Influence of Different Defoliation Timings on Quality and Phenolic Composition of the Wines Produced from the Serbian Autochthonous Variety Prokupac (Vitis vinifera L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Experiment Design
2.2. Chemicals and Materials
2.3. Microvinification
2.4. Evaluation of Total Phenolic Content (TPC), Radical-Scavenging Activity (RSA) and Total Anthocyianin Content (TAC)
2.5. UHPLC-DAD MS/MS Analysis of Phenols
2.6. The Method of Data Processing and Presentation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wine Phenolic Composition
3.2. Total Polyphenolic Content, Radical Scavenging Activity and Total Anthocyanins Content
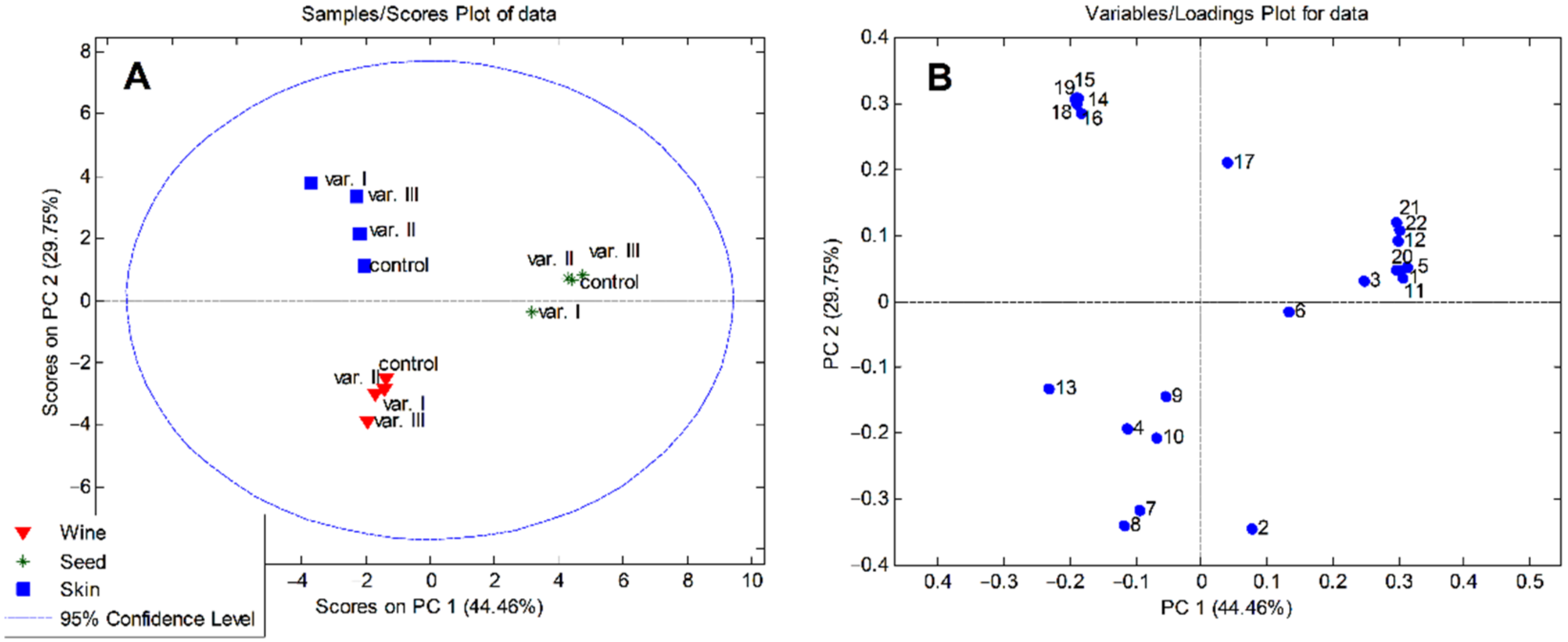
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asci, S.D.; Tangolar, S.; Kazan, K.; Ozmen, C.Y.; Oktem, M.; Kibar, U.; Mujtaba, M.; Tangolar, S.; Ergul, A. Evaluation of powdery mildew resistance of a diverse set of grape cultivars and testing the association between powdery resistance and PR gene expression. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2021, 45, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupe, M. Some ampelographic and biochemical characteristics of local grape accessions from Turkey. Genetika 2020, 52, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aazami, M.A.; Asghari-Aruq, M.; Hassanpouraghdam, M.B.; Ercisli, S.; Baron, M.; Sochor, J. Low temperature stress mediates the antioxidants pool and chlorophyll fluorescence in Vitis vinifera L. cultivars. Plants 2021, 10, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuelli, F.S.; Lorenzi, L.; Grzescowiak, V.; Catalano, M.; Stefanini, M.; Troggio, S.; Myles, J.; Martinez-Zapater, E.; Zyprian, F.; Moreira, M.; et al. Genetic diversity and population structure assessed by SSR and SNP markers in a large germplasm collection of grape. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bešlić, Z.; Todić, S.; Korać, N.; Lorenzi, S.; Emanuelli, F.; Grando, S. Genetic characterization and relationships of traditional grape cultivars from Serbia. Vitis 2012, 51, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Lakićević, S.; Popović Djordjević, J.; Pejin, B.; Djordjević, A.; Matijašević, S.; Lazić, M. An insight into chemical composition and bioactivity of ‘Prokupac’ red wine. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 34, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bešlić, Z.; Todić, S.; Matijasevic, S. Effect of timing of basal leaf removal on yield components and grape quality of grapevine cvs Cabernet sauvignon and Prokupac (Vitis vinifera L.). Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 19, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Poni, S.; Casalini, L.; Bernizzoni, F.; Civardi, S.; Interieri, C. Effects of early defoliation on shoot photosynthesis, yield components and grape composition. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2006, 57, 397–407. [Google Scholar]
- Poni, S.; Gatti, M.; Bernizzoni, F.; Civardi, S.; Bobeica, N.; Magnanini, E.; Palliotti, A. Late leaf removal aimed at delaying ripening in cv. Sangiovese: Physiological assessment and vine performance. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2013, 19, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, P.R.; Trought, M.C.T.; Howell, S.G. Fruit composition and ripening of Pinot Noir (Vitis vinifera L.) in relation to leaf area. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2000, 6, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candolfi-Vasconcelos, M.C.; Koblet, W. Yield, fruit quality, bud fertility and starch reserves of the wood as a function of leaf removal in Vitis vinifera—Evidence of compensation and stress recovering. Vitis 1990, 29, 199–221. [Google Scholar]
