Application of a Generic Participatory Decision Support System for Irrigation Management for the Case of a Wine Grapevine at Epirus, Northwest Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
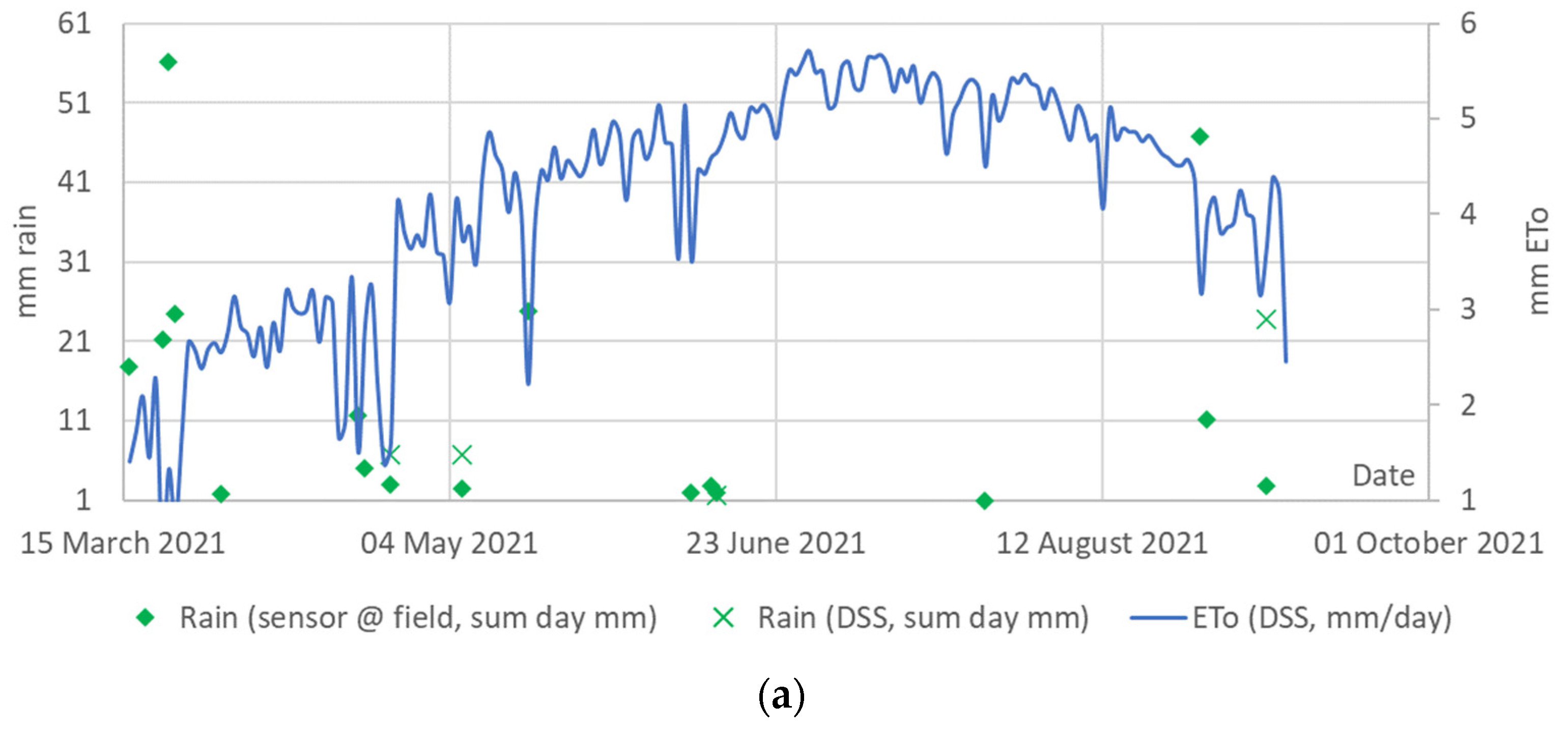
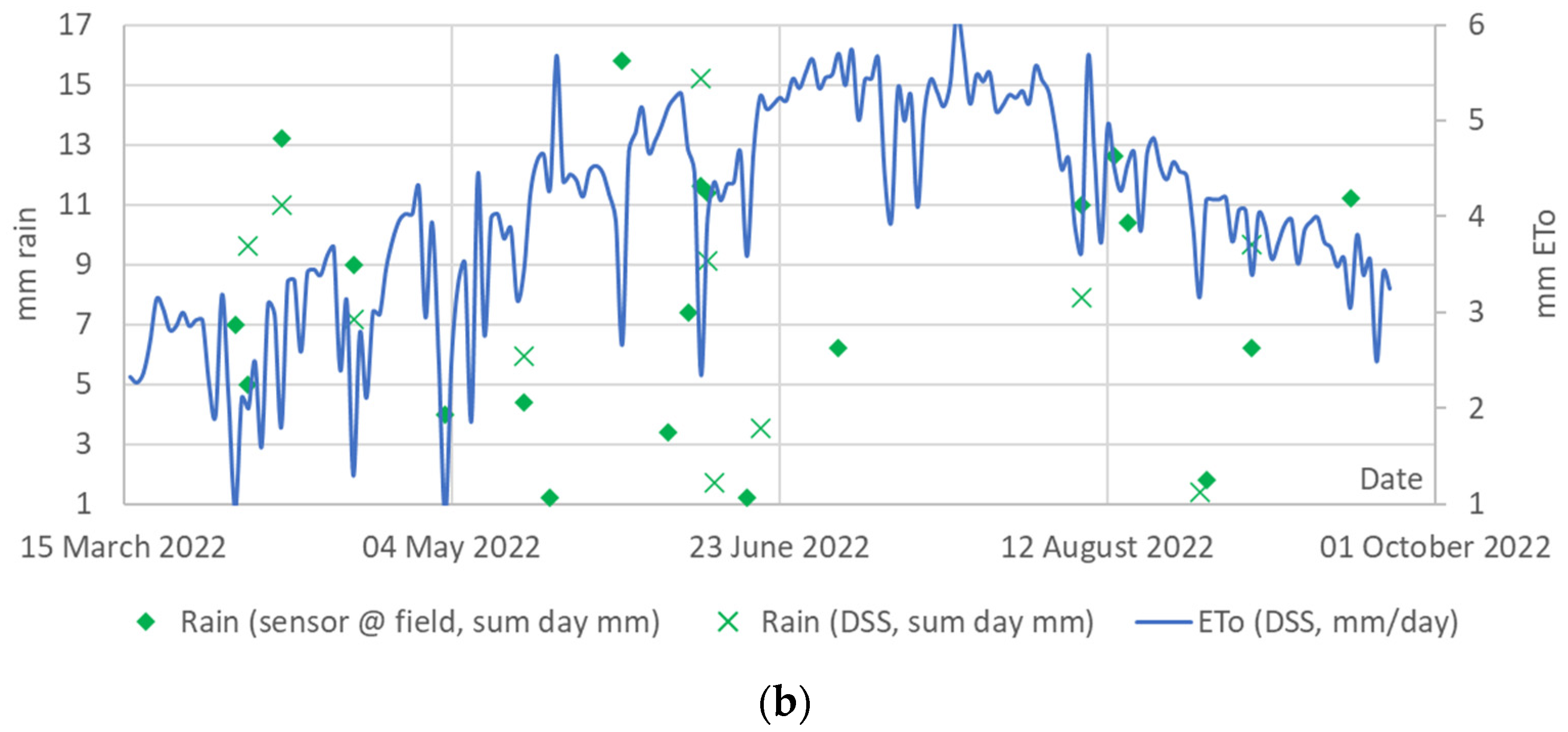
3.1. Agrometeorological Parameters
3.2. Measured Soil Moisture
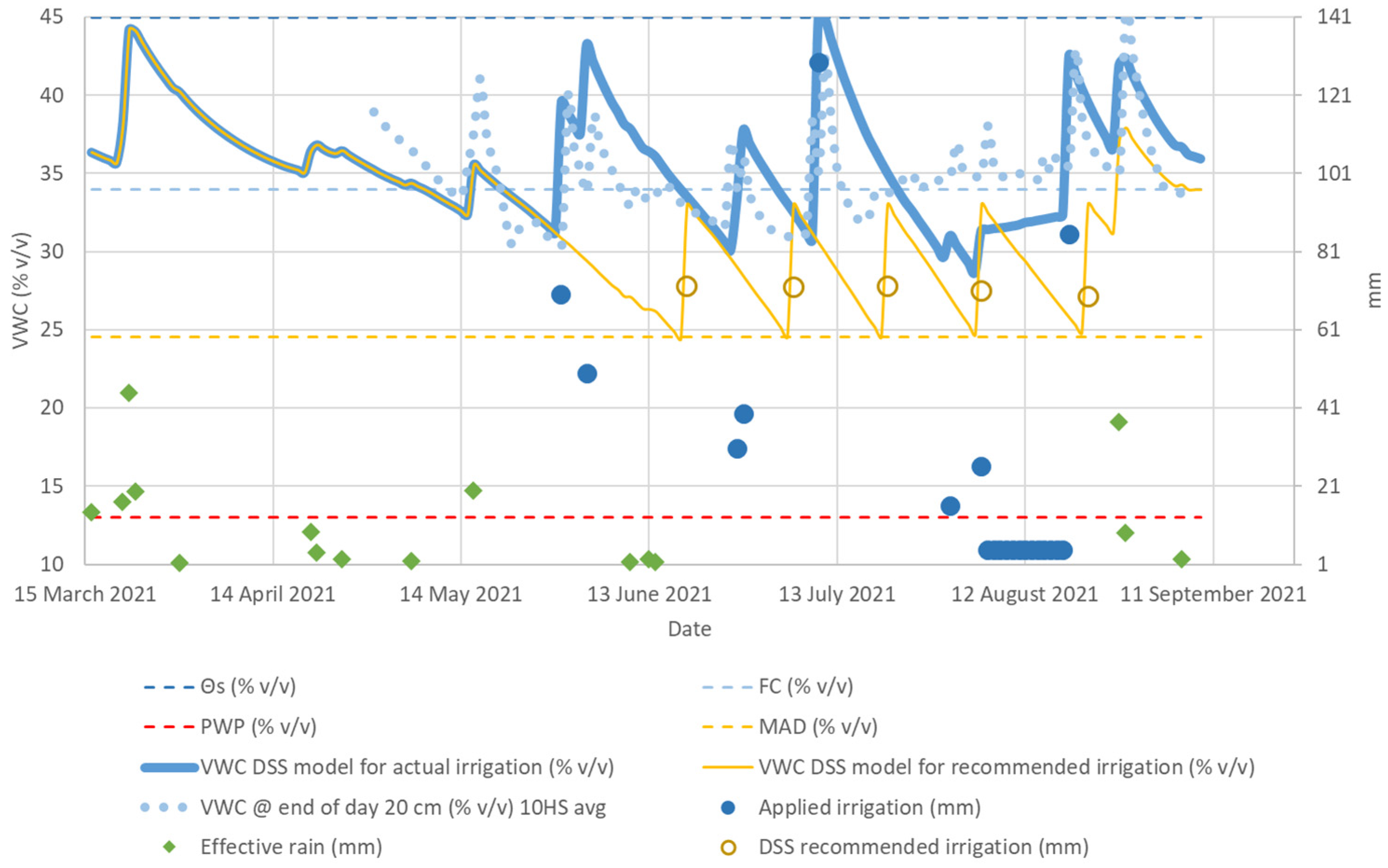
3.3. Adjustment and Evaluation of the DSS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaves, M.; Santos, T.; Souza, C.; Ortuño, M.; Rodrigues, M.; Lopes, C.; Maroco, J.; Pereira, J. Deficit irrigation in grapevine improves water-use efficiency while controlling vigour and production quality. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2007, 150, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillán, D.; Sotés, V.; Iglesias, A.; Garrote, L. Adapting viticulture to climate change in the Mediterranean region: Evaluations accounting for spatial differences in the producers-climate interactions. BIO Web Conf. 2019, 12, 01001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droulia, F.; Charalampopoulos, I. Future Climate Change Impacts on European Viticulture: A Review on Recent Scientific Advances. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naulleau, A.; Gary, C.; Prévot, L.; Hossard, L. Evaluating Strategies for Adaptation to Climate Change in Grapevine Production–A Systematic Review. Front. Plant Sci. Sec. Plant Abiotic Stress 2021, 11, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masia, S.; Sušnik, J.; Marras, S.; Mereu, S.; Spano, D.; Trabucco, A. Assessment of Irrigated Agriculture Vulnerability under Climate Change in Southern Italy. Water 2018, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuda, M.-I.; Esteban, E.; Martín-Retortillo, M.; Pinilla, V. The Blue Water Footprint of the Spanish Wine Industry: 1935–2015. Water 2020, 12, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.M.; Oliveira, M.; Egipto, R.J.; Cid, J.F.; Fragoso, R.A.; Lopes, C.M.; Duarte, E.N. Water and wastewater management for sustainable viticulture and oenology in South Portugal—A review. Cienc. Tec. Vitivinic. 2020, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourgialas, N.N. A critical review of water resources in Greece: The key role of agricultural adaptation to climate-water effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naulleau, A.; Gary, C.; Prévot, L.; Vinatier, F.; Hossard, L. How can winegrowers adapt to climate change? A participatory modeling approach in southern France. Agric. Syst. 2022, 203, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, M.; Elia, A.; Thompson, R.B. Decision support systems and models for aiding irrigation and nutrient management of vegetable crops. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 240, 106209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, I.; Turner, L.; Harrison, M.T.; Monjardino, M.; deVoil, P.; Rodriguez, D. Application, adoption and opportunities for improving decision support systems in irrigated agriculture: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 257, 107161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowling, M.J.; Bennett, B.; Ostendorf, B.; Westra, S.; Walker, R.R.; Pellegrino, A.; Edwards, E.J.; Collins, C.; Pagay, V.; Grigg, D. Bridging the gap between data and decisions: A review of process-based models for viticulture. Agric. Syst. 2021, 193, 103209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, V.; Salinari, F.; Poni, S.; Caffi, T.; Bettati, T. Addressing the Implementation Problem in Agricultural Decision Support Systems: The Example of vite.net. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 100, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic, M.; Riezzo, E.E.; Buono, V.; Zippitelli, M.; Galiano, A.; Cantore, V. Hydro-Tech: An automated smart tech Decision Support Tool for eco-efficient irrigation management. Int. Agric. Eng. J. 2016, 25, 44–56. [Google Scholar]
- Terribile, F.; Bonfante, A.; D’Antonio, A.; Mascellis, R.D.; Michele, C.D.; Langella, G.; Manna, P.; Mileti, F.; Vingiani, S.; Basile, A. A geospatial decision support system for supporting quality viticulture at the landscape scale. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 140, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeri, O.; Netzer, Y.; Munitz, S.; Mintz, D.F.; Pelta, R.; Shilo, T.; Horesh, A.; Meytal, S. Kc and LAI Estimations Using Optical and SAR Remote Sensing Imagery for Vineyards Plots. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Martínez, J.F.; Martínez, N.L.; Díaz, V.H. Applying case-based reasoning and a learning-based adaptation strategy to irrigation scheduling in grape farming. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OPEKEPE-Greek Payment Authority of Common Agricultural Policy. Provision of Data Regarding Vertzami Viticulture in Greece. Available online: http://aggregate.opekepe.gr/?triggerSelect=fytiko_poikilia&queryType=fytiko&year=2020&perifereia=&fytiko_eidos=362&fytiko_poikilia=4786 (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Stavrakas, D. Grape Varieties; Aristotle University of Thessaloniki: Thessaloniki, Greece, 1998; pp. 