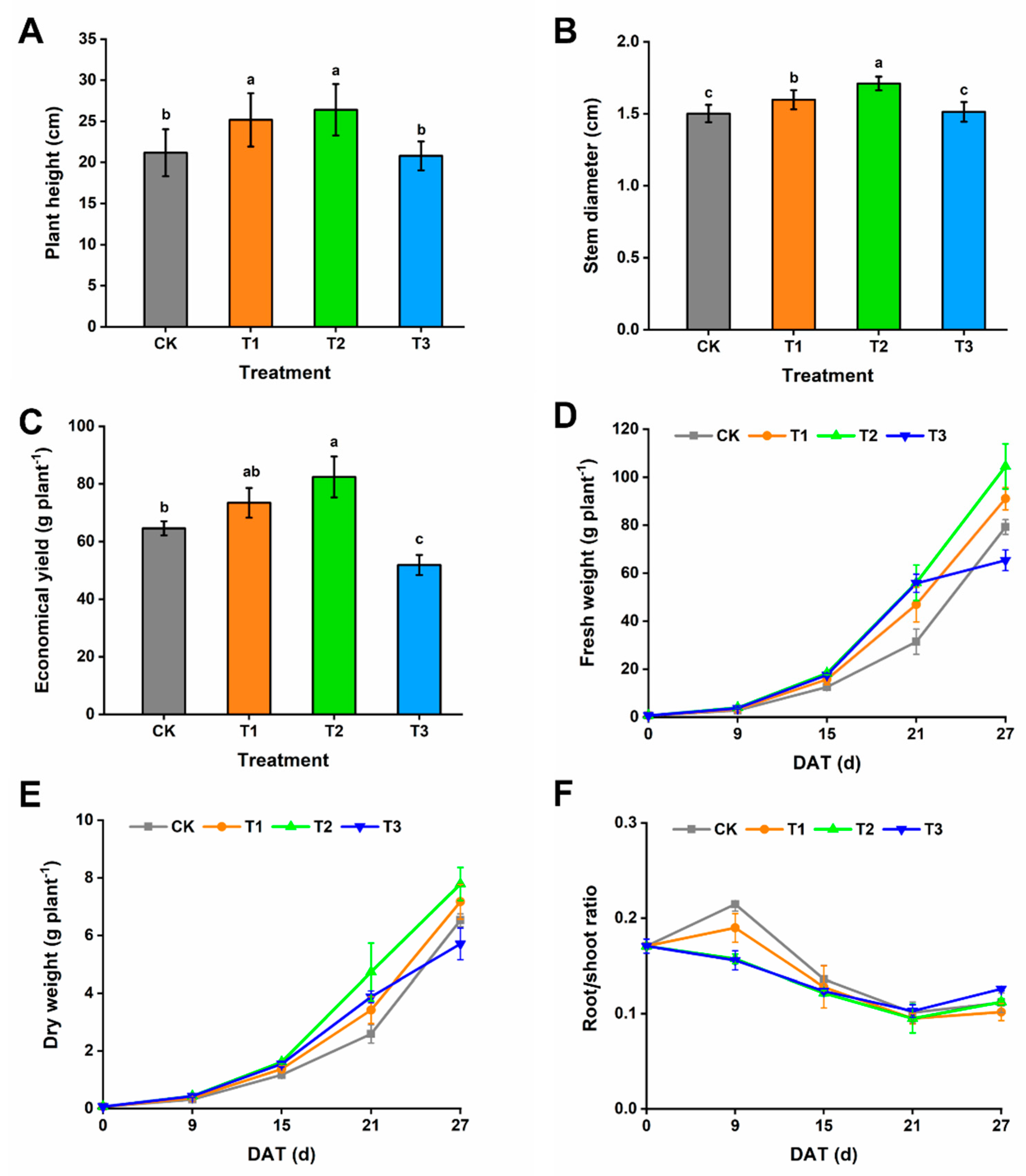
3.1. Growth and Biomass
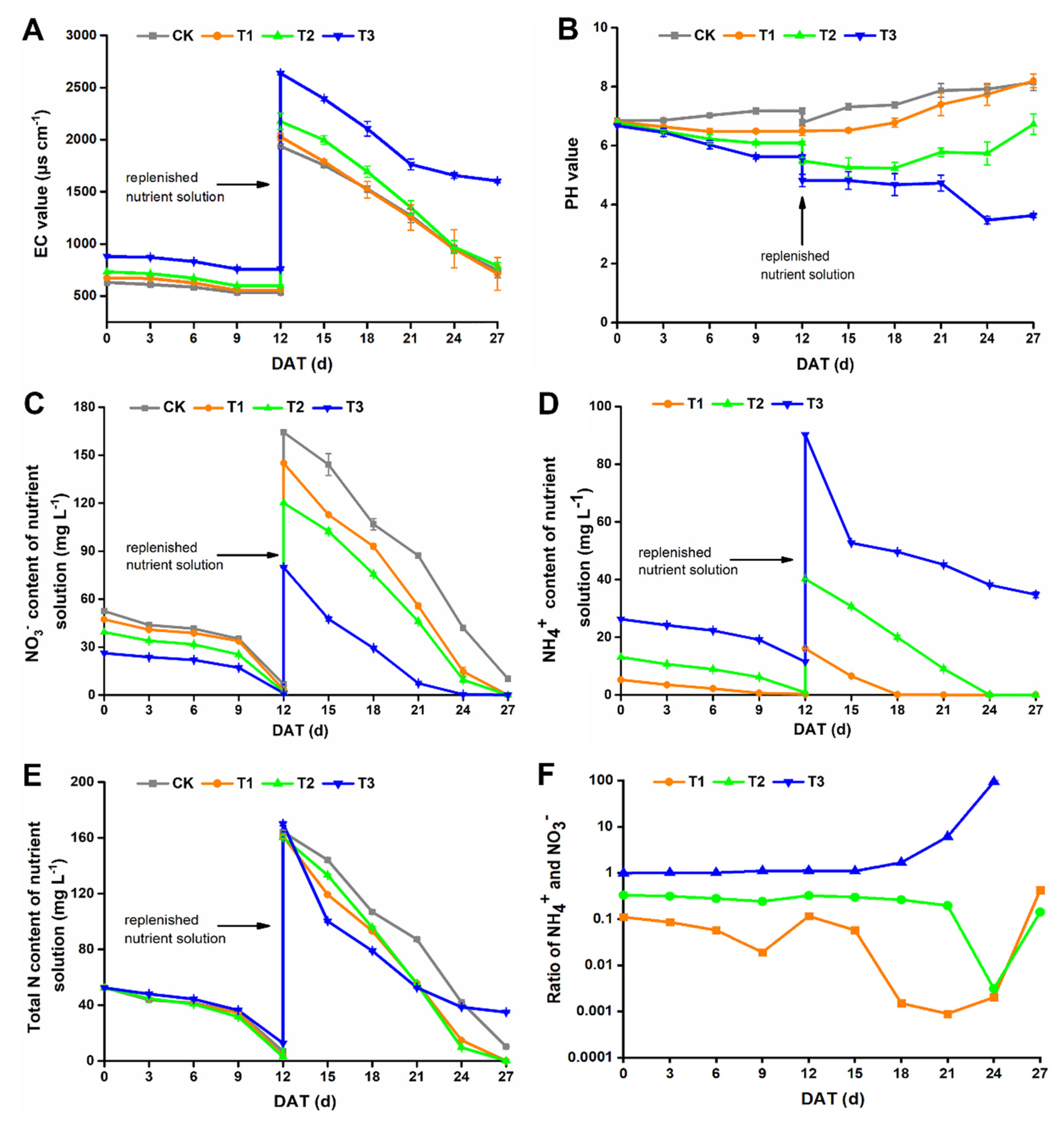
3.2. Dynamic Changes in Nutrient Solution Composition
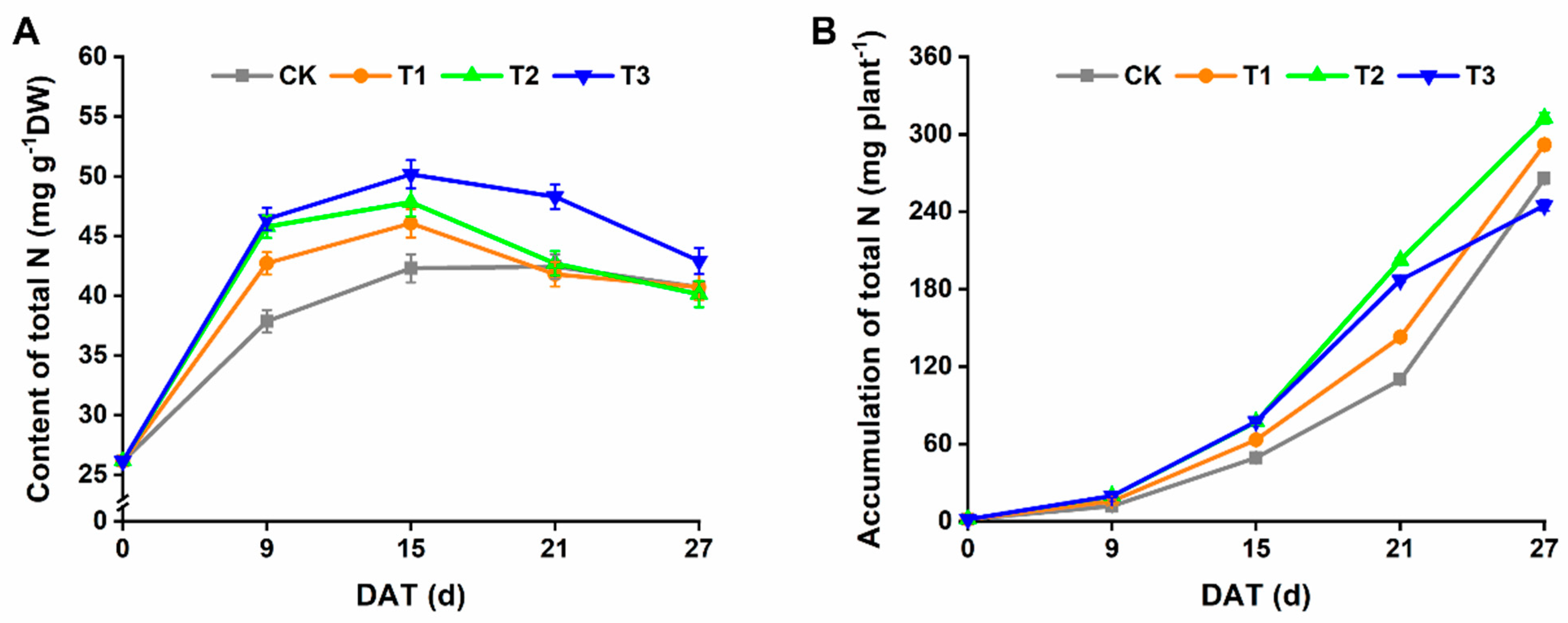
3.3. N Content and N Use Efficiency
3.4. Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.F.; Chang, D.; Zhang, X.; Shi, H.Z.; Yang, H.J. RNA-Seq, physiological, and biochemical analysis of burley tobacco response to nitrogen deficiency. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Zeng, H.Q.; Liu, G.; Di, T.J.; Shen, Q.R.; Xu, G.H. Involvement of plasma membrane H+-ATPase in adaption of rice to ammonium nutrient. Rice Sci. 2011, 18, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, A.; Sajitz-Hermstein, M.; Nikoloski, Z. Effects of varying nitrogen sources on amino acid synthesis costs in Arabidopsis thaliana under different light and carbon-source conditions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachiya, T.; Sakakibara, H. Interactions between nitrate and ammonium in their uptake, allocation, assimilation, and in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2501–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, R.; Ariz, I.; Cruz, C.; Moran, J.F. Mechanisms of ammonium toxicity and the quest for tolerance. Plant Sci. 2017, 248, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bittsánszky, A.; Pilinszky, K.; Gyulai, G.; Komives, T. Overcoming ammonium toxicity. Plant Sci. 2015, 231, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaei, S.J.; Yusefi, M.; Hajiloo, J. Effects of shading and NO3−: NH4+ ratio on the yield, quality and N metabolism in strawberry. Sci. Hortic. 2008, 116, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Yu, J.; Liao, W.; Zhang, G.; Xie, J.; Lv, J.; Xiao, X.; Yang, B.; Zhou, R.; Bu, R. Moderate ammonium: Nitrate alleviates low light intensity stress in mini Chinese cabbage seedling by regulating root architecture and photosynthesis. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 186, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.W.; Yi, L.Y.; Zhu, Y.N.; Liu, H.C.; Sun, G.W.; Chen, R.Y. Effects of ammonium and nitrate ratios on plant growth, 405 nitrate concentration and nutrient uptake in flowering Chinese cabbage. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2017, 46, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.N.; Li, G.; Liu, H.C.; Sun, G.W.; Chen, R.Y.; Song, S.W. Effects of partial replacement of nitrate with different nitrogen forms on the yield, quality, and nitrate content of Chinese kale. