Electrode Blending Simulations Using the Mechanistic Degradation Modes Modeling Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
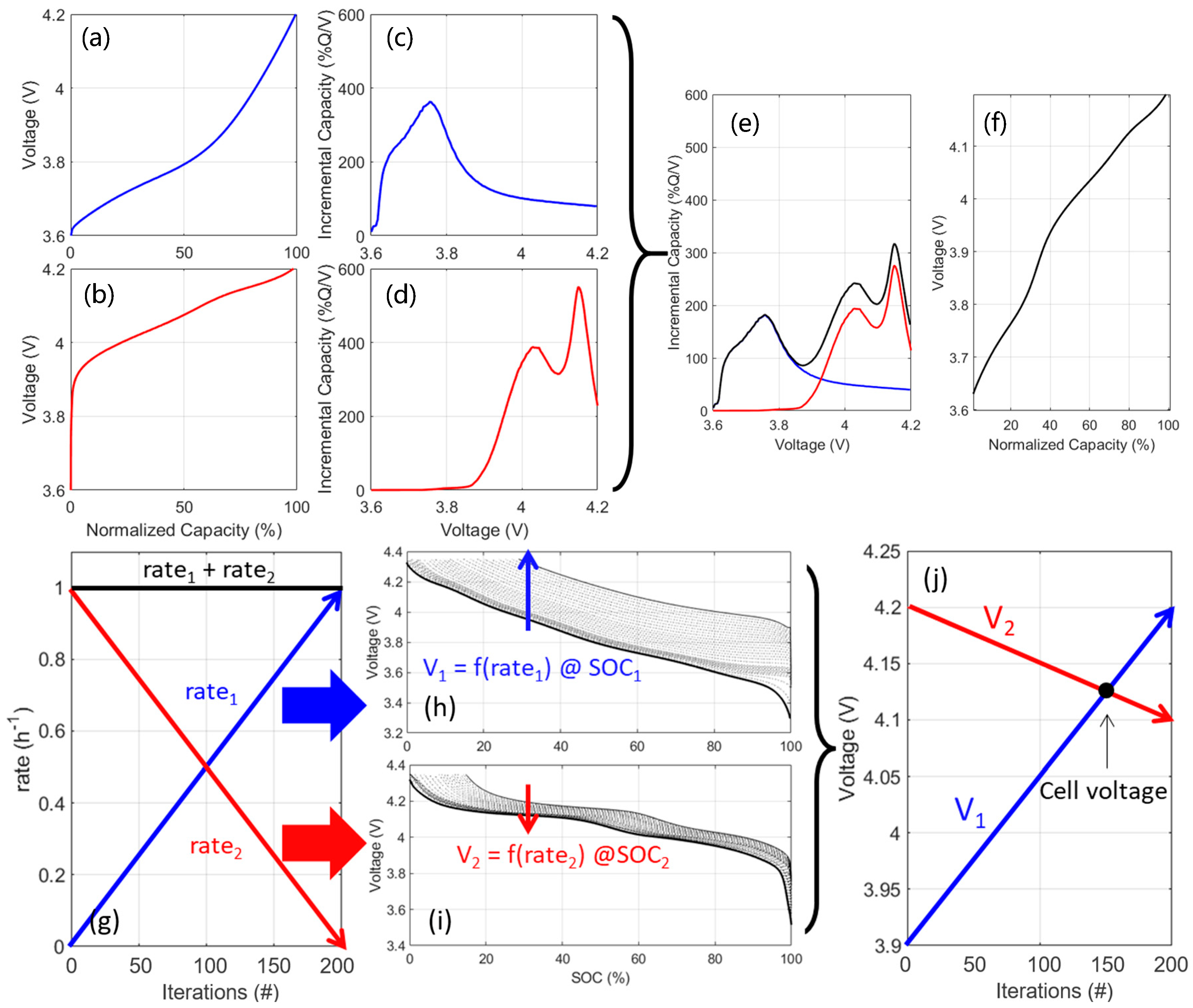
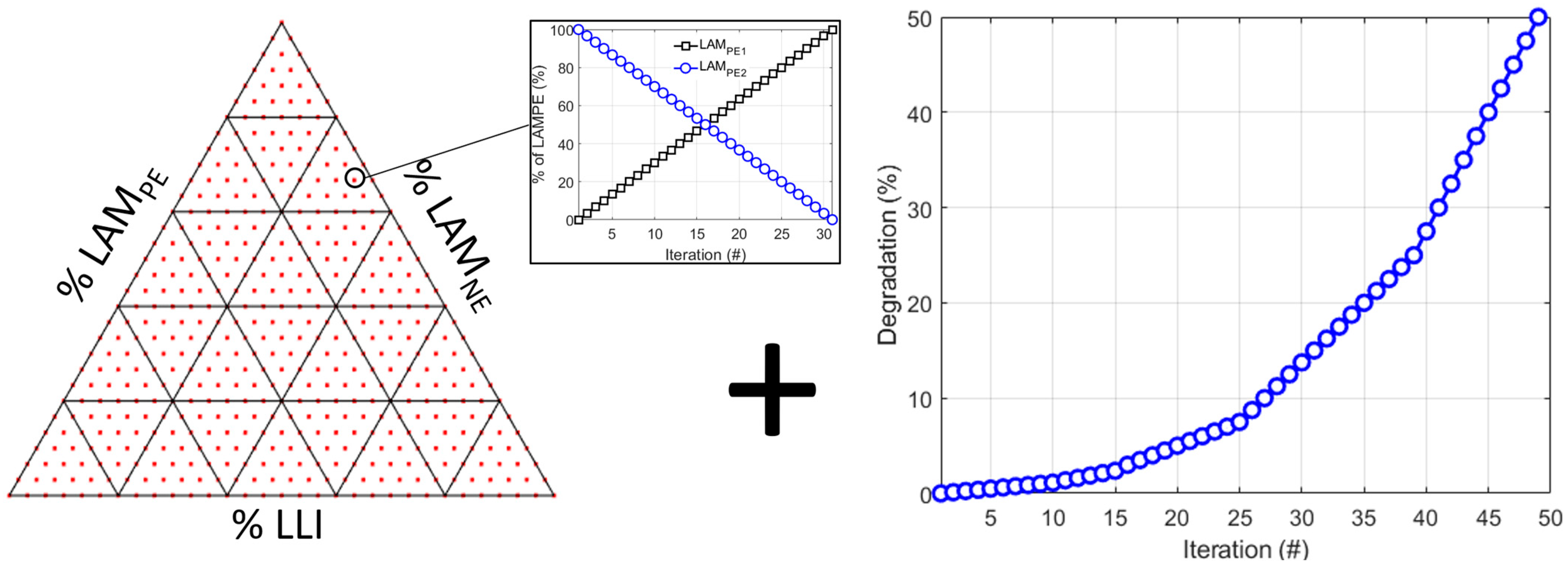
2. Materials and Methods
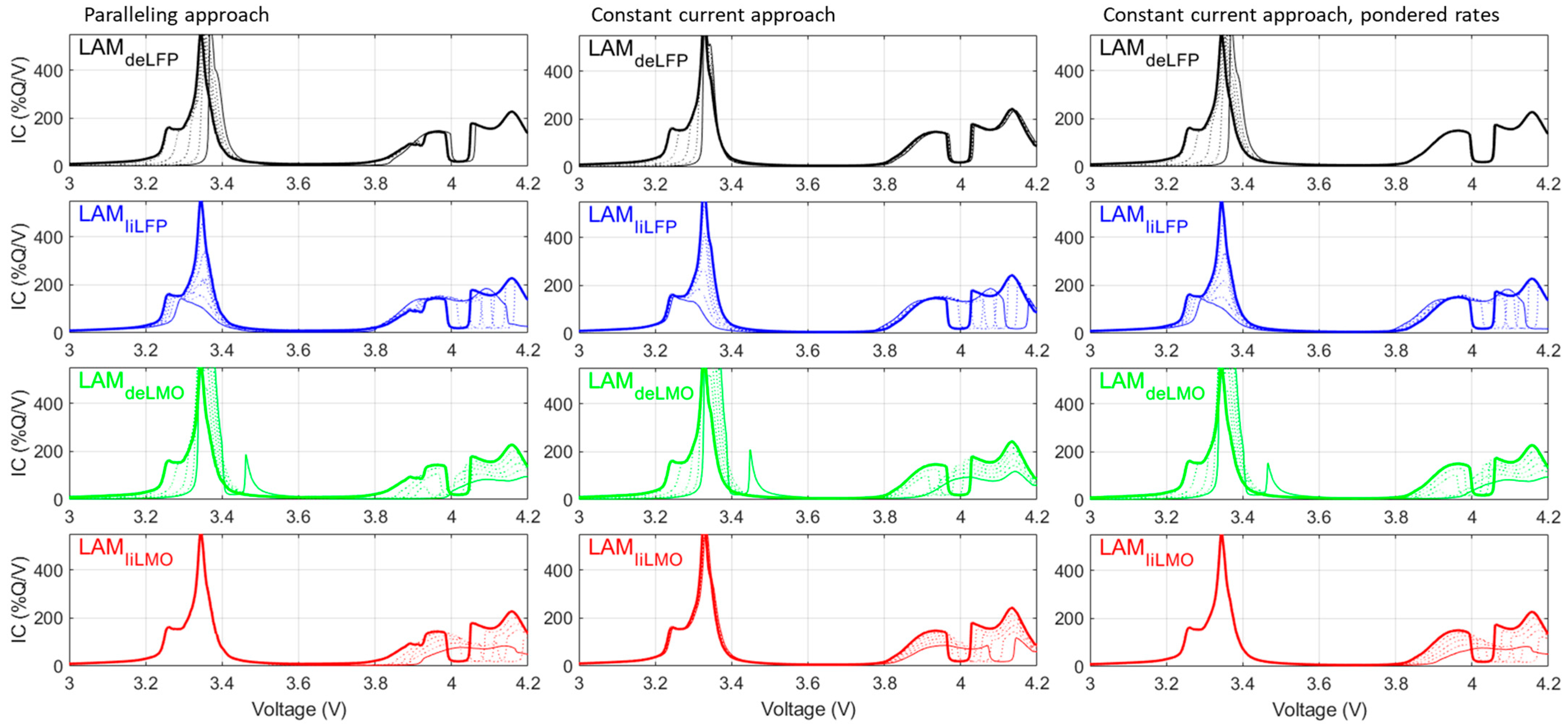
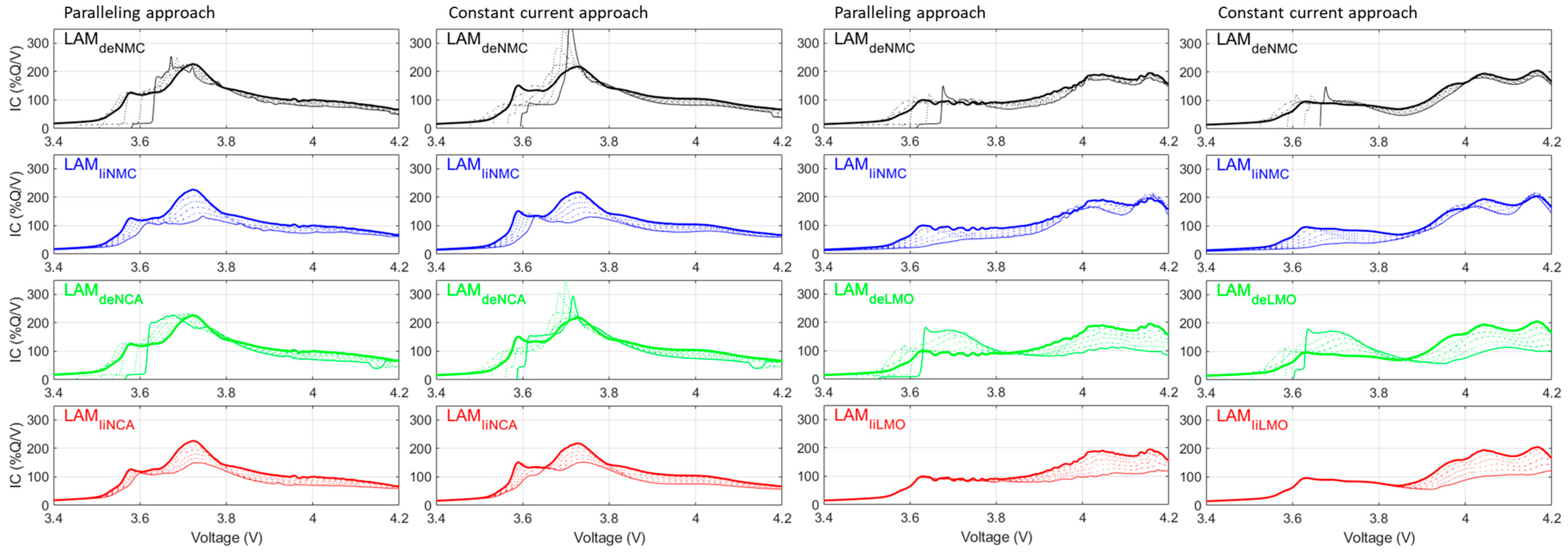
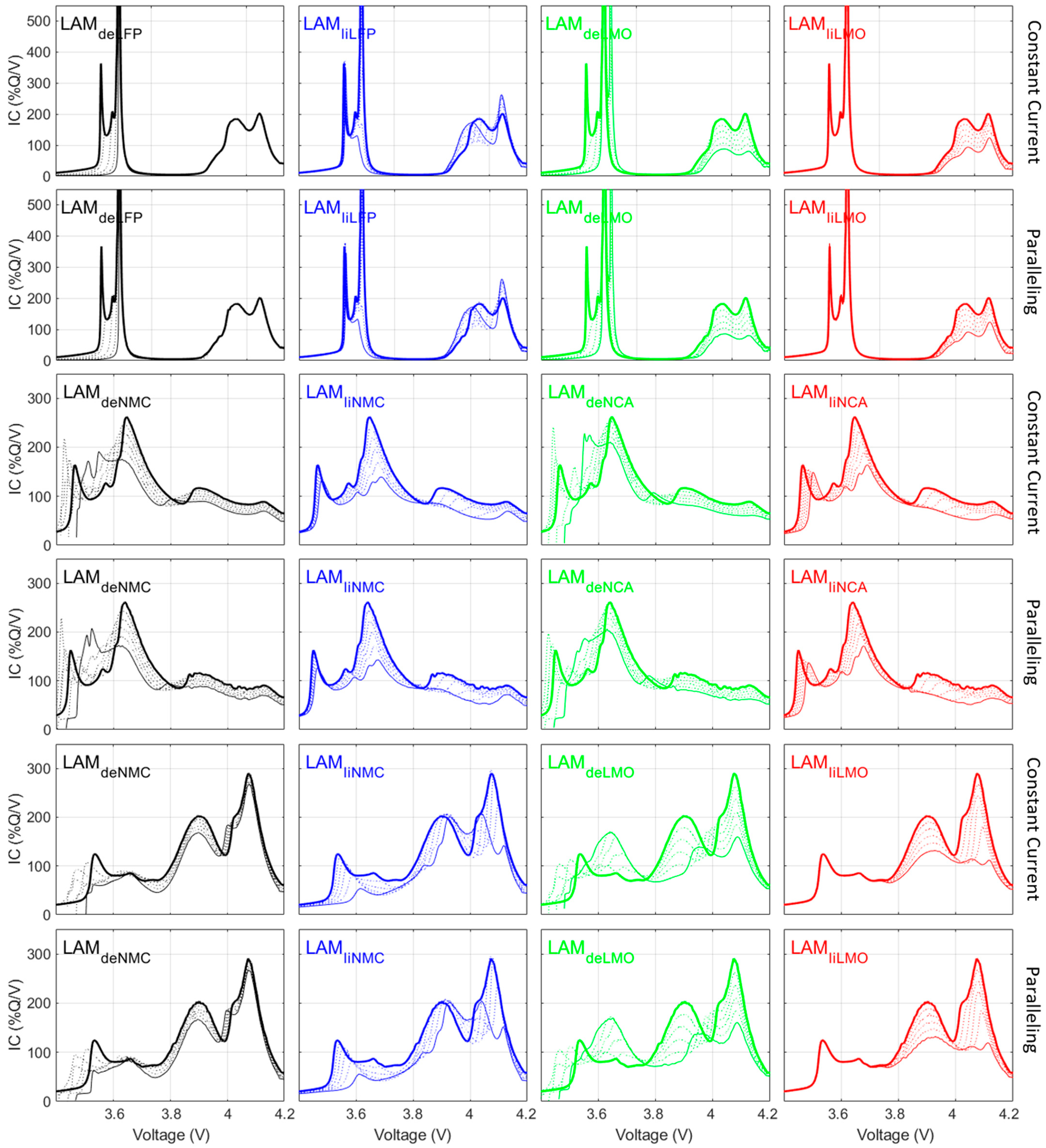
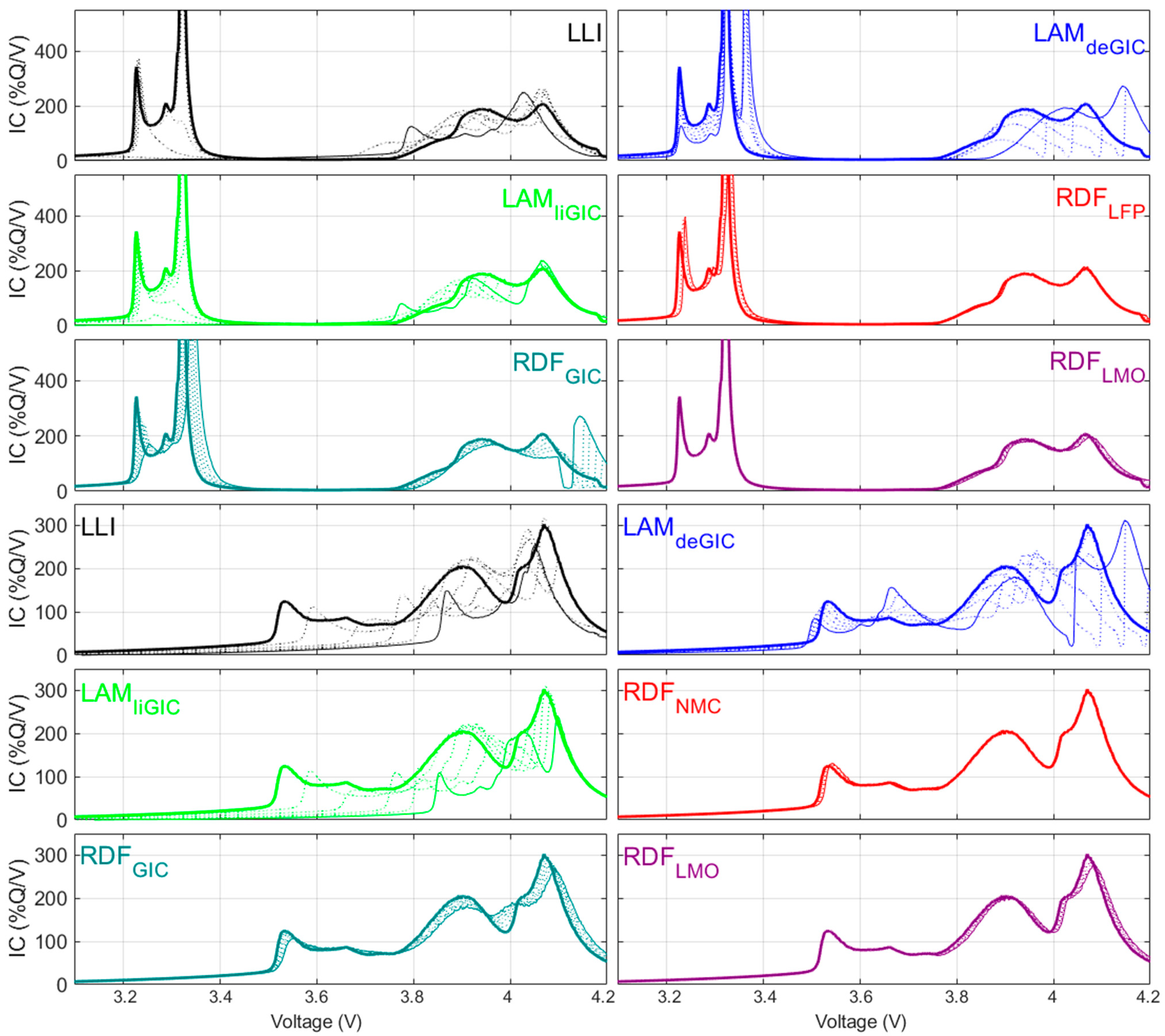
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Heubner, C.; Liebmann, T.; Schneider, M.; Michaelis, A. Recent insights into the electrochemical behavior of blended lithium insertion cathodes: A review. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 269, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotal, M.; Jakhar, S.; Roy, S.; Sharma, H.K. Cathode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries: Recent progress and future prospects. J. Energy Storage 2022, 47, 103534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuch, R.; Wagner, R.; Hörpel, G.; Placke, T.; Winter, M. Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergus, J.W. Recent developments in cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 939–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Cao, C.; Biesold, G.M.; Sewell, C.D.; Hao, S.M.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Lai, Y.; Lin, Z. Recent Advances in Silicon-Based Electrodes: From Fundamental Research toward Practical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2004577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, J.; Schindler, M.; Jossen, A. Change in the half-cell open-circuit potential curves of silicon–graphite and nickel-rich lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide during cycle aging. J. Power Sources 2021, 506, 230240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.F.; Yang, X.Q.; Liao, X.Z.; Sun, X.; McBreen, J. Electrochemical evaluation of composite cathodes base on blends of LiMn2O4 and LiNi0.8Co0.2O2. Electrochem. Commun. 2001, 3, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, T.; Amemiya, C.; Kumeuchi, T.; Shirakata, M.; Yonezawa, M. Advantages of blending LiNi0.8Co0.2O2 into Li1+xMn2−xO4 cathodes. J. Power Sources 2001, 97–98, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikkannanavar, S.B.; Bernardi, D.M.; Liu, L. A review of blended cathode materials for use in Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.