Abstract
Trehalose and some members of the trehalose 6-phosphate synthase (TPS) gene family play important roles in response to abiotic stress in plants. However, no studies investigating the TPS gene in rose have been reported. In this study, the trehalose content in the stems and roots of Rosa chinensis was significantly increased under heat stress, and nine TPS family members were identified from the genome of R. chinensis. The R. chinensis TPS (RcTPS) family members could be divided into two subfamilies based on the structure and phylogenetic analysis. In this study, we found that segmental duplications contributed to the expansion of the RcTPS gene family, and the type II subfamily gene pairs RcTPS9–RcTPS10 and RcTPS7a–RcTPS7b were created by segmental duplication events. The type I subfamily RcTPS members contained 17 exons in the protein-coding region, whereas type II subfamily members only had 3 or 4 exons. Most cis-acting elements in the promoters of RcTPS members were related to plant hormones, especially ABA hormones. A phylogenetic tree of 78 TPS homologous amino acids from R. chinensis and another 7 species was constructed, which could be divided into 5 clades, and purity selection was observed to be the dominant evolutionary selection pressure. Under heat stress, except for RcTPS1b, the other eight RcTPS members were upregulated in the roots, stems, orleaves. The type II subfamily members RcTPS7a and RcTPS7b showed significantly high expression patterns in response to heat stress in all three tissues. Our findings indicate that RcTPS7a and RcTPS7b may play important roles in the heat tolerance of R. chinensis and are helpful for future functional studies of the two RcTPS members during heat stress.
1. Introduction
Heat stress negatively affects most crops, resulting in stunted growth, abortive flowers, decreased productivity, and even death [1]. Currently known molecular mechanisms of plants’ response to abiotic stress include multistage response pathways involving the stress response, signal transduction, transcription, transcription processing, translation, and post-translational protein modification [2]. As the first defense response to abiotic stress, plants accumulate a variety of compounds that act as osmoprotective agents [3]. One such compound is trehalose, a nonreducing disaccharide formed by the α-1,1-glycosidic bond between two α-glucose molecules and found in bacteria, yeast, plants, and many other organisms [4,5]. Due to its unique physical and chemical properties, such as the lack of reductive terminals related to the formation of glycosidic bonds, trehalose can stabilize enzymes, proteins, and lipids in the cell membrane under heat stress or water-limited conditions [5,6]. Many studies have shown that the trehalose metabolism pathway is an important part of the plant sugar signaling pathway and plays an important role in plant resistance to abiotic stress [7].
At present, there are five known trehalose biosynthesis pathways, among which the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase–trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase (TPS-TPP) pathway exists in plants. In the two-step TPS-TPP pathway, the first TPS (EC: 2.4.1.15)-catalyzed step utilizes uridine diphosphate glucose and glucose-6-phosphate to synthesize trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P), followed by TPP (EC: 3.1.3.12), which catalyzes the dephosphorylation of T6P into trehalose [3,8]. Analysis of the various mutants and transgenic plants has shown that the trehalose metabolic pathway is important for the plant sugar signaling pathway, being mainly involved in plant growth and development (embryogenesis, reproductive growth, flowering) and stress tolerance, which is mediated by transcriptional control of the TPS and TPP genes and change in the T6P level [8,9,10,11].
Trehalose biosynthetic pathways exist in all plants. The TPS gene family was first identified in Arabidopsis, which contains 11 AtTPS genes [7,12]. Likewise, 11 genes (OsTPS) were found in Oryza sativa [13], 12 genes (TaTPS) in Triticum aestivum [14], 8 genes (StTPS) in Solanum tuberosum [15], and 9 (PmTPS) in Prunus mume [16]. According to these research reports, it was verified that the TPS orthologues could respond to different abiotic stresses and play an important role in the response to stress. The AtTPS genes are divided into two clades: group I (AtTPS1–AtTPS4) and group II (AtTPS5–AtTPS11) [12]. The group I AtTPS members have a conserved N-terminal TPS-like domain and a less-conserved C-terminal TPP domain. Group II members, also dual-domain proteins, harbor an N-terminal TPS-like domain and a high-conserved C-terminal TPP domain [8,17]. In general, the group I AtTPS members (except AtTPS3) have been found to functionally complement yeast tps1 mutants [18].
Transgenic plants overexpressing group I or II TPS genes show higher stress tolerance [7]. For example, the AtTPS1 gene enhances osmotic, drought, dryness, and temperature stress resistance in transgenic tobacco [19]. Overexpression of TaTPS11 in Arabidopsis leads to increased cold tolerance [20]. The GhTPS11 gene in cotton responds to heat stress, drought, and salt stress, with significantly higher trehalose and T6P contents in transgenic Arabidopsis plants than control plants [21]. Exogenous application of trehalose was reported to improve the heat stress tolerance of wheat, and had a direct effect on the clearance of hydrogen peroxide and superoxide anion in the wheat plants [22]. In Pleurotus tuoliensis, exogenous application of trehalose significantly reduced the heat-stress-mediated oxidative damage of the cell membrane and showed that high-temperature stress promotes an increase in the endogenous trehalose content [23].
