Abstract
Alternaria gaisen is one of the main fungi that cause fruit postharvest diseases due to its wide contamination and toxin production. The application of lactic acid bacteria shows great industrial application as a natural food preserver due to the advantages of being safe and non-toxic. In order to obtain a natural preservative against this fungus, this study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of cell- free supernatants (CFS) produced by Lactobacillus pentosus 86 as antimicrobials in vitro against A. gaisen. Results indicated that CFS displayed excellent thermostability and enzymatic stabilities with an antifungal activity over 85%. Under thermal (40–100 °C) treatments, different protease solution and acidic conditions (pH 2–4), the antifungal activity of CFS maintained up 80%. However, when the pH reached 6, its antifungal ability completely disappeared. CFS inhibited mycelial growth of A. gaisen by destroying the hyphae membrane, leading to the leakage of nucleic acids and proteins, and hyphae collapsed and shriveled. CFS also changed the spore’s morphology, resulting in cell membrane damage, intracellular leakage, and organelles aggregation. The increase of cell membrane permeability of spores caused a 30% mortality rate. Therefore, the CFS of L. pentosus 86 has the potential for controlling fruit diseases caused by A. gaisen.
1. Introduction
Postharvest fungal pathogens are considered a major problem for the disease and loss of fresh fruits. Fungi that contaminate fruits belong to the genus Aspergillus, Penicillium, Fusarium, and Alternaria, among others [1,2]. Alternaria is a ubiquitous genus causing fruit diseases and spoilage, and can produce mycotoxins. The infection of Alternaria species is present in a variety of fruits, including apple, blueberry, grape, walnut, tomato, and pear [3]. Alternaria species are primarily responsible for the spoilage of fruits during long-distance transport and refrigerated storage [4]. Therefore, control of Alternaria species is of great significance in prolonging the shelf life and improving the storage capacity of fruits.
Many approaches have been suggested to manage postharvest decay, while control of postharvest diseases by preservative agents after harvesting is the most widely used and effective method [5]. Chemical fungicides are traditionally used to control postharvest fungal diseases. Recently, increasing concerns about fungicide resistance problems and residues have prompted the search for safe and effective alternative strategies. Among these strategies, biological control based on naturally occurring microorganisms has been the most studied [6,7].
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB), as one of the earliest and widely used microorganisms, occupy a very special position in the food industry. LAB are traditionally used as fermentation strains and probiotics, whereas their antimicrobial properties are nowadays receiving more attention. LAB metabolites, including fatty acids, organic acids, and bacteriocin, exhibit extensive antifungal properties [8,9]. LAB strains or their metabolites show great industrial application as a natural food preservative due to the advantages of being safe and non-toxic. Cell-free supernatant (CFS) is defined as a microbiological culture medium removing bacterial cells while maintaining metabolites. Several studies have confirmed that CFS of LAB can be used against bacteria and molds, both in vitro and in foods [10]. CFS as an excellent alternative to conventional antimicrobials has enormous potential and extensive application prospects. Therefore, researchers are interested in exploring strains with excellent antimicrobial properties, focusing on the identification of strains, the characterization of the antimicrobial spectrum, the application effect of CFS, etc. [11].
Previously, we identified the inhibitory activity of 110 strains of LAB from Xinjiang dairy products against Alternaria, and found that Lactobacillus pentosus 86 had high antifungal activity [12]. In order to promote the application of this strain, the inhibitory effect of the CFS of this strain against Alternaria gaisen was investigated in this study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culturing Conditions
Lactobacillus pentosus strains 86 was isolated from Chinese traditional dairy food [13]. Alternaria gaisen was isolated from the Chinese pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) [12]. These two strains are obtained from Tarim University. L. pentosus 86 and A. gaisen were grown in deMan Rogosa Sharpe (MRS, Aobox Biotechnology Co., Beijing, China) medium at 37 °C and Potato Dextrosa Broth (PDB, Aobox Biotechnology Co., Beijing, China) at 28 °C, respectively. Most chemicals and reagents were of analytical-reagent grade and were obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.2. Preparation of Cell-Free Supernatant Concentration (CFS)
The cell-free supernatant concentration (CFS) of L. pentosus 86 was prepared according to the method described by Mani-López et al. with slight modifications [10]. L. pentosus 86 was inoculated into MRS medium and reached an initial cell density of 105 cfu/mL. The culture was incubated in a 1000 mL Erlenmeyer flask in a rotatory shaker incubator (Boxun Apparatus, Shanghai, China) at 37 °C and 120 rpm/min. After incubation, the supernatant was collected and centrifuged at 6000× g for 15 min. The centrifuged supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 µm membrane filter to obtain the CFS.
2.3. Evaluate Antifungal Activity by 96-Well Plate Assay
The antifungal activity of L. pentosus 86 culture medium was measured according to Massimo et al. with some modifications [14]. A. gaisen culture was filtered through glass wool to remove any mycelial fragments, and centrifuged at 200× g for 2 min to collect spores. Spores were resuspended with distilled water and the concentration was measured by counting with a hemocytometer. Seventy µL diluted sample was mixed with 100 µL PDB culture and 30 µL A. gaisen suspension (109 spores/mL) in a 96-well microwell plate. After 48 h incubation at 28 °C, the absorbance value at 580 nm was measured using a microplate reader (Tecan Sunrise, Molecular Devices, Shanghai, China). The antifungal rate (AR%) was calculated using the following formula: AR% = [1 − (ODt/OD0)] × 100, where ODt and OD0 are the absorbances at time 48 h and 0 h.
2.4. Assessment of Mycelial Growth by Agar Dilution Method
The CFS obtained from L. pentosus 86 was mixed with PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar, Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) culture and poured (25 mL in each dish) into a 90 mm diameter petri dish to solidify at room temperature. A 7 mm agar plug was transferred from the edge of a 7-day-old actively growing culture of A. gaisen to the center of PDA medium, and incubated at 28 °C for 7 d. The value of inhibition was measured using the formula which is [1 − (Dt/D0)] × 100, where Dt and D0 are respectively the diameter of A. gaisen in the PDA with CFS and without CFS.
2.5. Detection of Antimicrobial Stability
In order to study the stability of the CFS, thermal, enzymatic, and acid treatments were also performed according to Lee et al. with some modifications [15]. To evaluate thermostability, the CFS was heated at 40, 60, 80, and 100 °C for 30 min. CFS samples were added to various protease solutions, including Papain (1 mg/mL, pH 6.0), Pepsin (1 mg/mL, pH 2.0), Trypsin (1 mg/mL, pH 7.8), and Proteinase K (1 mg/mL, pH 4.0). After enzyme treatment at 37 °C for 2 h, samples were inactivated at 100 °C for 5 min. To evaluate the acid tolerance, the CFS was exposed to hydrochloric acid buffer (pH 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, and 6.0). Subsequently, the pH of treated samples was adjusted to the pH value of untreated samples and transferred to a 96-well plate. CFS untreated was diluted with MRS to the same volume of treated samples and used as the negative control (CK). Fungal inhibition was carried out by 96-well plate assay.
2.6. Spore Germination Assay
Spore germination assay was carried out according to Li et al. with some modifications [16]. After 48 h incubation, CFS was freeze-dried and added to PDB medium to reach the final concentration of 0, 4, 8, 16, 32, and 64 mg/mL. A. gaisen suspension was inoculated to this medium, and reached a cell density of approximately 1.0 × 107 spores/mL. All samples were incubated in at 900 rpm and 28 °C until the spore germination rate of A. gaisen in PDB medium without CFS reached 90%. Spore germination was observed using an optical microscope. At least 200 spores were examined in each visual field. Each replicate consisted of three observations and three replicates of each treatment were performed. The spore germination rate was calculated as the percentage of germinated spores in total spores.
2.7. Measurement of Cellular Leakage
The leakage of nucleic acids and proteins of A. gaisen was measured according to the method by Barman et al. with some modifications [17]. Freeze-dried CFS was added to a PDB medium with 1.0 × 107 spores/mL A. gaisen spores, and incubated at 28 °C. Samples were centrifuged at 300× g for 5 min. The absorbance values of 260 nm and 280 nm were measured at 1, 3, 6, 9, 12 and 24 h.
2.8. Morphology Observation
The mycelia and spores of A. gaisen were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), respectively. Samples were collected from a culture with or without CFS, and washed twice with 100 mmol/L phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution (pH 7.4). The mycelia and spores were prefixed with PBS (pH 7.2) containing 2.5% glutaraldehyde overnight at 4 °C, washed three times with 0.1 mol/L PBS, and dehydrated in 30–100% ethyl alcohol grades retaining them for 10 min in every dilution. For SEM observation of mycelia, the dehydrated mycelia were sprayed with gold and observed using a scanning electron microscope. For TEM observation of spores, the dehydrated spores were dipped into Epon 81, and examined with a Hitachi H-7650 transmission electron microscope.
