Leaf Epidermal Morphology of Ten Wild Tree Peonies in China and Its Taxonomic Significance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Light Microscope
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscope
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
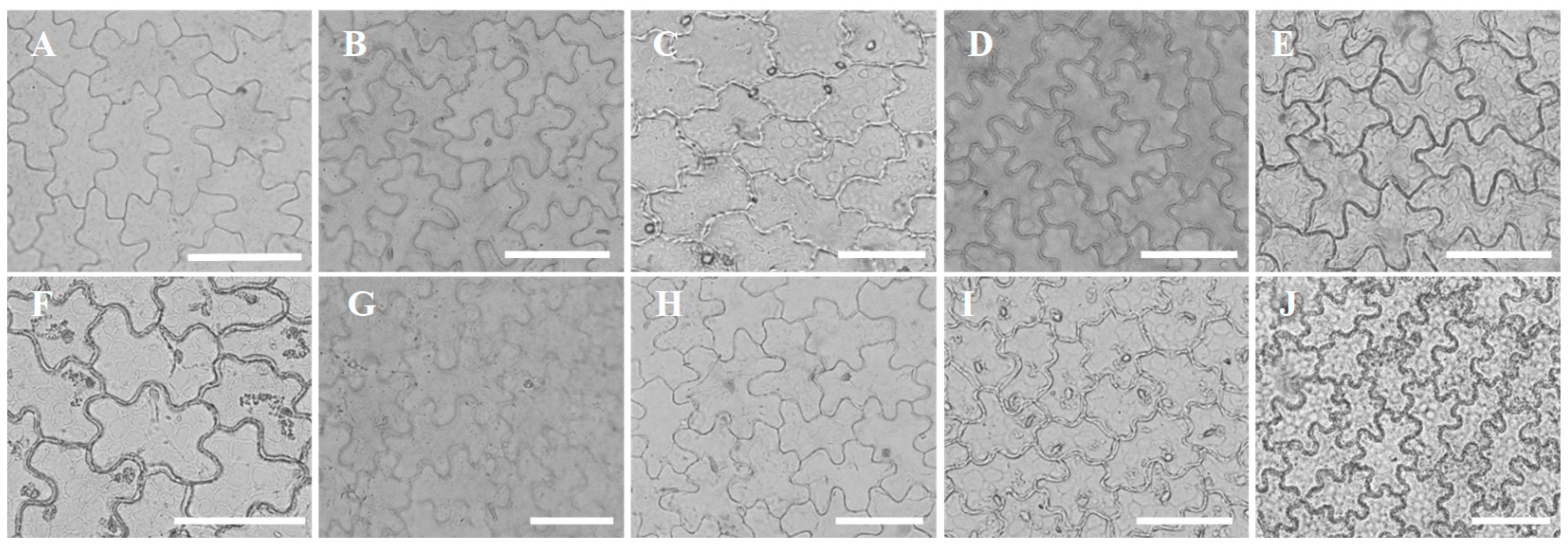
3.1. Leaf Epidermis Cell Shape and Anticlinal Wall Pattern
3.2. Cuticular Wax
3.3. Micromorphology of Stomata
3.4. Principal Component Analysis
3.5. Trichomes
| Leaf epidermis with hairs |
| Only with long conic trichomes or flat-shaped trichomes |
| Only with long conic trichomes----------------------------------P. jishanensi |
| Only with flat-shaped trichomes---------------------------------P. cathayana |
| Leaf epidermis with flat-shaped trichomes and conic trichomes |
| The trichomes only distributed on the areoles----------------P. qiui |
| The trichomes distributed on the areoles and the veins----P. rockii |
| Leaf epidermis glabrous |
| Elliptic stomata |
| Stomatal density (≥250)---------------------------------------------P. ludlowii |
| Stomatal density (<250) |
| Stomatal index (>25)------------------------------------------P. potanini |
| Stomatal index (<25) |
| Stomatal index (<20) -----------------------------------P. decomposita |
| Stomatal index (≥20, <25) -----------------------------P. delavayi |
| Rectangular stomata |
| Stomatal density (≥250) --------------------------------------------P. ostii |
| Stomatal density (<230) -------------------------------------------P. lutea |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.; Chen, T.; Tao, J. Single molecule, full-length transcript sequencing provides insight into the TPS gene family in Paeonia ostii. Peer J. 2021, 9, e11808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.-J.; Shi, Q.Q.; Niu, L.-X.; Zhang, Y.-L. Research progress of wild tree peony resources of Subsect. Vagintae. North Hortic. 2018, 10, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, E.-Q.; Pang, J.-J.; Ji, H.-L. Analysis of using value and protection measures of wild peony sources of Subsect. Delavayanae. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2020, 59, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, F.C.; Taylor, G. A new peony from S. E. Tibet. J. Roy. Hort. Soc. 1951, 76, 216–217. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, F.C.; Taylor, G. Paeonia lutea var. ludlowii. Curtis’ Bot. Mag. 1953, 169, 209. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.-P. Notes on Chinese Paeonies. Acta. Phytotax. Sin. 1958, 7, 297–323. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, B.-A. The origin of the tradional Chinese Medicine, “Mudanpi”—A new variety of Paeonia. J. Syst. Evol. 1997, 35, 360–361. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.-Y. Pictorial Record of Chinese Tree Peony Varieties, 1st ed.; China Forestry Publishing House Press: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D.-Y.; Pan, K.-Y. Paeonia cathayana D. Y. Hong &K. Y. Pan. A new tree peony, with revision of P. suffruticosa ssp. yinpingmudan. Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 2007, 45, 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D.-Y.; Zhou, S.-L.; He, X.-J.; Yuan, J.-H.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Cheng, F.-Y.; Zeng, X.-L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.-X. Current status of wild tree peony species with special reference to conservation. Biodivers. Sci. 2017, 59, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.