Characterization of New Grapevine Varieties Cross-Bred from Monastrell, Authorized for Winemaking in the Warm Region of Murcia (South-Eastern Spain)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Origin of the Genotypes
2.2. Experiment Set Up
2.3. Sampling and Measurements in Grapes
2.4. Winemaking
2.5. Measurements in Wines
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ampelographic Characteristics
3.2. Phenological, Agronomic and Qualitative Characteristics
3.3. Wine Characteristics
3.4. Wine Spectrophotometric Characteristics
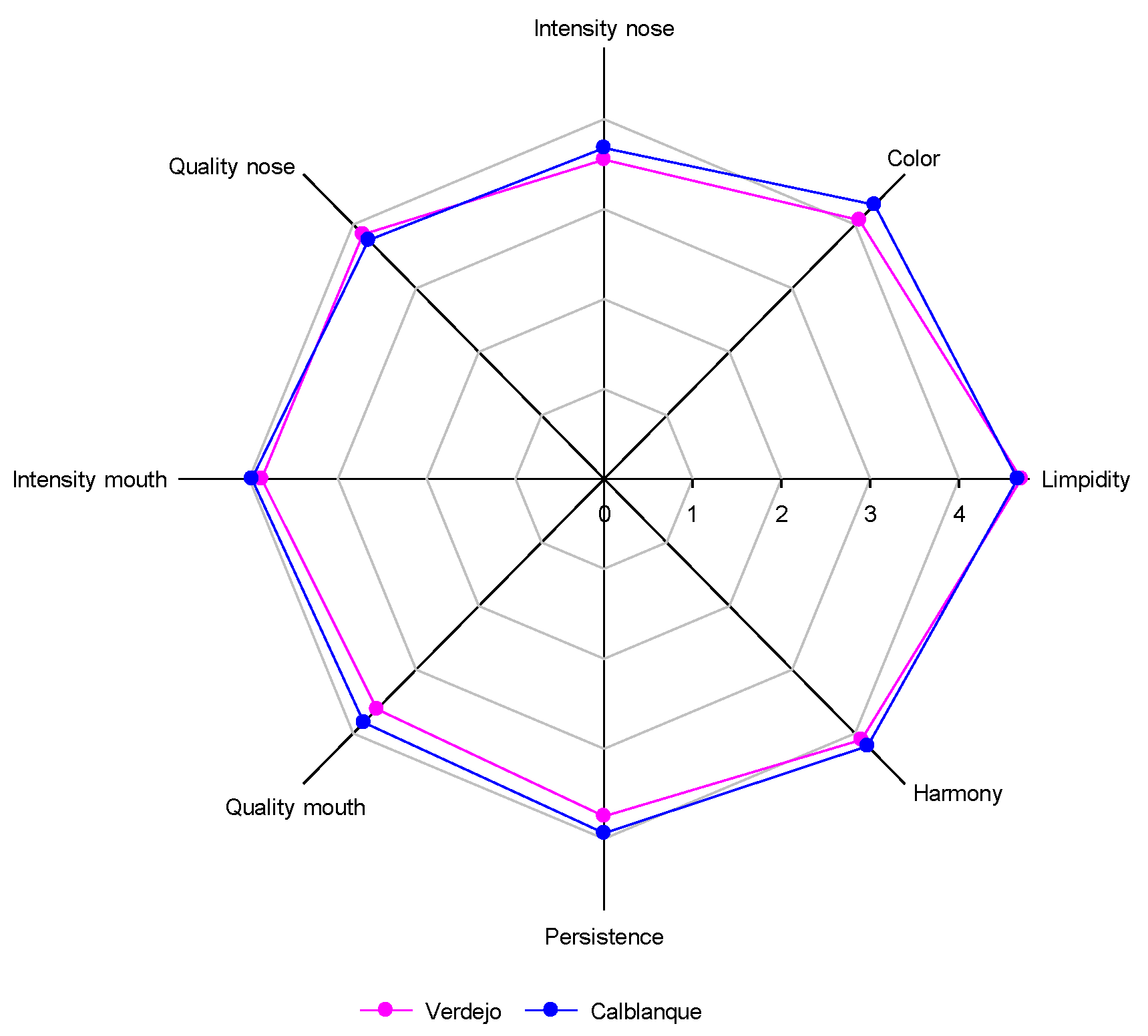
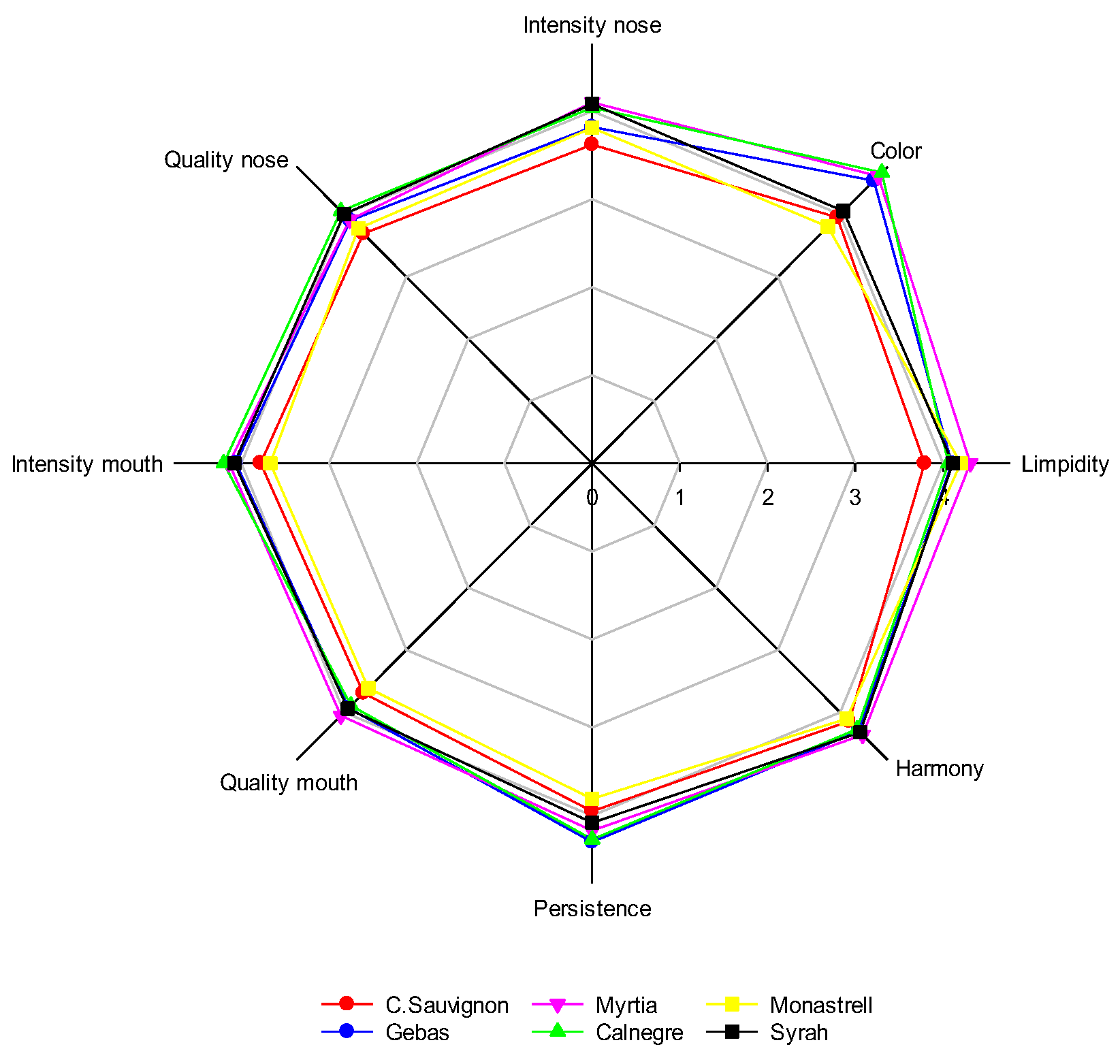
3.5. Wine Sensorial Analysis
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poni, S.; Gatti, P.; Dai, Z.W. Grapevine quality: A multiple choice issue. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 234, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.S. Wine Science Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Droulia, F.; Charalampopoulos, I. A Review on the observed climate change in Europe and its impacts on viticulture. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M. Managing grapevines to optimise fruit development in a challenging environment: A climate change primer for viticulturists. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2010, 16, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junquera, P.; Lissarrague, J.R.; Jiménez, L.; Linares, R.; Baeza, P. Long-term effects of different irrigation strategies on yield components, vine vigour, and grape composition in cv. Cabernet-Sauvignon (Vitis vinifera L.). Irrig. Sci. 2012, 30, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.A.; Saucier, C.; Glories, Y. Grape and wine phenolics: History and perspective. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2006, 57, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, V.; Vojnoski, B.; Stefova, M. Effect of winemaking treatment and wine aging on phenolic content in Vranec wines. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 49, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.; Dai, Z.; Wu, B.H.; Wu, J.; Merlin, I.; Hilbert, G.; Renaud, C.; Gomès, E.; Edwards, E.; Li, S.H.; et al. Anthocyanin biosynthesis is differentially regulated by light in the skin and flesh of white-fleshed and teinturier grape berries. Planta 2016, 243, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Mu, L.; Yan, G.L.; Liang, N.N.; Pan, Q.H.; Wang, J.; Reeves, M.J.; Duan, C.Q. Biosynthesis of anthocyanins and their regulation in colored grapes. Molecules 2010, 15, 9057–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rosas, I.; Deis, L.; Baldo, Y.; Cavagnaro, J.B.; Cavagnaro, P.F. High Temperature Alters Anthocyanin Concentration and Composition in Grape Berries of Malbec, Merlot, and Pinot Noir in a Cultivar-Dependent Manner. Plants 2022, 11, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, C.; Destrac-Irvine, A. Modified grape composition under climate change conditions requires adaptations in the vineyard. OENO One 2017, 51, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, H.; Malheiro, A.C.; Moutinho-Pereira, J.; Santos, J.A. An overview of climate change impacts on European viticulture. Food Energy Secur. 