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant 2018, 49, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.Q.; Liu, G.; Kinoshita, T.; Zhang, R.P.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Shen, Q.R.; Xu, G.H. Stimulation of phosphorus uptake by ammonium nutrition involves plasma membrane H+-ATPase in rice roots. Plant Soil. 2012, 357, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.H.; Ye, J.Y.; Cui, M.Q.; Chang, J.B.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.X.; Wu, Y.R.; Xu, J.M.; Harberd, N.P.; Mao, C.Z. A transcription factor STOP1-centered pathway coordinates ammonium and phosphate acquisition in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 1554–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.N.; Qi, B.F.; Hao, Y.W.; Liu, H.C.; Sun, G.W.; Chen, R.Y.; Song, S.W. Appropriate NH4+/NO3− Ratio Triggers Plant Growth and Nutrient Uptake of Flowering Chinese Cabbage by Optimizing the pH Value of Nutrient Solution. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 656144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Lei, J.J.; Cao, B.H.; Wu, S.Y.; Chen, G.J.; Chen, C.M. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of Three Glucosinolate Transporter (GTR) Genes from Chinese Kale. Genes 2019, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, J.J.; Chen, G.J.; Chen, C.M.; Cao, B.H. Germplasm Diversity of Chinese Kale in China. Hortic. Plant J. 2017, 3, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.W.; Liao, G.X.; Liu, H.C.; Sun, G.W.; Chen, R.Y. Effect of ammonium and nitrate ratios on growth and yield of Chinese kale. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 142, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K.; Shi, Z.Y.; Shi, J.P. Status Evaluation and Dynamic Change of farmland nutrient balance in 6 provinces in South China. Chin. J. Agric. Sci. 2000, 2, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein, R.L.; Karlsson, P.S. The effect of reproduction on nitrogen use-efficiency of three species of the carnivorous genus Pinguicula. J. Ecol. 2001, 89, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.F. Soil nutrients and their ecological stoichiometry of Pinus yunnanensis forest along an elevation gradient. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 672–679. [Google Scholar]