-L.; Zou, X.-H.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Liu, J.; Xu, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.-M.; Wang, X.-Q.; Ge, S.; et al. Multiple species of wild tree peonies gave rise to the “king of flowers” Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews. Proc. R. So. B. 2014, 281, 0141687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.-X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.-M.; Zhai, J.-W.; Chen, S.-P.; Wu, S.-S. Leaf epidermal micro-morphology and taxonomic significance of 15 species of Pleione. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2020, 40, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar]
- Gang, Z.; Liu, B.; Rohwer, J.G.; Ferguson, D.K.; Yang, Y. Leaf epidermal micromorphology defining the clades in Cinnamomum (Lauraceae). PhytoKeys 2021, 182, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.S.; Ahamd, M.; Zafar, M.; Athar, M.; Ozdemir, F.A.; Gilani, S.A.A.; Sultana, S.; Ahmad, S.; Butt, M.A.; Majeed, S.; et al. Morphological characterization of Hypnaceae (Bryopsida, Hypnales): Investigating four genera from Western Himalayas by using LM and SEM techniques. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 2020, 83, 676–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.N.; Ahamd, M.; Zafar, M.; Malik, K.; Rashid, N.; Ullah, F.; Zaman, W.; Ali, M. A light and scanning electron microscopic diagnosis of leaf epidermal morphology and its systematic implications in Dryopteridaceae: Investigating 12 Pakistani taxa. Micron 2018, 111, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.N.; Ahamd, M.; Zafar, M.; Razzaq, A.; Malik, K.; Rashid, N.; Ullah, F.; Iqbal, M.; Zaman, W. Foliar epidermal micromorphology and its taxonomic implications in some selected species of Athyriaceae. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 2018, 81, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.N.; Celik, A.; Ahmad, M.; Ullah, F.; Zaman, W.; Zafar, M.; Malik, K.; Rashid, N.; Iqbal, M.; Sohail, A.; et al. Leaf epidermal micromorphology and its implications in systematics of certain taxa of the fern family Pteridaceae from northern Pakistan. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 2019, 82, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.; Abidin, S.Z.; Ahmad, M.; Zafar, M.; Liu, J.; Jamshed, S.; Kiliç, Ö. Taxonomic importance of SEM and LM foliar epidermal micro-morphology: A tool for robust identification of gymnosperms. Flora 2019, 255, 42–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodenberg, W.; Govender, J.; Murugan, N.; Ramdhani, S. Cycad forensics: Leaflet micromorphology as a taxonomic tool for South African cycads. Plant Syst. Evol. 2019, 305, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.J.; Batista, L.K.; Clark, L.G.; Patricia, D.O.R. Leaf micromorphology in Poaceae subtribe Olyrinae Bambusoideae and its systematic implications. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 192, 184–207. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, H.K.; Hong, S.P.; Smets, E.; Huysmans, S. Phylogenetic significance of leaf micromorphology and anatomy in the tribe Mentheae (Nepetoideae: Lamiaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2009, 160, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, W.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Cao, C.-L.; Kou, J.