2012, 1, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlousek, P. Evaluation of drought tolerance of new grapevine rootstock hybrids. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, A.G. Grapevine Breeding Programs for the Wine Industry: Traditional and Molecular Techniques, 1st ed.; Reynolds, A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-1-78242-075-0. [Google Scholar]
- Berdeja, M.; Nicolas, P.; Kappel, C.; Dai, Z.W.; Hilbert, G.; Peccoux, A.; Lafontaine, M.; Ollat, N.; Gomès, E.; Delrot, S. Water limitation and rootstock genotype interact to alter grape berry metabolism through transcriptome reprogramming. Hortic. Res. 2015, 2, 15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, P.; Botía, P.; Navarro, J.M. Selecting rootstocks to improve vine performance and vineyard sustainability in deficit irrigated Monastrell grapevines under semiarid conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 209, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zombardo, A.; Mica, E.; Puccioni, S.; Perria, R.; Valentini, P.; Mattii, G.B.; Cattivelli, L.; Storchi, P. Berry quality of grapevine under water stress as affected by rootstock–scion interactions through gene expression regulation. Agronomy 2020, 10, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.A.; Costa, R.; Fraga, H. New insights into thermal growing conditions of Portuguese grapevine varieties under changing climates. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 135, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, P.; Williams, K.A.; Angers, P.; Pedneault, K. Changes in the flavan-3-ol and polysaccharide content during the fermentation of Vitis vinifera Cabernet-Sauvignon and cold-hardy Vitis varieties Frontenac and Frontenac blanc. OENO One 2021, 55, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillán, D.; Garrote, L.; Iglesias, A.; Sotes, V. Climate change risks and adaptation: New indicators for Mediterranean viticulture. Mitig. Adapt. Strat. Glob. Chang. 2020, 25, 881–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-López, D.J.; Fernández-Fernández, J.I.; Martínez-Mora, C.; Bleda-Sánchez, J.A.; Ruiz-García, L. Productiveness and berry quality of new wine grape genotypes grown under drought conditions in a semi-arid wine-producing Mediterranean Region. Plants 2022, 11, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlotte Brault, C.; Segura, V.; This, P.; Le Cunff, L.; Flutre, T.; François, P.; Pons, T.; Péros, J.-P.; Doligez, A. Across-population genomic prediction in grapevine opens up promising prospects for breeding. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, L.; Gil-Muñoz, R.; Martínez-Mora, C.; Bleda, J.A.; Fuentes-Denia, A.; Martínez-Jiménez, J.A.; Martínez-Cutillas, A.; Fernández-Fernández, J.I. Nuevas variedades de vid obtenidas en la Región de Murcia. Actas Hortic. 2018, 80, 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Fernández, J.I.; Gil-Muñoz, R.; Bleda-Sánchez, J.A.; Corredor-Cano, J.; Moreno-Olivares, J.D.; Cebrián-Pérez, A.; Martínez-Balsas, D.; Gómez-Martínez, J.C.; Palencia-Sigüenza, M.S.; Carcelén-Cutillas, J.C.; et al. Nuevas variedades procedentes de Monastrell adaptadas a clima cálido. Cosechas 2016–2019. Rev. Enólogos 2020, 126, 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Bayo-Canha, A.; Fernández-Fernández, J.I.; Martínez-Cutillas, A.; Ruiz-García, L. Phenotypic segregation and relationships of agronomic traits in Monastrell × Syrah wine grape progeny. Euphytica 2012, 186, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.F.; Adams, A.N. Characteristics of the microplate method of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of plant viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1977, 34, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, D.H.; Eichhorn, K.W.; Bleiholder, H.; Klose, R.; Meier, U.; Weber, E. Phenological growth stages of the grapevine (Vitis vinifera L. ssp. vinifera)-Codes and descriptions according to the extended BBCH scale. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 1995, 1, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Rustioni, L.; Maghradze, D.; Popescu, C.F.; Cola, G.; Abashidze, E.; Aroutiounian, R.; Brazão, J.; Coletti, S.; Cornea, V.; De-jeu, L.; et al. First results of the European grapevine collections collaborative network: Validation of a standard enocarpological phenotyping method. Vitis-J. Grapevine Res. 2014, 53, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- García-Barceló, J. Técnicas Analíticas Para Vinos, 1st ed.; GAB: Barcelona, Spain, 1990; ISBN 84-404-7827-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ribéreau-Gayon, P.; Pontallier, P.; Glories, Y. Some interpretations of colour changes in young red wines during their conservation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1983, 34, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.; Da Silva, M.; Hogg, T.A. Changes in colour and phenolic composition during the early stages of maturation of port in wood, stainless steel and glass. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Pradal, M.; Berud, F.; Romieu, C.; Torregrosa, L. Berry size variability in Vitis vinifera L. Vitis 2006, 45, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Río-Segade, S.; Vázquez, E.S.; Losada, E.D. Influence of ripeness grade on accumulation and extractability of grape skin anthocyanins in different cultivars. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2008, 21, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Jiménez, A.; Gil-Muñoz, R.; Ruiz-García, Y.; López-Roca, J.M.; Martinez-Cutillas, A.; Gómez-Plaza, E. Evaluating the polyphenol profile in three segregating grape (Vitis vinifera L.) populations. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2013, 2013, 572896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliewer, W.K.; Howarth, L.; Omori, M. Concentrations of tartaric acid and malic acids and their salts in Vitis vinifera grapes. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1967, 18, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-F.; Wu, B.-H.; Fan, P.-G.; Li, S.-H.; Li, L.-S. Sugar and acid concentrations in 98 grape cultivars analyzedby principal component analysis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, M. Comparison in changes in sugars, organic acids and amino acids during berry ripening of sucrose- and hexose-accumulating grape cultivars. Potential of table crape varieties (Vitis vinifera L.). Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2000, 73, 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Lakso, A.N.; Kliewer, W.M. The influence of temperature on malicacid metabolism in grape berries. II. Temperature responses of net dark CO2 fixation and malic acid pools. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1978, 29, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.W.; Ollat, N.; Gomès, E.; Decroocq, S.; Tandonnet, J.P.; Bordenave, L.; Pieri, P.; Hilbert, G.; Kappel, C.; van Leeuwen, C.; et al. Ecophysiological, genetic, and molecular causes of variation ingrape berry weight and composition: A review. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2011, 62, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiani, F.; Farinelli, D.; Palliotti, A.; Moscatello, S.; Battistelli, A.; Walker, R.P. Is stored malate the quantitatively most important substrate utilised by respiration and ethanolic fermentation in grape berry pericarp during ripening? Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 76, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadi, M.; Zira, A.; Magiatis, P.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Mikros, E. 1H NMR-Based metabonomics for the classification of Greek wines according to variety, region, and vintage. Comparison with HPLC data. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 11067–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupsa, J.; Pavloušek, P.; Kumšta, M.; Lampíř, L. Phenolic profiles of Riesling wines originating from different terroirs of the Czech Republic. Mitt. Klosterneubg. 2017, 67, 182–193. [Google Scholar]