Roses (Rosa spp.) are the most popular and top-selling cut flowers in the global market. Rosa chinensis ‘Old Blush’ is a traditional famous rose species in China that participates in R. hybrida breeding. Moreover, R. chinensis is one of the high thermotolerance species [24]. For most rose varieties, the optimum temperature is 15–26 °C, and plants usually grow poorly at temperatures above 35 °C, as reproductive growth is blocked, and some species even enter a semidormancy state [24,25]. At present, the molecular mechanism of heat stress tolerance in rose plants is mostly unknown. Trehalose and its key catalytic enzyme TPS play an essential role in plants’ tolerance of heat stress, such as Arabidopsis [26], wheat [22], and Pleurotus tuoliensis [23]. In this study, we first found that the trehalose content in the root and stem tissues of R. chinensis ‘Old Blush’ significantly increases during heat stress. To investigate the mechanism of the increase in trehalose in these tissues under heat stress, nine RcTPS gene family members were identified from the R. chinensis ‘Old Blush’ genome. Phylogenetic and selective force analysis of the RcTPS gene family were conducted. Moreover, the expression patterns of RcTPS genes were investigated in different tissues under heat stress. In this study, the basic genome bioinformatics analysis of the RcTPS gene family was implemented, and two RcTPS genes (RcTPS7a and RcTPS7b) were predicted with heat tolerance functions. This study will be helpful for analysis of the thermotolerance function and molecular mechanism of the two RcTPS genes in the future.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Heat Stress Experiment
The stock plants of R. chinensis ‘Old Blush’ were cultivated in the ornamental plant germplasm center of the Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China. Briefly, 1-year-old healthy cuttings of the same size (the height was about 13–17cm) were planted in plastic pots (10 cm diameter) containing coconut chaff, peat, and perlite in a 4:3:3 ratio in April 2021. Water-soluble fertilizer with large amounts of elements was irrigated once a week during cuttage cultivation. About 600 cuttings eventually grew into complete plants and were used for the subsequent heat stress experiments. Each pot contained about 630 cm3 of substrate. Firstly, the cuttings were cultured in incubators under a 12 h/12 h (day/night) photoperiod at a 25 °C/25 °C (day/night) temperature, with a 17 μmol m−2 s−1 light intensity and 60% humidity for 7 days. During this time, the plants were irrigated with neutral sterile water that contained no nutrients. Previous studies have shown that the heat stress semi-lethal temperature of most rose varieties is between 40 and 45 °C [24]. Subsequently, 30 cuttings were selected and then subjected to constant 40 °C heat stress for 72 h in the same incubators under a 12 h/12 h (day/night) photoperiod with a 17 μmoL m−2 s−1 light intensity and 60% humidity. The plants were irrigated with enough water two days before the heat treatment. Moreover, a water storage tray was placed under the plant pots, and water was added to a 1–2 cm depth to prevent water deficiency during heat stress. Mature leaves, tender stems, and lateral roots were collected from 3 biological replicates at different heat stress treatment time points (0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h) and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C for subsequent trehalose measurements and reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) experiments.
2.2. Trehalose Content Detection in R. chinensis
The rapid detection kit (Shanghai ZCIBIO Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) was used to measure the trehalose content in the samples. First, the trehalose-extracting solution was obtained from the mature leaves, tender stems, and lateral roots of R. chinensis according to the manufacturer’s instructions, with three biological replicates. After the subsequent chromogenic reaction, a BioMate 3S Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used to detect the optical density at 620 nm and to estimate the trehalose content using the standard curve. All the collected data were finally processed using the Excel tool of Microsoft Office 2010 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA), and an analysis of significant differences was conducted using SPSS Statistics 22.0 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) and 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the t-test. GraphPad (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) was used to draw the histograms.
2.3. Identification of Rose TPS Genes
The R. chinensis genome DNA data were downloaded from the R. chinensis ‘Old Blush’ Hm r2.0 genome portal (RchiOBHm-V2, https://lipm-browsers.toulouse.inra.fr/pub/RchiOBHm-V2, accessed on 27 July 2021). Combined with hidden Markov models (HMMs), BLASTN and BLASTP were used to search the genome and retrieve TPS family sequences. Pfam (https://pfam.xfam.org/, accessed on 22 August 2021) [27] and CDD at NCBI (NCBI, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd, accessed on 22 August 2021) were used to further verify the conserved domains. The sequences without the conserved TPS (the glycosyltransferase family 20 domain) or TPP (the trehalose phosphotase domain) domains were removed to determine the members of the R. chinensis TPS gene family.
2.4. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
Clustal X software (http://www.cluster-x.org/, accessed on 17 August 2021) was used to compare the TPS proteins of R. chinensis with the AtTPS (A. thaliana), OsTPS (O. sativa), and PmTPS (P. mume) protein sequences. Then, MEGA X software (https://www.megasoftware.net/, accessed on 17 August 2021) was used to construct a neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree, with bootstrap analysis (1000). The TPS members identified in R. chinensis were named according to their similarity to the corresponding AtTPS members.
Additionally, 78 protein sequences of TPS from R. chinensis, A. thaliana, and Nelumbo nucifera, and five Rosaceae species (P. yedoensis, P. persica, P. mume, P. armeniaca, and Malus domestica) were aligned and a phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method using Mega X. The genome database and gene identifier information about all the TPS orthologues are listed in Table S1.
2.5. Selective Pressure Analysis
Using the EasyCodeML site model, the M3 and M0 models were compared using a likelihood ratio test, and synonymous (dS) and non-synonymous (dN) substitution rates, and the dN/dS(ω) ratio for each node TPS were calculated to explore the selection force of each phylogenetic group of the 78 TPS family members, and conduct an analysis of its molecular adaptive evolution.
2.6. Protein Physicochemical Properties and Subcellular Localization Analysis
Protparam tool (http://web.Expasy.org/protparam/, accessed on 14 September 2021) was used to analyze the physicochemical properties of the RcTPS proteins. Furthermore, the PSORT (http://psort1.hgc.jp/form.html, accessed on 14 September 2021) online tool was employed to predict the location of RcTPS protein in cells.
2.7. TPS Gene Structure and Cis-Acting Element Analyses
The number and position of the exons and introns of RcTPS members were analyzed by GSDS (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/, accessed on 1 December 2021) [28]. Moreover, the 2000-bp sequence upstream of the initiation codon of TPS genes was extracted and submitted to PlantCARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/, accessed on 28 August 2021) for promoter cis-acting element analysis, and visualized using TBtools software (https://www.tbtools.com/, accessed on 28 August 2021) [29].
2.8. Protein Motif and Conserved Domain Analysis
The conservative motifs of the RcTPS family were analyzed by MEME (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme, accessed on 1 December 2021), and the motif number was set to 20. The protein sequence of RcTPS was submitted to the Pfam and NCBI CD-Search tool to further analyze the conserved domains of RcTPS members and TBtools software was used for visualization.
2.9. Gene Chromosomal Location and Collinearity Analysis
We downloaded the R. chinensis genome annotation gff3 file to the database and used TBtools software to extract the location information and perform visual analysis of the selected genes. MCscan X software was used to analyze the gene replication events and identify the genes with segmental duplication and tandem repeats. We used Circos (http://www.circos.ca/, accessed on 24 April 2022) to plot and show the results of the collinearity analysis.