- Konnerup, D.; Brix, H. Nitrogen nutrition of Canna indica: Effects of ammonium versus nitrate on growth, biomass allocation, photosynthesis, nitrate reductase activity and N uptake rates. Aquat. Bot. 2010, 92, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Lu, Z.F.; Gao, L.M.; Guo, S.W.; Shen, Q.R. Is nitrogen a key determinant of water transport and photosynthesis in higher plants upon drought stress? Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.H.D.S.; Bona, F.D.D.; Monteiro, F.A. Growth and productive responses of tropical grass Panicum maximum to nitrate and ammonium supply. Rev. Bras. Zootecn. 2013, 42, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashraf, M.; Naz, U.; Abid, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Aziz, A.; Akhtar, N.; Naeem, A.; Mühlinget, K.H. Salinity resistance as a function of NH4+:NO3− ratio and its impact on yield and quality of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2021, 184, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.K.; Lee, N.R.; Choi, J.M. Impact of Pre-planting NH4+:NO3− Ratios in Inert Media on the Growth of Chinese Cabbage Plug Seedlings. Korean J. Hortic. Sci. 2016, 34, 736–745. [Google Scholar]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Bio. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marschner, H.; Kirkby, E.A.; Cakmak, I. Effect of mineral nutritional status on shoot-root partitioning of photoassimilates and cycling of mineral nutrients. J. Exp. Bot. 1996, 47, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarasketa, A.; González-Moro, M.B.; González-Murua, C.; Marino, D. Nitrogen source and external medium pH interaction differentially affects root and shoot metabolism in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Luo, J.K.; Jiang, H.M.; Shen, Q.R. Effects of different nitrogen forms on biomass and nitrate content of different mini-Chinese cabbage varieties. Acta Pedol. Sinica. 2004, 41, 420–425. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Shen, Q.R.; Lai, T.; Shen, Q.R. Study on the effect of nutrient solution with different ammonium nitrate ratio on the growth and development of lettuce. Acta Pedol. Sinica. 2007, 44, 561–565. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Lv, J.; Dawuda, M.M.; Xie, J.M.