2.9. Measurement of Membrane Integrity
The effect of the CFS on cell membrane integrity was studied by flow cytometry following the method described by Wei with some modifications [18]. Spores were inoculated to PDB medium with or without CFS, incubated at 28 °C, harvested by centrifuging at 6000× g for 2 min, and washed twice with 100 mmol/L PBS (pH 7.4). The spores were stained with propidium iodide (PI, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) for 30 min at 28 °C in the dark, centrifuged at 5000× g for 5 min at 4 °C, washed twice with PBS to remove residual dye, and resuspended in PBS. The spores were visualized under a fluorescence microscope (Olympus BX53, Olympus Co., Tokyo, Japan). Then, the spores were detected using a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). The percentage of fluorescent spores in the population was calculated.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Three replicates of each treatment were performed and the entire experiment was performed three times. All data were reported as means ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using the software SAS version 8.2. Differences with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
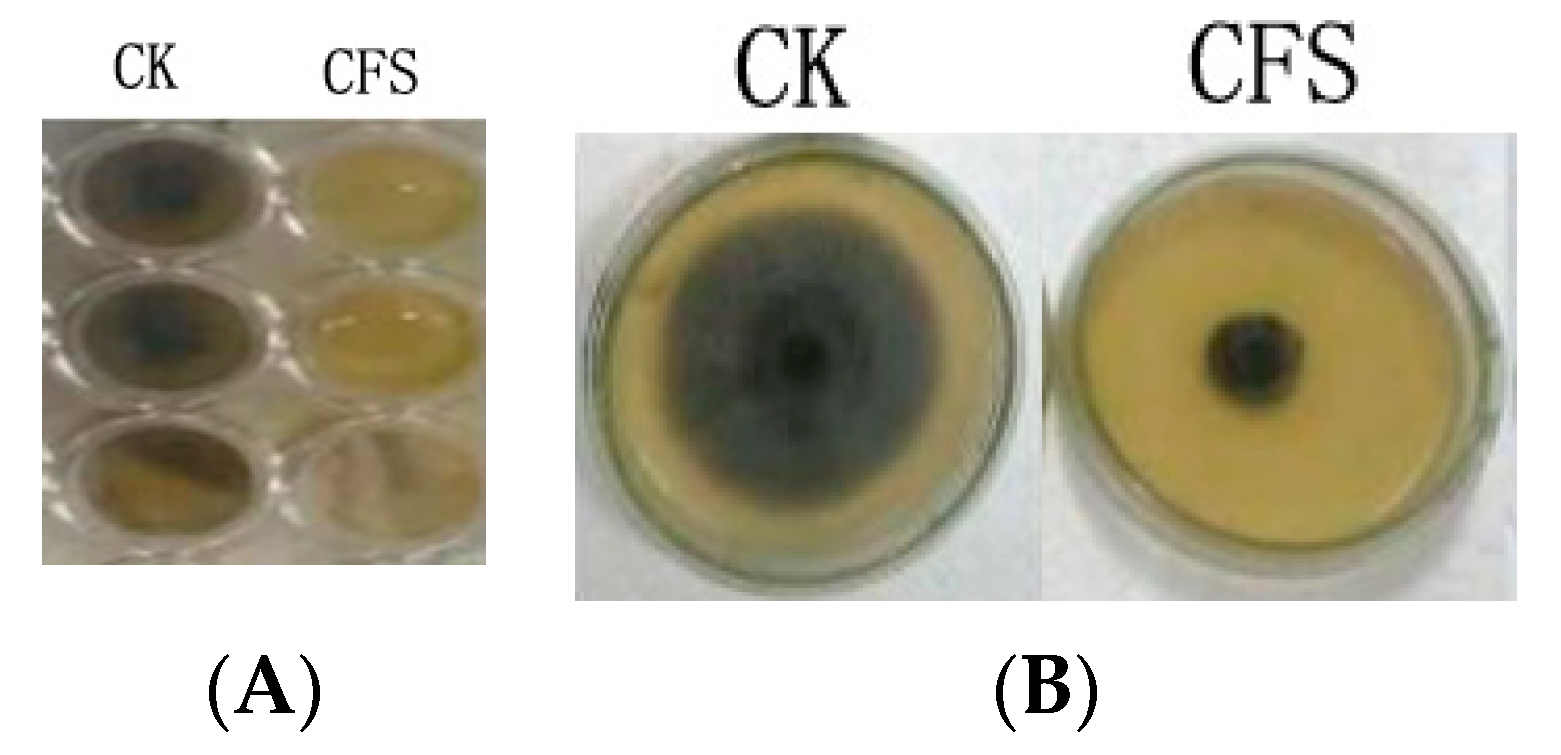
The effect of the cell-free supernatant (CFS) of Lactobacillus pentosus 86 against Alternaria gaisen was evaluated by two methods (96-well plate assay and agar dilution method). Figure 1 showed that CFS inhibited fungal growth both in liquid (PDB) and solid (PDA) medium.
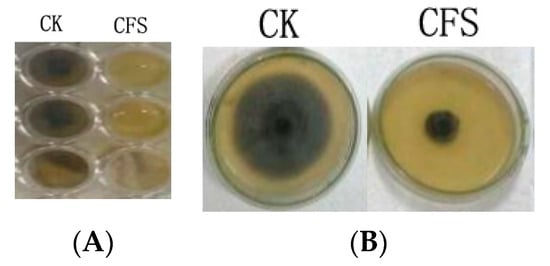
Figure 1.
CFS antibacterial ability in potato dextrose broth (A) and potato dextrose agar (B) media. CK indicated medium without CFS, CFS indicated medium with 20% CFS.
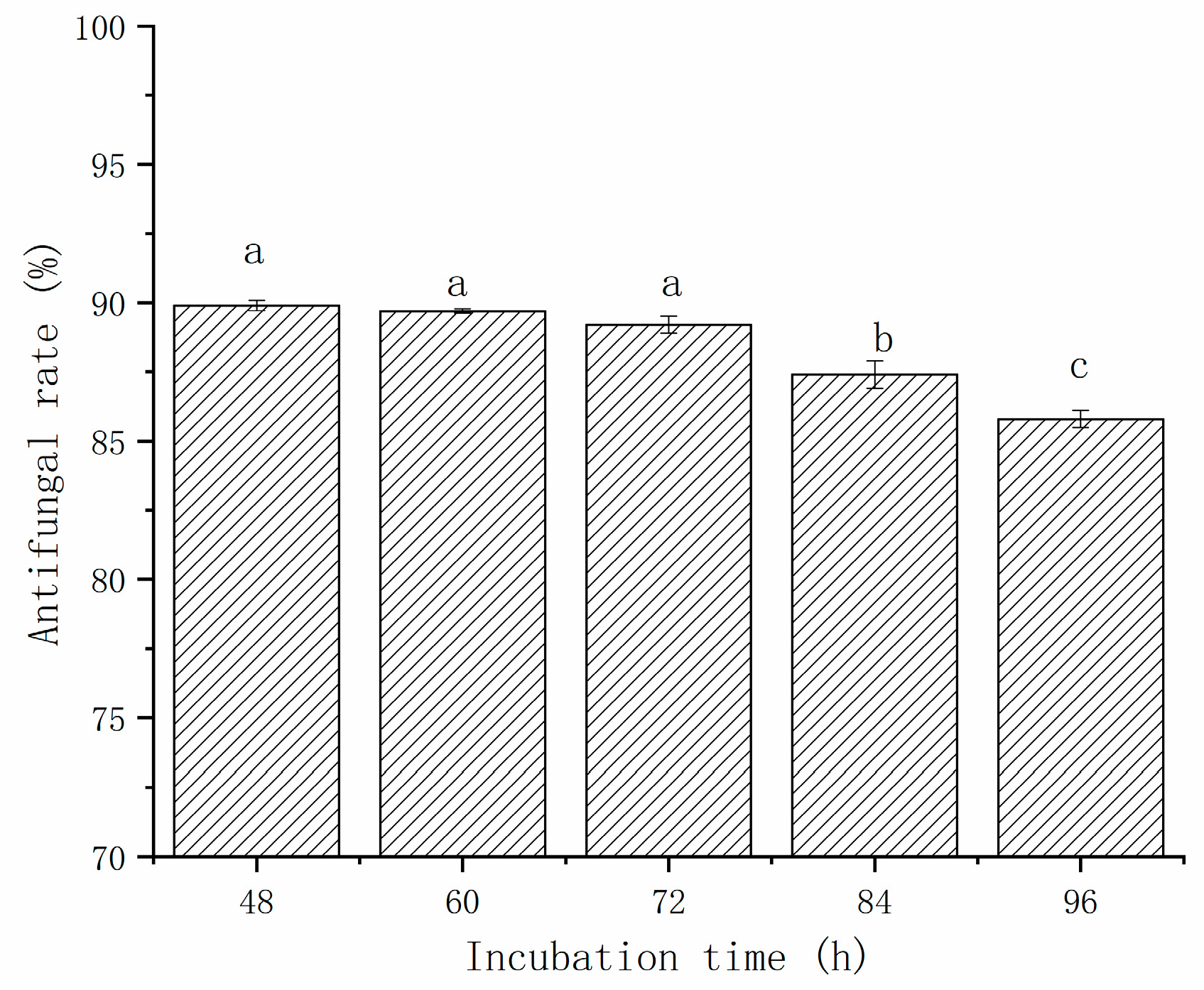
The effect of incubation time on the antifungal activity of CFS against A. gaisen was evaluated from 48 h to 96 h (Figure 2). The growth of A. gaisen was inhibited by the CFS of L. pentosus 86. The antimicrobial activity ranged from 89.9% to 85.8%, and was incubation time dependent. The antifungal rate of CFS decreased with the increase in incubation time. From 48 h to 72 h, no significant (p > 0.05) difference in growth inhibition rate was observed, indicating that after 48 h of incubation, a large number of antimicrobial metabolites have already accumulated. When the incubation time was extended, the inhibition rate of CFS at 84 h and 96 h were significantly lower (p < 0.05) than that obtained from the first 72 h of incubation. This phenomenon indicated that bacteriostatic metabolites were degraded during later 24 h incubation.