2.10. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
A plant RNA extraction kit (Accurate Biotechnology, Changsha, Hunan, China) was used to isolate RNA samples from different tissues according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After RNA purity and quality testing, complementary DNA (cDNA) was generated using the Evo M-MLV RT Premix (Accurate Biotechnology, China). The SYBR Green method and a 20 µL assay volume were used for RT-qPCR analysis of the RcTPS genes. The primers used are shown in Table S2. The expression level of the RcTPS genes was calculated using the 2−∆∆CT method, and RcCTP was used as the reference gene [30].
3. Results
3.1. Dynamics of the Trehalose Levels in the Leaf, Stem, and Root Tissues of R. chinensis under Heat Stress
To investigate the dynamic changes in the trehalose content in R. chinensis during heat stress, the trehalose content in the roots, stems, and leaves of R. chinensis was detected. The results indicate that the basal trehalose levels varied in the roots, stems, and leaves under normal conditions, ranging from 14.81 to 33.54 mg/g fresh weight (FW) (Figure 1), with the highest levels detected in the leaves, followed by the stems and leaves. After heat stress treatment, the trehalose content in the roots and stems increased significantly during the early stage. At 8 h of heat stress, the trehalose content in the roots reached its peak (up to 1.5-fold) compared to control plants and showed a rapid decline after the 24 h time point (Figure 1A). The trehalose content in the stem increased by up to 1.4-fold at 24 h of heat stress and then returned to close to normal levels (Figure 1B). The relatively higher trehalose content in the leaves did not change much during the early stage of heat stress but rapidly decreased after the 24 h time point (Figure 1C).
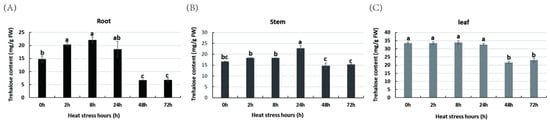
Figure 1.
The trehalose content in the roots (A), stems (B), and leaves (C) of Rose chinensis in response to heat stress. Error bars represent the SD of three biological replicates. The lowercase letter represents the significance level.
3.2. Identification and Analysis of the Characteristics of TPS Family Members in R. chinensis
A total of nine TPS family members were identified from the R. chinensis genome, and named RcTPS1a to RcTPS11. The physicochemical characteristics of all nine RcTPS members are listed in Table 1. The number of amino acids encoded ranged from as low as 854 (RcTPS6, RcTPS7b) to 977 (RcTPS1a). The isoelectric points (pI) ranged from 5.67 to 6.51, showing weak acidity. The molecular weight (MW) ranged from 96.32 to 109.54 kDa, with an average of 100.19 kDa. The RcTPS proteins were hydrophilic (hydrophobicity < 0) and most of them were predicted in the cytosol, except RcTPS1a, RcTPS1b, and RcTPS6, which were located in the nucleus.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the TPS gene family in R. chinensis.
The chromosome location results showed that RcTPS7a was located on Chr2; RcTPS6, RcTPS10, and RcTPS11 were distributed on Chr4; RcTPS1a, RcTPS1b, and RcTPS7b were distributed on Chr5; and RcTPS5 and RcTPS9 were distributed on Chr7 (Figure 2A). The results of the collinearity analysis showed that there were two segmental duplication events, which occurred in the gene pairs RcTPS9–RcTPS10 and RcTPS7a–RcTPS7b. These results indicate that segmental duplication may be important for the expansion of the RcTPS gene family and promotion of the diversity of gene functions (Figure 2B).
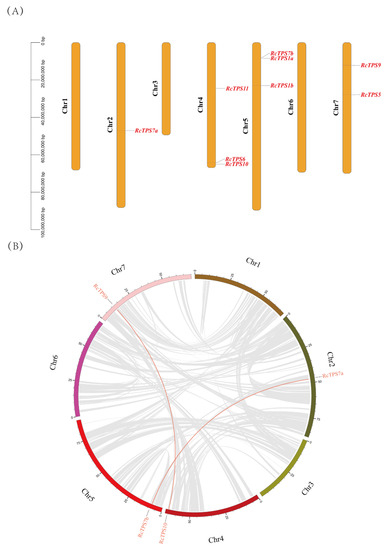
Figure 2.
Chromosomal locate and collinearity analysis of the TPS gene family in R. chinensis. (A) The chromosomal locate diagram of the RcTPS gene family. The left scale represents the corresponding length of the chromosomes. (B) The collinearity analysis diagram of the RcTPS gene family. Chr1, Chr2, Chr3, Chr4, Chr5, Chr6, and Chr7 represent the seven chromosomes of R. chinensis, respectively.
A phylogenetic tree was constructed using a total of 40 TPS orthologs of A. thaliana (11 members), rice (11 members), P. mume (9 members), and R. chinensis (9 members) (Figure S1). On the basis of the phylogenetic analysis, we categorized 40 TPS members into 2 groups: I and II TPS. R. chinensis TPS members were named on the basis of their similarity to the corresponding A. thaliana TPS members. Group II included a large number of TPS members, including 7 AtTPS (AtTPS5–AtTPS11), 10 OsTPS (OsTPS2–OsTPS11), 7 PmTPS (PmTPS5–PmTPS11), and 7 RcTPS (RcTPS5–RcTPS11) (Figure S1). The other two RcTPS members were clustered in the group I TPS subfamily and were named RcTPS1a and RcTPS1b on the basis of their highest homology level of the A. thaliana TPS1 member (Figure S1).
3.3. Gene Structure and cis-Acting Element Analyses of RcTPS Genes
All RcTPS genes contained three or more exons. Generally, the gene structures of the RcTPS genes clustered into the same subfamily were relatively similar. For example, group II-specific RcTPS contained only 3 or 4 exons while RcTPS1a and RcTPS1b of group I contained 17 exons. In addition, RcTPS1a, from group I, had the longest gene length while RcTPS7a from group II had the shortest gene length and lacked untranslated regions (UTRs) at both the 5′ and 3′ ends. The diversity of the RcTPS family gene structures implied a diversity regarding the evolutionary trends and gene function (Figure 3A).
