Identification of miRNAs Involved in Male Fertility and Pollen Development in Brassica oleracea var. capitata L. by High-Throughput Sequencing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials, Sample Collection, and Total RNA Extraction
2.2. Small RNA Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.3. Identification of Known and Novel miRNAs
2.4. Stem-Loop Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay
2.5. miRNA Target Prediction and Analysis
3. Results
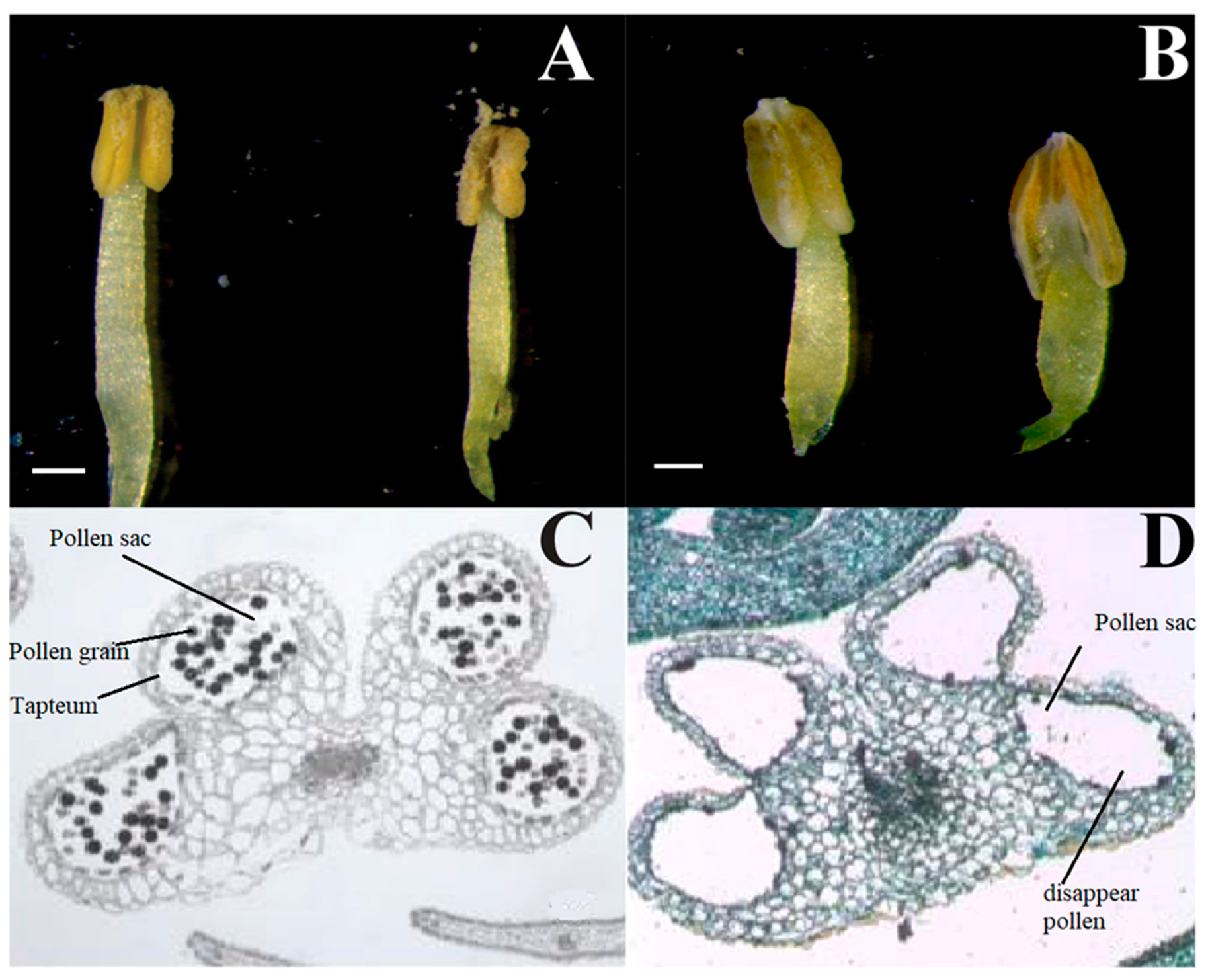
3.1. Morphological and Cytological Characterization of CMS and MF Lines
3.2. Overview Analysis of Sequences from Small RNAs in Cabbage Flower Buds
3.3. Identification of Known miRNAs in Cabbage MF and CMS Line
3.4. Identification of Novel miRNAs in Cabbage Flower Buds
3.5. Expression Analysis of Known and Novel miRNAs in Cabbage CMS and MF Line
3.6. Prediction and GO Function Analysis of miRNA Targets in Cabbage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCormick, S. Control of male gametophyte development. Plant Cell 2004, 16, S142–S153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, R.B.; Beals, T.P.; Sanders, P.M. Anther development: Basic principles and practical applications. Plant Cell 1993, 5, 1217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aukerman, M.J.; Sakai, H. Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a microRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2730–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, R.; Marashi, H.; Tomar, R.S.; Malekzadeh Shafaroudi, S.; Sabara, P.H. Transcriptome analysis identified aberrant gene expression in pollen developmental pathways leading to CGMS in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, B. MicroRNAs in control of plant development. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Liao, L.; Jin, X.; Mao, D.; Liu, R. Analysis of the meiotic transcriptome reveals the genes related to the regulation of pollen abortion in cytoplasmic male-sterile pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Gene 2018, 641, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ye, J.; Zhang, L.; Song, X. Blocked synthesis of sporopollenin and jasmonic acid leads to pollen wall defects and anther indehiscence in genic male sterile wheat line 4110S at high temperatures. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2020, 20, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriyama, K. Molecular basis of cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration in rice. Plant Biotechnol. 2021, 38, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasa, J.; Bosemark, N. Male sterility. In Plant Breeding; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 213–228. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro, S.; Ogasawara, K.; Fujino, K.; Sato, Y.; Kishima, Y. Low temperature-responsive changes in the anther transcriptome’s repeat sequences are indicative of stress sensitivity and pollen sterility in rice strains. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shahid, M.Q.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X. Cytological and transcriptome analyses reveal abrupt gene expression for meiosis and saccharide metabolisms that associated with pollen abortion in autotetraploid rice. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2018, 293, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, S.; Ding, X.; He, T.; Dai, J.; Yang, S.; Gai, J. Comparative transcriptome analysis between the cytoplasmic male sterile line NJCMS1A and its maintainer NJCMS1B in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Stewart, J.M.; Xing, C.; Wu, J.; Jin, S. Transcriptome, cytological and biochemical analysis of cytoplasmic male sterility and maintainer line in CMS-D8 cotton. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 97, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Song, X. Comparative transcriptome analysis indicates that a core transcriptional network mediates isonuclear alloplasmic male sterility in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, A.C.; Vaucheret, H. MicroRNAs: Something important between the genes. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoades, M.W.; Reinhart, B.J.; Lim, L.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D.P. Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell 2002, 110, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, L.; Dunoyer, P.; Jay, F.; Arnold, B.; Dharmasiri, N.; Estelle, M.; Voinnet, O.; Jones, J.D. A plant miRNA contributes to antibacterial resistance by repressing auxin signaling. Science 2006, 312, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Bartel, B. MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 19–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecchia, M.A.; Debernardi, J.M.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Schommer, C.; Palatnik, J.F. MicroRNA miR396 and RDR6 synergistically regulate leaf development. Mech. Dev. 2013, 130, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, D.; Muleke, E.M.; Sun, X.; Wang, R.; Xie, Y.; Gong, Y.; Liu, L. Identification of bolting-related microRNAs and their targets reveals complex miRNA-mediated flowering-time regulatory networks in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ma, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, R.; Liu, J.; Fan, B.; Wei, W.; Nie, L.Z. Identification of microRNAs and their target genes related to the accumulation of anthocyanin in purple potato tubers (Solanum tuberosum). Plant Direct 2022, 6, e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Lu, X.; Lian, C.; An, Y.; Xia, X.; Yin, W. Genome-wide analysis of microRNA responses to the phytohormone abscisic acid in Populus euphratica. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yu, H.; Tang, G.; Huang, T. Small but powerful: Function of microRNAs in plant development. Plant Cell Rep. 2018, 37, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, J.-Y. Identification and profiling of microRNAs expressed in elongating cotton fibers using small RNA deep sequencing. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; He, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Jin, L.; Song, Q.; Yang, S. Comparative analysis of circular RNAs between soybean cytoplasmic male-sterile line NJCMS1A and its maintainer NJCMS1B by high-throughput sequencing. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Y.; Song, W.; Chen, L. Identification and characterization of miRNAs associated with sterile flower buds in the tea plant based on small RNA sequencing. Hereditas 2021, 158, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ling, Y.; Xu, W.; Su, Z. PNRD: A plant non-coding RNA database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D982–D989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhu, X.; Muleke, E.M.; Liu, L. Comprehensive transcriptome-based characterization of differentially expressed genes involved in microsporogenesis of radish CMS line and its maintainer. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2016, 16, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alptekin, B.; Akpinar, B.A.; Budak, H. A comprehensive prescription for plant miRNA identification. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tong, C.; Edwards, D.; Parkin, I.A.; Zhao, M.; Ma, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, S. The Brassica oleracea genome reveals the asymmetrical evolution of polyploid genomes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H. Upregulation of the AT-hook DNA binding gene BoMF2 in OguCMS anthers of Brassica oleracea suggests that it encodes a transcriptional regulatory factor for anther development. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Yao, L.; Yu, Y.; Lv, M.; Miao, Y.; Cao, J. PECTATE LYASE-LIKE10 is associated with pollen wall development in Brassica campestris. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, G.; Bonnema, G.; Fang, Z.; Wang, X. Global analysis of gene expression in flower buds of Ms-cd1 Brassica oleracea conferring male sterility by using an Arabidopsis microarray. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 66, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D.; Liu, B.; Li, Q.; Si, J.; Ren, X.; Song, H. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated multiple gene editing in Brassica oleracea var. capitata using the endogenous tRNA-processing system. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Ge, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, H. BrSKS13, a multiple-allele-inherited male sterility-related gene in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis), affects pollen development and pollination/fertilization process. Gene 2019, 696, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lukasik, A.; Pietrykowska, H.; Paczek, L.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z.; Zielenkiewicz, P. High-throughput sequencing identification of novel and conserved miRNAs in the Brassica oleracea leaves. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ni, Z.; Gao, J. High-throughput sequencing discovery of conserved and novel microRNAs in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2012, 287, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-F.; Fang, Y.-Y.; Feng, L.; Guo, H.-S. Characterization of conserved and novel microRNAs and their targets, including a TuMV-induced TIR-NBS-LRR class R gene-derived novel miRNA in Brassica. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ridzon, D.A.; Broomer, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Lee, D.H.; Nguyen, J.T.; Barbisin, M.; Xu, N.L.; Mahuvakar, V.R.; Andersen, M.R. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem–loop RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varkonyi-Gasic, E.; Wu, R.; Wood, M.; Walton, E.F.; Hellens, R.P. Protocol: A highly sensitive RT-PCR method for detection and quantification of microRNAs. Plant Methods 2007, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.F. Stem-loop RT-qPCR for miRNAs. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2011, 95, 15.10.1–15.10.15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, L.; Chen, M.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.; Liang, X.; Yu, S. Identification and characterization of microRNAs from peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) by high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkar, R.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, J.-K. Identification of novel and candidate miRNAs in rice by high throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, R.; Vaucheret, H.; Trejo, J.; Bartel, D.P. A diverse and evolutionarily fluid set of microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 3407–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Korir, N.K.; Yu, H.; Ma, Z.; Fang, J. Deep sequencing discovery of novel and conserved microRNAs in trifoliate orange (Citrus trifoliata). BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, P.B.; Wang, Q.Q.; Chen, X.S.; Qiu, C.X.; Yang, Z.M. Enrichment of a set of microRNAs during the cotton fiber development. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, B.C.; Axtell, M.J.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D.P.; Baulcombe, D.; Bowman, J.L.; Cao, X.; Carrington, J.C.; Chen, X.; Green, P.J. Criteria for annotation of plant MicroRNAs. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 3186–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cox, S.; Cobb, G.; Anderson, T. Evidence that miRNAs are different from other RNAs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2006, 63, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenen-Stass, A.M.; Magen, I.; Brooks, T.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Greensmith, L.; Hornstein, E.; Fratta, P. Evaluation of methodologies for microRNA biomarker detection by next generation sequencing. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xing, S.; Salinas, M.; Höhmann, S.; Berndtgen, R.; Huijser, P. miR156-targeted and nontargeted SBP-box transcription factors act in concert to secure male fertility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3935–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.K.; Bregitzer, P.; Singh, J. Genome-wide analysis of the SPL/miR156 module and its interaction with the AP2/miR172 unit in barley. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacquard, T.; Clavel, M.; Baldrich, P.; Lechner, E.; Pérez-Salamó, I.; Schepetilnikov, M.; Derrien, B.; Dubois, M.; Hammann, P.; Kuhn, L. The Arabidopsis F-box protein FBW2 targets AGO1 for degradation to prevent spurious loading of illegitimate small RNA. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant-Downton, R.; Le Trionnaire, G.; Schmid, R.; Rodriguez-Enriquez, J.; Hafidh, S.; Mehdi, S.; Twell, D.; Dickinson, H. MicroRNA and tasiRNA diversity in mature pollen of Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, S.