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- HNMS–Hellenic National Meteorological Service. Climatological Data for Arta/Greece. Available online: http://www.emy.gr/emy/en/climatology/index_html? (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, A.R.; Bird, N.R.A. Methods for predicting the optimum and the range of soil water contents for tillage based on the water retention curve. Soil Tillage Res. 2001, 57, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GMA-Greek Ministry of Agriculture. Determination of Minimum and Maximum Iimits of the Necessary Quantities for the Sustainable Use of Water for Irrigation. Govern. Gazette (GG) B’ 42 2/6/1989 Ministerial Decision Φ.16/6631 1989. Available online: https://www.et.gr/api/DownloadFeksApi/?fek_pdf=19890200428 (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- ASAE (American Society of Agricultural Engineers). Field Evaluation of Microirrigation Systems; EP458; ASAE: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Trendov, N.M.; Varas, S.; Zeng, M. Digital Technologies in Agriculture and Rural Areas-Status Report; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019; p. 102. Available online: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/ca4985en/ (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration–Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements. FAO 1998, Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56, Rome, Italy. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/x0490e/x0490e00.htm (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Twarakavi, N.K.C.; Sakai, M.; Šimůnek, J. An objective analysis of the dynamic nature of field capacity. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamos, N.; Tsirogiannis, I.L.; Christofides, A. Modelling irrigation management services: The IRMA_SYS case. Int. J. Sustain. Agric. Manag. Inform. 2016, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamassis, N.; Mazi, K.; Dimitriou, E.; Kalogeras, D.; Malamos, N.; Lykoudis, S.; Koukouvinos, A.; Tsirogiannis, I.; Papageorgaki, I.; Panagopoulos, Y.; et al. OpenHi.net: A Synergistically Built, National-Scale Infrastructure for Monitoring the Surface Waters of Greece. Water 2021, 13, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulis, K.X.; Elmaloglou, S.; Dercas, N. Investigating the effects of soil moisture sensors positioning and accuracy on soil moisture based drip irrigation scheduling systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 148, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlandson, T.L.; Berg, A.A.; Bullock, P.R.; Ojo, E.R.; McNairn, H.; Wiseman, G.; Cosh, M.H. Evaluation of several calibration procedures for a portable soil moisture sensor. J. Hydrol. 