- Poni, S.; Bernizzoni, F. A three-year survey on the impact of pre-flowering leaf removal on berry growth components and grape composition in cv. Barbera vines. J. Int. Sci. Vigne Vin 2010, 44, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotseridis, Y.; Georgiadou, A.; Tikos, P.; Kallithraka, S.; Koundouras, S. Effects of severity of post-flowering leaf removal on berry growth and composition of three red Vitis vinifera L. cultivars grown under semiarid conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6000–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyce, P.W.; Steel, C.C.; Harper, J.D.I.; Wood, R.M. The basis of defoliation effects on reproductive parameters in Vitis vinifera L. cv. Chardonnay lies in the latent bud. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2016, 67, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aćimović, D.; Tozzini, L.; Green, A.; Sivilotti, P.; Sabbatini, P. Identification of a defoliation severity threshold for changing fruitset, bunch morphology and fruit composition in Pinot Noir. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2016, 22, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternad Lemut, M.; Trost, K.; Sivilotti, P.; Arapitsas, P.; Vrhovšek, U. Early versus late leaf removal strategies for Pinot Noir (Vitis vinifera L.): Effect on colour-related phenolics in young wines following alcoholic fermentation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 3670–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubola, M.; Persuric, Đ.; Ganic, K.; Cossetto, M. Influence of timing and intensity of basal leaf removal on aromatic composition of cv. Istrian Malvasia wines. In Proceedings of the Malvasias III International Symposium, La Palma, Spain, 27–31 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Baiano, A.; De Gianni, A.; Previtali, M.A.; Del Nobile, M.A.; Novello, V.; de Palma, L. Effects of defoliation on quality attributes of Nero di Troia (Vitis vinifera L.) grape and wine. Food Res. Int. 2015, 75, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osrečak, M.; Karoglan, M.; Kozina, B. Influence of leaf removal and reflective mulch on phenolic composition and antioxidant activity of Merlot, Teran and Plavac mali wines (Vitis vinifera L.). Sci. Hortic. 2016, 209, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokoozlian, N.K.; Kliewer, W.M. The light environment within grapes canopies II. Influence of leaf area density on fruit zone light environment and some canopy assessment parameters. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1995, 46, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Chorti, E.; Guidoni, S.; Ferrandino, A.; Novello, V. Effect of different cluster sunlight exposure levels on ripening and anthocyanin accumulation in Nebbiolo grapes. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2010, 61, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ristić, R.; Bindon, K.; Francis, L.I.; Herderich, M.J.; Iland, P.G. Flavonoids and C13-norisoprenoids in Vitis vinifera L. cv. Shiraz: Relationships between grape and wine composition, wine colour and wine sensory properties. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2010, 16, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarara, J.M.; Lee, J.M.; Spayd, S.E.; Scagel, C.F. Berry temperature and solar radiation alter acylation, proportion and concentration of anthocyanin in Merlot grapes. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2008, 59, 235–247. [Google Scholar]