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, C.; Wang, C.; Gan, Y. Appropriate Ammonium-Nitrate Ratio Improves Nutrient Accumulation and Fruit Quality in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Agronomy 2019, 9, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baracaldo, A.D.P.; Daz, M.C.; Flrez, V.J.; Gonzlez, C.A. Efecto de la disminución de N total y aumento de NH4+ en la fórmula de fertirriego en el cultivo de clavel. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Pec. 2018, 12, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.C.; Kang, S.Z.; Li, F.S.; Zhang, J.H. Growth and Major Nutrient Concentrations in Brassica campestris Supplied with Different NH4+:NO3− Ratios. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2007, 49, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.N.; Li, B.; Wang, X.F.; Xi, Z.M. Effect of Ammonium and Nitrate Supplies on Nitrogen and Sucrose Metabolism of Cabernet Sauvignon (Vitis vinifera cv.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 10574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, N.; Shi, W.M.; Hou, L.H.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Huang, L.; Gu, H.M.; Yang, Q.P.; Deng, G.; Yang, G. Superior growth, N uptake and NH4+ tolerance in the giant bamboo Phyllostachys edulis over the broad-leaved tree Castanopsis fargesii at elevated NH4+ may underlie community succession and favor the expansion of bamboo. Tree Physiol. 2020, 40, 1606–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Fan, X.; Miller, A.J.; Xu, G. Plant nitrogen uptake and assimilation: Regulation of cellular pH homeostasis. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 4380–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickson, R.W.; Fisher, P.R.; Argo, W.R.; Jacquesc, D.J.; Sartaina, J.B.; Trenholma, L.E.; Yeager, T.H. Solution Ammonium: Nitrate ratio and cation/anion uptake affect acidity or basicity with floriculture species in hydroponics. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 200, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jong, M.C. Influence of Pre-Plant Micronutrient Sources and Post-Plant NH4+:NO3− Ratios in Fertilizer Solution on Growth and Nutrient Uptake of Marigold in Plug Culture. Hortic. Environ. Biote. 