-C. Studies on the Leaf Epidermal Micromorphology of 12 Species of the Genus Lespedeza. Chin. J. Gras. 2019, 41, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.-L.; Zhao, N.; Shi, Y.-T.; Wang, F.; Yuan, T.; Wang, L.-Y. Distant hybridization compatibility of Paeonia lutea and morphological analysis of its progenies. Acta Hortic. Sinica. 2014, 41, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.F.; Cai, Y.-F.; Zhang, X.-X.; Xue, J.-Q.; Qu, S.-P. Phenotypic diversity of natural populations of Paeonia delavayi. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 29, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Fang, Z.-W.; Liu, H.-N.; Zhao, D.-Q.; Tao, J. Exogenous calcium-induced physiological and biochemical changes in tree peony (Paeonia section Moutan DC.) under drought stress. Photosynthetica 2019, 57, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, X.G.; Guo, D.L.; Cheng, S.P.; Zhang, J.Y. Development of thirty new polymorphic microsatellite primers for Paeonia suffruticosa. Biologia Plant. 2011, 55, 708–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cai, C.-F.; Cheng, F.-Y.; Cui, H.-L.; Zhou, H. Characterisation and development of EST-SSR markers in tree peony using transcriptome sequences. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 1853–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Tao, J.R. An introduction to a new system of terminology for plant cuticular analysis. Chin. Bull. Bot. 1991, 8, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrahman, A.A.; Kolawole, O.S.; Oladele, F.A. Leaf epidermal features as taxonomic characters in some Lannea spieces (Anacardiaceae) from Nigeria. Phytol. Balcan. 2014, 20, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Sosnovsky, Y.; Nachychko, V.; Prokopiv, A.; Honcharenko, V. Leaf architecture in Rhododendron Subsection Rhododendron (Ericaceae) from the Alps and Carpathian Mountains: Taxonomic and evolutionary implications. Flora 2017, 230, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Ahmad, M.; Zafar, M.; Bahadur, S.; Celep, F.; Sultana, S.; Begum, N.; Hanif, U.; Zaman, W.; Shuaib, M.; et al. Taxonomic significance of foliar epidermal morphology in Lamiaceae from Pakistan. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 2019, 82, 1507–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stace, C.A. The significance of the leaf epidermis in the taxonomy of the Combretaceae V: The genus Combretum subgenus cacoucia in Africa. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1980, 81, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundipe, O.T.; Olatunji, O.A. Vegetative Anatomy of Brachiaria obtussiflora (Hochst. ex A. Rich.) Stapf and Brachiaria callopus (Pilg.) Stapf (Poaceae). Feddes Repert 1991, 102, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Sun, W.-B.; Chen, G. Characters of the leaf epidermis of Stemonaceae and their taxonomical significance. J. Plant Sci. 2018, 36, 487–500. [Google Scholar]
- Dehgan, B. Application of epidermal morphology to taxonomic delimitations in the genus Jatropha L. (Euphorbiaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1980, 80, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, I.W.; Nast, C.G. The comparative morphology of Winteraceae V. Foliar epidermis and sclerenchyma. J. Arnold. Arbor. 1944, 25, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroof, A.; Saraj, B.; Abrar, H.; Sara, S.; Izaz, K.; Manzoor, U.; Shao, J.W.; Akhtar, N. Foliar epidermal micromorphology and its taxonomic significance in Polygonatum (Asparagaceae) using scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 2020, 83, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, N.; Zhang, J.-R.; Chang, Z.Y. Micromorphological characteristics of leaf epidemis and systematic significance of Rosa L. Guihaia 2017, 37, 169–185. [Google Scholar]