- Sabbatini, P.; Howell, G.S. Effects of early defoliation on yield, fruit composition and harvest season cluster rot complex of grapevines. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 45, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risco, D.; Perez, D.; Yeves, A.; Castel, J.R.; Intrigliolo, D.S. Early defoliation in a temperate warm and semiarid Tempranillo vineyard: Vine performance and grape composition. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2014, 20, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, M.; Meng, J.; Chi, M.; Xi, Z.; Zhang, Z. Promoting effect of foliage sprayed zinc sulfate on accumulation of sugar and phenolics in berries of Vitis vinifera cv. Merlot growing on zinc deficient soil. Molecules 2015, 20, 2536–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernanz, D.; Recamales, A.F.; Lourdes Gonzalez-Miret, M.; Jose Gomez-Miguez, M.; Vicario, I.M.; Heredia, F.J. Phenolic composition of white wines a prefermentative maceration at experimental and industrial scale. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergqvist, J.; Dokoozlian, N.K.; Ebisuda, N. Sunlight exposure and temperature effects on berry growth and composition of Cabernet Sauvignon and Grenanche in the central San Joaquin of California. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2001, 52, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.A. Grape and wine phenolics: Observations and recent findings. Cienc. Investig. Agrar. 2008, 35, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachman, J.; Sulc, M.; Faitova, K.; Pivec, V. Major factors influencing antioxidant contents and antioxidant activity in grapes and wines. Int. J. Wine Res. 2009, 1, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J. Phenolic contents and compositions in skins of red wine grape cultivars among various genetic backgrounds and originations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3492–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertolas, E.; Alvarez, I.; Raso, J. Changes in phenolic compounds of Aragon red wines during alcoholic fermentation. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2011, 17, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustioni, L.; Rossoni, M.; Calatroni, M.; Failla, O. Influence of bunch exposure on anthocyanins extractability from grapes skins (Vitis vinifera L.). Vitis 2011, 50, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Trad, M.; Le Bourvellec, C.; Hamda, H.B.; Renard, C.; Harbi, M. Flavan-3-ols and procyanidins in grape seeds: Biodiversity and relationships among wild and cultivated vines. Euphytica 2017, 213, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.S.; Demiray, S.; Egebo, M.; Meyer, A.S. Prediction of wine color attributes from the phenolic profiles of red grapes (Vitis vinifera). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lorenzis, G.; Rustioni, L.; Parisi, S.G.; Zoli, F.; Brancadoro, L. Anthocyanin biosynthesis during berry development in corvina grape. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 212, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.J.; De Villers, O.T.; Watts, J.E. The effect of partial defoliation on quality characteristics of Vitis Vinifera L. cv. Cabernet Sauvignon grapes. II. Skin color, skin sugar and wine quality. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1991, 2, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlović, A.; Dabić, D.; Momirović, N.; Dojčinović, B.; Milojković-Opsenica, D.; Tešić, Ž. Chemical composition of two different extracts of berries harvested in Serbia. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4188–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelić, M.; Dabić Zagorac, D.; Davidović, S.; Todić, S.; Bešlić, Z.; Gašić, U.; Tešić, Ž.; Natić, M. Indentification and quantification of phenolic compounds in berry skin, pulp, and seeds in 13 grapevine varieties grown in Serbia. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašić, U.; Natić, M.; Mišić, D.; Lušić, D.; Milojković-Opsenica, D.; Tešić, Ž.; Lušić, D. Chemical markers for the authentication of unifloral Salvia officinalis L. honey. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 44, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelić, M.; Dabić Zagorac, D.; Gašić, U.; Jović, S.; Bešlić, Z.; Todić, S.; Natić, M. Phenolic profiles of Serbian autochthonous variety ‘Prokupac’ and monovarietal international wines from the Central Serbia wine region. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 2356–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Zoecklein, B.; Zhou, K. Antioxidant properties and bioactive components of Norton (Vitis aestivalis) and Cabernet Franc (Vitis vinifera) wine grapes. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, A.S.; Martinez-Fernández, M.; Chicharro, M. The role of electroanalytical techniques in analysis of polyphenols in wine. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 34, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, D.; Vilanova, M.; Gamero, E.; Intrigliolo, D.; Talaverano, I.; Uriarte, D.; Valdes, E. Effects of preflowering leaf removal on phenolic composition of Tempranillo in the semiarid terroir of Western Spain. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2015, 66, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćirković, D.; Matijašević, S.; Deletić, N.; Ćirković, B.; Gašić, U.; Sredojević, M.; Jovanović, Z.; Đurić, V.; Tešić, Ž. The effect of early and late defoliation on phenolic composition and antioxidant properties of Prokupac variety grape berries (Vitis vinifera L.). Agronomy 2019, 9, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardaguila, J.; Martinez de Toda, F.; Poni, S.; Diago, M.P. Impact of early leaf removal on yield and fruit and wine composition of Vitis vinifera L. Graciano and Carignan. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2010, 61, 372–381. [Google Scholar]
- Diago, M.; Ayestaran, B.; Guadalupe, Z.; Garrido, A.; Tardaguila, J. Phenolic composition wines following early defoliation of the vines. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselgrove, L.; Botting, D.; van Heeswijck, R.; Hoj, P.B.; Dry, P.R.; Ford, C.; Land, P.G.I. Canopy microcliamte and berry composition: The effect of bunch exposure on the phenolic composition of Vitis vinifera L. cv. Shiraz grape berries. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2000, 6, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, C.; Teissedre, P.-L.; Gérain, P.; Lequeux, N.; Bornet, A.; Serisier, S.; Besançon, P.; Caporiccio, B.; Cristol, J.P.; Rouanet, J.M. Dietary wine phenolics catechin, quercetin, and resveratrol efficiently protect hypercholesterolemic hamsters against aortic fatty streak accumulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristić, R.; Pinchbeck, K.A.; Fudge, A.L.; Hayasaka, Y.; Wilkinson, K.L. Effect of leaf removal and grapevine smoke exposure on colour, chemical composition and sensory properties of Chardonnay wines. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2013, 19, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessarin, P.; Boliani, A.C.; Botelho, R.V.; Rusin, C.; Versari, A.; Parpinello, G.P.; Rombola, A.D. Effects of late defoliation on chemical and sensory characteristics of cv. Uva Longanesi wines. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 14, 1021–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Song, C.; Wang, C.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Z. Effects of leaf removal and cluster thinning on berry quality of Vitis vinifera cultivars in the region of Weibei Dryland in Chine. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardaguila, J.; Diago, M.P.; de Toda, F.M.; Poni, S.; Vilanova, M. Effects of timing of leaf removal on yield, berry maturity, wine composition and sensory properties of cv. Grenache grown under non irrigated conditions. J. Int. Sci. Vigne Vin 2008, 42, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavaresco, L.; Gatti, M.; Pezzutto, S.; Fregoni, M.; Mattivi, F. Effect of leaf removal on grape yield, berry composition, and stilbene concentration. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2008, 59, 292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, J.; Gardner, P.T.; O’Nell, J.; Crawford, S.; Morecroft, I.; McPhail, D.B.; Lister, C.; Matthews, D.; MacLean, M.R.; Lean, M.E.; et al. Relationship among antioxidant activity, vasodilation capacity, and phenolic content of red wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratil, P.; Kuban, V.; Fojtova, J. Comparison of the phenolic content and total antioxidant activity in wines as determined by spectrophotometric methods. Czech J. Food Sci. 2008, 26, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallithraka, S.; Tsoutsouras, E.; Tzourou, E.; Lanaridis, P. Principal phenolic compounds in Greek red wines. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Neves, G.; Gil, G.; Favre, G.; Baldi, C.; Hernández, N.; Traverso, S. Influence of winemaking procedure and grape variety in the colour and composition of young red wines. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2013, 34, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intrigliolo, D.; Llacer, E.; Revert, J.; Dolores Esteve, M.; Dolores Climent, M.; Palau, D.; Gomez, I. Early defoliation reduces cluster compactness and improves grape composition in Mando an autochthonous cultivar of Vitis vinifera from southeastern Spain. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 167, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, S.; Tanzawa, F.; Kobayashi, H.; Suzuki, S.; Takata, R.; Saito, H. Leaf removal accelerated accumulation of delphinidin-based anthocyanins in ‘Muscat Bailey A’ (Vitis × labruscana (Bailey) and Vitis vinifera (Muscat Hamburg) grape skin. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2014, 83, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternad Lemut, M.; Sivilotti, P.; Franceschi, P.; Wehrens, R.; Vrhovsek, U. Use of metabolic profiling to study grape skin polyphenol behavior as a result of canopy microclimate manipulation in a Pinot Noir vineyard. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8976–8986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, M.; Bernizzoni, F.; Civardi, S.; Poni, S. Effects of cluster thinning and preflowering leaf removal on growth and grape composition in cv. Sangiovese. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2012, 63, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardaguila, J.; Blanco, J.A.; Poni, S.; Diago, M.P. Mechanical yield regulation in winegrapes: Comparison of early defoliation and crop thinning. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2012, 18, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Yuan, F.; Skinkis, P.; Qian, M. Influence of cluster zone leaf removal on Pinot noir grape chemical and volatile composition. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intrieri, C.; Filippeti, I.; Allegro, G.; Centinari, M.; Poni, S. Early defoliation (hand vs. mehanical) for improved crop and grape composition in Sangiovese (Vitis vinifera L.). Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2008, 14, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliewer, W.M.; Smart, R.E. Canopy manipulation for optimizing vine microclimate, crop yield and composition of grapes. In Manipulation of Fruiting, 1st ed.; Wright, C.J., Ed.; Butterworth & Co.: Nottingham, UK, 1989; Volume 18, pp. 275–291. [Google Scholar]
- Downey, M.O.; Harvey, J.S.; Robinson, S.P. The effect of bunch shading on berry development and flavonoid accumulation in Shiraz grapes. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2004, 10, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, M.; Dokoozlian, N.; Krstic, M. Cultural practice and environmental impacts on the flavonoid composition of grapes and wine: A review of recent research. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2006, 57, 257–268. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, K.; Gotto-Yamamoto, N.; Kitayama, M.; Hashizume, K. Loss of anthocyanins in red-wine grape under high temperatures. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1935–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majo, D.D.; Guardia, M.L.; Giammanco, S.; Neve, L.L.; Giammanco, M. The antioxidant capacity of red wine in relationship with its polyphenolic constituents. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanović, A.; Radovanović, B.; Jovančićević, B. Free radical scavenging and antibacterial activities of southern Serbian red wines. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, M.; Bertelli, A.; Scalzo, R.L.; Morassut, M.; Morelli, R.; Das, S.; Cui, J.H.; Das, D.K. Comparison of cardioprotective abilities between the flesh and skin of grapes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6613–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnous, A.; Makris, D.P.; Kefalas, P. Correlation of pigment and flavanol content with antioxidant properties in selected aged regional wines from Greece. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2002, 15, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustioni, L.; Fracassetti, D.; Prinsi, B.; Geuna, F.; Ancelotti, A.; Fauda, V.; Tirelli, A.; Espen, L.; Failla, O. Oxidations in white grape (Vitis vinifera L.) skins: Comparison between ripening process and photooxidative sunburn symptoms. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 150, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Phenolic Compounds | Experiment Treatments | F 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treatment I | Treatment II | Treatment III | ||
| Hydroxybenzoic acids | |||||
| gallic acid | 10.63 bc | 8.87 a | 9.46 ab | 11.13 c | * |
| protocatechuic acid | 0.60 a | 0.90 ab | 1.08 b | 0.99 b | ns |
| p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid | -- 2 | -- | -- | 0.38 | -- |
| gentisic acid | 0.15 a | 0.16 a | 0.21 a | 0.22 a | ns |
| ellagic acid | 3.90 a | 2.33 a | 2.95 a | 3.59 a | ns |
| vanillic acid | -- | 0.11 a | -- | 0.18 a | ns |
| Hydroxycinnamic acids | |||||
| caffeic acid | 0.94 ab | 0.79 a | 0.83 ab | 0.97 b | ns |
| p-coumaric acid | 0.33 a | 0.21 a | 0.34 a | 0.39 a | ns |
| ferulic acid | -- | 0.42 | -- | -- | -- |
| sinapic acid | 0.11 a | -- | -- | 0.72 a | ns |
| Flavan-3-ols | |||||
| catechin | 8.17 a | 8.53 a | 7.87 a | 7.87 a | ns |
| gallocatechin gallate | 0.18 a | 0.27 a | 0.37 a | 0.13 a | ns |
