High Adsorption Graphene Oxide Prepared by Graphite Anode from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries for Methylene Blue Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
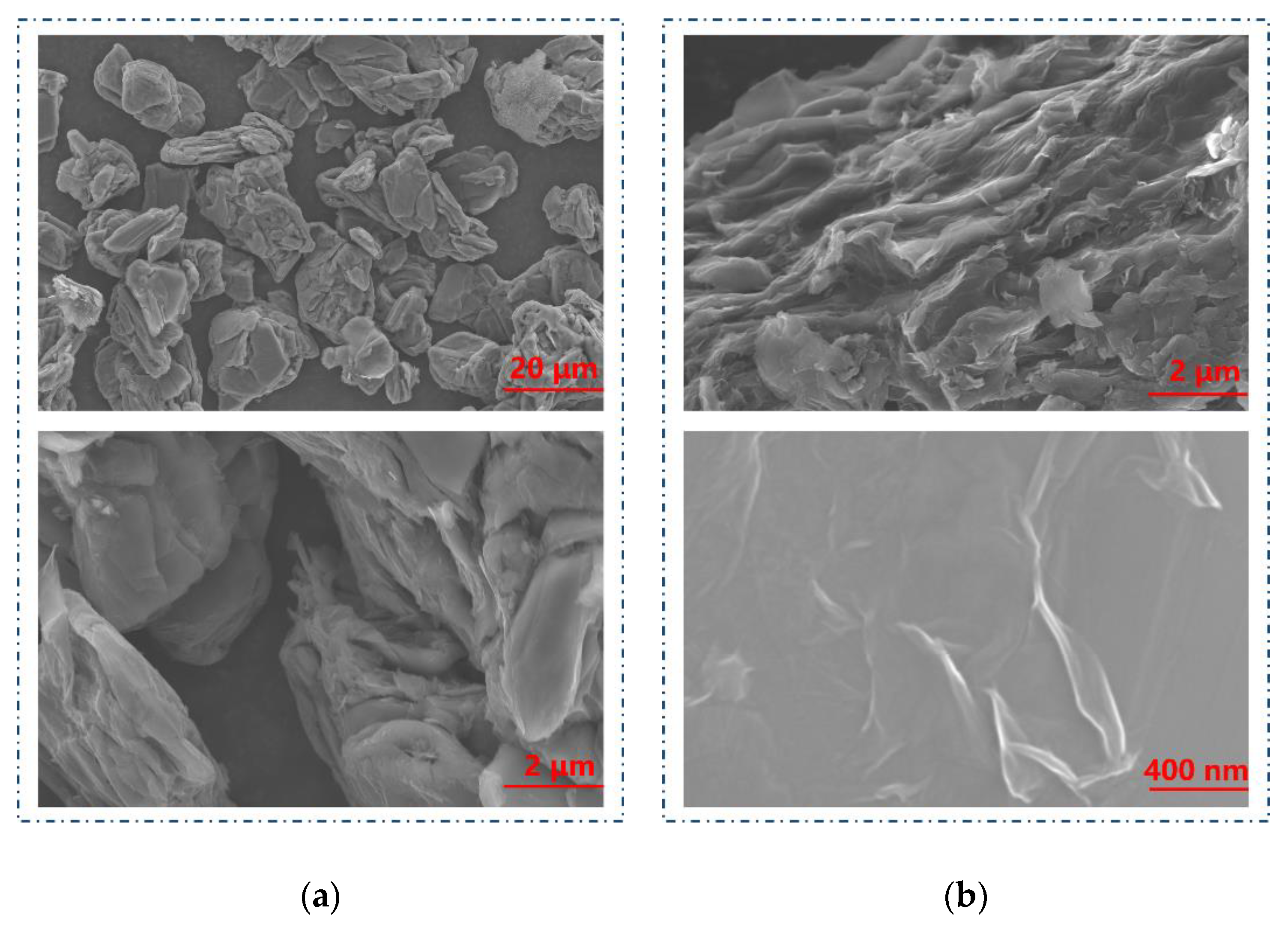
2.1. The Characteristics of GO
2.2. Adsorption Study
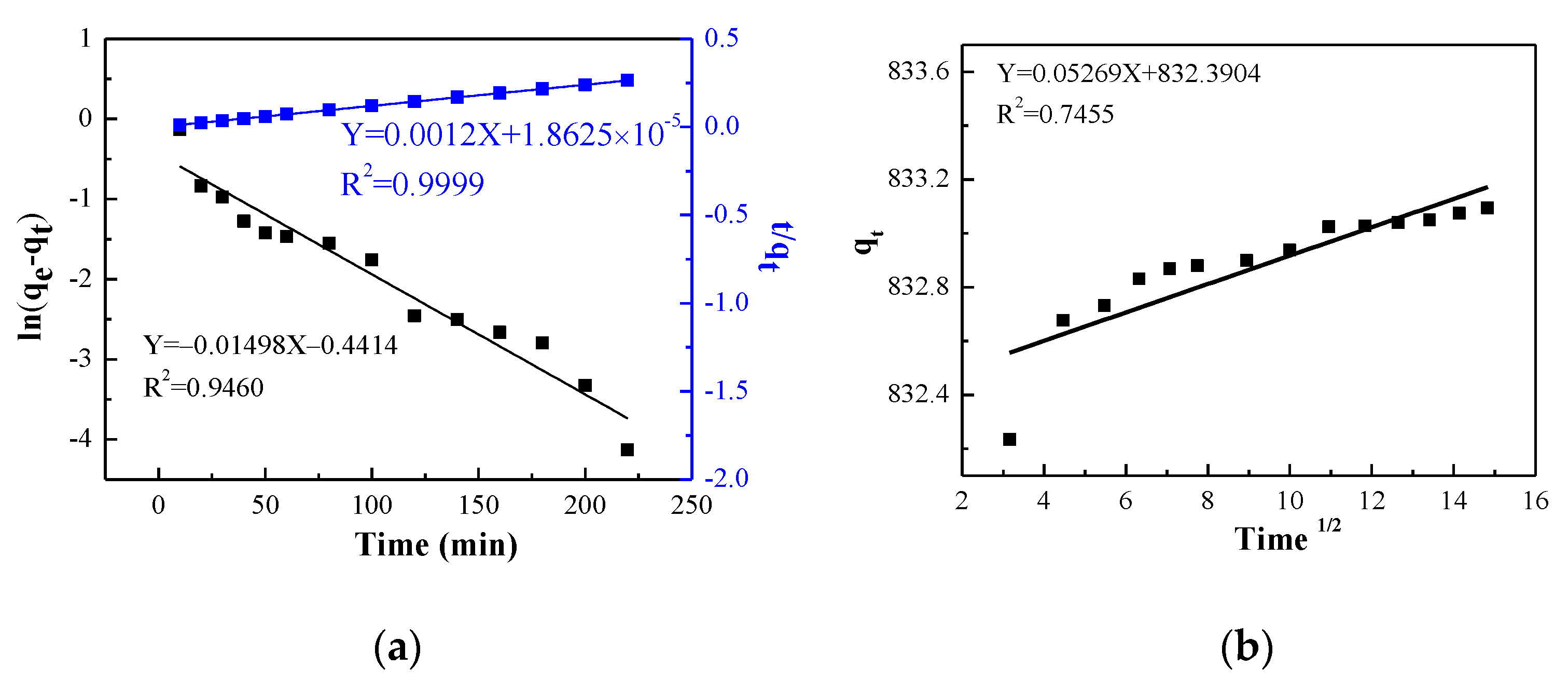
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
- Pseudo-First-Order kinetic equation reflecting the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the conditions of the substances involved in the reaction. The expression is as follows [39]:
- 2.
- The pseudo-second-order kinetic model is an assumption that the adsorption rate is governed by a chemisorption mechanism, which involves electron sharing or electron transfer between adsorbent and adsorbate. The behavior of the entire adsorption process can be revealed and is consistent with the speed control step. The equation is as follows [40]:
- 3.
- In order to obtain the intraparticle diffusion rate constant of the adsorbent, the Weber–Morris model is used to analyze the controlling steps in the reaction, and the expression is as follows [41].
2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
- The Langmuir adsorption model assumes that the adsorbate is adsorbed by a monolayer on the surface of the adsorbent. Meanwhile, the distribution of each adsorption position on the surface is uniform, and the enthalpy change during the adsorption process is the same. The linear form of the equation is as follows [44]:
- 2.