2013, 498, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, R.E.; Bingham, G.E. Rapid Estimates of Relative Water Content. Plant Physiol. 1974, 53, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.I.; Yue, X.F.; Zhao, X.F.; Zhao, H.; Fang, Y.I. Physiological, micro-morphological and metabolomic analysis of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) leaf of plants under water stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 130, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Han, F.; Wu, J.; Ma, Y.; Jacoby, P.W. Optimizing crop water productivity and altering root distribution of Chardonnay grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) in a silt loam soil through direct root-zone deficit irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 277, 108072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.R. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?—Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamos, N.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Field survey and modelling of irrigation water quality indices in a Mediterranean island catchment: A comparison between spatial interpolation methods. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 1447–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardikis, M.G.; Kalivas, D.P.; Kollias, V.J. Comparison of Interpolation Methods for the Prediction of Reference Evapotranspiration—An Application in Greece. Wat. Res. Man. 2005, 19, 251–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, Q.J.; Brugnach, M.; Temesgen, B.; Rueda, C.; Ustin, S.L.; Frame, K. Daily reference evapotranspiration for California using satellite imagery and weather station measurement interpolation. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2009, 26, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L. Rainfall Spatial Estimations: A Review from Spatial Interpolation to Multi-Source Data Merging. Water 2019, 11, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelbach, H.; Casini, F.; Lehner, I.; Teuling, A.J.; Seneviratne, S.I. Soil moisture monitoring for climate research: Evaluation of a low-cost sensor in the framework of the Swiss Soil Moisture Experiment (SwissSMEX) campaign. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D05111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, M. Review of Novel and Emerging Proximal Soil Moisture Sensors for Use in Agriculture. Sensors 2020, 20, 6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, Z.; Gheysari, M.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Amiri, S.; Tabatabaei, M.S. An attempt to find a suitable place for soil moisture sensor in a drip irrigation system. Inf. Process. Agric. 2022, 9, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.W.; Tang, J.; Sarwar, A.; Shah, S.; Saddique, N.; Khan, M.U.; Imran Khan, M.; Nawaz, S.; Shamshiri, R.R.; Aziz, M.; et al. Soil Moisture Measuring Techniques and Factors Affecting the Moisture Dynamics: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukal, M.S.; Irmak, S.; Sharma, K. Development and Application of a Performance and Operational Feasibility Guide to Facilitate Adoption of Soil Moisture Sensors. Sustainability 2020, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi Saab, M.T.; Jomaa, I.; Skaf, S.; Fahed, S.; Todorovic, M. Assessment of a Smartphone Application for Real-Time Irrigation Scheduling in Mediterranean Environments. Water 2019, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazafeiriou, Z.G. Water Needs of Crops; Ziti Publications: Thessaloniki, Greece, 1999; p. 212. [Google Scholar]
- Papamichail, D.; Babatzimopoulos, X. Applied Agricultural Hydraulics; Ziti Publications: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2014; pp. 333, 342, 348, 378. [Google Scholar]
- Chartzoulakis, K. Irrigation of Crops; Agrotypos Publications: Athens, Greece, 2019; pp. 275–289. [Google Scholar]
- Myriounis, C.; Tsirogiannis, I.L.; Malamos, N.; Barouchas, P.; Babilis, D.I.; Chalkidis, I. Agricultural and Urban Green Infrastructure Irrigation Systems Auditing–A Case Study for the Region of Epirus. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 4, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertamini, M.; Zulini, L.; Muthuchelian, K.; Nedunchezhian, N. Effect of water deficit on photosynthetic and other physiological responses in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Riesling) plants. Photosynthetica 2006, 44, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombesi, S.; Nardini, A.; Farinelli, D.; Palliotti, A. Relationships between stomatal behavior, xylem vulnerability to cavitation and leaf water relations in two cultivars of Vitis vinifera. Physiol. Plant. 2016, 152, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Year/Plot | Average Difference between Maximum and Minimum Measured Values from Soil Moisture Sensors (%) | Average Difference between Maximum Plus the Accuracy Limit of 3% and Minimum Minus the Accuracy Limit of 3% Measured Values from Soil Moisture Sensors (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 GRO | 7.39% (0.37) | 13.38% (0.37) |