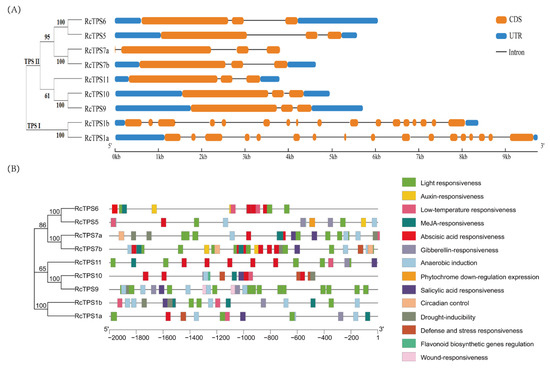
Figure 3.
RcTPS genes’ intron-exon organization and cis-acting elements. (A) Schematic diagram of the intron-exon of the RcTPS genes. (B) Schematic diagram of the cis-acting elements of the RcTPS genes.
To further understand the regulatory functions of the promoters of the RcTPS gene family at the transcriptional level and the functional differences between promoters of different members, analysis of the cis-acting elements in the PlantCARE database was carried out, which most motifs were identified responsive to environmental stress and phytohormones (Figure 3B).
Most of these cis-acting elements in the promoters of the RcTPS family were related to the light response and the response to phytohormones, especially abscisic acid (ABA). For example, G-box, Box 4, and MYB-recognition element (MRE) are related to light responsiveness while ABA-responsive element (ABRE), antioxidant response element (ARE), ethylene response element (ERE), gibberellic acid response element (GARE) motif, and TGA-box are related to the response to phytohormones (e.g., ABA, ethylene, gibberellin, auxin, and jasmonic acid). The promoter regions of the RcTPS genes also contained various cis-acting elements related to defense and stress responsiveness, drought inducibility, and low-temperature responsiveness. Within the promoter region, three RcTPS genes contained defense and stress-responsiveness elements, five RcTPS genes contained drought-inducibility elements, and eight RcTPS genes contained low-temperature-responsiveness elements. Thus, various abiotic stresses could induce the expression of RcTPS genes, which might, in turn, induce a homeostatic response to maintain normal growth and development under abiotic stress. The promoter regions of some RcTPS genes also contained binding sites of MYB transcription factors under abiotic stress, suggesting that RcTPS genes may be interacting with MYB transcription factors to resist abiotic stress by changing the degree of cell wall lignification.
3.4. Protein Domain Analyses and Multiple Sequence Alignment of the TPS Family in R. chinensis
Conserved domain analysis revealed that the RcTPS family proteins consisted of two conserved domains: a typical N-terminal TPS (Glyco_transf_20) domain and a C-terminal TPP (Trehalose_PPase) domain (Figure 4A).
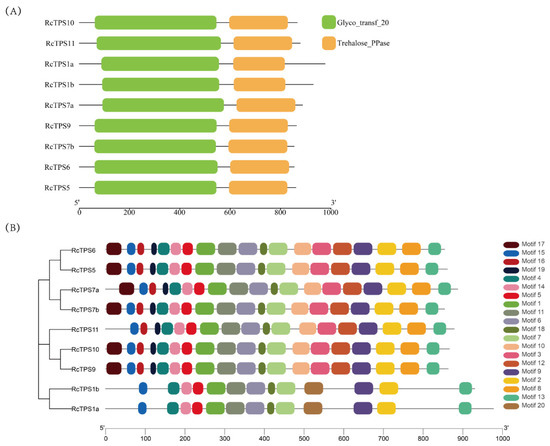
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the conserved domains and motifs of RcTPS proteins. (A) The protein conserved domains, where green boxes represent Glyco_transf_20 (TPS) and orange boxes represent Trehalose_PPase (TPP) domains, respectively. (B) Motif analysis of RcTPS proteins in R. chinensis.
To further elucidate the structural features of the RcTPS gene family, the conserved motifs of its members were analyzed. The results indicate that a total of 12 motifs, including motifs 1–2, 4–7, 9, 11, 13–15, and 18, were highly conserved and were present in 9 members of the RcTPS protein family (Figure 4B). All motifs of the RcTPS proteins were between 17 and 50 amino acid residues in length, and the number of motifs was between 13 and 19. There were similarities in the motifs among members of the same group, especially in adjacent gene pairs, including RcTPS5/RcTPS6, RcTPS7a/RcTPS7b, RcTPS9/RcTPS10, and RcTPS1a/RcTPS1b.
In addition, the similarity of the conserved motifs among members of the same group indicated that their functions might be similar. For example, all TPS I subfamily members had 13 conserved motifs, and all TPS II subfamily members had 19 conserved motifs, except RcTPS11, which had 18 conserved motifs. Compared with the TPS II subfamily members, RcTPS1a and RcTPS1b in the TPS I subfamily added motif 20 but lacked motifs 3, 8, 10, 12, 16, 17, and 19, indicating that these 2 subfamilies have experienced a divergence in gene function (Figure 4B).
Multiple sequence alignment showed that the similarity of the 9 RcTPS proteins was 59.14%, with the highest identity between RcTPS1a and RcTPS1b (77.96%) and the lowest identity between RcTPS1b and RcTPS7a (31.96%). The pairwise amino acid sequence identities ranged from 31.96% to 34.87% between group I (RcTPS1a, RcTPS1b) and group II (RcTPS5–RcTPS10) and varied from 77.10% to 57.19% within group II members. The average identities of the amino acid sequences of the TPS and TPP domains were 58.02% and 54.67%, respectively. In addition, the alignment results showed that several amino acid residues in the catalytic enzyme activity domains (TPS and TPP domain) are highly conserved (Figure S2), indicating that RcTPS proteins have corresponding enzyme activity. At the same time, amino acid regions outside the TPS and TPP domains also showed high diversity. These different regions may contribute to the functional diversity of the TPS family proteins in R. chinensis.
3.5. Evolution Analysis of RcTPS Genes
Pairwise comparisons were analyzed among the 78 full-length TPS protein sequences from R. chinensis, A. thaliana, and N. nucifera, and 5 Rosaceae plants (P. yedoensis, P. persica, P. mume, P. armeniaca, and Malus domestica). The proteins shared 20.18–99.88% identities while the average pairwise sequence identities were 33.97%, 43.12%, and 37.69% in the full, group I, and group II sequences, respectively.