-W.; Yoon, W.-S.; Shin, H.; Chung, K.Y.; Choi, S.; Yang, X.-Q. In situ X-ray diffraction studies of mixed LiMn2O4–LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 composite cathode in Li-ion cells during charge–discharge cycling. J. Power Sources 2009, 192, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.K.; Shin, J.S.; Nahm, K.S.; Kumar, T.P.; Stephan, A.M. Electrochemical studies on cathode blends of LiMn2O4 and Li[Li1/15Ni1/5Co2/5Mn1/3O2]. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 111, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Truchot, C.; Liaw, B.Y.; Gering, K.; Sazhin, S.; Jamison, D.; Michelbacher, C. Evaluation of commercial lithium-ion cells based on composite positive electrode for plug-in hybrid electric vehicle applications. Part II. Degradation mechanism under 2C cycle aging. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 10336–10343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Truchot, C.; Devie, A.; Liaw, B.Y.; Gering, K.; Sazhin, S.; Jamison, D.; Michelbacher, C. Evaluation of Commercial Lithium-Ion Cells Based on Composite Positive Electrode for Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A1787–A1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Smith, S.R.; Byrne, T.; Burns, J.C.; Dahn, J.R. Synergies in Blended LiMn2O4 and Li[Ni1/3Mn1/3Co1/3]O2 Positive Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A1696–A1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.P.; Tran, H.Y.; Richter, J.; Ivers-Tiffée, E.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. Analysis and prediction of the open circuit potential of lithium-ion cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 239, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.Y.; Täubert, C.; Fleischhammer, M.; Axmann, P.; Küppers, L.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. LiMn2O4 Spinel/LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 Blends as Cathode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, A556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.