Identification of Heat-Resistant Varieties of Non-Headed Chinese Cabbage and Discovery of Heat-Resistant Physiological Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Heat Treatment
2.2. Measurement of Morphological and Physiological Index
2.3. Determination of Gas Exchange Parameters
2.4. Measurement of Electron Transport Rate, Quantum Yield and PQ Pools
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
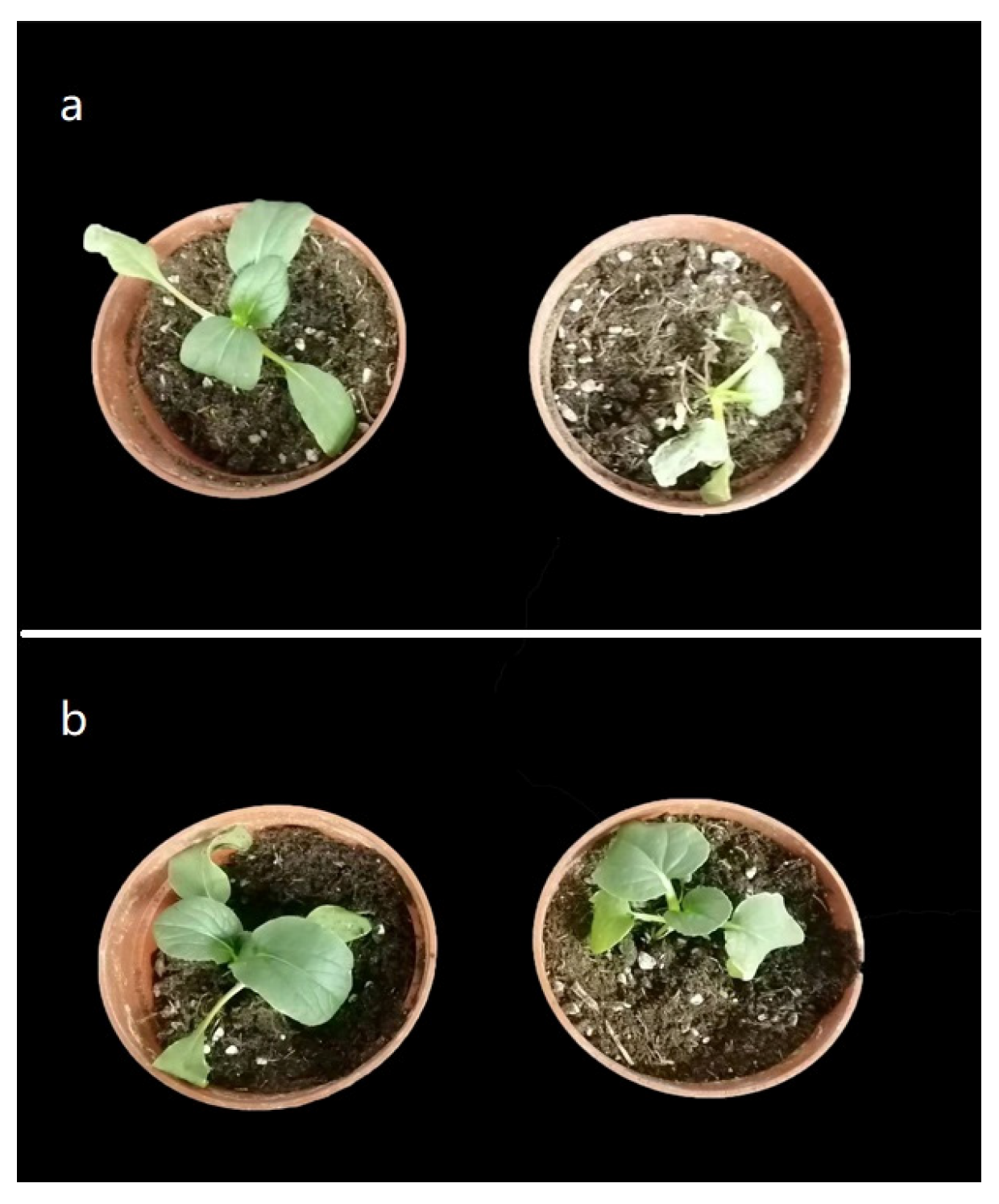
3.1. Agronomic Traits and Heat Damage Indicators of Brassica rapa under Heat Stress
3.2. Plant Growth Attributes of Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage under Heat Stress
3.3. The Chlorophyll Content, Soluble Sugar and Soluble Protein and the MDA of Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage under Heat Stress
3.4. Gas-Exchange Parameters of Different B. rapa Cultivars under Heat Stress
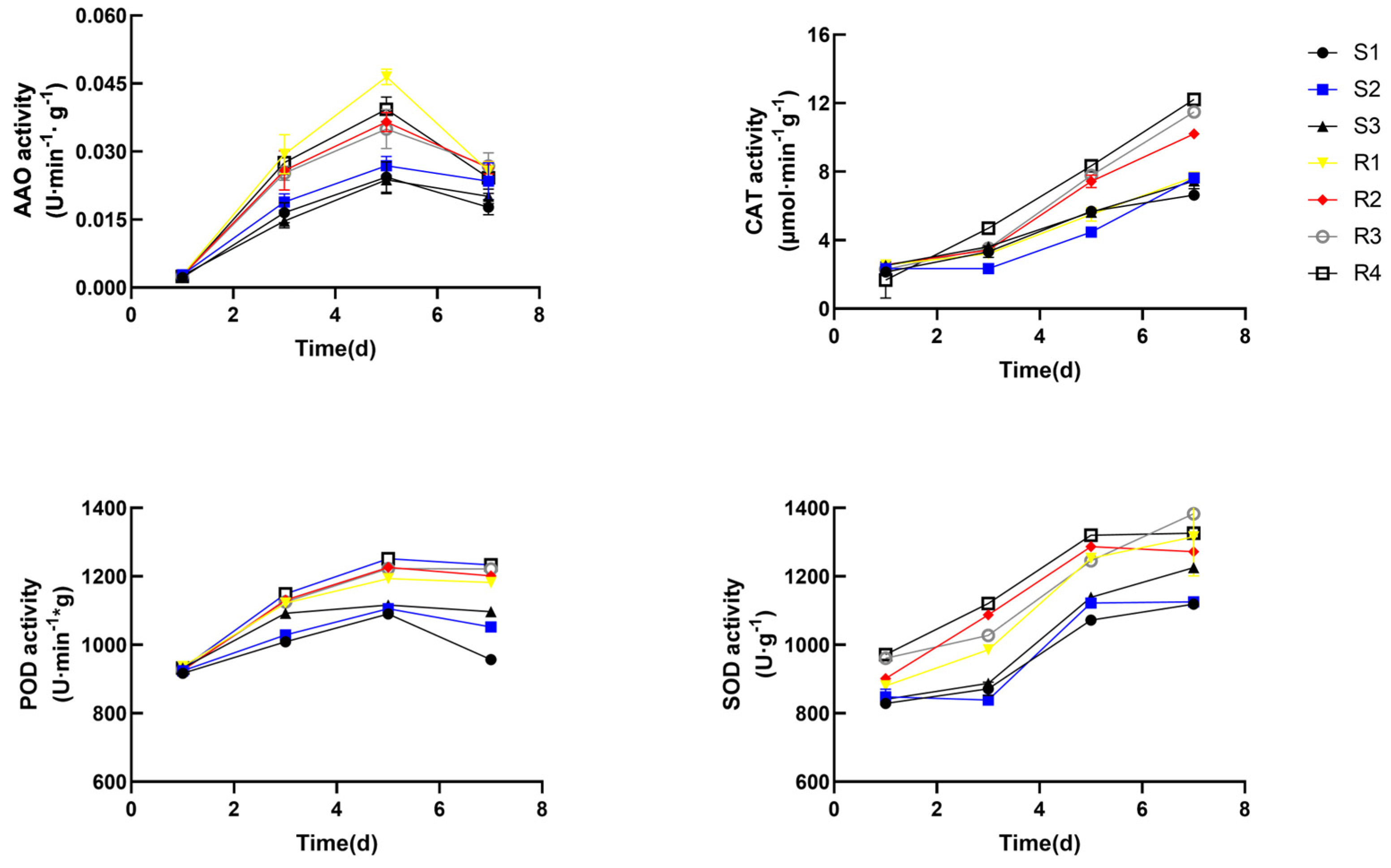
3.5. Biochemical Analysis of Enzymatic Activities and Hydroxyl Scavenging Capacity
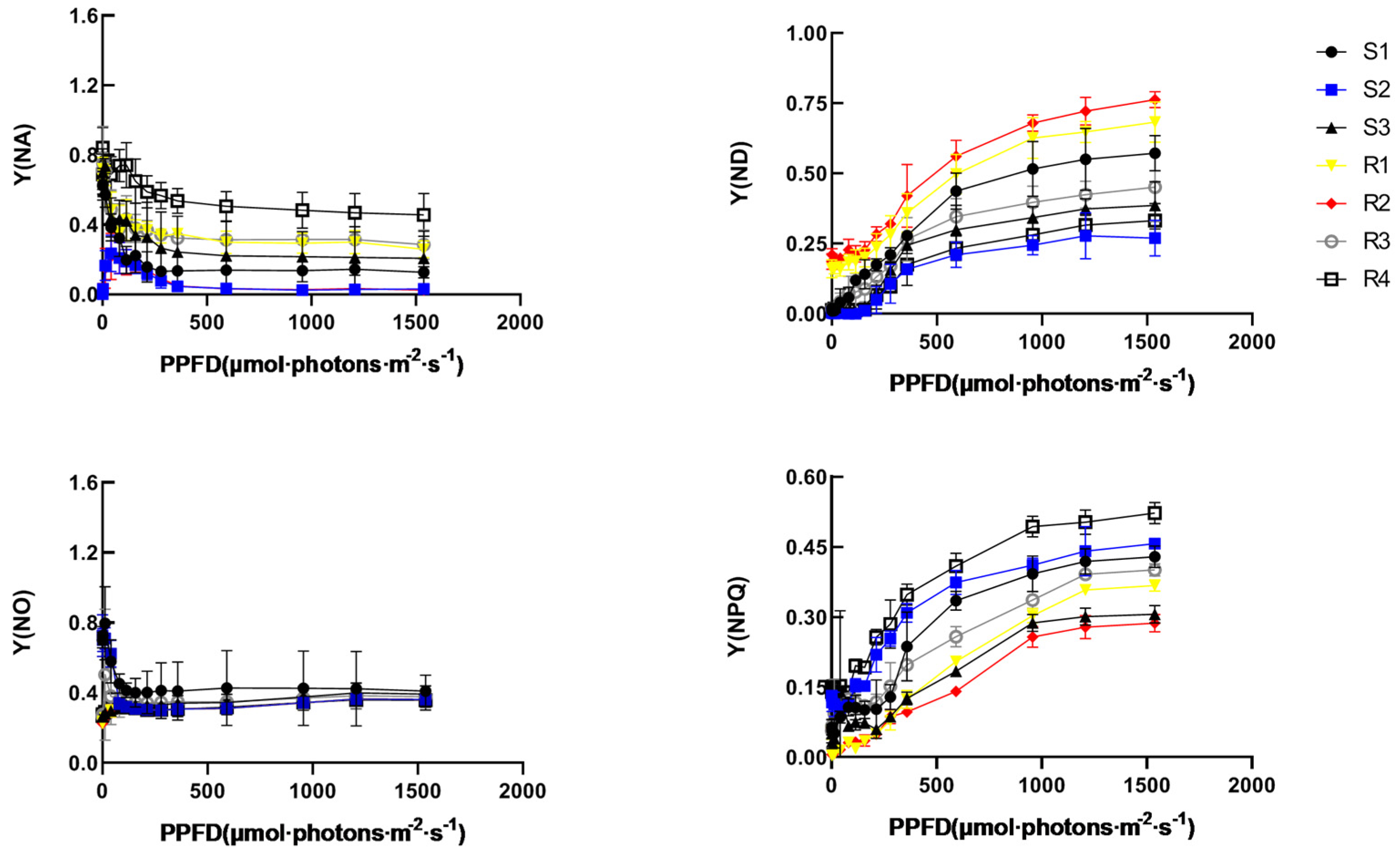
3.6. The PSII and PSI Activity of Brassica rapa Leaves under Heat Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, S. Gene co-expression network analysis reveals key pathways and hub genes in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L.) during vernalization. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Yu, S.; Zhang, F.; Shen, X.; Zhao, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, D. Reference gene selection for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction of mRNA transcript levels in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 28, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Chen, Z.; Marquis, M.; Averyt, K.B.; Tignor, M.; Miller, H.L. Summary for policymakers. Clim. Chang. 2007, 85, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Skalicky, M.; Brestic, M.; Maitra, S.; Ashraful Alam, M.; Syed, M.A.; Hossain, J.; Sarkar, S.; Saha, S.; Bhadra, P.; et al. Consequences and Mitigation Strategies of Abiotic Stresses in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under the Changing Climate. Agronomy 2021, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, A.L.; Ding, Y.F.; Jiang, Q.; Zhu, C. Molecular mechanisms of the plant heat stress response. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 432, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Li, G.; Dai, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Sun, R.; Zhang, S. Gene co-expression network analysis of the heat-responsive core transcriptome identifies hub genes in Brassica rapa. Planta 2021, 253, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Kim, E.D.; Ha, M.; Lackey, E.