Material and Waste Flow Analysis for Environmental and Economic Impact Assessment of Inorganic Acid Leaching Routes for Spent Lithium Batteries’ Cathode Scraps
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
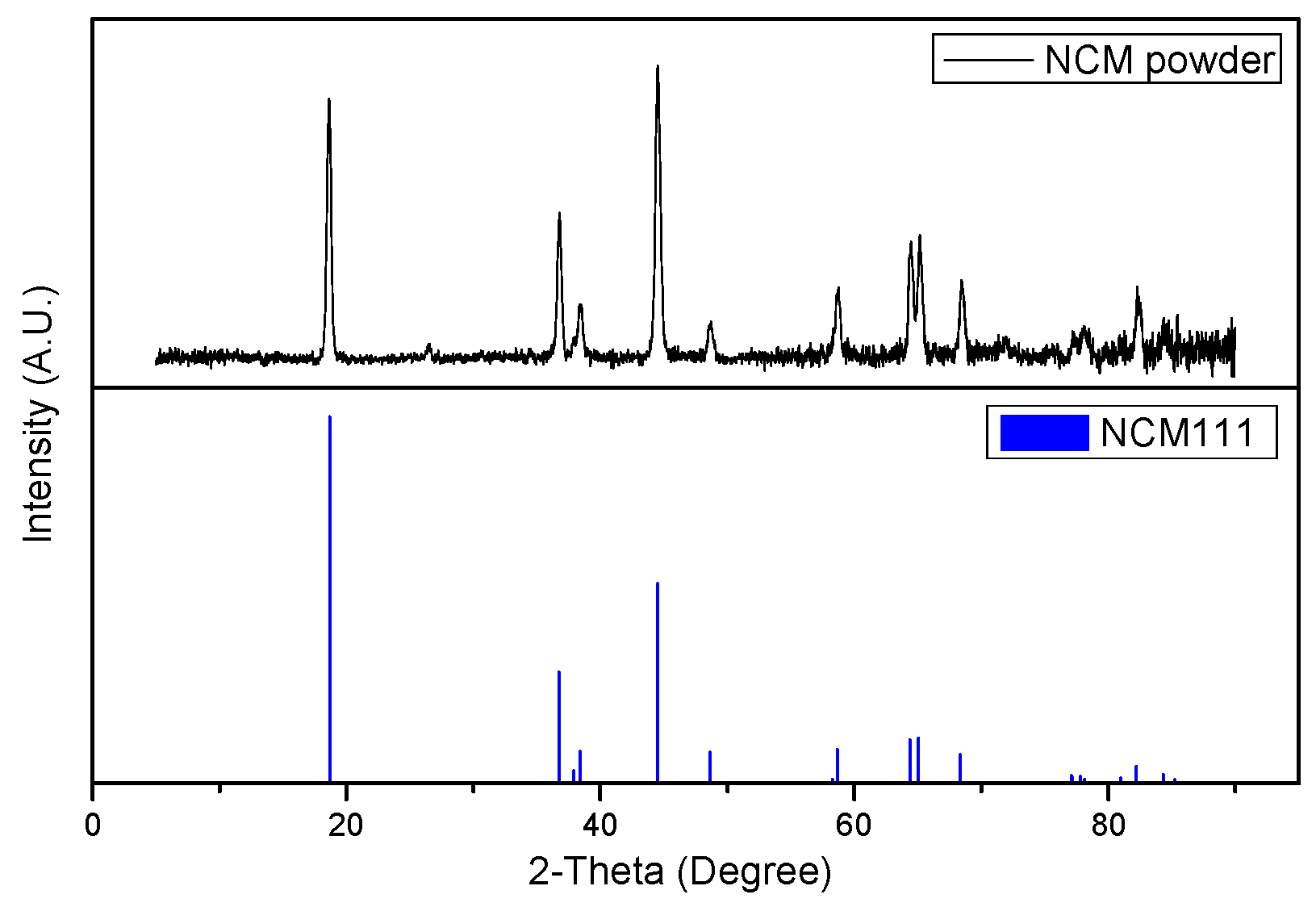
2.1. Materials
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Inorganic Acid Leaching
2.4. Material Flow Cost Accounting
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Taguchi Design
3.2. Sulfuric Acid Leaching
3.3. Hydrochloric Acid Leaching
3.4. Nitric Acid Leaching
3.5. Overall Leaching Efficiency
3.6. Material Flow Cost Accounting
3.7. Selection of Leachate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ordoñez, J.; Gago, E.J.; Girard, A. Processes and technologies for the recycling and recovery of spent lithium-ion batteries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.; Ansart, F.; Rpbert, C.L.; Portal, J. Advances in the recovering of spent lithium battery compounds. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkaman, R.; Asadollahzadeh, M.; Mostaedi, M.T.; Maragheh, M.G. Recovery of cobalt from spent lithium ion batteries by using acidic and basic extractants in solvent extraction process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 186, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Hoque, M.M.; Mohamed, A.; Ayob, A. Review of energy storage systems for electric vehicle applications: Issues and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 771–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.C.Y.; Sui, P.C.; Zhang, J. A review of recycling spent lithium-ion battery cathode materials using hydrometallurgical treatments. J. Energy Storage 2021, 35, 102217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineral Commodity Summaries. 2023. Available online: https://www.kriittisetmateriaalit.fi/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Mineral-Commodity-Summaries-2023-USGS-Jan-2023.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, G.; Liang, Z. Progress, Key Issues, and Future Prospects for Li-Ion Battery Recycling. Glob. Chall. 2022, 6, 2200067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Ang, E.H.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y. Progresses in Sustainable Recycling Technology of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energy Environ. Mater. 2022, 5, 1012–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Chang, X.; Meng, Q.; Wan, L.J.; Guo, Y.G. Progress in the sustainable recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries. SusMat 2021, 1, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.C.; Wang, J.Z.; Shen, Y.H. Separation of Valuable Metals in The Recycling of Lithium Batteries via Solvent Extraction. Minerals 2023, 13, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.J.; Rarotra, S.; Krikstolaityte, V.; Zhuoran, K.W.; Cindy, Y.D.L.; Tan, X.Y.; Carboni, M.; Meyer, D.; Yan, Q.; Srinivasan, M. Green Recycling Methods to Treat Lithium-Ion Batteries E-Waste: A Circular Approach to Sustainability. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2103346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.; Abhilash; Pandey, B.D.; Mankhand, T.R.; Deveci, H. Acid baking of spent lithium ion batteries for selective recovery of major metals: A two-step process. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 43, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuol, D.A.; Machado, C.M.; Silva, M.L.; Calgaro, C.O.; Dotto, G.L.; Tanabe, E.H. Recovery of cobalt from spent lithium-ion batteries using supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.K.; Kumari, A.; Jha, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Hait, J.; Pandey, B.D. Recovery of lithium and cobalt from waste lithium ion batteries of mobile phone. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1890–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, G.H.; Sohn, J.S. Hydrometallurgical process for recovery of cobalt from waste cathodic active material generated during manufacturing of lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2007, 167, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.M.; Kim, N.H.; Sohn, J.S.; Yang, D.H.; Kim, Y.H. Development of a metal recovery process from Li-ion battery wastes. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 79, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, D.; Peuker, U.A.; Mütze, T. Recycling Chain for Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Metals 2020, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, P.M.; Ballany, F.; Benhamou, L.; Bucar, D.K.; Tabor, A.B.; Sheppard, T.D. The application of design of experiments (DoE) reaction optimisation and solvent selection in the development of new synthetic chemistry. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.C.; Tsai, P.J.; Mou, J.L. Determining Optimal Operation Parameters for Reducing PCDD/F Emissions (I-TEQ values) from the Iron Ore Sintering Process by Using the Taguchi Experimental Design. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5298–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Ning, Z.; Mayne, J.; Moore, J.I.; Butcher, J.; Chiang, C.K.; Mack, D.; Stintzi, A.; Figeys, D. Evaluating in Vitro Culture Medium of Gut Microbiome with Orthogonal Experimental Design and a Metaproteomics Approach. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, J.; Walls, L.; Bandiera, L.; Menolascina, F. Statistical Design of Experiments for Synthetic Biology. ACS Synth. Biol. 2021, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.Y.; Mahtab, M.S.; Neo, T.H.; Farooqi, I.H.; Khursheed, A. A comprehensive review of Design of experiment (DOE) for water and wastewater treatment application—Key concepts, methodology and contextualized application. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.Q.; Wu, M.Y.; Li, R.; Deng, S.H.; Lee, B.C.Y.; Ong, S.L.; Hu, J.Y. Potential of combined advanced oxidation–Biological process for cost-effective organic matters removal in reverse osmosis concentrate produced from industrial wastewater reclamation: Screening of AOP pre-treatment technologies. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 123419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakoya, M.B.; Poll, H.M. Integrating ERP and MFCA systems for improved waste-reduction decisions in a brewery in South Africa. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 40, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, E.; Jodeiri, N.; Fatehifar, E. Implementation of material flow cost accounting for efficiency improvement in wastewater treatment unit of Tabriz oil refining company. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.K.; Ng, R.T.L.; Ng, D.K.S.; Tan, R.R. Material flow cost accounting (MFCA)–based approach for prioritisation of waste recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 107, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, M.; Redmann, C. Flow cost accounting, an accounting approach based on the actual flows of materials. Environ. Manag. Account. Inf. Inst. Dev. 2002, 9, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubu, K.; Tachikawa, H. Material flow cost accounting: Significance and practical approach. In Handbook of Sustainable Engineering; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, K.L.; Burritt, R.L. Material flow cost accounting: A review and agenda for future research. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.; Pandey, B.D.; Mankhand, T.R. Recovery of valuable metals from cathodic active material of spent lithium ion batteries: Leaching and kinetic aspects. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayl, A.A.; Elkhashab, R.A.; Badawy, S.M.; Khateeb, M.A.E. Acid leaching of mixed spent Li-ion batteries. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3632–S3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.C.; Wang, J.Z.; Shen, Y.H. Recycling Metal from Waste Lithium-ion Batteries for Use as Electrochemical Sensor Material. Sens. Mater. 2022, 34, 2025–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.P.; Sun, S.Y.; Song, X.F.; Yu, J.G. Leaching process for recovering valuable metals from the LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode of lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2017, 64, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, X.; He, M.; Lin, X.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Spent lithium-ion battery recycling—Reductive ammonia leaching of metals from cathode scrap by sodium sulphite. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refly, S.; Floweri, O.; Mayangsari, T.R.; Sumboja, A.; Santosa, S.P.; Ogi, T.; Iskandar, F. Regeneration of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 Cathode Active Materials from End-of-Life Lithium-Ion Batteries through Ascorbic Acid Leaching and Oxalic Acid Coprecipitation Processes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 16104–16114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, E.G.; Ruiz, M.C.; Ojeda, M.W.; Rodriguez, M.H. Cathodes of spent Li-ion batteries: Dissolution with phosphoric acid and recovery of lithium and cobalt from leach liquors. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xue, Q.; Fan, E.; Wu, F.; Chen, R. Economical recycling process for spent lithium-ion batteries and macro- and micro-scale mechanistic study. J. Power Sources 2018, 377, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Guo, J.; Lui, S.; Song, H.; Wu, W.; Zheng, C.; Gao, X. Recover value metals from spent lithium-ion batteries via a combination of in-situ reduction pretreatment and facile acid leaching. Waste Manag. 2023, 161, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalini, E.A.; Karimi, G.; Zandevakili, S. Treatment of valuable metals from leaching solution of spent lithium-ion batteries. Miner. Eng. 2021, 173, 107226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, S.P.; Prabaharan, G.; Kumar, L. Leaching and separation of Co and Mn from electrode materials of spent lithium-ion batteries using hydrochloric acid: Laboratory and pilot scale study. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Wu, S.H. A novel recovery process of metal values from the cathode active materials of the lithium-ion secondary batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 99, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Rhee, K.I. Preparation of LiCoO2 from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2002, 109, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Yang, J.; Huabg, Y.; Lin, J.; Arshad, F.; Wu, F.; Li, L.; Chen, R. Leaching Mechanisms of Recycling Valuable Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by a Malonic Acid-Based Leaching System. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 8532–8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Element | Li | Co | Ni | Mn | Fe | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | 8.04 | 21.46 | 22.27 | 15.09 | 0.127 | 0.122 |
| Materials | Price | Unit | Price | Unit |
| H2SO4 | 0.043 | TWD/mL | 116 | USD/gal |
| HCl | 0.043 | TWD/mL | 5.3 | USD/gal |
| HNO3 | 0.043 | TWD/mL | 5.3 | USD/gal |
| H2O2 | 1.4 | TWD/mL | 174.1 | USD/gal |
| Energytypes | Price | Unit | Price | Unit |
| Water | 0.000012 | TWD/mL | 1.4 | USD/m3 |
| Electricity | 3.79 | TWD/kWh | 432,000 | USD/J |
| Depreciation items | Price | Unit | Price | Unit |
| Thermostatic bath with magnetic stirring | 79,000 | TWD/set | 2604.2 | USD/set |
| Vacuum pump | 27,920 | TWD/set | 920.4 | USD/set |
| Waste type | Price | Unit | Price | Unit |
| Solid waste | 0.056 | TWD/g | 1.85 | USD/kg |
| No | This Study | Zhang et al. [38] | Asadi et al. [39] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 60 °C | 95 °C | 60 °C |
| Acid concentration | 2 mol L−1 | 2 mol L−1 | 2 mol L−1 |
| Solid-to-liquid ratio | 25 g L−1 | 100 g L−1 | 30 g L−1 |
| Time | 15 min | 240 min | 80 min |
| Addition of hydrogen peroxide | 1.5 vol.% | 0 vol.% | 4 vol.% |
| Li leaching rate | 96.41% | 100% | 98.40% |
| Co leaching rate | 82.53% | 98.13% | 99.0% |
| Ni leaching rate | 89.25% | 97.27% | 96.78% |
| Mn leaching rate | 99.99% | 97.37% | 97.53% |
| No | This Study | Barik et al. [40] | Wang et al. [41] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 70 °C | 50 °C | 80 °C |
| Acid concentration | 1 mol L−1 | 1.75 mol L−1 | 4 mol L−1 |
| Solid-to-liquid ratio | 20 g L−1 | 20 g L−1 | 20 g L−1 |
| Time | 12 min | 120 min | 60 min |
| Addition of hydrogen peroxide | 1.0 vol.% | 0 vol.% | 0 vol.% |
| Li leaching rate | 90.72% | >99% | >99% |
| Co leaching rate | 77.66% | >99% | >99% |
| Ni leaching rate | 87.07% | - | >99% |
| Mn leaching rate | 98.24% | >99% | >99% |
| No | This Study | Lee et al. [42] |
|---|---|---|
| Material | LiNi0.33Co0.33Mn0.33O2 | LiCoO2 |
| Temperature | 70 °C | 75 °C |
| Acid concentration | 1.5 mol L−1 | 1.0 mol L−1 |
| Solid-to-liquid ratio | 10 g L−1 | 20 g L−1 |
| Time | 15 min | 60 min |
| Addition of hydrogen peroxide | 0.5 vol.% | 1.7 vol.% |
| Li leaching rate | 90.60% | >95% |
| Co leaching rate | 82.26% | >95% |
| Ni leaching rate | 92.08% | - |
| Mn leaching rate | 95.42% | - |
| No. | Temp. | Acid | S/L | Time | H2O2 | Li | Co | Ni | Mn | Total Leaching Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | °C | mol L−1 | g L−1 | min | vol. | % | % | % | % | % |
| H2SO4 | 60 | 2.0 | 25 | 15 | 1.5 | 96.41 | 82.53 | 89.25 | 99.99 | 71.01 |
| HCl | 70 | 1.0 | 20 | 12 | 1.0 | 90.72 | 77.66 | 87.07 | 98.24 | 60.26 |
| HNO3 | 70 | 1.5 | 10 | 15 | 0.5 | 90.60 | 82.26 | 92.08 | 95.42 | 65.48 |
| Materials | Cost | Unit | Amount | Unit | Total Cost | Unit |
| H2SO4 | 0.043 | TWD/mL | 44.44 | mL | 1.92 | TWD |
| H2O2 | 1.47 | TWD/mL | 6 | mL | 8.82 | TWD |
| Energytypes | Cost | Unit | Amount | Unit | Total cost | Unit |
| Electricity | 3.79 | TWD/kWh | 1.28 | kWh | 4.8512 | TWD |