-S.; Nam, K.-W.; Jang, D.; Chung, K.Y.; Cho, Y.-H.; Choi, S.; Hanson, J.C.; Yang, X.-Q. The kinetic effect on structural behavior of mixed LiMn2O4–LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode materials studied by in situ time-resolved X-ray diffraction technique. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 15, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen-Wiegart, Y.-c.K.; Liu, Z.; Faber, K.T.; Barnett, S.A.; Wang, J. 3D analysis of a LiCoO2–Li(Ni1/3Mn1/3Co1/3)O2 Li-ion battery positive electrode using X-ray nano-tomography. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 28, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiaszny, B.; Ziegler, J.C.; Krauß, E.E.; Schmidt, J.P.; Ivers-Tiffée, E. Electrochemical characterization and post-mortem analysis of aged LiMn2O4–Li(Ni0.5Mn0.3Co0.2)O2/graphite lithium ion batteries. Part I: Cycle aging. J. Power Sources 2014, 251, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.; Wilka, M.; Kasper, M.; Fleischhammer, M.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. Temperature dependent ageing mechanisms in Lithium-ion batteries—A Post-Mortem study. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Miyashiro, H. Lithium migration between blended cathodes of a lithium-ion battery. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 8653–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Kong, D.; Wu, M.; Liu, H. Interaction between LMFP and NCMA and Its Effect on Blending Cathode-Based Cells. Energies 2024, 17, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Axmann, P.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. Origin of the Synergetic Effects of LiFe0.3Mn0.7PO4–Spinel Blends via Dynamic In Situ X-ray Diffraction Measurements. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A1936–A1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieg, J.; Schmid, A.U.; Rau, L.; Gesterkamp, A.; Storch, M.; Spier, B.; Birke, K.P.; Sauer, D.U. Fast-charging capability of lithium-ion cells: Influence of electrode aging and electrolyte consumption. Appl. Energy 2022, 305, 117747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baure, G.; Dubarry, M. Battery durability and reliability under electric utility grid operations: 20-year forecast under different grid applications. J. Energy Storage 2020, 29, 101391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-H.; Lee, P.