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Z.J. Altered circadian rhythms regulate growth vigour in hybrids and allopolyploids. Nature 2009, 457, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Rehman, A.; Li, P.; Chang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Q. Physiological and transcriptomic analysis reveals the responses and difference to high temperature and humidity stress in two melon genotypes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jia, A.; Ning, T.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, G. Potassium nitrate application alleviates sodium chloride stress in winter wheat cultivars differing in salt tolerance. J. Plant Physiol. 2008, 165, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Leul, M. Uniconazole-induced tolerance of rape plants to heat stress in relation to changes in hormonal levels, enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation. Plant Growth Regul. 1999, 27, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Ni, Y.; Meng, Z.; Lu, T.; Li, T. Exogenous calcium alleviates low night temperature stress on the photosynthetic apparatus of tomato leaves. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanelt, D. Photosynthesis assessed by chlorophyll fluorescence. In Bioassays; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 169–198. [Google Scholar]
- Asada, K.; Heber, U.; Schreiber, U. Pool size of electrons that can be donated to P700+ as determined in intact leaves: Donation to P700+ from stromal components via the intersystem chain. Plant Cell Physiol. 1992, 33, 927–932. [Google Scholar]
- Savitch, L.V.; Ivanov, A.G.; Gudynaite-Savitch, L.; Huner, N.P.; Simmonds, J. Cold stress effects on PSI photochemistry in Zea mays: Differential increase of FQR-dependent cyclic electron flow and functional implications. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Waraich, E.A.; Skalicky, M.; Hussain, S.; Zulfiqar, U.; Anjum, M.Z.; Habib ur Rahman, M.; Brestic, M.; Ratnasekera, D.; Lamilla-Tamayo, L.; et al. Adaptation strategies to improve the resistance of oilseed crops to heat stress under a changing climate: An overview. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 767150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Nahar, K.; Alam, M.M.; Roychowdhury, R.; Fujita, M. Physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms of heat stress tolerance in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9643–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, F.; Yusuf, M.; Faizan, M.; Faraz, A.; Hayat, S. Role of sugars under abiotic stress. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2016, 109, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, S.; Liu, S.; Ge, J.; Wang, C. Effects of heat stress on photosynthetic characteristics and chloroplast ultrastructure of a heat-sensitive and heat-tolerant cultivar of wucai (Brassica campestris L.). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ali, M.M.; Li, B.; Fang, T.; Chen, F. Transcriptome data-based identification of candidate genes involved in metabolism and accumulation of soluble sugars during fruit development in ‘Huangguan’ plum. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locato, V.; De Pinto, M.C.; De Gara, L. Different involvement of the mitochondrial, plastidial and cytosolic ascorbate–glutathione redox enzymes in heat shock responses. Physiol. Plant. 2009, 135, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Ali, B.; Wang, J.; Farooq, M.A.; Gill, R.A.; Ali, S.; Zhou, W. Combined herbicide and saline stress diferentially modulates hormonal regulation and antioxidant defense system in Oryza sativa cultivars. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 107, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Ali, S.; Abid, M.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, B.; Tanveer, A.; Ahmad, I.; Azam, M.; Ghani, M.A. Glycinebetaine alleviates the chromium toxicity in Brassica oleracea L. by suppressing oxidative stress and modulating the plant morphology and photosynthetic attributes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Song, S.; Wen, Y.; Zou, Y.; Liu, H. Toxicity of Cu (II) to the green alga Chlorella vulgaris: A perspective of photosynthesis and oxidant stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17910–17918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Banerjee, A.; Roychoudhury, A. Melatonin application differentially modulates the enzymes associated with antioxidative machinery and ascorbate-glutathione cycle during arsenate exposure in indica rice varieties. Plant Biol. 2021, 23, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.F.; Xu, T.F.; Wang, Z.Z.; Fang, Y.L.; Xi, Z.M.; Zhang, Z.W. The ameliorative effects of exogenous melatonin on grape cuttings under water-deficient stress: Antioxidant metabolites, leaf anatomy, and chloroplast morphology. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, A.; Close, T.J. Expression of dehydrins under heat stress and their relationship with water relations of sugarcane leaves. Biol. Plant. 2007, 51, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.X.; Liang, X.Q.; Min, L.; Lu, J.X.; Li, X.N.; Li, J.B. Study on preparation of xylan from high-temperature boliled pretreated sugarcane leaves. Food Ferment. Indus. 2012, 38, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Almeselmani, M.; Deshmukh, P.S.; Chinnusamy, V. Effects of prolonged high temperature stress on respiration, photosynthesis and gene expression in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varies differing in their thermotolerance. Plant Stress 2012, 6, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.L.; Chen, J.H.; He, N.Y.; Guo, F.Q. Metabolic reprogramming in chloroplasts under heat stress in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Prado, C.; Podazza, G.; Interdonato, R.; González, J.A.; Hilal, M.; Prado, F.E. Soluble sugars: Metabolism, sensing and abiotic stress: A complex network in the life of plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Liu, A.; Hua, X. Proline accumulation and transcriptional regulation of proline biothesynthesis and degradation in Brassica napus. BMB Rep. 2009, 42, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; He, M.; Zhi, Y.; Chang, S.X.; Gu, B.; Liu, X.; Xu, J. An integrated analysis on source-exposure risk of heavy metals in agricultural soils near intense electronic waste recycling activities. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Singh, A.; Banerjee, A.; Roychoudhury, A. Exogenous supplementation of melatonin alters representative organic acids and enzymes of respiratory cycle as well as sugar metabolism during arsenic stress in two contrasting indica rice cultivars. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 324, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Esawi, M.A.; Alayafi, A.A. Overexpression of Rice Rab7 gene improves drought and heat tolerance and increases Grain Yield in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genes 2019, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouil, R.; Wientjes, E.; Bultema, J.B.; Croce, R.; Boekema, E.J. High-light vs. low-light: Effect of light acclimation on photosystem II composition and organization in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1827, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamori, W. Photosynthetic response to fluctuating environments and photoprotective strategies under abiotic stress. J. Plant Res. 2016, 129, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

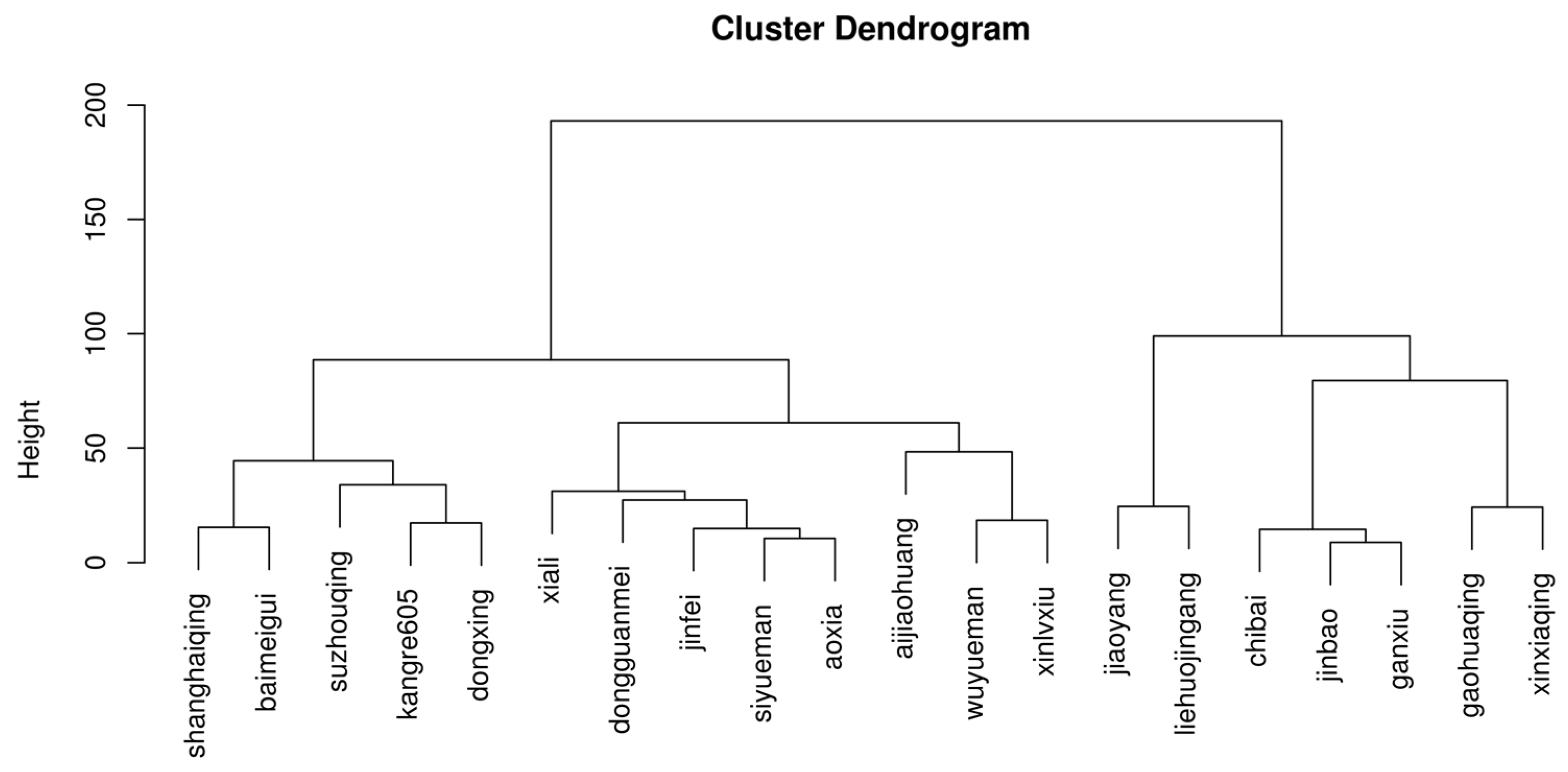


| Variety Name | Type of Heat Tolerance | Heat Damage Index | Fresh Weight | Dry Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| shanghaiqing | HS | 51.90 | 3.77 ± 0.15 bcd | 0.47 ± 0.03 b |
| wuyueman | HS | 58.67 | 4.16 ± 0.06 bcd | 0.31 ± 0.02 bcde |
| aijiaohuang | HS | 55.38 | 3.74 ± 0.09 bcd | 0.37 ± 0.02 bcde |
| baimeigui | HS | 44.75 | 4.60 ± 0.07 bc | 0.46 ± 0.03 b |
| dongguanmei | HS | 49.52 | 3.77 ± 0.22 bcd | 0.37 ± 0.02 bcde |
| gaohuaqing | HR | 37.8 | 5.12 ± 0.16 a | 0.51 ± 0.03 a |
| jiaoyang | HR | 38.00 | 4.91 ± 0.34 b | 0.47 ± 0.01 b |
| xinxiaqing | HR | 36.75 | 4.96 ± 0.16 b | 0.48 ± 0.04 b |
| Kangre605 | HR | 41.60 | 4.83 ± 0.09 b | 0.55 ± 0.03 a |
| jinfei | HS | 48.00 | 3.73 ± 0.22 bcd | 0.45 ± 0.03 b |
| liehuojingang | HR | 37.90 | 5.36 ± 0.11 a | 0.54 ± 0.03 a |
| dongxing | HS | 46.09 | 3.57 ± 0.20 bcd | 0.37 ± 0.02 bcde |
| suzhouqing | HS | 47.57 | 4.16 ± 0.53 bcd | 0.35 ± 0.02 bcde |
| jinbao | HR | 41.9 | 4.16 ± 0.14 bcd | 0.43 ± 0.03 bc |
| chibai | HS | 45.71 | 4.23 ± 0.31 bcd | 0.42 ± 0.04 bc |
| siyueman | HS | 58.00 | 3.66 ± 0.20 bcd | 0.35 ± 0.04 bcde |
| xinlvxiu | HS | 55.33 | 3.48 ± 0.20 bcd | 0.33 ± 0.11 bcde |
| xiali | HS | 46.67 | 4.30 ± 0.24 bcd | 0.34 ± 0.05 bcde |
| aoxia | HR | 41.90 | 4.22 ± 0.14 bcd | 0.44 ± 0.04 bc |
| hanxiu | HS | 50.76 | 3.91 ± 0.21 bcd | 0.32 ± 0.03 bcde |