- Parpinello, G.P.; Ricci, A.; Arapitsas, P.; Curioni, A.; Moio, L.; Rio-Segade, S.; Ugliano, M.; Versari, A. Multivariate characterisation of Italian monovarietal red wines using MIR spectroscopy. OENO One 2019, 4, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usseglio-Tomasset, L. Chimica Enologica, 2nd ed.; AEB Edizioni: Brescia, Italy, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuy, P. Les facteurs du développement de l’acescence dans le vin. Ann. Technol. Agric. 1957, 6, 391–407. [Google Scholar]
- Wibowo, D.; Eschenbruch, R.; Davis, C.R.; Fleet, G.H.; Lee, T.H. Occurrence and growth of lactic acid bacteria in wine: A review. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1985, 36, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, H.W. Stabilisation des anthocyanes. Comportement de la couleur dans les vins rouges. Ann. Technol. Agricol. 1963, 12, 247–259. [Google Scholar]
- Brouillard, R.; Delaporte, B. Chemistry of anthocyanin pigments. 2. Kinetic and thermodynamic study of proton transfer, hydration, and tautomeric reactions of malvidin-3-glucoside. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 8461–8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forino, M.; Picariello, L.; Rinaldi, A.; Moio, L.; Gambuti, A. How must pH affects the level of red wine phenols. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 129, 109546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Plaza, E.; Olmos, O.; Bautista-Ortín, A.B. Tannin profile of different Monastrell wines and its relation to projected market prices. Food Chem. 2016, 1, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paladines-Quezada, D.F.; Moreno-Olivares, J.D.; Fernández-Fernández, J.I.; Bautista-Ortín, A.B.; Gil-Muñoz, R. Influence of methyl jasmonate and benzothiadiazole on the composition of grape skin cell walls and wines. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.; Mullen, W.; Landrault, N.; Teissedre, P.L.; Lean, M.E.J.; Crozier, A. Variations in the profile and content of anthocyanins in wines made from Cabernet Sauvignon and hybrid grapes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4096–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulinacci, N.; Santamaria, A.R.; Giaccherini, C.; Innocenti, M.; Valletta, A.; Ciolfi, G.; Pasqua, G. Anthocyanins and flavan-3-ols from grapes and wines of Vitis vinifera cv. Cesanese d’Affile. Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 22, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikfardjam, M.S.P.; Márk, L.; Avar, P.; Figler, M.; Ohmacht, R. Polyphenols, anthocyanins, and trans-resveratrol in red wines from the Hungarian Villány region. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Muñoz, R.G.; Moreno-Olivares, J.D.; Paladines-Quezada, D.F.; Cebrián-Pérez, A.; Fernández-Fernández, J.I. High anthocyanin level of grape hybrids from Monastrell and their wines. Int. J. Hort. Agric. 2018, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Muñoz, R.; Moreno-Olivares, J.D.; Paladines-Quezada, D.F.; Bleda-Sánchez, J.A.; Cebrían-Pérez, A.; Giménez-Bañón, M.J.; Fernández-Fernández, J.I. Characterization of anthocyanins from intraspecific crosses of Monastrell with other premium varieties. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 664515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einstein, M.A. Descriptive techniques and their hybridization. In Sensory Science Theory and Applications in Foods; Lawless, H.T., Klein, B.P., Eds.; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, H.; Sidel, J.; Oliver, S.; Woolsey, A.; Singleton, C. Sensory evaluation by quantitative descriptive analysis. Descr. Sens. Anal. Pract. 1974, 28, 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Olivares, J.D.; Giménez-Bañón, M.J.; Paladines-Quezada, D.F.; Gómez-Martínez, J.C.; Cebrián-Pérez, A.; Fernández-Fernández, J.I.; Bleda-Sánchez, J.A.; Gil-Muñoz, R. Aromatic characterization of new white wine varieties made from Monastrell grapes grown in South-Eastern Spain. Molecules 2020, 25, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Sánchez, I.; Bartolomé-Suáldea, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. Malolactic Fermentation. Red Wine Technology; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
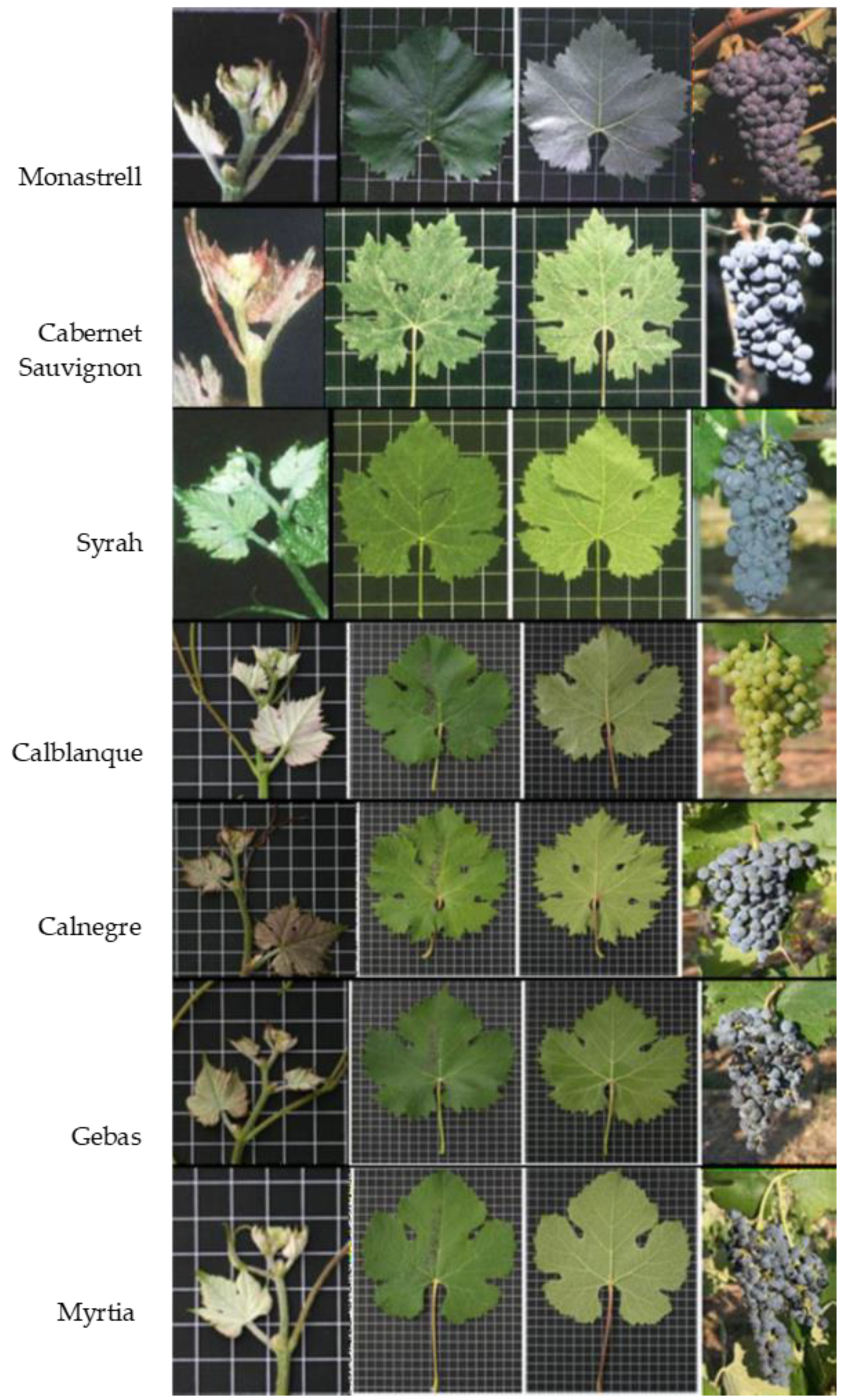
| Variety | VMC1A12 | VMC8G6 | VVMD27 | VVMD5 | VMC1E11 | VMC5E9 | VVMD28 | VVIV67 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monastrell | 119 | 137 | 139 | 173 | 177 | 187 | 223 | 238 | 188 | 194 | 214 | 228 | 243 | 256 | 357 | 364 |
| Cabernet S. | 121 | 150 | 161 | 165 | 173 | 187 | 229 | 238 | 192 | 196 | 195 | 218 | 233 | 235 | 364 | 372 |
| Syrah | 137 | 150 | 169 | 173 | 187 | 189 | 223 | 229 | 196 | 206 | 218 | 222 | 217 | 227 | 361 | 381 |
| Calblanque | 121 | 137 | 165 | 173 | 187 | 187 | 223 | 229 | 188 | 192 | 195 | 228 | 233 | 243 | 357 | 372 |
| Calnegre | 121 | 137 | 165 | 173 | 187 | 187 | 223 | 238 | 194 | 196 | 195 | 214 | 233 | 256 | 357 | 364 |
| Gebas | 119 | 121 | 139 | 165 | 173 | 177 | 223 | 238 | 188 | 196 | 214 | 218 | 235 | 243 | 357 | 372 |
| Myrtia | 137 | 150 | 139 | 169 | 187 | 189 | 223 | 229 | 188 | 206 | 214 | 218 | 217 | 256 | 357 | 381 |
| Variety | Budbreak | Flowering | Veraison | Harvest | Harvest Days before Monastrell |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monastrell | 22 April cd | 02 June | 10 August c | 27 September c | 0 a |
| Cabernet S. | 16 April bc | 27 May | 05 August bc | 09 September b | 18 c |
| Syrah | 08 April a | 23 May | 22 July a | 23 August a | 35 e |
| Calblanque | 13 April ab | 24 May | 08 August c | 25 August a | 33 d |
| Calnegre | 21 April cd | 30 May | 12 August c | 11 September b | 16 b |
| Gebas | 24 April d | 31 May | 09 August c | 09 September b | 18 c |
| Myrtia | 10 April ab | 24 May | 29 July ab | 23 August a | 35 e |