-H. Storage fading of a commercial 18650 cell comprised with NMC/LMO cathode and graphite anode. J. Power Sources 2017, 349, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baure, G.; Devie, A.; Dubarry, M. Battery Durability and Reliability under Electric Utility Grid Operations: Path Dependence of Battery Degradation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A1991–A2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Keil, P.; Schuster, S.F.; Jossen, A. Impact of Temperature and Discharge Rate on the Aging of a LiCoO2/LiNi 0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 Lithium-Ion Pouch Cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A1438–A1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, N.; Etiemble, A.; Douillard, T.; Dubrunfaut, O.; Tran-Van, P.; Gautier, L.; Franger, S.; Badot, J.-C.; Maire, E.; Lestriez, B. Multiscale Morphological and Electrical Characterization of Charge Transport Limitations to the Power Performance of Positive Electrode Blends for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Verbrugge, M.W.; Liu, P. Composite Titanate–Graphite Negative Electrode for Improved State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, A185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.H.; Goel, V.; Namkoong, M.J.; Wied, M.; Müller, S.; Wood, V.; Sakamoto, J.; Thornton, K.; Dasgupta, N.P. Enabling 6C Fast Charging of Li-Ion Batteries with Graphite/Hard Carbon Hybrid Anodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 11, 2003336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anseán, D.; Baure, G.; González, M.; Cameán, I.; García, A.B.; Dubarry, M. Mechanistic investigation of silicon-graphite/LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 commercial cells for non-intrusive diagnosis and prognosis. J. Power Sources 2020, 459, 227882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.