| epigallocatechin gallate | 0.15 a | 0.34 b | 0.17 a | 0.34 b | * |
| Flavonols | |||||
| kaempferol-3-O-glucoside | -- | 0.01 | -- | -- | -- |
| quercetin-3-O-galactoside | 0.32 a | 1.27 a | 1.29 a | 1.06 a | ns |
| rutin | 0.01 a | 0.01 a | 0.02 a | 0.01 a | ns |
| Flavanones | |||||
| naringenin | 0.004 a | 0.010 ab | 0.018 b | 0.017 b | * |
| hesperetin | -- | -- | -- | 0.005 | -- |
| Flavones | |||||
| luteolin-7-O-glucoside | 0.03 a | 0.18 a | 0.09 a | 0.12 a | ns |
| Dihydrochalcone derivatives | |||||
| phlorizin | 0.36 a | 0.33 a | 0.38 a | 0.37 a | ns |
| Years of the Investigation | Trial Treatments | F 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treatment I | Treatment II | Treatment III | ||
| Total polyphenolic content (mg GAE/L) | |||||
| 2014 | 859.56 ± 7.22 a | 828.95 ± 1.44 a | 932.01 ± 8.66 b | 1001.40 ± 14.43 b | * |
| 2015 | 814.66 ± 18.76 a | 867.72 ± 33.19 a | 986.09 ± 4.33 b | 958.54 ± 28.86 b | * |
| 2016 | 916.10 ± 9.73 a | 910.37 ± 1.62 a | 953.58 ± 0.16 a | 959.66 ± 9.73 a | * |
| AVG 2014-16 | 863.44 ± 11.90 a | 869.01 ± 12.08 a | 957.23 ± 4.38 b | 973.20 ± 17.67 b | * |
| Total anthocyanins content (mg mal 3-glu/L) | |||||
| 2014 | 163.81 ± 0.84 a | 131.75 ± 3.36 a | 138.45 ± 2.44 a | 164.52 ± 1.07 a | ns |
| 2015 | 134.57 ± 1.82 a | 128.94 ± 1.37 a | 118.72 ± 0.90 a | 149.37 ± 1.15 a | ns |
| 2016 | 87.01 ± 1.40 a | 103.57 ± 2.53 ab | 162.40 ± 2.41 c | 136.33 ± 1.88 bc | ns |
| AVG 2014-16 | 128.46 ± 1.35 a | 121.42 ± 2.42 a | 139.86 ± 1.92 a | 150.07 ± 1.37 a | ns |
| Radical scavenging activity (mmol TE/L) | |||||
| 2014 | 5.50 ± 0.12 a | 5.68 ± 0.20 ab | 6.40 ± 0.29 ab | 6.80 ± 0.12 b | ns |
| 2015 | 5.89 ± 0.26 a | 6.01 ± 0.09 a | 6.95 ± 0.03 a | 6.91 ± 0.09 a | ns |
| 2016 | 4.58 ± 0.00 a | 4.61 ± 0.42 a | 4.82 ± 0.20 a | 4.30 ± 0.19 a | ns |
| AVG 2014-16 | 5.32 ± 0.09 a | 5.43 ± 0.24 a | 6.06 ± 0.17 a | 6.00 ± 0.13 a | ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ćirković, D.; Matijašević, S.; Ćirković, B.; Laketić, D.; Jovanović, Z.; Kostić, B.; Bešlić, Z.; Sredojević, M.; Tešić, Ž.; Banjanac, T.; et al. Influence of Different Defoliation Timings on Quality and Phenolic Composition of the Wines Produced from the Serbian Autochthonous Variety Prokupac (Vitis vinifera L.). Horticulturae 2022, 8, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8040296
Ćirković D, Matijašević S, Ćirković B, Laketić D, Jovanović Z, Kostić B, Bešlić Z, Sredojević M, Tešić Ž, Banjanac T, et al. Influence of Different Defoliation Timings on Quality and Phenolic Composition of the Wines Produced from the Serbian Autochthonous Variety Prokupac (Vitis vinifera L.). Horticulturae. 2022; 8(4):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8040296
Chicago/Turabian StyleĆirković, Dušica, Saša Matijašević, Bratislav Ćirković, Darko Laketić, Zoran Jovanović, Boban Kostić, Zoran Bešlić, Milica Sredojević, Živoslav Tešić, Tijana Banjanac, and et al. 2022. "Influence of Different Defoliation Timings on Quality and Phenolic Composition of the Wines Produced from the Serbian Autochthonous Variety Prokupac (Vitis vinifera L.)" Horticulturae 8, no. 4: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8040296
APA StyleĆirković, D., Matijašević, S., Ćirković, B., Laketić, D., Jovanović, Z., Kostić, B., Bešlić, Z., Sredojević, M., Tešić, Ž., Banjanac, T., & Gašić, U. (2022). Influence of Different Defoliation Timings on Quality and Phenolic Composition of the Wines Produced from the Serbian Autochthonous Variety Prokupac (Vitis vinifera L.). Horticulturae, 8(4), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8040296