| Variety | kg per Vine | kg per ha | Weight of 100 Berries | Anthocyanins (mg kg−1 Berry) | TPC (mg kg−1 Berry) | ° Brix | pH | TA (g L−1 Tartaric Acid) | Tartaric Acid (g L−1) | Malic Acid (g L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monastrell | 3.25 ± 0.67 ab | 8648 ± 1400 abc | 152.2 ± 11.9 c | 1061 ± 86 a | 1554 ± 139 a | 24.1 ± 0.6 bc | 3.95 ± 0.30 b | 2.88 ± 0.35 a | 4.20 ± 0.19 a | 1.33 ± 0.11 a |
| Cabernet S. | 3.62 ± 0.67 b | 9658 ± 1797 c | 107.3 ± 7.7 a | 1287 ± 127 a | 1905 ± 81 ab | 24.3 ± 0.4 bc | 3.94 ± 0.20 b | 3.25 ± 0.22 a | 4.91 ± 0.17 b | 1.9 ± 0.13 b |
| Syrah | 3.53 ± 0.50 b | 9427 ± 1338 c | 125.5 ± 7.8 ab | 1791 ± 148 b | 2114 ± 172 b | 24.7 ± 0.4 c | 3.94 ± 0.19 b | 3.29 ± 0.48 a | 4.51 ± 0.12 ab | 2.35 ± 0.08 c |
| Calblanque | 3.37 ± 0.60 ab | 9329 ± 1516 bc | 135.8 ± 10.4 bc | 20.2 ± 0.7 a | 3.54 ± 0.04 a | 4.81 ± 0.26 b | 4.88 ± 0.26 b | 2.91 ± 0.10 d | ||
| Calnegre | 2.05 ± 0.16 a | 5401 ± 1506 a | 106.3 ± 4.4 a | 2925 ± 93 c | 3697 ± 69 d | 22.9 ± 0.5 b | 3.67 ± 0.06 a | 3.51 ± 0.18 a | 4.81 ± 0.18 b | 1.13 ± 0.15 a |
| Gebas | 2.48 ± 0.29 ab | 7262 ± 971 abc | 121.7 ± 7.2 ab | 2934 ± 160 c | 3151 ± 213 c | 23.7 ± 0.8 bc | 3.97 ± 0.09 b | 3.10 ± 0.22 a | 4.06 ± 0.22 a | 2.20 ± 0.06 bc |
| Myrtia | 2.18 ± 0.28 a | 5819 ± 739 ab | 107.2 ± 5.2 a | 3533 ± 241 d | 3521 ± 134 cd | 24.1 ± 0.4 bc | 3.64 ± 0.07 a | 4.32 ± 0.35 b | 4.90 ± 0.22 b | 2.27 ± 0.13 c |
| Variety | Alcohol (V/V) | TA (g L−1 Tartaric) | pH | Relative Density 20/20 | Total Dry Extract |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monastrell | 13.89 ± 0.41 bc | 7.37 ± 0.22 bc | 3.41 ± 0.03 a | 0.9922 ± 0.0004 a | 27.30 ± 0.13 b |
| Cabernet S. | 13.79 ± 0.46 bc | 7.12 ± 0.53 abc | 3.47 ± 0.03 ab | 0.9928 ± 0.0006 a | 27.52 ± 2.17 b |
| Syrah | 14.35 ± 0.46 c | 6.06 ± 0.46 a | 3.59 ± 0.06 bc | 0.9923 ± 0.0003 a | 28.13 ± 0.71 b |
| Calblanque | 12.09 ± 0.41 a | 6.40 ± 0.40 ab | 3.37 ± 0.04 a | 0.9919 ± 0.0006 a | 20.37 ± 0.86 a |
| Calnegre | 12.94 ± 0.41 ab | 7.39 ± 0.31 bc | 3.42 ± 0.03 a | 0.9957 ± 0.0002 b | 32.61 ± 0.90 c |
| Gebas | 13.56 ± 0.41 bc | 7.25 ± 0.48 bc | 3.64 ± 0.04 c | 0.9951 ± 0.0004 b | 32.21 ± 1.05 c |
| Myrtia | 13.40 ± 0.41 bc | 7.89 ± 0.32 c | 3.41 ± 0.04 a | 0.9948 ± 0.0004 b | 31.80 ± 0.88 c |
| Parameters | Monastrell | Cabernet S. | Syrah | Calnegre | Gebas | Myrtia | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color intensity | AF | 14.86 ± 0.52 a | 19.17 ± 0.65 a | 25.87 ± 2.56 b | 46.66 ± 1.58 d | 40.72 ± 2.31 c | 60.28 ± 1.61 e |
| MF | 11.69 ± 1.70 a | 16.00 ± 0.45 ab | 18.66 ± 1.09 b | 32.50 ± 2.46 d | 25.99 ± 1.45 c | 40.02 ± 1.97 e | |
| Taint | AF | 0.44 ± 0.02 a | 0.44 ± 0.02 a | 0.39 ± 0.01 a | 0.38 ± 0.02 a | 0.42 ± 0.03 a | 0.39 ± 0.01 a |
| MF | 0.57 ± 0.03 b | 0.56 ± 0.01 b | 0.55 ± 0.02 b | 0.48 ± 0.01 a | 0.54 ± 0.01 b | 0.48 ± 0.01 a | |
| Anthocyanins | AF | 571.00 ± 36.88 a | 698.00 ± 52.84 a | 1084.00 ± 58.57 b | 1598.00 ± 54.40 c | 1526.00 ± 90.92 c | 1936.00 ± 252.68 d |
| MF | 330.47 ± 75.00 a | 432.00 ± 54.00 a | 692.00 ± 65.83 b | 979.00 ± 110.38 c | 972.00 ± 91.18 c | 1262.00 ± 109.82 d | |