- Saba, G.; Mushtaq, A.; Muhammad, Z.; Saraj, B.; Shazia, S.; Fazal, O.; Fayyaz, U.H.; Zafar, S. Foliar epidermal anatomy of Lamiaceae with special emphasis on their trichomes diversity using scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 2019, 82, 206–223. [Google Scholar]
- Nazish, M.; Ahmad, M.; Ullah, R. Taxonomic implications of leaf epidermis in halophytes of Amaranthaceae from salt range of punjab, Pakistan. Plant Biosyst. 2020, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, S.; Ahmad, M.; Zafar, M. Foliar micromorphology of Convolvulaceous species with special emphasis on trichome diversity from the arid zone of Pakistan. Flora 2019, 255, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.-C.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, H.-T.; Tang, X.-H.; Ye, L.; Huang, D.-S.; Xu, L.-M. Quantitative taxonomic analyses of Actinidia (Actinidiaceae) in China based on micromorphological characters of foliar trichomes. J. Syst. Evol. 2000, 38, 121–136. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Z.; Mai, J.; Pan, W.; Li, H. Comparison of characteristics of leaf trichomes in Houpo a officinalis and their taxonomical significances. Guihaia 2016, 36, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Xiao, M.-H.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Y.-Q. Leaf epidermal micromorphology of Zingiber (Zingiberaceae) from China and its systematic significance. PhytoKeys 2022, 190, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyko, E.V. Trichomes of achenes of Asteraceae.I. Covering hairs. Turczaninowia 2011, 14, 130–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ugbogu, O.A.; Olowokudejo, J.D.; Ogundipe, O.T. Leaf epidermal morphology of Diospyros (Ebenaceae) in Nigeria. Phytologia balcanica 2016, 22, 377–385. [Google Scholar]
- Guyot, M. Phylogenetic and systematic value of stomata of Umbelliferae. In The Biology and Chemistry of Umbelliferae; Heywood, V.H., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1971; pp. 199–214. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.W.; Li, F.-L.; Li, C.-S. Variation coefficient and influencing factors of stomatal parameters. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2005, 27, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.Z.; Hou, X.G.; Liu, G.X.; Qiao, Q.; Zhang, Y.F. Comparative study on the anatomical leaf structure of five wild peony species. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univ. 2012, 41, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.-Y.; Fang, C.-J.; Guo, M.-L. Micromorphological characteristics of leaf epidermis of different varieties of peony. J. Heze Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2018, 40, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.-X.; Cheng, F.-Y.; Peng, L.-P.; Xian, H.-L. Suggestions on conservation and utilization of wild tree peony resources of Subsect. Vagintae based on recent investigation. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2017, 18, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Vislobokov, N.A.; Fu, L.-F.; Wei, Y.-G.; Nuraliev, M.S. Leaf epidermal micromorphology in Aspidistra (Asparagaceae): Diversity and taxonomic significance. PhytoKeys 2021, 185, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Taxon | Collection Information | Voucher Numbers | Storage Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| P. qiui Y. L. Pei and D. Y. Hong | Luoyang National Tree Peony Garden, Luoyang, Henan province, China | Jia 20200058 | Henan Institute of Science and Technology |