| Water | 0.000012 | TWD/mL | 355.56 | mL | 0.0043 | TWD |
| Depreciation items | Purchase cost | TWD/set | Durable number of years | Years of use | Depreciation | Unit |
| Thermostatic bath | 79,000 | TWD/set | 7 | 7 | 7090 | TWD |
| Vacuum pump | 27,920 | TWD/set | 7 | 7 | 2506 | TWD |
| Waste type | Cost | Unit | Amount | Unit | Total cost | Unit |
| Solid waste | 0.056 | TWD/g | 7.75 | g | 0.43 | TWD |
| Total price (Does not include the depreciation) | 16.03 | TWD | ||||
| Total price in USD (TWD 1 = USD 0.033) | 0.53 | TWD | ||||
| Materials | Cost | Unit | Amount | Unit | Total Cost | Unit |
| HCl | 0.043 | TWD/mL | 42.6 | mL | 1.84 | TWD |
| H2O2 | 1.47 | TWD/mL | 5 | mL | 7.35 | TWD |
| Energytypes | Cost | Unit | Amount | Unit | Total cost | Unit |
| Electricity | 3.79 | TWD/kWh | 1.28 | kWh | 4.8512 | TWD |
| Water | 0.000012 | TWD/mL | 457.4 | mL | 0.0055 | TWD |
| Depreciation items | Purchase cost | TWD/set | Durable number of years | Years of use | Depreciation | Unit |
| Thermostatic bath | 79,000 | TWD/set | 7 | 7 | 7090 | TWD |
| Vacuum pump | 27,920 | TWD/set | 7 | 7 | 2506 | TWD |
| Wastetype | Cost | Unit | Amount | Unit | Total cost | Unit |
| Solid waste | 0.056 | TWD/g | 7.14 | g | 0.40 | TWD |
| Total price (Does not include the depreciation) | 14.45 | TWD | ||||
| Total price in USD (TWD 1 = USD 0.033) | 0.48 | USD | ||||
| Materials | Cost | Unit | Amount | Unit | Total Cost | Unit |
| HNO3 | 0.043 | TWD/mL | 95.1 | mL | 4.11 | TWD |
| H2O2 | 1.47 | TWD/mL | 5 | mL | 7.35 | TWD |
| Energytypes | Cost | Unit | Amount | Unit | Total cost | Unit |
| Electricity | 3.79 | TWD/kWh | 3.2 | kWh | 12.128 | TWD |
| Water | 0.000012 | TWD/mL | 904.9 | mL | 0.0109 | TWD |
| Depreciation items | Purchase cost | TWD/set | Durable number of years | Years of use | Depreciation | Unit |
| Thermostatic bath | 79,000 | TWD/set | 7 | 7 | 7090 | TWD |
| Vacuum pump | 27,920 | TWD/set | 7 | 7 | 2506 | TWD |
| Wastetype | Cost | Unit | Amount | Unit | Total cost | Unit |
| Solid waste | 0.056 | TWD/g | 8.91 | g | 0.50 | TWD |
| Total price (Does not include the depreciation) | 24.10 | TWD | ||||
| Total price in USD (TWD 1 = USD 0.033) | 0.79 | USD | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Y.-C.; Wang, J.-Z.; Chou, C.-M.; Shen, Y.-H. Material and Waste Flow Analysis for Environmental and Economic Impact Assessment of Inorganic Acid Leaching Routes for Spent Lithium Batteries’ Cathode Scraps. Batteries 2023, 9, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040207
Tang Y-C, Wang J-Z, Chou C-M, Shen Y-H. Material and Waste Flow Analysis for Environmental and Economic Impact Assessment of Inorganic Acid Leaching Routes for Spent Lithium Batteries’ Cathode Scraps. Batteries. 2023; 9(4):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040207
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Yi-Chin, Jian-Zhi Wang, Chih-Ming Chou, and Yun-Hwei Shen. 2023. "Material and Waste Flow Analysis for Environmental and Economic Impact Assessment of Inorganic Acid Leaching Routes for Spent Lithium Batteries’ Cathode Scraps" Batteries 9, no. 4: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040207
APA StyleTang, Y.-C., Wang, J.-Z., Chou, C.-M., & Shen, Y.-H. (2023). Material and Waste Flow Analysis for Environmental and Economic Impact Assessment of Inorganic Acid Leaching Routes for Spent Lithium Batteries’ Cathode Scraps. Batteries, 9(4), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040207