| T.P.C. | AF | 43.35 ± 1.86 a | 45.10 ± 1.72 a | 60.73 ± 3.60 b | 94.41 ± 6.95 c | 91.84 ± 7.99 c | 100.78 ± 4.87 c |
| MF | 36.70 ± 3.99 a | 41.84 ± 1.00 ab | 53.83 ± 2.82 b | 85.94 ± 8.07 c | 82.73 ± 5.80 c | 86.05 ± 3.70 c | |
| L* | AF | 13.77 ± 0.43 d | 8.25 ± 0.81 c | 3.91 ± 0.58 b | 1.76 ± 0.16 a | 1.35 ± 0.56 a | 0.84 ± 0.20 a |
| MF | 14.18 ± 3.07 c | 6.86 ± 0.67 b | 5.03 ± 0.44 ab | 2.57 ± 0.14 a | 2.65 ± 0.34 a | 1.46 ± 0.42 a | |
| a* | AF | 46.10 ± 0.51 e | 38.43 ± 1.44 d | 26.01 ± 2.55 c | 12.74 ± 1.11 b | 9.72 ± 4.00 ab | 6.14 ± 1.47 a |
| MF | 44.89 ± 2.48 d | 35.89 ± 1.49 c | 31.30 ± 1.55 c | 18.55 ± 1.03 b | 18.91 ± 2.32 b | 10.65 ± 3.08 a | |
| b* | AF | 23.69 ± 0.73 d | 14.22 ± 1.40 c | 6.74 ± 1.01 b | 3.03 ± 0.27 a | 2.33 ± 0.97 a | 1.45 ± 0.35 a |
| MF | 19.15 ± 1.67 d | 11.80 ± 1.14 c | 8.66 ± 0.76 b | 4.43 ± 0.25 a | 4.58 ± 0.60 a | 2.48 ± 0.69 a | |
| C* (ab) | AF | 51.84 ± 0.83 d | 41.01 ± 1.82 c | 26.88 ± 2.73 b | 13.10 ± 1.14 a | 10.00 ± 4.11 a | 6.31 ± 1.51 a |
| MF | 48.87 ± 2.64 d | 37.83 ± 1.77 c | 32.48 ± 1.67 c | 19.07 ± 1.08 b | 19.46 ± 2.39 b | 10.94 ± 3.16 a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-García, L.; Fernández-Fernández, J.I.; Martínez-Mora, C.; Moreno-Olivares, J.D.; Giménez-Bañón, M.J.; Fernández-López, D.J.; Bleda-Sánchez, J.A.; Gil-Muñoz, R. Characterization of New Grapevine Varieties Cross-Bred from Monastrell, Authorized for Winemaking in the Warm Region of Murcia (South-Eastern Spain). Horticulturae 2023, 9, 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070760
Ruiz-García L, Fernández-Fernández JI, Martínez-Mora C, Moreno-Olivares JD, Giménez-Bañón MJ, Fernández-López DJ, Bleda-Sánchez JA, Gil-Muñoz R. Characterization of New Grapevine Varieties Cross-Bred from Monastrell, Authorized for Winemaking in the Warm Region of Murcia (South-Eastern Spain). Horticulturae. 2023; 9(7):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070760
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-García, Leonor, José Ignacio Fernández-Fernández, Celia Martínez-Mora, Juan Daniel Moreno-Olivares, María José Giménez-Bañón, Diego José Fernández-López, Juan Antonio Bleda-Sánchez, and Rocío Gil-Muñoz. 2023. "Characterization of New Grapevine Varieties Cross-Bred from Monastrell, Authorized for Winemaking in the Warm Region of Murcia (South-Eastern Spain)" Horticulturae 9, no. 7: 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070760
APA StyleRuiz-García, L., Fernández-Fernández, J. I., Martínez-Mora, C., Moreno-Olivares, J. D., Giménez-Bañón, M. J., Fernández-López, D. J., Bleda-Sánchez, J. A., & Gil-Muñoz, R. (2023). Characterization of New Grapevine Varieties Cross-Bred from Monastrell, Authorized for Winemaking in the Warm Region of Murcia (South-Eastern Spain). Horticulturae, 9(7), 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070760