- The Freundlich adsorption isotherm is an empirical adsorption equilibrium model established based on the adsorption of the adsorbent on the multiphase surface. If the solid surface of the adsorbent is not uniform, the adsorption equilibrium constant will be related to the surface coverage, and its expression equation is [45]:
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of GO
4.3. Adsorption of MB
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Theerthagiri, J.; Karuppasamy, K.; Lee, S.J.; Shwetharani, R.; Kim, H.-S.; Pasha, S.K.K.; Ashokkumar, M.; Choi, M.Y. Fundamentals and comprehensive insights on pulsed laser synthesis of advanced materials for diverse photo- and electrocatalytic applications. Light. Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.; Amine, K. 30 Years of lithium-Ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, J.; Lu, Y.-C. A retrospective on lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; You, C.; Lin, H.; Wang, J. Electrochemical Kinetic Modulators in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries: From Defect-Rich Catalysts to Single Atomic Catalysts. Energy Environ. Mater. 2022, 5, 731–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, S.; Yang, J.; Xi, Y.; Hou, X.; Xiao, Q.; Lin, H. Long-Life Dendrite-Free Lithium Metal Electrode Achieved by Constructing a Single Metal Atom Anchored in a Diffusion Modulator Layer. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 3245–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, L. Global lithium-ion battery market 2021 to 2030. 2021. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/global-lithium-ion-battery-market-2021-to-2030---declining-prices-of-lithium-ion-batteries-presents-opportunities-301333864.html (accessed on 14 July 2021).
- Tran, M.K.; Rodrigues, M.-T.F.F.; Kato, K.; Babu, G.; Ajayan, P.M. Deep eutectic solvents for cathode recycling of Li-ion batteries. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudet, A.; Larouche, F.; Amouzegar, K.; Bouchard, P.; Zaghib, K. Key Challenges and Opportunities for Recycling Electric Vehicle Battery Materials. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.H.P.; Chen, M.; Ogunseitan, O.A. Potential Environmental and Human Health Impacts of Rechargeable Lithium Batteries in Electronic Waste. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5495–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. Challenges to Future Development of Spent Lithium Ion Batteries Recovery from Environmental and Technological Perspectives. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Wang, Z.; Cao, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.H. A Critical Review and Analysis on the Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1504–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Aravindan, V. Recycling Strategies for Spent Li-Ion Battery Mixed Cathodes. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 2101–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Jiang, L.; Wen, J.; Wang, H.; Guan, R.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, G. Regeneration and reutilization of cathode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 383, 123089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Aravindan, V. An Urgent Call to Spent LIB Recycling: Whys and Wherefores for Graphite Recovery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2002238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Ede, S.R.; Bajaj, H.C.; Kundu, S. Environmental benign synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) from spent lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) graphite and its application in supercapacitor. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 543, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, X.; Sun, W.; Yi, L. A green and facile approach for regeneration of graphite from spent lithium ion battery. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Xia, J.; Li, F.; He, W.; Li, G.; Huang, J. Preparing graphene from anode graphite of spent lithium-ion batteries. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, N.; He, J.; Chen, R.; Li, X. Lithiation-Aided Conversion of End-of-Life Lithium-Ion Battery Anodes to High-Quality Graphene and Graphene Oxide. Nano Lett. 2018, 19, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, T.; Xu, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, P.; Song, B. Two-Dimensional High-Entropy Metal Phosphorus Trichalcogenides for Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3593–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Liu, S.; Du, Z.; Cui, Y.; Gu, J.; Shi, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, S. Charge-enriched strategy based on mxene-based polypyrrole layers toward. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 20103979. [Google Scholar]