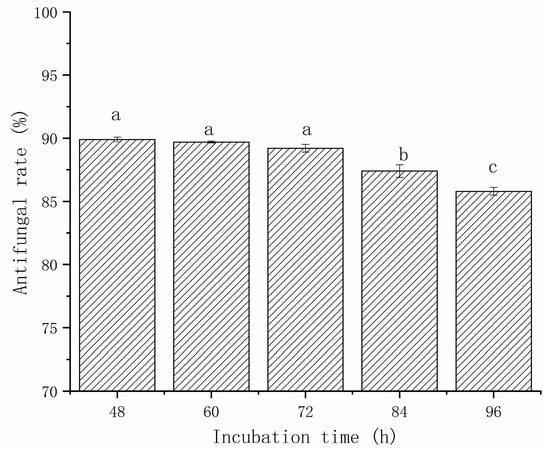
Figure 2.
The effect of incubation time on the antifungal activity of CFS against A. gaisen. Different letters above bars indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
The stability of the CFS against thermal, enzymatic, and acid treatments was evaluated (Table 1). For thermostability, the CFS samples were treated at 40, 60, 80, and 100 °C. There was no significant difference (p > 0.05) between the antifungal activities of untreated CFS and CFS treated after 40 °C for 30 min, and both reached 87%. Compared with the control group (CK), the antifungal activities of CFS samples were significantly (p < 0.05) decreased after 60, 80, and 100 °C treatment. However, even after 100 °C treatment, the antifungal activities of CFS only decreased 7.13%, suggesting that CFS showed a particularly high protease stability. During enzymatic stabilities experiments, all enzymes, except proteinase K, did not significantly (p > 0.05) reduce the CFS antimicrobial activity. The antifungal activity of CFS treated with papain, pepsin, and trypsin was higher than 86%, whereas samples treated with proteinase K had 82.60% antifungal activity. This result indicated that proteases did not cause the degradation of bacteriostatic substances in the CFS samples. Table 1 also showed that the antimicrobial activity of the CFS was affected by pH treatments. The antifungal activity of the CFS significantly (p < 0.05) decreases as the pH increased. The supernatant showed a high level of antifungal activity (ranging from 93.30% to 85.73%) at a pH between 2 to 4. When the pH value reached 6, the antifungal activity of the CFS cannot be detected. This result indicated that CFS was unstable under neutral or alkaline conditions. The decrease and disappearance of antimicrobial potency of L. pentosus 86 CFS at higher pH environments was mainly due to the degradation of bacteriostatic substances. The antifungal activities of the CFS were maintained at over 80% at heating, and proteases appeared in an acidic environment, suggesting that the bacteriostatic substances in the CFS of L. pentosus 86 were stable.

Table 1.
The effect of three treatments on the antifungal activity of CFS against A. gaisen. Different letters in the same row indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
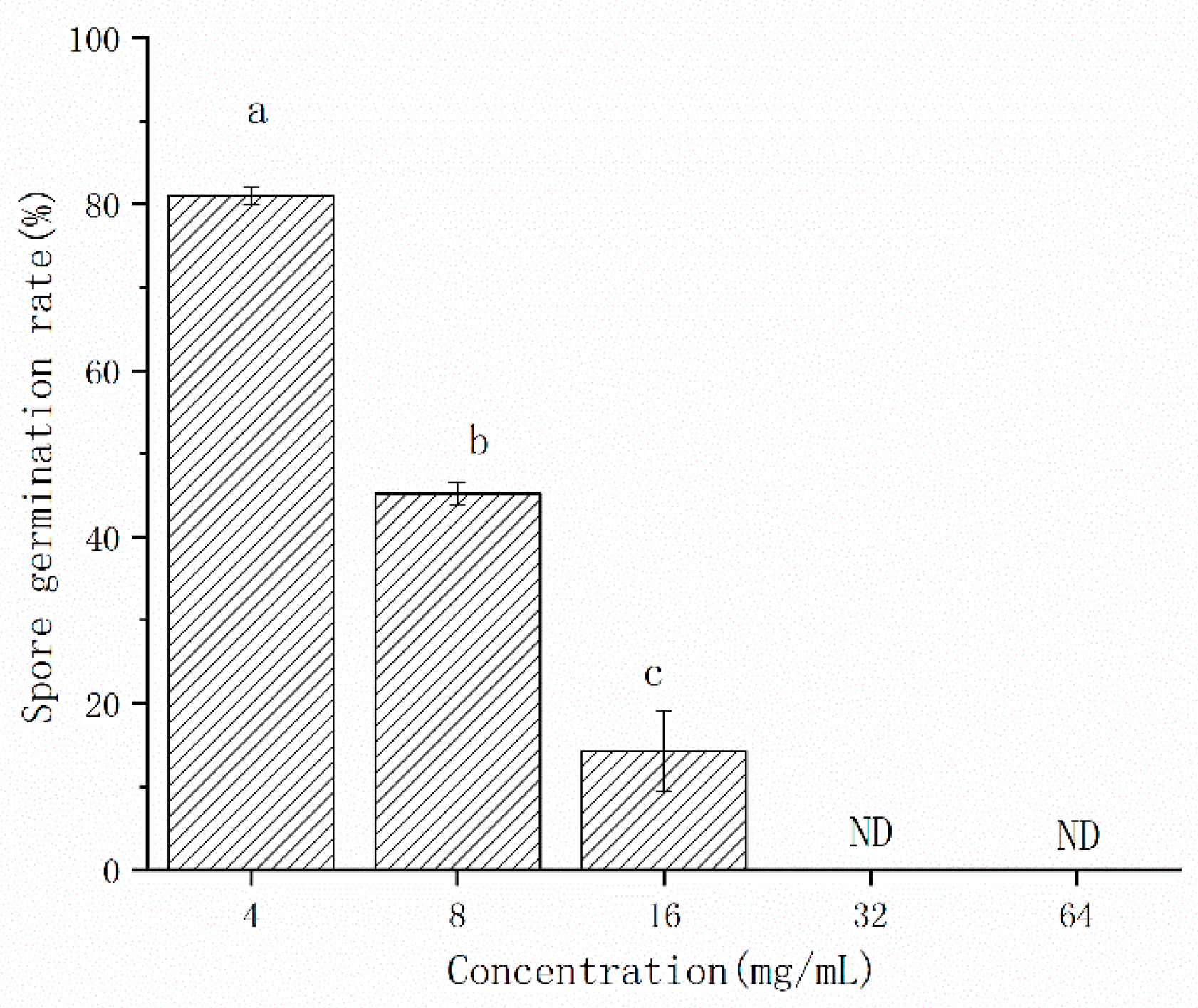
In order to evaluate the antifungal concentration, the CFS was used after freeze-drying. The CFS of L. pentosus 86 inhibited the spore germination of A. gaisen (Figure 3). The inhibitory efficacy on spore germination was positively correlated with concentration. When the concentration of CFS ranged from 4 mg/mL to 16 mg/mL, the spore germination rate decreased from 81.06% to 14.32%, although spore germination was not detected at 32 mg/mL and 64 mg/mL, indicating that the spore germination was completely inhibited.
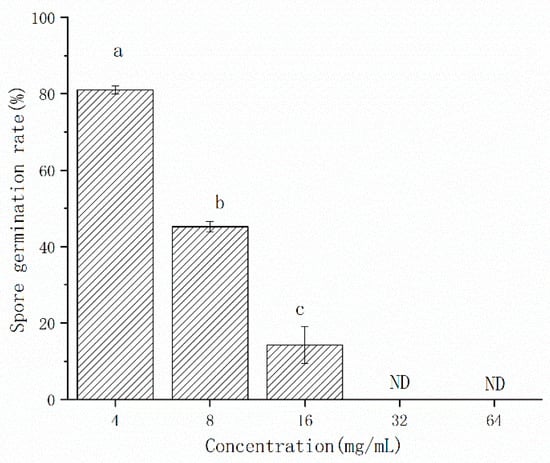
Figure 3.