| P. decomposita Hand.-Mazz | Luoyang Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, Luoyang, Henan province, China | Jia 20200056 | Henan Institute of Science and Technology |
| P. jishanensis T. Hong and W. Z. Zhao | Luoyang National Tree Peony Garden, Luoyang, Henan province, China | Jia 20200052 | Henan Institute of Science and Technology |
| P. ostii T. Hong and J. X. Zhang | Luoyang National Tree Peony Garden, Luoyang, Henan province, China | Jia 20200050 | Henan Institute of Science and Technology |
| P. delavayi Franch | Gansu Forestry Science and Technology Promotion Station, Lanzhou, Gansu province, china | Jia 20200060 | Henan Institute of Science and Technology |
| P. lutea Delavay ex Franch | Luoyang Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, Luoyang, Henan province, China | Jia 20200062 | Henan Institute of Science and Technology |
| P. potanini Kom | Cangshan Erhai National Nature Reserve, Dali, Yunnan province, China | Wang 2020004 | Luoyang National Peony Garden |
| P. rockii (S. G. Haw and Lauener) T. Hong and J. J. Li ex D. Y. Hong | Gansu Forestry Science and Technology Promotion Station, Lanzhou, Gansu province, China | Wang 2020005 | Luoyang National Peony Garden |
| P. ludlowii (Stern and G. Taylor) D. Y. Hong | Tibet Agricultural and Animal Husbandry University, Linzhi, Tibet, China | Wang 2020006 | Luoyang National Peony Garden |
| P. cathayana D. Y. Hong and K. Y. Pan | Luoyang National Tree Peony Garden, Luoyang, Henan province, China | Wang 2020007 | Luoyang National Peony Garden |
| Code | Adaxial Epidermis | Abaxial Epidermis | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | AWP | Cell Length (μm) | Cell Width (μm) | L/W | SA | AWP | Cell Length (μm) | Cell Width (μm) | L/W | |
| P. qiui | A | W | 58.17 ± 1.38 c | 20.38 ± 0.65 b | 2.88 | P | W | 36.25 ± 2.01 g | 14.50 ± 0.50 ef | 2.50 |
| P. decomposita | A | W | 53.73 ± 1.23 d | 14.80 ± 0.35 d | 3.60 | P | SC | 45.70 ± 1.15 e | 20.53 ± 0.27 b | 2.25 |
| P. jishanensis | A | SC | 60.25 ± 1.00 b | 12.83 ± 0.21 e | 4.75 | P | SC | 56.40 ± 1.04 b | 24.80 ± 0.60 a | 2.30 |
| P. ostii | A | W | 48.25 ± 2.08 ef | 14.83 ± 0.46 d | 3.22 | P | W | 50.20 ± 1.27 d | 17.15 ± 0.75 cd | 2.90 |
| P. delavayi | A | W | 49.32 ± 1.09 e | 14.35 ± 0.58 d | 3.42 | P | W | 50.30 ± 1.58 d | 15.40 ± 0.58 e | 3.29 |
| P. lutea | A | SC | 42.12 ± 1.12 f | 12.50 ± 0.35 e | 3.41 | P | SC | 51.15 ± 0.89 d | 15.30 ± 0.39 e | 3.36 |
| P. potanini | A | W | 53.79 ± 2.05 d | 22.70 ± 1.02 a | 2.37 | P | W | 59.85 ± 1.02 a | 23.40 ± 0.84 a | 2.50 |
| P. rockii | A | W | 46.65 ± 2.16 f | 13.64 ± 0.55 de | 3.40 | P | W | 54.31 ± 1.55 c | 16.28 ± 0.29 d | 3.35 |
| P. ludlowii | A | SC | 40.52 ± 1.87 g | 15.86 ± 0.35 c | 2.52 | P | SC | 41.76 ± 2.32 f | 15.60 ± 0.38 de | 2.70 |
| P. cathayana | A | VW | 73.15 ± 1.34 a | 14.72 ± 0.46 d | 4.50 | P | SC | 40.21 ± 1.28 f | 17.40 ± 0.29 c | 2.32 |
| Taxon | Shape of Stomata | Stomata Length (μm) | Stomata Width (μm) | L/W | Stomatal Density (Num per mm2) | Stomatal Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. qiui | Elliptic | 25.64 ± 0.52 b | 19.25 ± 0.24 a | 1.07 | 300.25 ± 5.25 a | 26.35 ± 0.85 a |