A phylogenetic tree of 78 TPS orthologues was constructed to characterize their evolutionary relationships in 8 species (Figure 5). In addition to A. thaliana and M. domestica, the TPS gene family of the other six species all shared nine members. The A. thaliana TPS family contained 11 members, and the MdTPS family contained 13 members. All the TPS homologous protein sequences were named and clustered into two main subfamilies: group I TPS (17 proteins) and group II TPS (61 proteins) (Figure 5). To analyze orthologous relations in each subfamily, the 61 group II TPS members were further classified into 4 clusters (II1, II2, II3, and II4) with high bootstrap support (Figure S3 and Figure 5). Groups II1, II2, and II3 all contained at least one TPS orthologue of the eight species, while no NnTPS orthologues belonged to group I and no MdTPS orthologues belonged to group II4. The 17 group I TPS orthologues could be further assigned to 2 clades: the 3 A. thaliana group I TPS orthologues (AtTPS2, AtTPS3, and AtTPS4) were classified into subclade I, and the 14 other group I TPS1 orthologues were classified into subclade II (Figure 5). The quantity variance of group I TPS orthologues may suggest that subclade II TPS genes were lost from the other seven species genomes, except for A. thaliana.
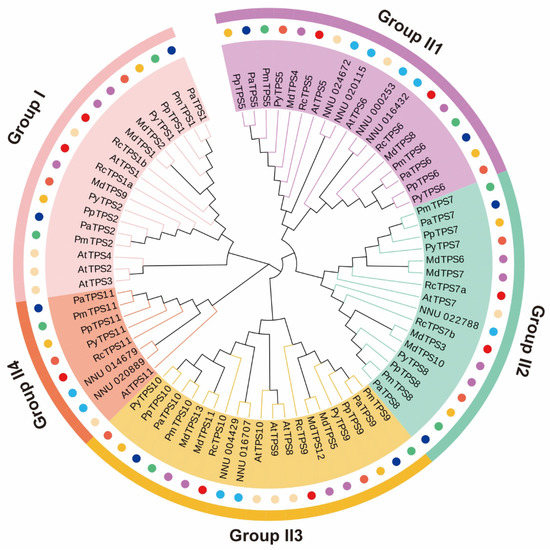
Figure 5.
The phylogenetic tree of TPS family members from R. chinensis (RcTPS), Prunus persica (PpTPS), Prunus yedoensis (PyTPS), Prunus armeniaca (PaTPS), Prunus mume (PmTPS), Malus domestica (MdTPS), Nelumbo nucifera (NnTPS), and Arabidopsis thaliana (AtTPS). The light pink, violet, olive green, light yellow, and dark pink colored regions represent groups I, II1, II2, II3, and II4, respectively. TPSs from 8 plants are labeled by circles of red, orange, tangerine, mazarine, green, purple, baby blue, and light yellow colors, respectively.
The evolutionary relationship among the 78 TPS gene family members indicated that the TPS orthologues in the same cluster may have originated from a common ancestor and may have a similar function. Notably, most RcTPS genes were clustered with the TPSs of M. domestica, indicating that the RcTPS family is more closely related to the MdTPS family.
The results of the selection pressure analysis of the eight TPS family members in the eight plants is shown in Table 2. In the M0 model, the estimated ω values of the five clusters were <1, indicating that purity selection is the main selection mode acting on the TPS family. However, there were significant differences between the M3 and M0 chi-square tests in the TPS family, indicating that some specific sites were still affected by positive selection forces. Therefore, we compared model M8 and model M7 to test whether some positive selection of specific codon substitutions contributes to an effect on TPS family gene divergences. By comparison and estimation, 11, 2, 13, 5, and 25 codon-positive selection sites were found in group I, group II1, group II2, group II3, and group II4, respectively, but only 2 positive selection sites were found at the 95% cut-off points in group II1 and group II3. Therefore, purity selection is the main selection mode acting on the TPS family members of these eight plants, indicating that most TPS family members in the same group were relatively conserved during evolution.

Table 2.
Selection force analysis of the TPS family under the site models.
3.6. Expression Pattern Analysis of RcTPS Genes under Heat Stress
To investigate the functions of RcTPS genes in heat tolerance, the expression patterns of the nine RcTPS genes in the roots, stems, and leaves were detected. The results suggest that the expression profiles of the nine RcTPS genes differed, except for RcTPS1b, while the other members of the RcTPS family were upregulated in at least one tissue under heat stress.
RcTPS1a showed significantly increased expression after heat treatment, which peaked at 1 and 2 h in root and leaf tissues, respectively (Figure 6A,C). However, RcTPS1a was not upregulated in stem tissues under heat stress (Figure 6B). In addition, the other group I TPS family member RcTPS1b was not upregulated in all the roots, stems, and leaves under heat stress (Figure 6).
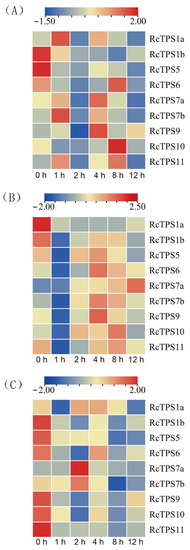
Figure 6.
Expression patterns of RcTPS genes in R. chinensis roots, stems, and leaves under heat stress. (A–C) represent roots, stems, and leaves, respectively. The number under the heat map represents the heat treatment time for 0 (control), 1, 2, 4, 8, and 12 h. The color scale represents fold changes (heat treatment/control) normalized log2 transformed data.
Regarding the group II TPS family members, except for RcTPS5, the expression of the other six RcTPS members in the root tissue increased at different time points after heat stress (Figure 6A). However, in the stem tissue, all seven group II TPS members were upregulated at different time points after heat stress (Figure 6B). In the leaf tissue, only RcTPS7a and RcTPS7b tended to show significantly increased expression at 2 h after heat stress (Figure 6C). In summary, most RcTPS members showed upregulated expression in the roots and stems, and RcTPS7a and RcTPS7b especially showed significantly increased expression after heat treatment in all root, stem, and leaf tissues.
4. Discussion
Trehalose is a nonreducing sugar that is used as a carbon source and a pressure protector in various organisms. This compound can withstand heating at 100 °C for 24 h and protects protein and membrane invariance [3,31]. Some drought-resistant plants, such as Selaginella lepidophylla, accumulate large amounts of trehalose under drought conditions and can maintain metabolic dormancy for several years until the environmental humidity increases [4].