- Theerthagiri, J.; Lee, S.J.; Karuppasamy, K.; Arulmani, S.; Veeralakshmi, S.; Ashokkumar, M.; Choi, M.Y. Application of advanced materials in sonophotocatalytic processes for the remediation of environmental pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesha, G.K.; Kumara, A.V.; Muralidhara, H.B.; Sampath, S. Graphene and graphene oxide as effective adsorbents toward anionic and cationic dyes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Ren, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Few-Layered Graphene Oxide Nanosheets As Superior Sorbents for Heavy Metal Ion Pollution Management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10454–10462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Ren, X.; Gao, X.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X. Removal of Pb(ii) ions from aqueous solutions on few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets. Dalton. Trans. 2011, 40, 10945–10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Wen, T.; Yang, X.; Yang, S.; Liao, J.; Hu, J.; Shao, D.; Wang, X. Preconcentration of U(VI) ions on few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets from aqueous solutions. Dalton. Trans. 2012, 41, 6182–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradder, P.; Ling, S.K.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Dye Adsorption on Layered Graphite Oxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 56, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chung, S.; Oh, G.; Seo, T.S. Three-Dimensional Graphene Oxide Nanostructure for Fast and Efficient Water-Soluble Dye Removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 4, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Yu, H.; Fugetsu, B. Graphene oxide adsorption enhanced by in situ reduction with sodium hydrosulfite to re-move acridine orange from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 203–204, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.-T.; Chen, S.; Chang, Y.; Cao, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Liu, T.; Peng, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; et al. Comparative study of methylene blue dye adsorption onto activated carbon, graphene oxide, and carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, R.; Andersan, G.; Santoso, S.P.; Irawaty, W. Green Reduction of Graphene Oxide using Kaffir Lime Peel Extract (Citrus hystrix) and Its Application as Adsorbent for Methylene Blue. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, D.; Nguyen, T.; Doan, T.; Doan, T.-H.; Dang, V.-C.; Nghiem, L.D. Removal of direct blue 71 and methylene blue from water by graphene oxide: Effects of charge interaction and experimental parameters. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudagar, S.; Akash, S.; Venkat, M.S.; Poiba, V.R.; Vangalapati, M. Adsorption of methylene blue dye on nano graphene ox-ide-thermodynamics and kinetic studies. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 59, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, C.M.B.; Nascimento, G.F.O.D.; Da Costa, G.R.B.; Da Silva, K.S.; Baptisttella, A.M.S.; Ghislandi, M.; Sobrinho, M.A.D.M. Adsorptive removal of dye from real textile wastewater using graphene oxide produced via modifications of hummers method. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2018, 206, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cote, L.J.; Huang, J. Two Dimensional Soft Material: New Faces of Graphene Oxide. Accounts Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboutalebi, S.H.; Gudarzi, M.M.; Zheng, Q.B.; Kim, J.