Characterization and Expression of Phospholipase D Putatively Involved in Colletotrichummusae Disease Development of Postharvest Banana Fruit
Abstract
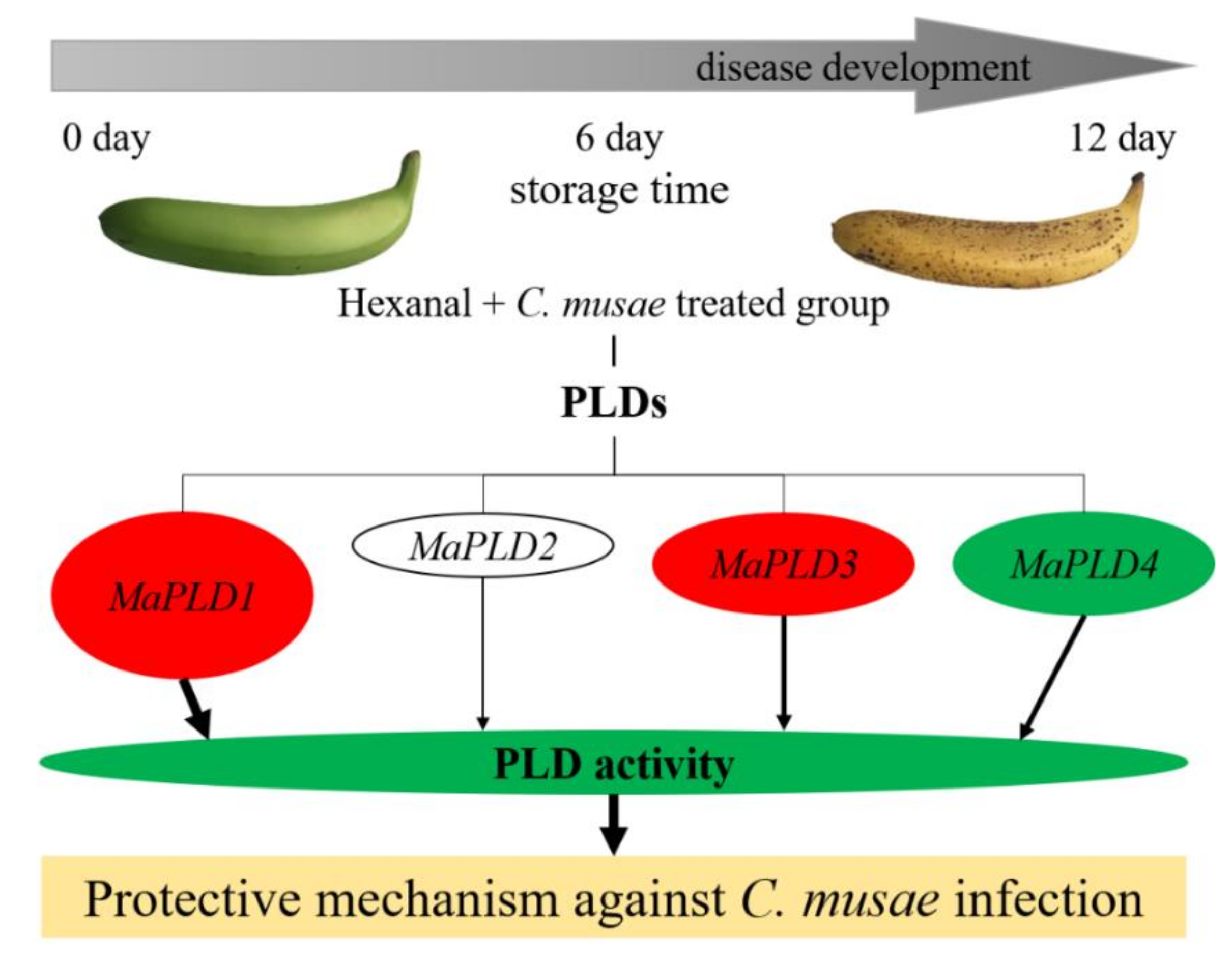
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Treatments
2.2. Evaluation on Disease Index (DI)
2.3. Cloning of Phospholipase D (PLD) Genes
2.4. Determination of MaPLDs Protein Sequences
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Assays of Enzyme Activities, DAG and PA Content
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
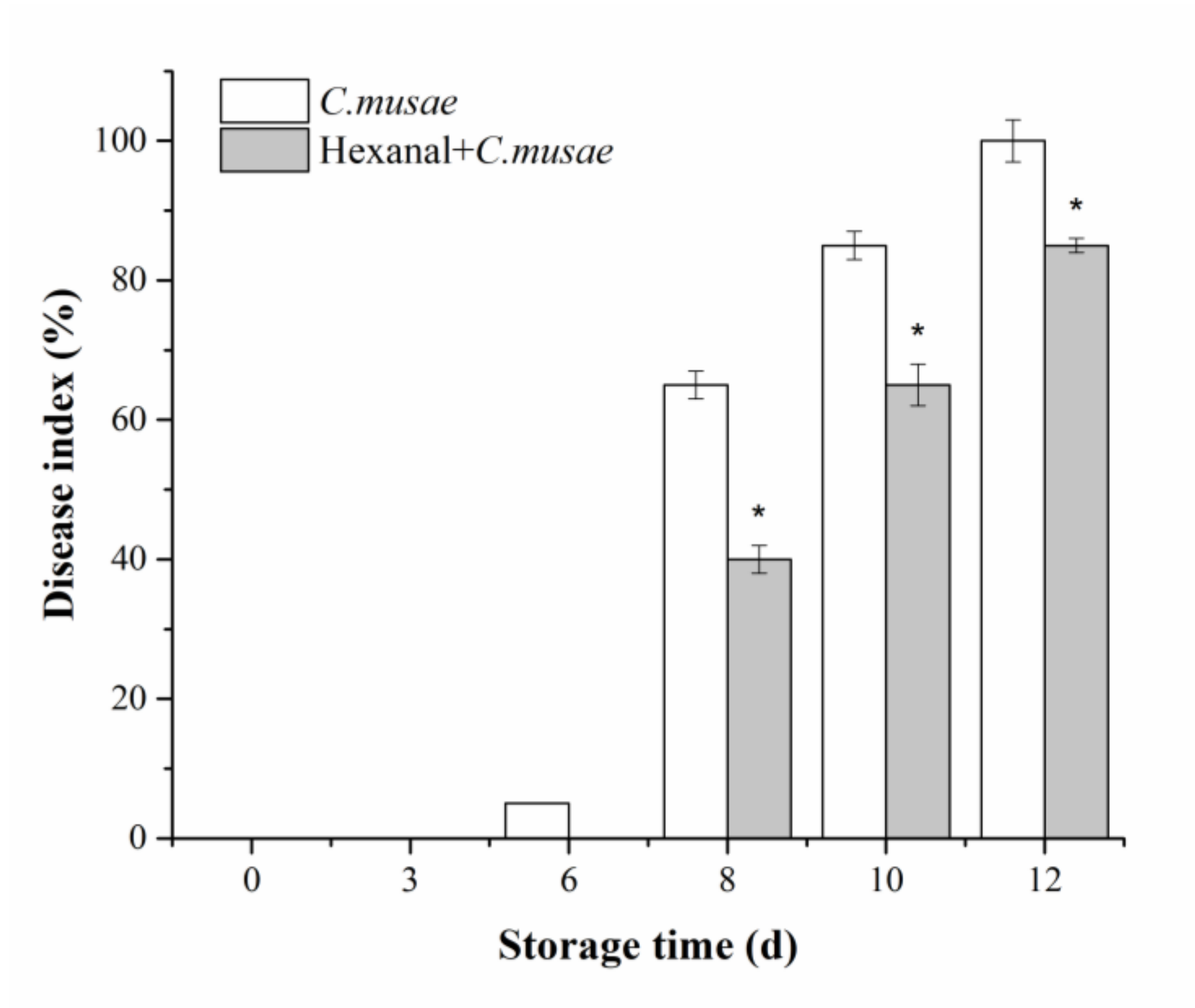
3.1. Disease Development
3.2. Analysis of MaPLDs
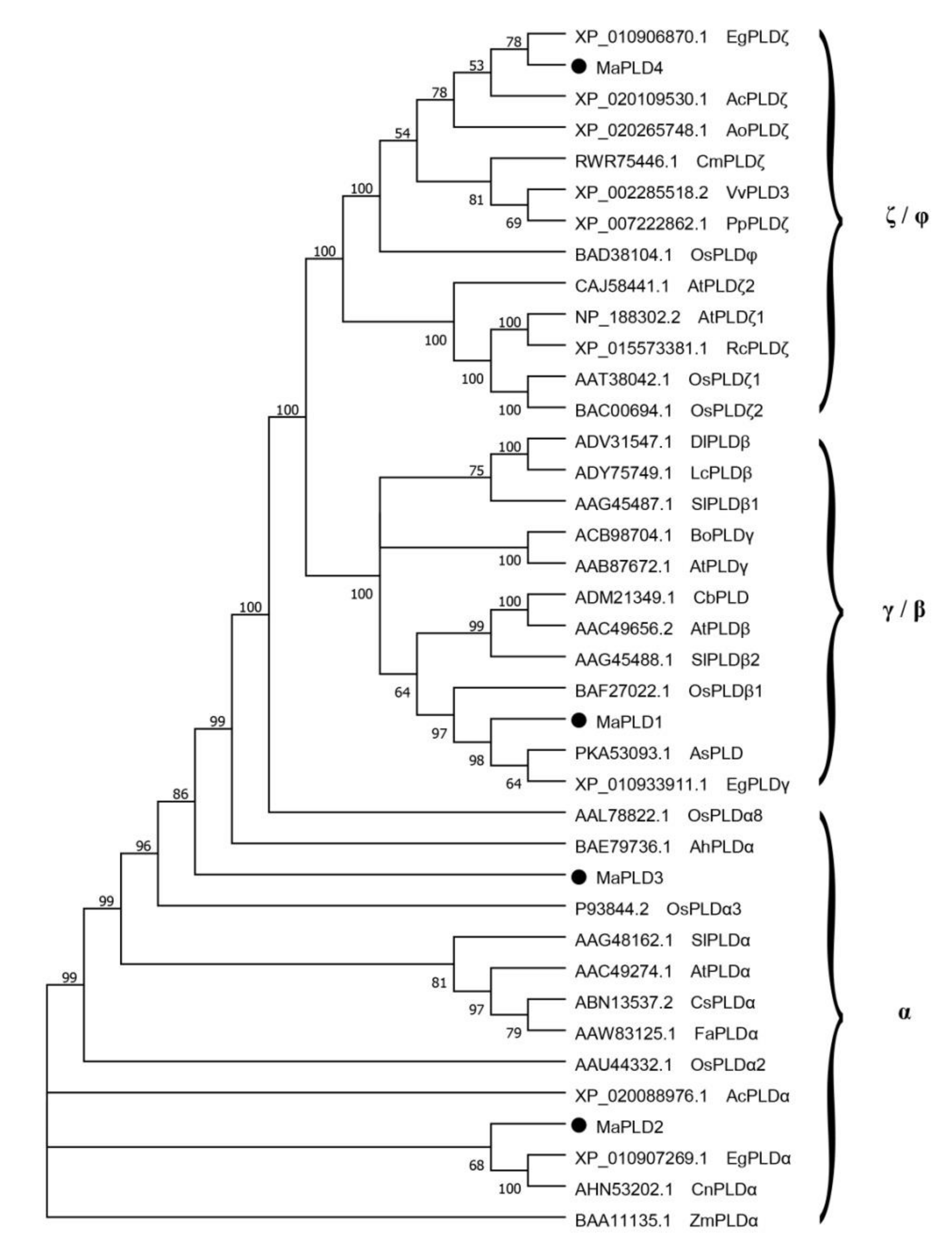
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of MaPLDs
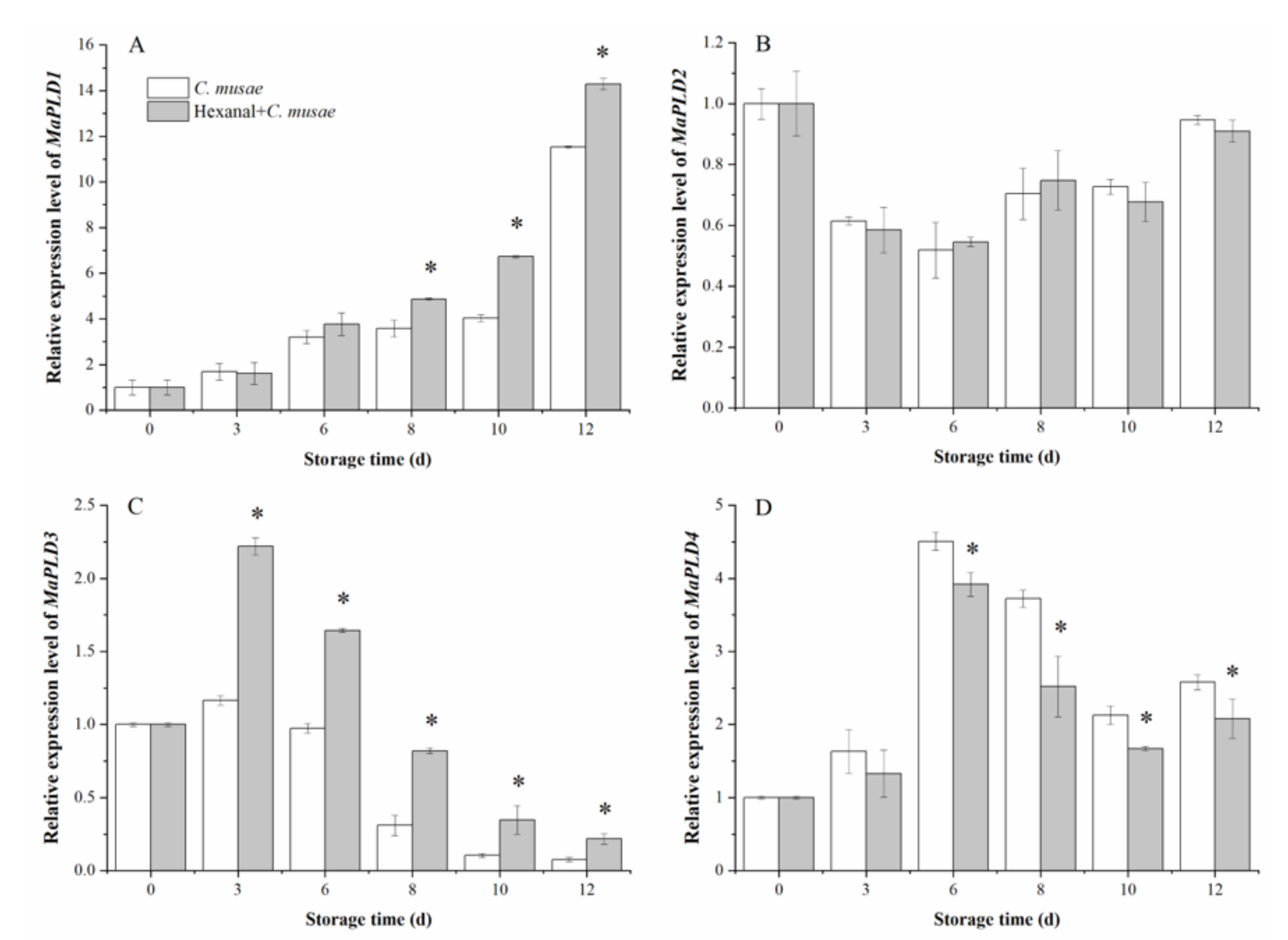
3.4. Effect of Hexanal Treatment on Expression of MaPLD Genes in Banana Fruit under the Infection of C. musae
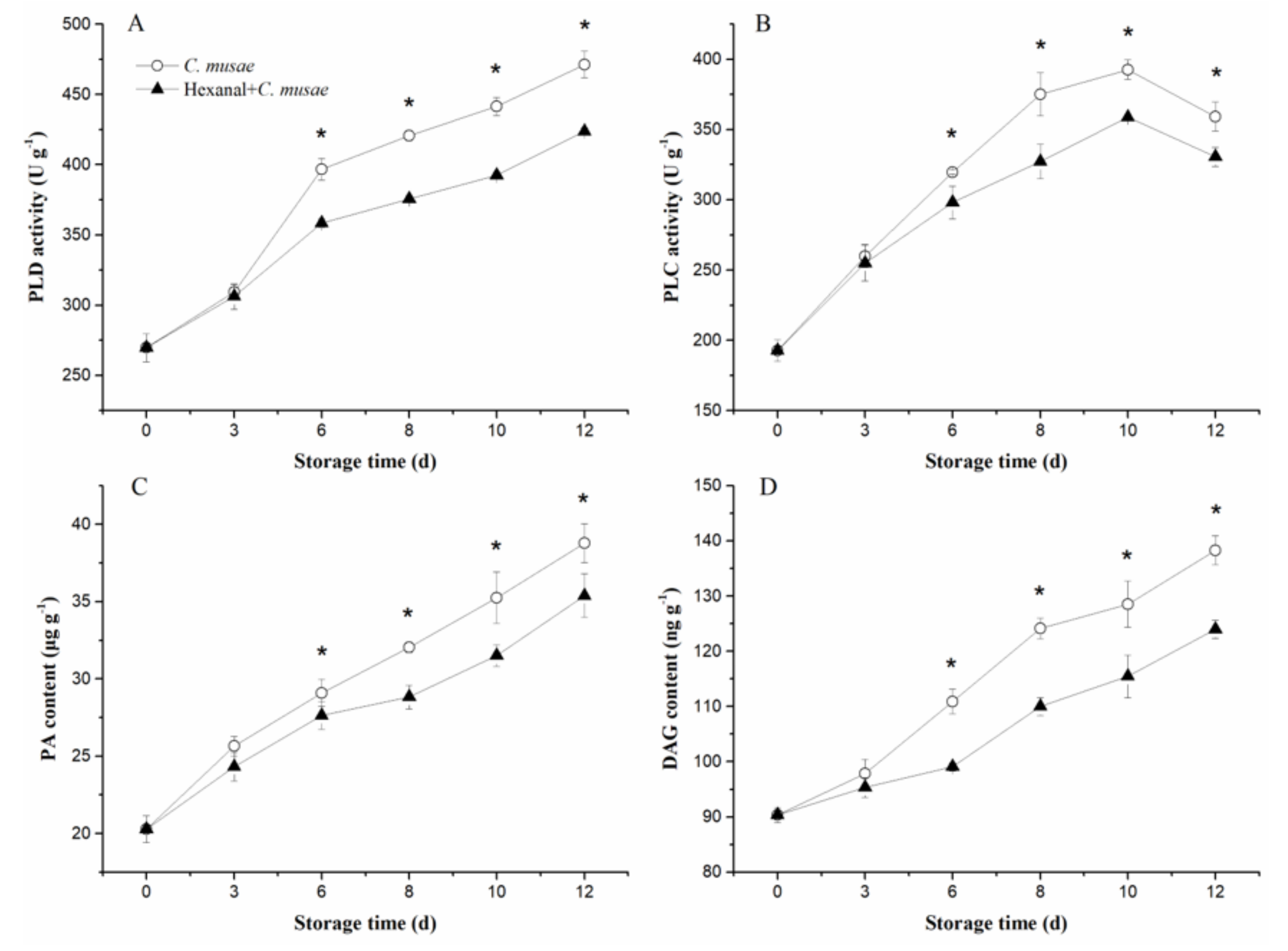
3.5. Hexanal Treatment Induced Changes in Activities of PLD and PLC, and Contents of PA and DAG
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González-Mendoza, V.M.; Sánchez-Sandoval, M.E.; Castro-Concha, L.A.; Hernández-Sotomayor, S.M.T. Phospholipases C and D and their role in biotic and abiotic stresses. Plants 2021, 10, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X. Regulatory functions of phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid in plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, L.; Kim, S.C.; Deng, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, G.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Plant phospholipases D and C and their diverse functions in stress responses. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 62, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, M.; Gao, Z.; An, F.; Li, M.; Jiang, Y. Low-temperature conditioning induces chilling tolerance in stored mango fruit. Food Chem. 2017, 219, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Huang, M.; Wang, X.; Wei, M.; Shi, Q.; Li, Y.; Gong, B.; Yang, F. Cucumber Phospholipase D alpha gene overexpression in tobacco enhanced drought stress tolerance by regulating stomatal closure and lipid peroxidation. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, X. Phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid in plant immunity. Plant Sci. 2019, 279, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Wang, X. The Arabidopsis phospholipase D family. Characterization of a calcium-independent and phosphatidylcholine-selective PLD zeta 1 with distinct regulatory domains. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X. Phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid signalling in plant response to drought and salinity. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lin, F.; Xue, H. Genome-wide analysis of the phospholipase D family in Oryza sativa and functional characterization of PLDβ1 in seed germination. Cell Res. 2007, 17, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X. Genome-wide and molecular evolution analyses of the phospholipase D gene family in Poplar and Grape. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W. Genomic analysis of phospholipase D family and characterization of GmPLDαs in soybean (Glycine max). J. Plant Res. 2012, 125, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, R.; Huang, B.; Song, K.; Jia, Z. Identification and characterization of phospholipase D genes putatively involved in internal browning of pineapple during postharvest storage. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.; Fadlalla, T.; Tang, S.; Li, L.; Ali, U.; Li, Q.; Guo, L. Genome-wide analysis of phospholipase D gene family and profiling of phospholipids under abiotic stresses in Brassica napus. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 1556–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Kuroda, M.; Yamakawa, H.; Ashizawa, T.; Hirayae, K.; Kurimoto, L.; Shinya, T.; Shibuya, N. Suppression of a phospholipase D gene, OsPLDβ1, activates defense responses and increases disease resistance in rice. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Yamakawa, H.; Nakata, M.; Kuroda, M.; Hakata, M. Suppression of phospholipase D genes improves chalky grain production by high temperature during the grain-filling stage in rice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Li, S.; Huang, M.; Di, Q.; Wang, X.; Wei, M.; Shi, Q.; Li, Y.; Gong, B.; Yang, F. Overexpression of cucumber phospholipase D alpha gene (CsPLDα) in tobacco enhanced salinity stress tolerance by regulating Na+-K+ balance and lipid peroxidation. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinosa, F.; Buhot, N.; Kwaaitaal, M.; Fahlberg, P.; Thordal-Christensen, H.; Ellerström, M.; Andersson, M. Arabidopsis phospholipase Dδ is involved in basal defense and nonhost resistance to powdery mildew fungi. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Devaiah, S.P.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Welti, R.; Wang, X. Arabidopsis phospholipase Dβ1 modulates defense responses to bacterial and fungal pathogens. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; You, X.; Li, L.; Peng, H.; Su, W.; Li, C.; He, Q.; Liao, F. Effects of a phospholipase D inhibitor on postharvest enzymatic browning and oxidative stress of litchi fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2011, 62, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, J.; Sun, J.; Yi, P.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Xin, M.; Sheng, J.; Shuai, L.; Li, Z.; et al. Role of phospholipase D inhibitor in regulating expression of senescence related phospholipase D gene in postharvest longan fruit. Curr. Bioinform. 2019, 14, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak Dek, M.; Padmanabhan, P.; Subramanian, J.; Paliyath, G. Inhibition of tomato fruit ripening by 1-MCP, wortmannin and hexanal is associated with a decrease in transcript levels of phospholipase D and other ripening related genes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 140, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; El Kayal, W.; Sullivan, J.A.; Paliyath, G.; Jayasankar, S. Pre-harvest application of hexanal formulation enhances shelf life and quality of ‘Fantasia’ nectarines by regulating membrane and cell wall catabolism-associated genes. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 229, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jincy, M.; Djanaguiraman, M.; Jeyakumar, P.; Subramanian, K.S.; Jayasankar, S.; Paliyath, G. Inhibition of phospholipase D enzyme activity through hexanal leads to delayed mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit ripening through changes in oxidants and antioxidant enzymes activity. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 218, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumbya, P.; Hutchinson, M.; Ambuko, J.; Owino, W. Effect of hexanal as a post-harvest treatment to extend the shelf-life of banana fruits (Musa acuminata var. Sweet Banana) in Kenya. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2019, 29, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, X.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Ling, D.; Sheng, J.; You, X.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Zheng, F. Cloning, characterization, and functional expression of phospholipase Dα cDNA from banana (Musa acuminate L.). J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 2510949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, D.; Zhu, S.; Gu, H.; Zhang, L.; Hong, K.; Xie, J. Disease resistance of ‘Zill’ and ‘Keitt’ mango fruit to anthracnose in relation to defence enzyme activities and the content of anti-fungal substances. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhong, H.; Kuang, J.; Li, J.; Lu, W.; Chen, J. Validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR studies of gene expression in banana fruit under different experimental conditions. Planta 2011, 234, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, L.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Liao, Y.; Duan, Z.; Li, C.; He, X. Role of phospholipase C in banana in response to anthracnose infection. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utto, W.; Mawson, A.J.; Bronlund, J.E. Hexanal reduces infection of tomatoes by Botrytis cinerea whilst maintaining quality. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2008, 47, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Dong, C.; Liu, J. Genome-wide comparative analysis of the phospholipase D gene families among allotetraploid cotton and its diploid progenitors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Lin, H.; Lin, M.; Lin, Y.; Wang, H.; Hung, Y.C. Salicylic acid treatment suppresses Phomopsis longanae Chi-induced disease development of postharvest longan fruit by modulating membrane lipid metabolism. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 164, 111168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, M.T.; Ballester, A.R.; Holland, N.; Cerveró, J.; Romero, P. Interrelation between ABA and phospholipases D, C and A2 in early responses of citrus fruit to Penicillium digitatum infection. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 175, 111475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Noireung, P.; Liu, F.; Hyde, K.D.; Moslem, M.A.; Bahkali, A.H.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Cai, L. Epitypification of Colletotrichum musae, the causative agent of banana anthracnose. Mycoscience 2011, 52, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abayasekara, C.L.; Adikaram, N.K.; Wanigasekara, U.W.; Bandara, B.M. Phyllosticta musarum infection-induced defences suppress anthracnose disease caused by Colletotrichum musae in Banana Fruits cv ‘Embul’. Plant Pathol. J. 2013, 29, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Ma, B. Benzothiadiazole- or methyl jasmonate-induced resistance to Colletotrichum musae in harvested banana fruit is related to elevated defense enzyme activities. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2007, 82, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Lin, H.Z.; Si, Z.W.; Xia, Y.H.; Chen, W.X.; Li, X.P. Benzothiadiazole-mediated induced resistance to Colletotrichum musae and delayed ripening of harvested banana fruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | GenBank No. | C2 Domain | HKD1//HKD2 | PLD C Terminal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MaPLD1 | MK516209 | 233–352 aa | +/331 aa/+ | 962–1030 aa |