In this study, the trehalose content in the root and stem tissues of R. chinensis significantly increased by about 1.4-fold compared to control plants after 8 and 24 h, respectively, of heat stress. The trehalose content in the leaf tissue showed little change before 24 h of heat stress but rapidly decreased after 24 h. In this study, the trehalose content in the leaf tissue of R. chinensis was the highest compared to the root and stem tissues. In general, the results of this experiment show that the trehalose content in R. chinensis increased after heat stress, but the increased amount was not very large, and slowly decreased after 24 h. These results are consistent with those of other species. According to some studies, trehalose is present in low concentrations in most cultivated plants [3]. Trehalose contents are slightly increased in wheat, cotton, cassava, and P. mume grown under water-deficit conditions [3,16,32]. In addition, due to the low content of trehalose synthesized in higher plants, current studies have confirmed that trehalose is mainly involved in abiotic stress as a signal molecule [7]. Therefore, a small increase in the trehalose content in plants after abiotic stress may activate the metabolic regulatory pathways related to abiotic stress [3,7].
Transcriptome and metabonomics analyses of plants exposed to cold and heat stress have revealed changes in the expression levels of TPS genes [33,34]. Heat treatment upregulates the expression of AtTPS5 and enhances the heat tolerance of A. thaliana while it decreases the heat tolerance of tps5 mutants [26]. When the mycelia of Pleurotus tuoliensis were exposed to heat stress, the expression of the partial TPS gene increased and trehalose was accumulated [35]. The yeast TPS1-TPS2 fusion gene was transferred to A. thaliana and the heat tolerance of the transgenic plants was improved [36]. The Escherichia coli TPS/TPP fusion gene (TPSP), when overexpressed in Lycopersicon esculentum, increased the trehalose content in transgenic tomato seeds. Moreover, the germination rate of TPSP transgenic tomato seeds significantly increased as the expression of various heat stress-responsive genes was increased, and the heat resistance of seeds was improved [37].
In this study, under heat stress, seven of the nine RcTPS genes were highly expressed in the root tissue in response to heat stress, the transcription of seven RcTPS members increased in the stem tissue, and only three RcTPS members showed increased expression in the leaf tissue. This result was consistent with the increasing trend of the trehalose content in different tissues under heat stress. Among the nine RcTPS members, the most important group I TPS member, RcTPS1a, was highly expressed in root and leaf tissues, and the group II TPS members RcTPS7a and RcTPS7b showed high transcript accumulation in the leaf, stem, and root tissues. In addition, all group II TPS members were highly expressed in the stem tissue. Thus, RcTPS7a and RcTPS7b may play important roles in the molecular mechanism of the R. chinensis heat stress response. However, the exact functions of RcTPS1a, RcTPS7a, and RcTPS7b in R. chinensis need to be further explored.
In higher plants, the TPS enzyme is a key synthase in the trehalose synthesis pathway [12]. In recent years, the TPS gene families of many plants have been identified. For example, A. thaliana [17], O. sativa [13], T. aestivum [14], Zea mays [38], N. nucifera [39], S. tuberosum [15], Saccharum officinarum [40], Cucumis sativus [41], Populus trichocarpa [42], M. domestica [43], and Gossypium arboretum [44] have 11, 11, 12, 9, 8, 9, 7, 12, 13, and 14 TPS genes, respectively. TPS gene family members differ between different plants, including monocotyledons and dicotyledons.
Initially, researchers believed that only the protein encoded by AtTPS1 among the 11 TPS genes in Arabidopsis has TPS enzyme catalytic activity [17]. However, studies have shown that in addition to AtTPS3, AtTPS2 and AtTPS4, which belong to group I, also have TPS enzyme catalytic activity [18]. In group II genes, AtTPS6 proved to be complementary to yeast tps1∆ mutants, possibly possessing TPS enzyme catalytic activity [45,46]. Studies have also shown that group II TPS genes are related to heat resistance, growth, and development in Arabidopsis. For example, AtTPS5 is involved in heat resistance while AtTPS6 can control cell morphogenesis [26]. There are 11 OsTPS genes in rice, of which only OsTPS1, a group I TPS gene, can encode the TPS protein with enzyme catalytic activity [27]. The group I TPS gene MoTPS1 in Moringa oleifera also has enzymatic activity [47]. Of the 12 members of the maize TPS gene family, ZmTPS1 belongs to group I and ZmTPS2–ZmTPS12 belong to group II. ZmTPS1 and ZmTPS3 have TPS enzyme catalytic activity [28]. In our study, according to the phylogenetic analysis, RcTPS1a and RcTPS1b were most closely related to AtTPS1 in Arabidopsis; however, more experiments are needed to verify which RcTPS gene family members have TPS enzyme catalytic activity.
The ABA metabolism pathway is one of the important pathways in plant resistance to abiotic stress [48]. Abiotic stress causes changes in the osmotic pressure of cells, which accumulates ABA as a stress response [49]. Studies have shown that plants that overexpress TPS genes induce a high expression of stress-related genes, including genes involved in ABA synthesis signaling pathways [50,51]. In this study, the promoter sequence of RcTPS7b contained the largest number of ABA responsive elements, and RcTPS7b expression significantly improved under heat stress in the roots, stems, and leaves. These results indicate that RcTPS7b genes might be involved in the ABA signal transduction pathway of heat stress resistance, but more studies need to be implemented in the future.
According to the results of the collinearity analysis, the type II subfamily gene pairs RcTPS9–RcTPS10 and RcTPS7a–RcTPS7b were created by segmental duplication events. The same segmental duplication events were also identified in rice and populous TPS family members [42]. Thus, segmental duplications may significantly contribute to the expansion and gene functional diversity of these TPS gene families. In this study, 78 TPS gene family members were identified in R. chinensis, A. thaliana, N. nucifera, P. yedoensis, P. persica, P. mume, P. armeniaca, and Malus domestica. The number of TPS family members of these species ranged from 9 to 13, indicating that they experience different gene duplication events. The 78 genes were divided into 2 main subfamilies (groups I and II). To explore homologous relationships, group II subfamilies were further classified into four subgroups: II1, II2, II3, and II4, similar to the classification in sugarcane [36] and P. mume [14]. To explore the division mechanism of these TPS family members, selection force analysis was implemented among the five clusters. The results showed that most members of the TPS family experienced strong purity selection, indicating that the functions of the members in the same group were mostly conservative. However, two significant positive selection sites were identified in groups I and group II3, suggesting that these members may have some specific gene functions. These two codon sites may have important functions and may be a guiding force in the evolution of TPS genes in the group.