The effect of CFS concentrations on the germination rate of A. gaisen spores. ND means that spore germination was not detected. Different letters above bars indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
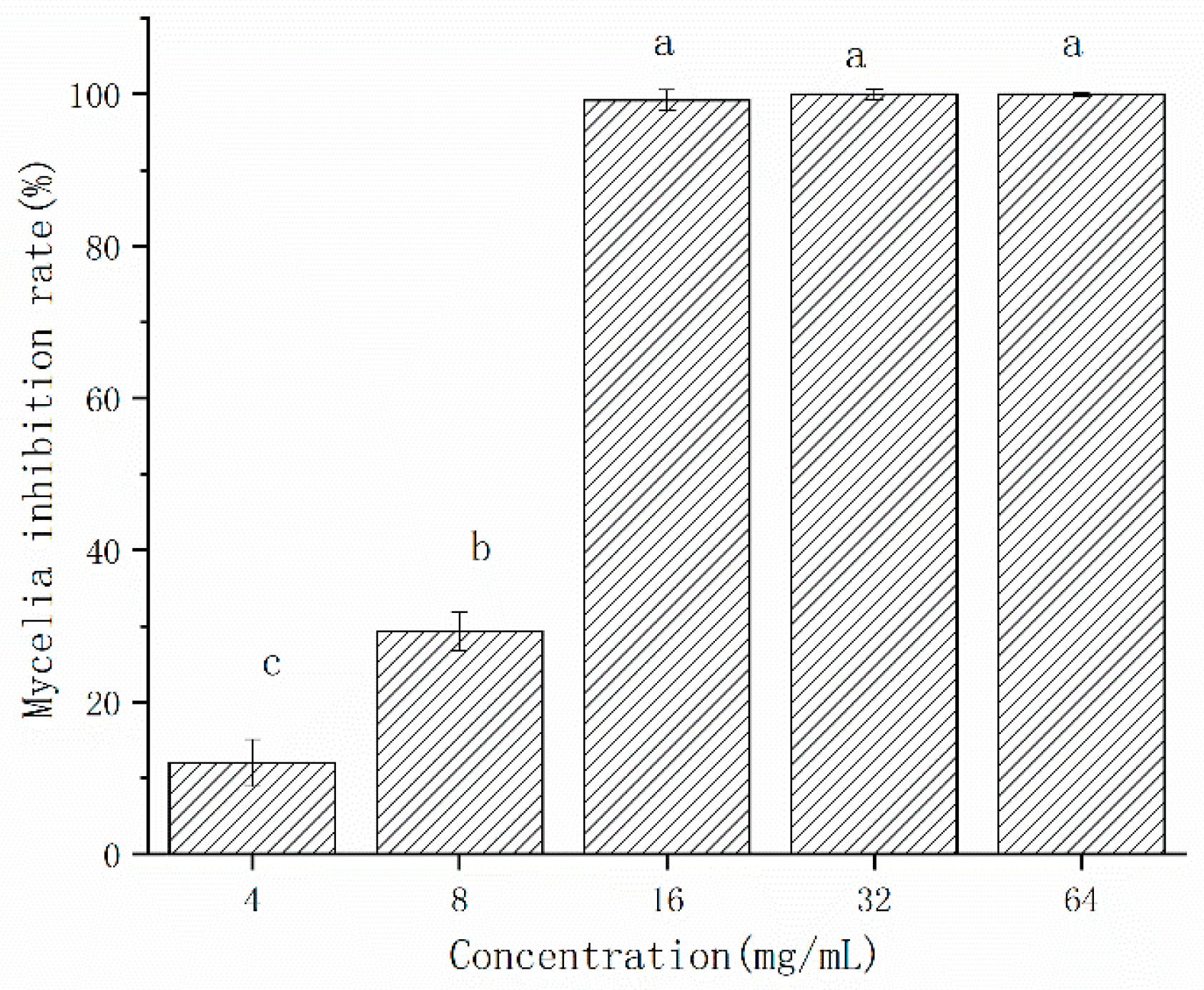
The inhibition effect of CFS on the mycelial growth of A. gaisen was shown in Figure 4. The mycelial inhibition rate by freeze-dried CFS was 12.01% and 29.34% at the concentration of 4 and 8 mg/L, respectively (Figure 4). The mycelial growth of A. gaisen was completely inhibited by CFS at 16 mg/L, indicating that this concentration reached the minimum inhibition concentration. When the concentration ranged from 16 to 64 mg/L, the mycelia inhibition rate was maintained at 100%. Therefore, the inhibitory efficacy of CFS on the mycelial growth of A. gaisen depended on concentration until a minimum inhibition concentration was reached.
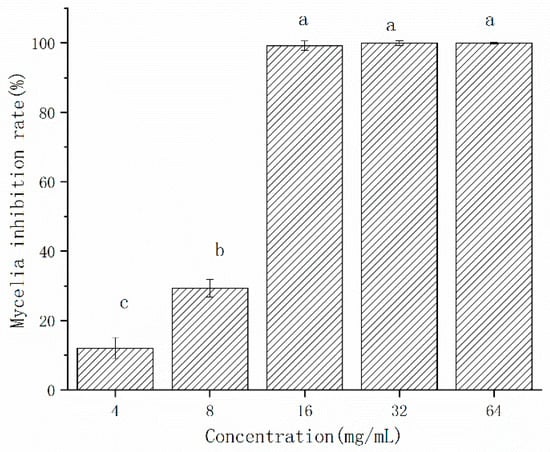
Figure 4.
Mycelial growth of A. gaisen treated by different concentration of CFS. Different letters above bars indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
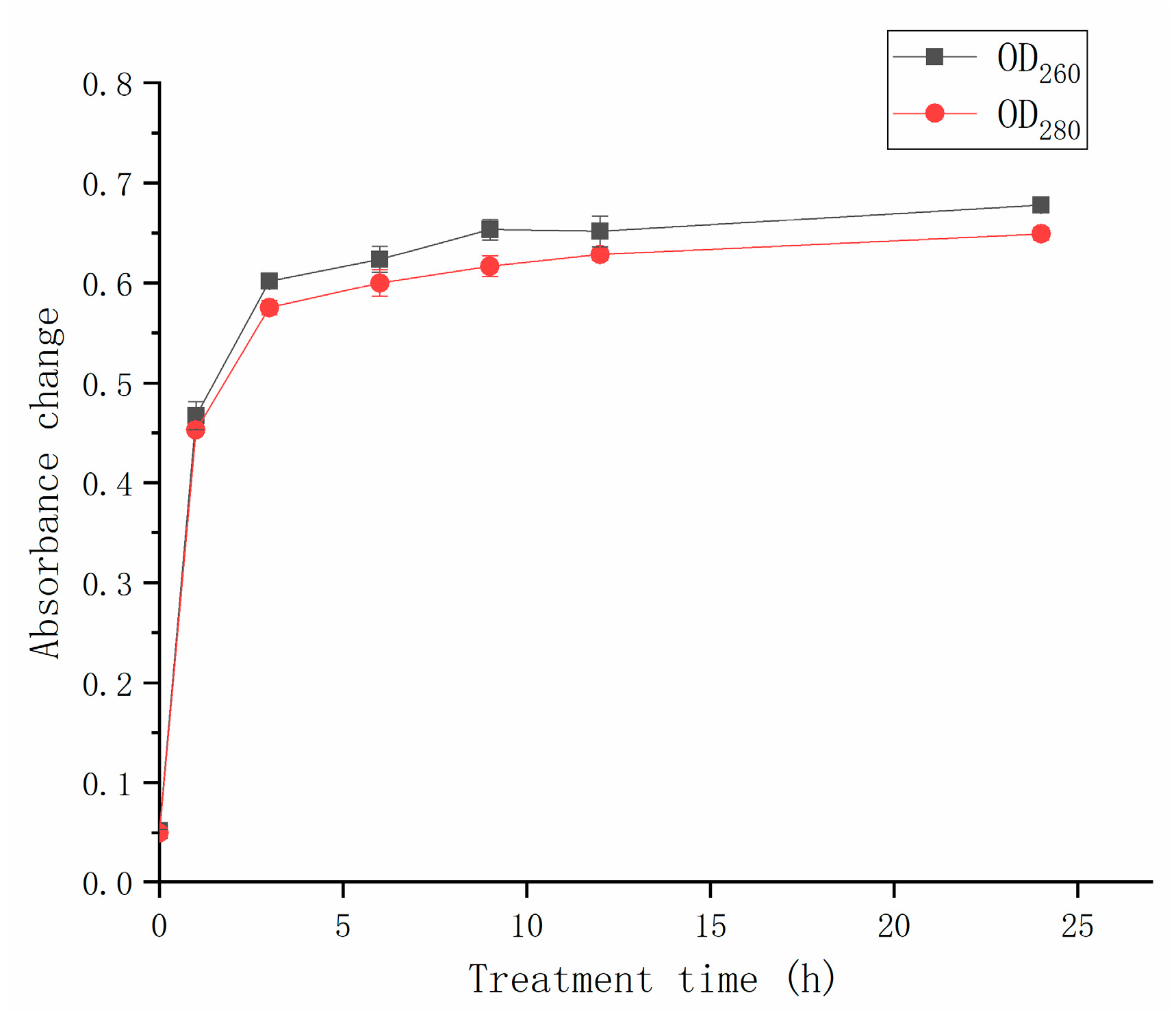
The leakage of intracellular substances, including nucleic acids and proteins, was observed after the CFS treatment (Figure 5). The increase in OD260 and OD280, respectively, represented the leakage of nucleic acids and proteins. After 1 h of CFS treatment, the absorbances at 260 nm and 280 nm reached 0.47 and 0.45, respectively. When treatment time ranged from 3 h to 24 h, the absorbances at 260 nm and 280 nm were around 0.60. The values did not change significantly (p > 0.05) as the treatment time increased. The nucleic acid and protein releases were associated with cell membrane permeability. The increase in OD260 and OD280 was due to the fact that cell membrane damage occurred. The protein concentration and nucleic acid content increased conspicuously depending on CFS treatment time, indicating that more severe damage to the cell membrane. After 5 h of treatment, the absorbance no longer increased, suggesting that the hyphal membrane of A. gaisen was completely destroyed.