-K. Spontaneous Formation of Liquid Crystals in Ultralarge Graphene Oxide Dispersions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 2978–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Song, S. A review on heavy metal ions adsorption from water by graphene oxide and its composites. J. Mol. Liquids 2017, 230, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, X.; Bai, R. Removal of mercury II and methylene blue from a wastewater environment with mag-netic graphene oxide adsorption kinetics, isotherms and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2016, 86, 82523–82536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, L. Comparison between linear and non-linear forms of pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order ad-sorption kinetic models for the removal of methylene blue by activated carbon. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2009, 3, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Huang, S.-C.; Juang, R.-S. Characteristics of pseudo-second-order kinetic model for liquid-phase adsorption: A mini-review. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 151, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svilović, S.; Rušić, D.; Bašić, A. Investigations of different kinetic models of copper ions sorption on zeolite 13X. Desalination 2010, 259, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption isotherm models: Classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majd, M.M.; Kordzadeh-Kermani, V.; Ghalandari, V.; Askari, A.; Sillanpää, M. Adsorption isotherm models: A comprehensive and systematic review (2010−2020). Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 812, 151334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kang, S.-O.; Park, S.; Park, H.S. Adsorption isotherms and kinetics of cationic and anionic dyes on three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide macrostructure. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nounou, M.N.; Nounou, H.N. Multiscale estimation of the Freundlich adsorption isotherm. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Hossain, F.; Duan, C.; Lu, J.; Tsang, Y.F.; Islam, S.; Zhou, Y. Isotherm models for adsorption of heavy metals from water—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, W.Z.; Nasrullah, A.; Khan, A.S.; Fagieh, T.M.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Akhtar, K.; Khan, S.B.; Din, I.U.; Khan, M.A.; Bokhari, A. Adsorption efficiency of date palm based activated carbon-alginate membrane for methylene blue. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




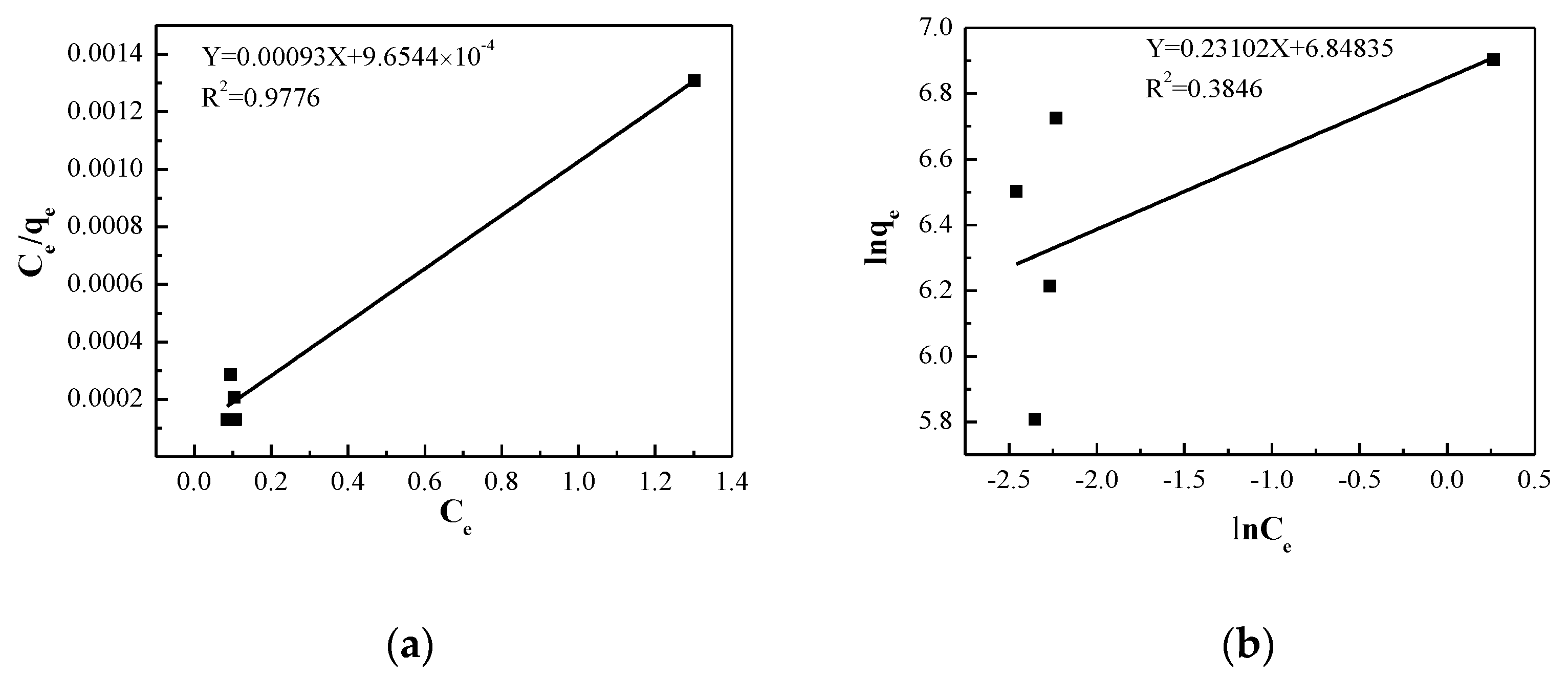

| Raw Materials | pH | qe (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | - | 351.1 | [26] |
| Graphite | 6 | 714 | [29] |
| Expandable graphite | 9 | 243.9 | [30] |
| Natural graphite powder by PT. Brataco | - | 276.06 | [31] |
| Graphite powder | 7 | 476.19 | [32] |
| Graphite fine powder (98%, Loba Chemicals) | 8 | 428.485 | [33] |
| Graphite | 12 | 308.11 | [34] |
| Spent GA | 9 | 833.11 | This study |
| Kinetic Model | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order kinetic | qe (mg/g) | 0.6431 |
| k1 (1/min) | 0.01498 | |
| R2 | 0.9460 | |
| Pseudo-second-order kinetic | qe (mg/g) | 833.33 |
| k2 (g/(mg min)) | 0.077 | |
| R2 | 0.9999 | |
| Weber–Morris model | kip | 0.05269 |
| C | 832.904 | |
| R2 | 0.7455 |
| Isotherm Model | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qm | 1075.26 |
| KL | 0.9632 | |
| R2 | 0.9776 | |
| Freundlich | n | 4.328 |
| KF | 942.27 | |
| R2 | 0.1795 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Rao, Z.; Lei, Y. High Adsorption Graphene Oxide Prepared by Graphite Anode from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries for Methylene Blue Removal. Batteries 2022, 8, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8110249
Qiao Y, Zhao H, Rao Z, Lei Y. High Adsorption Graphene Oxide Prepared by Graphite Anode from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries for Methylene Blue Removal. Batteries. 2022; 8(11):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8110249
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Yu, Huaping Zhao, Zhonghao Rao, and Yong Lei. 2022. "High Adsorption Graphene Oxide Prepared by Graphite Anode from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries for Methylene Blue Removal" Batteries 8, no. 11: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8110249
APA StyleQiao, Y., Zhao, H., Rao, Z., & Lei, Y. (2022). High Adsorption Graphene Oxide Prepared by Graphite Anode from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries for Methylene Blue Removal. Batteries, 8(11), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8110249