| MaPLD2 | MK516210 | 48–129 aa | +/329 aa/+ | 733–802 aa |
| MaPLD3 | MK516211 | 2–153 aa | +/329 aa/+ | 736–805 aa |
| MaPLD4 | MK516212 | - | +/281 aa/+ | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, P.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; He, X.; Li, C.; Sheng, J.; Xin, M.; Ling, D.; Li, Z.; Tang, Y.; et al. Characterization and Expression of Phospholipase D Putatively Involved in Colletotrichummusae Disease Development of Postharvest Banana Fruit. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8040312
Yi P, Li L, Sun J, He X, Li C, Sheng J, Xin M, Ling D, Li Z, Tang Y, et al. Characterization and Expression of Phospholipase D Putatively Involved in Colletotrichummusae Disease Development of Postharvest Banana Fruit. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(4):312. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8040312
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Ping, Li Li, Jian Sun, Xuemei He, Changbao Li, Jinfeng Sheng, Ming Xin, Dongning Ling, Zhichun Li, Yayuan Tang, and et al. 2022. "Characterization and Expression of Phospholipase D Putatively Involved in Colletotrichummusae Disease Development of Postharvest Banana Fruit" Horticulturae 8, no. 4: 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8040312
APA StyleYi, P., Li, L., Sun, J., He, X., Li, C., Sheng, J., Xin, M., Ling, D., Li, Z., Tang, Y., & Liu, G. (2022). Characterization and Expression of Phospholipase D Putatively Involved in Colletotrichummusae Disease Development of Postharvest Banana Fruit. Horticulturae, 8(4), 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8040312