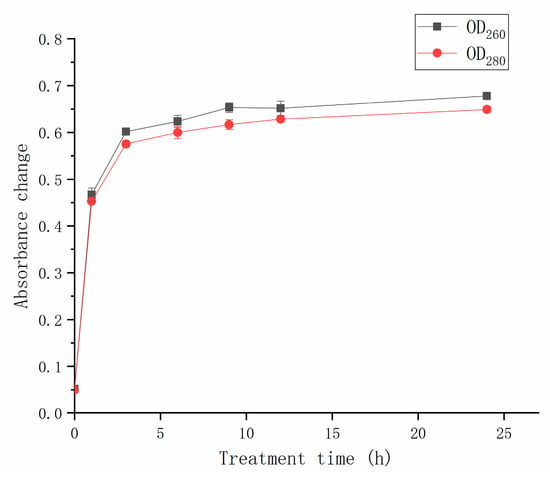
Figure 5.
Effect of CFS on the cell leakage of A. gaisen.
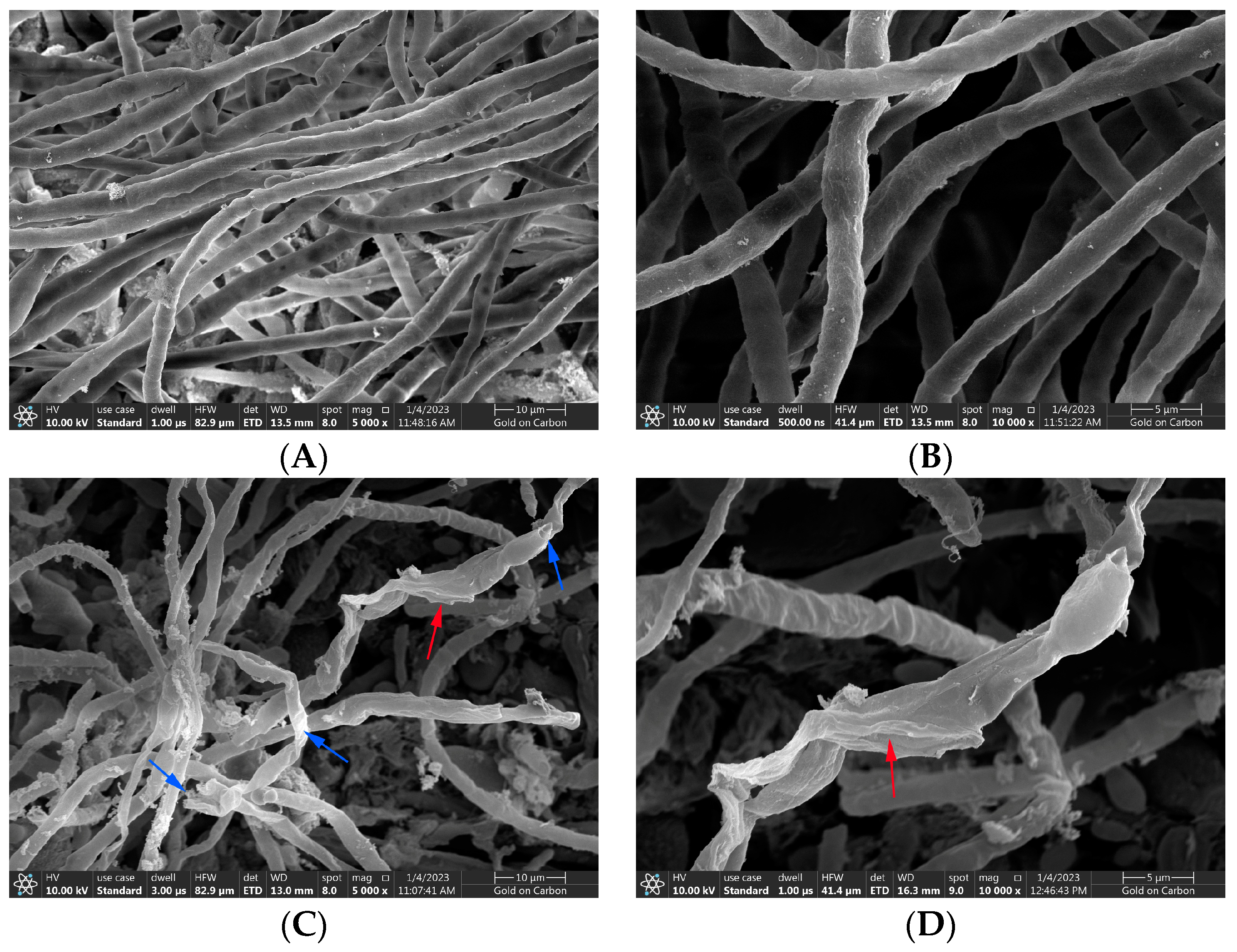
The normal hyphal and spore morphology and the integrity of cell structure are necessary for the growth and pathogenicity of A. gaisen. Figure 6A,B were SEM micrographs of normal morphological hyphae. The SEM micrographs showed that A. gaisen without CFS treatment exhibited ordinary status with a smooth and regular surface, and uniform size and distribution. The area around the mycelium was very clean. There was little attached substance. Figure 6C,D showed the effect of CFS treatment on the hyphal morphology of A. gaisen. After CFS treatment, most damaged hyphae revealed fractures or dents (blue arrows), whereas collapsed and shriveled hyphae were left (red arrows). There are a lot of attached substances around the hyphae, which may be the leakage of cell contents. Therefore, mycelial damage and breakage may be responsible for the mycelia inhibition effect of CFS.
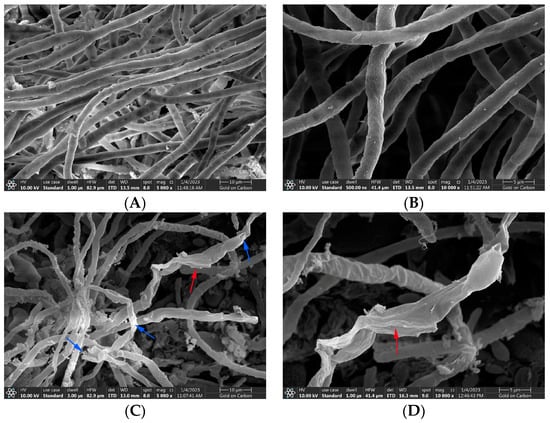
Figure 6.
The hyphael morphology of A. gaisen before (A,B) and after (C,D) CFS treatment. Arrows: damaged hyphae. 10,000 in figure. Blue arrows indicated damaged hyphae; red arrows indicated collapsed hyphae.