2007, 48, 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Berendse, F.; Aerts, R. Nitrogen-use-efficiency: A biologically meaningful definition? Funct. Ecol. 1987, 1, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Aerts, R. Interspecific competition in natural plant communities: Mechanisms, trade-offs, and plant-soil feedbacks. J. Exp. Bot. 1999, 50, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.C.; Inanaga, S. Nitrogen Losses in Relation to Rice Varieties, Growth Stages, and Nitrogen Forms Determined with the 15N Technique. In Controlling Nitrogen Flows and Losses; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 496–497. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, D.R.; Bloom, A.J. Wheat leaves emit nitrous oxide during nitrate assimilation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7875–7878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, S.G.; Chen, N.C.; Zhou, J.M.; Wu, Q.T.; Bi, D.; Lu, W.S. Regulation mechanism of light and nitrogen application on nitrogen oxide (NO and NO2) exchange between leaves of rice at tillering stage. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2009, 23, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.L.; Shi, L.; Xu, F.S.; Wang, C.; Cai, H.M.; Ding, G.D. The rapeseed genotypes with contrasting NUE response discrepantly to varied provision of ammonium and nitrate by regulating photosynthesis, root morphology, nutritional status, and oxidative stress response. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 166, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouphael, Y.; Kyriacou, M.C.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Pascale, S.D.; Colla, G. Improving vegetable quality in controlled environments. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 234, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | NH4+/NO3− | KNO3 | Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | KH2PO4 | MgSO4·7H2O | (NH4)2SO4 | K2SO4 | CaCl2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0/100 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 1.4 | - | - | - |
| T1 | 10/90 | 1.75 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.375 | 0.375 | - |
| T2 | 25/75 | 0.625 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.9375 | 0.9375 | - |
| T3 | 50/50 | - | 1.875 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 1.875 | 1.25 | 0.625 |
| Treatments | NH4+/NO3− | 0~9 | 9~15 | 15~21 | 21~27 | 0~21 | 0~27 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0/100 | 27.7 ± 2.8 b | 141.8 ± 4.9 c | 237.5 ± 47.5 c | 656.1 ± 17.0 a | 120.2 ± 15.3 c | 239.0 ± 8.1 bc |
| T1 | 10/90 | 33.7 ± 2.0 ab | 167.1 ± 17.5 b | 341.3 ± 65.9 b | 625.1 ± 27.0 a | 159.7 ± 22.2 bc | 263.0 ± 22.3 ab |