| Variety Name | Plant Height | Plant Width | Leaf Area | Fv/Fm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| shanghaiqing | 18.12 ± 1.47 a | 24.77 ± 0.61 bcd | 54.82 ± 0.63 bcde | 0.56 ± 0.03 b |
| wuyueman | 19.46 ± 1.52 bc | 21.37 ± 0.14 bcd | 43.23 ± 0.63 bcde | 0.40 ± 0.01 bc |
| aijiaohuang | 18.16 ± 0.27 a | 25.522 ± 0.29 bcd | 44.70 ± 0.59 bcde | 0.37 ± 0.00 bcd |
| baimeigui | 19.63 ± 0.30 b | 26.44 ± 0.34 bcd | 64.68 ± 1.60 a | 0.46 ± 0.01 bc |
| dongguanmei | 21.11 ± 0.53 bc | 23.94 ± 0.40 bcd | 75.35 ± 1.22 b | 0.46 ± 0.01 b |
| gaohuaqing | 23.87 ± 0.74 b | 30.85 ± 0.47 bcd | 82.74 ± 0.49 a | 0.65 ± 0.01 b |
| jiaoyang | 22.72 ± 0.40 b | 33.477 ± 0.34 a | 84.52 ± 0.07 a | 0.73 ± 0.00 b |
| xinxiaqing | 25.39 ± 0.68 bc | 23.39 ± 0.24 bcd | 85.13 ± 0.27 a | 0.78 ± 0.01 a |
| Kangre605 | 22.51 ± 0.66 a | 25.02 ± 0.42 bcd | 75.21 ± 0.42 bc | 0.53 ± 0.24 bc |
| jinfei | 18.21 ± 1.33 a | 32.95 ± 0.78 a | 72.73 ± 0.31 bc | 0.46 ± 0.01 bc |
| liehuojingang | 21.38 ± 0.38 a | 32.36 ± 0.41 a | 78.22 ± 1.09 bc | 0.75 ± 0.01 a |
| dongxing | 22.97 ± 0.62 b | 27.28 ± 0.45 bcd | 66.14 ± 2.38 bcde | 0.72 ± 0.01 a |
| suzhouqing | 20.65 ± 0.13 a | 24.91 ± 0.67 bcd | 52.88 ± 0.61 bcde | 0.62 ± 0.00 b |
| jinbao | 18.86 ± 0.83 bc | 24.10 ± 0.57 bcd | 46.80 ± 1.16 bcde | 0.50 ± 0.01 b |
| chibai | 18.98 ± 0.29 bc | 22.54 ± 0.59 bcd | 49.20 ± 0.94 bcde | 0.33 ± 0.24 bc |
| siyueman | 21.62 ± 0.81 a | 28.68 ± 0.45 bcd | 77.20 ± 0.19 bcd | 0.35 ± 0.00 bcd |
| xinlvxiu | 16.11 ± 0.67 bc | 25.30 ± 0.31 bcd | 44.79 ± 0.59 bcde | 0.36 ± 0.00 bcd |
| xiali | 19.05 ± 1.38 bc | 26.09 ± 0.39 bcd | 74.39 ± 1.30 bc | 0.54 ± 0.00 b |
| aoxia | 20.15 ± 0.54 bc | 31.18 ± 0.74 bcd | 74.37 ± 1.43 bc | 0.48 ± 0.00 bc |
| hanxiu | 20.16 ± 0.80 bc | 24.11 ± 0.15 bcd | 53.05 ± 0.53 bcde | 0.46 ± 0.01 bc |
| Variety Name | Root Shoot Ratio | Root Activity | Soluble Sugar | Soluble Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| shanghaiqing | 0.044 ± 0.001 a | 33.30 ± 1.18 bcd | 2.81 ± 0.07 bc | 4.39 ± 0.05 bc |
| wuyueman | 0.038 ± 0.001 b | 38.62 ± 2.14 bcd | 2.41 ± 0.09 bc | 3.34 ± 0.02 c |
| aijiaohuang | 0.039 ± 0.001 b | 43.56 ± 0.77 bcd | 2.17 ± 0.09 bc | 3.19 ± 0.10 c |
| baimeigui | 0.039 ± 0.003 b | 41.38 ± 0.26 bcd | 2.60 ± 0.09 bc | 3.81 ± 0.04 c |
| dongguanmei | 0.040 ± 0.002 b | 51.04 ± 0.60 a | 3.35 ± 0.30 bc | 3.68 ± 0.05 c |
| gaohuaqing | 0.045 ± 0.001 a | 43.59 ± 2.50 bcd | 5.90 ± 0.11 bc | 5.80 ± 0.06 b |
| jiaoyang | 0.046 ± 0.001 a | 34.09 ± 1.15 bcd | 6.68 ± 0.22 a | 5.62 ± 0.05 b |
| xinxiaqing | 0.047 ± 0.000 a | 53.68 ± 2.94 a | 6.49 ± 0.32 b | 6.08 ± 0.09 a |
| Kangre605 | 0.042 ± 0.005 b | 36.99 ± 2.82 bcd | 5.11 ± 0.02 bc | 4.95 ± 0.05 b |
| jinfei | 0.043 ± 0.001 b | 40.80 ± 1.99 bcd | 4.67 ± 0.07 bc | 4.71 ± 0.07 b |
| liehuojingang | 0.044 ± 0.001 b | 51.34 ± 0.84 a | 6.82 ± 0.30 a | 6.31 ± 0.03 a |
| dongxing | 0.043 ± 0.001 b | 48.07 ± 2.76 b | 5.70 ± 0.16 b | 6.01 ± 0.05 a |