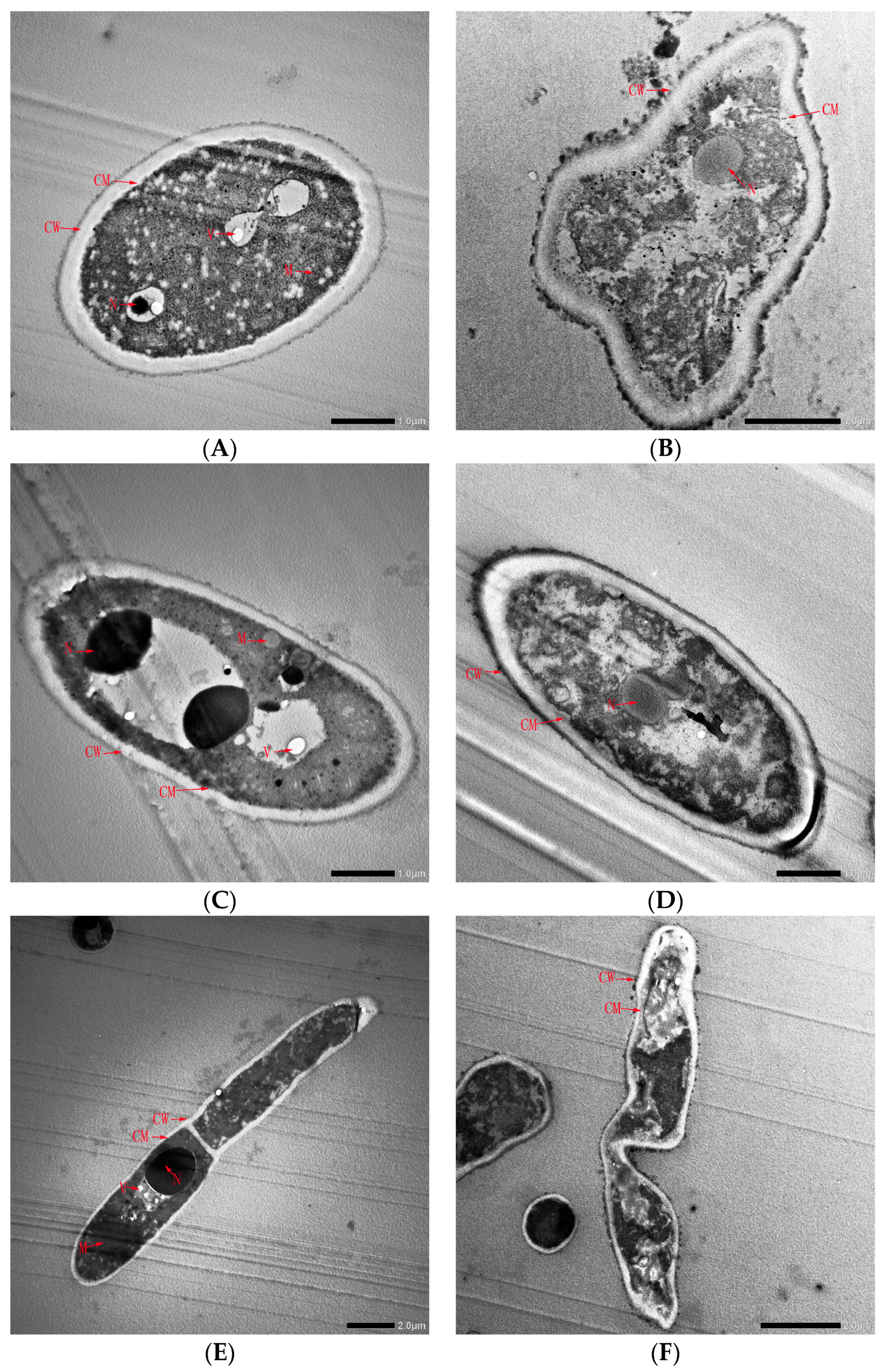
To further understand the inhibitory effect of CFS on spore germination, spore morphology before and after CFS treatment was observed by TEM (Figure 7). Before CFS treatment, the cell wall and membrane of the A. gaisen spore were intact and exhibited a smooth surface (Figure 7A). The intracellular matrix was well defined and uniform. All the cellular organelles, especially the cell nucleus and vacuole, were intact and visibly arranged appropriately. This division of the nucleus in the spore was clearly observed (Figure 7C). A. gaisen sporulates and the spores germinate normally (Figure 7E). After CFS treatment, deformation of conidia was observed. The cell surface was not smooth and attached substances appeared (Figure 7B). This result indicated that cell walls and membranes were damaged, resulting in the leak of intracellular contents. Cellular organelles, such as the nucleus, mitochondrion, and vacuole, were unclearly visible and abnormally aggregated (Figure 7D). These spores germinated poorly with distortion and shriveled morphology (Figure 7F). Therefore, the spore germination inhibition effect of CFS was due to the shape deformation, the destruction and leakage of cell contents.
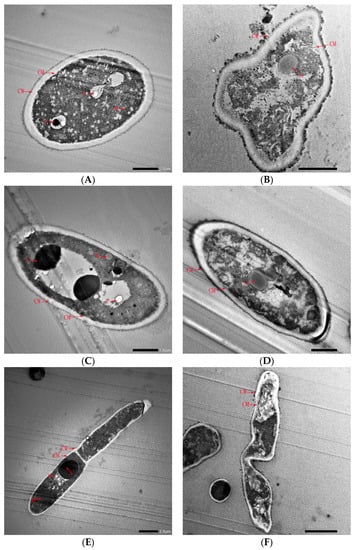
Figure 7.
Transmission electron microscopy of A. gaisen spore before (A,C,E) and after (B,D,F) CFS treatment. Abbreviations: CM, cell wall; CW, cell membrane; M, mitochondria; N, nucleus; V, vacuole.
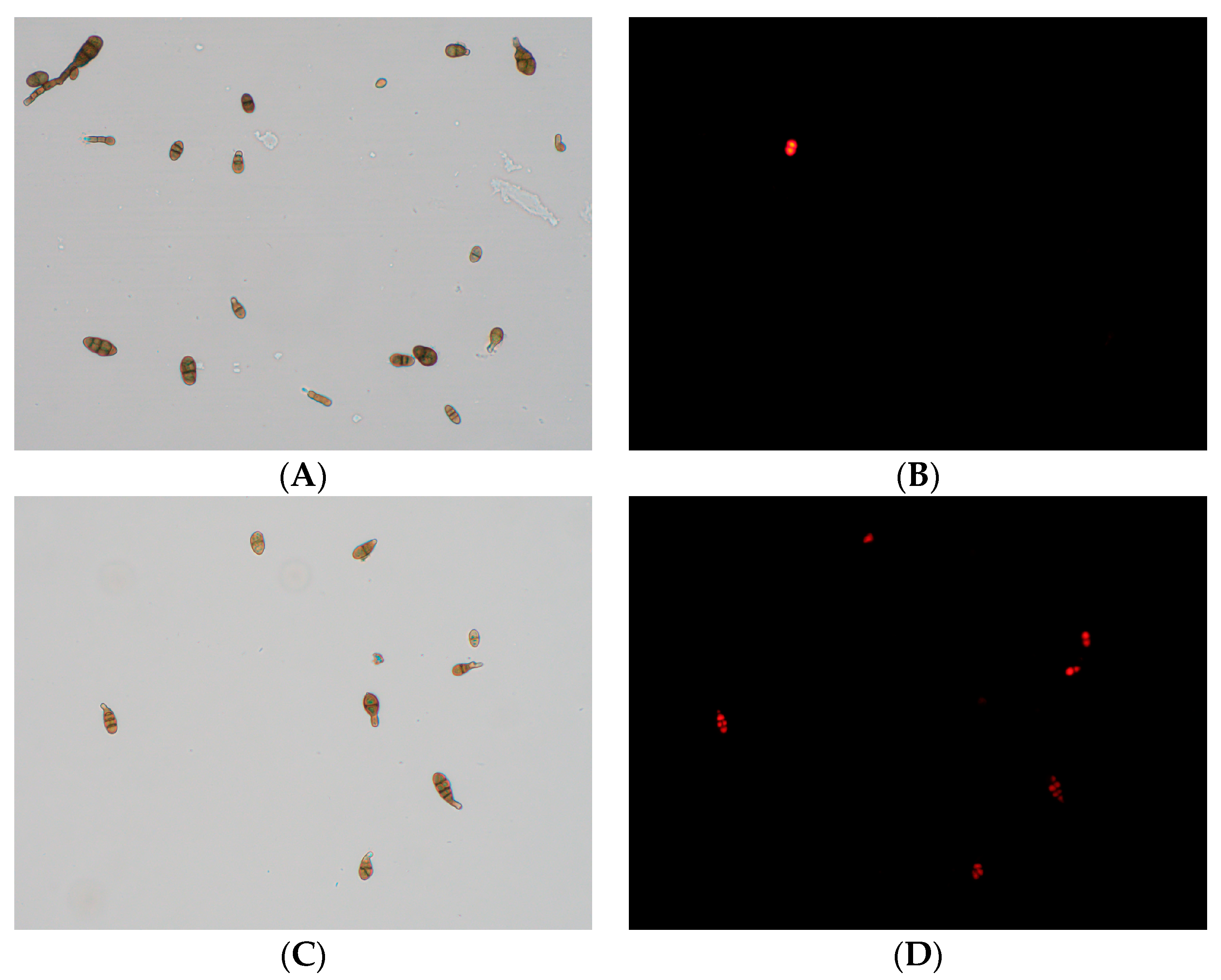
The adverse effects of CFS on the cell membrane of A. gaisen spores were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy using PI staining (Figure 8). In the untreated spores, no fluorescence was observed and these spores grew well (Figure 8A,B). In contrast, after CFS treatment, an evident enhancement in fluorescence intensity was observed (Figure 8C,D). The increasing fluorescence intensity indicated that the cell membranes were damaged, resulting in the entry of the dye.
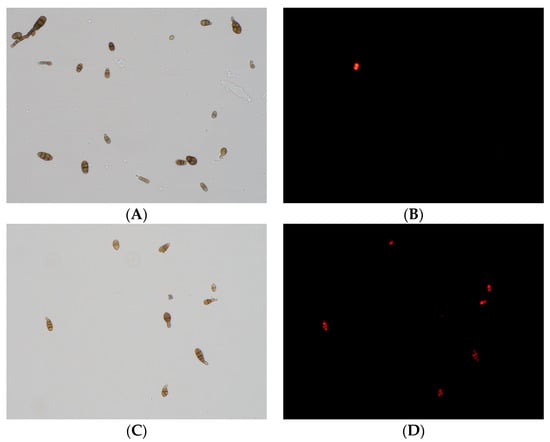
Figure 8.
Effect of CFS treatment on cell membrane permeability of A. gaisen spores (×400 magnification). Untreated (A,B) and treated (C,D) A. gaisen spores.