| T2 | 25/75 | 40.5 ± 3.9a | 197.2 ± 4.2 a | 519.6 ± 156.0 a | 509.0 ± 76.4 b | 222.2 ± 47.7 a | 286.0 ± 21.4 a |
| T3 | 50/50 | 39.9 ± 5.3 a | 186.8 ± 9.3 a | 388.4 ± 17.5 ab | 304.9 ± 57.7 c | 181.4 ± 9.7 ab | 209.0 ± 20.4 c |
| Treatments | NH4+/NO3− | Main Root Length (cm plant−1) | Root Total Length (cm plant−1) | Root Surface Area (cm2 plant−1) | Root Volume (cm3 plant−1) | Average Root Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0/100 | 6.91 ± 0.77 ab | 65.8 ± 11.5 c | 13.7 ± 3.2 c | 0.23 ± 0.07 cd | 0.66 ± 0.04 b |
| T1 | 10/90 | 7.23 ± 0.38 ab | 90.8 ± 2.7 b | 20.9 ± 5.1 b | 0.40 ± 0.19 b | 0.73 ± 0.16 ab |
| T2 | 25/75 | 7.72 ± 0.84 a | 126.0 ± 8.9 a | 31.9 ± 4.2 a | 0.66 ± 0.16 a | 0.81 ± 0.09 a |
| T3 | 50/50 | 6.63 ± 0.49 b | 61.4 ± 12.4 c | 14.5 ± 3.7 c | 0.28 ± 0.09 bc | 0.75 ± 0.07 ab |
| Treatments | NH4+/NO3− | N Loss (mg Plant−1) | Rate of N Loss (%) | N Residence Time (d) | N Productivity (mg mg−1 d−1) | N Use Efficiency (mg mg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0/100 | 102.1 ± 5.1 a | 27.9 ± 1.2 a | 13.9 ± 0.1 c | 4.6 ± 0.6 a | 63.3 ± 1.7 c |
| T1 | 10/90 | 94.6 ± 1.5 b | 24.6 ± 0.4 b | 16.1 ± 0.4 b | 4.7 ± 0.2 a | 75.1 ± 5.4 b |
| T2 | 25/75 | 74.1 ± 3.2 c | 19.3 ± 0.8 c | 21.8 ± 0.3 a | 4.8 ± 0.7 a | 104.1 ± 4.1 a |
| T3 | 50/50 | 77.9 ± 3.3 c | 24.3 ± 0.9 b | 17.0 ± 0.4 b | 4.3 ± 0.6 a | 72.3 ± 4.2 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Sun, G.; Song, S.; Chen, R. High NH4+/NO3− Ratio Inhibits the Growth and Nitrogen Uptake of Chinese Kale at the Late Growth Stage by Ammonia Toxicity. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010008
Wang Y, Zhang X, Liu H, Sun G, Song S, Chen R. High NH4+/NO3− Ratio Inhibits the Growth and Nitrogen Uptake of Chinese Kale at the Late Growth Stage by Ammonia Toxicity. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yudan, Xiaoyun Zhang, Houcheng Liu, Guangwen Sun, Shiwei Song, and Riyuan Chen. 2022. "High NH4+/NO3− Ratio Inhibits the Growth and Nitrogen Uptake of Chinese Kale at the Late Growth Stage by Ammonia Toxicity" Horticulturae 8, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010008
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, H., Sun, G., Song, S., & Chen, R. (2022). High NH4+/NO3− Ratio Inhibits the Growth and Nitrogen Uptake of Chinese Kale at the Late Growth Stage by Ammonia Toxicity. Horticulturae, 8(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010008