5. Conclusions
Our study showed that the trehalose content in the different tissues of R. chinensis under heat stress was higher than that under normal conditions, which indicates that trehalose has an important effect on the heat tolerance of R. chinensis. We identified nine members of the RcTPS gene family and analyzed their gene structure, phylogenetic relationships, and selection force. Most cis-acting elements in the promoters of RcTPS members were related to plant hormones, especially ABA hormones. Segmental duplications contributed to the expansion of the RcTPS family, and RcTPS9–RcTPS10 and RcTPS7a–RcTPS7b were created by segmental duplication events. Phylogenetic trees of 78 TPS orthologous proteins of R. chinensis and 7 other species were constructed, which could be divided into 5 groups. Purity selection is the main selection mode acting on the 78 TPS members of these 8 plants, thus these TPS orthologous proteins were relatively conserved during evolution. Under heat stress, eight of the nine members of RcTPS could respond to heat treatment in the root, stem, or leaf tissues, among which RcTPS7a and RcTPS7b showed significantly high expression levels in all three tissues. Therefore, the results show that RcTPS genes play an important role in the heat stress of rose. This study provides valuable information that reveals the roles of trehalose and RcTPS family members in the heat tolerance of R. chinensis, and will be helpful for heat tolerance function and molecular mechanism analysis of RcTPS7a and RcTPS7b in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae8050429/s1. Table S1: The TPS protein sequences used to reconstruct phylogenetic trees; Figure S1: Phylogenetic tree of 40 TPS protein sequences from Arabidopsis, Oryza sativa, Prunus mume and Rosa chinensis; Table S2: Specific primers of TPS family members and reference gene in Rosa chinensis; Figure S2: Multiple sequences alignment of 9 TPS family members in Rosa chinensis; Figure S3: The phylogenetic tree of TPS family members from R. chinensis (RcTPS), Prunus persica (PpTPS), Prunus yedoensis (PyTPS), Prunus armeniaca (PaTPS), Prunus mume (PmTPS), Malus domestica (MdTPS), Nelumbo nucifera (NnTPS) and Arabidopsis thaliana (AtTPS).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-F.L. and J.-R.C.; methodology, X.-R.W. and W.L.; software, X.-R.W.; validation, Y.-W.M., W.L., F.-X.C. and J.-L.D.; formal analysis, H.-X.C.; investigation, W.L.; resources, Y.-F.L.; data curation, W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.-R.W. and Y.-F.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.-F.L.; visualization, X.-R.W. and Y.-F.L.; supervision, Y.-F.L.; project administration, Y.-F.L. and J.-R.C.; funding acquisition, Y.-F.L. and J.-R.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Subproject of National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2020YFD1001104 and 2018YFD1000400, National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 3177232, and Open project of Horticulture in Hunan Agricultural University of China, grant number 2021YYXK005.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, B.; Gao, K.; Ren, H.; Tang, W. Molecular mechanisms governing plant responses to high temperatures. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 757–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhu, J. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatsyshyn, V.Y.; Kvasko, A.Y.; Yemets, A.I. Genetic approaches in research on the role of trehalose in plants. Cytol. Genet. 2017, 51, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, J.E.; Delorge, I.; Figueroa, C.M.; Van Dijck, P.; Stitt, M. Trehalose metabolism in plants. Plant J. 2014, 79, 544–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Perez, P.; Camacho-Zamora, B.D.; Espinoza-Sanchez, E.A.; Gutierrez-Soto, G.; Zavala-Garcia, F.; Jazmin Abraham-Juarez, M.; Ramona Sinagawa-Garcia, S. Characterization of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase genes and analysis of its differential expression in maize (Zea mays) seedlings under drought stress. Plants 2020, 9, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Wang, Z.; Kong, B.; Lin, T. Exogenous trehalose differentially modulate antioxidant defense system in wheat callus during water deficit and subsequent recovery. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 70, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner, F.; Lunn, J.E. The role of trehalose 6-phosphate (Tre6P) in plant metabolism and development. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 737–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesteene, L.; Lopez-Galvis, L.; Vanneste, K.; Feil, R.; Maere, S.; Lammens, W.; Rolland, F.; Lunn, J.E.; Avonce, N.; Beeckman, T.; et al. Expansive evolution of the trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase gene family in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Houtte, H.; López-Galvis, L.; Vandesteene, L.; Beeckman, T.; Van Dijck, P. Redundant and non-redundant roles of the trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatases in leaf growth, root hair specification and energy-responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e23209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahl, V.; Ponnu, J.; Schlereth, A.; Arrivault, S.; Langenecker, T.; Franke, A.; Feil, R.; Lunn, J.E.; Stitt, M.; Schmid, M. Regulation of flowering by trehalose-6-phosphate signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 2013, 339, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.C.M.; Hejazi, M.; Fettke, J.; Steup, M.; Feil, R.; Krause, U.; Arrivault, S.; Vosloh, D.; Figueroa, C.M.; Ivakov, A. Feedback inhibition of starch degradation in Arabidopsis leaves mediated by trehalose 6-phosphate. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 1142–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lunn, J.E. Gene families and evolution of trehalose metabolism in plants. Funct. Plant Biol. 2007, 34, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Pan, R.; Hu, W.; Guan, Y.; Hu, J. Seed priming with spermidine and trehalose enhances chilling tolerance of rice via different mechanisms. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.W.; Wang, X.N.; Fu, L.S.; Sun, J.; Zheng, W.; Li, Z.F. Identification of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene family in winter wheat and expression analysis under conditions of freezing stress. J. Genet. 2015, 94, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mattson, N.; Yang, L.; Jin, Q. Genome-wide analysis of the Solanum tuberosum (potato) trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) gene family: Evolution and differential expression during development and stress. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, K.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q. Characteristics and expression analyses of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase family in Prunus mume reveal genes involved in trehalose biosynthesis and drought response. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesteene, L.; Ramon, M.; Roy, K.L.; Dijck, P.V.; Rolland, F. A single active trehalose-6-P synthase (TPS) and a family of putative regulatory TPS-like proteins in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorge, I.; Figueroa, C.M.; Feil, R.; Lunn, J.E.; Van Dijck, P. Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1 is not the only active TPS in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem. J. 2015, 466, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.M.; Villalobos, E.; Araújo, S.S.; Leyman, B.; Van Dijck, P.; Alfaro-Cardoso, L.; Fevereiro, P.S.; Torné, J.M.; Santos, D.M. Transformation of tobacco with an Arabidopsis thaliana gene involved in trehalose biosynthesis increases tolerance to several abiotic stresses. Euphytica 2005, 146, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fu, L.; Qin, P.