-J.; Wu, X.-M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.-L.; Xu, Q.; Guo, W.-W. Selection and validation of suitable reference genes for miRNA expression normalization by quantitative RT-PCR in citrus somatic embryogenic and adult tissues. Plant Cell Rep. 2012, 31, 2151–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, L.; Zhao, M.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, W.-H. Identification of drought-responsive microRNAs in Medicago truncatula by genome-wide high-throughput sequencing. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.Q.; Yan, L.F.; Wang, T. Deep sequencing on genome-wide scale reveals the unique composition and expression patterns of microRNAs in developing pollen of Oryza sativa. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Cui, D.; Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, C.; Xu, C.; Li, P.; Li, S. Deep sequencing of maize small RNAs reveals a diverse set of microRNA in dry and imbibed seeds. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Peng, H.; Cao, M.; Rong, T.; Pan, G. Cytoplasmic male sterility-regulated novel microRNAs from maize. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2011, 11, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Wei, H.; Wu, M.; Song, M.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Fan, S.; Yu, S. Comparative expression profiling of miRNA during anther development in genetic male sterile and wild type cotton. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Lv, M.; Liang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Cao, J. Identification of novel and conserved miRNAs involved in pollen development in Brassica campestris ssp. chinensi s by high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 146. [Google Scholar]
- Kasschau, K.D.; Fahlgren, N.; Chapman, E.J.; Sullivan, C.M.; Cumbie, J.S.; Givan, S.A.; Carrington, J.C. Genome-wide profiling and analysis of Arabidopsis siRNAs. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, R.D.; Aksay, G.; Dolgosheina, E.; Ebhardt, H.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Sahinalp, S.C.; Unrau, P.J. Comparative analysis of the small RNA transcriptomes of Pinus contorta and Oryza sativa. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szittya, G.; Moxon, S.; Santos, D.M.; Jing, R.; Fevereiro, M.P.; Moulton, V.; Dalmay, T. High-throughput sequencing of Medicago truncatula short RNAs identifies eight new miRNA families. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.-Z.; Xia, H.; Frazier, T.P.; Yao, Y.-Y.; Bi, Y.-P.; Li, A.-Q.; Li, M.-J.; Li, C.-S.; Zhang, B.-H.; Wang, X.-J. Deep sequencing identifies novel and conserved microRNAs in peanuts (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertpanyasampatha, M.; Gao, L.; Kongsawadworakul, P.; Viboonjun, U.; Chrestin, H.; Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Narangajavana, J. Genome-wide analysis of microRNAs in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis L.) using high-throughput sequencing. Planta 2012, 236, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuperus, J.T.; Fahlgren, N.; Carrington, J.C. Evolution and functional diversification of MIRNA genes. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Coruh, C.; Axtell, M.J. Arabidopsis lyrata small RNAs: Transient MIRNA and small interfering RNA loci within the A. rabidopsis genus. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Z.; Ai, X.-Y.; Guo, W.-W.; Peng, S.-A.; Deng, X.-X.; Hu, C.-G. Identification of miRNAs and their target genes using deep sequencing and degradome analysis in trifoliate orange [Poncirus trifoliate (L.) Raf]. Mol. Biotechnol. 2012, 51, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, C.; Shuai, B. Profiling microRNA expression in Arabidopsis pollen using microRNA array and real-time PCR. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, C.R.; Iriyama, R.; Fernando, D.D. Expression patterns of conserved microRNAs in the male gametophyte of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda). Plant Reprod. 2014, 27, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axtell, M.J.; Snyder, J.A.; Bartel, D.P. Common functions for diverse small RNAs of land plants. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1750–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. A microRNA as a translational repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis flower development. Science 2004, 303, 2022–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unver, T.; Parmaksız, I.; Dündar, E. Identification of conserved micro-RNAs and their target transcripts in opium poppy (Papaver somniferum L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2010, 29, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, T.P.; Xie, F.; Freistaedter, A.; Burklew, C.E.; Zhang, B. Identification and characterization of microRNAs and their target genes in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Planta 2010, 232, 1289–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-H.; Qi, X.-H.; Zhang, M.-F.; Yu, J.-Q. MADS-box genes are associated with cytoplasmic homeosis in cytoplasmic male-sterile stem mustard as partially mimicked by specifically inhibiting mtETC. Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 56, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, D.E.; Kim, W.-Y.; Geng, R. The F-box protein ZEITLUPE confers dosage-dependent control on the circadian clock, photomorphogenesis, and flowering time. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, Y. Comparative expression profiling of miRNAs between the cytoplasmic male sterile line MeixiangA and its maintainer line MeixiangB during rice anther development. Planta 2015, 241, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Category | MF | CMS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unique | Percent | Redundant | Percent (%) | Unique | Percent | Redundant | Percent (%) | |
| exon_antisense | 89,744 | 2.84% | 127,721 | 2.48% | 84,956 | 2.60% | 124,397 | 2.33% |
| exon_sense | 101,550 | 3.21% | 136,054 | 2.64% | 97,802 | 2.99% | 139,259 | 2.61% |
| intron_antisense | 33,720 | 1.07% | 40,735 | 0.79% | 30,272 | 0.93% | 38,399 | 0.72% |
| intron_sense | 31,781 | 1.00% | 46,920 | 0.91% | 28,267 | 0.86% | 45,752 | 0.86% |
| rRNA | 75,067 | 2.37% | 385,277 | 7.47% | 63,993 | 1.96% | 389,106 | 7.29% |
| snRNA | 820 | 0.03% | 3769 | 0.07% | 817 | 0.02% | 3792 | 0.07% |
| snoRNA | 713 | 0.02% | 3576 | 0.07% | 689 | 0.02% | 3168 | 0.06% |
| tRNA | 5768 | 0.18% | 169,111 | 3.28% | 4612 | 0.14% | 225,707 | 4.23% |
| miRNA | 273 | 0.01% | 8984 | 0.17% | 303 | 0.01% | 9426 | 0.18% |
| Others | 2,825,652 | 89.27% | 4,235,933 | 82.12% | 2,957,566 | 90.47% | 4,359,798 | 81.66% |
| Total | 3,165,088 | 100.00% | 5,158,080 | 100.00% | 3,269,277 | 100.00% | 5,338,804 | 100.00% |
| miRNA | Accession No. | miRNA-Seq | Count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF | CMS | |||
| bol-miR157a | MIMAT0010169 | TTGACAGAAGATAGAGAGCAC | 1730 | 868 |
| bol-miR171a | MIMAT0010170 | TTGAGCCGTGCCAATATCACG | 152 | 256 |
| bol-miR172a | MIMAT0010171 | AGAATCTTGATGATGCTGCAT | 698 | 1100 |
| bol-miR172b | MIMAT0010172 | AGAATCTTGATGATGCTGCAT | 59 | 87 |
| bol-miR398a-3p | MIMAT0010174 | TGTGTTCTCAGGTCACCCCTT | 21 | 40 |
| bol-miR398a-5p | MIMAT0010173 | GGAGTGTCATGAGAACACGGA | 23 | 35 |
| bol-miR824 | MIMAT0005597 | TAGACCATTTGTGAGAAGGGA | 3124 | 2908 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sajad, S.; Dai, Q.; Yang, J.; Song, J. Identification of miRNAs Involved in Male Fertility and Pollen Development in Brassica oleracea var. capitata L. by High-Throughput Sequencing. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040515
Sajad S, Dai Q, Yang J, Song J. Identification of miRNAs Involved in Male Fertility and Pollen Development in Brassica oleracea var. capitata L. by High-Throughput Sequencing. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(4):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040515
Chicago/Turabian StyleSajad, Shoukat, Qian Dai, Jing Yang, and Jianghua Song. 2023. "Identification of miRNAs Involved in Male Fertility and Pollen Development in Brassica oleracea var. capitata L. by High-Throughput Sequencing" Horticulturae 9, no. 4: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040515
APA StyleSajad, S., Dai, Q., Yang, J., & Song, J. (2023). Identification of miRNAs Involved in Male Fertility and Pollen Development in Brassica oleracea var. capitata L. by High-Throughput Sequencing. Horticulturae, 9(4), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040515