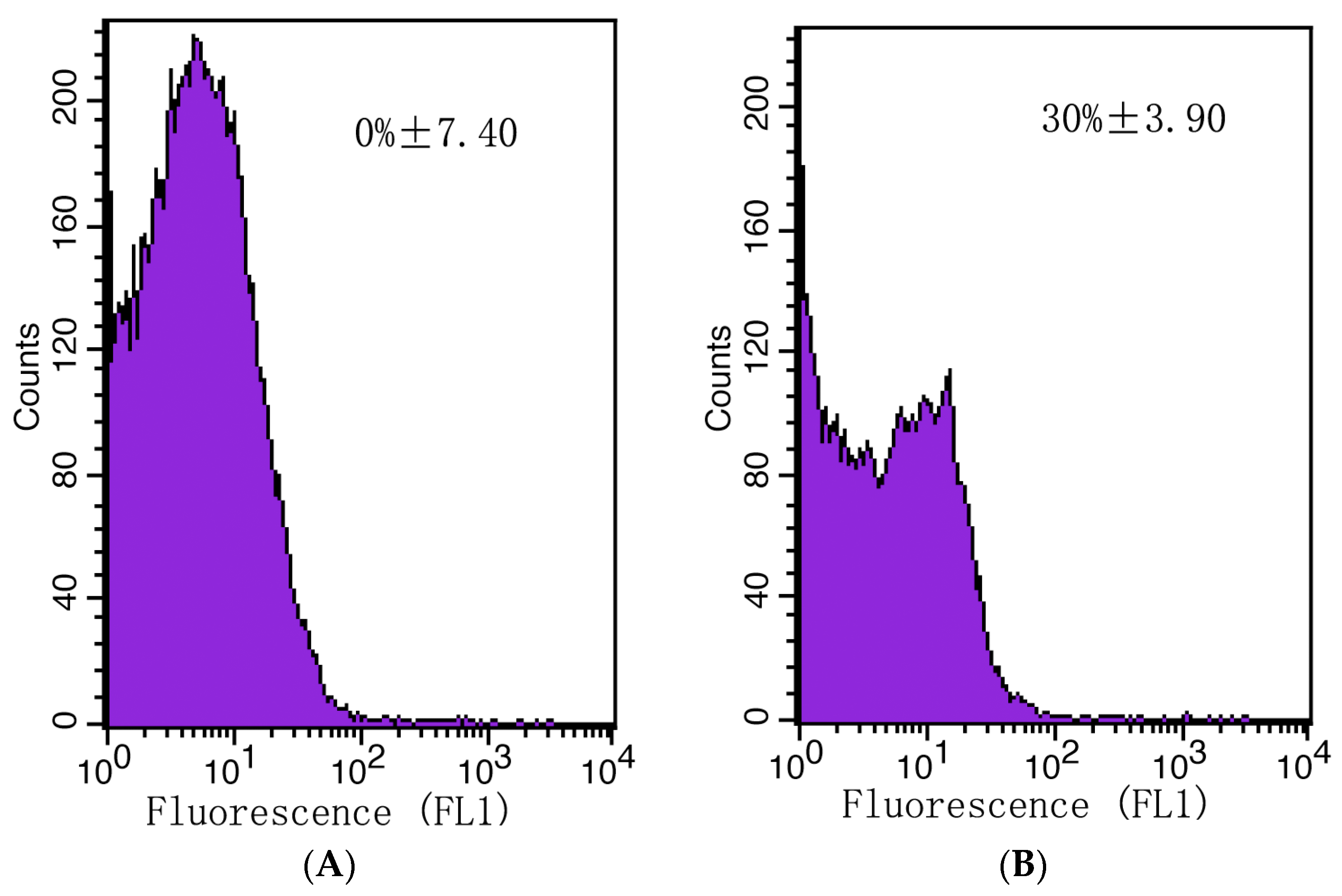
The plasma membrane integrity of A. gaisen spores was evaluated with a flow cytometer (Figure 9). Initially, no dead cells were detected (Figure 9A). After CFS treatment, the counts of live cells were reduced by 30% (Figure 9B). This result illustrated that CFS destroyed the integrity of cell membranes and regulated cell death.
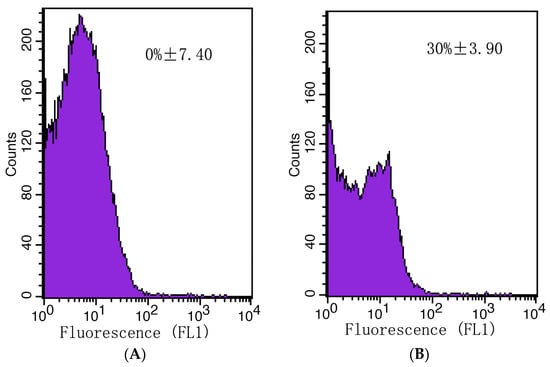
Figure 9.
The mortality rate of A. gaisen spores calculated by flow cytometry analysis. Untreated (A) or treated (B) A. gaisen spores with CFS.
4. Discussion
In the present study, the antifungal activity of CFS from L. pentosus 86 decreased after a long period of incubation. This result corresponded with previous studies, which reported that the inhibitory activities of CFS from probiotics culture became less effective when it had continued for a long period of incubation time [19,20]. This phenomenon is due to the fact that the production and consumption of metabolites is related to the microbial growth stage [21]. In this study, L. pentosus 86 was cultured in an MRS medium at 37 °C, under which the growth rate was high. The incubation period of 84 h was enough for L. pentosus 86 to enter the decay stage, resulting in antimicrobial metabolite consumption. Yang et al. reported that the bacteriocin production of LAB is affected by culture media, initial pH, and culture temperature [22]. Therefore, in order to improve the antifungal activity of CFS, the incubation temperature, pH, and culture medium of L. pentosus 86 can be optimized in later studies. Moreover, chemical modifications and delivery systems can be used to enhance the activity and biocompatibility of LAB metabolites [23].
The present study indicated that the CFS of L. pentosus 86 displayed excellent thermostability and enzymatic stabilities, and was stable in an acidic environment. Antimicrobial activities of the CFS obtained from LAB were resistant to diverse temperature intervals, which is due to their low molecular weight and chemically diverse secondary structures [24]. For example, Lee et al. reported that the CFS of Ligilactobacillus animalis was only stable at temperatures between 40 and 60 °C, and sensitive to Trypsin [15]. Due to the high thermostability, the CFS of L. pentosus 86 has a wide range of application potential in high-temperature processes, especially pasteurization of foods.
Protease treatment is effective for protein or peptide substances. If the antimicrobial activity is due to proteinaceous compounds, it will be removed after protease treatment [10]. The antifungal activity of L. pentosus 86 CFS was slightly inactivated and retained after being treated with four proteases, suggesting that the main bacteriostatic substances in the CFS may not be protein-based metabolites. Besides bacteriocin classified as a proteinaceous compound, Lactobacillus spp. also produces other antimicrobial substances with thermal and chemical stability, such as organic acids, fatty acids, methyl ester, etc. [8,21,25,26,27]. In this study, the CFS of L. pentosus 86 demonstrates poor effect in alkaline as well as neutral pH, which may be due to the dissociation of organic acids. Therefore, acid–base conditions of food should be considered for the use of the CFS of L. pentosus 86 as a biopreservative. In order to solve the poor alkali tolerance, CFSs can be loaded with nanoparticles to enhance their antimicrobial activities and stability [28]. Some CFSs obtained from LAB have good stability and can be stored for 1 to 5 months at temperatures ranging from 4 °C to 35 °C [10]. However, previous studies have also shown that CFSs from different LAB exhibited high thermal stability, but their enzyme and acid stability differ greatly [10,15,29]. In order to clarify the application scope of CFS of L. pentosus 86, the antimicrobial components in CFS and the factors affecting their stability should be studied in the future.
The present study indicated that the inhibition effects on mycelial growth and spore germination were due to the cell membrane damage by CFS of L. pentosus 86. Zhao et al. indicated that the leakage of intracellular substances was due to the hyphae membrane peroxidation damage [30]. The appearance of population shifts in the flow cytometric dot-plots was due to the cells’ lost membrane integrity and increased membrane permeability [31]. Previous studies also found that antimicrobial substances of CFS obtained from LAB target the cell membranes of pathogenic microorganisms, resulting in morphological changes, collapse of conidial surface structures, and disruption of membranes [32]. Alteration of cell membrane permeability is one of the principal antimicrobial mechanisms of LAB. This mode of action has been reported in various Lactobacillus strains, such as L. rhamnosus and L. caseietc [18,33].
LAB are generally recognized as safe bacteria in foods and play an important role in food preservation. The differences in their antimicrobial functions and action modes were caused by the great diversity of chemical structures of metabolites from different LAB strains. Huang et al. reported that acetic acid and lactic acid produced by Lactobacillus sp. showed a strong ability to dissipate the membrane potential of bacterial cells and affect the ATP synthesis [29]. He et al. reported that antimicrobial peptides produced by Lactobacillus sp. caused cell death by damaging the phospholipid membrane [33]. Xu et al. found that bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus sp. exerted its antimicrobial activity by forming pores on the surface of the cell membrane, increasing the permeability of the cell membrane, and dissipating the cytoplasmic membrane potential and transmembrane pH gradient [34]. Most CFS of LAB showed both antifungal and antimicrobial activities given their great potential as biopreservatives.