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Overexpression of the wheat trehalose 6-phosphate synthase 11 gene enhances cold tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene 2019, 710, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Zhang, S.C.; Qi, S.D.; Zheng, C.C.; Wu, C.A. Delayed germination of Arabidopsis seeds under chilling stress by overexpressing an abiotic stress inducible GhTPS11. Gene 2016, 575, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Li, W.M.; Wang, W. Trehalose: Protector of antioxidant enzymes or reactive oxygen species scavenger under heat stress? Environ. Exp. Bot. 2008, 63, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hou, Z.; Huang, C.; Chen, Q.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J. Cloning, purification and characterization of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase from Pleurotus tuoliensis. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Xing, W.; Luo, P.; Zhang, F.; Jin, X.; Zhang, M. Comparative transcriptome analysis of Rosa chinensis ‘Slaters’ crimson China’ provides insights into the crucial factors and signaling pathways in heat stress response. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2019, 142, 312–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.; Li, M.; Ming, F. A cytosolic class I small heat shock protein, RcHSP17.8, of Rosa chinensis confers resistance to a variety of stresses to Escherichia coli, yeast and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 1046–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Bajad, S.; Shuman, J.; Shulaev, V.; Mittler, R. The transcriptional co-activator MBF1c is a key regulator of thermotolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 9269–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finn, R.D.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Mistry, J.; Mitchell, A.L.; Potter, S.C.; Punta, M.; Qureshi, M.; Sangrador-Vegas, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database: Towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2016, 44, D279–D285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various HTS-data handling tools with a user-friendly interface. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yu, C.; Luo, L.; Wan, H.; Zhen, N.; Xu, T.; Tan, J.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Q. Transcriptome of the floral transition in Rosa chinensis ‘Old Blush’. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, M.J.; Primavesi, L.F.; Jhurreea, D.; Zhang, Y. Trehalose metabolism and signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 417–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, B.; Fu, L.; Zhang, D.; He, X.; Chen, Q.; Peng, M.; Zhang, J. Interspecies and intraspecies analysis of trehalose contents and the biosynthesis pathway gene family reveals crucial roles of trehalose in osmotic-stress tolerance in cassava. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghera, G.S.; Wani, S.H.; Hussain, W.; Singh, N.B. Engineering cold stress tolerance in crop plants. Curr. Genom. 2011, 12, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Usadel, B.; Blaesing, O.E.; Gibon, Y.; Retzlaff, K.; Hoehne, M.; Guenther, M.; Stitt, M. Global transcript levels respond to small changes of the carbon status during progressive exhaustion of carbohydrates in Arabidopsis rosettes. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 1834–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, W.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, Q.; Zou, Y.-J.; Zhao, M.-R.; Zhang, J.-X. Nitric oxide is involved in the regulation of trehalose accumulation under heat stress in Pleurotus eryngii var. tuoliensis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 34, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.A.; Avonce, N.; Suarez, R.; Thevelein, J.M.; Van Dijck, P.; Iturriaga, G. A bifunctional TPS-TPP enzyme from yeast confers tolerance to multiple and extreme abiotic-stress conditions in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 2007, 226, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, J.I.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.K.; Bae, C.H.; Jeong, W.J.; Min, S.R.; Liu, J.R. Enhanced tolerance to heat stress in transgenic tomato seeds and seedlings overexpressing a trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase fusion gene. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 12, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Fu, F.L.; Zhang, S.Z.; Wu, L.; Li, W.C. Cloning and characterization of functional trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene in maize. J. Plant Biol. 2010, 53, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Mattson, N.; Xu, Y. Genome-wide identification and evolution analysis of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene family in Nelumbo nucifera. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wu, Z.D.; Luo, Z.Y.; Burner, D.M.; Wu, C.W. Genome-wide analysis of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) gene family and expression profiling of ScTPS genes in sugarcane. Agronomy 2020, 10, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, Y.; Niu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yan, M.; Liao, W. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) gene family in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). PeerJ 2021, 9, e11398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.-L.; Liu, Y.-J.; Wang, C.-L.; Zeng, Q.-Y. Molecular evolution of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) gene family in Populus, Arabidopsis and rice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Qi, S.; Ma, J.; Xing, L.; Fan, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Han, M. Identification of TPS family members in apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.) and the effect of sucrose sprays on TPS expression and floral induction. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 120, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, M.; Lu, X.K.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, D.L.; Yin, Z.J.; Wang, S.; Fan, W.L.; Ye, W.W. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the stress-resistance function of the TPS (trehalose-6-phosphate synthase) gene family in cotton. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon, M.; De Smet, I.; Vandesteene, L. Extensive expression regulation and lack of heterologous enzymatic activity of the class II trehalose metabolism proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 1015–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chary, S.N.; Hicks, G.R.; Choi, Y.G. Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase regulates cell shape and plant architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.; Jia, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X. Evolution and expression patterns of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene family in drumstick tree (Moringa oleifera Lam.). Planta 2018, 248, 999–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Seomun, S.; Yoon, Y.; Jang, G. Jasmonic acid in plant abiotic stress tolerance and interaction with abscisic acid. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M. A new look at stress: Abscisic acid patterns and dynamics at high-resolution. New Phytol. 2016, 210, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon, M.; Rolland, F. Plant development: Introducing trehalose metabolism. Trends. Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avonce, N.; Leyman, B.; José, O.M.-G.; Dijck, P.V.; Iturriaga, T.G. The arabidopsis trehalose-6-p synthase AtTPS1 gene is a regulator of glucose, abscisic acid, and stress signaling. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 3649–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).