-T.F. Capacity and Coulombic Efficiency Measurements Underestimate the Rate of SEI Growth in Silicon Anodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 080524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, J.; Schindler, M.; Oberbauer, A.; Jossen, A. Determination of degradation modes of lithium-ion batteries considering aging-induced changes in the half-cell open-circuit potential curve of silicon–graphite. J. Power Sources 2022, 532, 231296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertus, P.; Christensen, J.; Newman, J. Experiments on and modeling of positive electrodes with multiple active materials for lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, A606–A618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Truchot, C.; Liaw, B.Y. Synthesize battery degradation modes via a diagnostic and prognostic model. J. Power Sources 2012, 219, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S. Mathematical model of lithium-ion batteries with blended-electrode system. J. Power Sources 2014, 264, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Choe, S.-Y.; Joe, W.T. A reduced order electrochemical and thermal model for a pouch type lithium ion polymer battery with LiNixMnyCo1−x−yO2/LiFePO4 blended cathode. J. Power Sources 2015, 294, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, W.A.; Park, J.; Van Khue, L.; Lee, Y.; Choi, J.; Ryou, M.-H.; Lee, Y.M. Comparative study on experiments and simulation of blended cathode active materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 187, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Yan, L.; Xie, J. Degradation Analysis of a Lithium-Ion Battery with a Blended Electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 164, A295–A303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Farkhondeh, M.; Pritzker, M.; Fowler, M.; Chen, Z. Charge/Discharge Asymmetry in Blended Lithium-Ion Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 164, A39–A47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Farkhondeh, M.; Pritzker, M.; Fowler, M.; Chen, Z. Dynamics of a Blended Lithium-Ion Battery Electrode During Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 222, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Plett, G.L. Controls-oriented models of lithium-ion cells having blend electrodes. Part 2: Physics-based reduced-order models. J. Energy Storage 2017, 11, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, K.P.; Budarapu, P.R. Design and analysis of Lithium-ion pouch cell with LMO-NMC blended cathode using coupled thermo-electro-chemical model. J. Energy Storage 2024, 78, 109958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tredenick, E.C.; Wheeler, S.; Drummond, R.; Sun, Y.; Duncan, S.R.; Grant, P.S. A multilayer Doyle-Fuller-Newman model to optimise the rate performance of bilayer cathodes in Li ion batteries. Res. Sq. 2024. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carelli, S.; Quarti, M.; Yagci, M.C.; Bessler, W.G. Modeling and Experimental Validation of a High-Power Lithium-Ion Pouch Cell with LCO/NCA Blend Cathode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A2990–A3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kawasaki, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shono, K.; Mita, Y.; Miyashiro, H. A method of separating the capacities of layer and spinel compounds in blended cathode. J. Power Sources 2014, 245, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahbaz, A.; Meishner, F.; Li, W.; Ünlübayirl, C.; Uwe Sauer, D. Non-Invasive Identification of Calendar and Cyclic Ageing Mechanisms for Lithium-Titanate-Oxide Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 42, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Kirkaldy, N.; Offer, G.J.; Wu, B. Diagnosing health in composite battery electrodes with explainable deep learning and partial charging data. Energy AI 2024, 16, 100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Svens, P.; Varini, M.; Lindbergh, G.; Lindström, R.W. Expanded in situ aging indicators for lithium-ion batteries with a blended NMC-LMO electrode cycled at sub-ambient temperature. J. Electochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 110530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, W. Capacity Decay Mechanism of the LCO + NMC532/Graphite Cells Combined with Post-Mortem Technique. Energies 2017, 10, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Matsuda, T.; Imamura, D. Degradation diagnosis of lithium-ion batteries with a LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 and LiMn2O4 blended cathode using dV/dQ curve analysis. J. Power Sources 2018, 390, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubner, C.; Liebmann, T.; Lämmel, C.; Schneider, M.; Michaelis, A. Deconvolution of Cyclic Voltammograms for Blended Lithium Insertion Compounds by using a Model-like Blend Electrode. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubner, C.; Liebmann, T.; Lämmel, C.; Schneider, M.; Michaelis, A. Internal dynamics of blended Li-insertion electrodes. J. Energy Storage 2018, 20, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, T.; Heubner, C.; Lämmel, C.; Schneider, M.; Michaelis, A. Investigations on the Effective Electric Loads in Blended Insertion Electrodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 5728–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Beck, D. Perspective on Mechanistic Modeling of Li-Ion Batteries. Acc. Mater. Res. 2022, 3, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Baure, G.; Pastor-Fernández, C.; Yu, T.F.; Widanage, W.D.; Marco, J. Battery energy storage system modeling: A combined comprehensive approach. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Devie, A.; Liaw, B.Y. Cell-balancing currents in parallel strings of a battery system. J. Power Sources 2016, 321, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Berecibar, M.; Devie, A.; Anseán, D.; Omar, N.; Villarreal, I. State of health battery estimator enabling degradation diagnosis: Model and algorithm description. J. Power Sources 2017, 360, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Beck, D. Analysis of Synthetic Voltage vs. Capacity Datasets for Big Data Li-ion Diagnosis and Prognosis. Energies 2021, 14, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Beck, D. Big data training data for artificial intelligence-based Li-ion diagnosis and prognosis. J. Power Sources 2020, 479, 228806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yi, Z.; Chen, B.-R.; Tanim, T.R.; Dufek, E.J. Rapid failure mode classification and quantification in batteries: A deep learning modeling framework. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 45, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, D.; Dubarry, M. Synthetic data for LFP/LMO, NMC/LMO, and NCM/NCA blended electrodes vs. Graphite. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- HNEI. Alawa Central. Available online: https://www.hnei.hawaii.edu/alawa (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- Weng, A.; Movahedi, H.; Wong, C.; Siegel, J.B.; Stefanopoulou, A. Current Imbalance in Dissimilar Parallel-Connected Batteries and the Fate of Degradation Convergence. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2024, 146, 011106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lang, M.; Yu, X.; Yang, X. Influence of connection impedance on the performance of parallel-connected lithium-ion batall tery modules. J. Power Sources 2024, 593, 233949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor Marlow, M.; Chen, J.; Wu, B. Degradation in parallel-connected lithium-ion battery packs under thermal gradients. Commun. Eng. 2024, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Anseán, D. Best practices for incremental capacity analysis. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 1023555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beck, D.; Dubarry, M. Electrode Blending Simulations Using the Mechanistic Degradation Modes Modeling Approach. Batteries 2024, 10, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10050159
Beck D, Dubarry M. Electrode Blending Simulations Using the Mechanistic Degradation Modes Modeling Approach. Batteries. 2024; 10(5):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10050159
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeck, David, and Matthieu Dubarry. 2024. "Electrode Blending Simulations Using the Mechanistic Degradation Modes Modeling Approach" Batteries 10, no. 5: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10050159
APA StyleBeck, D., & Dubarry, M. (2024). Electrode Blending Simulations Using the Mechanistic Degradation Modes Modeling Approach. Batteries, 10(5), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10050159