The action mechanisms of LAB are associated with the production of organic acids, antifungal peptides, hydrogen peroxide, diacetyl, and other antifungal compounds [9]. This study shows that the CFS of L. pentosus 86 can both cause cell membrane damage and inhibit spore germination. Its antifungal activity may be related to peptides, fatty acids, and organic acids. Antifungal peptides obtained from LAB could reduce gene expression levels involved in fungal meristem [35]. Fatty acids can insert into the lipid bilayers of fungal membranes and increase the membrane permeability, resulting in an uncontrolled release of intracellular electrolytes and proteins [36]. Organic acids can traverse the cell membrane, and dissociate in the cytoplasm, resulting in acid stress [37]. Although this study confirmed that CFS showed an inhibitory effect on the mycelial growth and spore germination of A. gaisen, its effect in vivo and antimicrobial substance is still unclear. Therefore, in the later study, the antimicrobial substance and the preservation effect of L. pentosus 86 CFS can be studied in vivo on various fruits which often contaminated with A. gaisen, such as pears, cantaloupe, peaches, etc.
5. Conclusions
Biopreservation is an important field in the food industry. Most LAB strains are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) microorganisms, and their metabolic products have a wide range of applications in the food industry. The present study evaluated the antifungal effect of the CFS from L. pentosus 86 against A. gaisen, and found that the CFS of L. pentosus 86 was stable under thermal and protease treatments. Moreover, the CFS was able to compromise the integrity of cell membranes of both hyphal and spore, resulting in complete inhibition of hyphal growth and spore germination. Given the excellent antifungal activity, L. pentosus 86 and its metabolites would have a promising application as a biopreservative in fruit in place of chemical preservatives. Further research can be conducted on the detection of the antimicrobial metabolites of L. pentosus 86 and its application in vivo on various fruits.
Author Contributions
Investigation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft, H.L.; conceptualization, resources, data curation, R.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Z.; writing—review and editing, M.T. and X.R.; formal analysis, L.W.; supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Project of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, grant number 2015AG003.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nan, M.; Xue, H.; Bi, Y. Contamination, Detection and Control of Mycotoxins in Fruits and Vegetables. Toxins 2022, 14, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xing, M.; Chen, T.; Tian, S.; Li, B. Effects and Mechanisms of Plant Bioactive Compounds in Preventing Fungal Spoilage and Mycotoxin Contamination in Postharvest Fruits: A Review. Food Chem. 2023, 415, 135787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patriarca, A. Alternaria in Food Products. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacha, S.; Li, Y.; Nie, J.; Xu, G.; Han, L.; Farooq, S. Comprehensive Review on Patulin and Alternaria Toxins in Fruit and Derived Products. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1139757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaro, D.; Droby, S. Development of Biocontrol Products for Postharvest Diseases of Fruit: The Importance of Elucidating the Mechanisms of Action of Yeast Antagonists. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 47, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukare, A.S.; Paul, S.; Nambi, V.E.; Gupta, R.K.; Singh, R.; Sharma, K.; Vishwakarma, R.K. Exploitation of Microbial Antagonists for the Control of Postharvest Diseases of Fruits: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1498–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usall, J.; Torres, R.; Teixidó, N. Biological Control of Postharvest Diseases on Fruit: A Suitable Alternative? Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 11, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, S.; Mahony, J.; van Sinderen, D. Current Perspectives on Antifungal Lactic Acid Bacteria as Natural Bio-Preservatives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Xu, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Ao, X.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Hu, K.; Yang, Y.; et al. Antifungal Mechanisms and Application of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Bakery Products: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 924398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani-López, E.; Arrioja-Bretón, D.; López-Malo, A. The Impacts of Antimicrobial and Antifungal Activity of Cell-Free Supernatants from Lactic Acid Bacteria in Vitro and Foods. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 604–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Taheur, F.; Mansour, C.; Kouidhi, B.; Chaieb, K. Use of Lactic Acid Bacteria for the Inhibition of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus Carbonarius Growth and Mycotoxin Production. Toxicon 2019, 166, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xie, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, R. Identification of the Alternaria and Screening of the Lactic Acid Bacteria against Alternaria in South Xinjiang. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2017, 38, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Tuo, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, N. Isolation, Identification and Detection of the Ability of Biofilm Formation of the Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Yogurt and Yogurt Lump with Xinjiang Ethnic Characteristics. J. Tarim Univ. 2014, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Iorizzo, M.; Ganassi, S.; Albanese, G.; Letizia, F.; Testa, B.; Tedino, C.; Petrarca, S.; Mutinelli, F.; Mazzeo, A.; De Cristofaro, A. Antimicrobial Activity from Putative Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria for the Biological Control of American and European Foulbrood Diseases. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Park, S.; Choi, I.; Lee, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Ligilactobacillus animalis Swla-1 and its Cell-Free Supernatant Against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and its Potential Use as an Alternative to Antimicrobial Agents. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yuan, S.; Sun, J.; Li, Q.; Jiang, W.; Cao, J. Ethyl P-Coumarate Exerts Antifungal Activity in vitro and in vivo against Fruit Alternaria alternata via Membrane-Targeted Mechanism. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 278, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.; Ghosh, R.; Sengupta, S.; Mandal, N.C. Longterm Storage of Post-Packaged Bread by Controlling Spoilage Pathogens Using Lactobacillus fermentum C14 Isolated from Homemade Curd. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e184020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Pei, J.; Brennan, C.; Abd El-Aty, A.M. Isolation and Characterization of Bacteriocin-Producing Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Xn2 from Yak Yoghurt and its Bacteriocin. Molecules 2022, 27, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeratikunakorn, K.; Kaewchomphunuch, T.; Kaeoket, K.; Ngamwongsatit, N. Antimicrobial Activity of Cell Free Supernatants from Probiotics Inhibits Against Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated from Fresh Boar Semen. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewchomphunuch, T.; Charoenpichitnunt, T.; Thongbaiyai, V.; Ngamwongsatit, N.; Kaeoket, K. Cell-Free Culture Supernatants of Lactobacillus spp. and Pediococcus spp. Inhibit Growth of Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Pigs in Thailand. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehata, M.G.; Badr, A.N.; El Sohaimy, S.A.; Asker, D.; Awad, T.S. Characterization of Antifungal Metabolites Produced by Novel Lactic Acid Bacterium and their Potential Application as Food Biopreservatives. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2019, 64, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Fan, L.; Yan, J.; Jiang, Y.; Doucette, C.; Fillmore, S.; Walker, B. Influence of Culture Media, pH and Temperature on Growth and Bacteriocin Production of Bacteriocinogenic Lactic Acid Bacteria. AMB Express 2018, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashant, K.; Jayachandran, K.; Suzana, S. Antimicrobial Peptides: Diversity, Mechanism of Action and Strategies to Improve the Activity and Biocompatibility In Vivo. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, A.; Aemiro, A. Antibacterial Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Ethiopian Traditional Dairy Products against Food Spoilage and Pathogenic Bacterial Strains. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 9978561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.A.; Paula, A.T.; Casarotti, S.N.; Penna, A.L.B. Lactic Acid Bacteria Antimicrobial Compounds: Characteristics and Applications. Food Eng. Rev. 2012, 4, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalán, Z.; Hudáček, J.; Štětina, J.; Chumchalová, J.; Halász, A. Production of Organic Acids by Lactobacillus Strains in Three Different Media. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 230, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shi, J.; Luo, S.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Molnár, I.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, B. Antimicrobial Substances and Mechanisms of Lactobacillus rhamnosus against Gardnerella Vaginalis. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, O.M.; Al-Gamal, M.S.; Ibrahim, G.A.; Dabiza, N.M.; Salem, S.S.; El-Ssayad, M.F.; Youssef, A.M. Evaluation and Characterization of Some Protective Culture Metabolites in Free and Nano-chitosan-loaded Forms Against Common Aontaminants of Egyptian Cheese. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, M.; Hu, H.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Ni, J.; Zhao, W.; Huang, S.; et al. Biological Degradation of Aflatoxin B1 by Cell-Free Extracts of Bacillus velezensis Dy3108 with Broad Ph Stability and Excellent Thermostability. Toxins 2018, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, K.; Fan, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Miao, M. Cell-free supernatant of Bacillus velezensis Suppresses Mycelial Growth and Reduces Virulence of Botrytis cinerea by Inducing Oxidative stress. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ho, L.; Hobson, P.; Brookes, J. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Copper Sulphate, Chlorine, Potassium Permanganate, Hydrogen Peroxide and Ozone on Cyanobacterial Cell Integrity. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5153–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Lv, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Z. Antifungal Activity and Functional Components of Cell-Free Supernatant from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Lzn01 Inhibit Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum Growth. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2019, 33, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Jin, D.; Luo, X.; Zhang, T. Lhh1, a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide with Anti-Cancer Cell Activity Identified from Lactobacillus casei Hz1. AMB Express 2020, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Fu, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Ma, J.; Jiang, R.; Song, C.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, J. Purification and Antimicrobial Mechanism of a Novel Bacteriocin Produced by Lactobacillus rhamnosus 1.0320. LWT 2021, 137, 110338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, R.; Ruiz, M.; Valero, Y.; Cardenas, C.; Guzman, F.; Vila, M. Exploring Small Cationic Peptides of Different Origin as Potential Antimicrobial Agents in Aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimares, A.; Venncio, A. The Potential of Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives as Antifungal Agents: A Review. Toxins 2022, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Humayun, S.; Park, S.; Oh, H.; Lim, S. Characteristics of Sourdough Bread Fermented with Pediococcus pentosaceus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Its Bio-preservative Effect against Aspergillus flavus. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).