| P. decomposita | Elliptic | 23.09 ± 0.36 c | 19.50 ± 0.15 a | 1.18 | 201.50 ± 2.25 g | 19.10 ± 0.35 d |
| P. jishanensis | Elliptic | 28.12 ± 0.28 a | 19.56 ± 0.20 a | 1.42 | 198.30 ± 2.20 g | 19.20 ± 0.52 d |
| P. ostii | Rectangular | 21.69 ± 0.35 cd | 16.75 ± 0.25 c | 1.29 | 267.25 ± 5.24 d | 21.20 ± 0.50 c |
| P. delavayi | Elliptic | 23.22 ± 0.52 c | 15.41 ± 0.21 cd | 1.53 | 207.50 ± 3.65 f | 23.65 ± 1.20 b |
| P. lutea | Rectangular | 23.81 ± 0.24 bc | 15.65 ± 0.35 cd | 1.52 | 225.50 ± 4.25 f | 20.55 ± 1.02 c |
| P. potanini | Elliptic | 25.55 ± 0.19 b | 18.16 ± 0.25 b | 1.41 | 242.20 ± 3.26 e | 27.30 ± 0.50 a |
| P. rockii | Rectangular | 22.51 ± 0.28 c | 16.54 ± 0.24 c | 1.36 | 215.30 ± 2.55 g | 20.40 ± 0.58 c |
| P. ludlowii | Elliptic | 19.05 ± 0.38 d | 13.85 ± 0.20 e | 1.38 | 275.20 ± 2.35 c | 18.35 ± 0.55 d |
| P. cathayana | Rectangular | 21.82 ± 0.54 cd | 15.88 ± 0.21 c | 1.41 | 287.50 ± 4.20 b | 24.20 ± 0.48 b |
| Variables | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | PC7 | PC8 | PC9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADCL | 0.383 | −0.052 | −0.333 | 0.432 | −0.017 | −0.326 | 0.110 | 0.374 | 0.381 |
| ADCW | 0.249 | −0.348 | 0.437 | 0.033 | −0.178 | −0.053 | −0.152 | 0.503 | 0.105 |
| ADCL/ADCW | 0.146 | 0.316 | −0.518 | 0.257 | 0.161 | 0.010 | 0.162 | 0.073 | −0.319 |
| ABCL | 0.026 | 0.422 | 0.435 | 0.076 | −0.140 | −0.090 | 0.597 | 0.056 | −0.021 |
| ABCW | 0.359 | 0.312 | 0.126 | −0.060 | −0.497 | 0.045 | 0.107 | −0.056 | −0.196 |
| ABCL/ABCW | −0.418 | 0.098 | 0.234 | 0.127 | 0.503 | −0.098 | 0.303 | 0.242 | 0.158 |
| Stomata length | 0.383 | 0.222 | 0.189 | 0.068 | 0.444 | 0.621 | −0.218 | 0.238 | −0.129 |
| Stomata width | 0.458 | 0.090 | 0.043 | −0.328 | 0.306 | −0.092 | 0.102 | −0.439 | 0.550 |
| SL/SW | −0.239 | 0.320 | 0.117 | 0.559 | −0.243 | 0.234 | −0.346 | −0.238 | 0.444 |
| Stomatal density | 0.017 | −0.504 | −0.119 | 0.189 | −0.136 | 0.579 | 0.547 | −0.153 | 0.117 |
| Stomatal index | 0.227 | −0.278 | 0.324 | 0.511 | 0.236 | −0.296 | −0.045 | −0.456 | −0.386 |
| Eigenvalue | 3.653 | 3.129 | 1.893 | 1.175 | 0.759 | 0.206 | 0.169 | 0.014 | 0.002 |
| Contribution rate | 0.332 | 0.284 | 0.172 | 0.107 | 0.069 | 0.019 | 0.015 | 0.001 | 0 |
| CVCR | 0.332 | 0.617 | 0.789 | 0.896 | 0.964 | 0.983 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, W.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Q.; He, S.; Mi, Z.; Zhu, X. Leaf Epidermal Morphology of Ten Wild Tree Peonies in China and Its Taxonomic Significance. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060502
Jia W, Wang Y, Qi Q, He S, Mi Z, Zhu X. Leaf Epidermal Morphology of Ten Wild Tree Peonies in China and Its Taxonomic Significance. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(6):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060502
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Wenqing, Yanli Wang, Qing Qi, Songlin He, Zhaorong Mi, and Xiaopei Zhu. 2022. "Leaf Epidermal Morphology of Ten Wild Tree Peonies in China and Its Taxonomic Significance" Horticulturae 8, no. 6: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060502
APA StyleJia, W., Wang, Y., Qi, Q., He, S., Mi, Z., & Zhu, X. (2022). Leaf Epidermal Morphology of Ten Wild Tree Peonies in China and Its Taxonomic Significance. Horticulturae, 8(6), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060502