| suzhouqing | 0.043 ± 0.003 b | 33.17 ± 1.26 bcd | 3.27 ± 0.13 bc | 3.81 ± 0.09 c |
| jinbao | 0.043 ± 0.001 b | 32.86 ± 0.77 bcd | 3.76 ± 0.13 bc | 3.54 ± 0.04 c |
| chibai | 0.043 ± 0.001 b | 41.26 ± 1.88 bcd | 3.47 ± 0.29 cc | 3.35 ± 0.06 c |
| siyueman | 0.044 ± 0.001 b | 44.84 ± 3.56 bc | 1.80 ± 0.18 c | 3.27 ± 0.09 c |
| xinlvxiu | 0.036 ± 0.005 c | 37.33 ± 5.33 bcd | 1.98 ± 0.08 c | 3.07 ± 0.04 c |
| xiali | 0.041 ± 0.002 b | 50.71 ± 0.31 a | 4.50 ± 0.08 bc | 3.47 ± 0.09 c |
| aoxia | 0.041 ± 0.001 b | 46.90 ± 0.79 bc | 3.89 ± 0.06 bc | 3.30 ± 0.09 c |
| hanxiu | 0.041 ± 0.001 b | 43.53 ± 1.04 bcd | 3.42 ± 0.18 bc | 3.90 ± 0.02 c |
| Correlation | Fresh Weight | Dry Weight | Fv/ Fm | MDA | Ascorbic Acid | Chlb | Tr | Root Activity | Root Shoot Ratio | Heat Damage Index | Leaf Area | Plant Height | Plant Width | Ci | Gs | Pn | Chla | SS | VC | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fresh weight | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| dry weight | 0.730 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Fv/ Fm | 0.611 ** | 0.51 0 * | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| MDA | −0.580 ** | −0.4 85 * | −0.5 76 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| ascorbic acid | 0.813 ** | 0.65 0 ** | 0.5 99 ** | −0.6 57 ** | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| chlb | 0.711 ** | 0.567 ** | 0.6 38 ** | −0.73 5 ** | 0.8 26 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Tr | 0.734 ** | 0.580 ** | 0.693 ** | −0.77 8 ** | 0.6 75 ** | 0.6 22 ** | 1 | |||||||||||||
| root activity | 0.595 ** | 0.680 ** | 0.531 * | −0.84 1 ** | 0.7 41 ** | 0.7 35 ** | 0.6 95 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||
| root shoot ratio | 0.489 * | 0.5 59 * | 0.682 ** | −0.39 | 0.60 3 ** | 0.71 9 ** | 0.4 02 | 0.5 36 * | 1 | |||||||||||
| heat damage index | −0.799 ** | −0.7 66 ** | −0.7 35 ** | 0.6 28 ** | −0.85 9 ** | −0.7 97 ** | −0.6 79 ** | −0.68 4 ** | −0.63 1 ** | 1 | ||||||||||
| leaf area | 0.550 * | 0.552 * | 0.5 83 ** | −0.6 93 ** | 0.67 8 ** | 0.7 04 ** | 0.5 50 * | 0.76 3 ** | 0.60 6 ** | −0.61 9 ** | 1 | |||||||||
| Plant hight | 0.594 ** | 0.425 | 0.7 08 ** | −0.6 07 ** | 0.66 5 ** | 0.6 96 ** | 0.5 95 ** | 0.67 8 ** | 0.68 3 ** | −0.60 4 ** | 0.72 7 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| plant width | 0.305 | 0.449 * | 0.3 67 | −0.5 14 * | 0.3 | 0.4 91 * | 0.3 71 | 0.50 5 * | 0.3 74 | −0.4 14 | 0.62 1 ** | 0.2 06 | 1 | |||||||
| Ci | 0.611 ** | 0.586 ** | 0.6 81 ** | −0.4 02 | 0.67 7 ** | 0.6 76 ** | 0.6 41 ** | 0.45 0 * | 0.62 3 ** | −0.67 3 ** | 0.4 02 | 0.44 6 * | 0.4 23 | 1 | ||||||
| Gs | 0.679 ** | 0.446 * | 0.5 94 ** | −0.4 88 * | 0.69 6 ** | 0.7 10 ** | 0.6 07 ** | 0.50 7 * | 0.62 8 ** | −0.68 2 ** | 0.2 87 | 0.55 4 * | 0.1 57 | 0.58 2 ** | 1 | |||||
| Pn | 0.713 ** | 0.594 ** | 0.8 37 ** | −0.6 74 ** | 0.82 5 ** | 0.8 00 ** | 0.7 20 ** | 0.64 1 ** | 0.63 2 ** | −0.84 3 ** | 0.63 2 ** | 0.68 4 ** | 0.3 95 | 0.70 5 ** | 0.75 7 ** | 1 | ||||