| 2022 DSI | 7.90% (0.12) | 13.90% (0.12) |
| 2022 GRO | 3.74% (0.19) | 9.74% (0.19) |
| Parameter | 2021 GRO | 2022 DSI | 2022 GRO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potential effective rain coefficient | 0.8 | ||
| Total plot area (m²) | 380 | 190 | 190 |
| Wetted area (m²) | 220 | 110 | 110 |
| Irrigation efficiency | 0.75 | ||
| Maximum allowed depletion (MAD) | 0.45 | 0.52 | |
| Refill factor (RF) | 0.9 | 0.5 | |
| Estimated root depth (max) (m) | 0.6 | ||
| Kc off-season | 0.1 | ||
| Start of water balance season for each year | 15/3 | ||
| Planting date | 20/4 | 15/4 | |
| Kc on planting date | 0.1 | ||
| Kc stages duration (initial, development, mid-season, late-season) (days) | 30 | ||
| 60 | |||
| 40 | |||
| 12 | 32 | ||
| Κc (initial, mid-season, end) | 0.4 | ||
| 0.7 | |||
| 0.4 | |||
| Soil moisture at saturation (Θs, v/v) | 0.45 | ||
| Field capacity (FC, v/v) | 0.34 | ||
| Wilting point (WP, v/v) | 0.13 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsirogiannis, I.L.; Malamos, N.; Baltzoi, P. Application of a Generic Participatory Decision Support System for Irrigation Management for the Case of a Wine Grapevine at Epirus, Northwest Greece. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020267
Tsirogiannis IL, Malamos N, Baltzoi P. Application of a Generic Participatory Decision Support System for Irrigation Management for the Case of a Wine Grapevine at Epirus, Northwest Greece. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(2):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020267
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsirogiannis, Ioannis L., Nikolaos Malamos, and Penelope Baltzoi. 2023. "Application of a Generic Participatory Decision Support System for Irrigation Management for the Case of a Wine Grapevine at Epirus, Northwest Greece" Horticulturae 9, no. 2: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020267
APA StyleTsirogiannis, I. L., Malamos, N., & Baltzoi, P. (2023). Application of a Generic Participatory Decision Support System for Irrigation Management for the Case of a Wine Grapevine at Epirus, Northwest Greece. Horticulturae, 9(2), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020267