| Chla | 0.765 ** | 0.684 ** | 0.7 72 ** | −0.7 26 ** | 0.86 5 ** | 0.8 29 ** | 0.7 50 ** | 0.79 1 ** | 0.61 9 ** | −0.83 6 ** | 0.67 6 ** | 0.68 4 ** | 0.47 2 * | 0.73 7 ** | 0.72 0 ** | 0.93 1 ** | 1 | |||
| SS | 0.708 ** | 0.641 ** | 0.8 64 ** | −0.6 65 ** | 0.77 3 ** | 0.8 15 ** | 0.6 75 ** | 0.68 1 ** | 0.68 9 ** | −0.85 5 ** | 0.69 7 ** | 0.69 8 ** | 0.49 8 * | 0.65 9 ** | 0.67 3 ** | 0.92 4 ** | 0.92 6 ** | 1 | ||
| VC | 0.8 13 ** | 0.6 50 ** | 0.5 99 ** | −0.6 57 ** | 10.0 00 ** | 0.8 26 ** | 0.6 75 ** | 0.74 1 ** | 0.60 3 ** | −0.85 9 ** | 0.67 8 ** | 0.66 5 ** | 0.3 | 0.67 7 ** | 0.69 6 ** | 0.82 5 ** | 0.86 5 ** | 0.77 3 ** | 1 | |
| SP | 0.6 10 ** | 0.6 56 ** | 0.8 85 ** | −0.6 22 ** | 0.57 7 ** | 0.6 84 ** | 0.7 07 ** | 0.67 9 ** | 0.69 1 ** | −0.69 5 ** | 0.63 1 ** | 0.73 0 ** | 0.45 2 * | 0.64 5 ** | 0.61 9 ** | 0.83 5 ** | 0.84 7 ** | 0.89 6 ** | 0.57 7 ** | 1 |
| Variety Name | MDA | Chlb | Chla | Ascorbic Acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| shanghaiqing | 5.50 ± 0.07 a | 0.18 ± 0.00 bcd | 0.49 ± 0.02 bcde | 0.22 ± 0.01 bcde |
| wuyueman | 5.49 ± 0.04 a | 0.17 ± 0.08 bcd | 0.46 ± 0.02 bcde | 0.20 ± 0.00 bcde |
| aijiaohuang | 5.73 ± 0.14 a | 0.19 ± 0.01 bcd | 0.42 ± 0.01 bcde | 0.19 ± 0.00 bcde |
| baimeigui | 4.49 ± 0.06 b | 0.24 ± 0.01 bc | 0.53 ± 0.01 bcde | 0.25 ± 0.01 bcde |
| dongguanmei | 4.62 ± 0.05 b | 0.26 ± 0.01 b | 0.62 ± 0.01 bcde | 0.31 ± 0.00 bc |
| gaohuaqing | 2.85 ± 0.33 bcd | 0.37 ± 0.01 a | 0.82 ± 0.01 bc | 0.34 ± 0.01 b |
| jiaoyang | 2.98 ± 0.09 bcd | 0.39 ± 0.01 a | 0.87 ± 0.01 b | 0.37 ± 0.00 a |
| xinxiaqing | 3.62 ± 0.05 bc | 0.36 ± 0.00 a | 0.83 ± 0.01 bc | 0.36 ± 0.00 bc |
| Kangre605 | 3.51 ± 0.00 bc | 0.32 ± 0.01 a | 0.72 ± 0.01 bcd | 0.34 ± 0.00 bc |
| jinfei | 5.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.28 ± 0.00 bc | 0.55 ± 0.01 bc | 0.21 ± 0.02 bcde |
| liehuojingang | 3.36 ± 2.89 bc | 0.38 ± 0.10 a | 1.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.38 ± 0.00 a |
| dongxing | 3.84 ± 0.33 bc | 0.29 ± 0.00 bc | 0.76 ± 0.02 bcd | 0.24 ± 0.00 bcde |
| suzhouqing | 4.87 ± 0.14 b | 0.31 ± 0.01 b | 0.46 ± 0.01 bcde | 0.24 ± 0.01 bcde |
| jinbao | 4.64 ± 0.05 b | 0.25 ± 0.01 bc | 0.60 ± 0.02 bcde | 0.30 ± 0.00 bc |
| chibai | 5.07 ± 0.05 b | 0.34 ± 0.01 b | 0.65 ± 0.02 bcde | 0.31 ± 0.00 bc |
| siyueman | 4.05 ± 0.06 bc | 0.28 ± 0.01 bc | 0.47 ± 0.01 bcde | 0.24 ± 0.00 bcde |
| xinlvxiu | 3.50 ± 0.01 bc | 0.22 ± 0.01 bc | 0.46 ± 0.02 bcde | 0.20 ± 0.00 bcde |
| xiali | 4.30 ± 0.07 bc | 0.28 ± 0.01 bc | 0.59 ± 0.00 bcde | 0.29 ± 0.00 bcde |
| aoxia | 4.32 ± 0.10 bc | 0.27 ± 0.01 bc | 0.63 ± 0.01 bcde | 0.31 ± 0.00 bc |
| hanxiu | 5.14 ± 0.11 a | 0.25 ± 0.01 bc | 0.55 ± 0.02 bcde | 0.27 ± 0.01 bcde |
| Variety Name | Pn | Tr | Gs | Ci |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| shanghaiqing | 11.57 ± 4.02 bc | 2.72 ± 0.06 b | 254.85 ± 1.51 bcde | 374.67 ± 1.75 bc |
| wuyueman | 9.94 ± 0.53 bc | 2.57 ± 0.07 b | 241.00 ± 3.26 bcde | 308.14 ± 1.45 bcde |
| aijiaohuang | 10.44 ± 0.40 bc | 2.79 ± 0.077 b | 281.04 ± 6.86 bcde | 334.81 ± 2.08 bcde |
| baimeigui | 11.33 ± 0.27 bc | 3.76 ± 0.06 b | 245.27 ± 4.01 bcde | 369.811 ± 0.87 bcd |
| dongguanmei | 13.42 ± 0.42 bc | 2.91 ± 0.01 bc | 249.82 ± 3.71 bcde | 357.97 ± 1.58 bcde |
| gaohuaqing | 16.93 ± 0.78 b | 3.68 ± 0.08 bc | 395.21 ± 3.99 a | 365.38 ± 0.73 bcde |
| jiaoyang | 15.36 ± 0.43 b | 4.15 ± 0.04 bcd | 344.28 ± 3.01 bcde | 439.41 ± 0.43 bc |
| xinxiaqing | 16.12 ± 0.62 b | 3.96 ± 0.11 bc | 372.86 ± 2.82 b | 361.53 ± 1.01 bcde |
| Kangre605 | 14.61 ± 0.17 b | 3.74 ± 5.60 a | 270.18 ± 3.52 bcde | 369.81 ± 0.87 bcd |
| jinfei | 12.15 ± 0.53 bc | 2.62 ± 0.10 bc | 237.26 ± 5.94 bcde | 336.09 ± 2.22 bcde |
| liehuojingang | 18.76 ± 030 ac | 4.35 ± 0.03 bc | 365.24 ± 4.79 bc | 449.77 ± 5.15 a |
| dongxing | 15.60 ± 0.26 b | 3.32 ± 0.13 bc | 281.91 ± 5.27 bcde | 376.78 ± 1.50 b |
| suzhouqing | 12.750 ± 0.25 bc | 2.91 ± 0.03 bc | 284.66 ± 3.86 bcde | 384.44 ± 1.60 b |
| jinbao | 13.87 ± 0.29 bc | 3.37 ± 0.05 b | 328.47 ± 4.84 bcde | 368.29 ± 3.561 bcd |
| chibai | 12.504 ± 0.40 bc | 2.46 ± 0.02 bc | 331.84 ± 5.98 bcd | 375.511 ± 1.65 bc |
| siyueman | 10.47 ± 0.39 bc | 3.05 ± 0.03 b | 246.4 ± 3.52 bcde | 338.16 ± 1.98 bcde |
| xinlvxiu | 10.57 ± 0.31 b | 3.25 ± 0.01 b | 254.99 ± 3.94 bcde | 306.54 ± 2.08 bcde |
| xiali | 14.28 ± 0.24 bc | 3.03 ± 0.03 b | 266.68 ± 4.16 bcde | 337.47 ± 4.38 bcde |
| aoxia | 12.75 ± 0.25 bc | 2.76 ± 0.02 bc | 244.54 ± 3.59 bcde | 346.96 ± 2.65 bcde |
| hanxiu | 13.51 ± 0.28 bc | 3.29 ± 0.17 b | 323.42 ± 3.67 bcde | 365.45 ± 2.99 bcde |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Li, P.; Tu, S.; Feng, N.; Chang, L.; Niu, Q. Identification of Heat-Resistant Varieties of Non-Headed Chinese Cabbage and Discovery of Heat-Resistant Physiological Mechanisms. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060619
Yu J, Li P, Tu S, Feng N, Chang L, Niu Q. Identification of Heat-Resistant Varieties of Non-Headed Chinese Cabbage and Discovery of Heat-Resistant Physiological Mechanisms. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(6):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060619
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jing, Pengli Li, Song Tu, Ningxiao Feng, Liying Chang, and Qingliang Niu. 2023. "Identification of Heat-Resistant Varieties of Non-Headed Chinese Cabbage and Discovery of Heat-Resistant Physiological Mechanisms" Horticulturae 9, no. 6: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060619
APA StyleYu, J., Li, P., Tu, S., Feng, N., Chang, L., & Niu, Q. (2023). Identification of Heat-Resistant Varieties of Non-Headed Chinese Cabbage and Discovery of Heat-Resistant Physiological Mechanisms. Horticulturae, 9(6), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060619





